Science Stars Unit 2 Vocabulary
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:50 PM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
Star
A ball of hot burning gas
2
New cards
Luminosity
The actual brightness of a star (on a scale compared to the brightness of the sun)
3
New cards
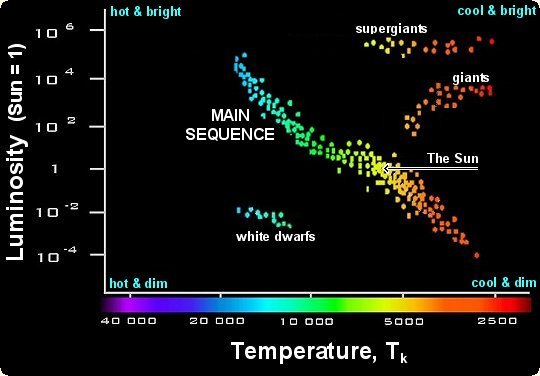
HR Diagram
Hertz sprung-Russell diagram, a graph that shows patterns in star properties, such as luminosity and temperature.
4
New cards
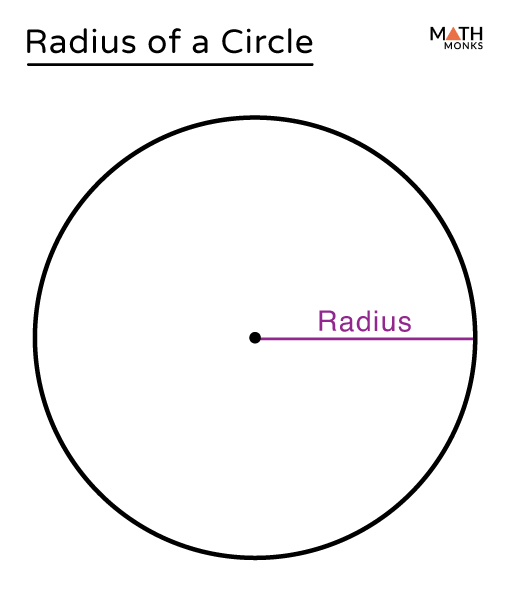
Radius
The distance from the center of a circle to any point on circle edge.
5
New cards
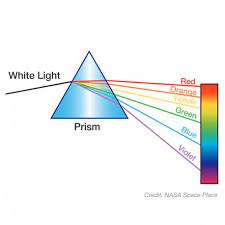
Light Diffraction
Occurs when light bends and reveals its parts. Ex) white light bends through a prism and is separated into colors of the spectrum.
6
New cards
Spectroscope
An instrument which spreads light out into its wavelengths, creating a spectrum. Used to view spectra produced by various sources of light.
7
New cards
Telescope
an instrument that uses mirrors to collect electromagnetic radiation from the sky and concentrates it for better observation of bodies in space
8
New cards
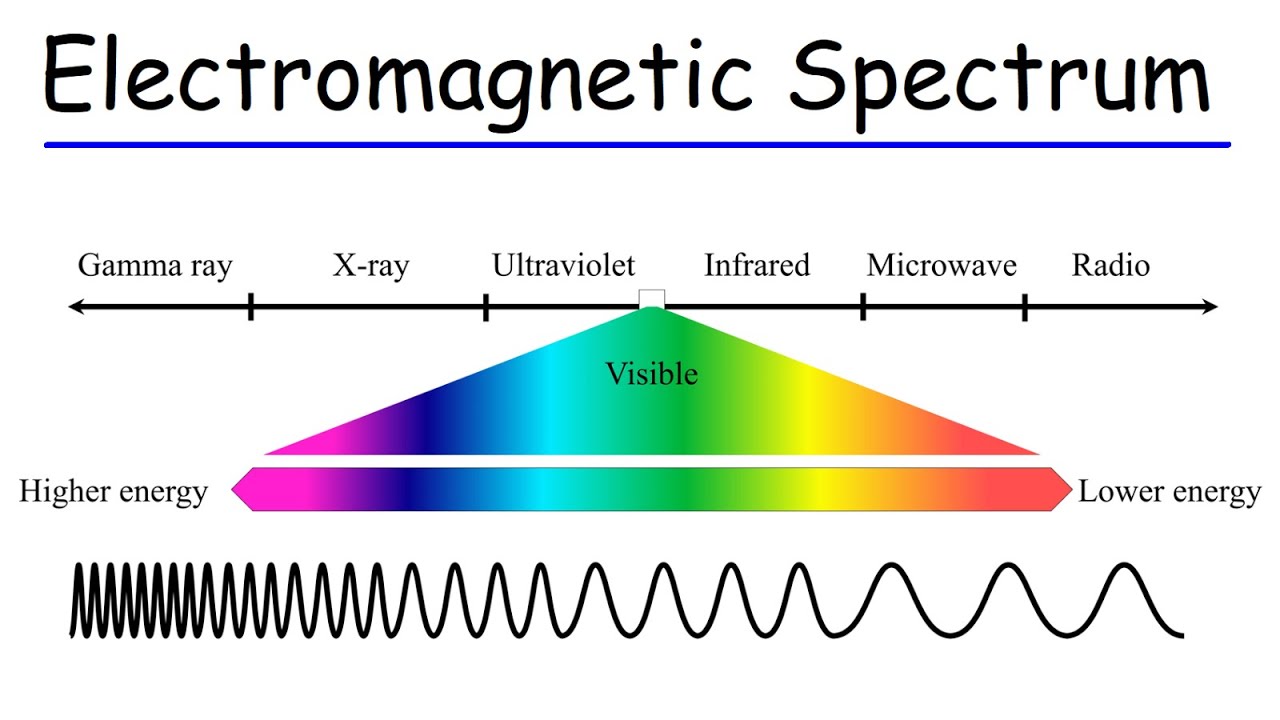
Electromagnetic Spectrum
All of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation (light energy)
9
New cards
Radiation
a type of energy that travels through space as waves
10
New cards
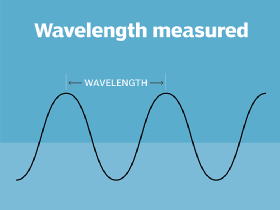
Wavelength
the distance from the peak (top) of one light wave to the peak (top) of the next light wave. Electromagnetic wavelengths vary from the short blips of cosmic rays to the long pulses of radio transmission
11
New cards
Light Spectrum/Spectra
Colored band produced when a beam of light is bent to show its individual wavelengths, such as the colored band produced when white light travels through a prism
12
New cards
ROYGBIV
Colors of the visible spectrum in order of wavelength and frequency.
13
New cards
Emission Spectra
What is produced when a heated gas gives off energy (typically how we see nebula clouds)

14
New cards
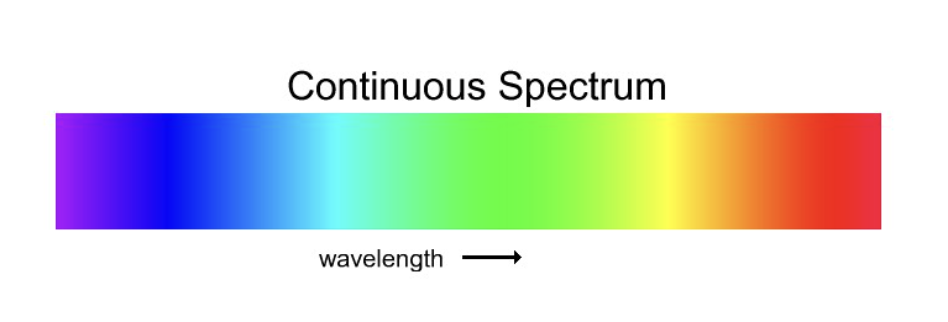
Continuous Spectra
Starlight with no interference (ROYGBIV)
15
New cards
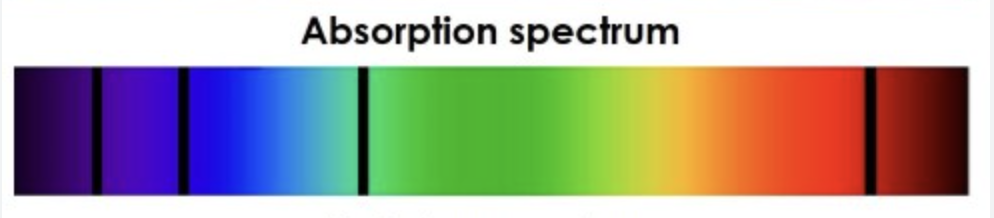
Absorption Spectra
What is produced when starlight passing through a cloud of dust/gas
16
New cards
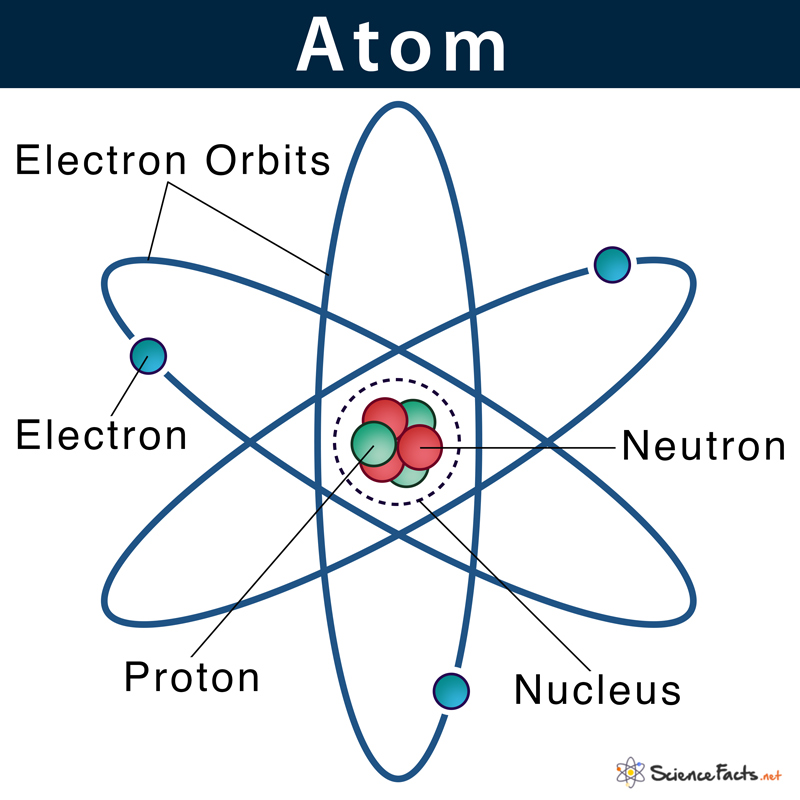
Atom
the basic unit of a chemical element.
17
New cards
Element
A pure substance made up of similar atoms
18
New cards
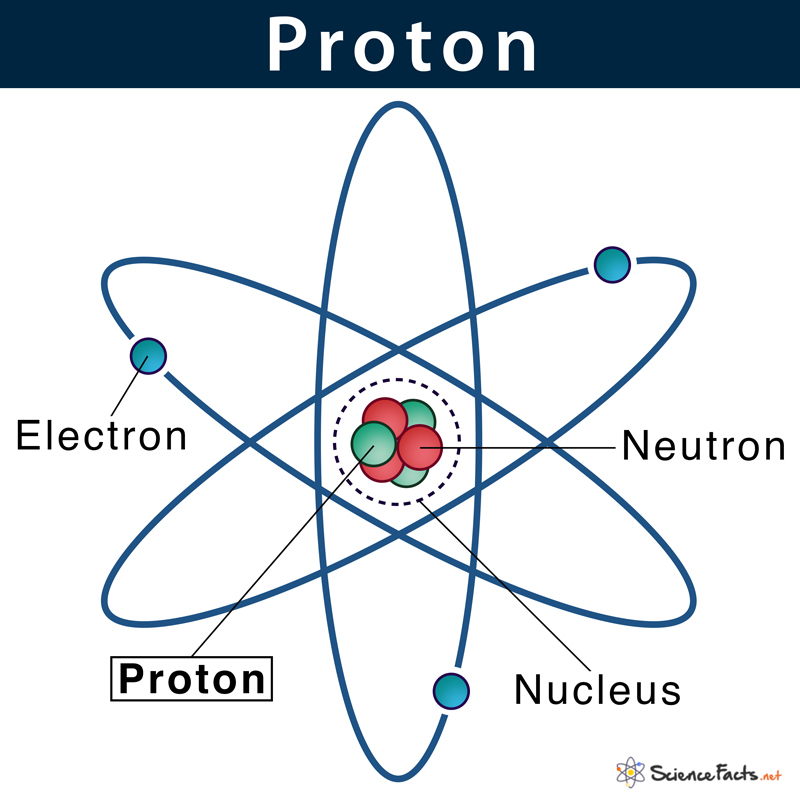
Protons
a subatomic particle found in the nucleus of every atom. The particle has a positive electrical charge, equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons is the atomic number
19
New cards
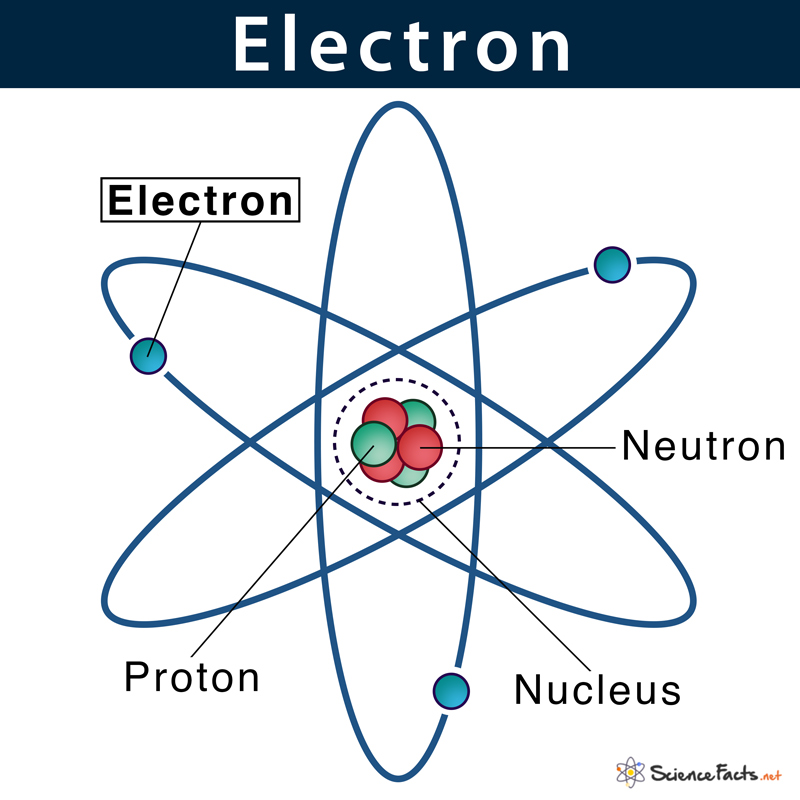
Electrons
a negatively charged subatomic particle that can be either bound to an atom or free (not bound).
20
New cards
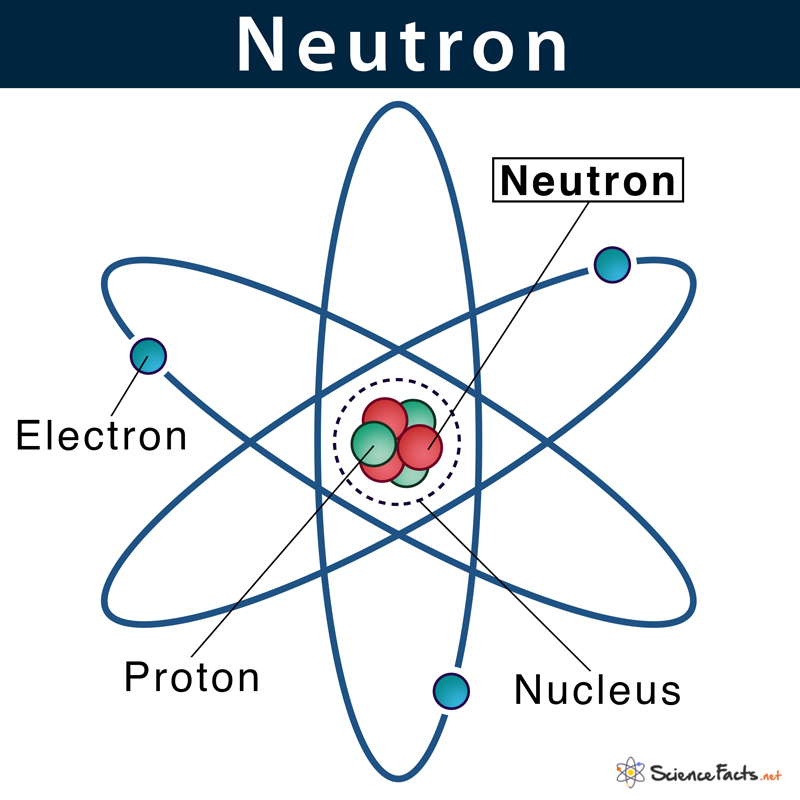
Neutrons
a subatomic particle found in the nucleus of every atom except that of simple hydrogen. The particle derives its name from the fact that it has no electrical charge; it is neutral.
21
New cards
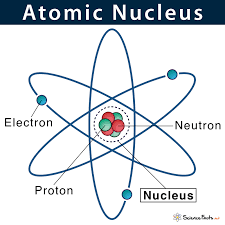
Nucleus
the positively charged central core of an atom, consisting of protons and neutrons and containing nearly all its mass.
22
New cards
Atomic Number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table.

23
New cards
Periodic Table
a table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in vertical columns.
