States of Matter
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Definition of Chemistry
The study of the composition, structure, properties and reactions of matter.
Definition of Matter
Anything that has volume and mass.
Three states of matter
• The solid state
• The liquid state
• The gaseous state
4 main ideas of the Particulate Theory of Matter
Matter is made of particles. 2. Particles are in constant motion and temperature affects their speed of motion. 3. Empty spaces exist between particles. 4. Forces of attraction exist between particles.
Two processes providing evidence for the particulate theory of matter
Diffusion and Osmosis (both prove particles are moving).
Definition of Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, until the particles are evenly distributed.
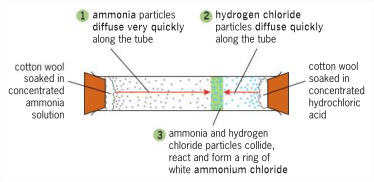
Observation: Ammonia (NH3) vs Hydrogen Chloride (HCl) experiment
White ring (NH4Cl) forms closer to HCl because NH3 particles are lighter and diffuse faster.
Definition of Osmosis
Osmosis is the net movement of water particles from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration through a differentially permeable membrane.
Why living tissue (paw-paw/potato) swells in water
Water enters cells by osmosis; cells become turgid (rigid) and increase in length.
Why living tissue shrinks in salt/sucrose solution
Water leaves cells by osmosis; cells become flaccid (soft) and decrease in length.
Uses of Osmosis
To control garden pests like slugs and snails
To preserve foods such as meat, fish and fruit
How salt controls garden pests
The salt dissolves in the moisture around the bodies of the garden pests like slugs and snails, whose skin if differentially permeable and always moist. Then, water inside their bodies moves out by osmosis into the solution, resulting in the pests dying from dehydration if their bodies lose more water than they can tolerate.
How salt / sugar preserves food
It draws water out of food and microorganism cells by osmosis; prevents chemical reactions and inhibits the growth of the microorganisms that cause decay.
Three types of particles that make up matter
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions.
Definition of an Atom
Smallest unit of a chemical element, having all characteristics of that element. (E.g, iron is made of iron atoms)
Definition of a Molecule
A group of two or more atoms bonded together, which can exist on its own. E.g, H2 made up of hydrogen atoms, H, and CO2 which is made up of carbon atoms, C, and oxygen atoms, O.
Definition of an Ion
An electrically charged particle. E.g, the potassium ion, K+, the nitrate ion, NO3-
Solid: Shape and Volume
Fixed shape and volume; particles vibrate in fixed positions due to very strong attraction.
Liquid: Shape and Volume
Fixed volume but takes shape of container; particles move slowly past each other with weaker attraction than solids.
Gas: Shape and Volume
Variable shape and volume (expands to fill space); particles move rapidly and randomly with negligible attraction.
Why Gases are easy to compress
Particles are very far apart with large empty spaces between them.
Why Solids have a fixed shape
Particles are packed closely together in a regular way with no room to move.
Heating a solid: The Process
Particles gain kinetic energy, vibrate more violently, and eventually overcome forces of attraction to change state.
Difference between Evaporation and Boiling
Evaporation (any temp) vs Boiling (specific temp). 2. Evaporation (surface only) vs Boiling (throughout liquid).
Definition: Melting Point and Freezing Point
Melting: Temp solid becomes liquid. Freezing: Temp liquid becomes solid. (Both occur at the same value for pure substances).
Definition: Boiling Point
The constant temperature at which a liquid changes into a gas.
Why temperature is constant during state changes
Energy is used to overcome/break the forces of attraction between particles instead of raising the temperature.
Substances that sublime
Dry ice (CO2), iodine, and naphthalene (moth balls).