Ejaculation/Semen
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Describe the nervous control of erection
parasympathetic causes relaxation of smooth muscles in penis allowing erectile tissue to rapidly engorge with blood. veins surrounding the erectile tissue are compressed cutting of venous drainage
describe the nervous control of ejaculation
sympathetic contracts smooth muscles of ductus deferens and remain ducts to expel semen. constrict the smooth muscle of the arteries into the penis allowing blood flow out of the penis through deep dorsal vein.
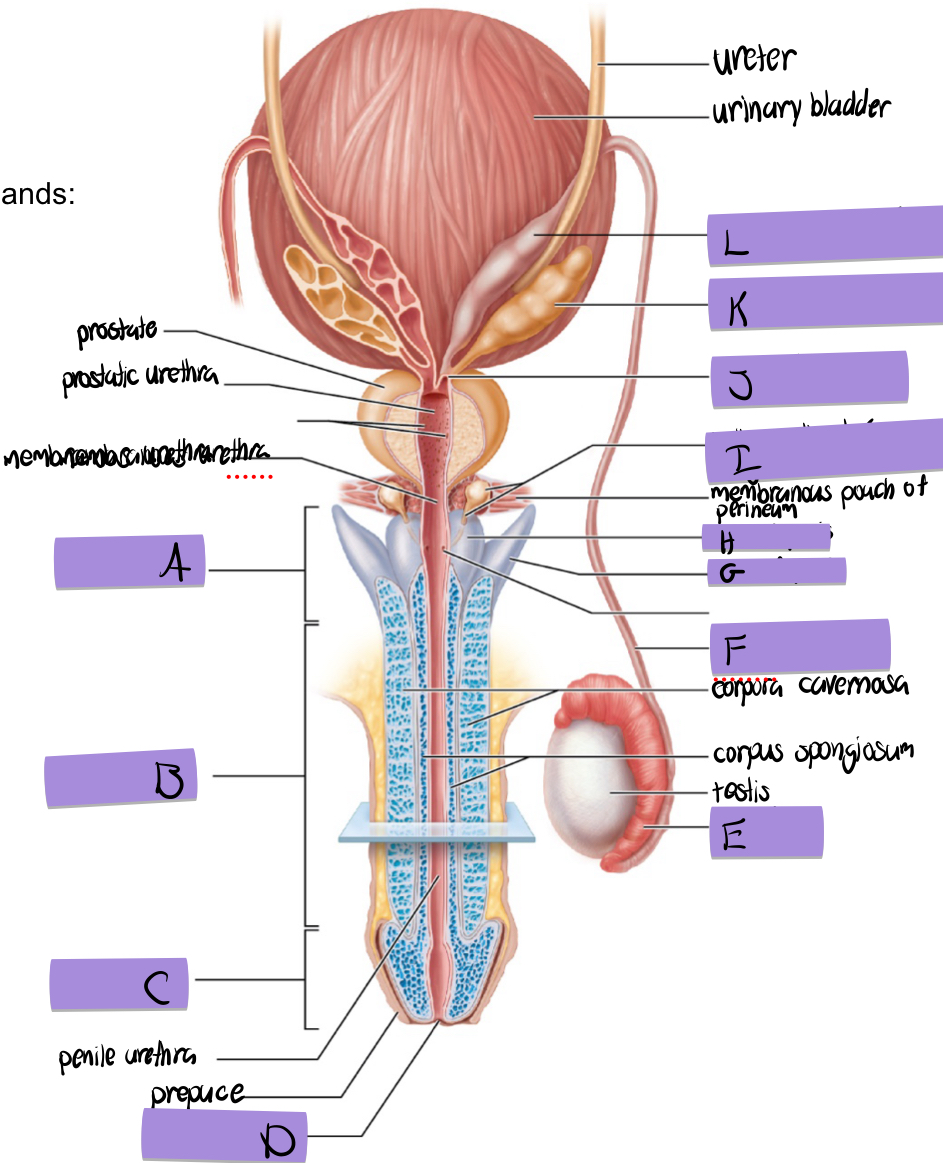
what is A
root of penis
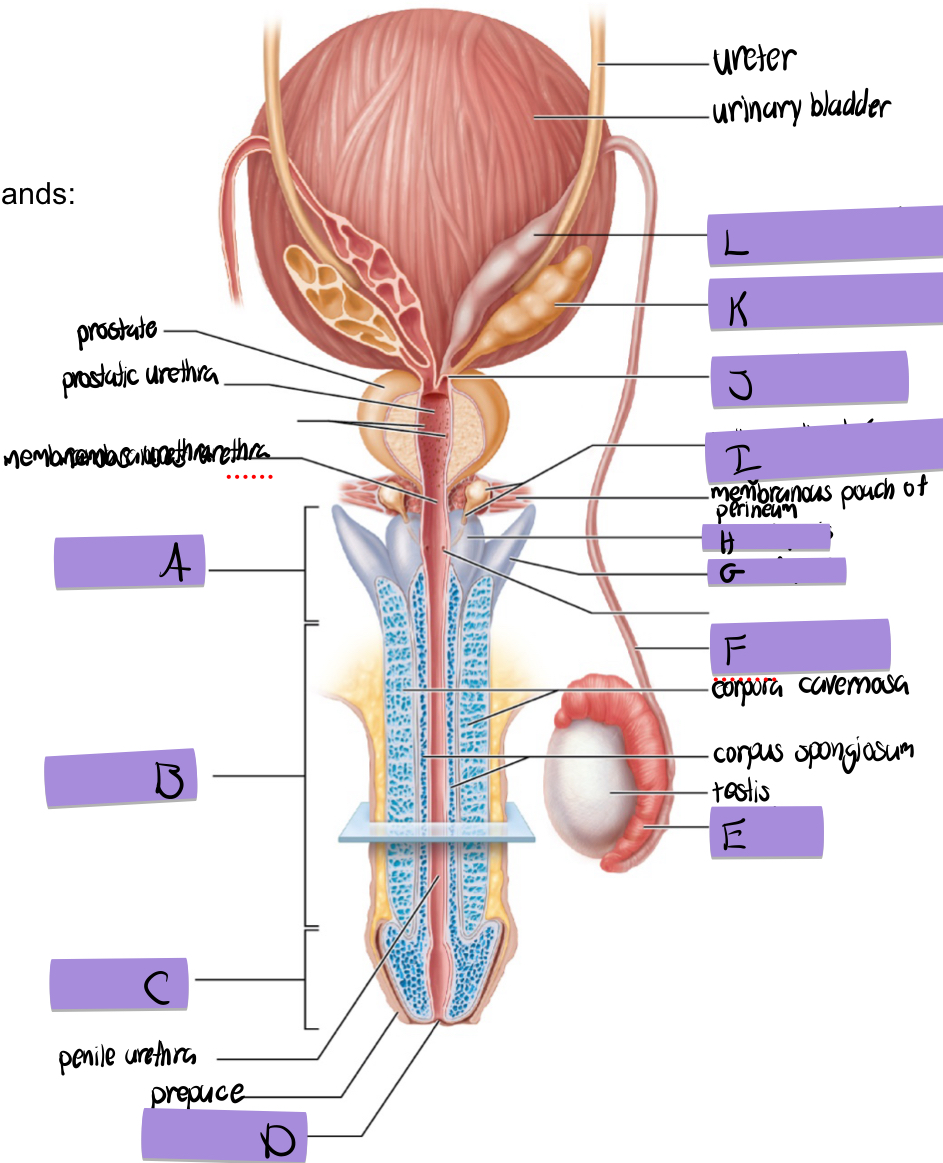
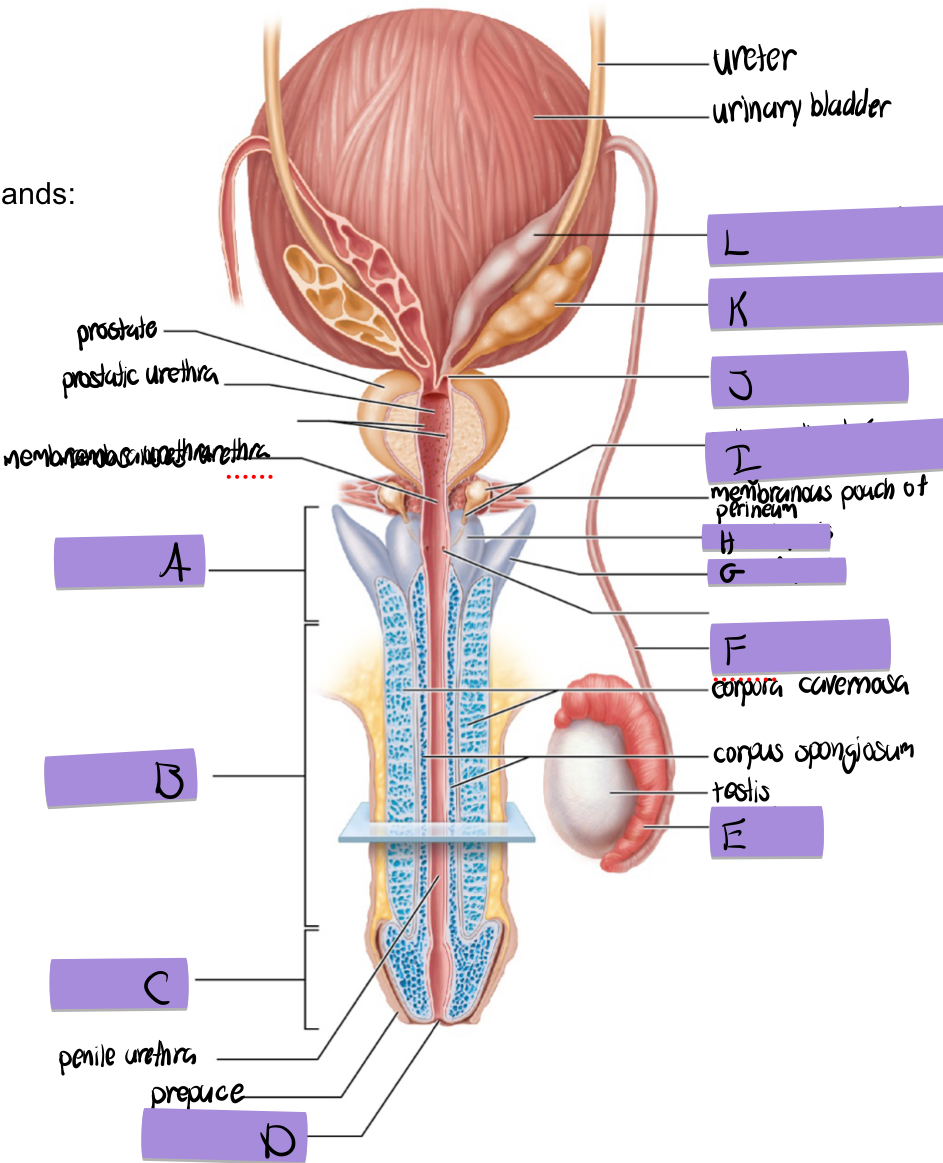
what is B
body of penis
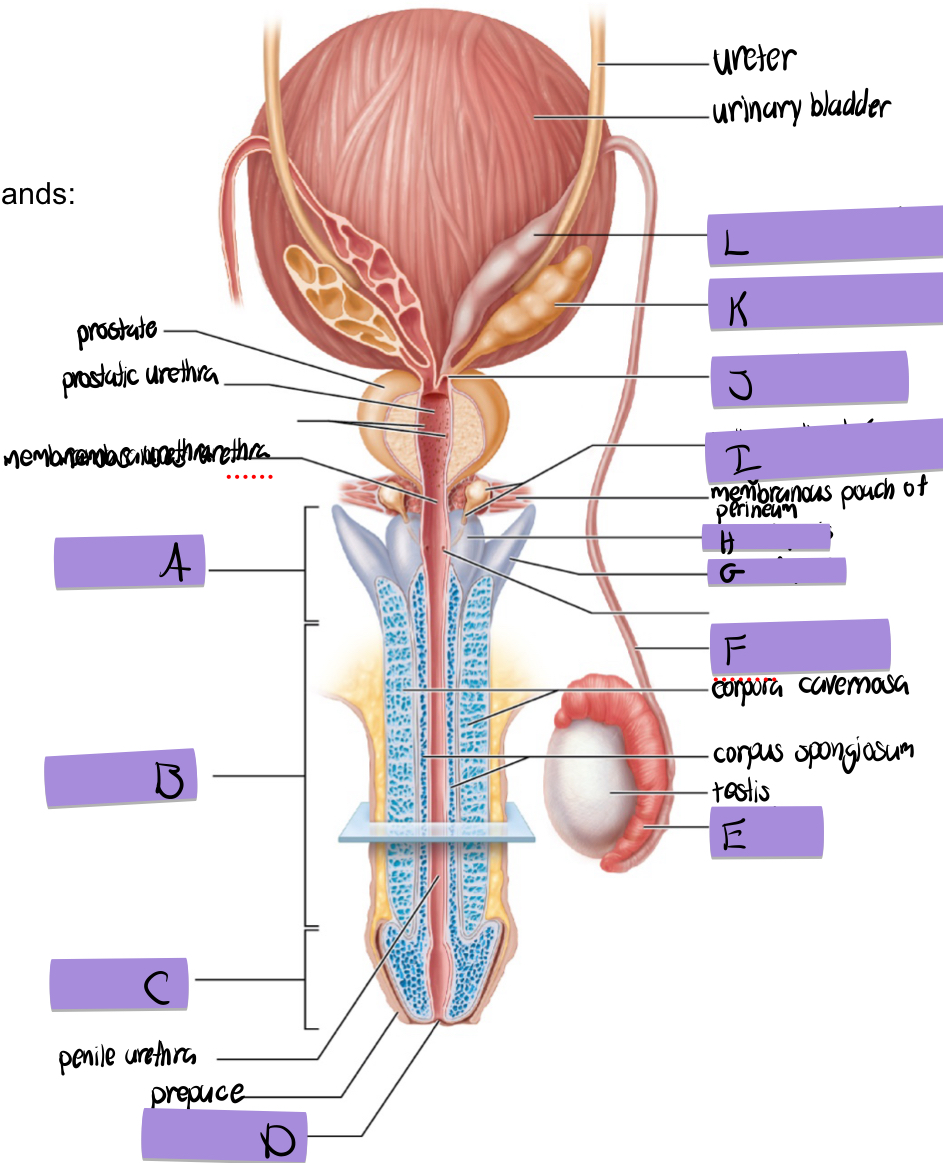
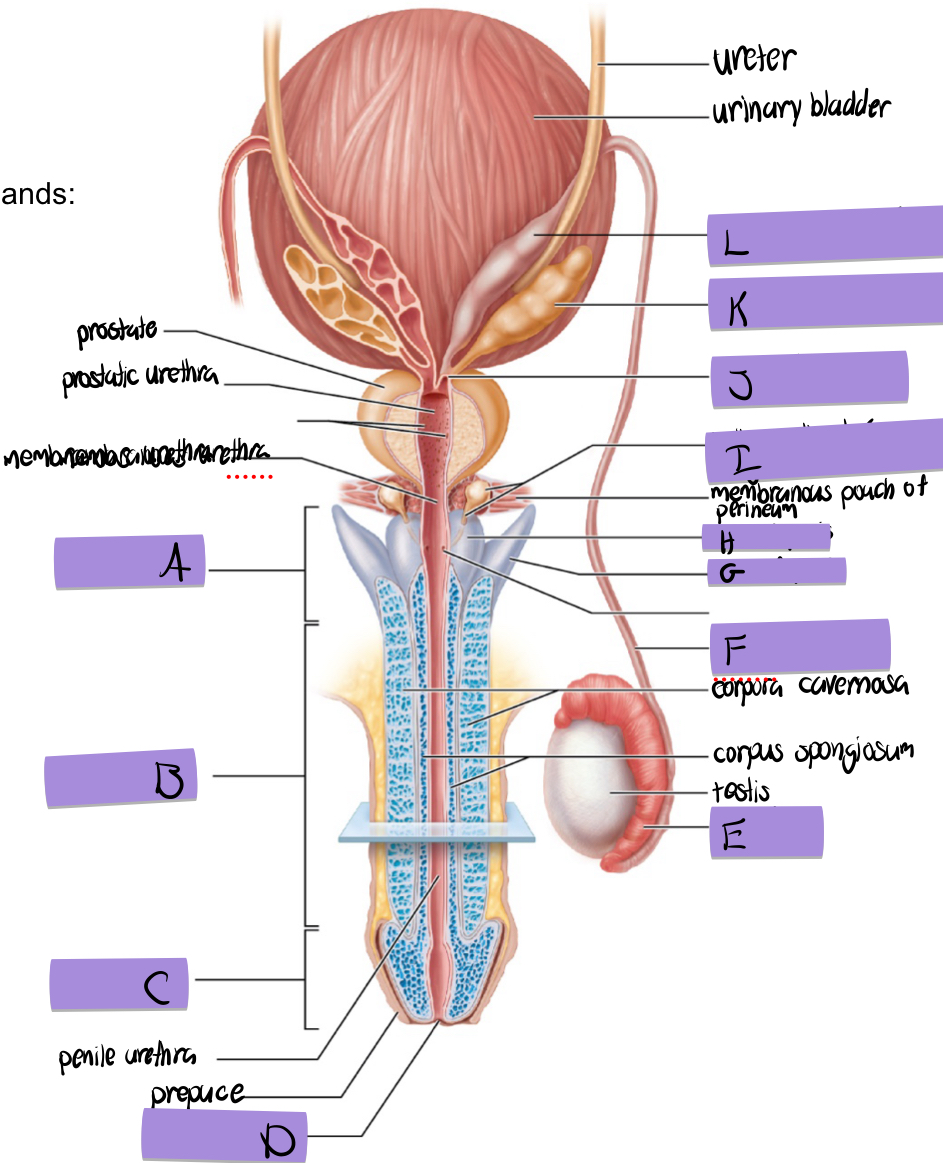
what is C
glans penis
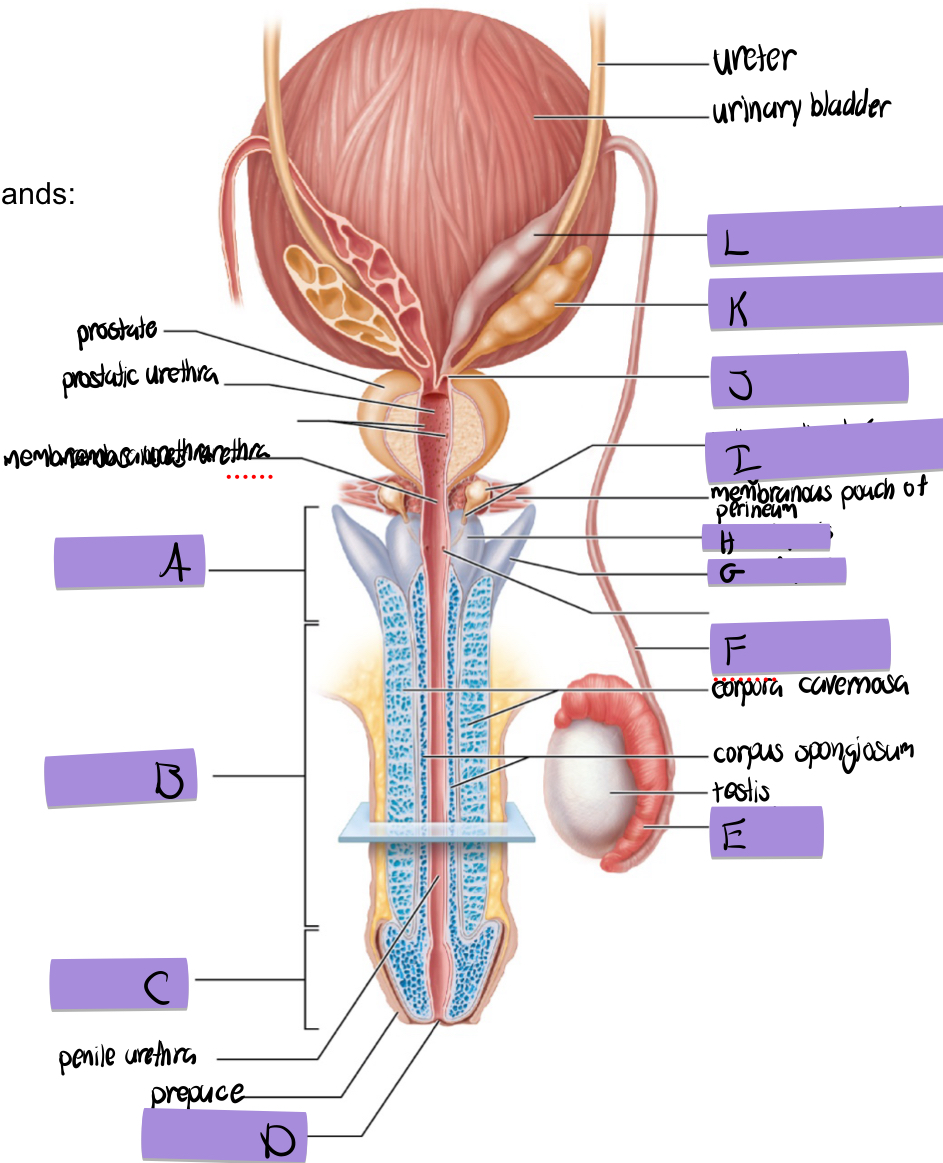
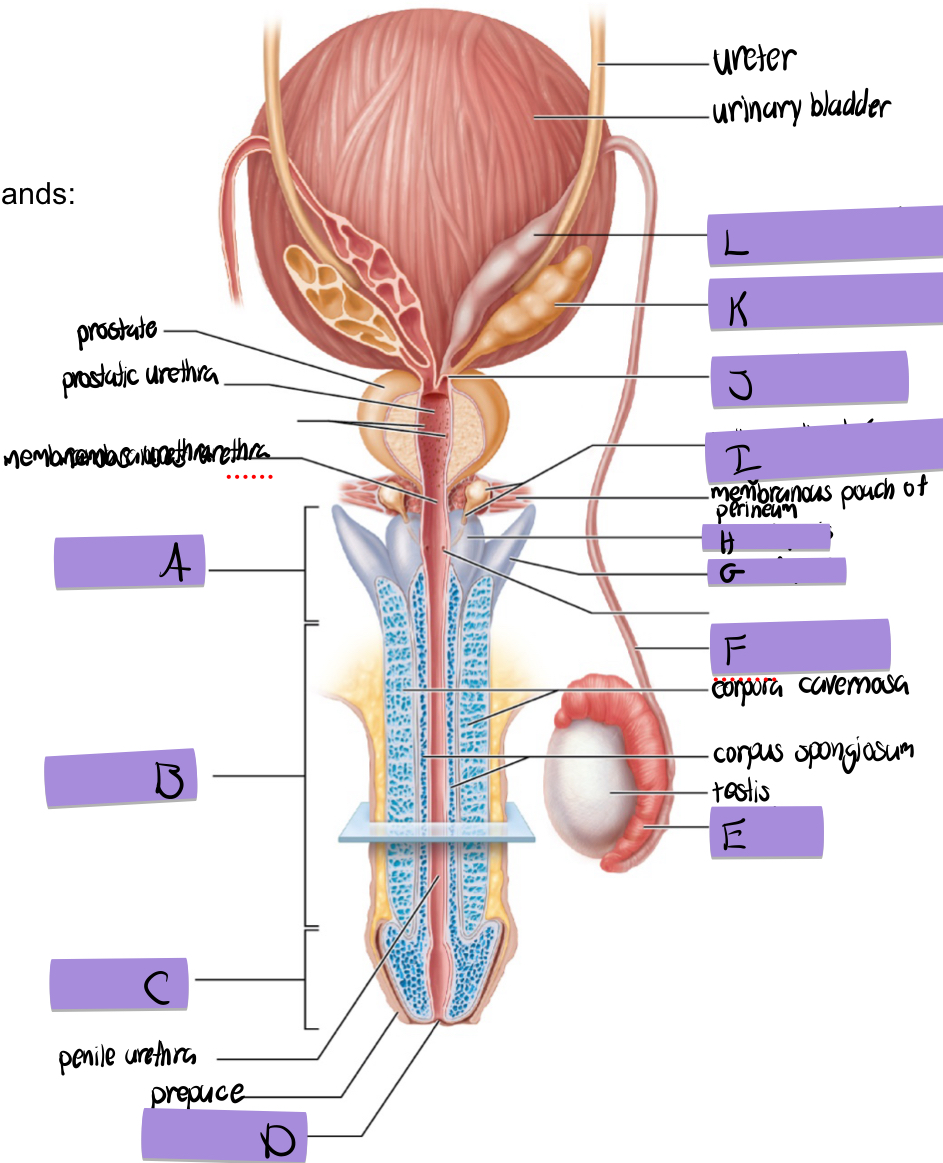
what is D
navicular fossa
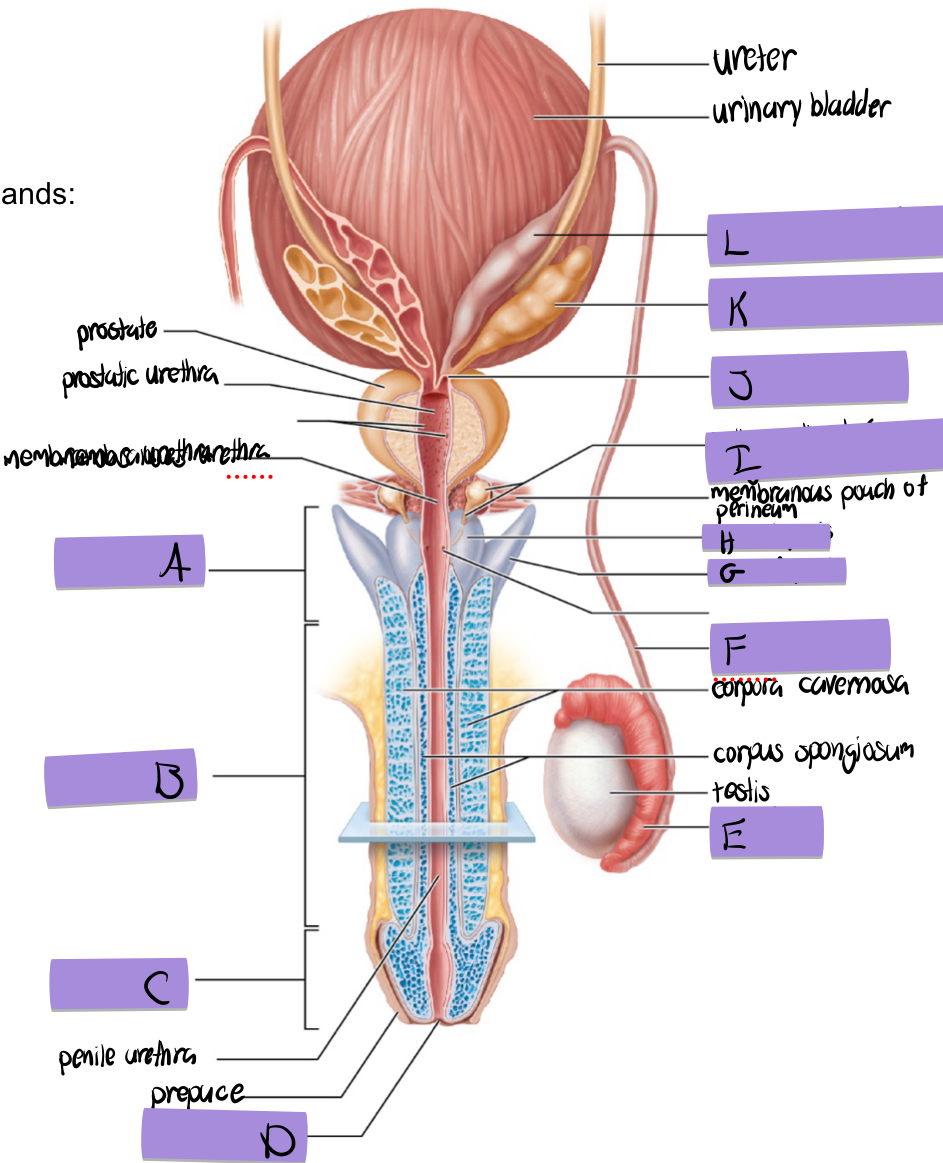
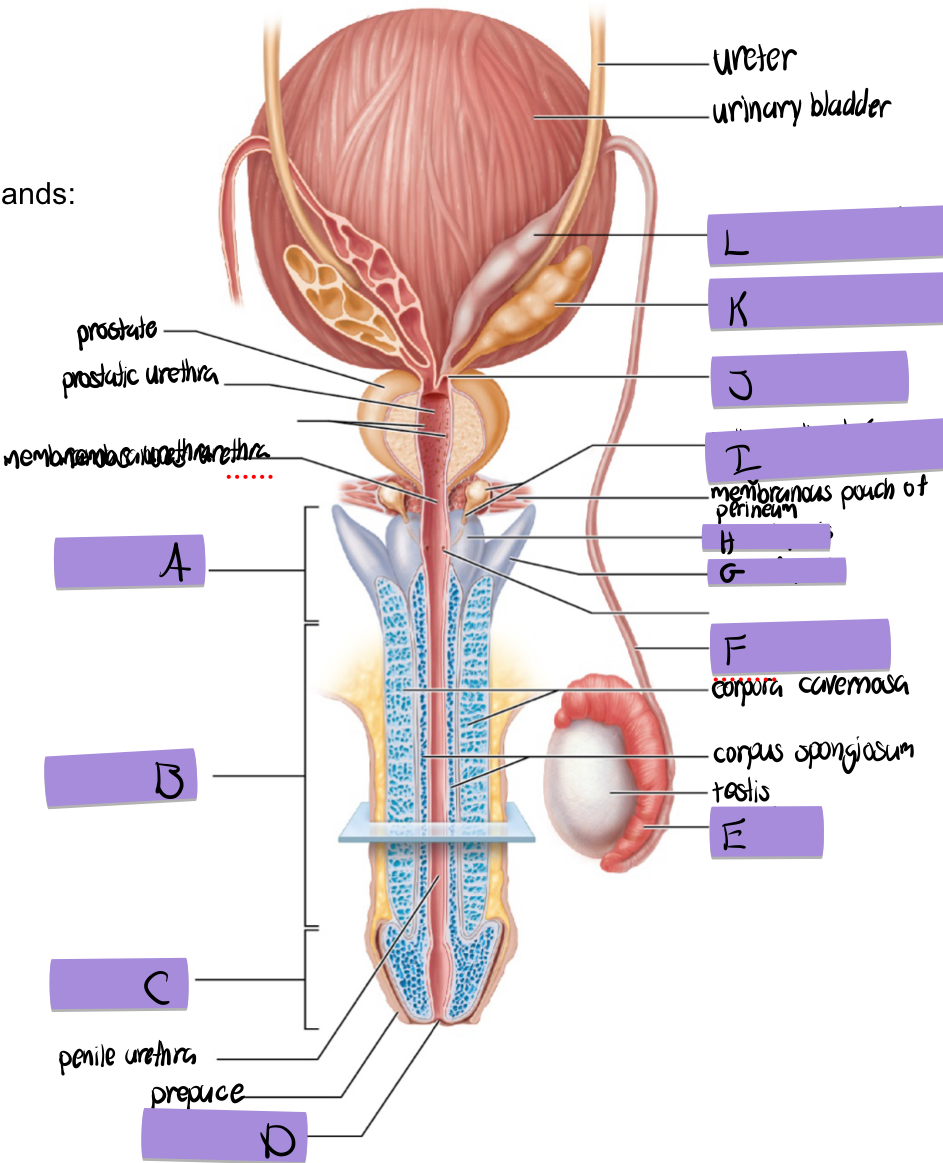
what is E
epididymis
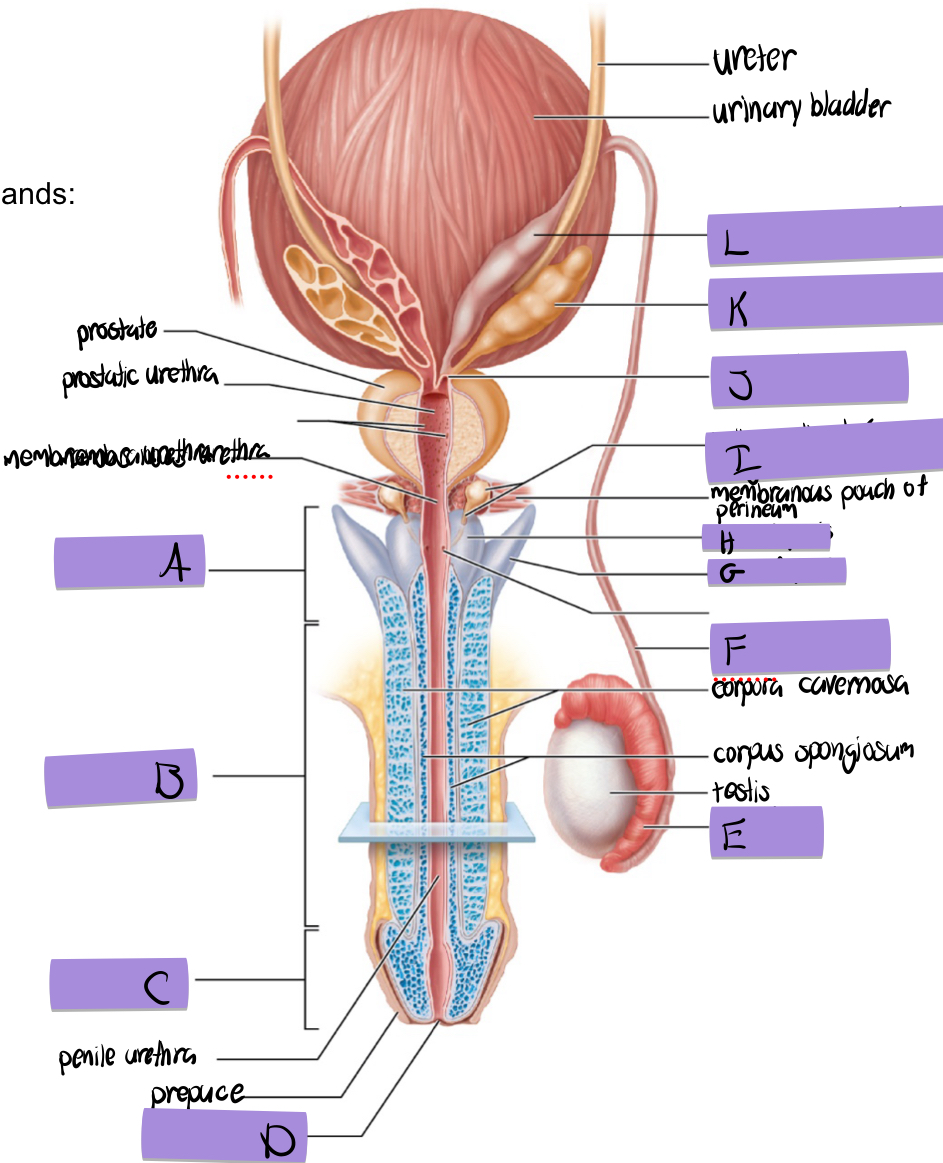
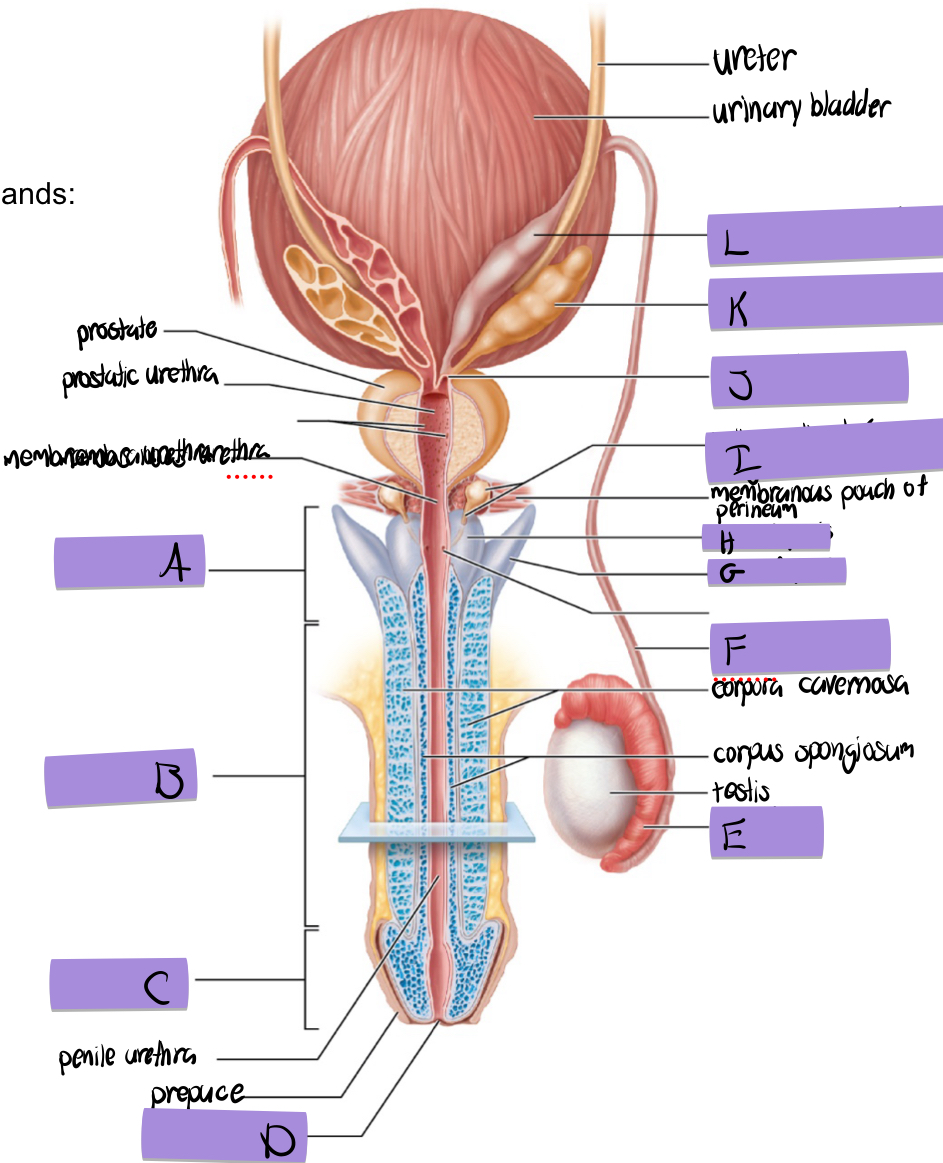
what is F
ductus deferens
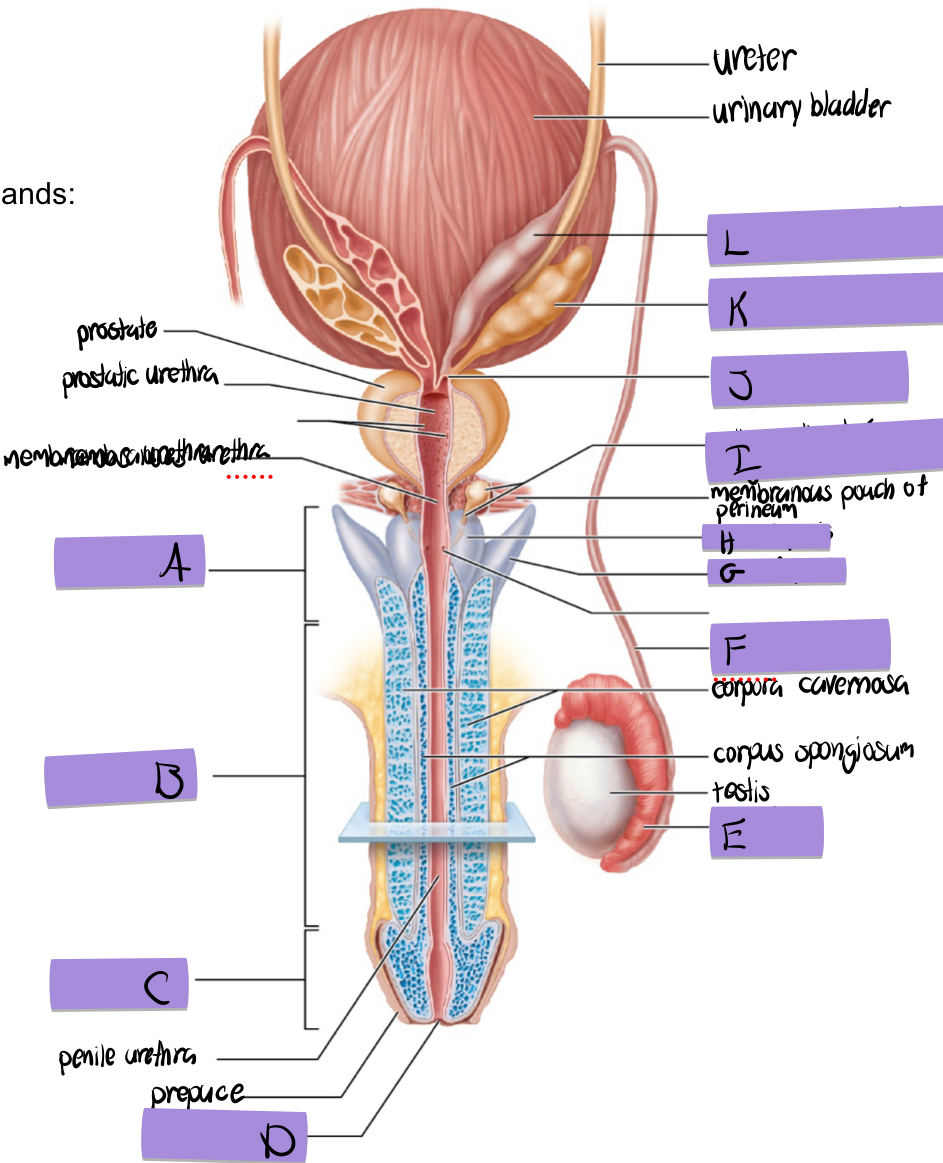
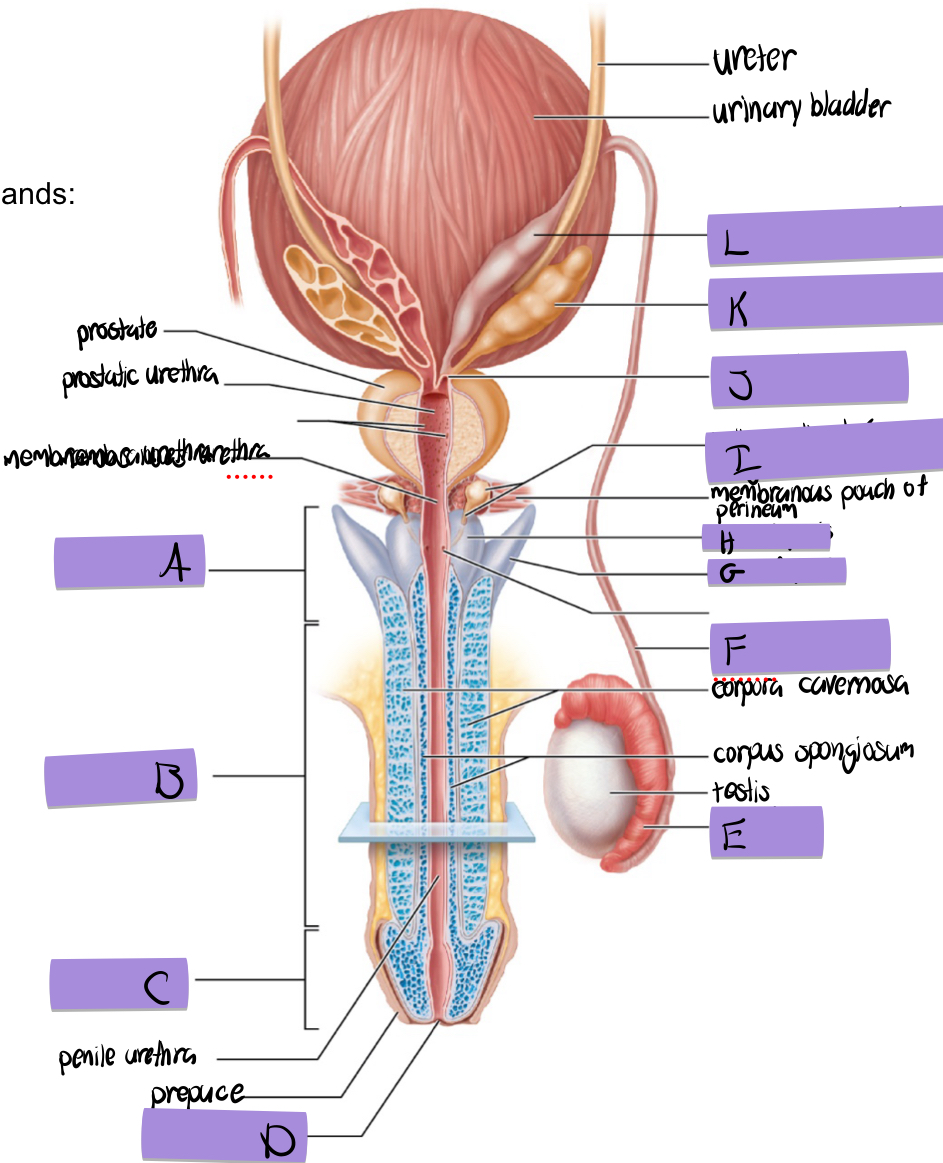
what is G
crus of penis
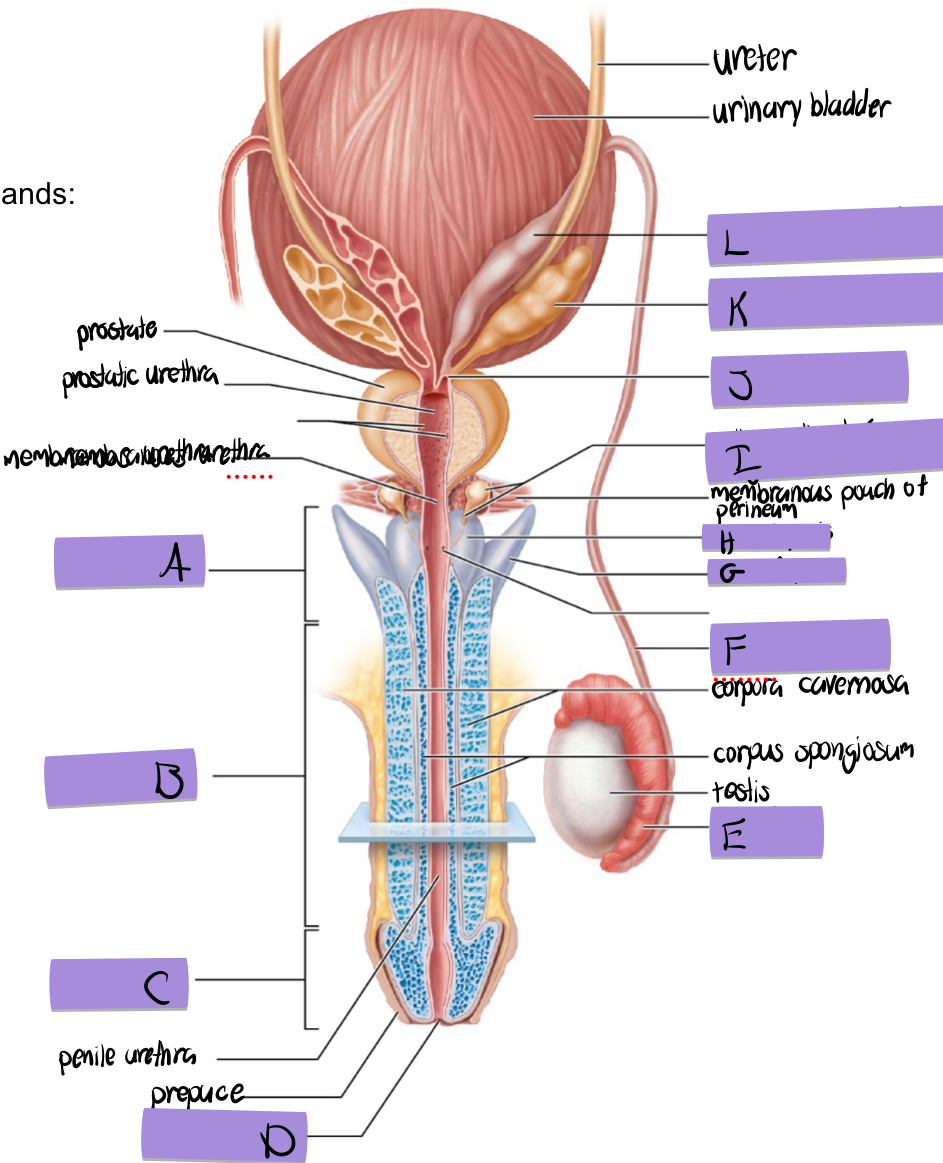
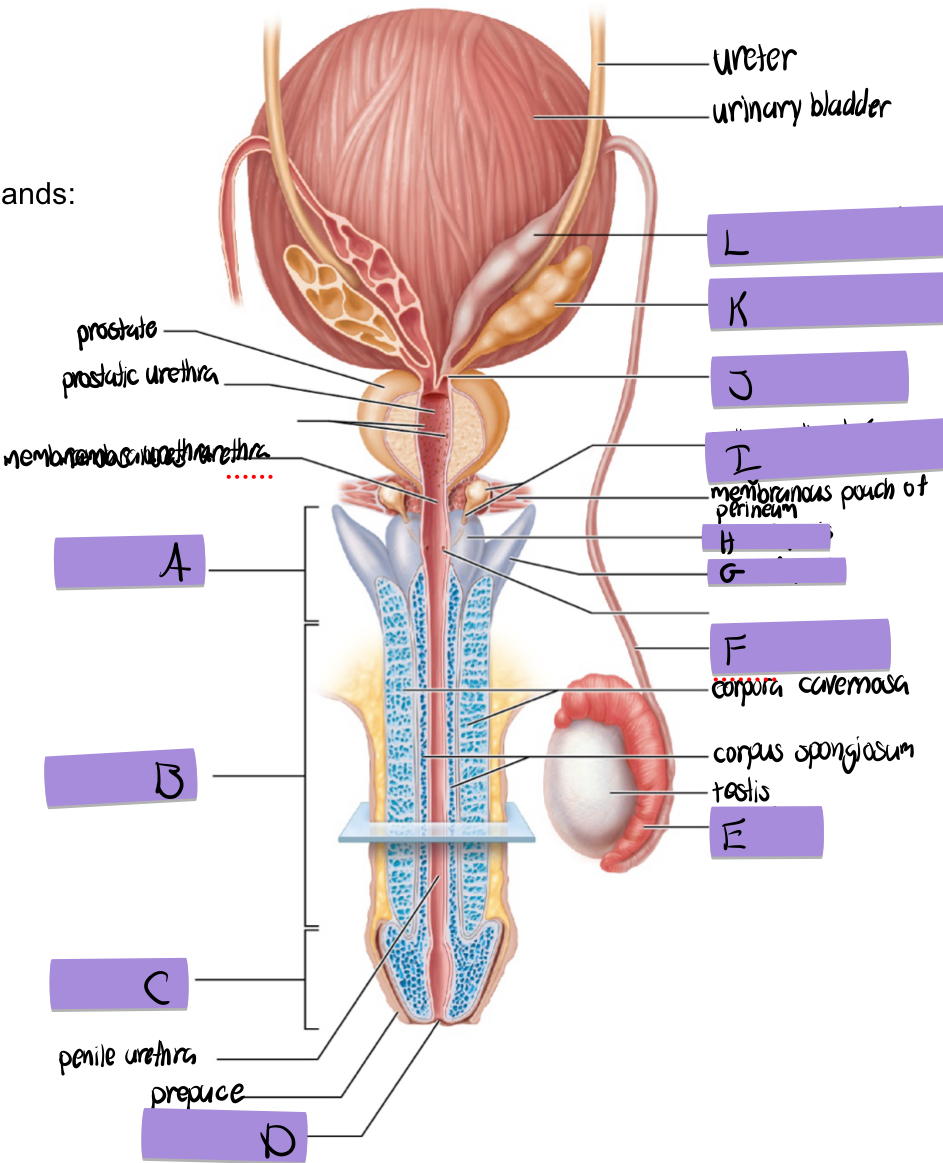
what is H
bulb of penis
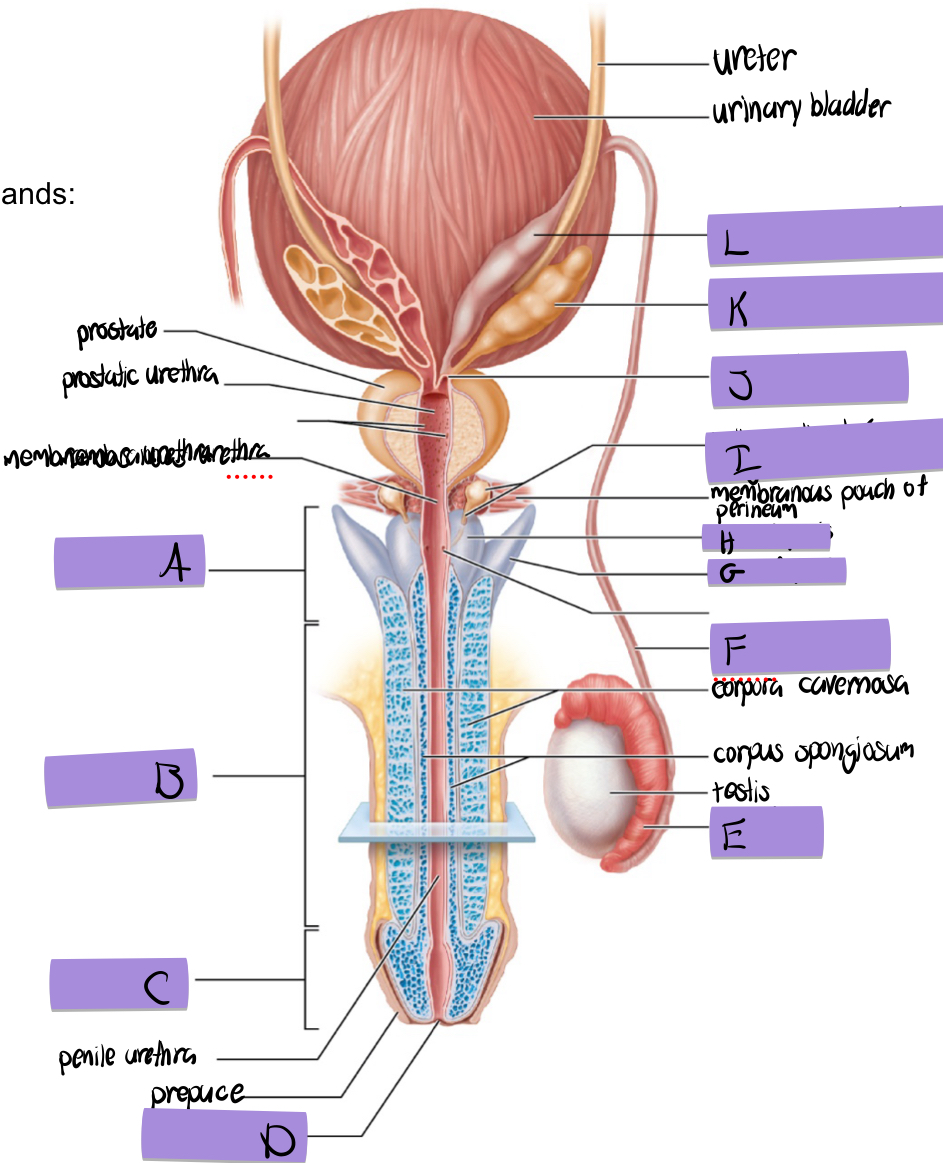
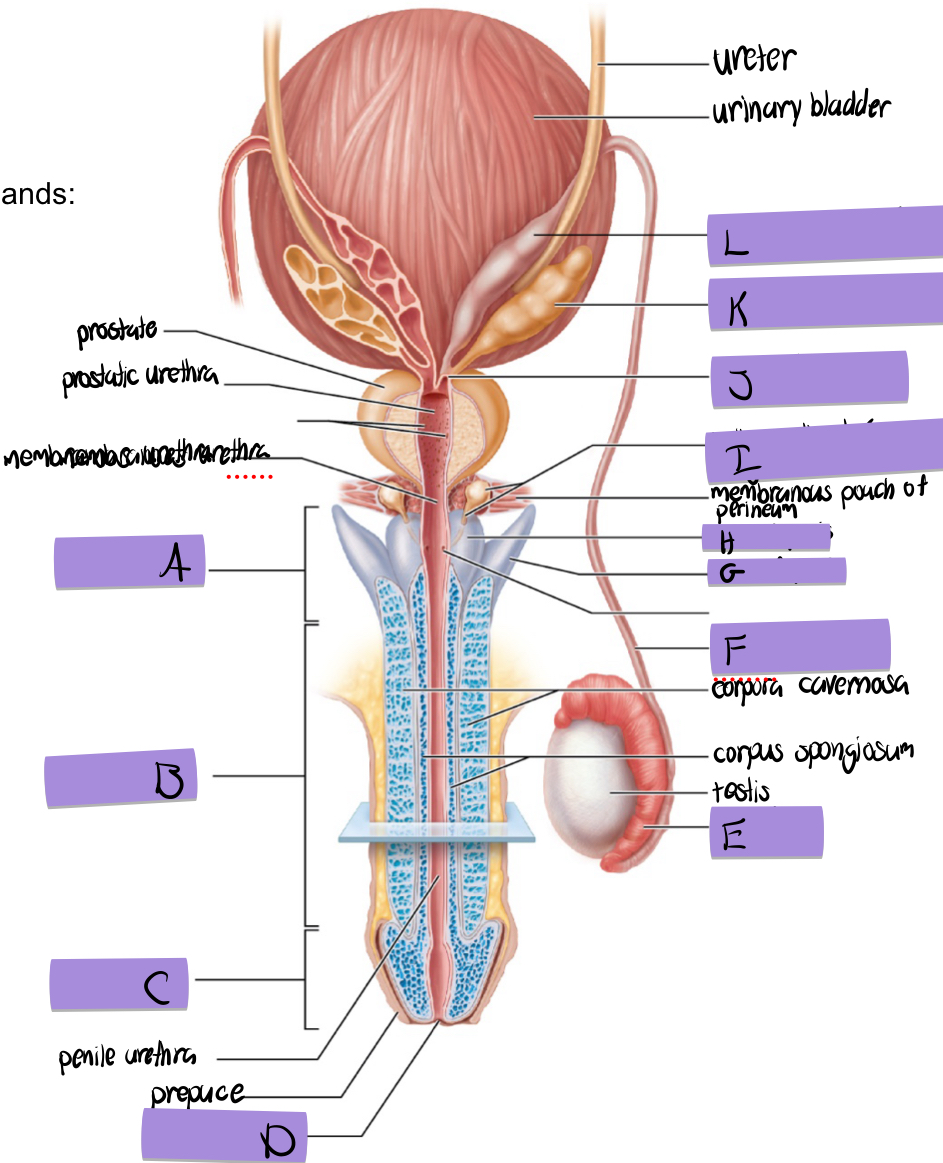
what is I and how does it contribute to semen
bulbourethral (aka cowper’s) gland
lubricates and clears out the urethra prior to ejaculation
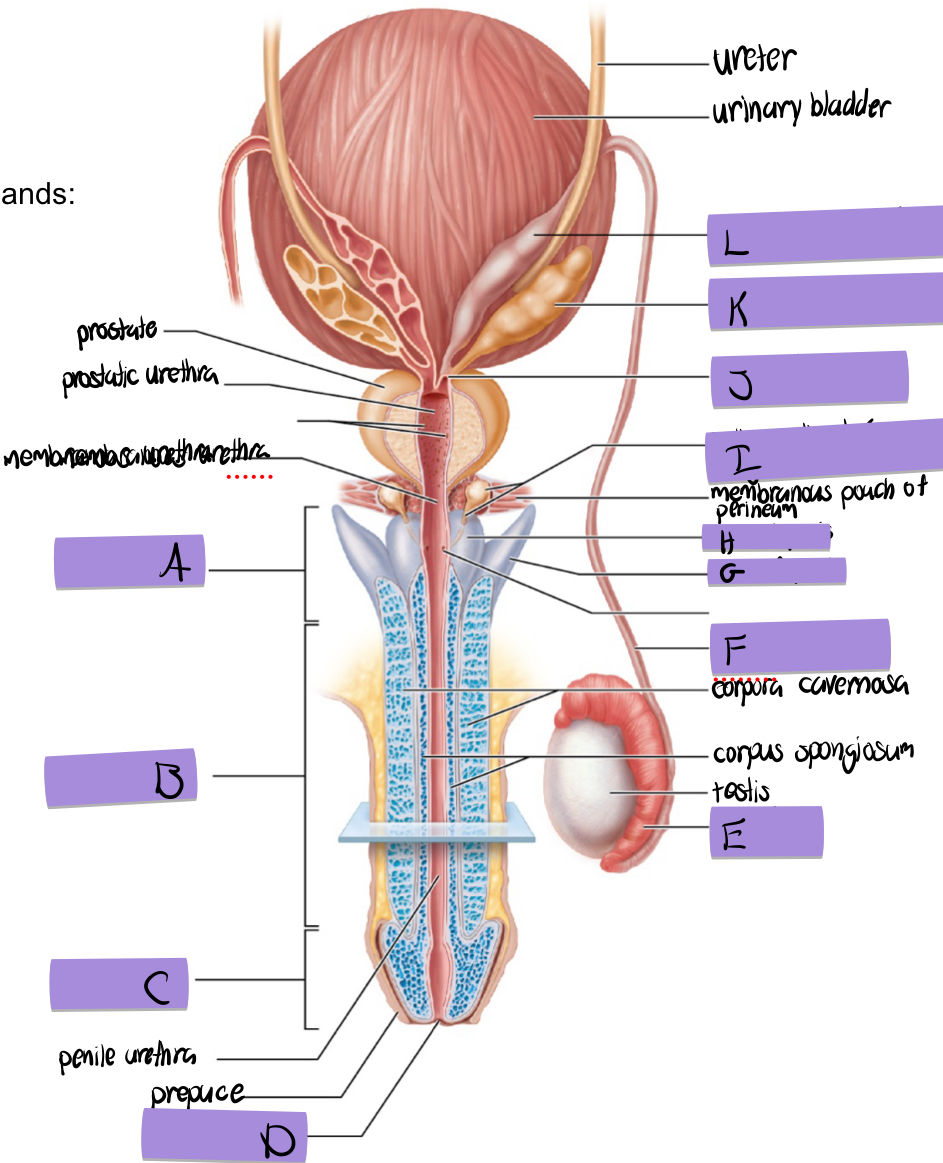
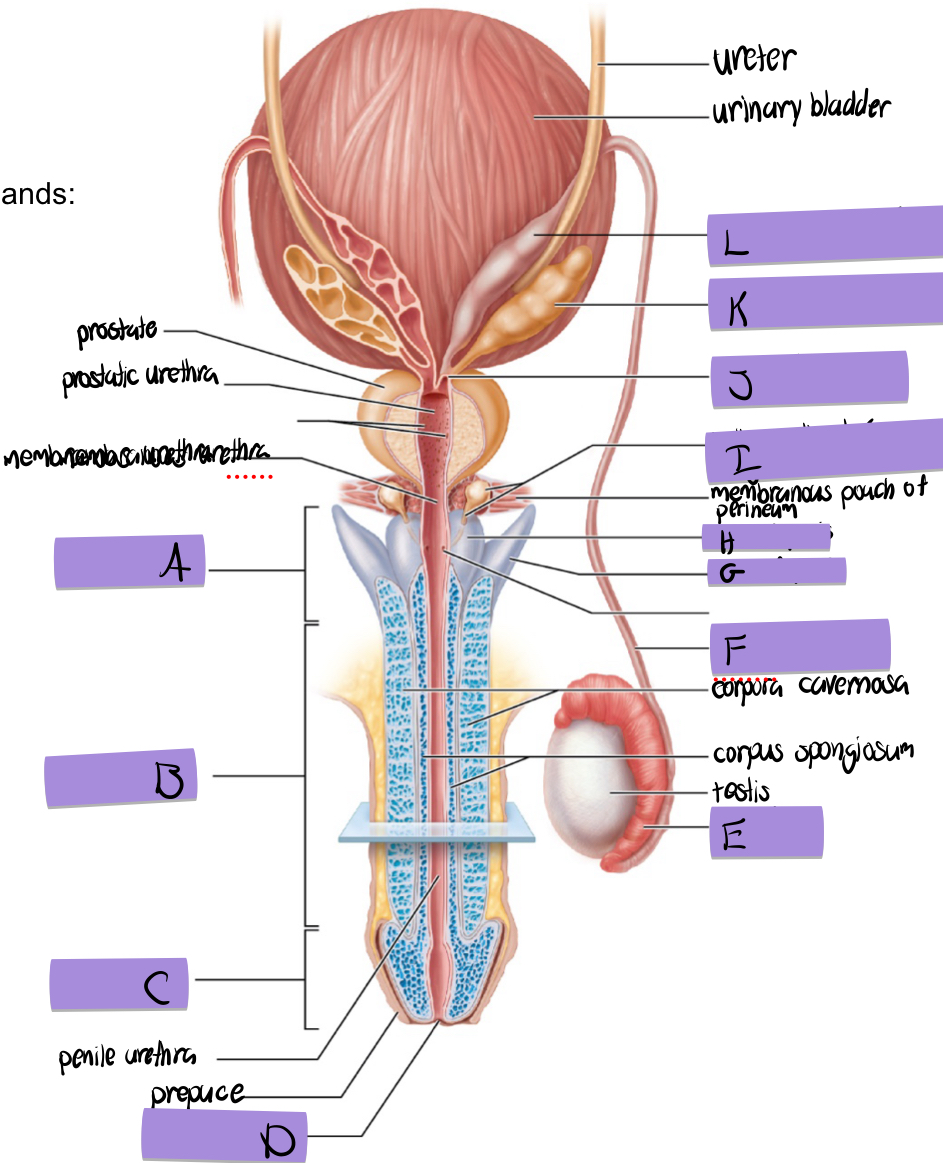
what is J
ejaculatory duct
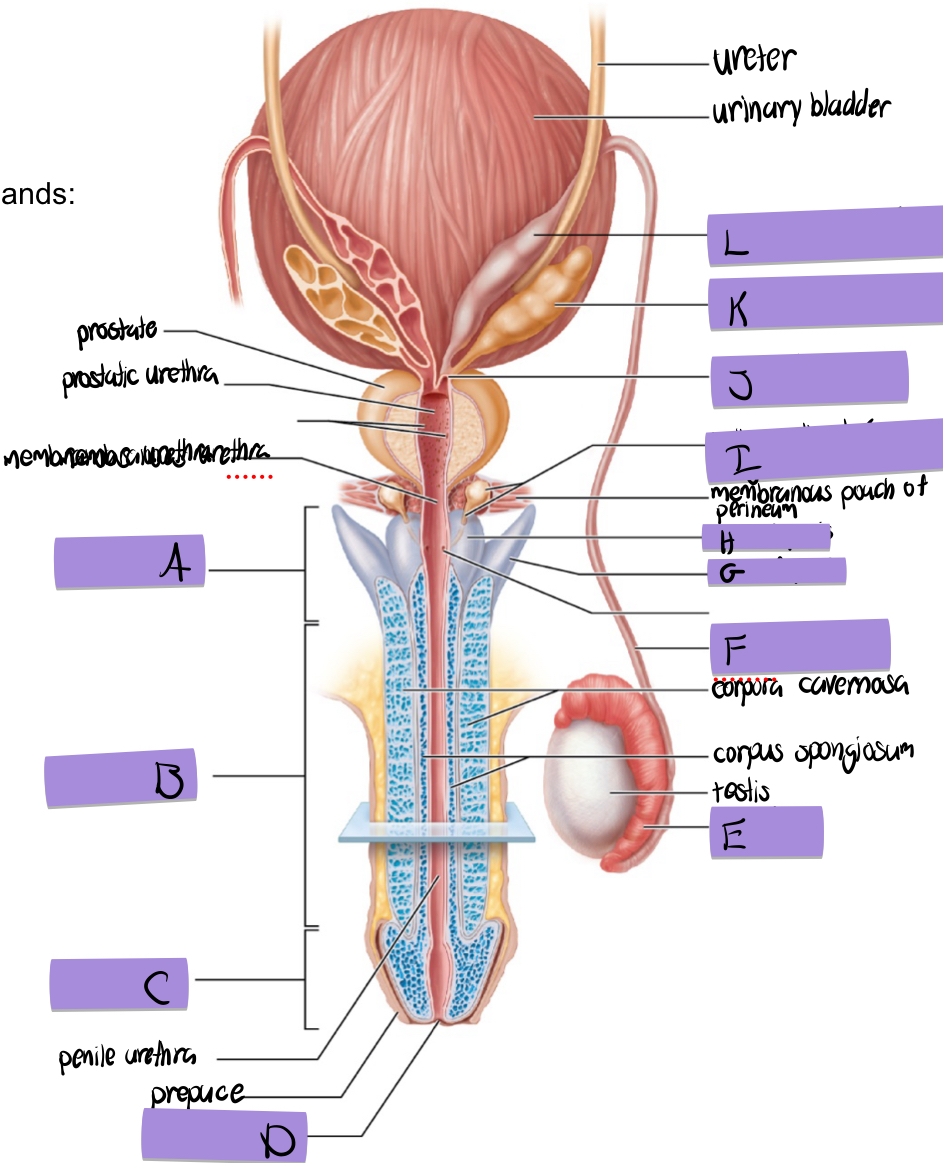
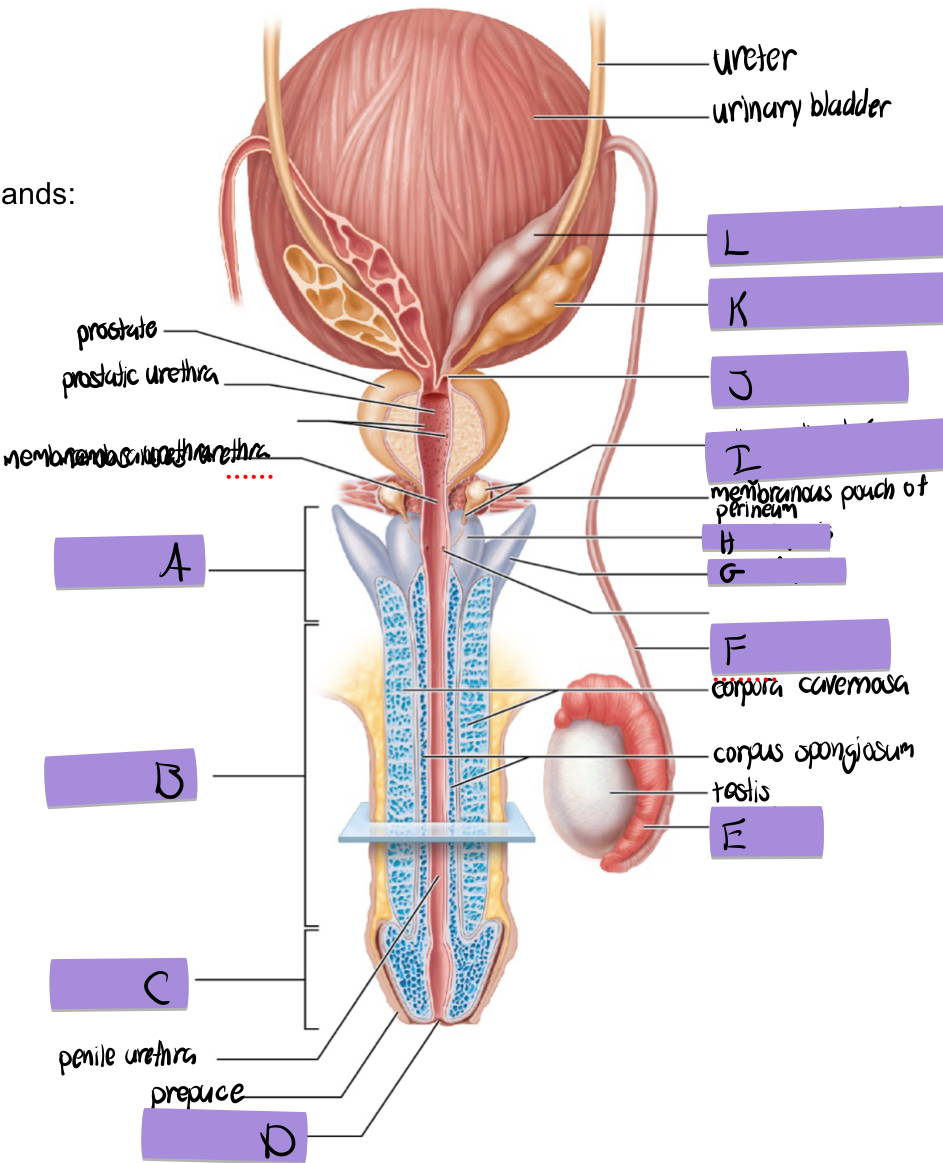
what is K and how does it contribute to semen
seminal vesicles
fructose to sustain ATP production
stimulated smooth muscle contraction to push semen
proteins and enxymes
70% of semen volume
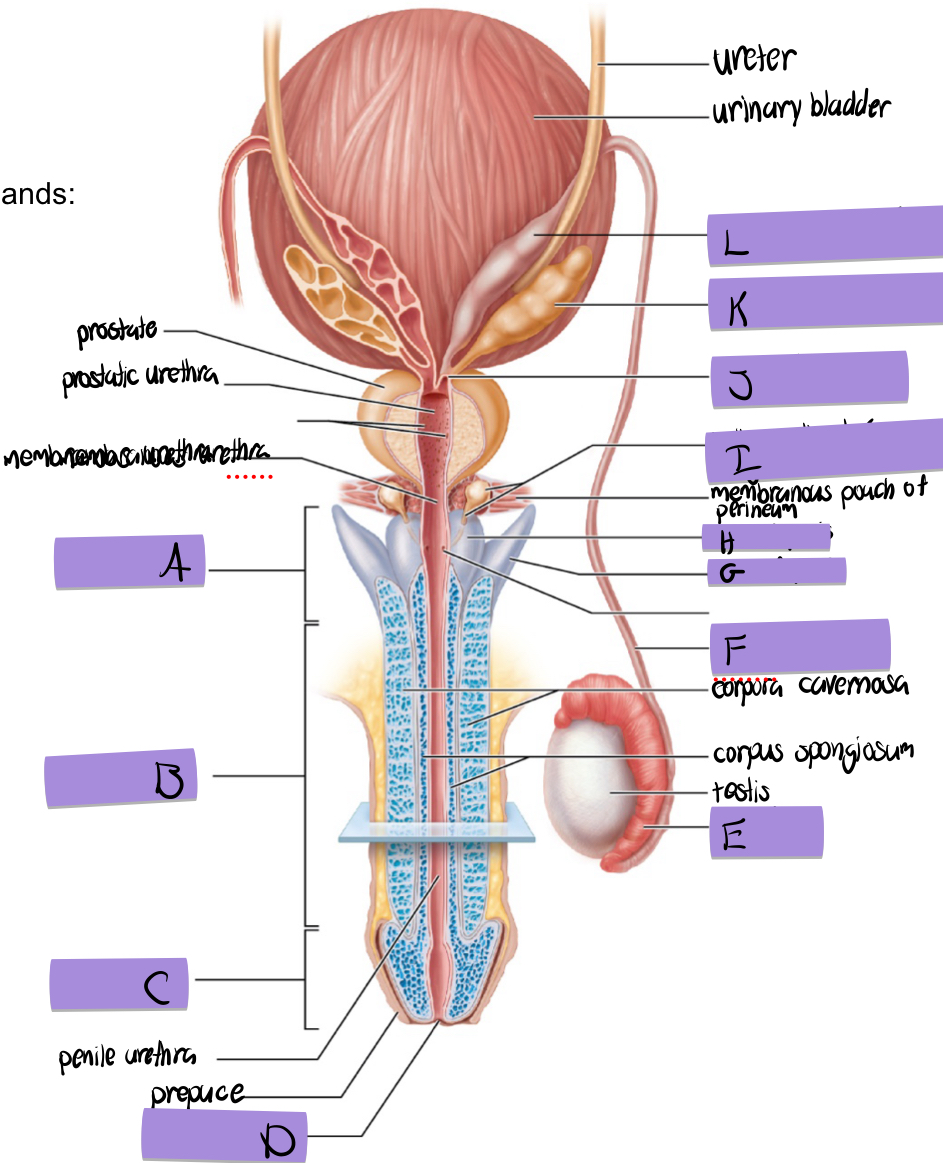
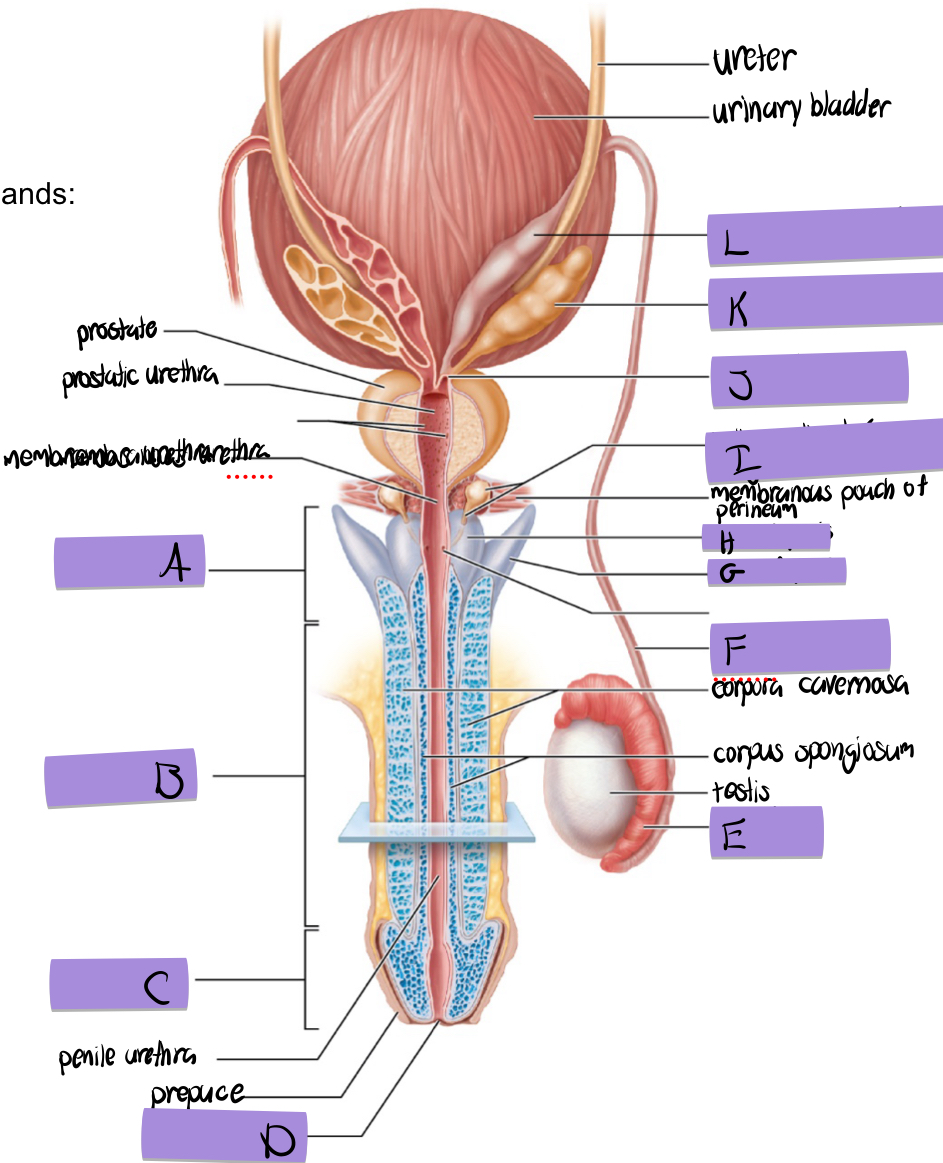
what is L
dilated ampulla of ductus deference
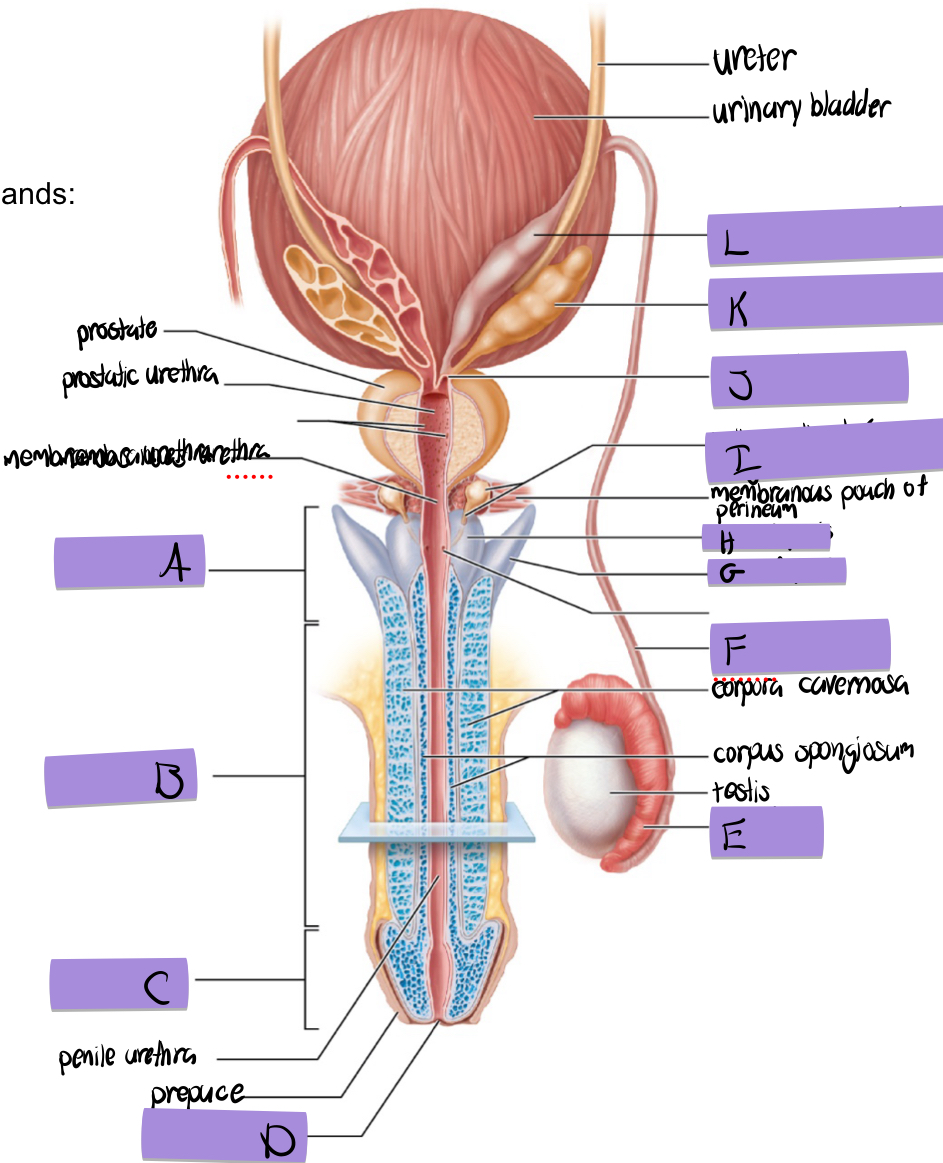
how does the prostate contribute to semen
citrate to sustain ATP production
prostate specific antigen
antimicrobial chemicals