Cell Bio- Microscopy
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
light microscopy
resolution= 2um
for dead and alive subjects
alive (different optics)
dead(staining)
sample ~thin/transparent
allows examination of cells and some of their content
three types of light microscopy
bright field optics
phase contrast optics
interference contrast optics
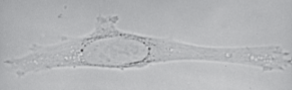
brightfield optics
low contrast
usually need staining
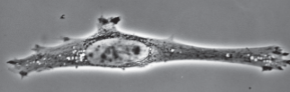
phase contrast optics
observing living cells
halo effects
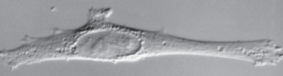
interference contrast optics
3d like image, no halo
expensive
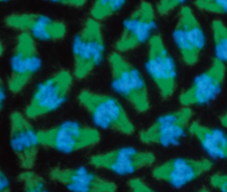
fluorescence microscopy
resolution=.2um
cellular structures labeled by dyed/antibodies
glowy-like effect
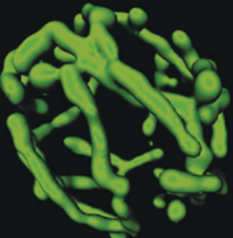
confocal microscopy
type of fluorescence microscopy
resolution=.2um
3D like image
ideal of live/thicker samples
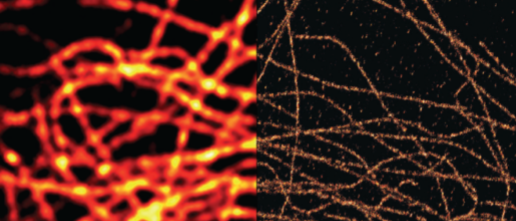
super resolution microscopy
resolution=10-20 nm
insight into intracellular processes
electron microscopy
major cell biology breakthrough
100x better resolution than light microscopy
2 types: TEM/SEM
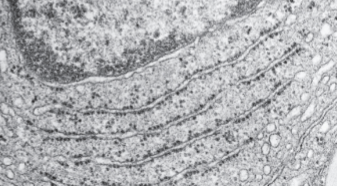
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Resolution=1nm
electrons and magnets used to create/focus image
dead samples sectioned and stained for contrast
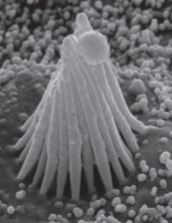
scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
resolution= 3-20nm
heavy metal coated, dead samples are scanned by electron bean
3-D like image
nucleus
contains nuclear envelope
contains nuclear pores
transcription and RNA processing occurs in
the nucleus
translation of mRNA into proteins @ ribosomes occurs in the
cytosol after mRNA exports through nuclear pores
ER contain flattened or tubular sacs called
cisternae
lysosomes
molecular digestion of biomolecules
peroxisomes
hydrogen peroxide chemistry for breakdown/synthesis of moleculessm
small vesicles
transport components throughout cell
endosomes
sorts components brought into cells via endocytosis
actin filaments
thinnest, cell shape, muscle contration, intracellular transport
microtubules
thickest, hollow tubes, cell division & intracellular transport
intermediate filaments
widespread & diffuse for strength & support.