Allosteric Regulation- Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
why does O2 bind to Mb or Hb?
oxygen has limited solubility
Myoglobin function
stores oxygen in muscle cells
myoglobin structure
single subunit protein with heme
hemoglobin function
transports oxygen from lungs to tissues; can also transport CO2 and protons
adult hemoglobin structure
2 alpha and 2 beta subunits, each with a heme
myoglobin has ___ helices
8 (mostly helical, less beta sheets)
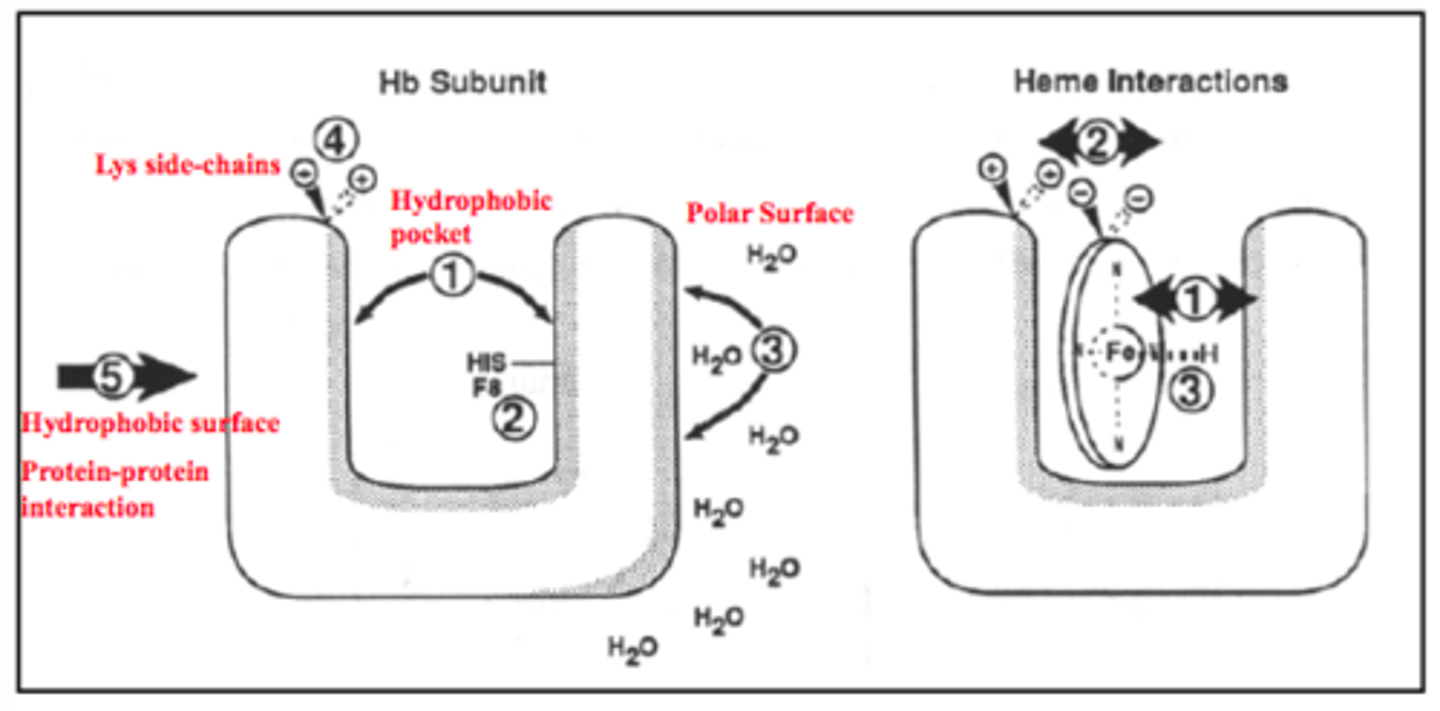
Where is the heme group located in myoglobin? why?
within a hydrophobic crevice, except for some polar histidines. nonpolar residues protect Fe2+ from oxidation to Fe3+
list shortest to longest- myoglobin, alpha chain Hb, or beta chain Hb?
alpha chain Hb, beta chain Hb, myoglobin
heme group
contains organic porphyrin ring and an iron ion in center, which binds oxygen for transport
3 types of myoglobin oxidation states
- deoxymyoglobin (Fe2+)
- oxymyoglobin (Fe2+, O2)
- metamyoglobin (Fe3+), can't carry oxygen
distal histidine function
weakens binding of carbon monoxide to heme, allowing for better oxygen binding
globin pocket
hydrophobic pocket protects iron from oxidation; has lysine side chains to form electrostatic interactions to position heme
unlike Mb, Hb affinity for oxygen is dependent on these molecule concentrations...
H+, CO2, and 2,3BPG
Advantages of quaternary structure
- stability
- genetic economy and efficiency
- bringing catalytic sites together
- cooperativity
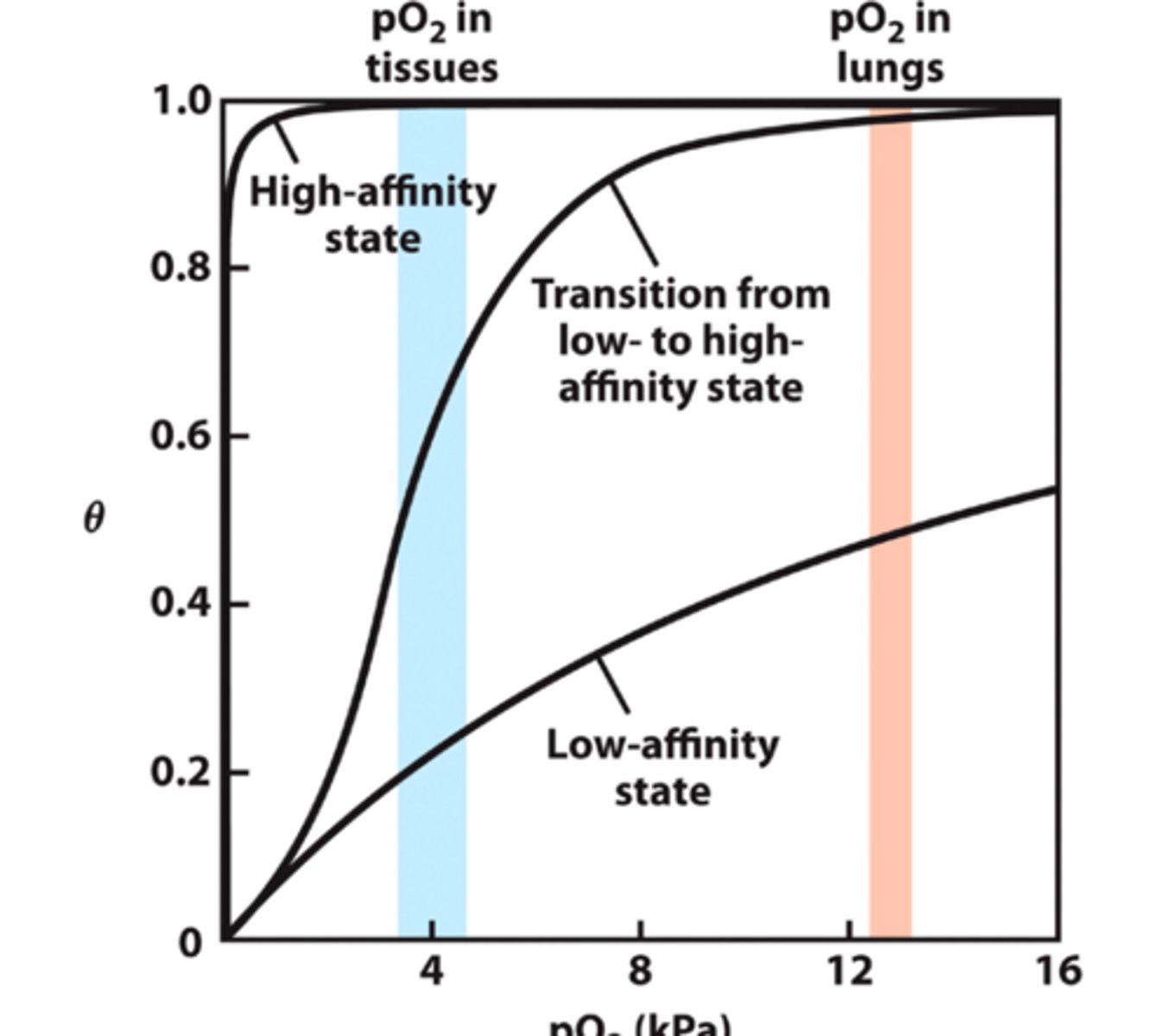
deoxyHb exists in the ____ state, meaning ____ affinity for oxygen
tense T; reduced
oxyHb exists in the ____ state, meaning _____ affinity for oxygen
relaxed R; increased
CO2, bisphosphoglycerate, and H+ all _____ proportion of T state subunits
increase
how is the observed O2 binding curve plotted compared to R-state and T-state binding curves?
observed O2 binding curve is between the theoretical curves for O2 binding to the R-state and T-state
the binding of each O2 molecule to Hb shifts the equilibria more toward the _____ state
relaxed R
which amino acid is often found at helix terminals?
proline
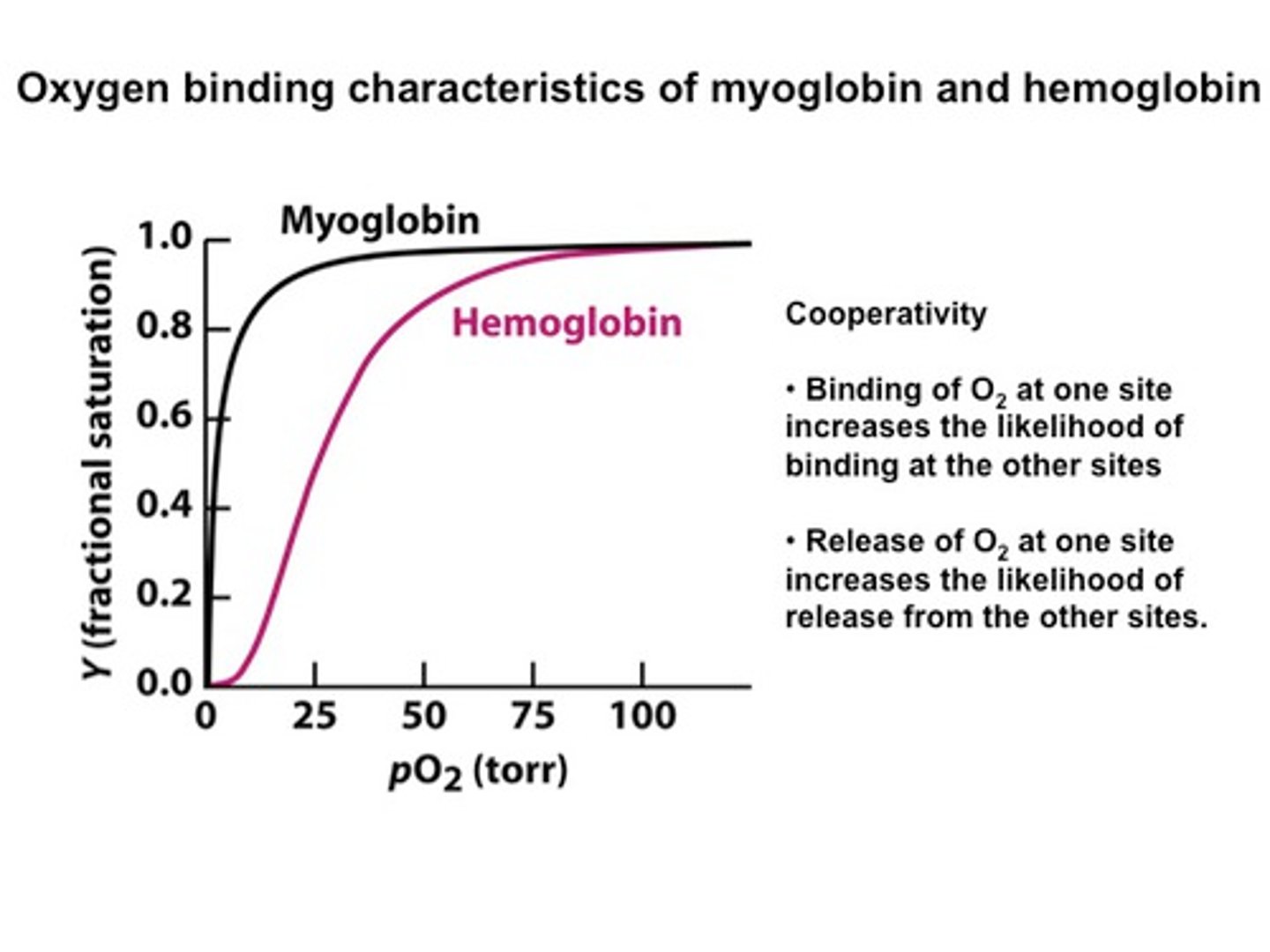
oxygen binding curve of myoglobin is _______. oxygen binding curve of hemoglobin is _____
hyperbolic; sigmoidal
at all [O2], Hb fetal binds oxygen more/less tightly than Hb adult
more
HbA has 2 alpha and 2 beta subunits- how is HbF different?
2 alpha and 2 gamma
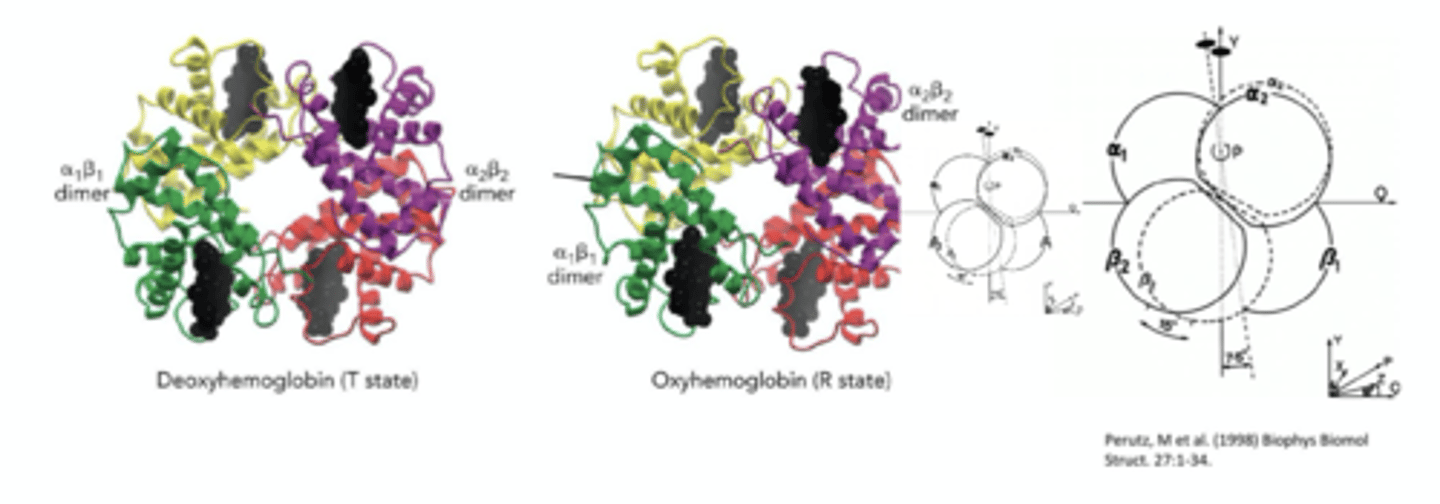
what conformational change occurs when Hb is oxygenated?
one aB dimer rotates relative to other aB dimer
BPG has what charge?
negative
Which Hb state has higher affinity for BPG?
deoxy T state
what interactions allow for BPG to bind to hemoglobin?
electrostatic interactions with basic amino acid residues, like His and Lys
situations with increased BPG concentration in RBC's include
- high altitude
- congestive heart failure
- pregnancy
steps for cooperativity (slide 28)
1. Fe2+ moves out of heme plane in deoxy Hb
2. O2 binding fulls iron into heme plane
3. iron-His92 bond moves F helix since iron moves
4. rotation of aB dimer in respect to other aB dimer
5. movement of helix changes other non-covalent interactions, signaling to alpha chain that beta chain has bound oxygen
6. oxygen binding releases CO2 and H+ in the lungs
Bohr effect
a decrease in the amount of oxygen associated with hemoglobin (more goes into tissues) in response to a lowered blood pH resulting from an increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood
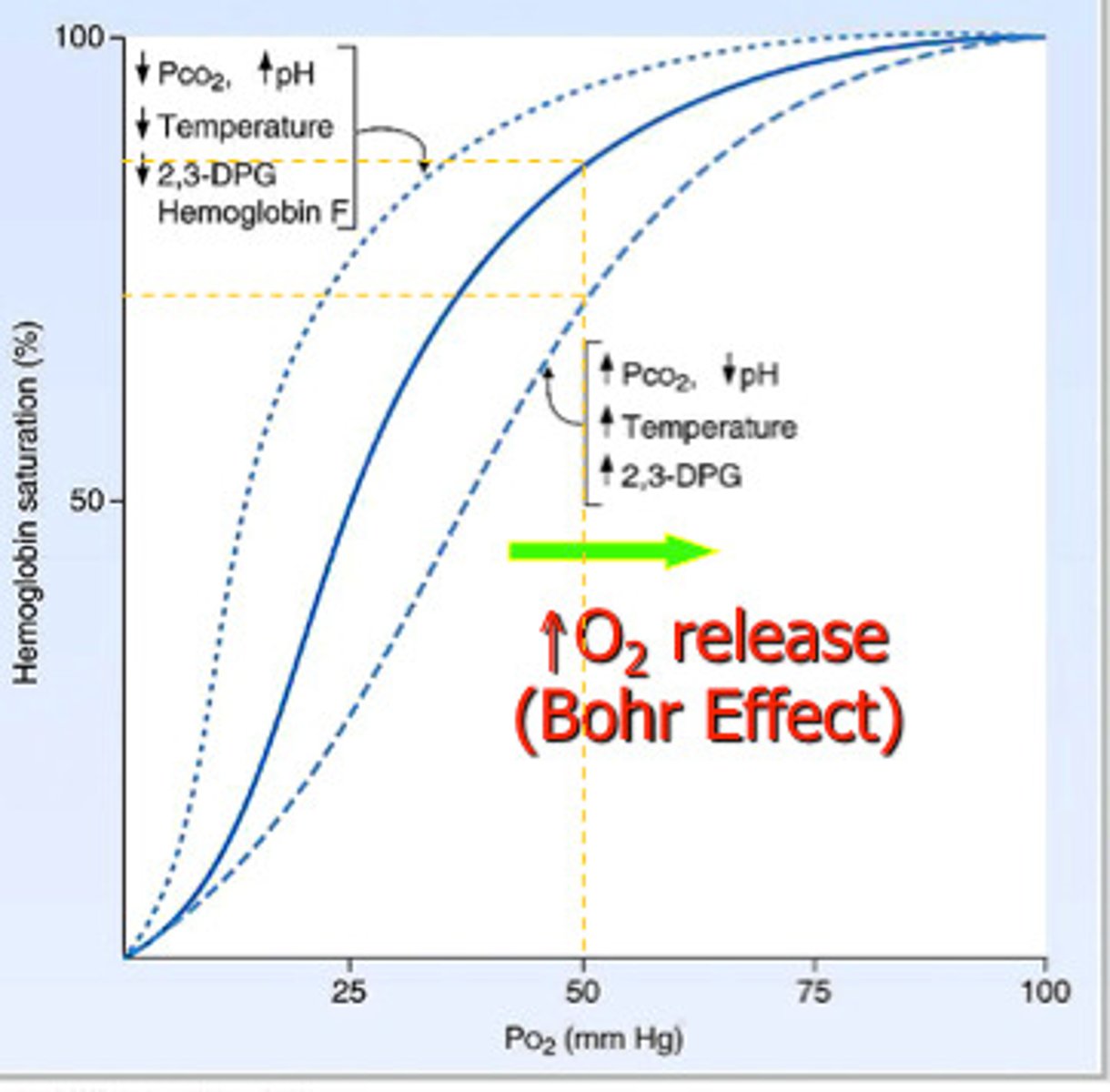
which pH-dependent bond forms in
Hb in acidic conditions, stabilizing structure of deoxyhemoglobin (Bohr effect)?
His 146 - Asp 94; histidine is protonated in acidic conditions, resulting in this interaction
role of carbonic anhydrase
Converts CO2 and H2O to carbonic acid in RBC's, which is soluble
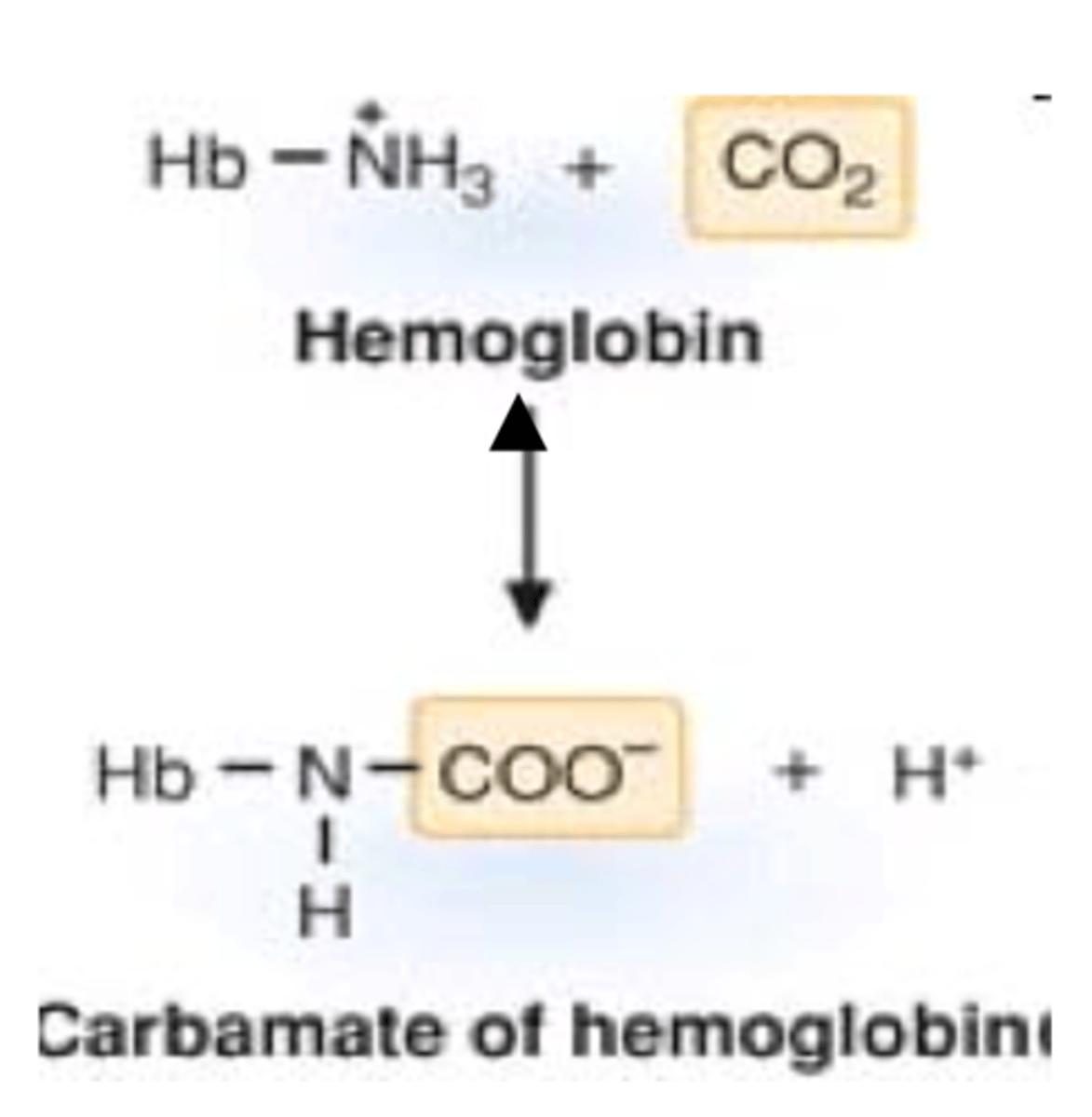
carbaminohemoglobin
the compound formed by the union of carbon dioxide with hemoglobin
what point mutation causes HbS?
valine replaced by glutamate
Hydroxyurea
increases HbF in RBC's for sickle cell patients
what factor influences the binding of oxygen to myoglobin?
partial pressure of oxygen only
when binding oxygen to myoglobin at low pH, what type of oxygen binding curve do you expect?
hyperbolic
in deoxy hemoglobin, the Fe is five-coordinated to which of the following?
four pyrole nitrogens of heme moiety, proximal His of Hb
what would be effect of A83K mutation located within allosteric binding pocket for 2,3BPG on the function of adult hemoglobin?
mutation would increase proportion of T state HbA molecules
in which of the following conditions will binding of oxygen to HbA be weakest?
- when pH increases from 7 to 7.2
- when H+ concentration decreases
- when partial pressure of oxygen increases
- when concentration of 2,3BPG decreases
- when concentration of CO2 increases
- when concentrations of H+ and 2,3BPG decrease
when concentration of CO2 increases
carbon monoxide poisoning is due to...
tight binding of CO to iron in heme group
in both hemoglobin and myoglobin, heme group is called a _____ group
prosthetic
in HbS, the basis of the malfunction of hemoglobin is due to...
substitution of single amino acid in beta chain of HbA
porphyrins are cyclic compounds that are formed through methylene bridges linking how many pyrrole groups?
4