AP WORLD HISTORY FINAL EXAM REVIEW
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
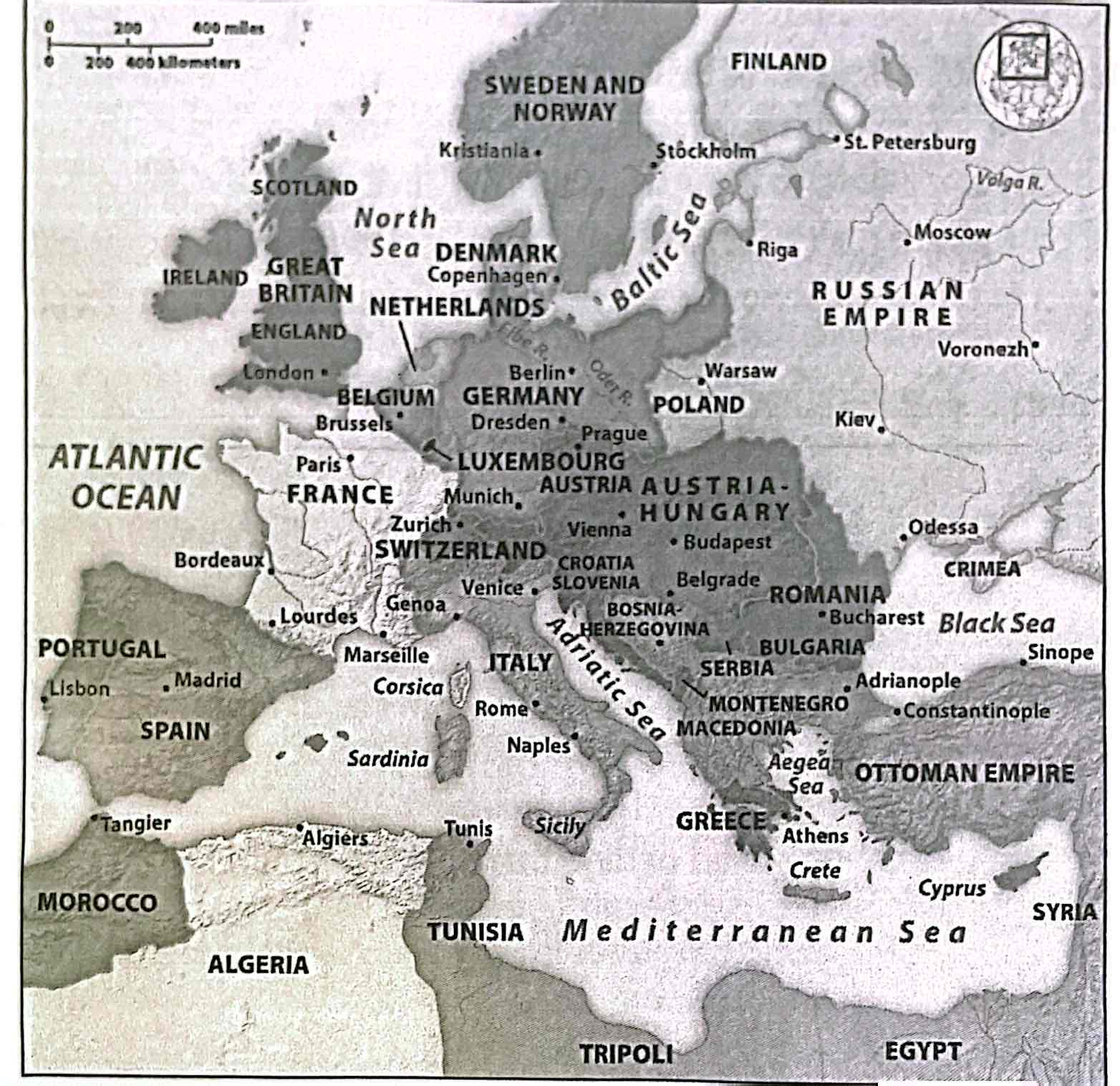
7-1. The map above shows Europe around
a) 1790
b) 1820
c) 1850
d) 1880
d) 1880
7-2. A consequence of European imperialism in the 19th century was the
a) rise of nationalism in the countries that felt victimized by imperialism
b) triumph of agricultural societies over industrial societies
c) wholesale rejection of industrialization and socialism
d) rejection of global capitalism in favor of communist revolution
a) rise of nationalism in the countries that felt victimized by imperialism
7-3.
“…the race to which we belong, the Aryan, has always played the leading part in the great drama of the world’s progress.“ William O. Swinton, An Outline of the World’s History, 1874
Which of the following offers a counterargument to the view of world history presented above?
a) Western culture is the most widely imitated of the world’s cultures
b) European domination of the world reflects the will of Providence
c) Christianity is uniquely suited to modernization and innovation
d) The Arabs, Chinese, and Mongols have each dominated the world stage
d) The Arabs, Chinese, and Mongols have each dominated the world stage
7-4.
“…We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men and all women are created equal.“ Elizabeth Candy Stanton, 1848
The statement above reflects all of the following EXCEPT the
a) influence of the American Declaration of Independence
b) use of Enlightenment ideals to improve women’s status
c) dependence on Marxist historical analysis to argue for women’s emancipation
d) expression of a feminist consciousness reflected in the women’s suffrage movement
c) dependence on Marxist historical analysis to argue for women’s emancipation
7-5.
“Men are born and remain free and equal in rights.“
The quotation above from the French Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen reflects the influence of the
a) Renaissance
b) Enlightenment
c) Scientific Revolution
d) Protestant Reformation
b) Enlightenment
7-6. Like the Atlantic revolutions that had happened earlier, the Spanish American revolutions challenged the absolute authority of
a) nations
b) republics
c) monarchies
d) empires
c) monarchies
7-7. What common set of circumstances contributed to the abolition of slavery in the Atlantic world and the end of serfdom in Russia in the 19th century?
a) demands for suffrage, labor shortages, and pacifist sentiments
b) fear of rebellion, economic inefficiency, and moral concerns
c) campaigns for civil rights, Marxist ideas, and nativist feelings
d) spread of imperialism, economic protectionism, and racist ideas
b) fear of rebellion, economic inefficiency, and moral concerns
7-8. Which of the following represents the influence of nationalism in the 19th century?
a) the political unification of Germany and Italy
b) the creation of the United States of Latin America
c) the extension of the vote to women in New Zealand
d) the end of feudalism and the abolition of slavery
a) the political unification of Germany and Italy
7-9. Because human activity since the late 18th century has fundamentally altered the earth, some scholars refer to the past several centuries as the
a) Enlightenment
b) Global Village
c) Columbian Exchange
d) Anthropocene
d) Anthropocene
7-10. Which of the following demonstrates that Toussaint L’Ouverture was greatly influenced by Enlightenment ideals?
a) He started the revolts in Haiti that ended slavery
b) He negotiated with the Spanish against the French
c) He won control of the territory that would become Haiti
d) He produced a constitution that granted equality to all residents of Haiti
d) He produced a constitution that granted equality to all residents of Haiti
7-11. Which of the following best describes an important demand that helped bring on the French Revolution?
a) The First Estate, or clergy, demanded that the Church have more power in government
b) The Second Estate, or nobility, demanded that workers and peasants pay higher taxes
c) The Third Estate, or workers, peasants, and bourgeoisie, demanded more equal taxation and a constitution
d) King Louis XVI demanded more taxes from the First and Second Estates
c) The Third Estate, or workers, peasants, and bourgeoisie, demanded more equal taxation and a constitution
7-12.
“Do not adopt the best system of government, but the one which is most likely to succeed… for it must be admitted that there is nothing more difficult in the political world than the maintenance of a limited monarchy. Moreover it must also be agreed that only a people as patriotic as the English are capable of controlling the authority of a king and of sustaining the spirit of liberty under the rule of scepter an crown.“ -Simon Bolívar, letter to a Jamaican gentleman
Which statement most accurately summarizes Simon Bolívar’s attitude toward establishment of new governments in the Americas?
a) It would be impractical for the new Latin American states to establish a limited monarchy like England’s
b) The Latin American states should establish absolute monarchies, not limited ones
c) New Latin American governments should be based on conservative ideals
d) It would be advisable for the new Latin American states to establish a limited monarchy like England’s
a) It would be impractical for the new Latin American states to establish a limited monarchy like England’s
8-1. How did the Industrial Revolution solve an emerging energy crisis in the 18th century?
a) It emphasized intensive use of the renewable energy sources of wind and water
b) It introduced the use of coal, oil, and natural gas as sources of fuel
c) It facilitated the migration of the rural population to towns and cities
d) It encouraged the global trend toward economic protectionism
b) It introduced the use of coal, oil, and natural gas as sources of fuel

8-2. Which group would agree with the view of the capitalist system offered by the poster?
a) Pacifists
b) Nationalists
c) Socialists
d) Bourgeoisie
c) Socialists
8-3. How did Britain’s geography affect its Industrial Revolution?
a) Proximity to France made it vulnerable to invasions during the reign of Napoleon
b) Its northern location minimized the effects of the Little Ice Age
c) Coal and iron ore deposits were abundant and close to each other
d) Trees covered most of the country, providing a renewable source of energy
c) Coal and iron ore deposits were abundant and close to each other
8-4. Which of the following groups benefited the most from the Industrial Revolution in 19th-century Britain?
a) The aristocracy
b) The middle classes
c) The laboring classes
d) Women
b) The middle classes
8-5. Which of the following describes how the movement toward industrialization in the 19th century affected Latin America?
a) A large market for manufactured goods developed in Latin America
b) Latin America provided cheap labor for foreign-owned manufacturing industries
c) Latin America exported textiles, machinery, tools, weapons, and luxury goods to the United States and Europe
d) Latin America provided the food products, raw materials, and markets for industrializing countries
d) Latin America provided the food products, raw materials, and markets for industrializing countries
8-6.
“In place of the old bourgeois society, with its classes and class antagonism, we shall have as association in which the free development of each is the condition for the free development of all.“ -Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, The Communist Manifesto, 1848
The society envisioned in the quote above can best be described as one
a) controlled by a totalitarian state
b) made up only of the middle class
c) without classes and inequality
d) run by the captains of industry
c) without classes and inequality
8-7.
“…These laborers, who must sell themselves piecemeal, are a commodity, like every other article of commerce, and are consequently exposed to all the vicissitudes of competition.“ -Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, The Communist Manifesto, 1848
“the earning of increased wages will only furnish him[skilled workman] with increased means for indulging in the gratification of his grosser appetities…“ -Samuel Smiles, Thrift, 1875
Which of the following statements captures the explanations for the poverty of the working class offered by the writers above?
a) The first passage blames the capitalist system, while the second passage blames the workers’ habits
b) The first passage blames increasing demand for unskilled labor, while the second passage blames declining wages
c) Both agree that industrial capitalism will ultimately improve the lives of the working class
d) Both agree that the government should establish a minimum wage for workers
a) The first passage blames the capitalist system, while the second passage blames the workers’ habits
8-8.
“…a class of laborers, who live only so long as they find work, and who find work only as long as their labor increases capital. These laborers, who must sell themselves piecemeal, are a commodity, like every other article of commerce, and are consequently exposed to all the vicissitudes of competition, to all the fluctuations of the market.“ -Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, The Communist Manifesto, 1848
The class of laborers described in the quote above emerged as a result of the
a) French Revolution
b) Agricultural Revolution
c) Industrial Revolution
d) Scientific Revolution
c) Industrial Revolution
8-9. What is the special term that Marx and Engels used to distinguish the “class of laborers” produced by industrial capitalism from workers in pre-industrial society?
a) anarchists
b) capitalists
c) bourgeoisie
d) proletariat
d) proletariat
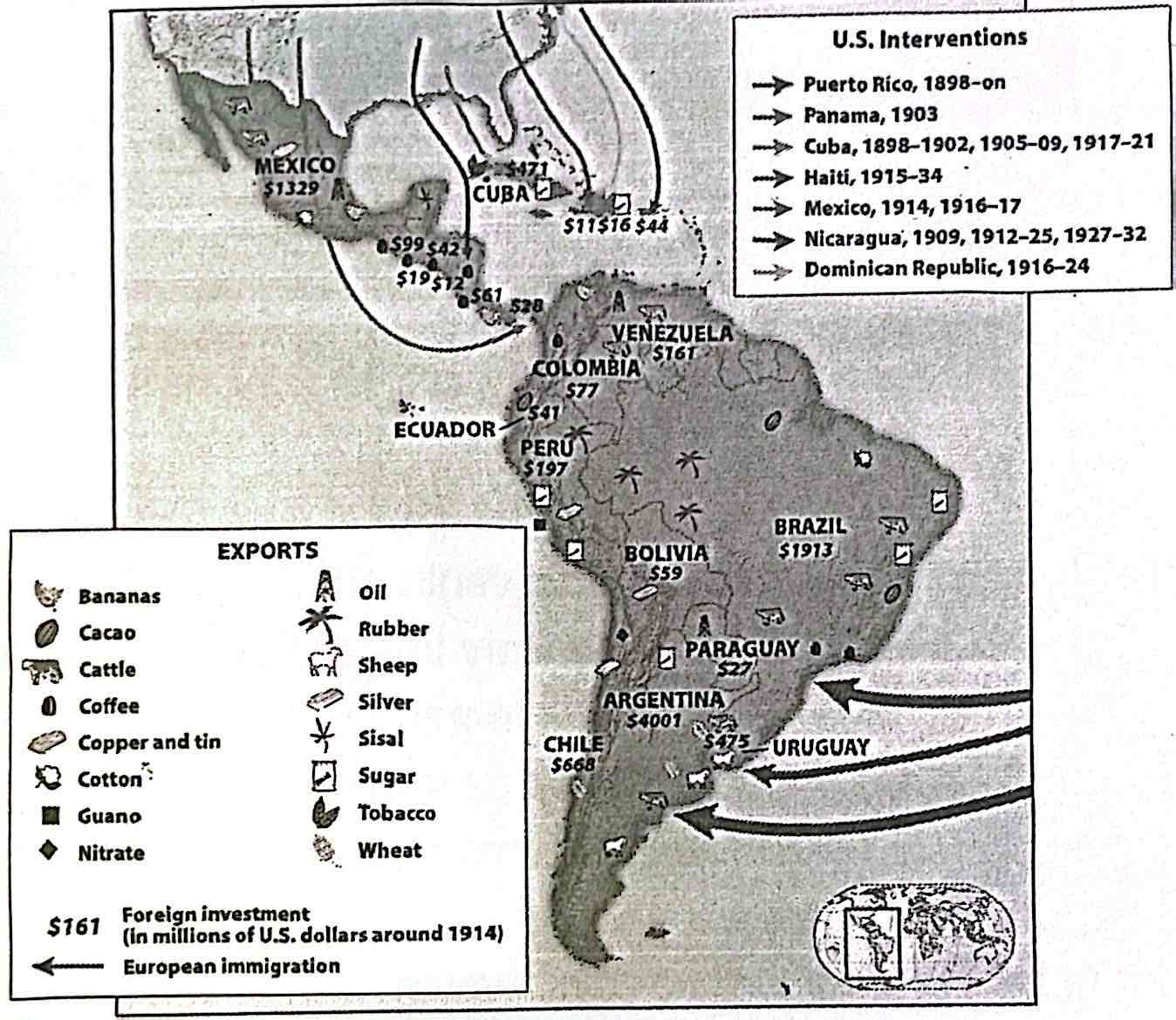
8-10. Which of the following benefited from the U.S. military interventions depicted in the map?
a) United Fruit Company
b) Standard Oil Company
c) General Motors
d) League of Nations
a) United Fruit Company
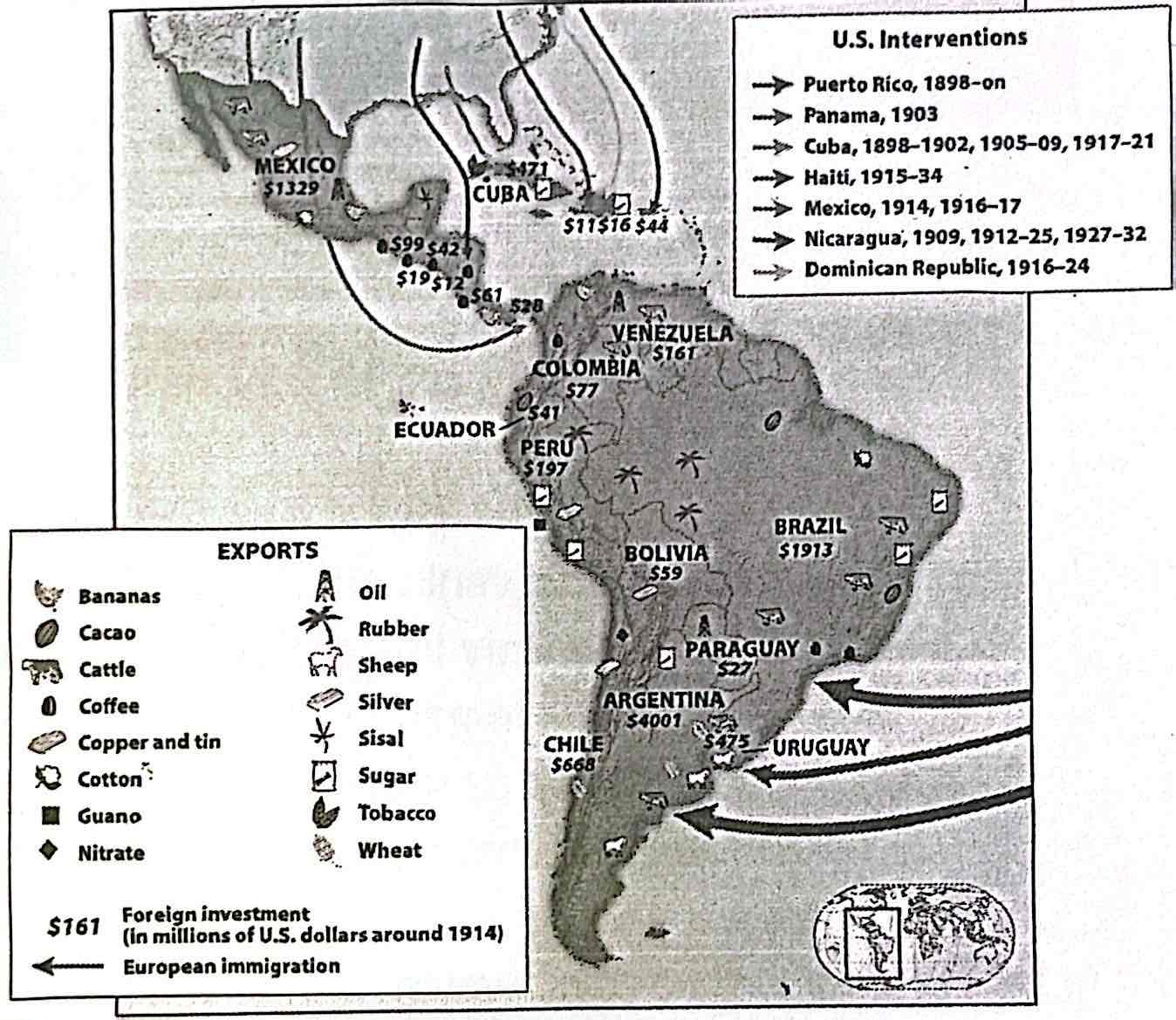
8-11. Which of the following can be inferred from the information provided in the map above?
a) Economic development in Latin America was dependent on foreign capital and export of raw materials
b) Trade with the U.S. jump-started a thorough process of industrialization across Latin America
c) European indentured servants became the largest underclass in Latin America
d) Bolivia was the most dependent on U.S. military intervention to maintain its economy
a) Economic development in Latin America was dependent on foreign capital and export of raw materials
8-12. Which of the following would be the most useful source of evidence for researching the new working conditions created by the Industrial Revolution?
a) Tax records of skilled and unskilled workers
b) Birth certificates with no father’s name identified
c) City maps showing the major transportation points
d) Company manuals listing rules for factory workers
d) Company manuals listing rules for factory workers
9-1. All of the following represent responses of Asian or African societies to the European presence in the 19th EXCEPT
a) Indian Rebellion
b) Boxer Rebellion
c) Maji Maji Uprising
d) Bolshevik Revolution
d) Bolshevik Revolution
9-2. In what respect were Qing China and the Ottoman Empire similar in the 19th century?
a) Both created industrial economies that enabled them to compete with Europe on an equal footing
b) Both successfully strengthened and centralized their states to defend their territory from European intrusion
c) Both lost their independence to Japan in the late 19th century
d) Both launched programs of defensive modernization to achieve parity with the West
d) Both launched programs of defensive modernization to achieve parity with the West
9-3. All of the following established empires in the Asia and/or Pacific in the 19th century EXCEPT
a) Spain
b) France
c) the United States
d) Japan
a) Spain
9-4. After the Meiji restoration, how did Japan seek to remain free of foreign domination?
a) by closing off the country to all Western influence
b) by drawing on examples Western modernization to transform Japanese society
c) by allying itself with China to collectively resist Western influence
d) by embracing universal suffrage and equality for women
b) by drawing on examples Western modernization to transform Japanese society
9-5. In contrast to the sixteenth century, China during the 19th century
a) declined in international prominence and pwoer
b) became a leading industrial power
c) became a colonial power that rivaled European powers in the Indian Ocean
d) absorbed Korea and Japan into its tribute system
a) declined in international prominence and pwoer
9-6. Which of the following was the only country outside of Europe and North America that successfully industrialized by the late 19th century?
a) Qing China
b) Meiji Japan
c) Mughal India
d) Ottoman Empire
b) Meiji Japan
9-7. The form of governance that characterized Swahili civilization from 1000 to 1500 was most similar to
a) empires of ancient Rome and China
b) khanates of the Mongol Empire
c) complex societies of the eastern woodlands in North America
d) competitive and independent city-states of ancient Greece
d) competitive and independent city-states of ancient Greece
9-8. Which of the following played an important role in the growth of Venice, Jenne-jeno, and Cahokia in the 10th century?
a) War
b) Religion
c) Commerce
d) Diplomacy
c) Commerce
9-9. Recent reinterpretations of the role of pastoral peoples in world history have highlighted all of the following EXCEPT their
a) adaption to inhospitable environments
b) innovations in technology and state-building
c) role in promoting cross-cultural exchange
d) development of an elite literary culture
d) development of an elite literary culture
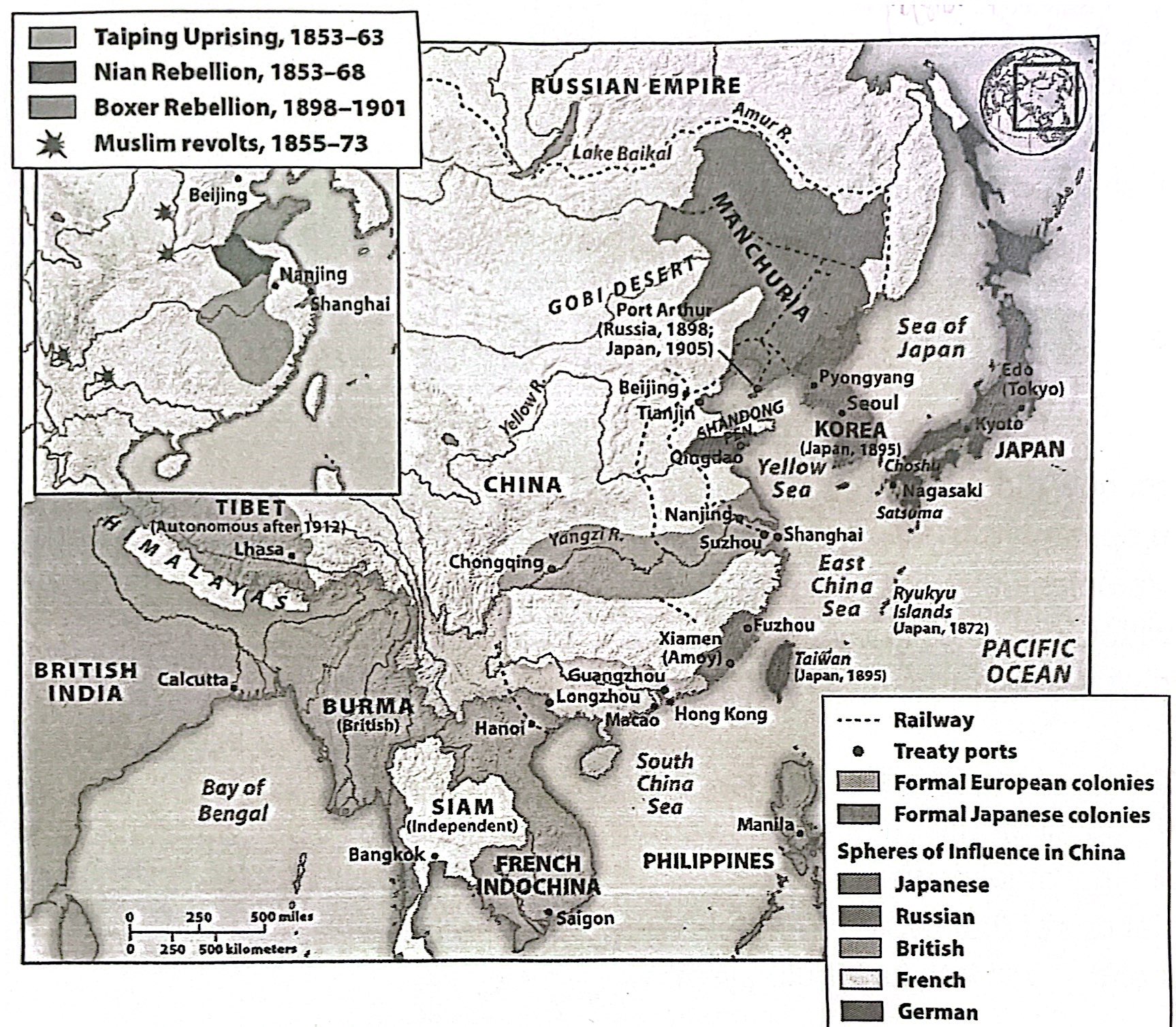
9-10. Which of the following was a new form of economic imperialism, shown in the map above, that was practiced in the 19th century?
a) colony
b) caliphate
c) Sphere of influence
d) Zone of autonomy
c) Sphere of influence
9-11. In 1853, the arrival in Japan of the “black ships“ from which country contributed to the collapse of the Tokugawa shogunate?
a) Ottoman Empire
b) United States
c) Britain
d) China
b) United States
9-12. Which of the following contributed to the contraction of the Ottoman Empire in the 19th century?
a) Disagreement among the European states on how to divide the Ottoman Empire among themselves
b) Nationalist-inspired independence movements in Greece, Serbia, Bulgaria, and Romania
c) Explosive population growth in the 19th century
d) Ottoman control of Afro-Eurasian commerce
b) Nationalist-inspired independence movements in Greece, Serbia, Bulgaria, and Romania
10-1. Which of the following resulted from the employment of colonial subjects in European-owned plantations, mines, construction projects, and businesses?
a) Migration of colonial subjects to work sites overseas
b) Resurgence of the slave trade in Africa and Asia
c) Decrease in racial discrimination
d) Normalcy and stability for colonial subjects
a) Migration of colonial subjects to work sites overseas
10-2.
“Everyone who knows a little about aboriginal races is aware that those races which are of a low type mentally and who are at the same time weak in constitution rapidly die out when their country comes to be occupied by a different race much more rigorous, robust, and pushing than themselves.“ Reverend Bishop Hale, late 18th century
The perspective expressed in the above quotation was used by Europeans to justify which of the following in the 19th century?
a) Communism
b) Imperialism
c) The Great Dying
d) The Crusades
b) Imperialism
10-3. Which of the following reflects a new element in European views of non-Europeans in the 19th century?
a) The idea that non-Europeans could assimilate into European society by Westernizing
b) The belief that the racial inferiority of non-Europeans could be scientifically proven
c) The portrayal of less technologically developed people as “noble savages“
d) The view of non-Christians as “heathen”
b) The belief that the racial inferiority of non-Europeans could be scientifically proven
10-4. In what respect were Ethiopia’s and Siam’s encounters with European imperialism in the 19th century similar?
a) Both avoided the colonization to which their neighbors succumbed
b) Both negotiated an agreement with the U.S. to guarantee their independence
c) Both became settler colonies
d) Both became neo-European societies
a) Both avoided the colonization to which their neighbors succumbed
10-5. The second wave of European conquests that occurred between 1750 and 1914 differed from the first phase in all of the following ways EXCEPT
a) the rise of Germany, Italy, Belgium, the U.S., and Japan as new colonial powers
b) the greater reliance on economic penetration
c) the focus on Asia and Africa
d) the dominant role played by Spain and Portugal
d) the dominant role played by Spain and Portugal
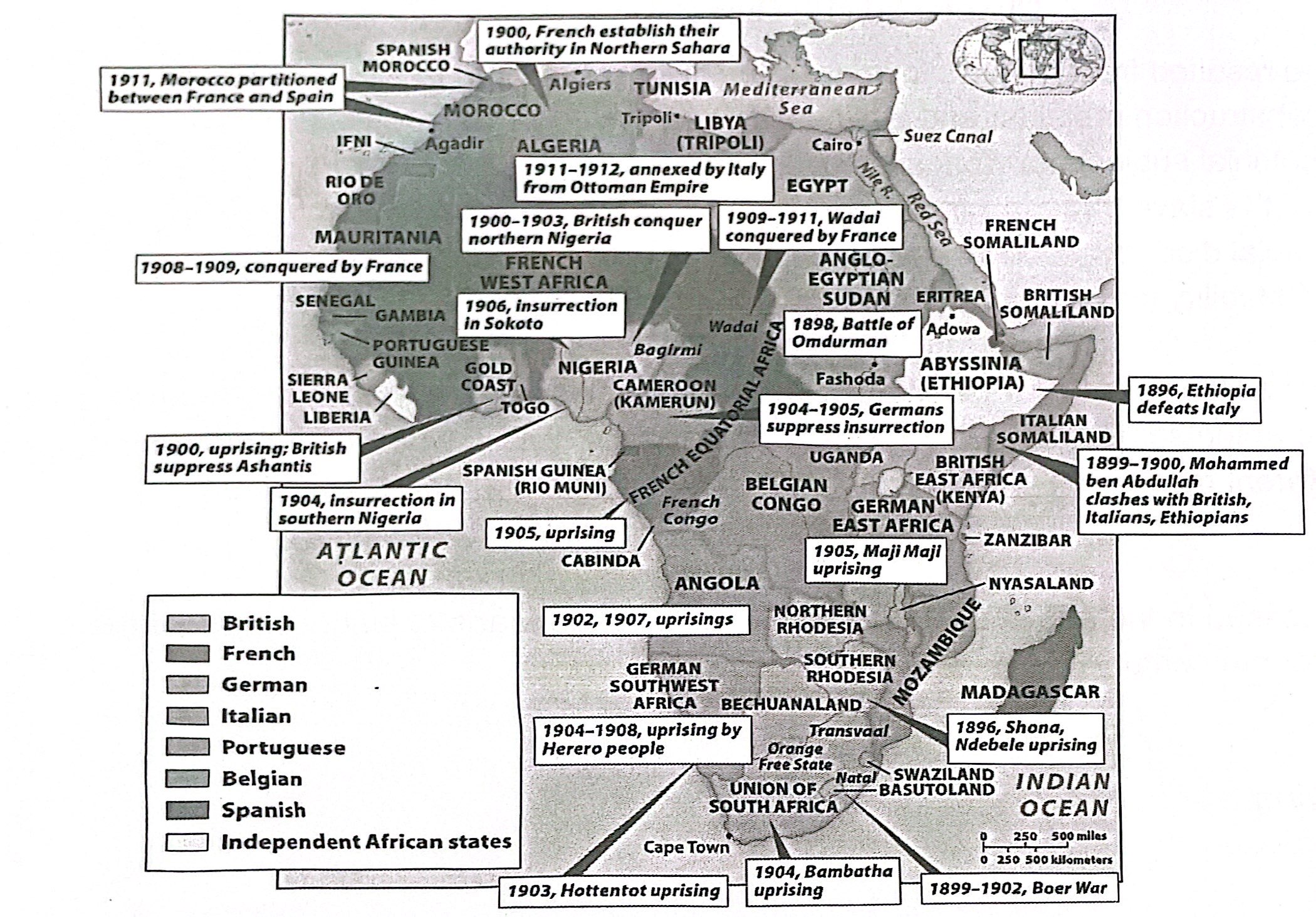
10-6. The map above reflects the outcome of which of the following?
a) The scramble for Africa
b) The Great Dying
c) The Middle Passage
d) The African National Congress
a) The scramble for Africa
10-7. In the late 19th century, the governments of Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and the United States all responded to Chinese immigration by
a) promoting values of multiculturalism and celebrating ethnic diversity
b) implementing policies that made it easier for Chinese immigrants to acquire citizenship
c) passing legislation to curb the flow of Chinese immigrants into their country
d) concluding treaties with China guaranteeing a fixed quota of Chinese immigrants
c) passing legislation to curb the flow of Chinese immigrants into their country
10-8. Which of the following is the term used to refer to the period during which humans spread from Africa, using stone tools to adapt to the different environments they encountered?
a) Paleolithic
b) Neolithic
c) “Secondary products revolution“
d) “the original affluent society“
a) Paleolithic
10-9. By the 1st century C.E., the languages spoken by most people living in the southern half of Africa were linguistically similar. Which of the following contributed to this linguistic similarity?
a) The Arab conquest
b) The Bantu migration
c) The Middle Passage
d) The Columbian Exchange
b) The Bantu migration
10-10. All of the following were conditions that enabled Britain to be the first country to industrialize EXCEPT
a) a scientific culture that emphasized technology
b) the development of electricity
c) a large and mobile labor force
d) the abundance of coal
b) the development of electricity
10-11. All of the following countries were involved in the “scramble for Africa“ EXCEPT
a) Germany
b) France
c) United States
d) Belgium
c) United States
10-12. All of the following represent new forms of forced labor in colonial economies in the 19th and early 20th centuries EXCEPT
a) the cultivation system in the Dutch East Indies
b) statute labor French West Africa
c) coerced labor servitude in the Congo Free State
d) indentured servitude in British North America
d) indentured servitude in British North America

11-1. What does the French poster with the caption that reads “Day of the African Army and Colonial Troops“ suggest about the role of North and West Africans in World War I?
a) They fought for France
b) They rebelled against France
c) They aided Germany
d) They sided with the Central Powers
a) They fought for France
11-2. All of the following aspects of Europe’s 19th-century history contributed to World War I EXCEPT
a) The emergence of Germany as a new nation-state
b) The system created by the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance
c) The tolerance of Serbian terrorist acts
d) The spread of popular nationalism
c) The tolerance of Serbian terrorist acts
11-3. Which of the following reflects a response of some European countries to the Great Depression?
a) Cultural revolution
b) Laissez-faire capitalism
c) Economic liberalization
d) Democratic socialism
d) Democratic socialism
11-4. Which of the following did Japan, Italy, and Germany share in the 1930s?
a) Widespread arrest and execution of political opponents
b) Aggressive ambition for conquest and empire-building
c) Strong traditions of parliamentary democracy
d) Political takeover by socialist parties
b) Aggressive ambition for conquest and empire building
11-5.
“By educating the young generation along the right lines, the People’s State will have to see to it that a generation of mankind is formed whcih will be adequate to this supreme combat that will decide the destinies of the world…“ -Adolf Hitler, Mein Kampf, 1925-1926
“…hence, offering our lives for the sake of the Emperor does not mean so-called sacrifice, but the casting aside of our little selves to live under his august grace and the enhancing of the genuine life of the people of a state…“ -Japanese Ministry of Education, Cardinal Principles of the National Entity of Japan, 1937
Both passages reflect the state’s control of education to prepare students for
a) War
b) Politics
c) Sports
d) Trade
a) War
11-6. In what way were the origins of World War II in Asia and Europe similar to each other?
a) Both Japan and Germany felt they had been treated unfairly because of their defeat in World War I
b) Both Japan and Germany were driven by strategic and economic rivalries with the League of Nations
c) Both Japan and Germany fought to end racism within their own countries and in international relations.
d) Both Japan and Germany expanded their territories through force, creating tensions with other powers
d) Both Japan and Germany expanded their territories through force, creating tensions with other powers
11-7. Which of the following reflects a new pattern in Europe in the period since World War II?
a) The economic integration of Western European countries
b) The colonial exploitation of Eastern European countries
c) The military and cultural dominance of the United Nations
d) The economic and political leadership exercised by Britain
a) The economic integration of Western European countries
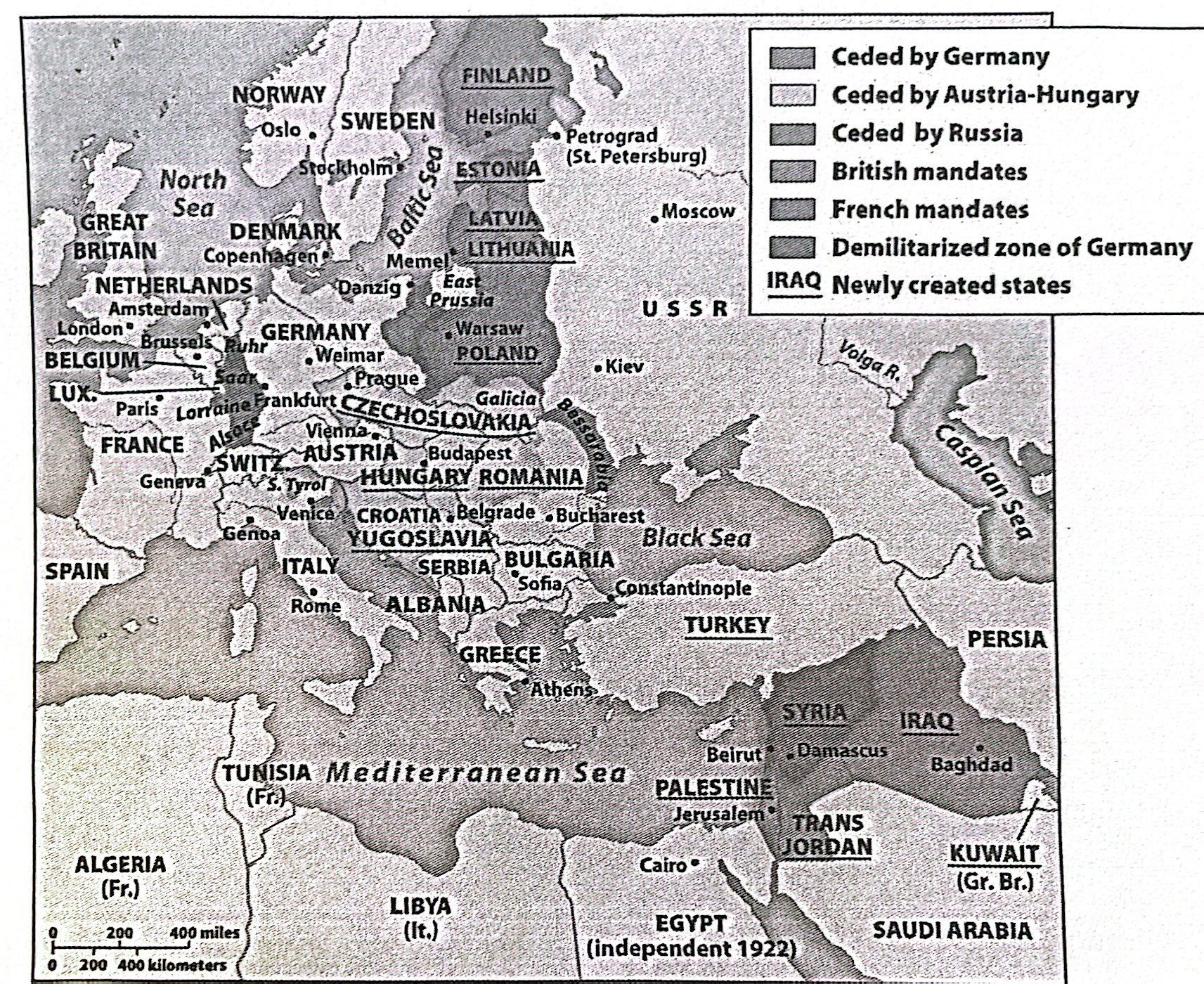
11-8. The map above shows Europe and the Middle East during the period
a) Between the Renaissance and Reformation
b) Between the two world wars
c) Of the New Imperialism
d) Of the Cold War
b) Between the two world wars
11-9. All of the following reflect a growing internationalism in the world after 1945 EXCEPT
a) The League of Nations
b) The United Nations
c) The World Bank
d) The International Monetary Fund
a) The League of Nations
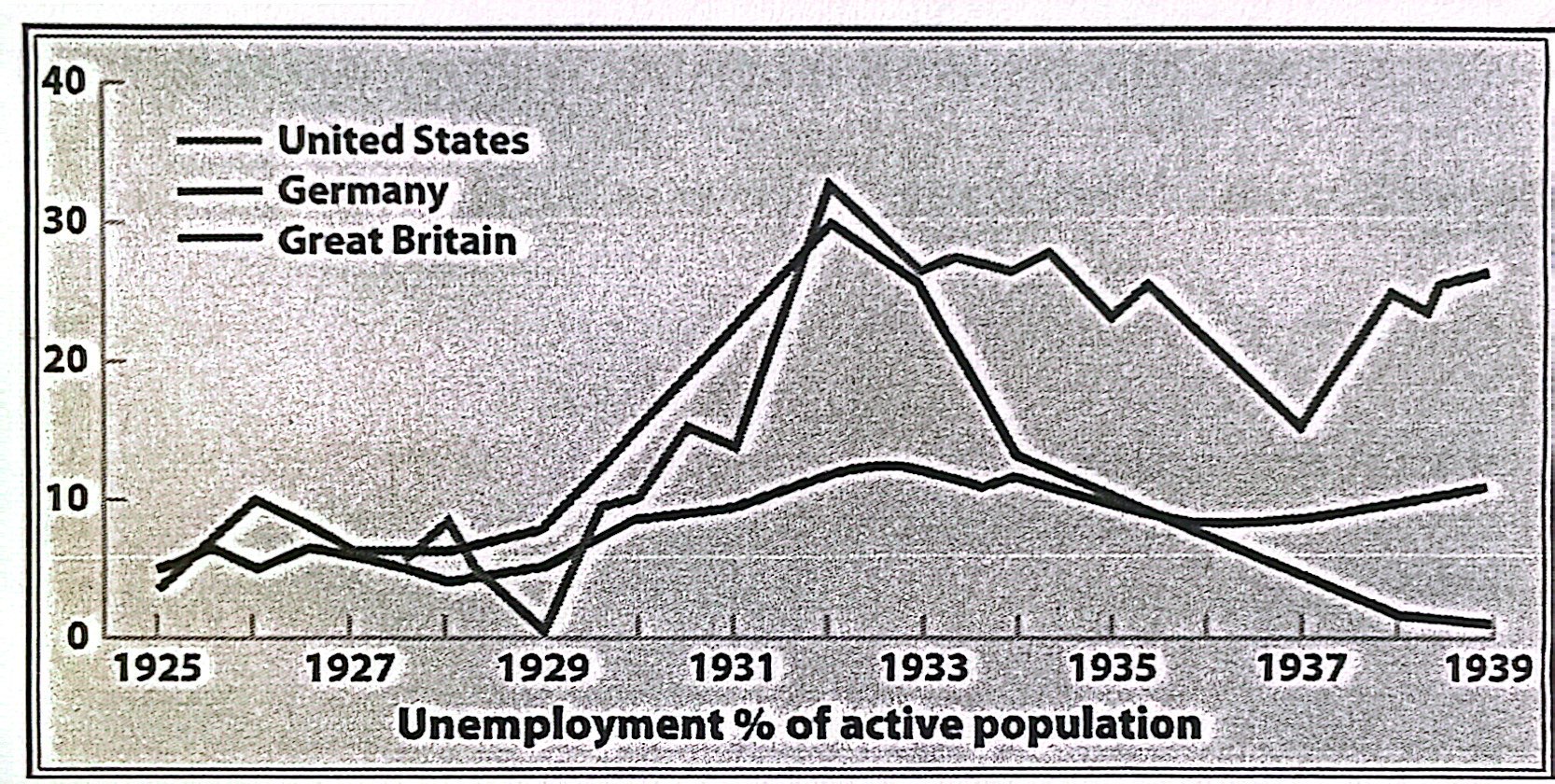
11-10. Which of the following conclusions is supported by the data in the chart above?
a) Unemployment declined in Germany as a result of the rearmament program launched by the Nazi Party
b) Unemployment in Germany, Britain, and the U.S. was at its highest when the Great Depression started
c) The movement of women into the labor force directly affected unemployment rates
d) Republican forms of government were the most effective at confronting the root causes of unemployment
a) Unemployment declined in Germany as a result of the rearmament program launched by the Nazi Party
11-11.
“To many historians, that century [the 20th], and a new era in the human journey, began in 1914 with the outbreak of World War I.”
“…this most recent century both carried on from the past and developed distinctive characteristics, as well. Whether that combination of the old and new merits the designation of a seperate era in world history will likely be debated…“ Robert Strayer, world historian, 2012
In contrast to the view expressed in the first quotation, the second quotation
a) Challenges the notion that the 20th century representing anything new
b) Insists that the 20th century constituted a new period
c) Questions the significance of World War I as an epoch-marking turning point
d) Argues that World War I dramatically transformed the world
a) Challenges the notion that the 20th century representing anything new

13-1. Which of these comparisons between the two posters above is most accurate?
a) Both posters emphasize traditional Buddhist values concerning social hierarchies and government bureaucracies
b) While the New Year’s Good Luck poster shows the success of Mao’s policies, the Great Leap Forward poster provides a commentary on the failure of capitalism
c) The Great Leap Forward poster emphasizes the equality of society, while the New Year’s Good Luck poster shows more of an emphasis on consumerism
d) Both posters celebrate the success of collectivization and rapid industrialization brought about by Mao’s policies
c) The Great Leap Forward poster emphasizes the equality of society, while the New Year’s Good Luck poster shows more of an emphasis on consumerism
13-2. Based on your knowledge of world history, what was the result of Mao’s Great Leap Forward in the People’s Republic of China?
a) The Great Leap Forward caused significant economic hardship on the people, including a major famine
b) The Great Leap Forward allowed China to produce enough food for its entire population
c) The Great Leap Forward was successful in turning China into a modern industrial power
d) The success of the Great Leap Forward helped the international spread of communism
a) The Great Leap Forward caused significant economic hardship on the people, including a major famine

13-3. What global pattern of consumerism in the late 20th century is best represented in the second poster?
a) A world-wide trend towards communist states continued to expand
b) Communist economies focused increasingly on industrialization
c) Communism failed and was abandoned in all nations
d) Many communist countries began to turn towards more capitalist economic policies
d) Many communist countries began to turn towards more capitalist economic policies
13-4. Based on your knowledge of world history and the images above, what changes occurred in China after the death of Mao Zedong in 1976?
a) Communism in China began to slowly collapse beginning in 1976, eventually resulting in the creation of a Western-style democracy
b) While the communist party maintained its political power after Mao’s death, many traditional communist values were replaced by Western-style consumerism
c) After the death of Mao in 1976, communist hardliners created a totalitarian state much like that of Stalin’s Soviet Union.
d) Taiwan (The Republic of China) and the People’s Republic of China merged into one nation.
b) While the communist party maintained its political power after Mao’s death, many traditional communist values were replaced by Western-style consumerism
13-5. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights is most clearly an example of which of the following?
a) A response to the horrors of World War II and a growing belief in the West of certain human rights
b) A reaction to the increased number of women voters immediately after World War II
c) The push by the West to stop the spread of communism during the Cold War
d) The move toward decolonization after World War II
a) A response to the horrors of World War II and a growing belief in the West of certain human rights
13-6.
“Everyone is entitled to all the rights an freedoms set forth in this Declaration…“
“Everyone has the right to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution…“
“Men and women of full age,… have the right to marry and to found a family… Marriage shall be entered int only with the free and full consent of the indenting spouses…“
Which of the following conclusions about the 20th century is most directly supported by the passage?
a) The idea of global free trade spread after World War II
b) The United Nations’ forces were authorized to invade any nation that did not support the United Nations Declaration on Human Rights
c) There was a growing movement following the Second World War to protect the rights of women, children, and refugees.
d) After World War II, there were fewer attempts to create international political and economic organizations
c) There was a growing movement following the Second World War to protect the rights of women, children, and refugees.
13-7. After the end of World War II, the world became more interdependent. This was facilitated most directly by:
a) The global increase in tariffs on imported goods
b) The elimination of international borders
c) The decline of Industrial economic powers, allowing for more global economic growth
d) The creation of new international organizations, such as the UN and the International Criminal Court
d) The creation of new international organizations, such as the UN and the International Criminal Court
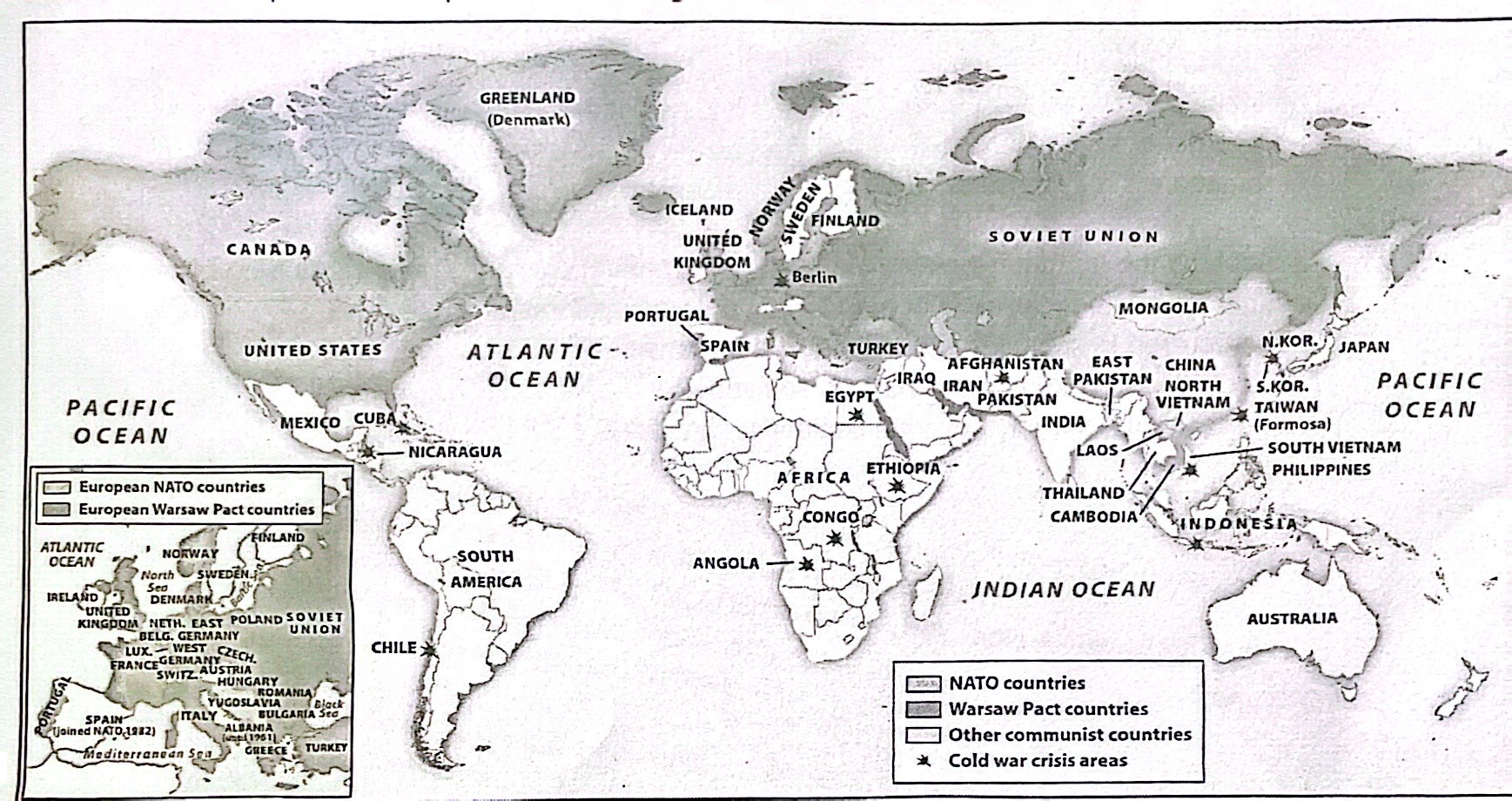
13-8. Based on the map above and your knowledge of world history, which of the European countries was not a member of the neither NATO nor the Warsaw Pact?
a) Turkey
b) Yugoslavia
c) Norway
d) Poland
b) Yugoslavia
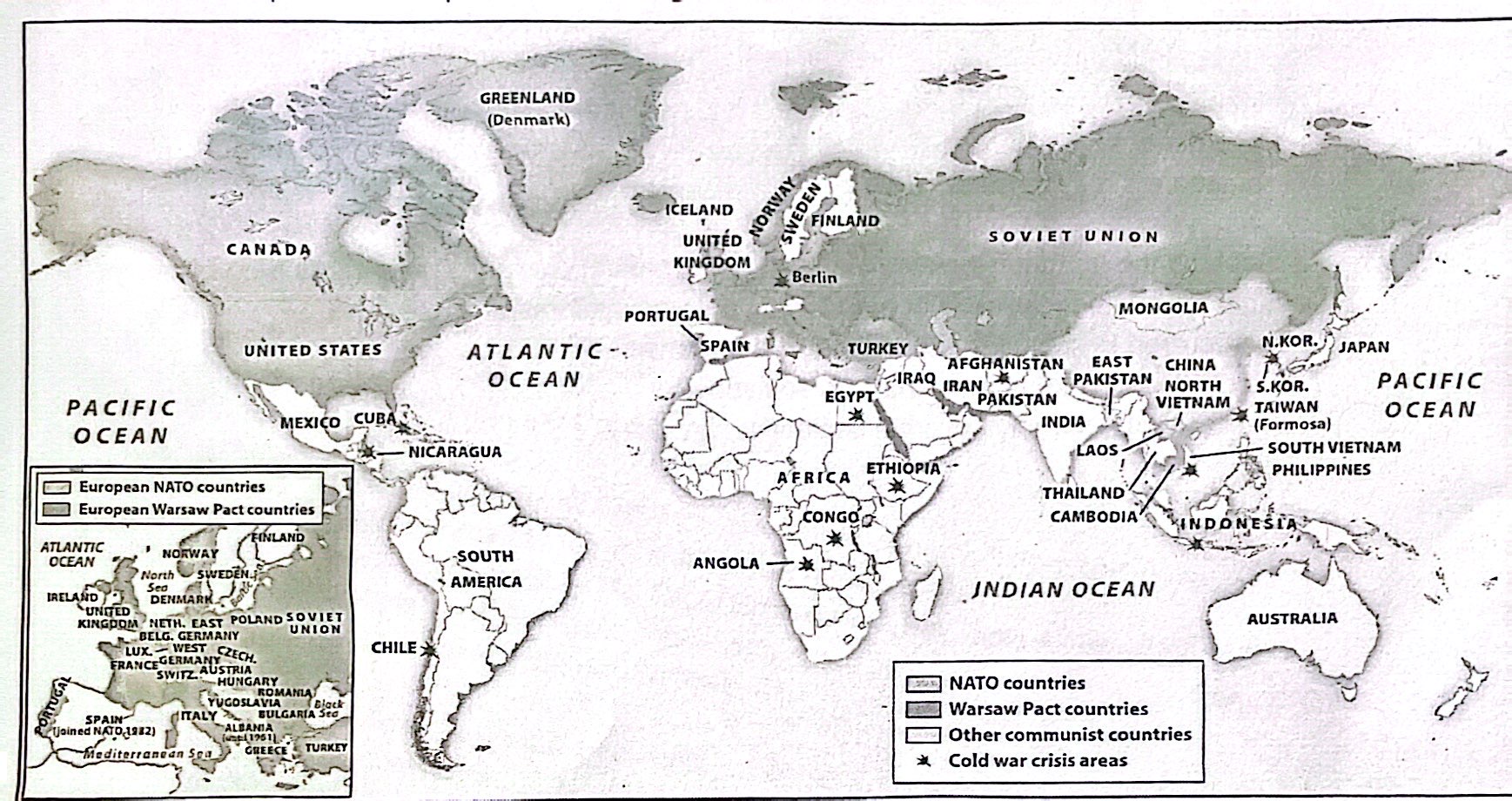
13-9. A historian researching the Cold War period would most likely find this map useful as a source of information about which of the following?
a) The formation of new regional economic organizations during the Cold War era
b) The position of major nuclear sites during the Cold War era
c) The location of proxy wars fought during the Cold War era
d) The extent of global patterns of decolonization during the Cold War era
c) The location of proxy wars fought during the Cold War era
13-10. Which of the following is a direct result of the formation of the Western Bloc and Eastern Bloc during the Cold War?
a) Many Asian, African, and Latin American nations claimed membership in the Non-Aligned Movement
b) Western Bloc nations and Eastern Bloc nations frequently met in small military clashes in order to advance their agenda
c) Nations around the world began to sign nuclear non-proliferation agreements out of fear of global nuclear war
d) Poland was divided into two separation zones of occupation and served as the physical representation of the divide of the Cold War
a) Many Asian, African, and Latin American nations claimed membership in the Non-Aligned Movement
13-11. Which of the following contributed to the outbreak of the Russian Revolution?
a) The class struggle between the urban poor and the impoverished peasantry
b) The inability of the newly established Soviets to speak for ordinary people
c) The popularity of the Romanov dynasty
d) The pressure of World War I
d) The pressure of World War I
13-12. In what respect did the communist movements in the 20th century depart from Marxist theory?
a) They occurred in societies with democratic political systems
b) They occurred in societies with capitalist economies
c) They occurred in highly industrialized societies
d) They occurred in largely agrarian societies
d) They occurred in largely agrarian societies

14-1. How did Gandhi win Indian independence from Britain?
a) By siding with Japan during World War II
b) With decades of non-violent resistance and civil disobedience
c) By cleverly playing Muslims against Hindus
d) With major financial support from the Soviet Union
b) With decades of non-violent resistance and civil disobedience
14-2. Which of the following occurred as a result of the partition of India?
a) The slaughter of Sikhs in Pakistan
b) A half million deaths as Muslims and Hindus migrated throughout the subcontinent to find new homes
c) Pakistan was invaded by Iran
d) Both India and Pakistan became models of pluralistic democracies for the developing world
b) A half million deaths as Muslims and Hindus migrated throughout the subcontinent to find new homes
14-3. What distinguished the end of Europe’s African and Asian colonial empires in the second half of the 20th century from other cases of imperial disintegration?
a) The mobilization of the masses around a nationalist ideology
b) The claim of new nation-states to equal status with their former colonial rulers
c) The wholesale adoption of Western culture by former colonies
d) The almost complete absence of violence in the struggle for independence
a) The mobilization of the masses around a nationalist ideology
14-4. In contrast to the first decolonization of the Americas in the 18th and early 19th centuries, the struggles for independence in Africa and Asia in the second half of the 20th century
a) occurred through peaceful negotiations
b) resulted in political independence
c) affirmed the vitality of precolonial cultures
d) excluded women from participation
c) affirmed the vitality of precolonial cultures
14-5. Which of the following represented a fundamental contradiction that undermined the colonial enterprise in the second half of the 20th century?
a) The prestige of scientific racism and beliefs in European uniqueness challenged colonial exploitation and poverty
b) The authoritarian tendencies of European states ran counter to the democratization of colonial society
c) The decline of colonies as trade partners and sources of raw materials ran counter to the original logic of colonization
d) The ideal of national self-determination was at odds with the denial of independence to their colonies
d) The ideal of national self-determination was at odds with the denial of independence to their colonies
14-6. Which of the following changes in the international arena in the second half of the 20th century contributed to the end of European colonial rule?
a) The United Nations provided an international platform from which to conduct anticolonial agitation
b) The United States and the Soviet Union absorbed the colonies of the former European empires
c) The Westernized elite in the colonies assimilated into European society and ruled on behalf of European states
d) The World Bank offered to compensate those colonial powers willing to grant independence to their colonies
a) The United Nations provided an international platform from which to conduct anticolonial agitation
14-7. Which of the following was a social or economic circumstance within the European colonies that contributed to anti-colonial movements?
a) Rapid industrialization within some colonies, which led to a growing working class that took a leadership role in the independence movement
b) The growing number of Western-educated colonial elites who no longer viewed colonial rule as a vehicle for their people’s progress
c) The spread of a militant anticolonial version of Christianity that expressed itself in anticolonial agitation
d) The rising prosperity of most colonies, which left their populations richer than the populations of their colonial overlords
b) The growing number of Western-educated colonial elites who no longer viewed colonial rule as a vehicle for their people’s progress
14-8. How did the system of apartheid in South Africa come to an end?
a) As a result of a military coup organized and led by the Black Consciousness movement
b) As a result of a decade-long racially divided civil war between white and black South Africans
c) Through negotiations between the white South African government and black South African nationalist leaders
d) Through the mass exodus of white South Africans as racial violence escalated after the Soweto rebellion
c) Through negotiations between the white South African government and black South African nationalist leaders
14-9. In Africa in the early 1980s, what happened to the political parties that had led the movements for independence from colonial rule?
a) Most were soon swept away by military coups
b) Most became as oppressive as the colonial rulers they had ousted
c) Most splintered into different factions
d) Most became personal dictatorships
a) Most were soon swept away by military coups
14-10. In Africa, which of the following contributed to the loss of popular support for the democratic institutions established in the wake of independence from colonial rule?
a) Human rights violations
b) Pan-African unity
c) Marxist class solidarity
d) Poor economic performance
d) Poor economic performance
14-11. Which of the following resulted from the so-called White Revolution of Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi in Iran?
a) Popular demands for a Western-style democratic republic
b) Rapid economic growth and widespread economic prosperity
c) Discontent and resentment that paved the way for an Islamic revolution
d) Civil war between Sunni and Shiite Muslims in Iran
c) Discontent and resentment that paved the way for an Islamic revolution
14-12. Which of the following countries became a new nation-state in the late 1940s?
a) South Africa
b) Ukraine
c) Bangladesh
d) Israel
d) Israel
15-1. All of the following have contributed to the environmental changes of the 20th century EXCEPT
a) Explosive increase in world population
b) New energy resources
c) Worldwide decline in service industries
d) Phenomenal economic growth
c) Worldwide decline in service industries
15-2. How have modernity, science, and globalization affected the world's religions since 1945?
a) Religion contributed to the scientific and secular focus of global modernity
b) Religion offered a means to oppose elements of a secular and global modernity
c) Religion was universally criticized for fostering superstition and ignorance
d) Religions experienced sharp declines in membership and conversions.
b) Religion offered a means to oppose elements of a secular and global modernity
15-3. Which of the following reflects a neo-liberal approach to economic development?
a) Government regulation of the economy
b) Promotion of global equality
c) Privatization of state-run companies
d) Increase in tariffs and taxes
c) Privatization of state-run companies
15-4. Beginning in the 1960s, which of the following were identified as key issues in Western feminism by women of color?
a) Gaining the right to vote
b) Promoting cultural imperialism
c) Challenging patriarchal domination
d) Ending racism and poverty
d) Ending racism and poverty
15-5. What do those who speak of an "American Empire" point to in support of their opinion?
a) American control of the International Criminal Court
b) American control of the United Nations
c) American economic, military, and cultural influence around the world
d) American territorial possessions in the Caribbean and South Pacific
c) American economic, military, and cultural influence around the world
15-6. In the permissive economic climate of recent decades, transnational corporations frequently relocate their facilities in search of
a) the least restrictive environmental regulations
b) a highly skilled and university-trained workforce
c) markets subsidized by the International Monetary Fund
d) tightening credit markets and inflated housing markets
a) the least restrictive environmental regulations
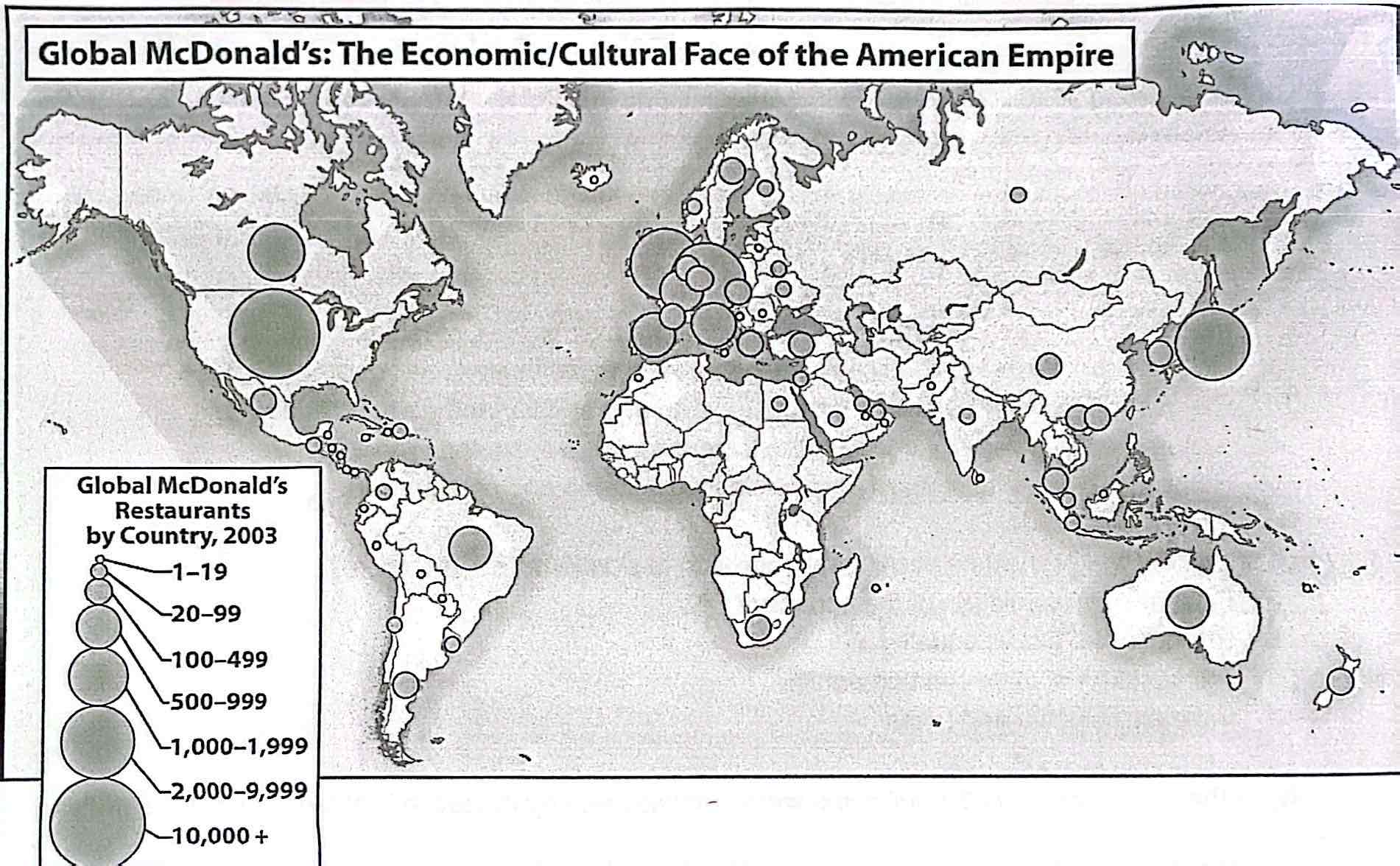
15-7. The map showing the global distribution of McDonald's highlights which aspect of the so-called American empire?
a) Counterculture
b) Soft power
c) Cultural revolution
d) Grassroots democracy
b) Soft power
15-8. Which of the following was the original meaning of the phrase “third world“?
a) A global attempt to create “socialism with a human face“
b) A universal struggle for liberation through guerilla warfare
c) An alternative to Western capitalism and Soviet communism
d) A movement for global justice and equality
c) An alternative to Western capitalism and Soviet communism
15-9. Describing the current era since the Industrial Revolution as the Anthropocene Era calls attention to the
a) psychological trauma caused by wars
b) lasting impact of human activity on the planet
c) temporary solutions during times of scarcity
d) social inequalities generated by economic development
b) lasting impact of human activity on the planet
15-10. What do the Gulen movement in Turkey and the Amman Message issued in Jordan in 2005 share in common?
a) Both emphasized a literal and dogmatic interpretation of the Quran
b) Both affirmed violent jihad as a legitimate part of Islamic life
c) Both defined those who disagreed with them as “non-Muslims“
d) Both sought to encourage cross-cultural and inter-religious dialogue
d) Both sought to encourage cross-cultural and inter-religious dialogue
15-11. All of the following are conventionally identified as early signs of the modern world that first emerged in the centuries from 1450 to 1750 EXCEPT the
a) Emergence of Islam as the dominant faith in Africa and Asia
b) Processes of globalization initiated by European expansion
c) Elements of modernity expressed in the Scientific Revolution
d) Dominance of Europeans in the Americans as the seas
a) Emergence of Islam as the dominant faith in Africa and Asia
15-12. Which of the following has been identified as a factor contributing to the collapse of the Moche, Maya, and Chaco cultures?
a) Foreign invasion
b) A century of devastating flooding
c) A long-term drought
d) Massive rebellions that overthrew the Maya emperor
c) A long-term drought