Lab final
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
in a ______ of a skeletal muscel fiber we find myofilaments composed of thick filaments constructed of ______ and thin filaments made of _____.
myofibril
myosin
actin
how do we electrically record muscle activity?
through an electromyogram
muscles of the human body contract following the….
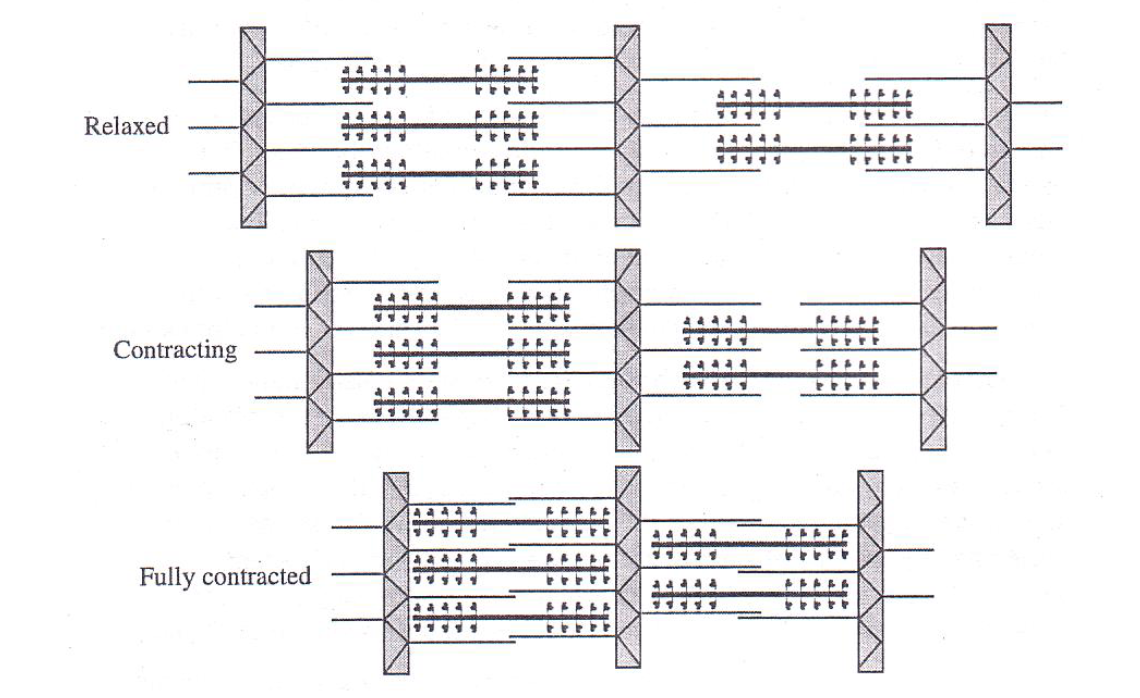
sliding filament theory
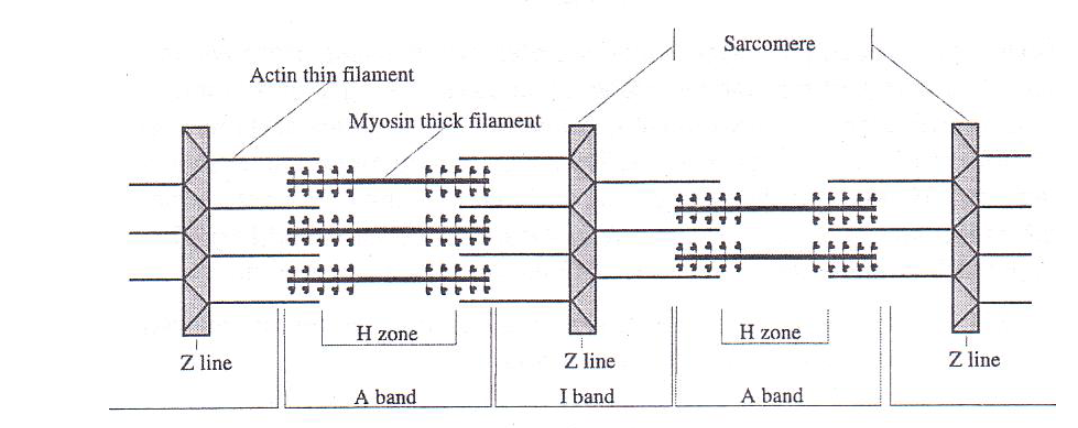
when a skeletal muscle is initiated to contract, the width of the _____ gets smaller
I band
the contractile unit of a muscle is called a
sarcomere
the primary function of muscle is to convert _____ energy into _____ energy
chemical to mechanical
a skeletal muscle subjected to the glycerination process :
permits investigation of muscle contraction with the addition of ATP and ions to initiate the contraction process
also removes ions and ATP from the tissue, disrupting regulatory proteins so that binding sites on actin are no longer blocked
a somatic motor nueron and all the skeletal muscle fibers it innervates is called a
motor unit
organization of a skeletal muscle
myofilaments, myofibril, muscle fiber, fascicle, muscle
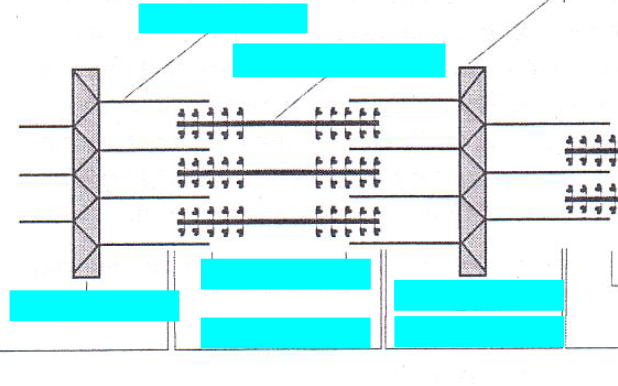
label the sarcomere
sliding filament theory
actin filaments are pulled centrally when the myosin crossbridges bind to the actin filaments
for a muscle fiber to contract, what must first happen
myosin heads must first be activated by ATP
Contraction process
signals received by NS
release of Ca ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca interacts with troponin which moves the tropomyosin on actin to allow activated myosin heads to bind
myosin head with ADP and P binds to actin
Phosphate released- power stroke
ADP released and ATP binds, detaching myosin head
ATP hydrolyzes
electromyogram
the detection, amplification and recording of changes in skin voltage produced by underlying skeletal muscle contraction
used to dx neuropathies and myopathies
signal is consequence of propogation of motor nerve impulses and their transmission at the nueromuscular jxns and propagation of muscle impulses by the sarcolemma and t tuble resulting in excitation contraction coupling
glycerinated skeletal muscle
glycerin creates holes in sarcolemma → removes ions and ATP and disrupts regulatory proteins so that binding sites on actin are no longer blocked
no Ca or ATP found here
length tension relationship
too flexed- myofilaments are too close together and cannot generate enough force to contract well, start associating too close together
too relaxed- myofilaments are too far apart to form cross-bridges
a muscle generates the most force when it is at a medial length
muscle fatigue
reduction in ability of muscle to generate force as a result of previous contractile activity
glycerinated muscle contraction with salts and ATP
we can conclude that the addition of ATP and salts in a muscle needs to occur at the same time for optimal contraction
how is muscle movement related to an electrical signal
muscle fibers are innervated by a motor neuron which means that when the motor neuron is activated, the muscle fibers associated with it respond by generating their own electrical signals that lead to the contraction of the muscle fibers
relationship btwn strength of muscle contraction and amount of electrical activity generated
higher energy produced= higher strength of muscle contraction
more energy is produced by your muscles when they are extended
hand position and muscle activity
higher muscle activity is seen with extension and flexion
lower muscle activity is seen when the muscles are at rest
grip strength in dominant vs nondominant hands
dominant hand is usually stronger
gender and grip strength
males have stronger grip strength than females
grip strength in fingers
the grip strength decreased from the index to the pinky
least difference was from index to middle, most difference from middle to pinky
force and hand position
hand position determines how much the actin and myosin fibers overlap each other and couse the muscle to either shorten or lengthen
flexion and extension produced the least muscle force, no angle produced the most muscle force
weight and muscle fatigue
muscles fatigue quicker when weight is added
explain muscle loss and stroke
loss of blood flow→ lack of muscle function
stroke causes issues in communication btwn the muscle and the brain causing them to no longer work normally
how does a muscle know how much force is required to perform an action?
motor neurons can signal for how much force the muscle needs to in order to perform a task.
what causes difference btwn fingers and pinch strength
frequency of fingers used and dominant hand
functions of blood
carry O2 and nutrients to the cells in organs
remove wastes
contribute to hormonal and temperature regulation
protection via clotting and defense mechanisms (immunity)
cellular portion of blood
formed elements
formed elements include
erythrocytes, leukocytes and thrombocytes
hematocrit
the proportion of blood that consists of RBCs
expressed as percentage
higher the HCT, the more RBC available to transport O2
normal: 41-53% in males, 36-46% in females
low HCT term
anemia
high HCT term, high altitudes and chronic smokers
polycythemia
differences in human blood type due to
antigens on surface of RBC
granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils
agranulocytes
lymphocytes and monocytes
the _____ are reservoirs for venous blood and the _____ are the major pumping chambers for delivering blood to pulmonary and systemic circulation
atria, ventricles
path of electricla conduction in the heart
SA node→ AV node→ atrioventricular bundle→ atrioventricular bundle fibers → purkinje fibers
ECG
measures the electrical activity of the heart through electrodes on the skin
changes in ECG due to interruptions of electrical signal generated or its transmission
computes the difference btwn positive and negative electrodes and displays changes in voltage differences with time
negative to the positive
the direction of activity during the cardiac cycle
mean electrical axis (MEA)
bipolar lead
lead composed of 2 discrete electrodes of opposite polarity
lead axis
hypothetical line joining poles of a lead
einthovens law
lead 1 + lead 3= lead 2
einthovens triangle can be collapsed to create an axial reference system
ECG vectors
length- magnitude of current
orientation- direction of current flow
tip of arrow- positive pole
base of arrow- negative pole
plot lead 1 and lead 3 to find MEA(direction) and mean potential of the heart (length)
left axis deviation
btwn -30 and -90
results from conditions that cause the left ventricle to take longer than normal to depolarize
right axis deviation
btwn 90 and 180 deg
can be normal in people with long narrow chests but in many adults is associated with damage to conduction system in right ventricle
total RBC count
normal: 4.5 to 5.9 million/mm³
layers of heart wall
fibrous layer, parietal layer, pericardial cavity, visceral layer, myocardium, endocardium
P wave
atrial depolarization
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
t wave
ventricular repolarization
PR interval
delay in electrical activates of ventricles after SA node fires
ST interval
entire cardiac muscle is depolarized
QT interval
ventricular systole
avg HCT for males
41-55%
avg HCT for females
36-46%
what factors can influences the R wave
height and limb length
low WBC count
low immune respons
high WBC count
autoimmune disease
airflows through the conducting zone of the respiratory system and into the respiratory zone due to
a pressure gradient
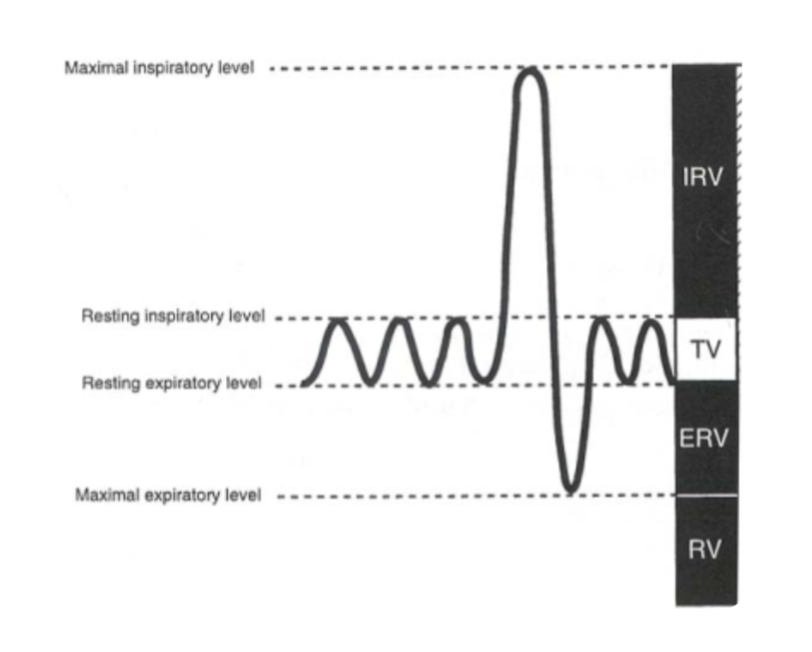
residual volume
the volume of air left in the lung after the max exhalation
categories of pulmonary disorders
restrictive and obstructive
where does the respiratory zone begin
the external nares and ends at alveoli
what is spirometry
medical test that measure the volume of air an individual inhales or exhales as a fxn of time
asses normal lung fxn and capacity
dx of disease
help monitor progression of disease and effectiveness of treatment
tidal volume
volume of air inhaled or exhaled with each breath during normal breathing
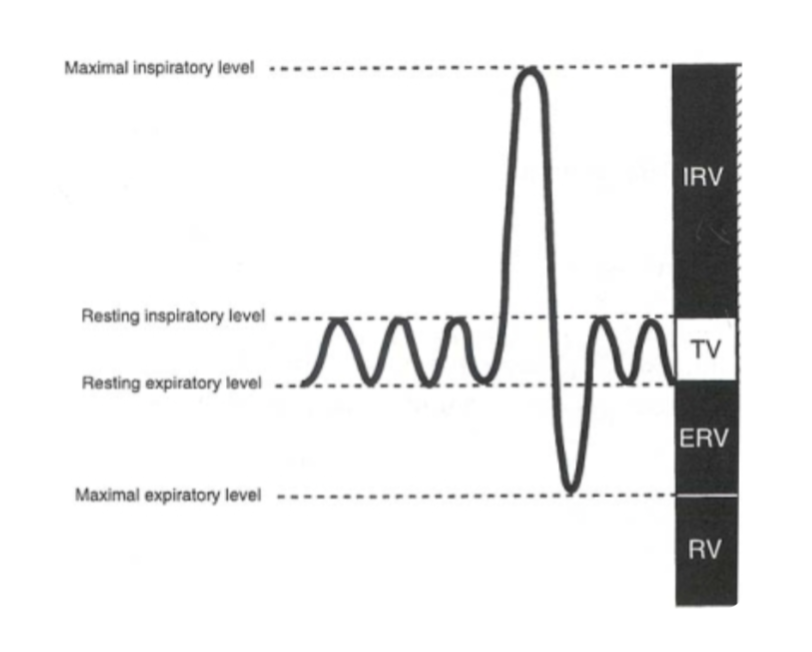
inspiratory reserve volume
max vol of air inhaled from the end inspiratory tidal position
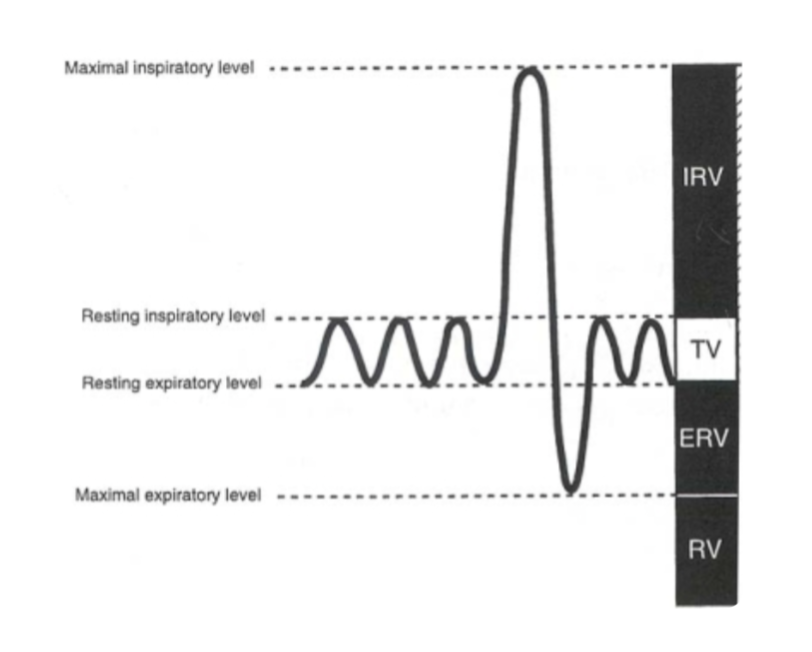
expiratory reserve volume
max volume of air that can be exhaled from resting end-expiratory tidal position
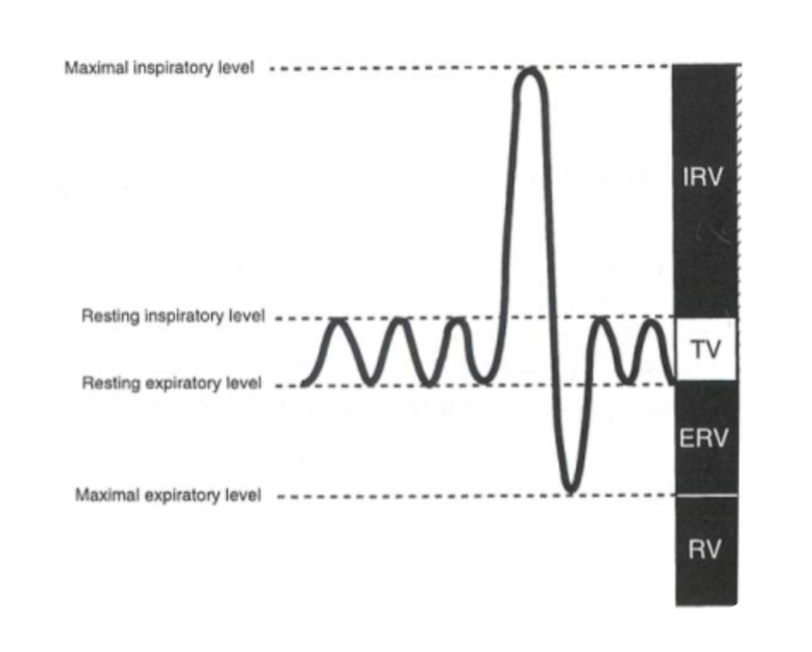
total lung capacity
sum of all volume compartments or vol of air in lungs after maximum inspiration
inspiratory reserve vol + tidal volume + expiratory reserve vol + reserve volume
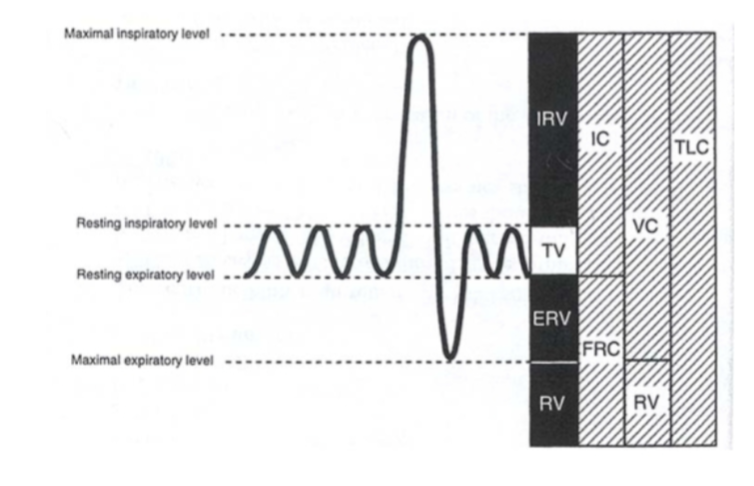
vital capacity
total lung capacity minus reserve volume
or
inspiratory reserve vol + expiratory reserve vol + tidal vol
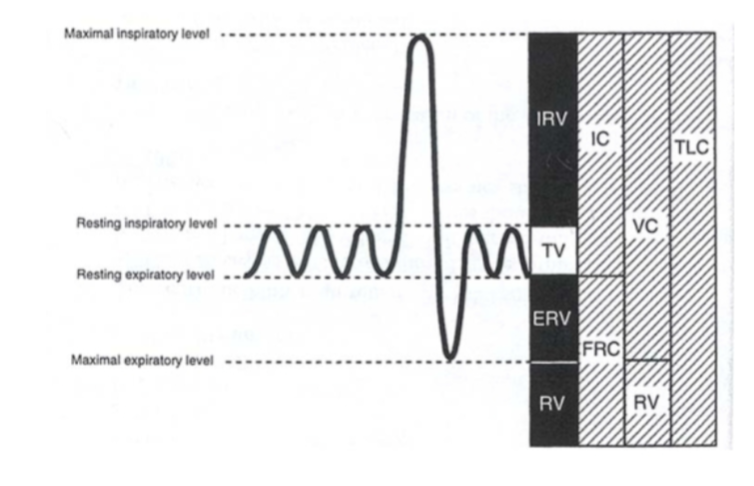
inspiratory capacity
sum of inspiratory reserve vol and tidal volume
spirometry normal values depend on
height, age, gender, and ethnicity
when does the diaphragm contract?
inspiration, contracts down
functional residual capacity
volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal exhalation
expiratory reserve vol + residual volume
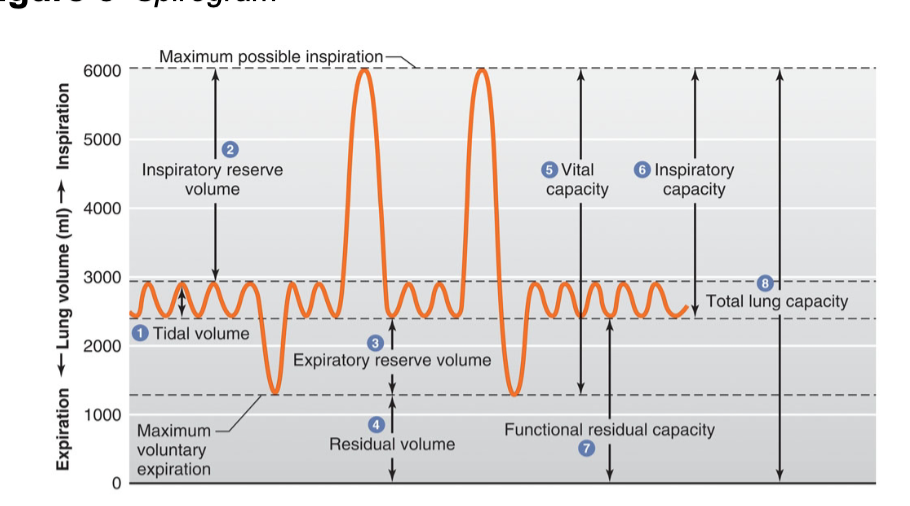
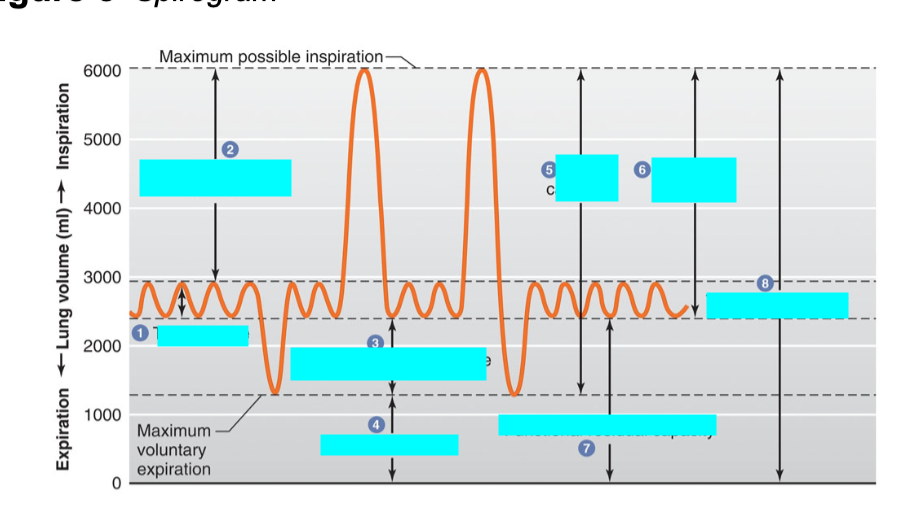
what is 1
tidal volume
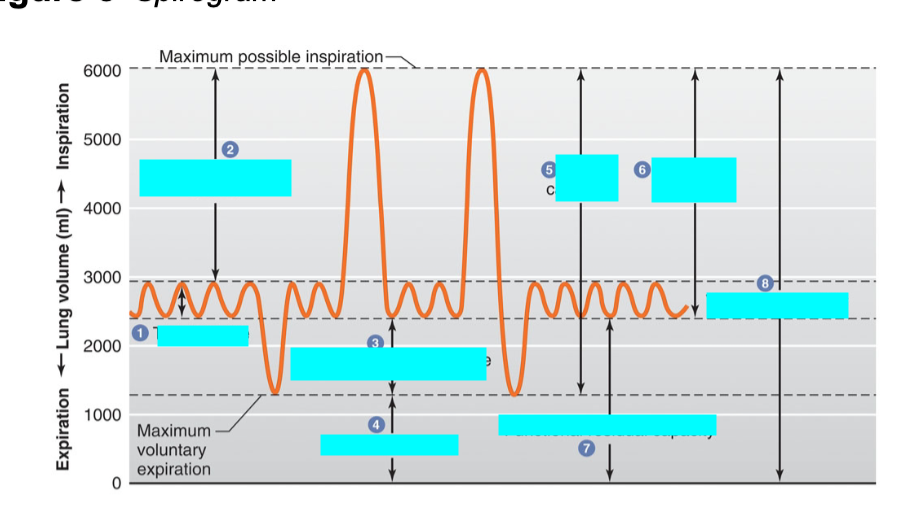
what is 2
inspiratory reserve volume
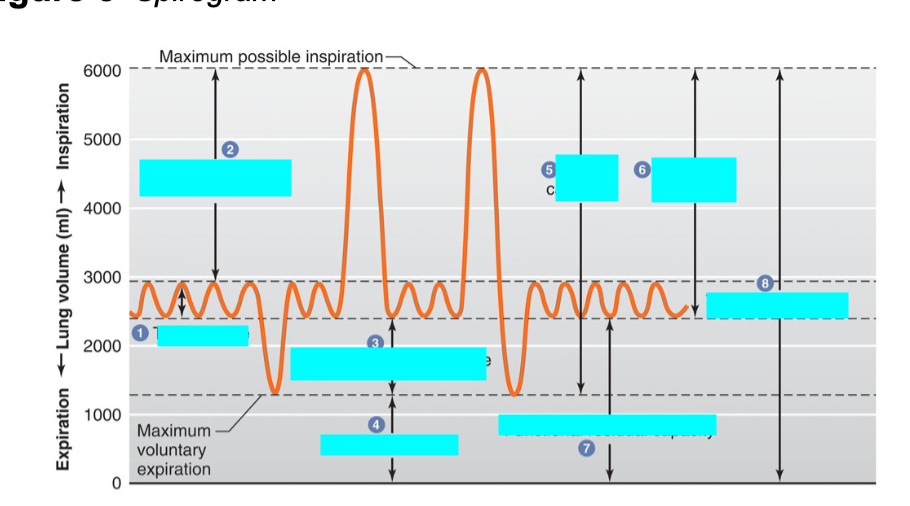
what is 3
expiratory reserve volume
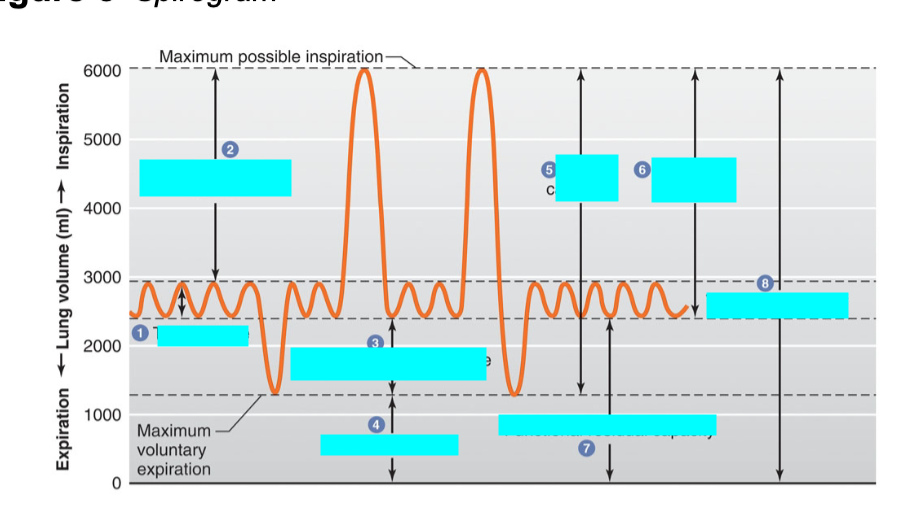
what is 4
residual volume
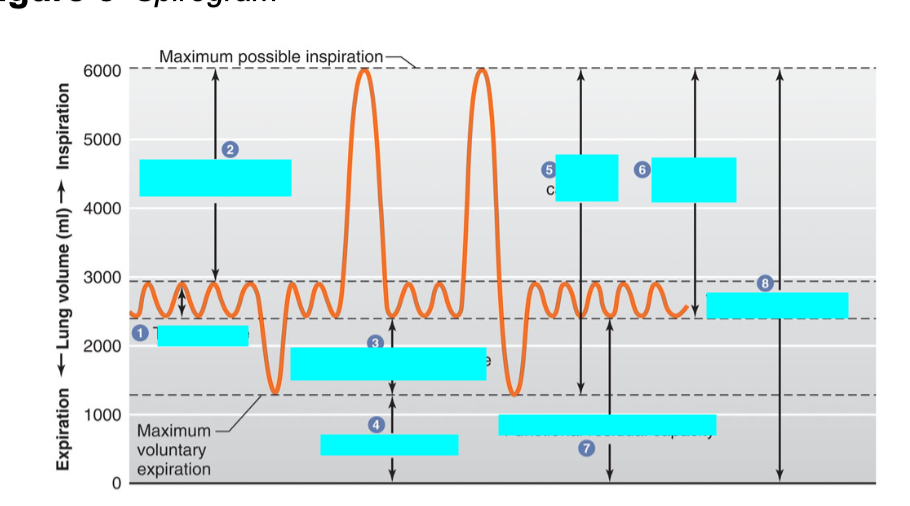
what is 5
vital capacity
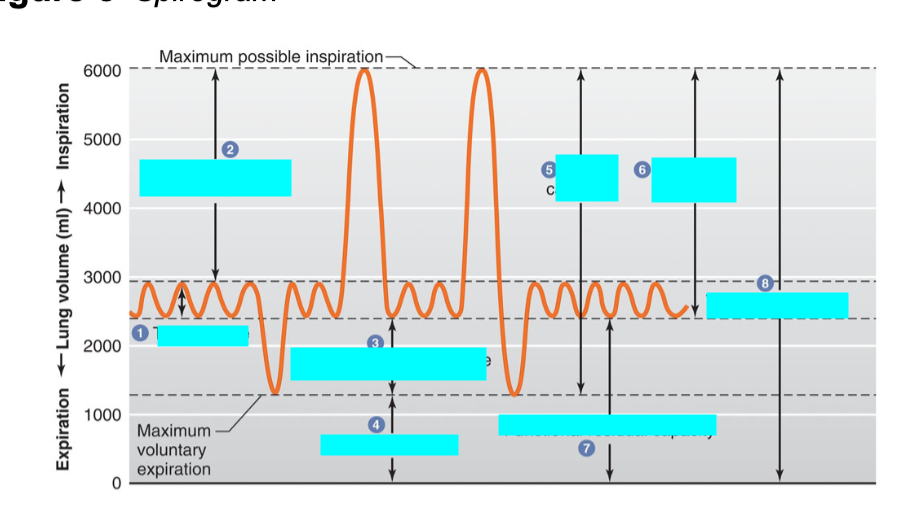
what is 6
inspiratory capacity
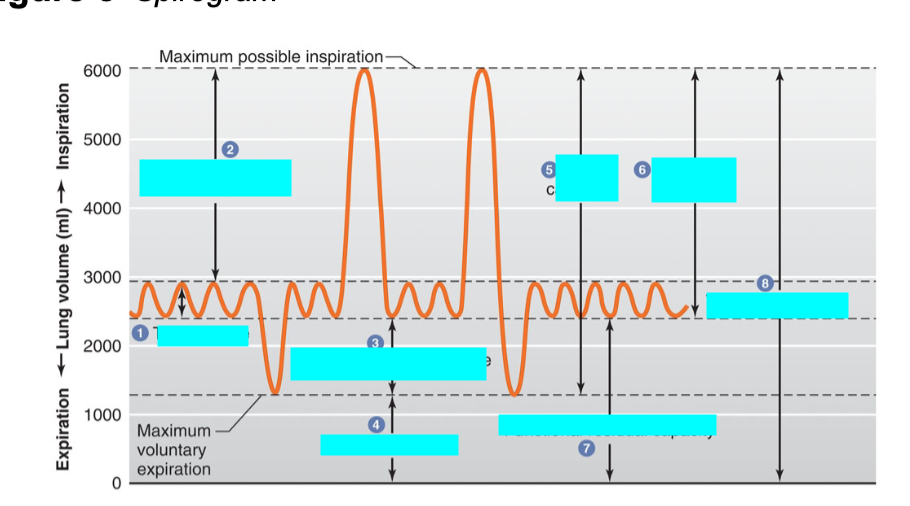
what is 7
functional residual capacity
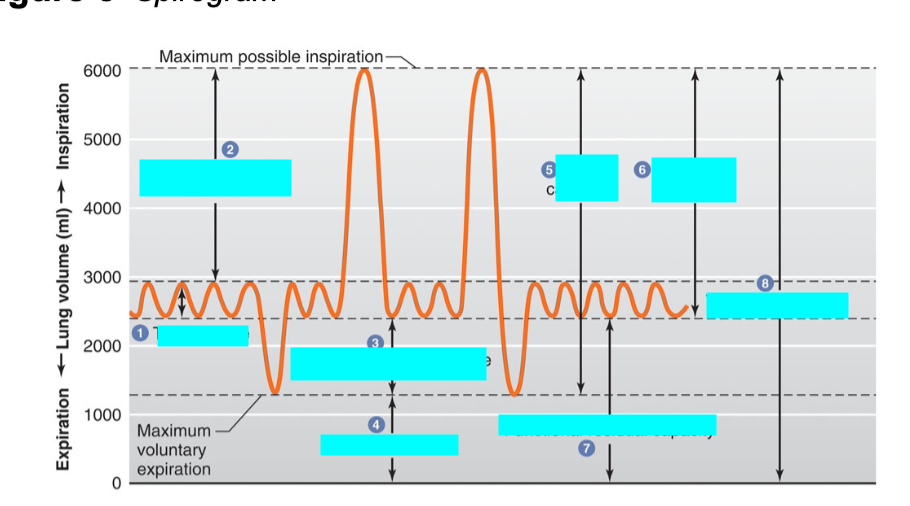
what is 8
total lung capacity
difference btwn lung volumes in males and females
women have proportionally smaller airway size and lungs than men so they typically have a lower vital capacity than men
total minute volume calculation
tidal volume * breaths/min
represents that amount of air inhaled or exhaled from a subject in 1 minute
how does breath holding affect tidal volume, respiratory rate and total minute volume?
inc in tidal volume and total minute volume
dec in resp rate
how does rapid breathing affect tidal volume, respiratory rate and total minute volume?
dec in tidal volume, resp rate and total minute volume
how does excercise affect tidal volume, respiratory rate and total minute volume?
inc in tidal volume and total minute volume
dec in resp rate
what would happen to the expiratory reserve volume when you are treading water?
dec in expiratory resrve volume
what happens to the lungs during emphysema?
In severe emphysema, due to the destruction of lung tissue and reduced recoil, the
total lung capacity will either be the same or slightly increase because the lungs can lose their elasticity and can maybe hyperinflate or not which can cause some issues with exhalation and trapped air.
The tidal volume would decrease due to the decreased recoil and contraction issues which will cause agony in breathing or dyspnea as the lung and individual finds difficulty to accommodate air and breathe properly.
During ________ blood pressure drives the movement of water and dissolved substances through the fenestrations ad filtration slits of the filtration membrane . This basic component of renal function occurs in the ________. In _______ we observe about 99% of useful solutes being reclaimed from the glomerular filtrate and returned to the blood. This basic component component of renal function primarily occurs in the _______. Unwanted substances like urea and creatine, are transported from the blood back into the renal tubule, this process is called ______ and occurs mainly in the _______.
glomerular filtration, renal corpuscle, tubular reabsorption, proximal convoluted tubule, tubular secretion, distal tubular secretion
nephron
functional unit of kidney
responsible for urine formation
comprised of renal corpuscle and renal tubules
filter blood to form filtrate
reabsorption
from lumen of nephron to blood
occurs in proximal convoluted tubule, loop of henle and distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
glucose, amino acids and bicarbonate
secretion
from blood to lumen of nephron
occurs in PCT, DCT, and collecting duct
removes wastes such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine; drugs such as penicillin, aspirin, and morphine; and excess ions such as H+, K+ and
HCO3-.
filtration
occurs in renal corpuscle
resulting from hydrostatic pressure of blood pushing fluid out of the capillary wall of the glomerulus producing filtrate
contains same molecules as plasma minus proteins
passive process
urinalysis
checking appearance, conc and content of urine
used to detect and manage a wide range of disorders such as UTI, kidney disease and diabetes
central role of kidneys
regulate volume and chemical composition of body fluids
influences blood plasma, IF and lymph
glomerulus
tightly woven, highly permeable capillary bed at end of afferent arteriole
inner visceral layer of the glomerular capsule covers the glomerulus, epithelium is composed of podocytes with foot-like processes called pedicels that interdigitate to form filtration slits.
the outer parietal layer is separated from the inner visceral layer by the capsular space
Both layers of the glomerular capsule are composed of simple squamous epithelium.
renal tubule
a convoluted tubule lined by epithelial cells
countercurrent multiplier
the nephron loop/loop of Henle, and it establishes the osmotic gradient