Lecture 20 - Cell-to-cell interactions: Part 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
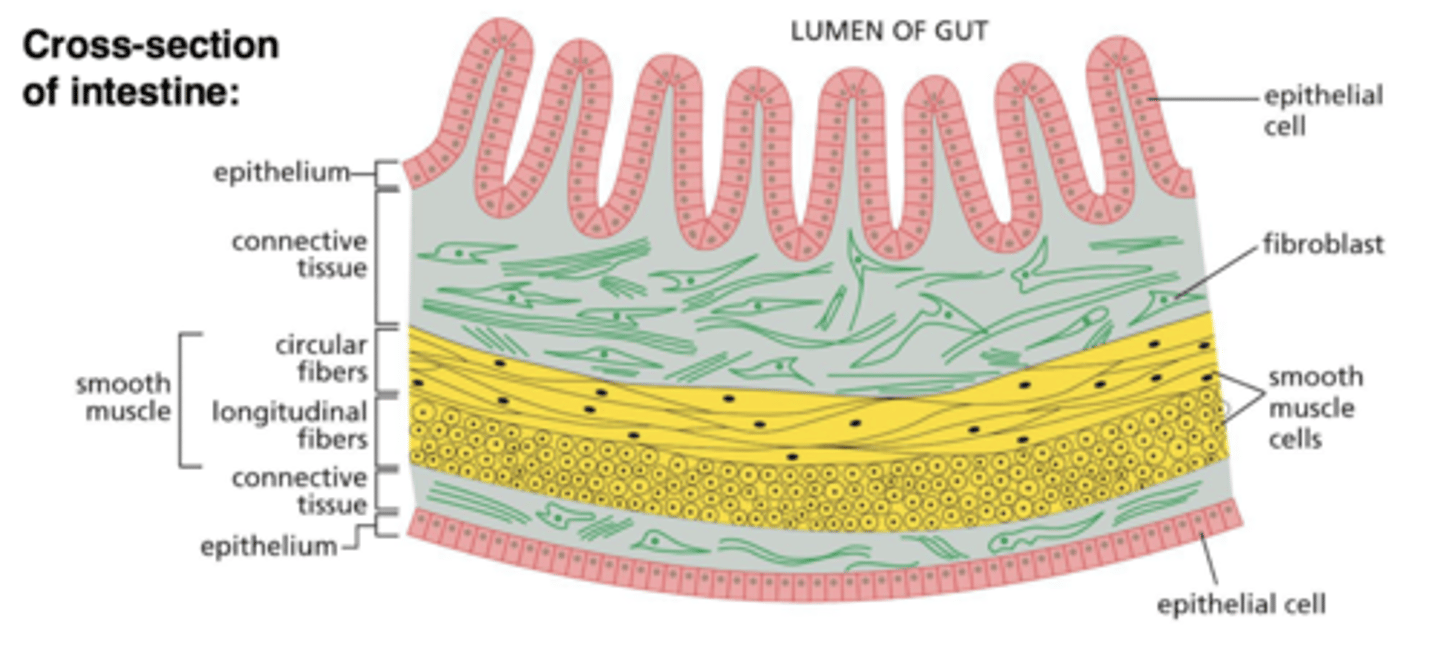
what is a tissue made of?
cells + ECM
four major tissue types
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
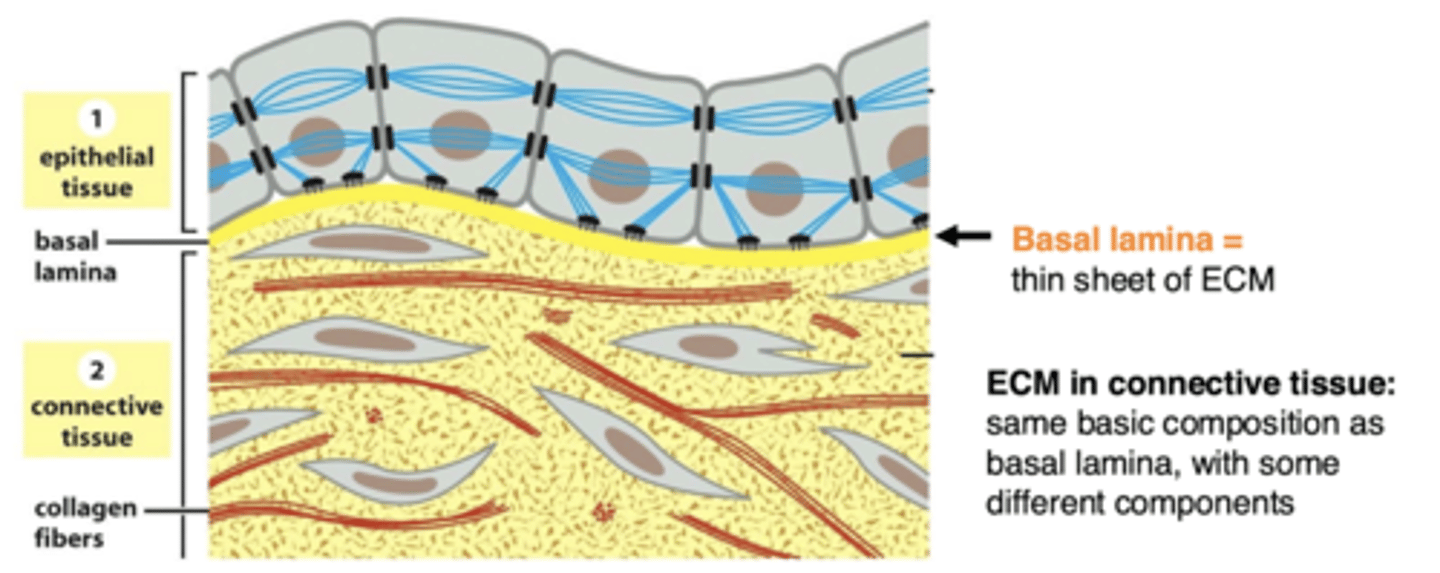
ECM in epithelial tissues
not abundant in epithelial tissue (is only a thin sheet of basal lamina)
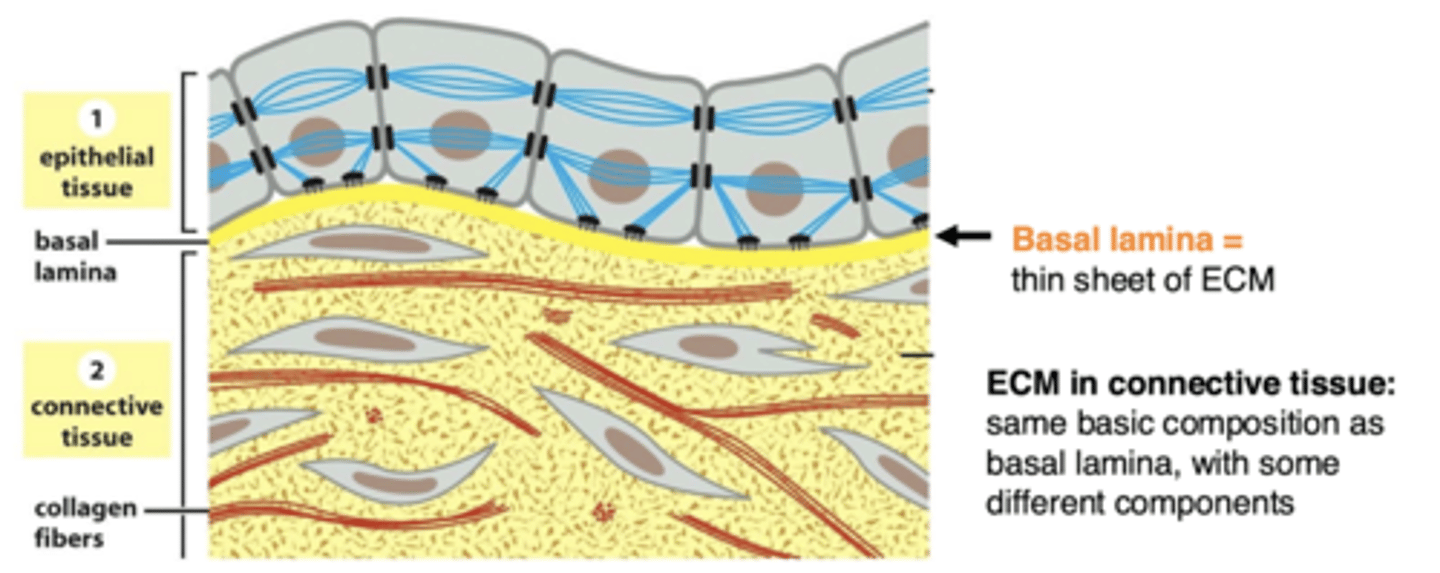
ECM in connective tissues
very abundant in connective tissue (cells are more sparse and don't necessarily contact each other)
what provides mechanical strength to epithelial tissue?
cell-cell contacts/cytoskeleton
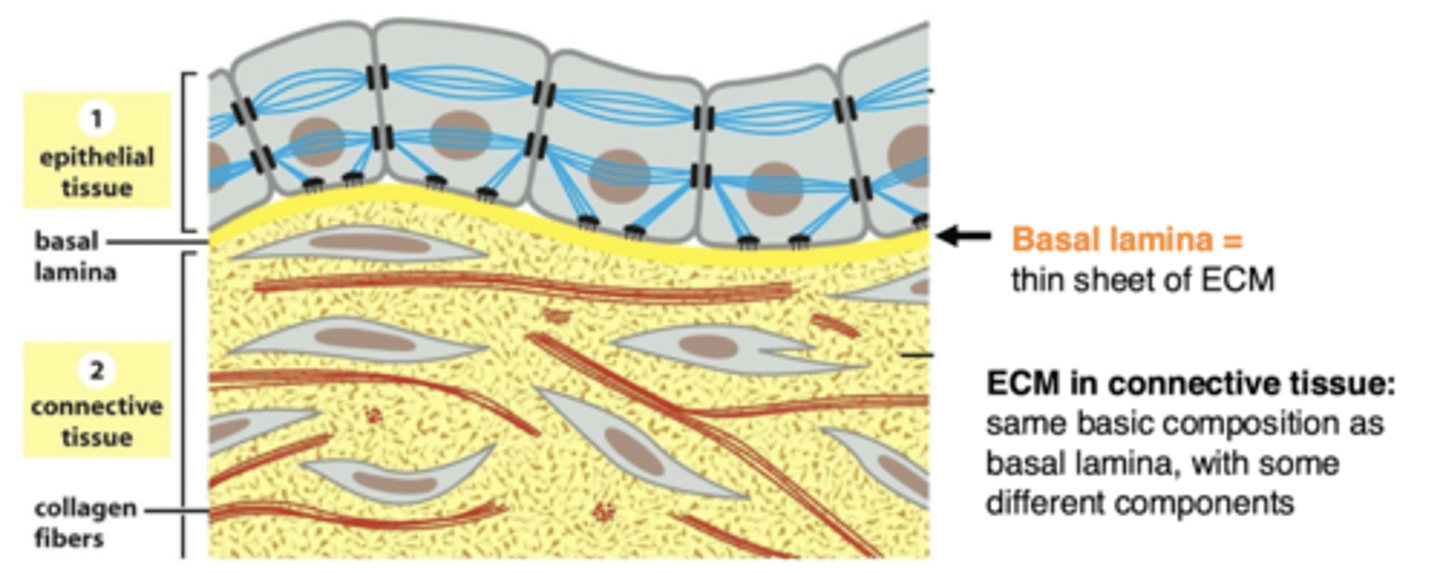
what provides mechanical strength to connective tissue?
the ECM, as cells are spare (connective tissue ECM has collagen fibers)
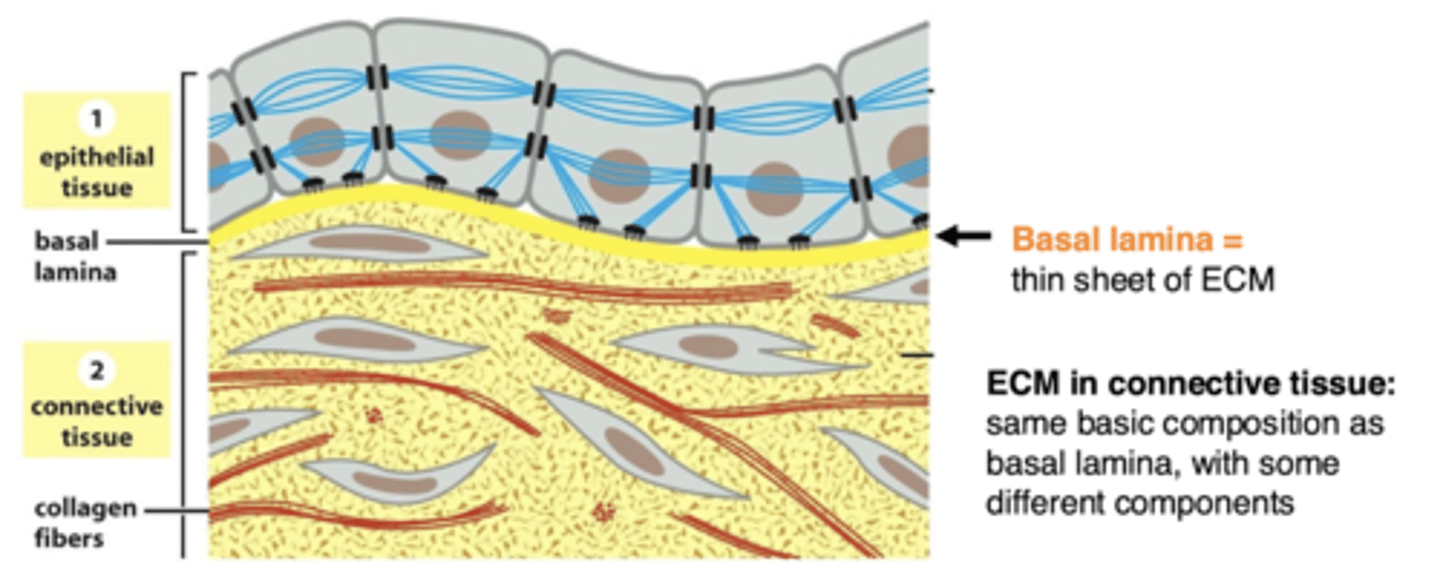
the basal lamina of epithelial cells is located between...
epithelial (or muscle) cells and the connective tissue
basal lamina
sheet-like meshwork of ECM (basal lamina is a type of ECM)
connective tissue
isolated cells, with a large amount of ECM
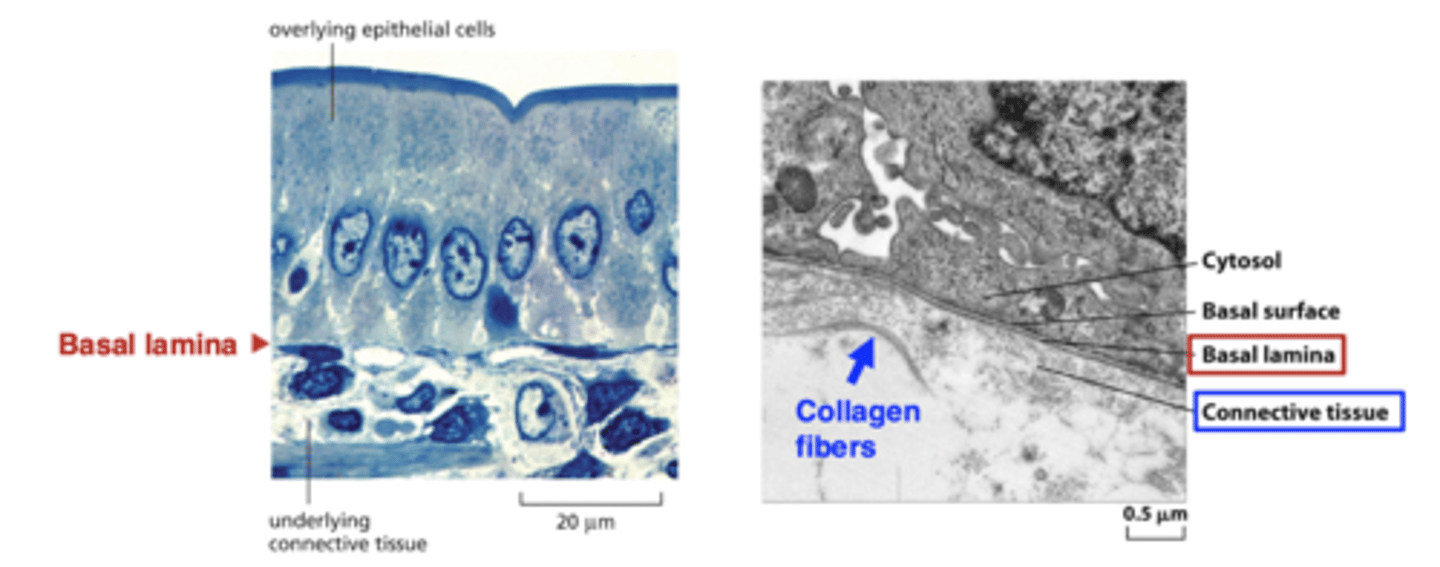
True or False: the basal lamina is structured differently in different tissues
True
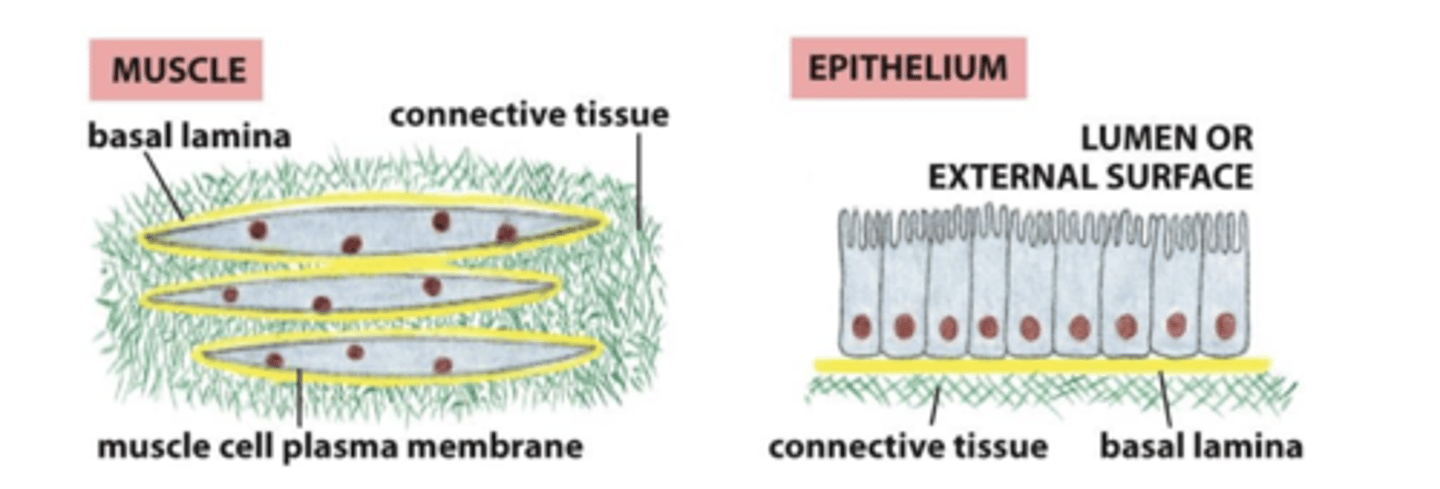
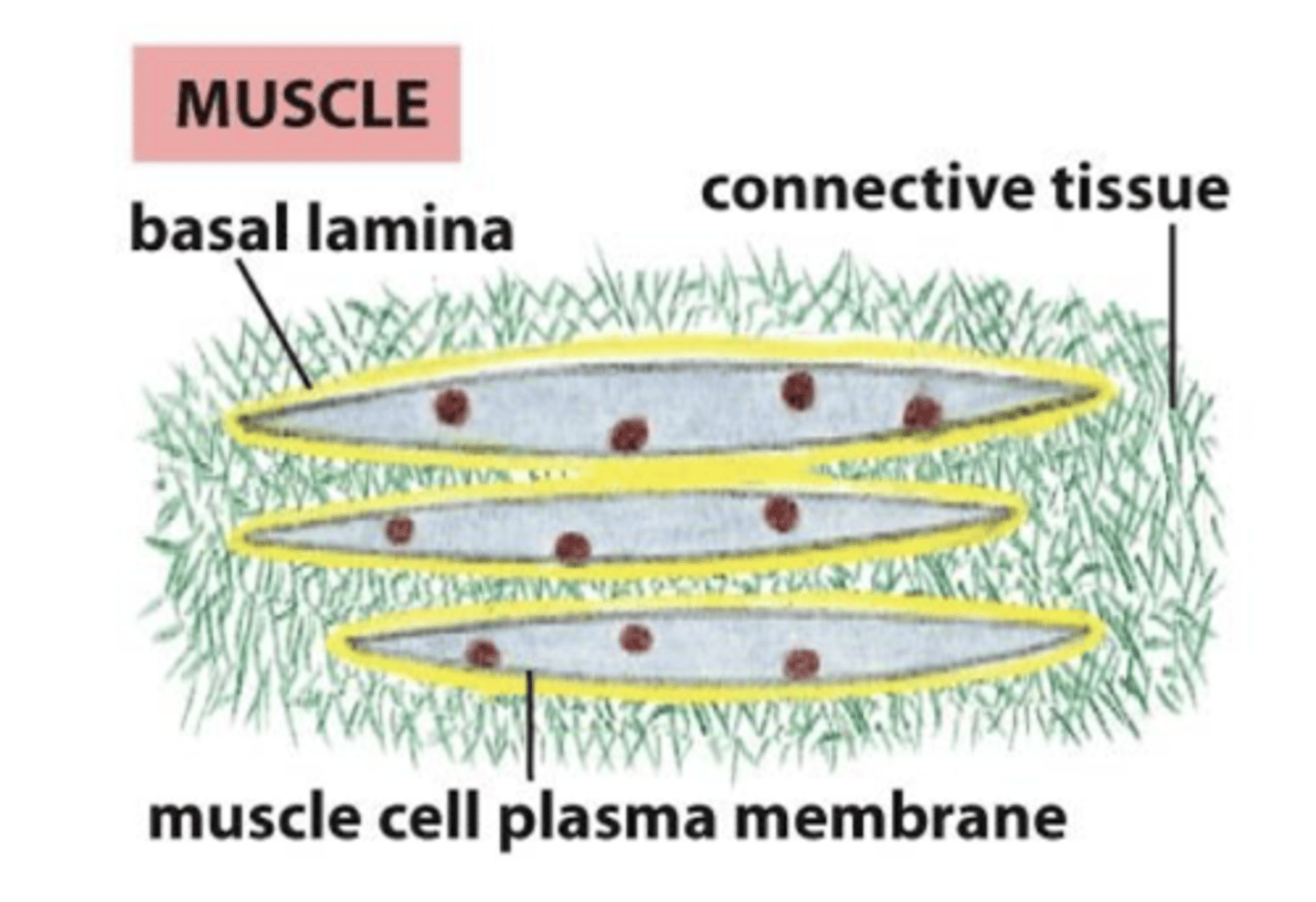
basal lamina and muscle cells
the basal lamina surrounds the muscle cells
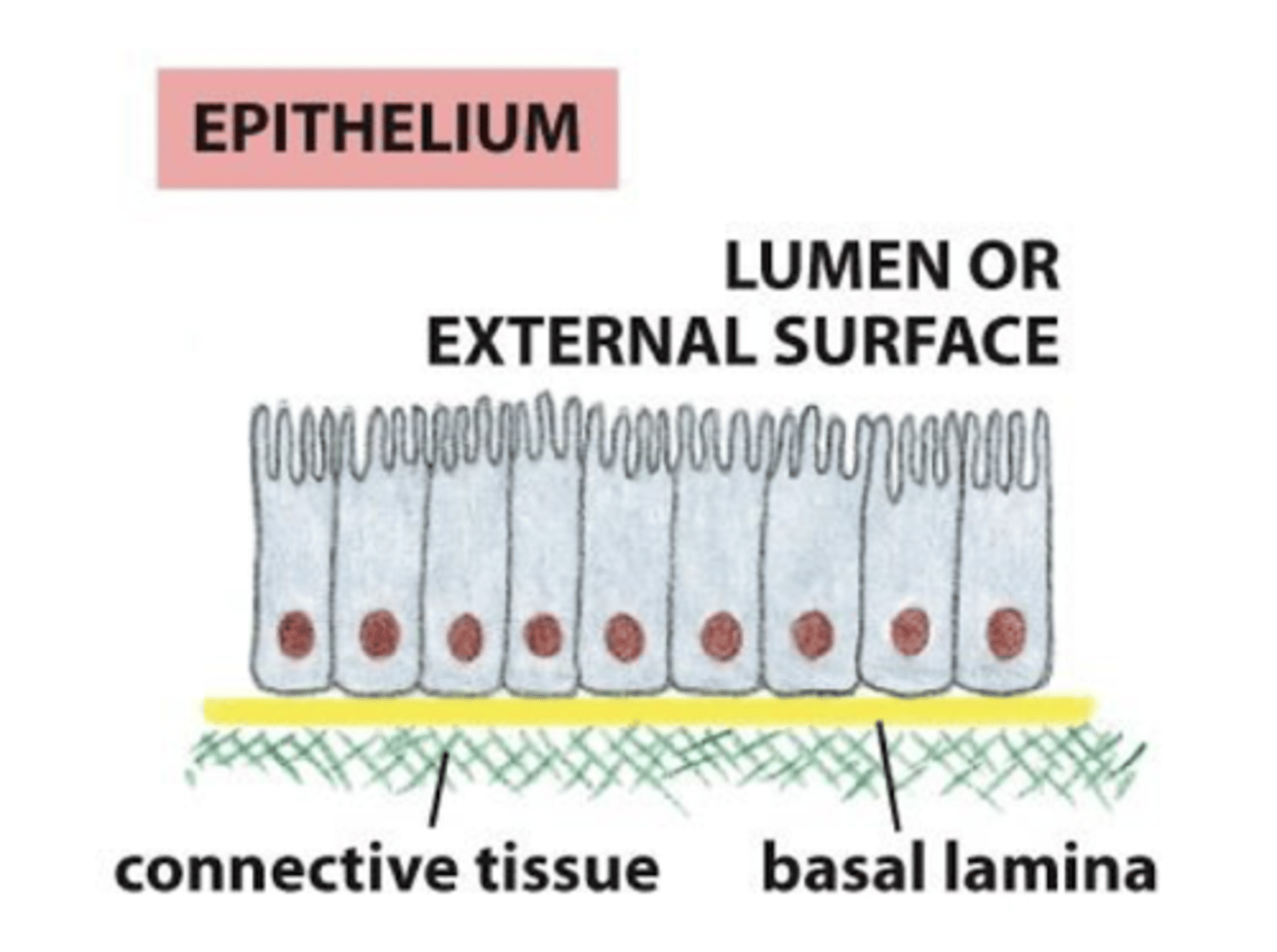
basal lamina and epithelial cells
the basal lamina is sheet-like, one surface of the cells rests on it
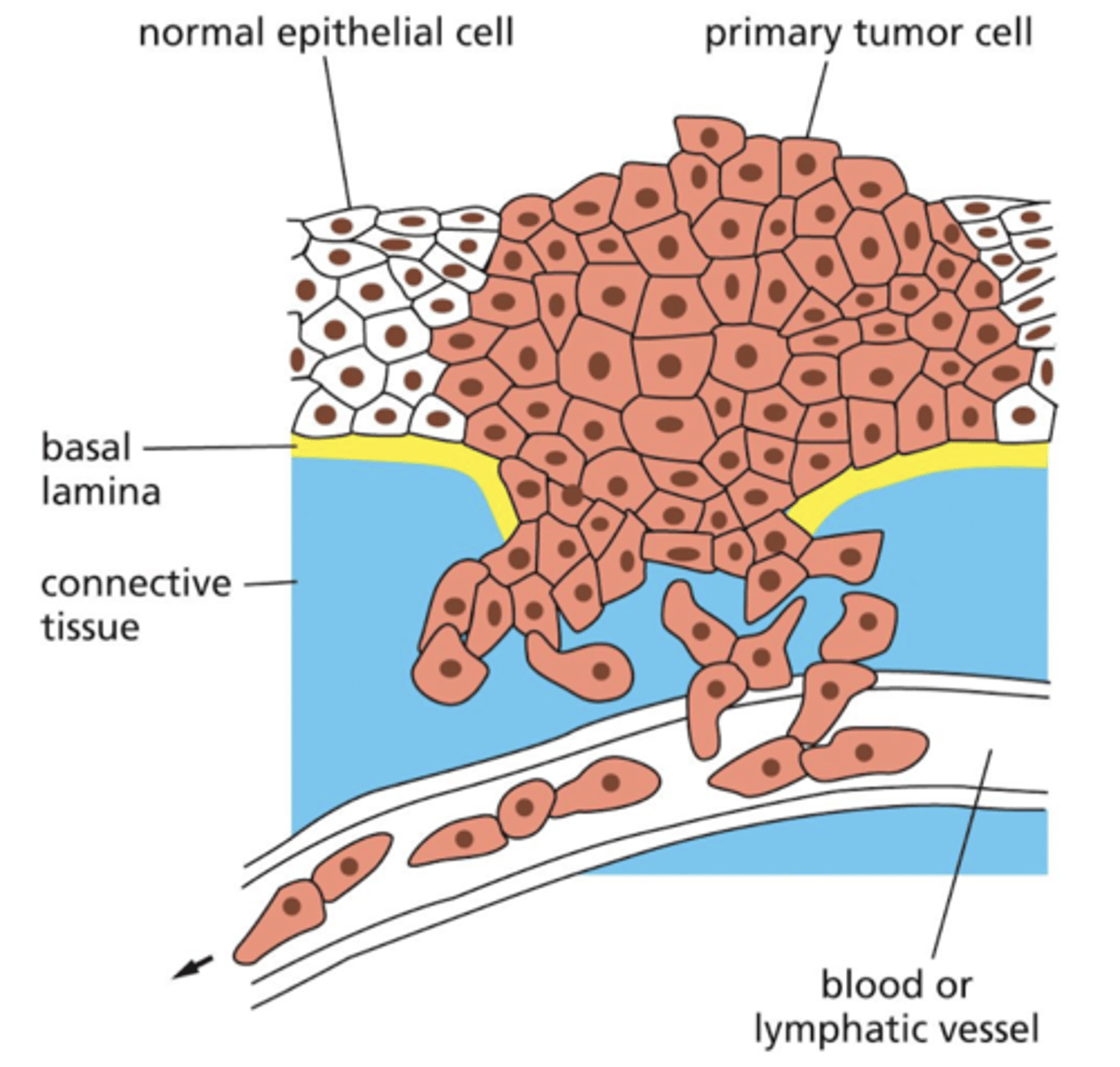
how does cancer metastasize?
cells invade and migrate through barriers between tissues
cancer cells have mechanisms to break through ECM so they can invade other parts of the body
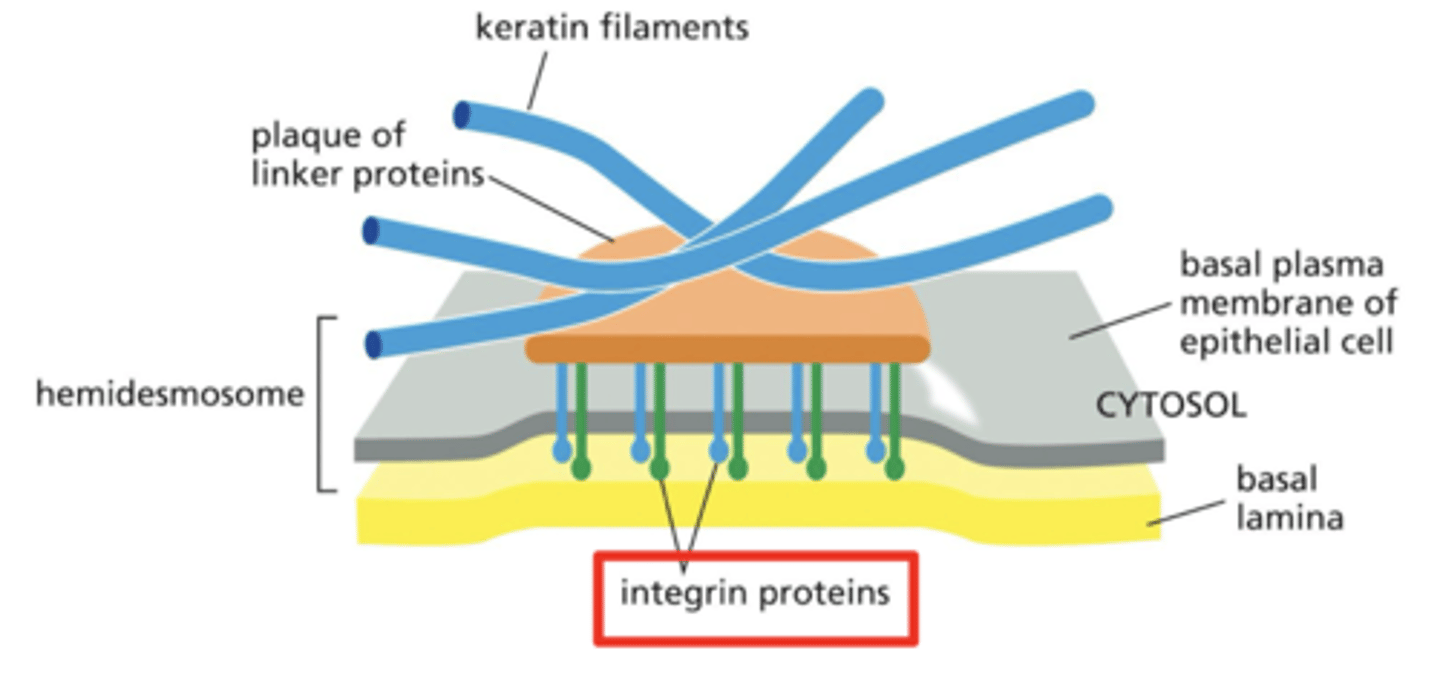
integrins
link the cell to the ECM
integrins are transmembrane proteins on the surface of the cell
cluster into adhesive structures that can mediate cell-ECM interactions
components of focal adhesions and hemidesmosomes
integrin structure
consist of two subunits (alpha and beta)
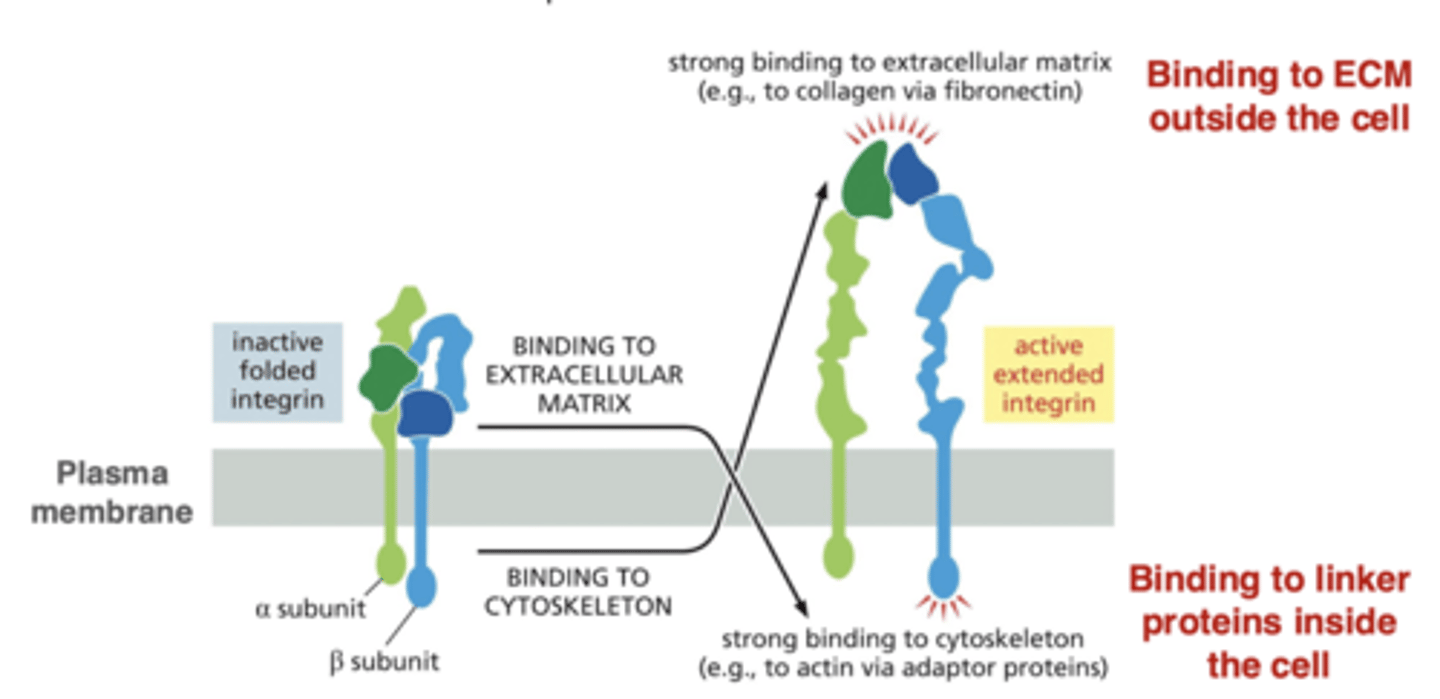
integrin conformation changes
integrins activate by changing from bent to extended
integrin activation can be triggered by ECM components outside the cell or by proteins inside the cell
collagen
provides structural integrity, mechanical strength
proteoglycans
proteins with attached sugar molecules; provide cushioning (they have a gel-like quality)
multi-adhesive matrix proteins
proteins that cross-link proteins and create the ECM meshwork; these proteins can also bind integrins (to link ECM to the cell)
collagen, proteoglycans, and multi-adhesive matrix proteins are found in...
both basal lamina and in the ECM of connective tissues, though the relative abundance of components can differ in these two types of ECM
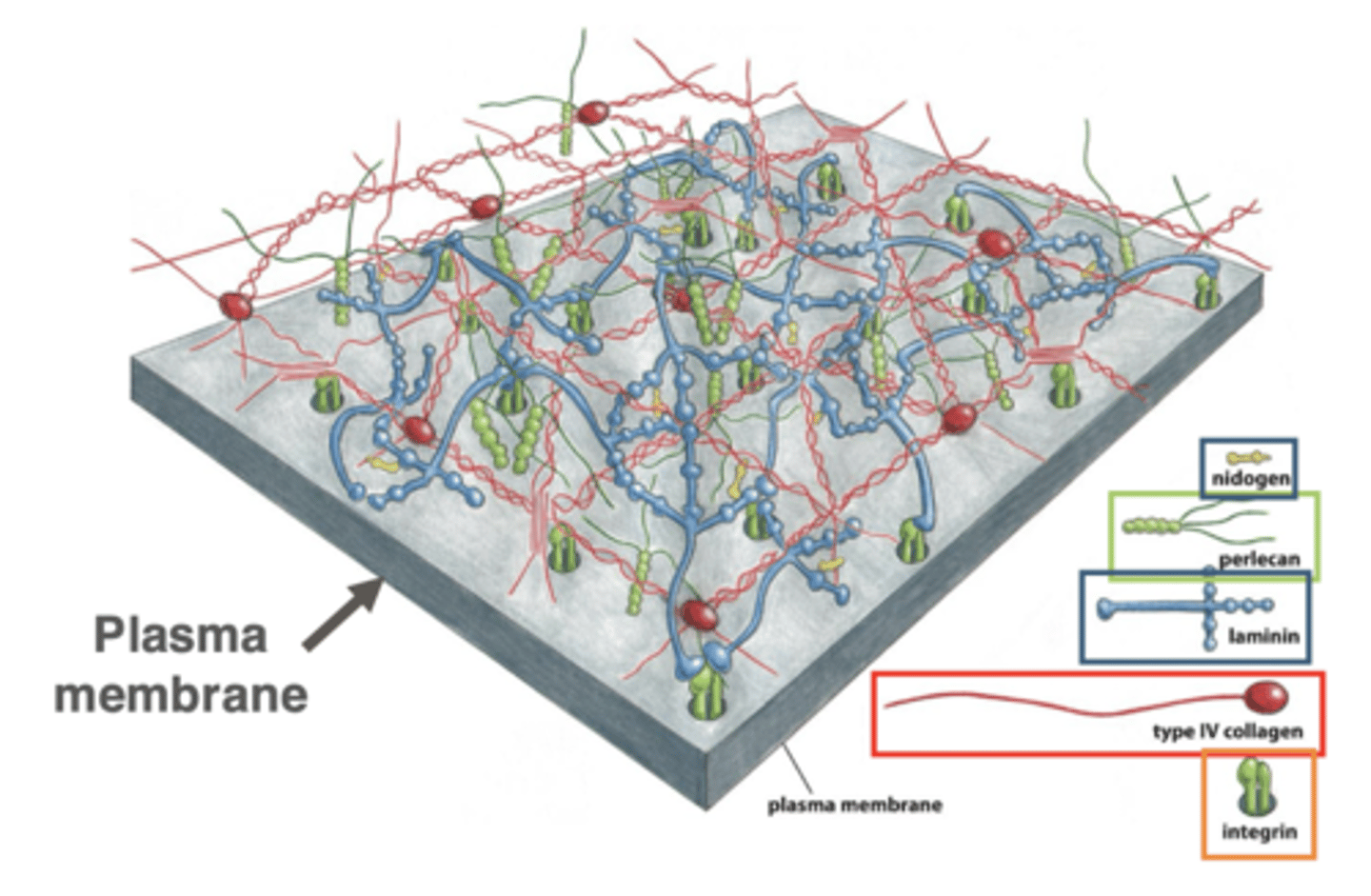
structure of basal lamina
cross-linked networks of collagen, proteoglycans, and multi-adhesive matrix proteins
integrins (transmembrane proteins in the plasma membrane) bind to ECM components, linking the ECM to cells
two major types of collagen in the ECM
1. "sheet forming" collagen in basal lamina (collagen IV)
2. "fibrillar" collagen in the ECM of connective tissue
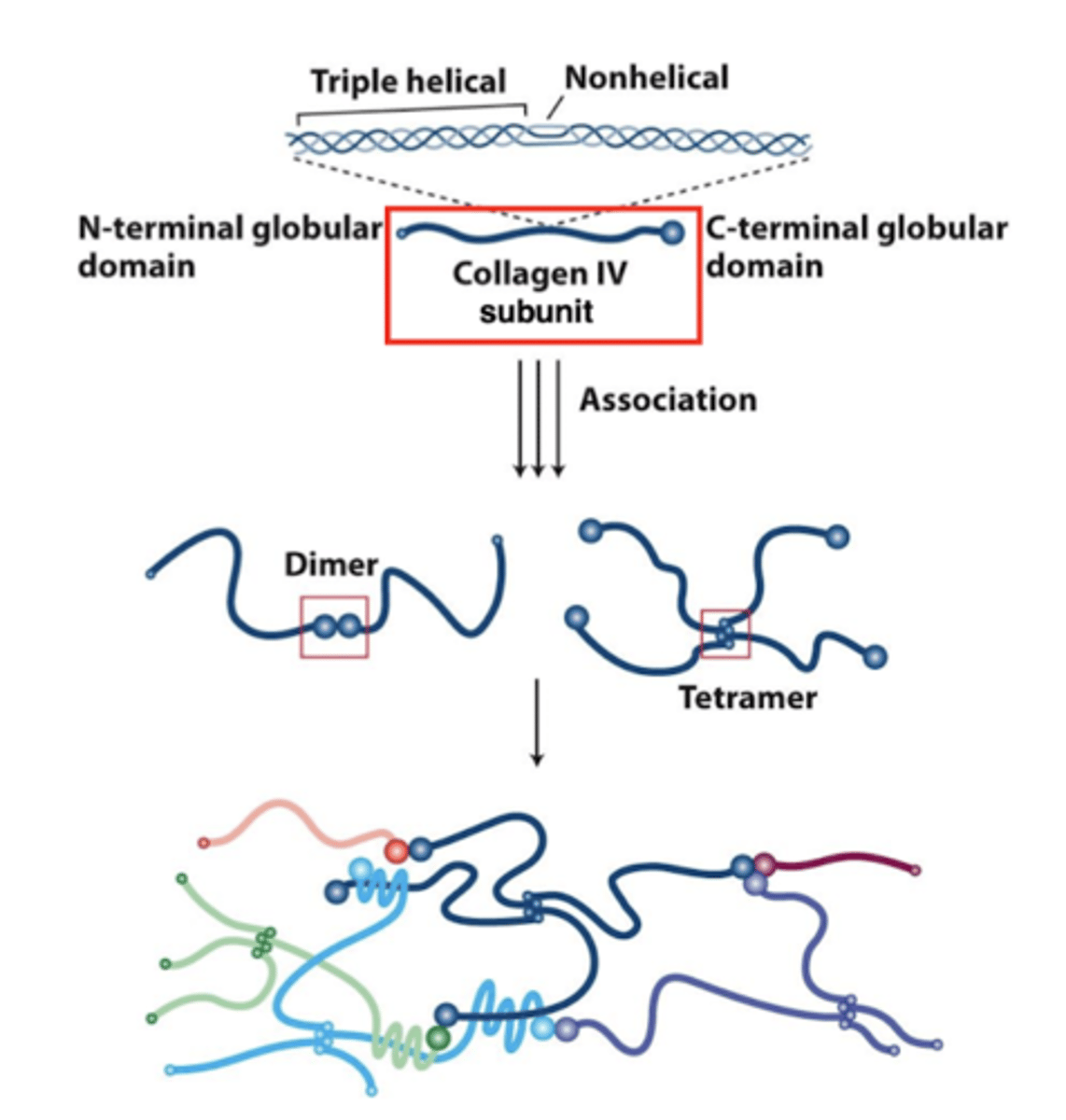
"sheet forming" collagens
three collagen IV molecules come together to form a triple helix - this is the subunit
these collagen IV triple helices interact via their N- and C- terminal globular domains
subunits associate into a 2D network (not into fibers)
"fibrillar" collagens
form fibers and are present in connective tissue
assemble into triple-stranded molecules (no globular domains)
subunits associate along their lengths (not via N- or C- termini) to form fibrils
these assemble into the fibers found in connective tissue
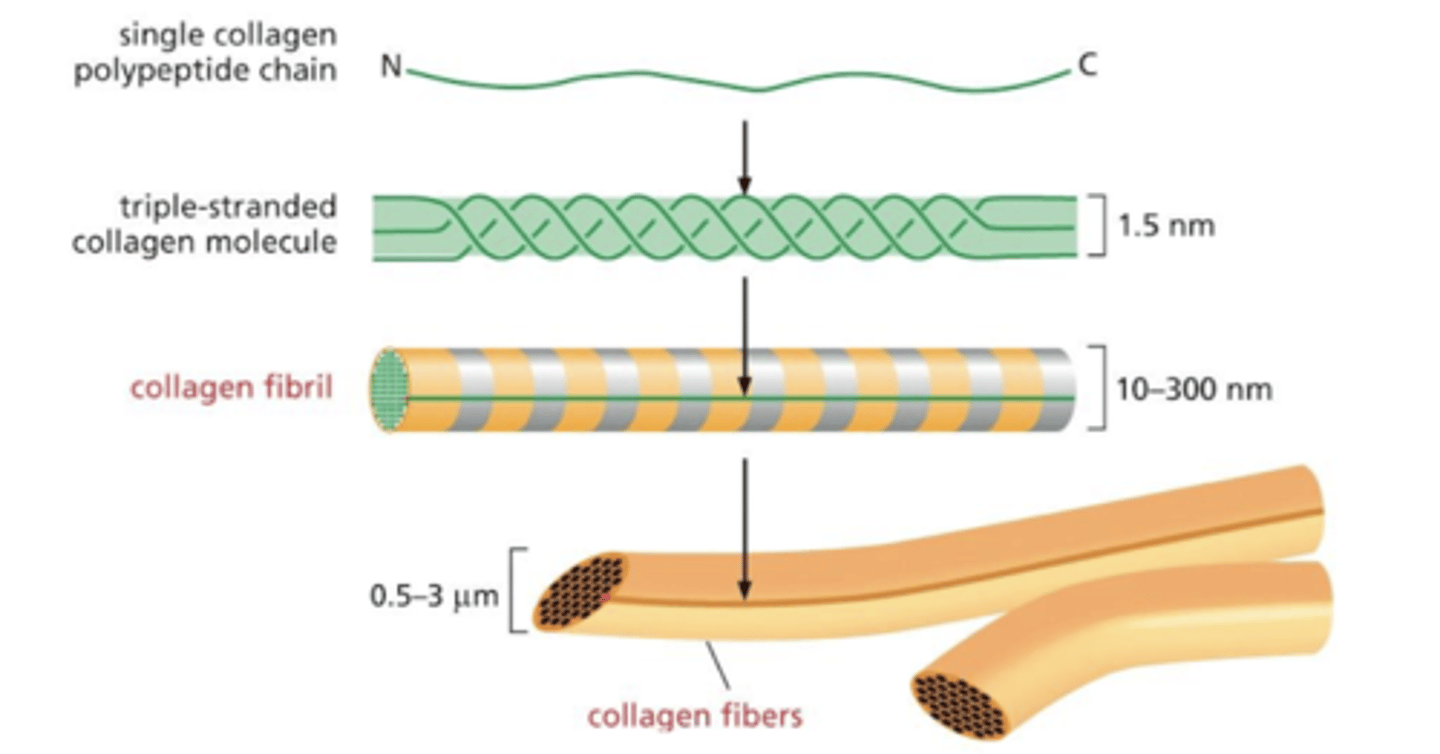
levels of "fibrillar collagen" assembly from smallest to largest
1. single collagen polypeptide chain
2. triple stranded molecule molecule (subunit)
3. collagen fibril
4. collagen fiber
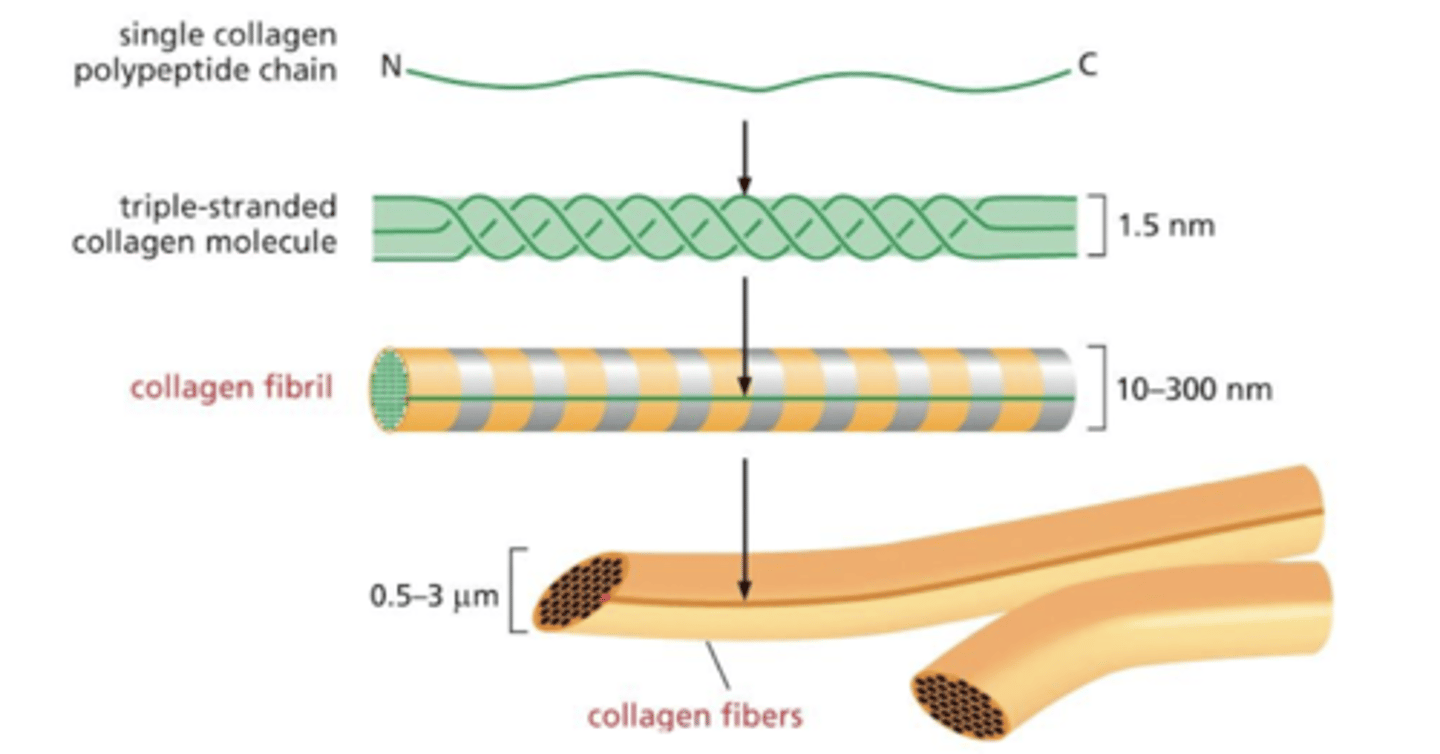
the basal lamina has ______ collagens
"sheet forming"
the connective tissue has _____ collagens
"fibrillar"
True or False: collagen fibers are stronger than steel
True
True or False: collagen is secreted from cells in connective in a form that is ready for fiber assembly
False
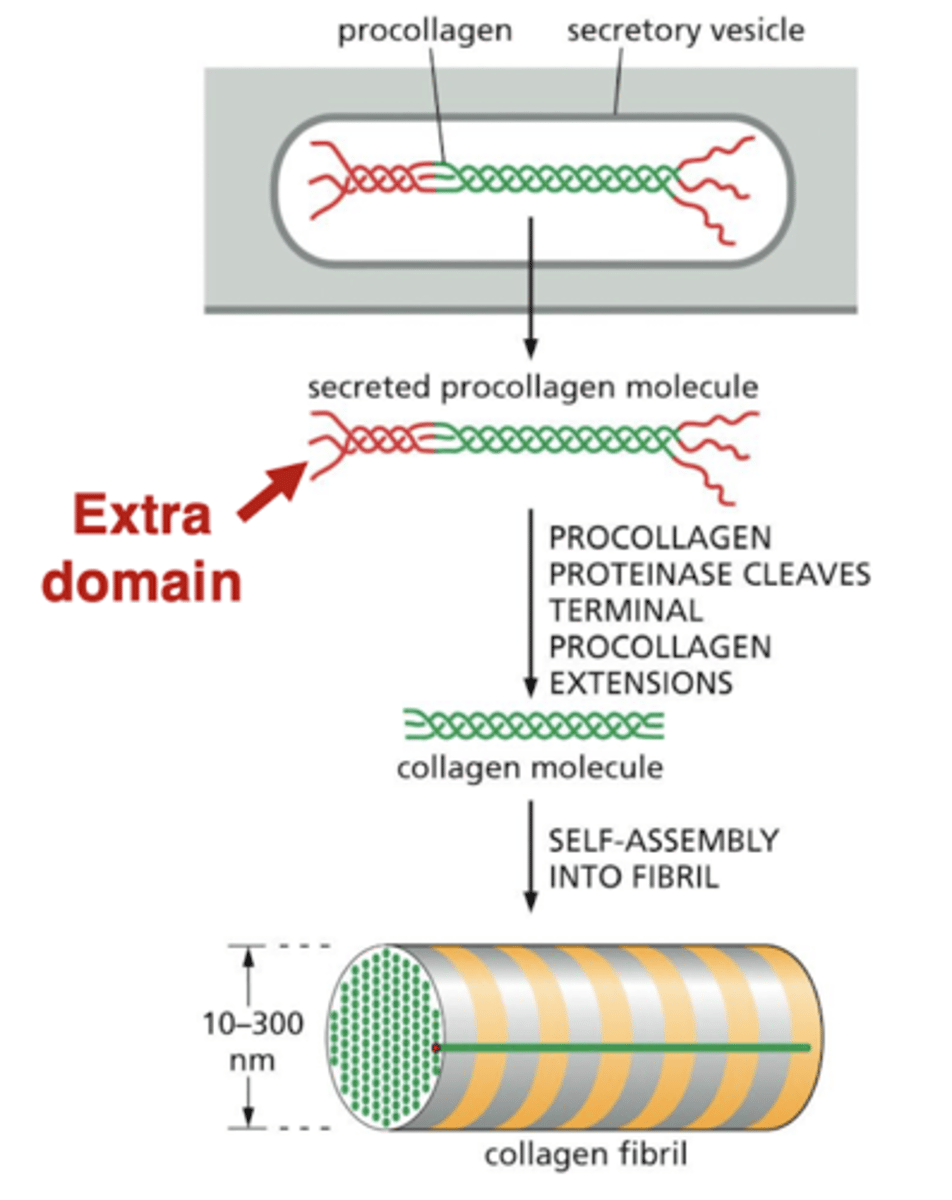
procollagen
cells secrete collagen in a form that cannot assemble into fibrils - this "procollagen" has extra domains on the ends
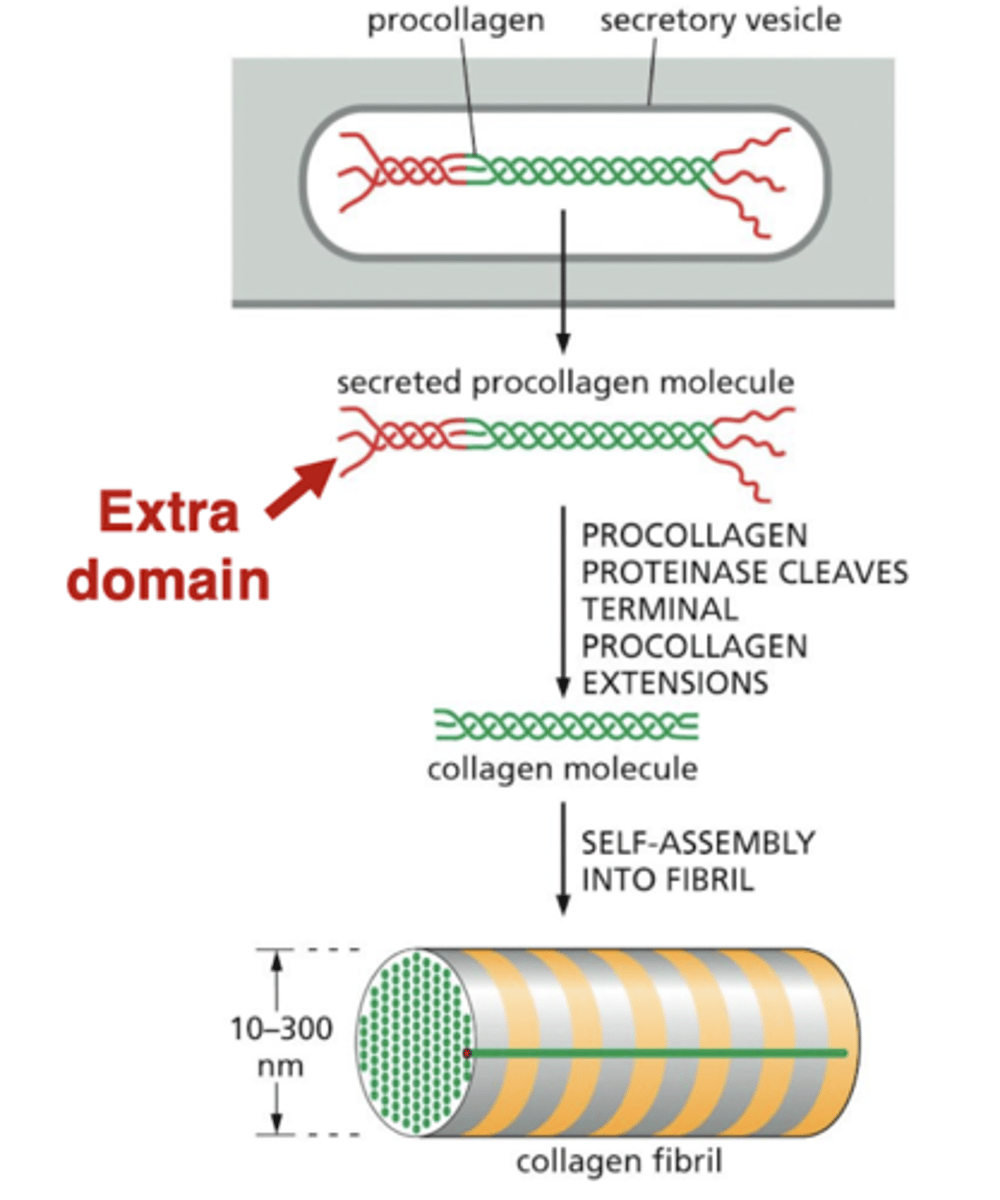
what happens after procollagen is secreted?
outside the cell, the procollagen is processed by a protease in the ECM
the cleaved collagen molecules can then form fibers outside the cell
defects in processing collagen lead to...
hyperflexible skin

how do defects in processing collagen occur?
1. lack of the enzyme that converts procollagen to collagen
2. defect in procollagen itself
structure of proteoglycans
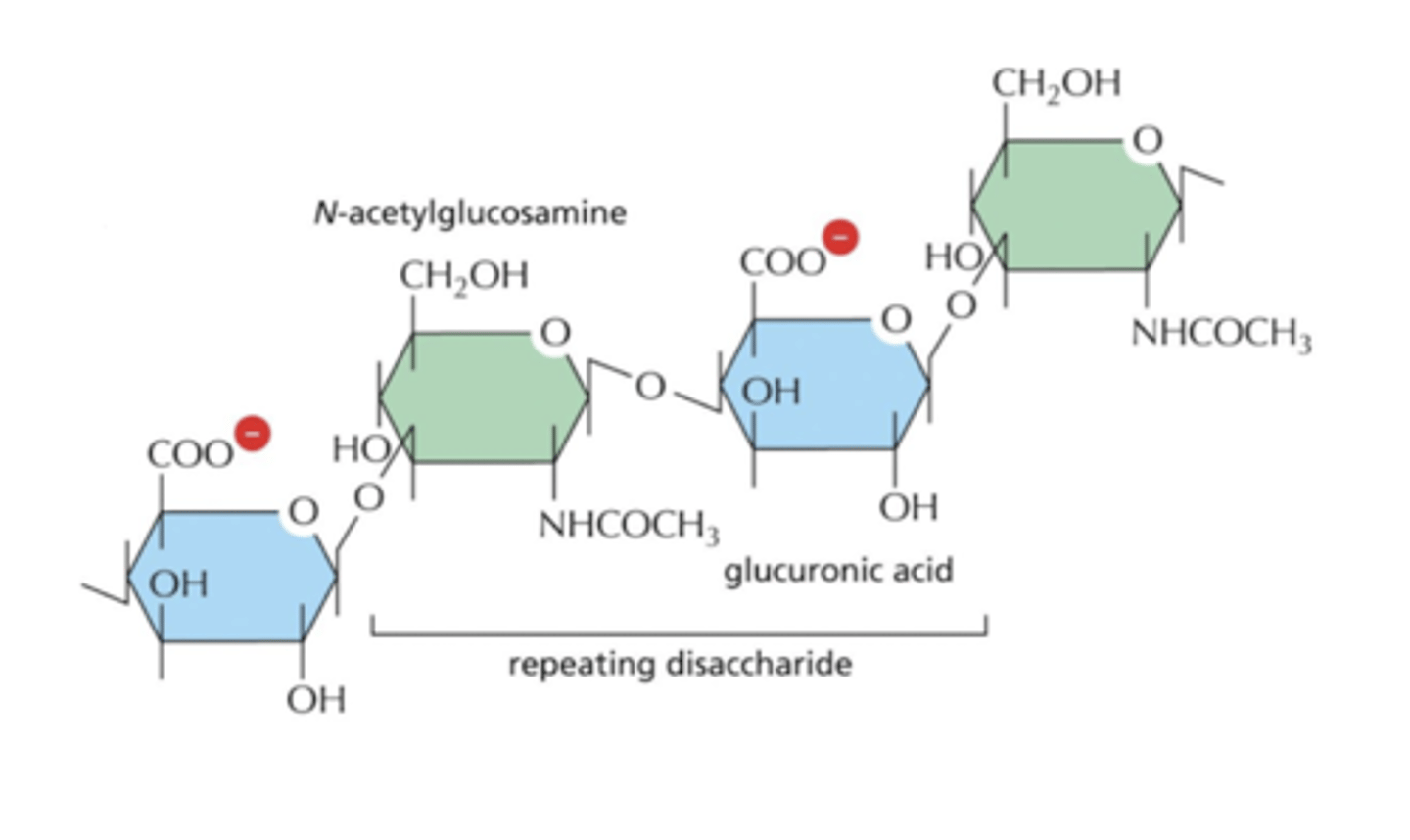
proteoglycans have attached polysaccharide (sugar) chains called GAGs (glycosaminoglycans)
GAGs are covalently-linked polysaccharide chains
proteoglycans give the ECM its gel-like properties, which resists compression on tissues
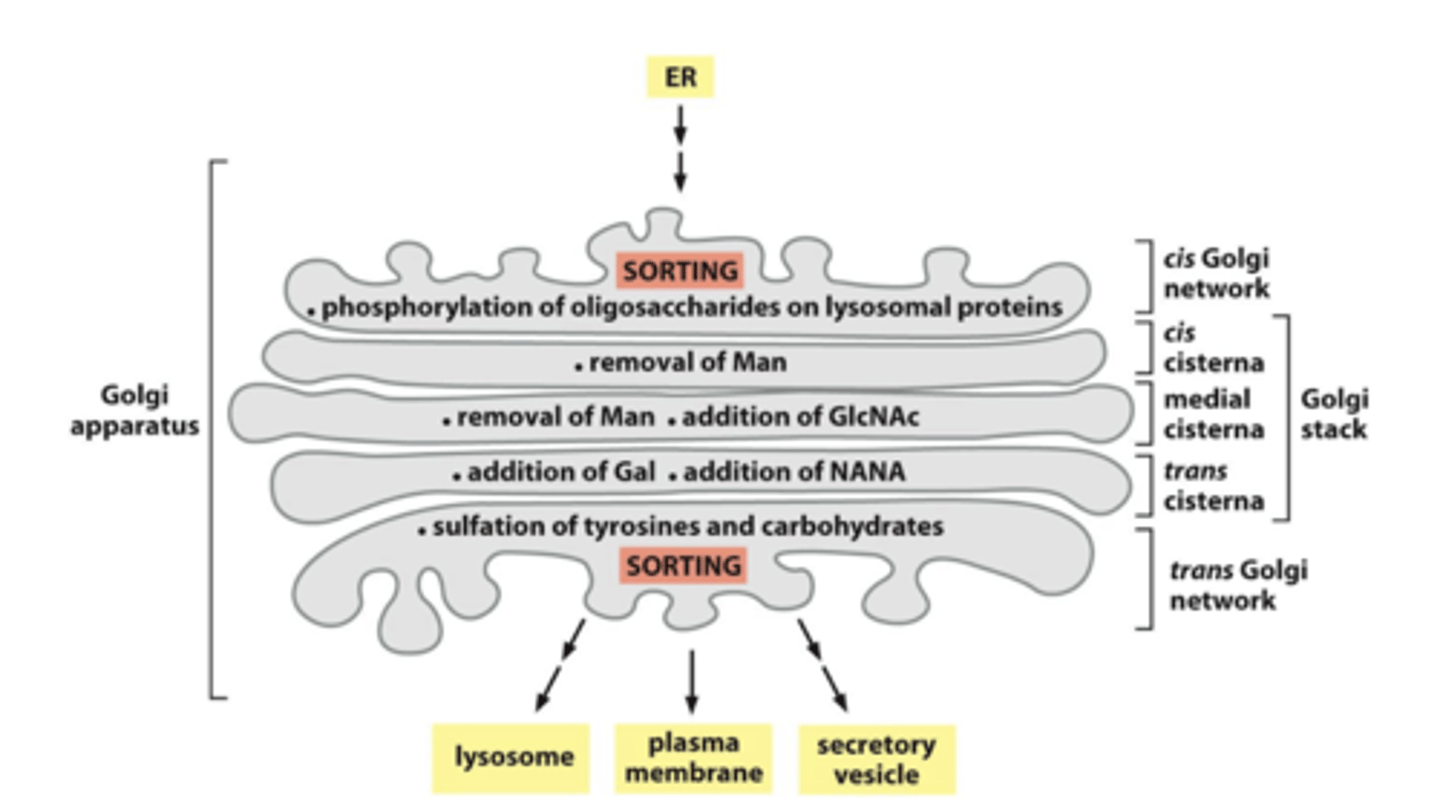
GAGs are assembled on the proteoglycans in the...
Golgi
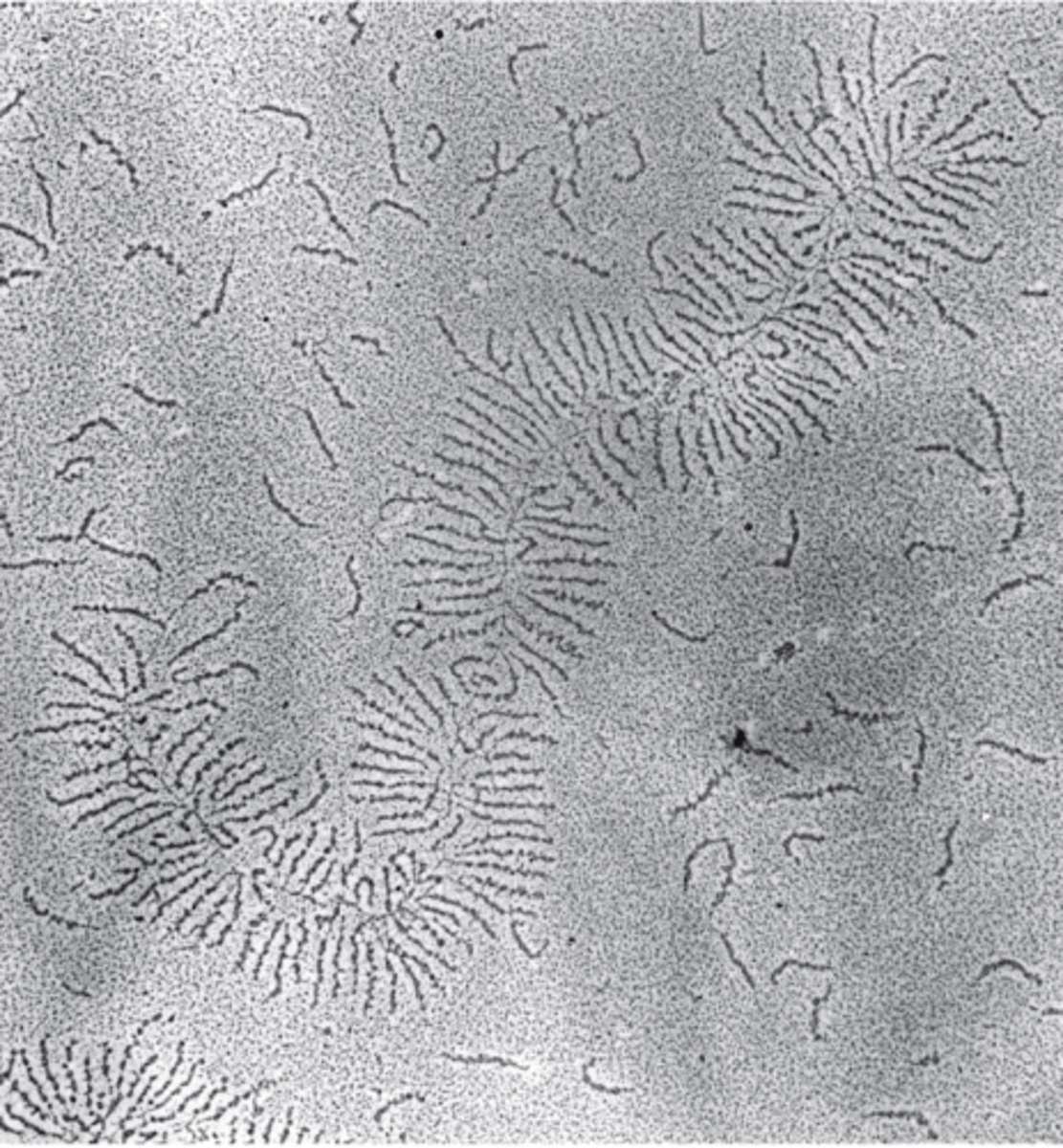
proteoglycans in the ECM
proteoglycans with GAGs can form large aggregates
GAGs tend to adopt highly extended conformations, which occupy a large volume
they can therefore act as "space fillers" that provide cushioning to the ECM
what do multi-adhesive matrix proteins have their name?
"multi-adhesive" because they bind to lots of other proteins
"matrix" because they help form the extracellular matrix, by crosslinking ECM proteins
multi-adhesive matrix proteins bind _____ to link the ECM to the cell
integrins
examples of multi-adhesive matrix proteins
laminin and fibronectin
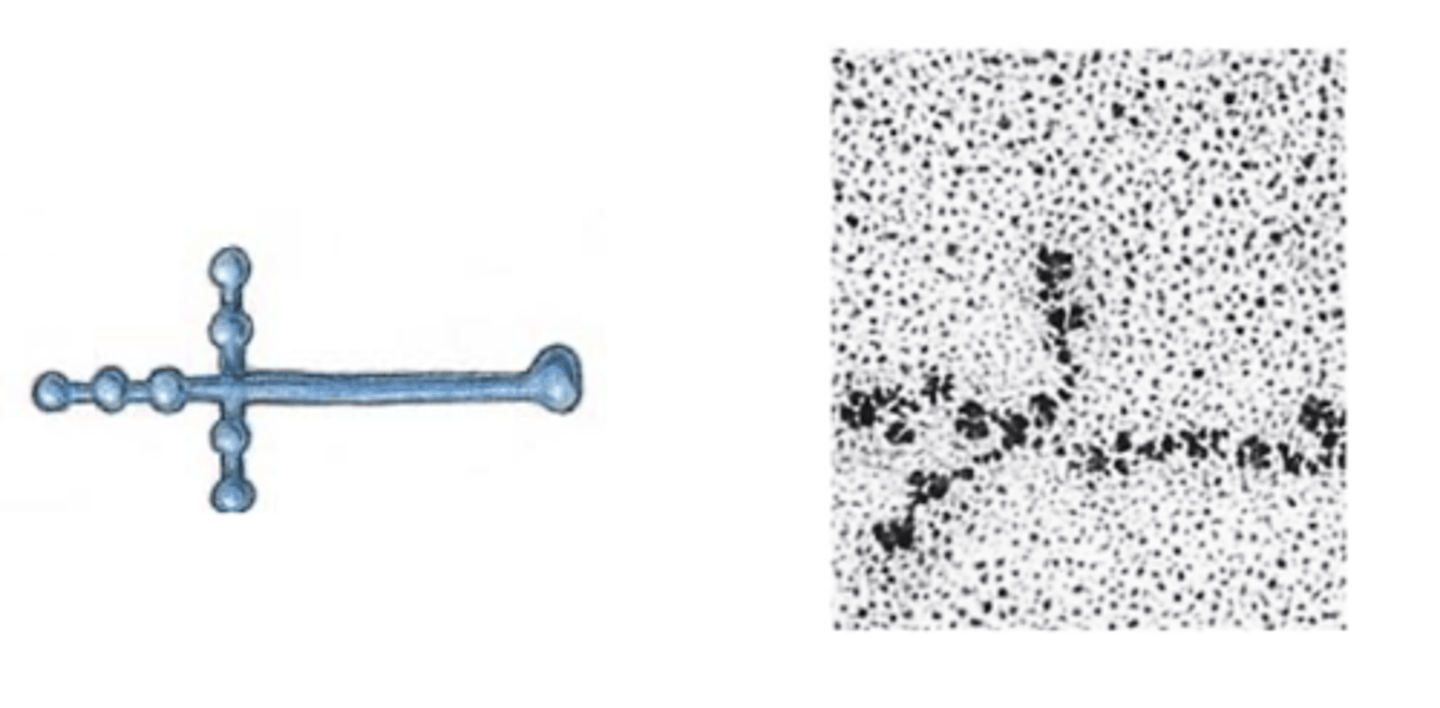
laminin
component of the basal lamina
cross-shaped protein with binding domains for other ECM proteins and for integrins
interacts with other proteins through the globular domains
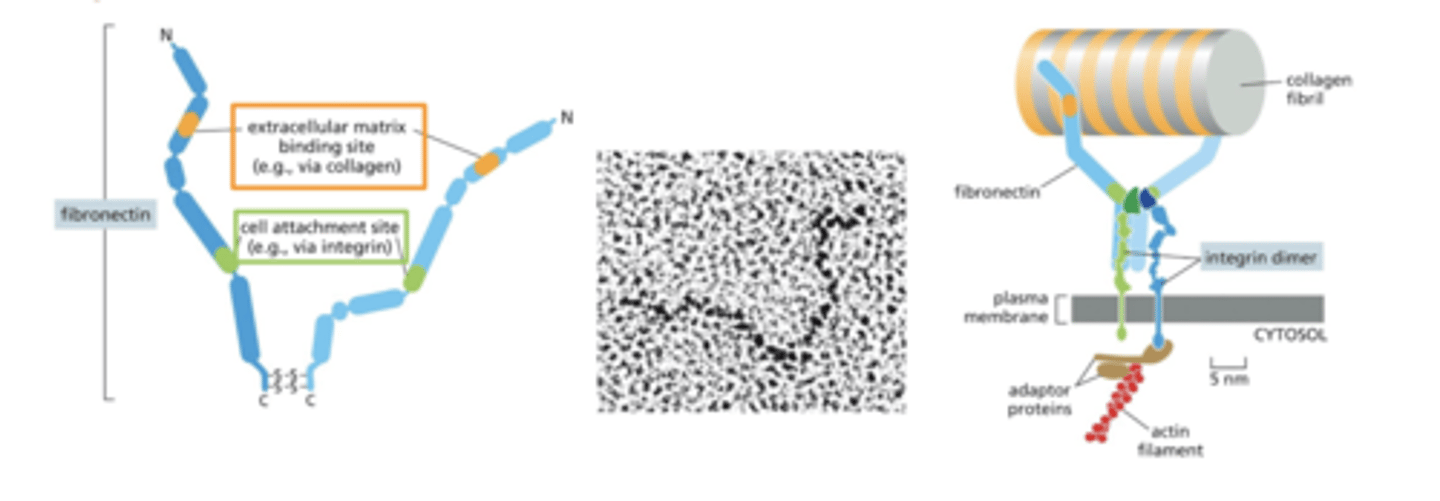
fibronectin
fibronectin has a domain that binds ECM components (collagens)
can bind fibrillar collagens (in connective tissue) or sheet-forming collagens (in basal lamina)
also has a domain the binds integrins
fibronectin therefore helps anchor collagens in the ECM to the cell via integrins
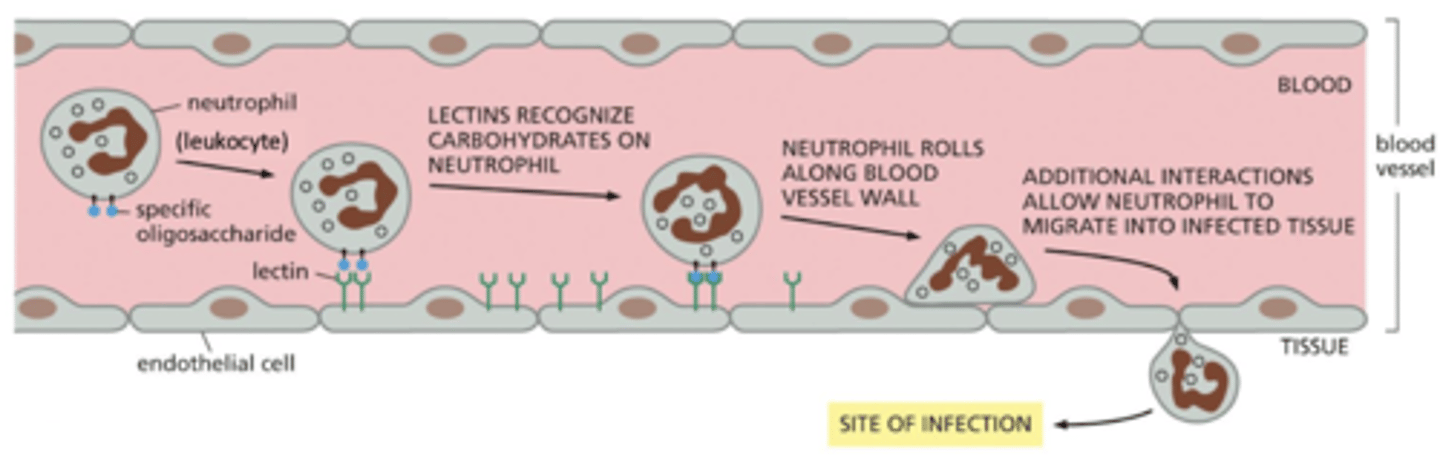
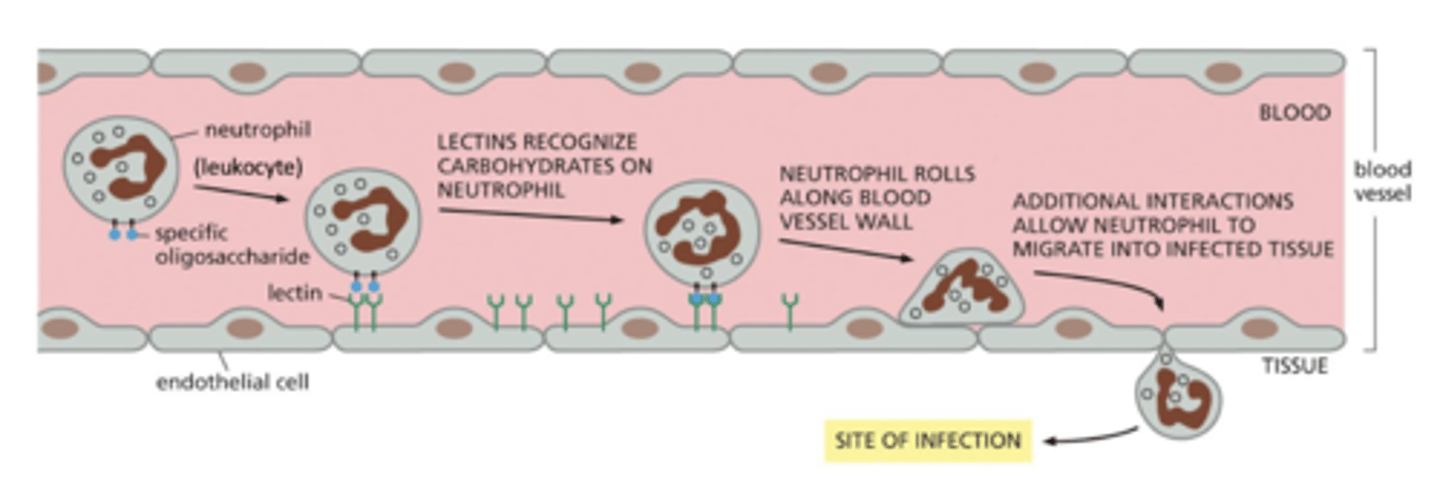
extravasation
movement of leukocytes (white blood cells) to areas of infection until they ultimately invade the underlying tissue (extravasation)
if there is an infection, leukocytes respond to inflammatory signals (e.g. chemokines) and start associating with the endothelial cells - this is loose adhesion
cells "roll" along the endothelial cells of the blood vessel
when reach the site of infection, this switches to strong adhesion
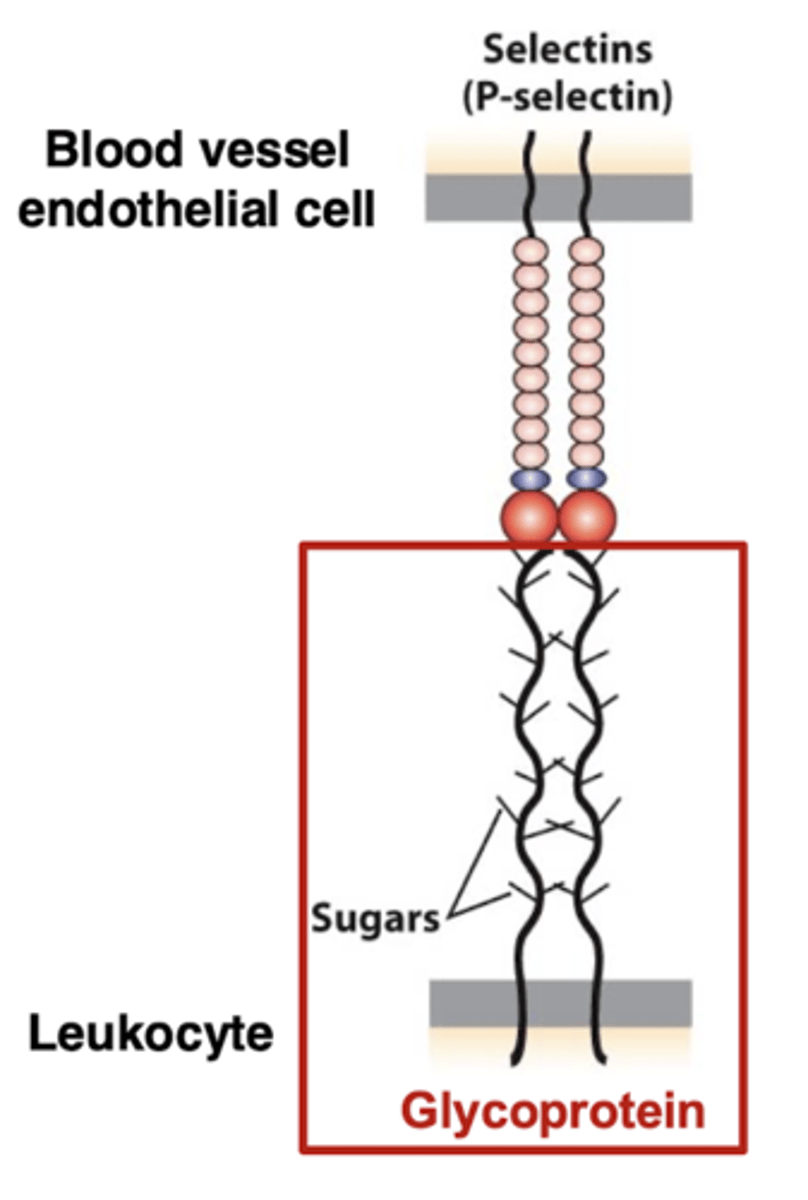
loose adhesion in extravasation - glycoproteins
cell rolling is mediated by loose adhesion
glycoproteins with attached sugar residues are on the surface of the leukocyte (white blood cell)
similar to the proteoglycans of the ECM, these proteins have sugar residues added in the Golgi
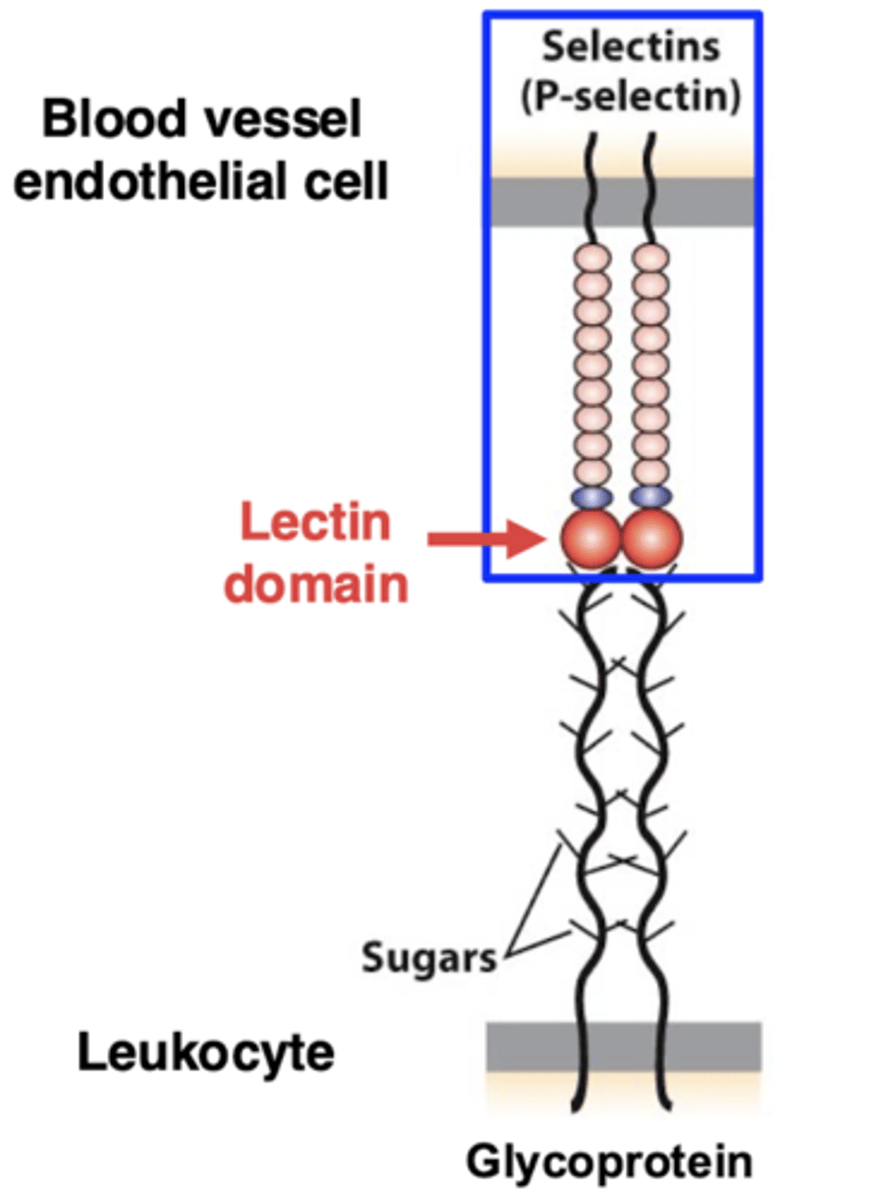
loose adhesion in extravasation - P-selectin
cell rolling is mediated by loose adhesion
P-selectin (a protein with a "lectin" domain that binds sugars) is on the surface of the cells lining the blood vessel
selectins bind to the sugar residues of the glycoproteins
this binding is weak, so it allows the rolling of the leukocytes along the surface of the blood vessel
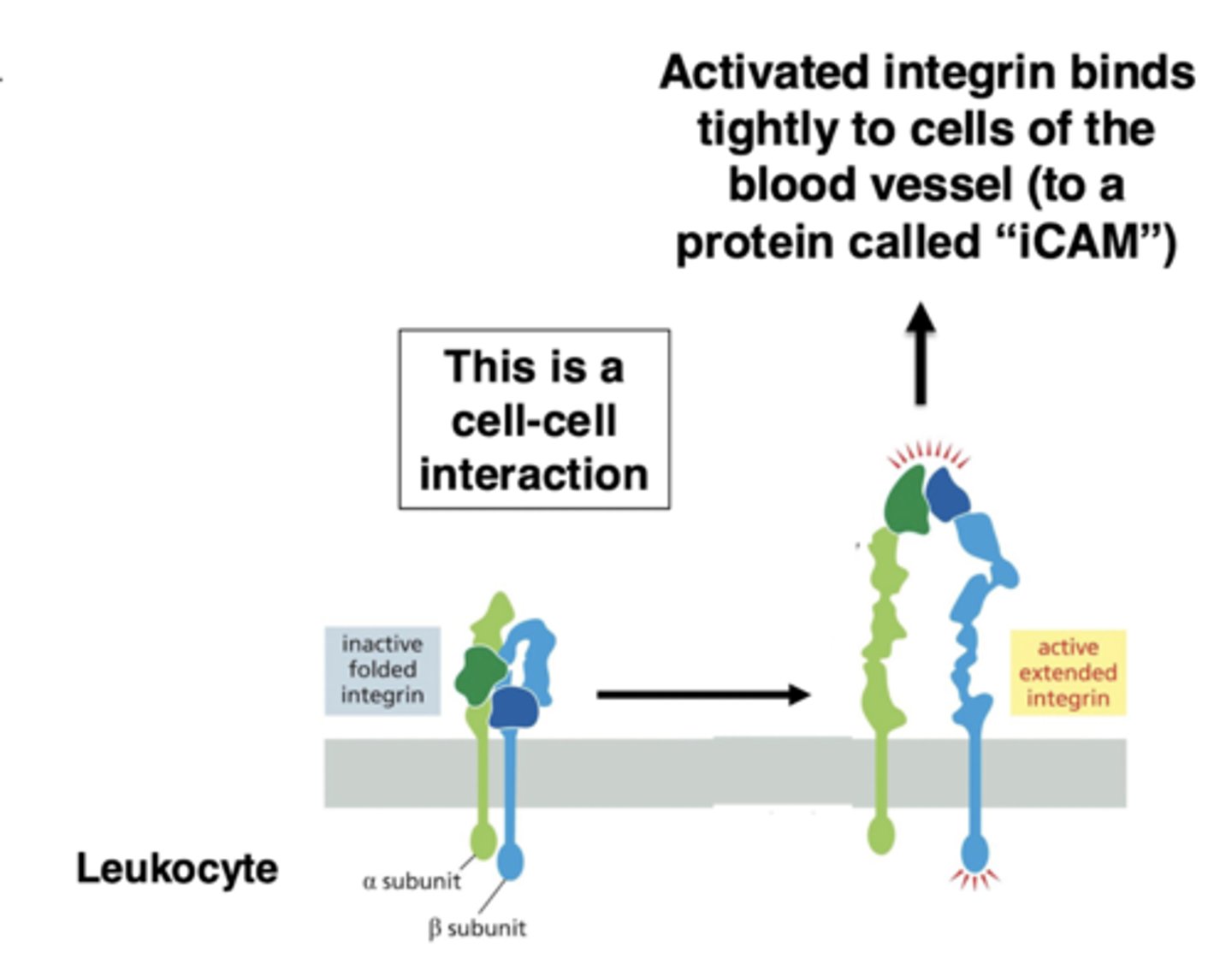
strong adhesion in extravasation
integrins mediate the switch to tight adhesion
when the cell reaches the site of inflammation, there is a signal to switch to tight adhesion
this signal activates integrin (on the leukocyte) - switches from bent to straight conformation
activated integrin tightly binds a protein ("iCAM") that is on the surface of the endothelial cells
this stops the rolling
summary of extravasation initiation and adhesion
1. inflammatory signals (e.g. chemokines) cause leukocytes to associate with the endothelial cells on the walls of the blood vessel
2. binding of selectins to glycoproteins recruits the leukocytes
3. this is a loose adhesion - blood flow pushes the cell and it rolls
4. activation of integrins at site of infection triggers tight binding to the blood vessel
5. leukocyte stops rolling and then can crawl between the cells of the blood vessel onto the infected tissue