Arthrology [COMPLETE]
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards was created to help on the exam 2 of GAC Anat&Phys I with Harbitz. It covers the Arthrology section of the exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
How do we classify joints?
Functional classification (ROM) and/or Structural classification
What are the 3 types of joints based on functional classification?
Synarthroses - immovable joints
Amphiartroses - sligthly movable
Diarthroses - highly movable
What are the types of synarthroses?
Sutures
Gomphosis
Sychondrosis
Synostosis
Synarthroses - What is an example of suture joint?
Joints between the skull bones.
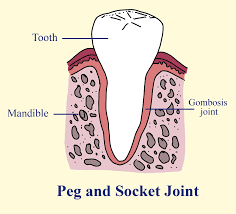
Synarthroses - What is one example of gomphosis?
Teeth in socket joint.
(What are synchondrosis?)
Hyaline cartilage that separate bones
Synarthroses - What is one example of synchondrosis?
Xyphoid process
(What are synostosis?)
Previous joint that has been fused by bone
What is an exampple of synostosis?
Closed epiphyseal plate.
What are the types of Amphiarthroses?
Syndesmosis - large space between bones with little movement possible
Symphysis - bones separated by pad or fibrous cartilage
What is an example of syndesmosis?
Distal tibofibular joint
What is one example of symphysis?
Intervertebral disks.
What are the types of diarthroses?
Gliding - no angulation
Hinge - monoaxial movement
Pivot - rotation only
Ellipsoid - biaxial movement
Saddle - biaxial movement
Ball and socket - triaxial
Diarthroses - What is one example of gliding joint?
Intercarpal joint.
What is one example of hinge joints?
Elbow joint.
What is one example of pivot joint?
Atlas/axis joint.
What is one example of saddle joint?
First metacarpal joint.
What is one example of ball and socket joint?
Shoulder joint.
What are the types of motion?
Linear (gliding)
Angular
Rotation
What are the axes of angular motion?
Monoaxial
Biaxial
Triaxial
Flexion/extension
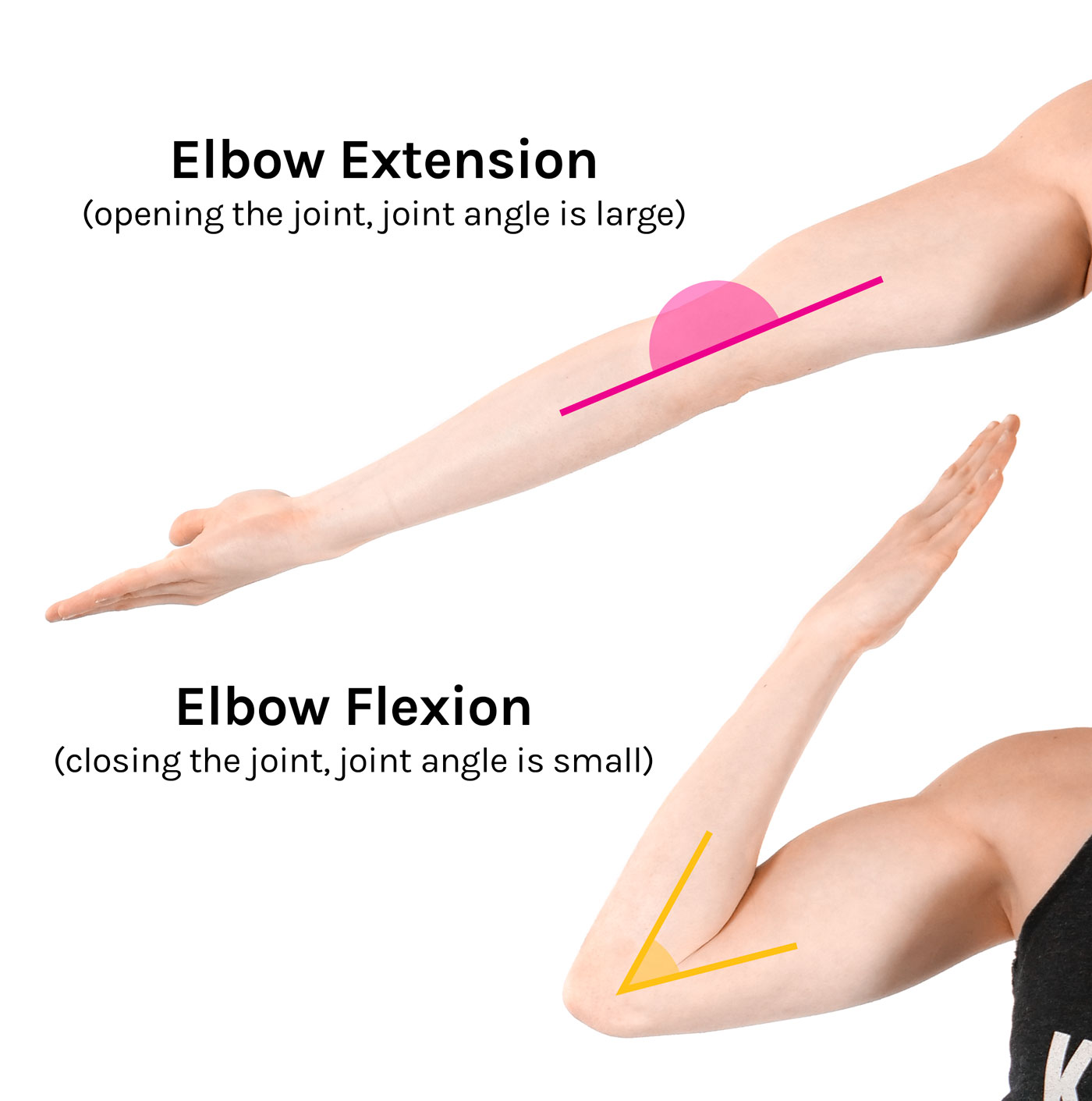
Abduction/adduction
Opposition
Inversion/eversion
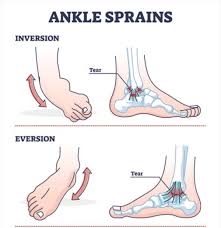
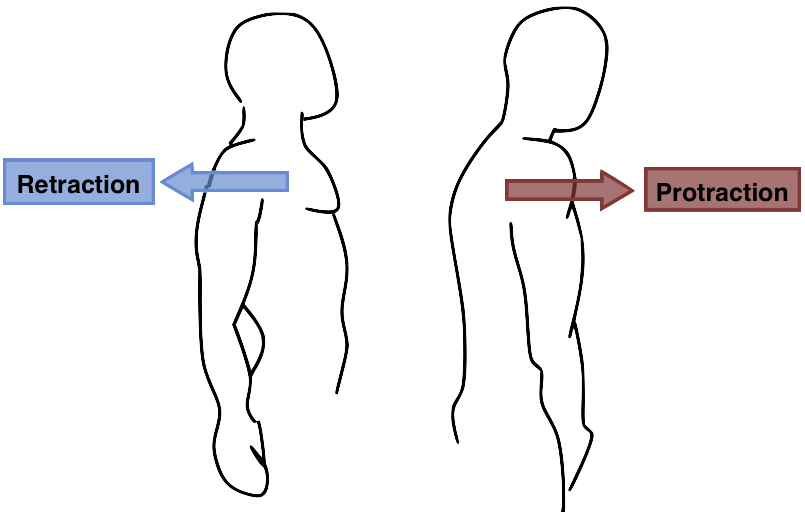
Protraction/retraction
Elevation/depression

Circumduction
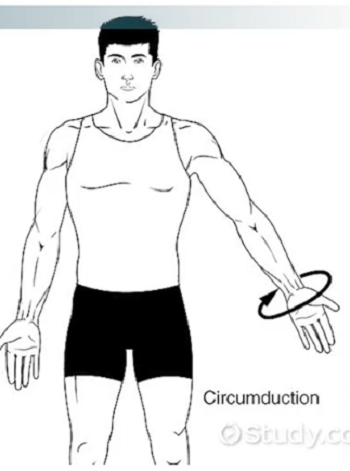
Rotation

Injuries
Sprain - ligament
Strain - tendon/muscle
Dislocation - complete (luxation) or partial (subluxation)
Spinal joints
3 joint complex
2 facet joints (gliding diarthroses)
Symphysis joint between vertebral bodies, and
Atlantoaxial (C1/C2) is the exception (pivot joint)
Spinal ligaments
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Ligamentum flavum (yellow ligament)
Intervertebral discs
Contain two parts: annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus.

Explain Intervertebral herniations.
Happen when the gel-like center of the intervertebral disc (nucleus pulposus) pushes through the outer layer (annulus fibrosus) of the disc and presses on nearby nerves or the spinal cord.
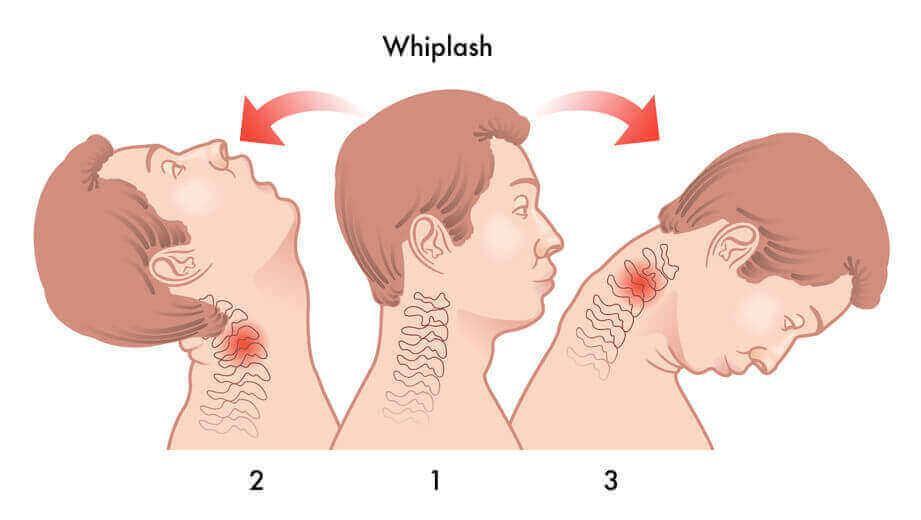
What is a whiplash?
Sprain/strain injury to the neck.
What composes the pectoral girdle?
2 Clavicles
2 Scapulae
Acromioclavicular joint - gliding diarthrosis
Sternoclavicular joint - gliding diarthrosis
AC joint separation.
Disruption of AC joint and surrounding ligaments.
The glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint).
Ball and socket joint/supported by glenoid labrum, rotator cuff muscles, and numerous other ligaments and muscles.
The elbow joint.
Complex joint located at the distal end of humerus and the proximal end of ulna. It is a hinge joint diarthrosis. It is composed of distinct joints that make up the elbow joint:
Humeroulnar joint - trochlea of humerus and trochlear notch of ulna
Humeroradial joint - capitulum of humerus and head of radius
It also includes:
Supporting muscles: biceps brachii (flexes) and triceps brachii (extends)
Ligaments: annular (radial head/radial notch); ulnal collateral lig.; and the radial collateral lig.
Elbow injuries - “Golfer’s elbow”
Medial epicondylitis
Elbow injuries - “Pitcher’s elbow”
Damage to ulnar collateral ligament
Elbow injuries - “Tennis elbow”
Lateral epicondylitis
What are the types of joints in the wrist?
Mostly gliding joints.
The pelvic girdle.
Composed by
Pelvis bones (ilium, ischium, pubis = innominate)
Sacrum
Coccyx
The hip joint.
Is a ball and socket diarthrosis. Head of femur connects to the acetabulum of innominate. The Labrum and ligament of femoral head increase stability.
Also composed by many surrounding ligaments and muscles.
Types of Injuries
Dislocations
Sprains
Strains
Labrum tears
Fractures of femoral neck
The knee joint.
Is a hinge diarthrosis. Composed of:
Femur-tibia articulations - lateral and medial condyles
Patella-femur articulation
Ligaments:
Anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
Medial and lateral collateral ligaments
Menisci:
Medial and lateral menisci - give knee lateral stability
Other structures:
Fat pads
Bursae
Injuries of the knee joint.
ACL
MCL/LCL
Meniscus
Unhappy triad (ACL, MCL, Meniscus)
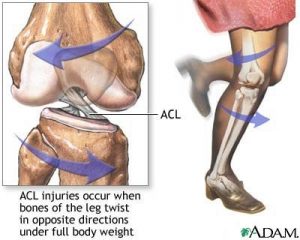
The ankle joint.
Is a hinge diarthrosis (talus/tibia articulation).
Ligaments:
Lateral ligament (most commonly sprained) - Anterior talofibular ligament, calcaneofibular, and posterior talofibular
Medial ligament - deltoid ligament
Define arthritis.
Inflammation or swelling of 1+ joints.
What is osteoarthritis?
Degeneration of joint cartilage. Causes pain and stiffness. Most common type of arthritis.
Define rheumatoid arthritis.
Autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the synovial membrane, leading to joint destruction.
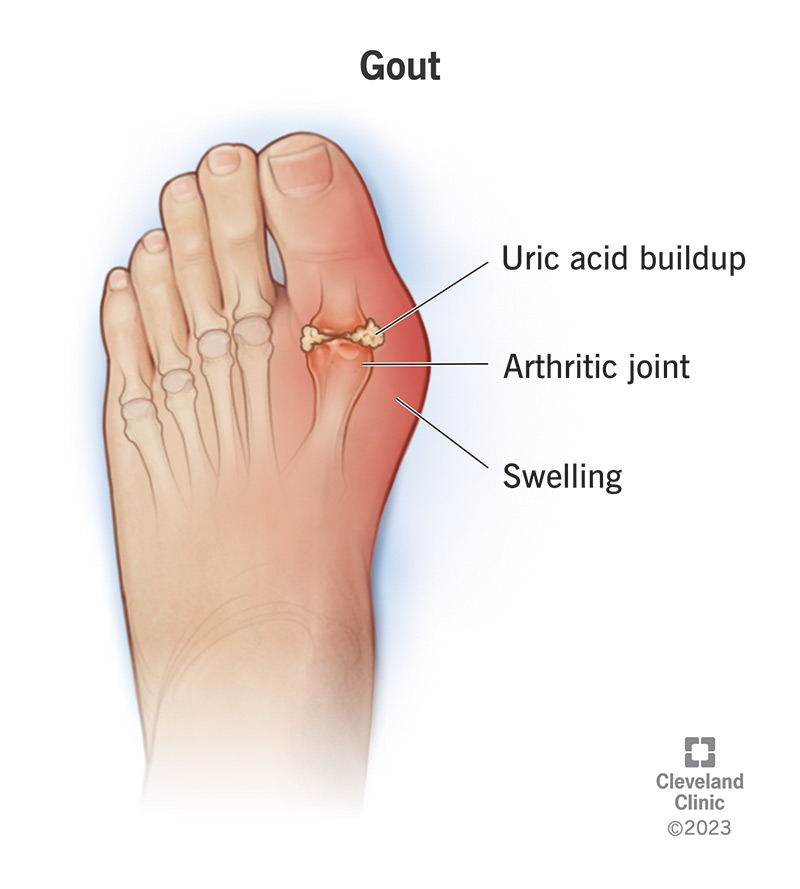
Define gouty arthritis.
Condition caused by Uric Acid buildup, which starts to form crystals around joints.
Define arthroscopy.
Procedure to look inside and repair a joint.
Define arthroplasty.
Surgical procedure to replace a joint.