Clinical Chemistry I - Laboratory Analysis of Protein (Module 1) Review
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Hypoproteinemia
Total plasma protein level less than reference interval.
Occurs in any condition where a negative nitrogen balance exists.
Hyperproteinemia
An increase of total plasma proteins above reference interval.
Hypoproteinemia
Due to:
◦Excessive loss (renal disease, fluid loss, burns)
◦Decreased intake (nutritional)
◦Decreased synthesis (liver)
◦Accelerated breakdown (trauma)
◦Immunodeficiency (decreased synthesis)
Hyperproteinemia
Due to:
◦Dehydration - Relative change when concentration of proteins is elevated due to decreased volume of water
◦Excess production of proteins (g-globulins) - Multiple myeloma, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
Total Protein testing
Very common, routine lab test utilizing serum or plasma; reflects nutritional status, hepatic and renal function, overall protein value; values low at birth, reach adult levels by age 3
6.5-8.3 g/dL
Total protein (TP) reference range/interval
Total protein measurement methods
Biuret, dye binding, turbidimetry and nephelometry
Biuret method
Method of total protein measurement based on cupric ions (Cu2+) chelating with peptide bonds - Forms violet colored complex where Beer's law can be used
Dye binding method
Method of total protein measurement based on the affinity of protein with a specific dye.
- Bromocresol green (BCG) - can be falsely elevated by Hb and alpha globulins
- Bromocresol purple (BCP) - Preferred, less interferents
- Amido black
Turbidimetry and nephelometry method
Method of measuring total protein based on light transmission or light scatter due to particles present
3.5-5.5 g/dL
Albumin reference range/interval
Albumin/Globulin ratio
Total protein minus (-) albumin = globulins,
Albumin divided (/) by globulins =
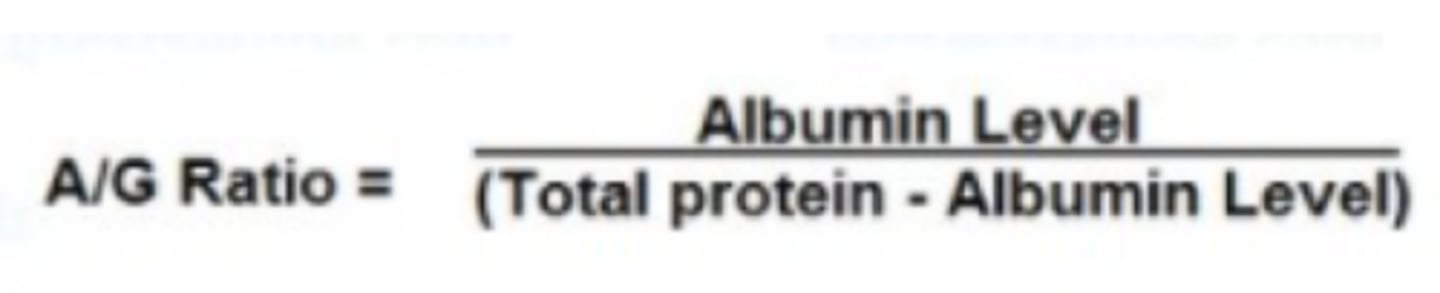
1.1-1.8 g/dL
Serum A/G ratio reference range/interval
Low A/G Ratio
Indicative of autoimmune disorder, cirrhosis, kidney disease
High A/G Ratio
Indicative of leukemia, liver disease, hyperthyroidism
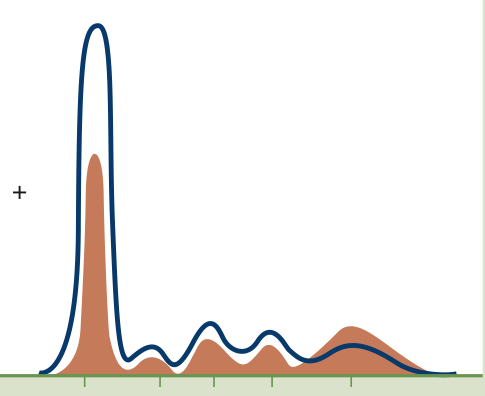
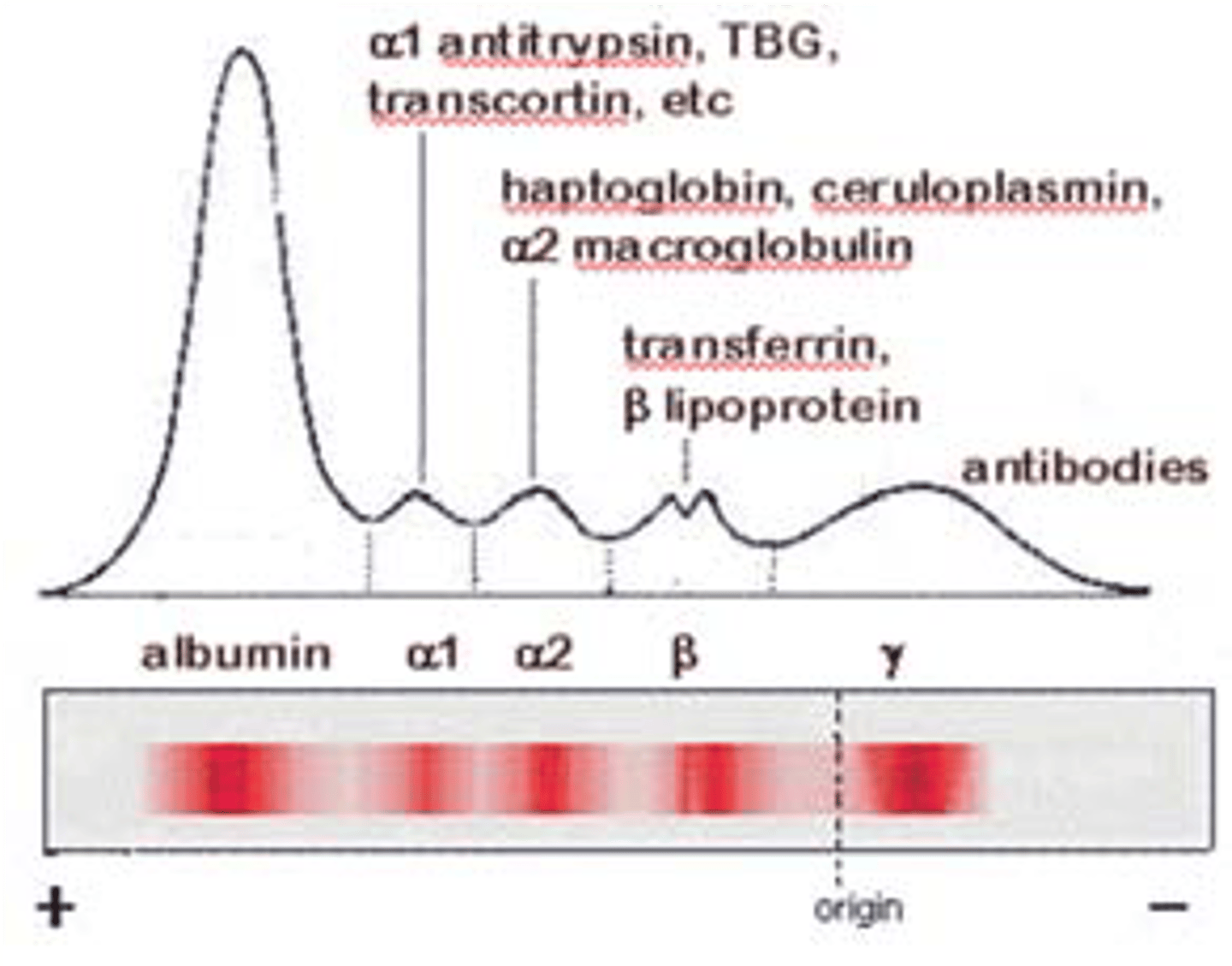
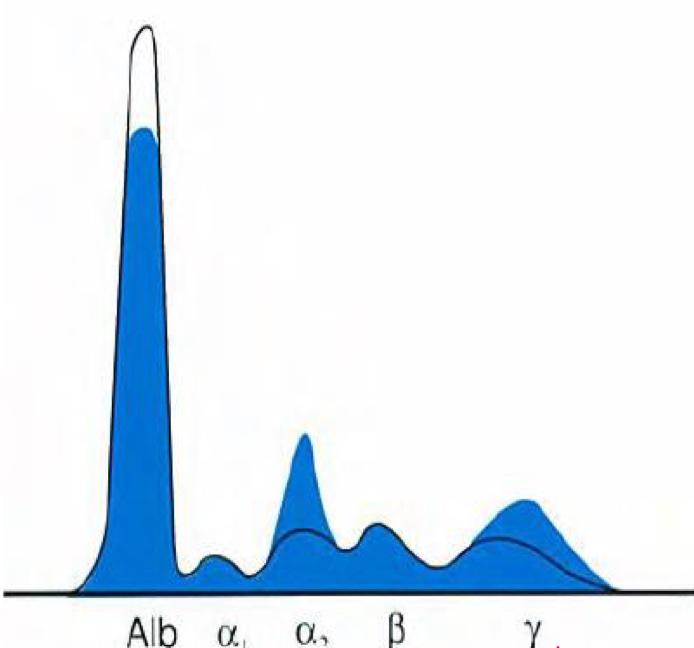
Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPE)
- Proteins at pH 8.6 carry a net negative charge and migrate toward the positive terminal, the anode
- After separation, fix and stain the proteins
- Migration depends on size, shape, temperature, pH, and ionic strength of the test system
Overall net negative charge on the protein at pH 8.6
High resolution electrophoresis
Electrophoresis that uses higher voltage and a cooling system to increase separation into 15 bands
Capillary electrophoreesis
Separation of molecules takes place in buffer filled silica capillary tubes
Isoelectric focusing
Zone electrophoresis that separates on basis of pI (isoelectric point)
Immunofixation electrophoresis
Electrophoresis specific for monoclonal gammopathy isolation on gel
CSF proteins
95% ____ _________ is from plasma active transport across blood-brain barrier
Ratio of serum albumin with CSF albumin identifies the degree of permeability
CSF proteins
Elevated based on 2 factors:
- Increased permeability of blood-brain barrier -> Multiple sclerosis, bacterial viral & fungal meningitis, neoplasm/tumor
- Synthesis by inflammatory cells (neurosyphilis, hematoma, heemorrhage)
CSF protein electrophoresis
Used in detecting multiple sclerosis - unexpected oligoclonal bands in gamma-globulin region
Alpha 1 Globulins
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT),
Alpha-1 Fetoprotein (AFP), Alpha 1 Lipoprotein
Alpha 2 Globulins
Haptoglobin, Ceruloplasmin,
Alpha-2 Macroglobulin
Beta Globulins
Transferrin, hemopexin, Beta-2 Microglobulin (B2M), C3, C4, Beta Lipoproteins, C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Fibrinogen (Plasma only)
Gamma Globulins
IgG, IgM, IgE, IgA, IgD
Transport binding
Function for albumin, prealbumin, haptoglobin, hemopexin, transferrin
Oncotic pressure
Function for albumin
Immune defense
Function for Immunoglobulins, complement, CRP
Acute phase reactants
C-Reactive protein (CRP), Alpha 1 Antitrypsin (AAT), ceruloplasmin - markers of inflammation
Nephrotic syndrome
- Loss of albumin
- Increased alpha 2 macroglobulin in α2 region since it is too large to be excreted, is retained
- Takeaway: Decrease of all fractions with the exception of α2
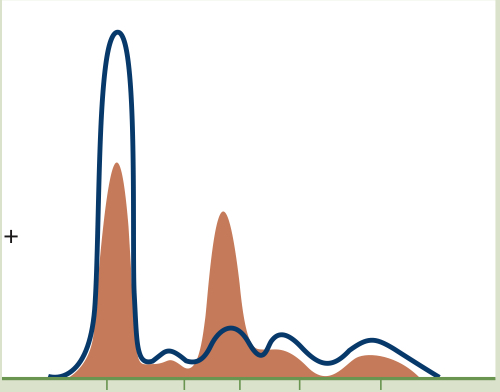
Acute Inflammation
Increase in acute phase proteins in α2 region
Takeaway: Decreased Albumin, increased α1 & α2, normal gamma
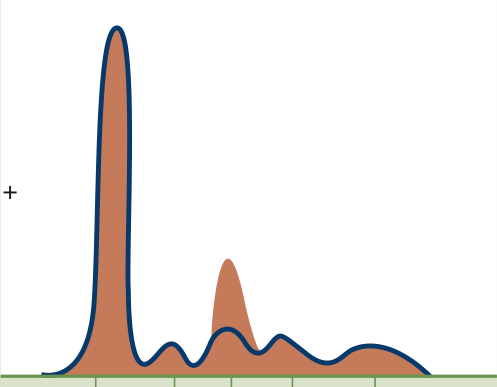
Inflammation
Alpha 1 or Alpha 2 globulin fraction increase means:
Chronic inflammation
Decreased Albumin, increased alpha 2 (α2), increased Gamma
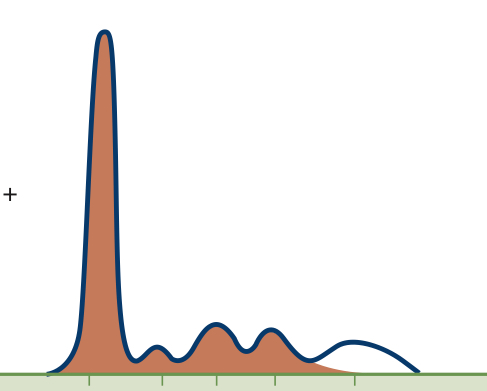
Hypoglobulinemia
No Gamma (ɣ) globulin peak
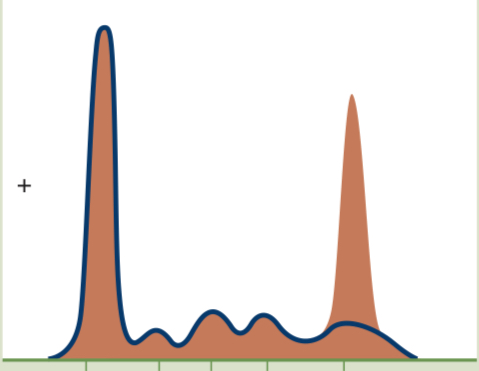
Hyperglobulinemia (monoclonal gammopathy)
Spike at Gamma (ɣ) globulin peak
Hepatic Cirrhosis
Decreased albumin production
Classic beta-gamma bridge due to immunoglobulin subclasses
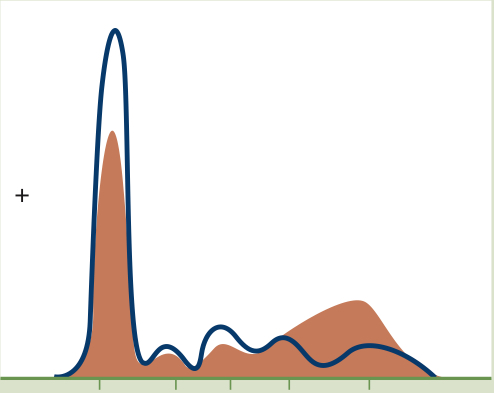
Alpha1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
Decreased Alpha 1
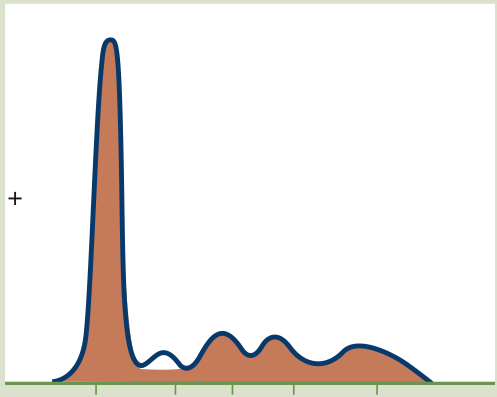
Severe Hepatic Disease
Decrease in all zones except gamma (increased) due to a failure of the liver to synthesize proteins (Decreased albumin, alpha 1 and 2, beta, Increased gamma)