A&PII Exam 3
1/353
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
354 Terms
Two groups of organs for the digestive system
Gastrointestinal tract and accessory digestive organs
Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (alimentary canal) consists of
mouth, most of the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine
Accessory digestive organs
teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
Functions of Digestive System
Ingestion of foods and liquids
Secretion of -7L/day of water, acid, buffers, and enzymes into the lumen by lining of digestive tract and accessory organs
Mixing and propulsion
Digestion
Absoption
Defecation
Mixing and propulsion
alternating contraction and relaxation of the wall of smooth muscle in digestive organs, also aids in motility to mix and propel food
Digestion
breakdown of food into smaller pieces
Absorption
uptake of nutrient molecules into the epithelial cells of the digestive tract and then into the blood and the lymph
Defecation
elimination of feces this includes wastes, bacteria, indigestible substances, cells from the GI lining and materials that are not absorbed
Layers of the GI tract
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa
Mucosa is the
inner lining
Mucosa consists of
epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosae
Epithelium
protection, secretion, absorption
Muscularis mucosae makes
folds that helps to increase surface area
Submucosa is the
connective tissue binding mucosa to muscularis
Muscularis
voluntary skeletal muscle found in mouth pharynx and upper 2/3 of the esophagus and anal sphincter
Serosa (visceral peritoneum)
outermost covering of organs suspended in the abdominopelvic cavity
Enteric Nervous System (ENS)
intrinsic set of nerves extending from esophagus to anus (part of the ANS)
ENS contains
submucosal plexus and myenteric plexus
Submucosal plexus
controlling secretions
Myenteric plexus
GI tract motility
Myenteric plexus is located between the
longitudinal and circular smooth muscle
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
extrinsic set of nerves that regulate the ENS
parasympathetic ENS
when stimulated increases secretion and activity by stimulating ENS
sympathetic ENS
when stimulated decreases secretion and activity by inhibiting the ENS
Peritoneum
largest serous membrane in the body
Parietal peritoneum
lines the wall of cavity
Visceral peritoneum
touching the organs
5 major peritoneal folds
greater omentum, falciform ligament, lesser omentum, messentary, and the mesocolon
The 5 major peritoneal folds functions
bind organs together and provide a path for blood and lymph vessels
Lesser omentum
suspends stomach and duodenum from liver
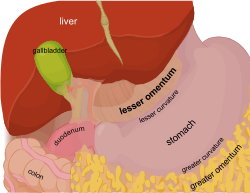
Mesocolon
bind colon to posterior abdominal wall
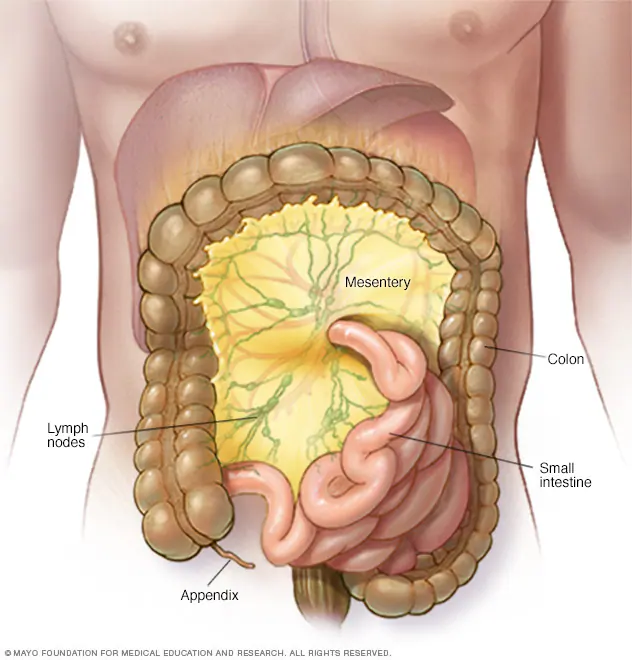
Mesentery
bind small intestine to posterior abdominal wall
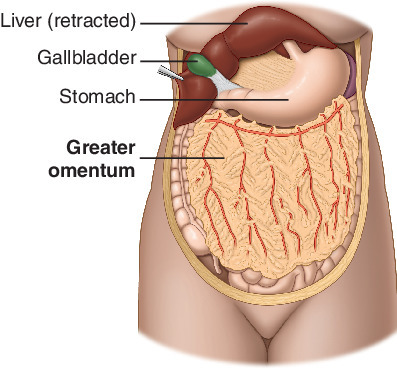
Greater omentum
“fatty apron”, drapes over intestines
Falciform ligament
attaches liver to anterior abdominal wall and diaphragm
Mouth (oral or buccal cavity) extends from
gums and teeth to fauces
Uvula and soft palate
close off the nasal cavity during swallowing
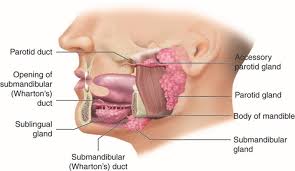
Salivary glands secrete
most of the saliva in the mouth
Salivary glands
parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands
Saliva is mostly
water 99.5%, 0.5% solutes
Solutes in saliva
ions, dissolved gases, urea, uric acid, mucus, immunoglobulin A, lysozyme, and salivary amylase
Tongue is made of
skeletal muscle that is covered by a mucous membrane
Tongue maneuvers
food while chewing, shaping food, and pushes food to back of mouth
Teeth found within
gingivae (gums)
Crown
visible portion. made of dentin and enamel
Neck of teeth
between crown and root
Root of teeth
embedded within gums
Esophagus
secretes mucus and transports food
Esophagus does not
produce enzymes nor absorbs
Esophagus consists of
mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis (superior 1/3 skeletal muscle, middle 1/3 skeletal and smooth muscle, and inferior 1/3 smooth muscle)
Upper esophageal sphincter
regulates movement of food into esophagus
Lower esophageal sphincter
Regulates movement from esophagus to the stomach
Adventitia
attaches esophagus to surroundings
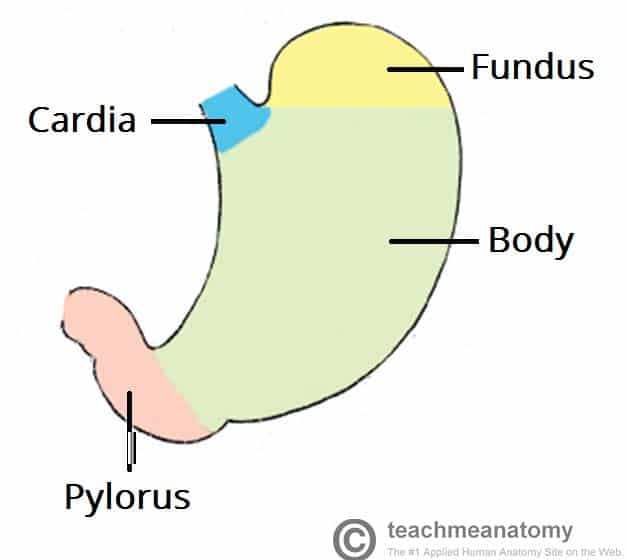
Stomach
mixing chamber and holding resevoir
Four main regions of the stomach
cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus
Mucosa of stomach contains
mucosa neck cells, parietal cells, chief cells, G cells, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa
Mucous neck cells produce
mucous and protect stomach
Parietal cells secrete
hydrochloric acid
Muscularis in the stomach has a
additional 3rd inner oblique layer
Exocrine
glands that secrete into ducts
Endocrine
Ductless glands secrete into blood stream
Pancreas
secretes pancreatic juice which is secreted by exocrine glands; bicarbonate juice that neutralizes the acidity of chyme in the small intestine
Pancreas lies posterior to the
greater curvature of the stomach
99% of the pancreas are
acini that secrete pancreatic juice
1% of the cells are
pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans)
Islets of Langerhans are
endocrine cells that secrete hormones
Liver
heaviest gland of the body
Falciform ligament
connects the two lobes of the Liver
Hepatocytes secrete
bile (800-1000mL/day)
Hepatocytes make up
80% of liver’s weight
Bile canaliculi collects
bile
Hepatic sinusoids
fenestrated blood capillaries that are fixed macrophages
Hepatic laminae
make the liver look like wagon wheels
pH of bile
7.6-8.6
Bile consists of
water, bile salts, cholesterol, phospholipid lecithin, bile pigments, and several ion
Bilirubin
principle bile pigment (when RBCs are broken down)
Bile salts play an active role in
emulsification
Emulsification
the breakdown of large lipid globules into a suspension of small lipid globules
Functions of the liver
Secretion of bile
carbohydrate metabolism
Lipid metabolism
Protein metabolism
Processing of drugs and hormones
Excretion of bilirubin
Synthesis of bile salts
Storage of vitamins and minerals
Phagocytosis of old RBCs
Activation of vitamin D
Gallbladder
stores and concentrates bile produced by liver
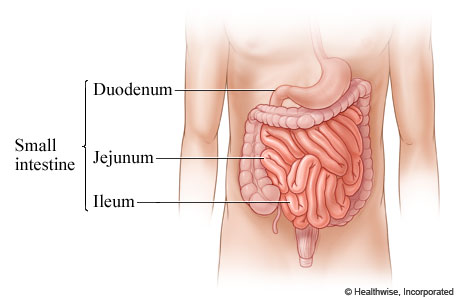
Small intestine
most digestion and absorption occurs
Small intestine is made of
Duodenum, Jejunum, and Ileum
Absorptive cells (in the small intestine)
digest and absorb
Goblet cells (in the small intestine)
produce mucus
Intestinal glands (in the small intestine)
produce intestinal juice
Paneth cells (in the small intestine)
produce antimicrobial proteins
Muscularis (in the small intestine)
inner circular layer: thicker and outer longitudinal layer: thinner
Small intestine wall contains
circular folds, villi, and microvilli
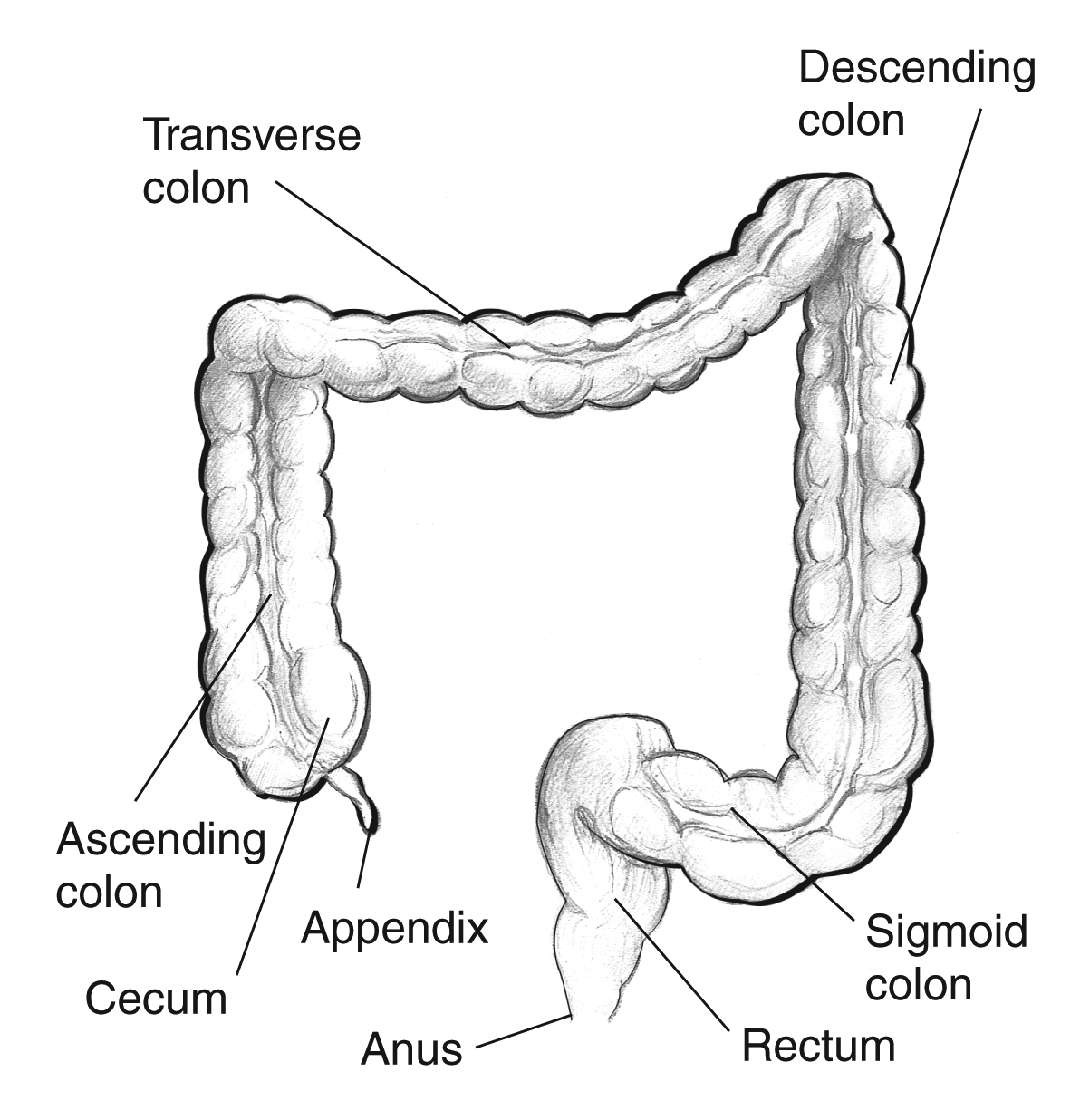
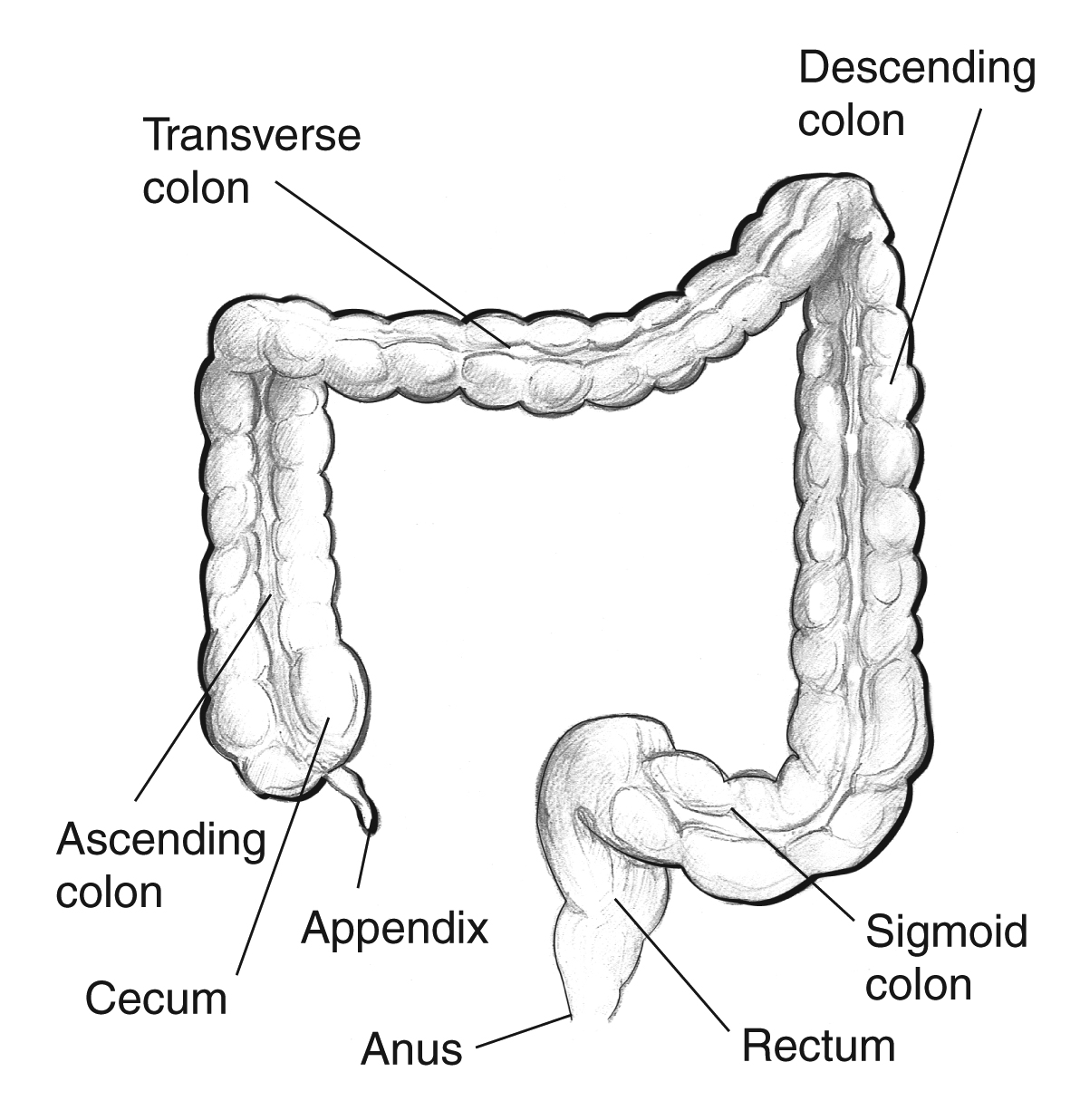
Large intestine completes
absorption, produce certain vitamins, and form and expel feces
Four main region of large intestine
cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal
illeocecal sphincter
between small and large intestine
Colon separated into
ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid
Internal anal sphincter
smooth muscle
external anal sphincter
skeletal muscle
Muscularis longitudinal layer of the large intestine if modified to form
teniae coli
Mechanical digestion starts in the
mouth (chewing)
Bolus
lump of soft food that is easy to swallow
Bolus is pushed to back of mouth by
tongue, food passes to pharynx
Epiglottis blocks
trachea
Upper esophageal sphincter opens allowing
food to pass into esophagus
Upper esophageal sphincter close as food travels
down esophagus to stomach passing through lower esophageal sphincter