PT 742 Geri Lecture 2 normal / pathological changes with aging +successful aging and frailty
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Describe a programmed theory on aging
non-stochanstic
Genetically controlled, cellular senescence
DNA: biological timetable
hormonally regulated
continuation of the theory that regulates childhood growth and development
describe a non-programmed theory of aging
damage or error theories: stochastic
epigenetics: changes of gene expression, via lifestyle and environmet
DNA mutations
oxidative stress
wear and tear theory
free radical theory
differentiate between normal aging and pathologic aging
normal: age related changes that occur due to passage of time (muli organ related changes seen in all elderly)
pathological aging: age related pathologic conditions that occur in most older adults (alzheimer’s)
What are age related changes related to connective tissue (msk system) in older adults?
loss of water from matrix
increase # collagen cross links
loss of elastic fibers
clinical consequence > stiffness
What are age related changes to the muscle in older adults?
increase in fat mass, decrease muscle mass (fiber necrosis), decrease BMR
true or false: PT can reverse cachexia but not sarcopenia
FALSE; it can reverse sarcopenia but NOT cachexia
In regards to stretching, how is it different for older adults?
Spend more time actively in their end ranges and use it more
True or false: LE are more affected than UE in terms of type II muscle atrophy
true
Which are these are non-modifiable factors contributing to bone mass:
a. family hx of osteroporosis
b. hormones
c. low birth weight
d. inactivity
e. medications
a. family hx of osteroporosis
b. hormones
c. low birth weight
true or false: there is a greater loss of cortical bone than trabecular as you age
false: trabecular > cortical (1% yr vs 0.5 % yr)
What type of training should those with low bone mass according to the LiftMor Trial?
a. low intensity aerobic
b. high intensity aerobic
c. high intensity resistance
d. low intensity aerobic
What classifies an osteoporotic fracture?
low level trauma
fall from standing height or less
adults over age 50
what are common major sites of osteoporotic fractures?
hip, spine, distal radius, proximal humerus
What are changes that occur at the joint level in older adults?
decreased joint space, increase laxity, altered distribution of load, decreased ROM
What is the avg height loss per decade?
1-2 cm, up to 12 cm ; postural changes begin at 40 yrs old greater at 60
What complications can occur from hyperkyphosis (Dowager’s Hump)?
pain, difficulty sleeping, difficulty breathing, fall
What are vascular changes that occur in older adults?
high bp common
thicker walls in arteries
veins thicker more dilated
valves stiffer
What areas are common to find varicose veins? (enlarged, twisted dilated veins)
the lower extremities
causes = family hx, age, sex, obesity, prolonged standing
what are common areas to find spider veins? (small, dilated veins near surface)
face (skin, nose, cheeks), legs (thigh below knee ankle)
causes = heredity, age, females more affected
what is a common cardiac change in older adults?
a. ventricular hypertrophy
b. spider veins
c. varicose veins
d. decrease VO2 max
a. ventricular hypertrophy
A common cardiac change in older adults includes a ____(increase/decrease) in SBP and _____ (increase/decrease) in DBP
increase SBP, decrease in DBP
How do you expect the cardiac output to change in the geriatric population?
it was decrease with age since SV and HRmax decrease with age
What are respiratory changes you expect to see in older adults?
decreased height of T/S vertebrae (kyphosis), calcification of the rib cage (decreased expansion), diaphragm placed a mechanical disadvantage, increased x links in costal sternal cartilage
True or false: as you age, your residual volume decreases with leads to air trapping and higher risks of infection
FALSE, the residual volume INCREASES
Match the respiratory changes with the best description
__decrease in elastic recoil of lungs, mismatched ventilation/perfusion
__ loss of muscular pharyngeal support, respiratory effort in response to airway occulsion
__can occur due to poor oral hygiene and decreased saliva flow
__protective mechanisms, coughing, swallowing
a. aspiration
b. pneumonia
c. atelectasis
d. upper airway obstruction
c. atelectasis - decrease in elastic recoil of lungs, mismatched ventilation/perfusion
b. pneumonia-loss of muscular pharyngeal support, respiratory effort in response to airway occulsion
b. pneumonia-can occur due to poor oral hygiene and decreased saliva flow
a. aspiration _ protective mechanisms, coughing, swallowing
A decrease in these types of cells play a role in the reduction of immune function
a. t cells
b. white blood cells
c. red blood cells
e. langerhans cells
e. langerhans cells
What contributes toward geriatrics skin darkening, decreased protection from UV, and increased risk of skin CA
melanocyte senescence
In regards to nervous system, what changes do you expect to see in the CNS and PNS with aging?
CNS: neuronal atrophy
PNS: loss of myelin sheath, slower nerve conduction velocity
What are endocrine changes you may see in regards to the thyroid?
hypo-reduced metabolism: weakness, fatigue, weight gain
hyper-increase cardiac arrhythmias and weight loss
What are functional changes relevant to the endocrine system in older adults?
loss of muscle, bone; body temp regulation, fluid regulation, fatigue, comorbidities: DM, CVD, visceral
Which of these fall under the category of multicomplexity? (5M’s) choose all
a. social determinants of health
b. safety and fall risk
c. declining function
d. advanced illness
e. fraility
f. recurrent hospital hospitalization
a. social determinants of health
b. safety and fall risk (mobility)
c. declining function (mobility)
d. advanced illness
e. fraility
f. recurrent hospital hospitalization
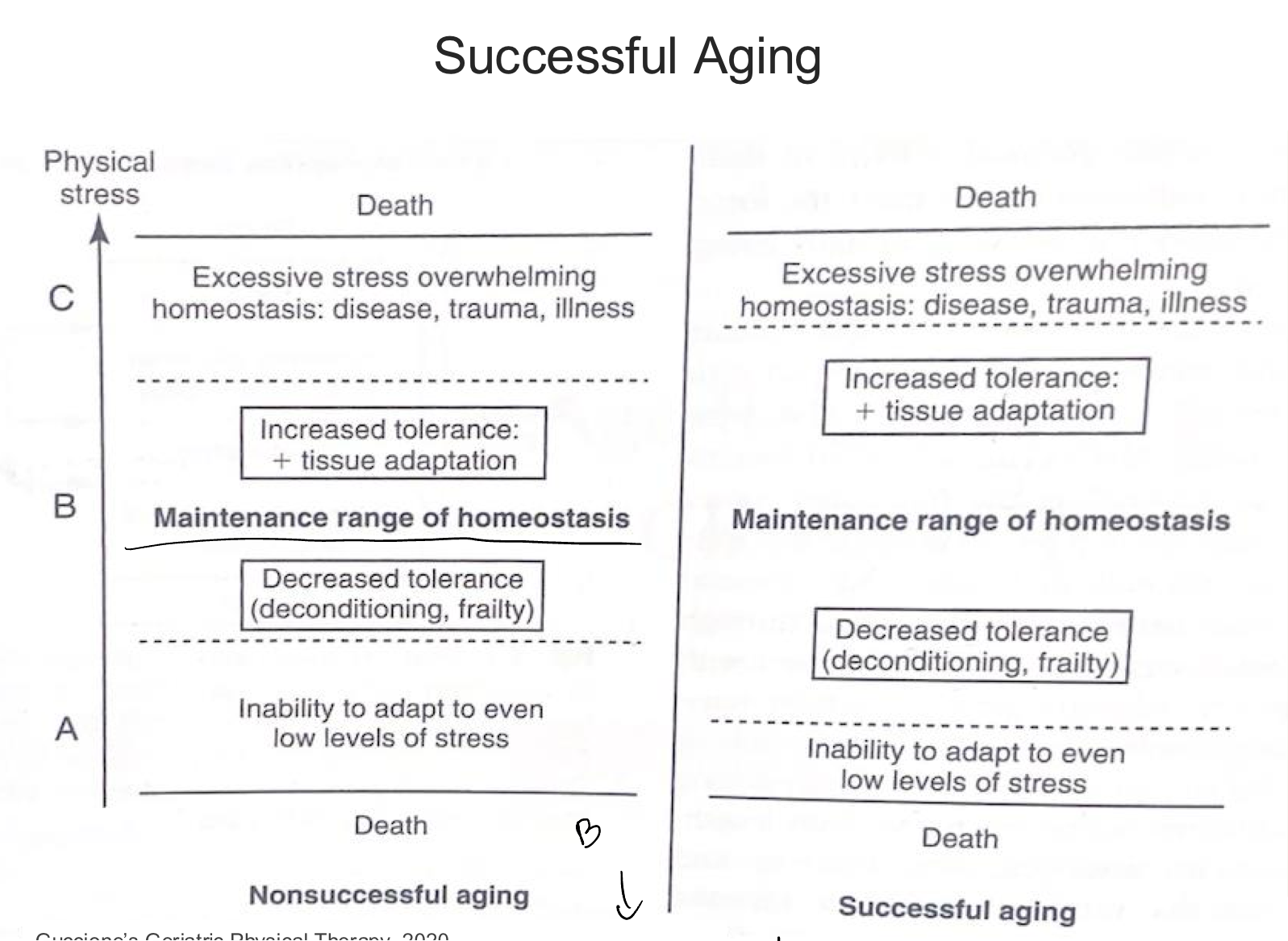
decribe “successful aging” based on this chart
successful aging = higher tolerance/threshold for maintaining homeostasis during stressful experiences (disease, trauma, illness)
what are the 3 main categories for successful aging?
avoid disease
physical and cognitive function
social and productive activity
what is the significance of the hormonal axis in males vs females?
females: decrease ovarian estradiol output: menopause
men: slow decrease in testosterone (andropause)
loss of sex hormones=loss of muscle strength and bone
what is frailty? choose the best answer
a. weakness due to aging
b. decline across multiple physiologic systems due to aging
c. decline in physical and cognitive function leading to disability
d. being unable to perform tasks you used to due to old age
b. decline across multiple physiologic systems due to aging
What determines frailty? 5 things
a. unintentional weight loss
b. exhaustion, low energy
c. low physical activity
d. slow gait speed (<0.8 m/s)
e. weakness (grip strength: men <28.6 =, women: 16.4)