physics - topic 2: forces
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the formula for speed?
Speed = Distance/Time
What is a vector quantity, and what is an example of this?
A quantity with magnitude and direction. Examples include velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, weight.
What is a scalar quantity, and what is an example of this?
A quantity with only magnitude. Examples include speed, time, mass, distance.
On a distance-time graph, what does the gradient show?
Velocity.
The steeper the gradient, the ____ the speed.
Faster.
What does a negative gradient show on a distance-time graph?
Indicates the object is moving back to starting point.
What does a horizontal line show on a distance-time graph?
The object is stationary.
What does a curved line represent on a distance-time graph?
The object is accelerating or decelerating (velocity is changing).
On a velocity-time graph, what does the gradient show?
Acceleration.
The steeper the gradient, the ____ the acceleration.
Greater.
What does a negative gradient represent?
The object is decelerating.
What does a horizontal line represent?
The object is travelling at constant speed.
What does the area under a velocity-time graph represent?
Displacement.
When charged particles experience an attractive or repulsive force, what is this called?
Electrostatic Interaction.
What diagram can you use to show the forces on an object?
A free body diagram.
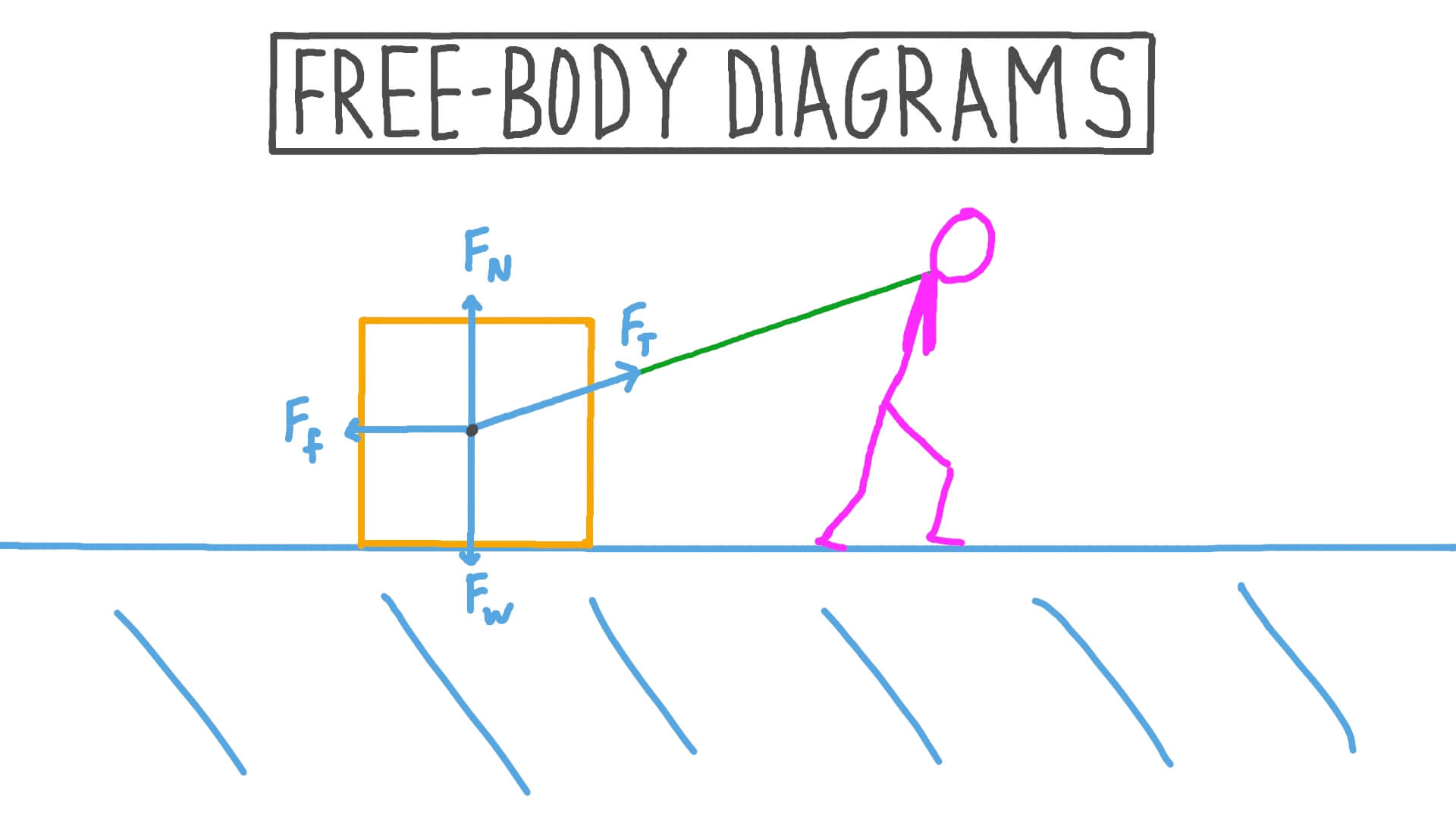
What is a reaction force?
The force exerted in response to another force.
On a scaled drawing, what does a larger arrow show?
Larger/greater force.
If the arrows are in opposite directions with equal length, what’ll happen?
Forces will cancel out, so the object will be in equilibrium. It’ll travel at constant velocity.
What is Newton’s First Law (law of inertia)?
States that an object will remain at rest (or continue moving at a constant velocity) unless acted upon by an external force.
What is Newton’s Second Law and the equation that comes with it?
Acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to its mass.
Resultant force = Mass × Acceleration
F = ma
What is the equation for momentum?
Momentum = Mass × velocity
p = mv
Is momentum conserved?
Yes: Total momentum before = Total momentum after
What is Newton’s Third Law?
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
e.g. When a rocket launches, of the forces being ejected from the rocket is equal to the force that lifts the rocket from the surface.
What is spring deformation?
The change in shape or size of a spring when a force is applied to it.
What are two main types of deformation and their outcomes?
Elastic Deformation: The object returns to it’s original shape when the load has been removed, for example an elastic band.
Plastic Deformation: The object doesn’t return to it’s original shape when the load has been removed, for example bending a steel rod.
What is Hooke’s Law, and what is the equation linked to this?
Force is directly proportional to the distance stretched, as long as the elastic limit hasn’t been reached.
Force = Spring constant × Extension.
F = kx
What is the equation for elastic potential energy?
Energy = ½ × Spring Constant × Extension2
E = ½ kx2
On a graph representing Hooke’s Law, what has happened when the line stops being linear?
This is the elastic limit. This is the point where the spring will not return to it’s original shape.
What is ‘Work Done’?
The energy transferred when a force causes an object to move.
What is the equation for weight?
Weight = Mass × Gravitational Field Strength
W = mg
What is the difference between weight and mass?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, a fundamental property that doesn't change with location.
Weight, on the other hand, is the force exerted on an object due to gravity, and therefore depends on the gravitational pull of the planet
What is the equation for Gravitational Potential Energy?
Gravitational Potential Energy = Mass × Field strength × Height
GPE = mgh
What is a moment?
The turning effect of a force.
What is the equation for a moment?
Moment = Distance × Force
What is the equation linking area, pressure, and force?
Force = Pressure × Area
F = PA
What is the value of gravitational field strength on Earth?
10 N/kg.
Why will a gear turn faster if it has less teeth?
It will have a smaller circumference and radius, so it requires a smaller amount of rotation to do a 360° turn.