L24-amino acids and peptides and proteins
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are alpha amino acids
They are the structures that make up polymers
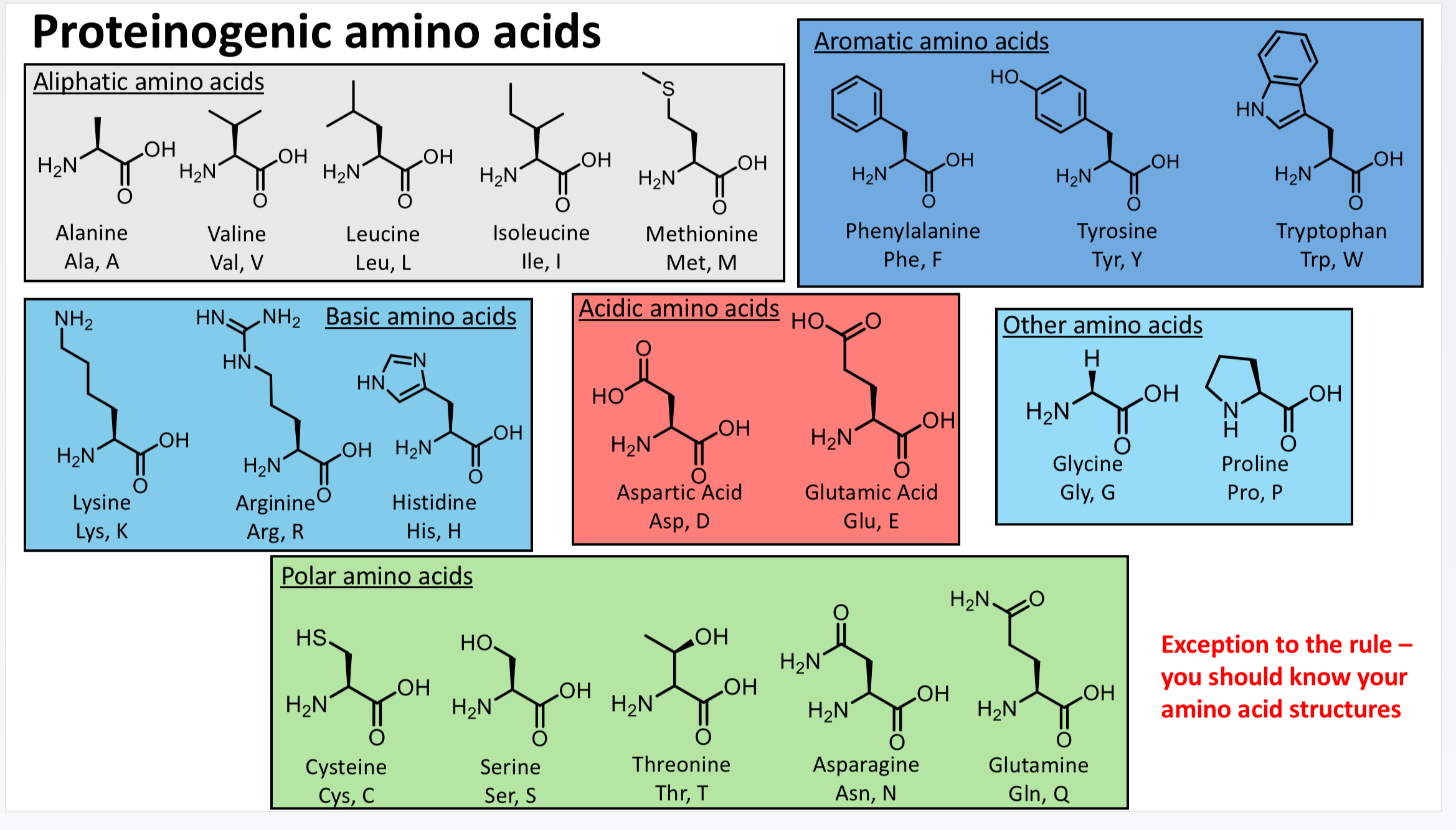
What are the proteinogenic amino acids ( 20 amino acids ) and their categories
Explain what a zwitterion is
it’s a molecule with functional groups of which at least one has a positive charge and one has a negative charge
what is the isoelectric point (pl)
its the PH where the molecule has no net charge
explain how polymers form
polymer a a long chain of amino acid monomers joined together using peptide bonds
the peptide bonds are formed by reaction of the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the other
they react in a condensation reaction
the peptide bonds are uncharged which allows them to form the tightly packed globular structures that they form
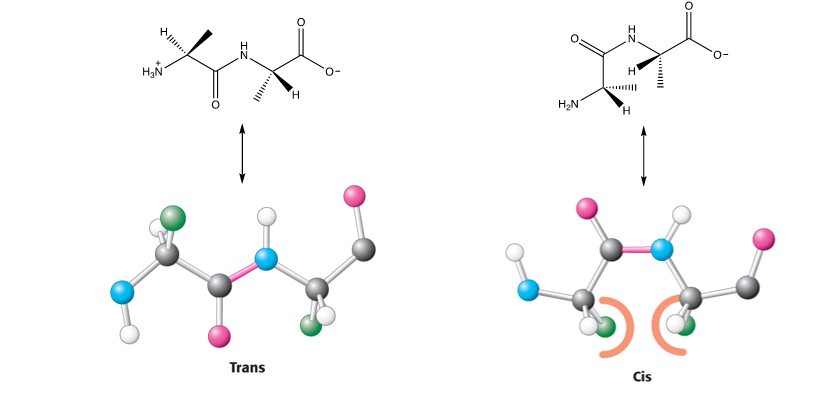
what configuration do most peptide bonds take up in proteins and why ( but think of why proline is an exception )
the trans configuration as in the cis form there’s unfavourable steric clashes
proline is an exception though as both trans and cis configuration cause steric clashes so they are equally favoured
how do amino acids interact with each other to form folded protein structures
hydrogen bonding ( needed for secondary structures )
hydrophobic effect ( hydrophobic region of a molecule clustering together as its entropically favoured )
van de Waals ( interaction between uncharged atoms in proximity )
ionic bonds
disulphide bonds ( covalent bonds linking two cystines together )
pi- interactions ( non covalent interactions involving the electron density of aromatic rings )
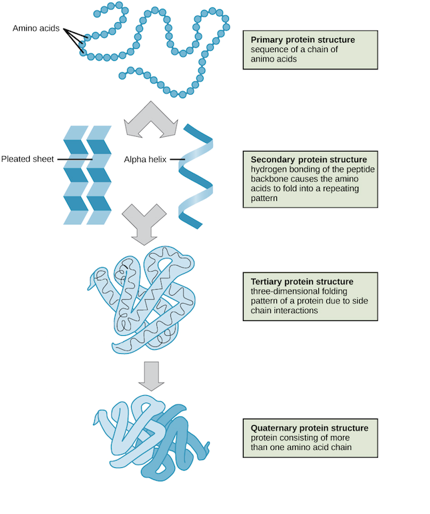
explain how polypeptides fold into proteins
proteins form local interactions through hydrogen bond networks to form secondary structures
then interaction between residues distant in the primary sequence produce tertiary and quaternary structures which fold the protein more
the quaternary structure is the interaction between 2 or more polypeptide chains
many interaction occur in order o find the most stable conformation
what are chaperone proteins
they are other proteins in a cell which bind to a protein as its folding in order to increase the likelihood of it taking on its correct conformation
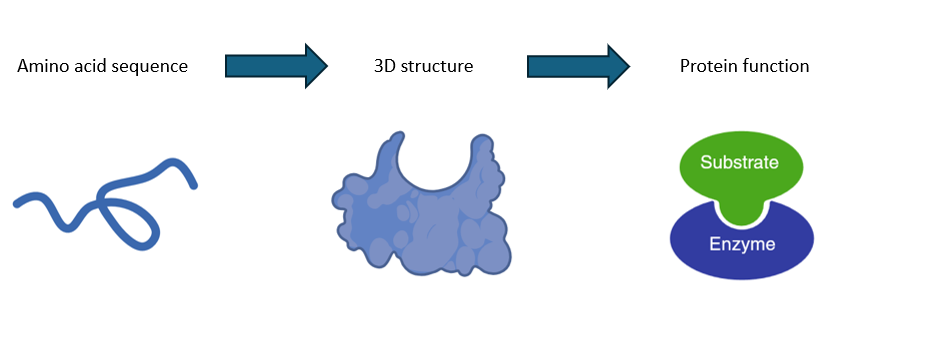
what is protein function determined by
it is determined by the amino acids sequence which determines the d structure
what are PTM’S
posttranslational modifications
they are chemical changes that occur after a protein has been synthesised, the changes are typically reversible
but the change in protein structure alters function stability and localisation
e.g. adding on a small group, adding a hydrophobic lipid