CH 6: Skeletal System - Bones and Bone Tissue
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Functions of Skeletal System (5)
SUPPORT
PROTECTION
MOVEMENT
STORAGE
BLOOD CELL PRODUCTION
Ligament VS Tendons
TENDONS connect MUSCLES TO BONES
LIGAMENTS connect BONES TO BONES
Hematopoiesis
The process where BODY PRODUCES ALL TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS
This involves differentiation of stem cells where it DEVELOPS INTO MATURE BLOOD CELL TYPES
Bone Matrix
BONES ARE COMPOSED OF THIS
Made of 1/3 (35%) ORGANIC MATERIALS
Like… COLLAGEN AND PROTEOGLYCANS
2/3 (65%) INORGANIC MATERIALS
HYDROXYAPATITE
These are the MINERALS of the bone
What happens when minerals (inorganic materials) are removed? If collagen is removed?
If minerals were removed…BONE BECOMES TOO BENDABLE
If collagen were removed…BONES BECOME TOO BRITTLE
Osteocytes
It’s within the lacunae
It ASSIST WITH NUTRITION OF BONE
These are MATURE BONE CELLS
Canaliculi
These are LITTLE CANALS/SMALL PASSAGEWAYS for OSTEOCYTES TO COMMUNICATE WITH EACH OTHER
This is like a hangout road/lounge for other osteocytes to communicate
Lacunae
This is a SMALL, EMPTY SPACE that the osteocytes would LIVE IN
These are those UNFINISHED NEW YORK APARTMENTS that the osteocytes would live in
Osteoblasts
These are CELLS that FORM NEW BONES AND GROW + HEAL EXISTING BONES
The “B” in blasts could mean BUILD
Would FORM NEW BONE TISSUE ON ALREADY FORMED CARTILAGE
Ossification
This is the PROCESS of FORMATION OF BONES via osteoblasts
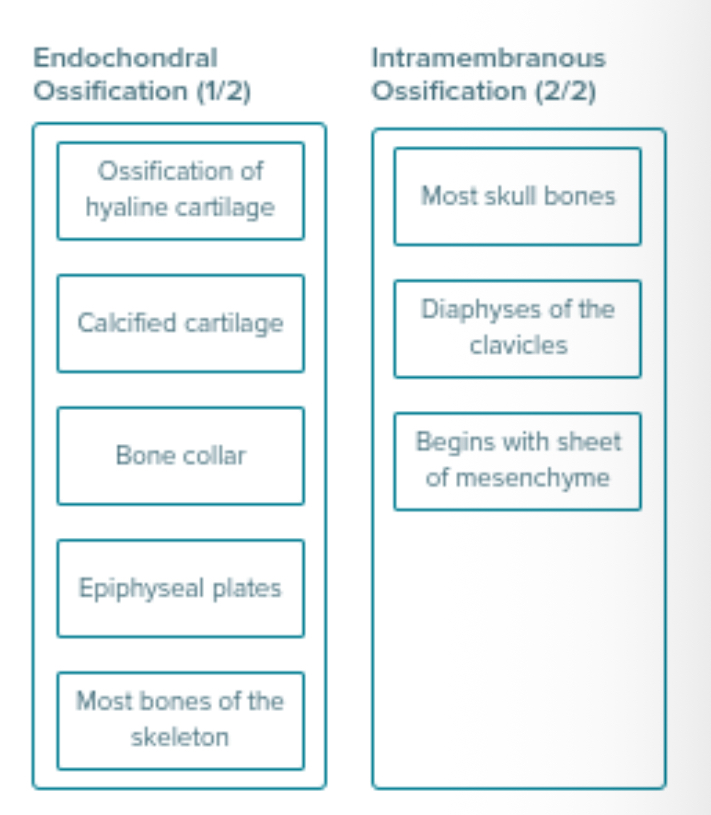
Intramembrane ossification
Forms FLAT BONES (like those in the skull and clavicle)
In the EMBRYONIC CONNECTIVE TISSUE MEMBRANE
STARTS during the 5TH WEEK OF EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT
Endomembrane ossification
Using the CARTILAGE AS A TEMPLATE and is GRADUALLY REPLACED BY BONES
Forms MAJORITY OF SKELETON
This TAKES PLACE IN THE CARTILAGE
Cartilage formation happens at the end of the 4th week of development
Osteoclasts
Cells that BREAK DOWN BONE TISSUE and REABSORB BONES
Think “C” for CHIP AWAY
Plays roles in bone remodeling, calcium homeostasis, and repair of bone injuries
When these BREAK DOWN THE BONES, THEY RELEASE MINERALS WITHIN THE BONES WHICH CAN BE REUSED AGAIN
PRODUCE COLLAGENASES
Collagenases
group of enzymes that break down collagen, a major protein in animal connective tissues
Osteochondral progenitor cells
These are the TYPE OF CELLS THAT CAN DIFFERENTIATE INTO OSTEOBLASTS OR CHONDROBLASTS
Spongy Bones
These are bones INSIDE THE COMPACT BONE that ALLOWS DISTRIBUTION OF ANY STRESS + PRESSURE
NO OSTEON inside
Trabeculae
INTERCONNECTIVE RODS/PLATES OF BONE
Kinda like scaffolding
GIVES STRUCTURAL SUPPORT AND REDUCE WEIGHT
Compact bone
These are HARD, EXTERNAL BONES that surrounds spongy bones
Osteon
FUNCTIONAL UNIT of the compact bone matrix
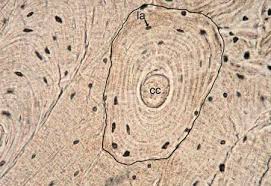
Central canal
Canals in the MIDDLE of osteon that HOUSES NERVES + BLOOD VESSELS and GIVES BONES NUTRIENTS
Lamellae (s. lamella)
The LAYER within a compact bone and THE BUILDING BLOCK OF COMPACT BONE
Canaliculi
These are LITTLE CANALS that CONNECT LACUNAE together for OSTEOCYTES TO COMMUNICATE WITH EACH OTHER
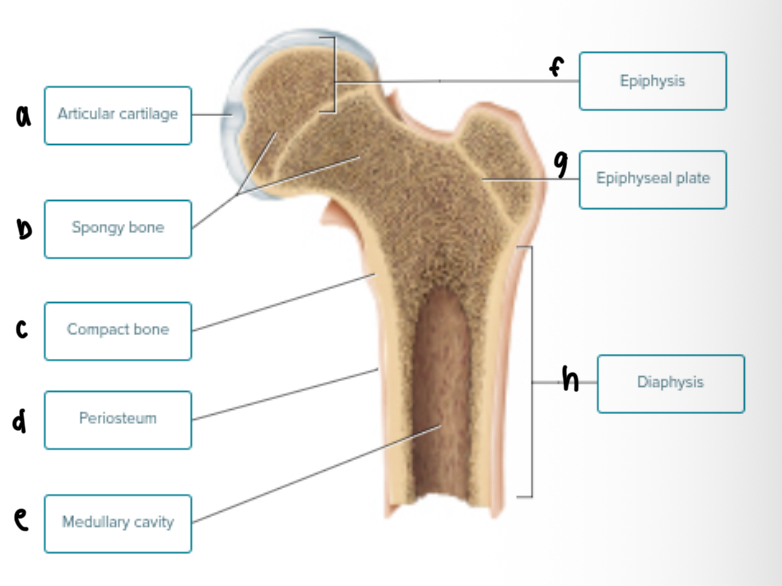
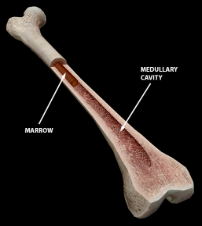
Diaphysis
The SHAFT of a LONG BONE
Medullary Cavity
The CENTRAL, HOLLOW SPACE WITHIN THE DIAPHYSIS
Epiphysis
The ENDS of a LONG BONE
Mostly spongy bone, very little compact bone
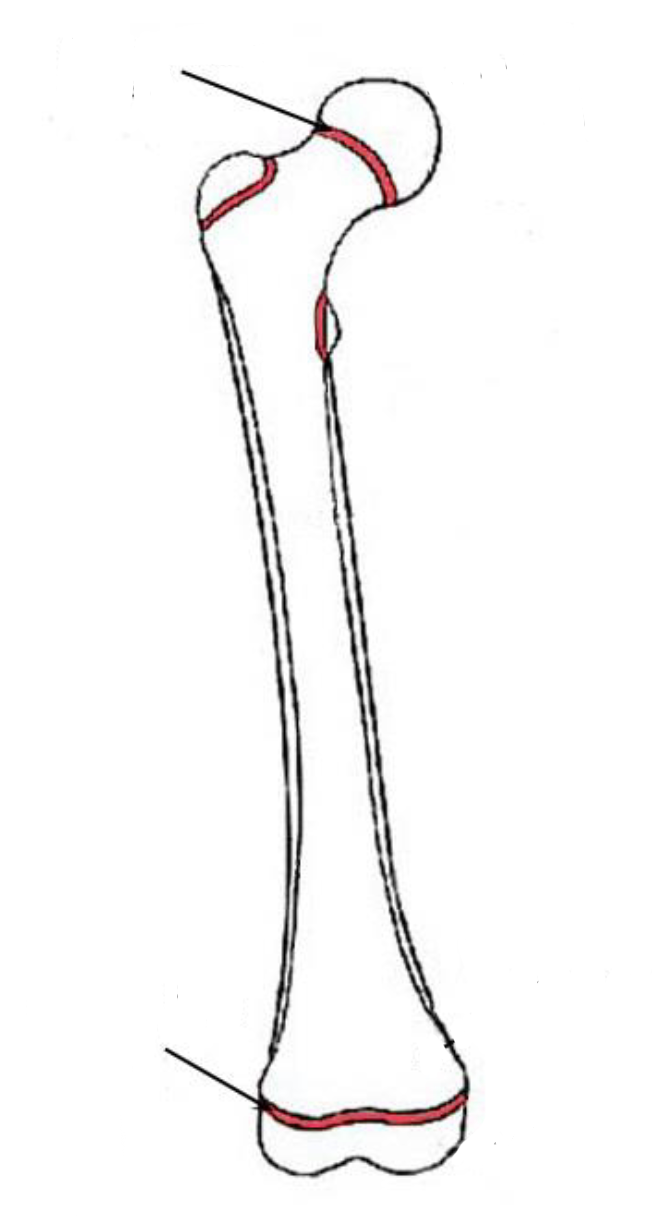
Epiphyseal plate
GROWTH PLATE for new bone growth
This is BETWEEN EPIPHYSIS AND DIAPHYSIS
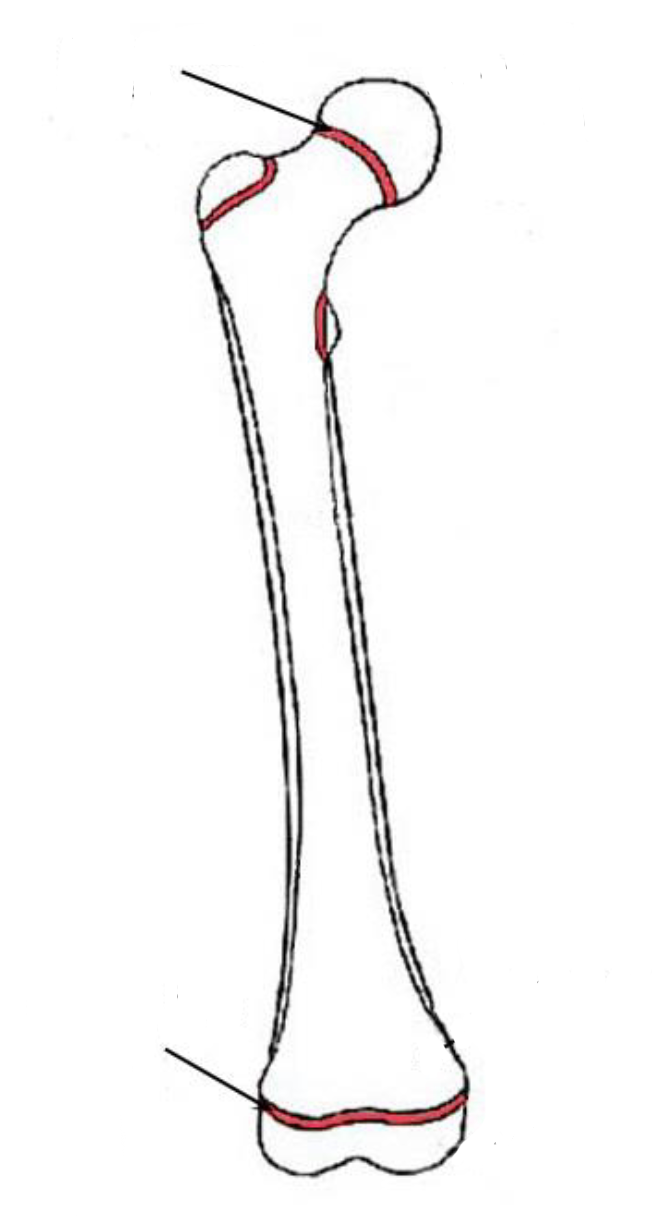
How do osteoblasts form? What happens after the embedding of osteoblasts in the bone matrix?
Some embryonic mesenchymal cells in the connective tissue DIFFERENTIATE INTO OSTEOCHONDRAL PROGENITOR CELLS which THEN FORMS OSTEOBLASTS
After EMBEDDING IN THE BONE MATRIX, OSTEOBLASTS TURN INTO OSTEOCYTES
The embedding happens when they get stuck within the lacunae after building new bone structures
How do spongy bone form?
Osteoblasts form on the surface of trabeculae + produce more bones → the trabeculae grows bigger/longer + remodels (because it’s getting added on) → trabeculae joins together in interconnected networks to form spongy bone
How does compact bones form?
specialized cells within the spongy bone forms red bone marrow while cell surrounding the developing bone becomes the periosteum → osteoblast in the periosteum create the outer compact bone layer
What are the steps to bone repair when someone fractures their bone? (A LOT of steps)
Hematoma Formation (Inflammatory Stage)
This MAKES BLOOD CLOT which HELPS STOP BLEEDING and give foundation for healing
Hematoma = Blood Clot
INFLAMMATION OCCURS
This happens because the hematoma attracted cells relating to inflammation to help repair the bone
Callus Formation occurs with fibro/chondroblasts (Soft Callus Formation)
This is after inflammation where MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS DIFFERENTIATE INTO CHONDRO AND FIBROBLASTS
Creates SOFT CALLUS which HELPS TEMP. STABILIZE FRACTURED BONE and GIVE FRAMEWORK for hard callus
Callus Ossification (Hard Callus Formation)
OSTEOBLASTS invade soft callus and DEPOSIT MINERALS (hydroxyapatite) which HARDENS SOFT CALLUS AND INCREASE STABILITY
Bone Remodelling occurs with osteoclasts (Bone remodelling)
The HARD CALLUS IS RESHAPED
OsteoCLASTS REMOVE EXCESS BONE TISSUE
OsteoBLAST BUILD NEW BONES
What are the roles of calcium for the bone? (3)
STIMULATE MUSCLE CONTRACTION
STIMULATE + REGULATION OF CARDIAC MUSCLE
EXOCYTOSIS FOR NEURAL SIGNALING
How does the body go back into homeostasis when there’s LOW BLOOD CALCIUM LEVELS?
Parathyroid hormones are going to secrete which MAKES MORE OSTEOCLASTS
The osteoclasts are going to BREAK DOWN/CHIP AWAY FROM REGULAR BONES TO RECEIVE MORE CALCIUM
Since there’s more calcium, homeostasis is restore
Having LOW BLOOD CA LVLS are bad because if parathyroid hormones keep making osteoclasts which break down the bones, the BONES BECOME REALLY BRITTLE
How does the body go back into homeostasis when there’s HIGH BLOOD CALCIUM LEVELS?
CALCITONIN hormones are RELEASED from thyroid to DECREASE ACTIVITY OF OSTEOCLASTS
REDUCE PTH (parathyroid hormones) which are responsible for making osteoclasts
This helps with lowering blood calcium because osteoclasts can’t break down bone for calcium
OSTEOBLASTS are STIMULATED to USE EXCESS CALCIUM TO MAKE NEW BONE TISSUE
Osteoporosis
It’s a condition with A LOSS OF BONE MATRIX and DECREASED BONE MASS/DENSITY
Makes bones fragile
Could occur because of decreased blood calcium
WHY? This is because the parathyroid stimulates creation of osteoclasts which chips away the bones for calcium, making the bones more fragile and delicate
The primary function of osteoblasts is to…
A. stimulate bone growth.
B. Inhibit the growth of bone.
C. Resorb bone along the epiphyseal plate
D. Prevent osteocytes from forming.
E. Lay down bone matrix.
E. Lay down bone matrix
Explain:
A (stimulate bone growth) would NOT be the correct answer because, although that is the job of osteoblasts, it’s a very BORAD DESCRIPTION of their job whenever there are other answers that are more specific (e.g, lay down the bone matrix)
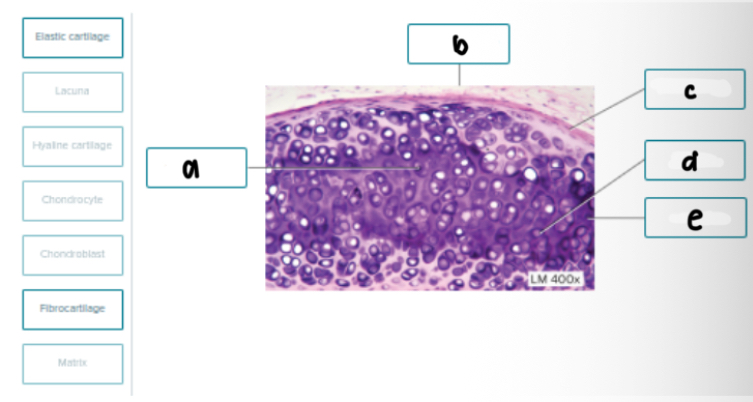
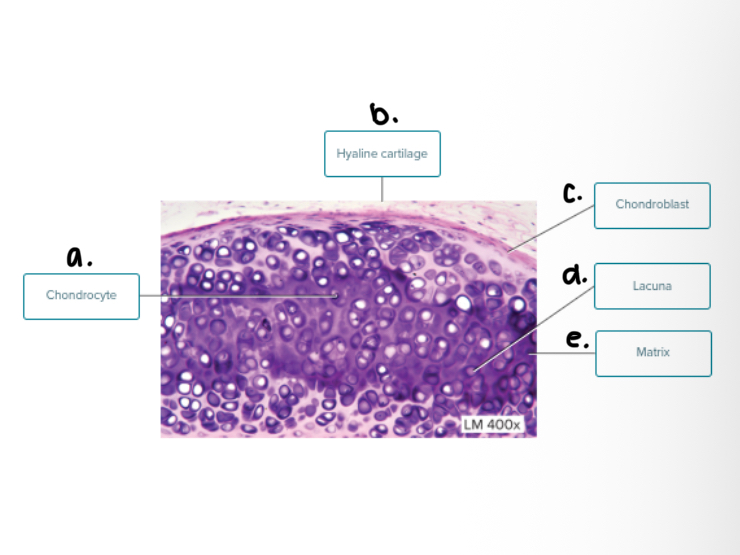
Match the following
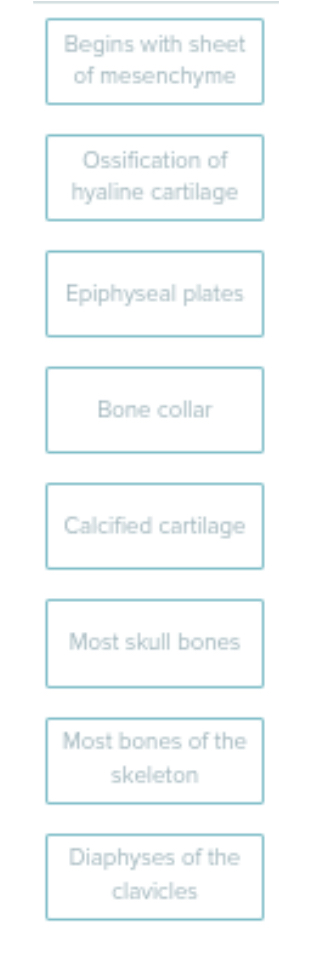
Sort the Following into Endochondral and Intramembranous Ossification
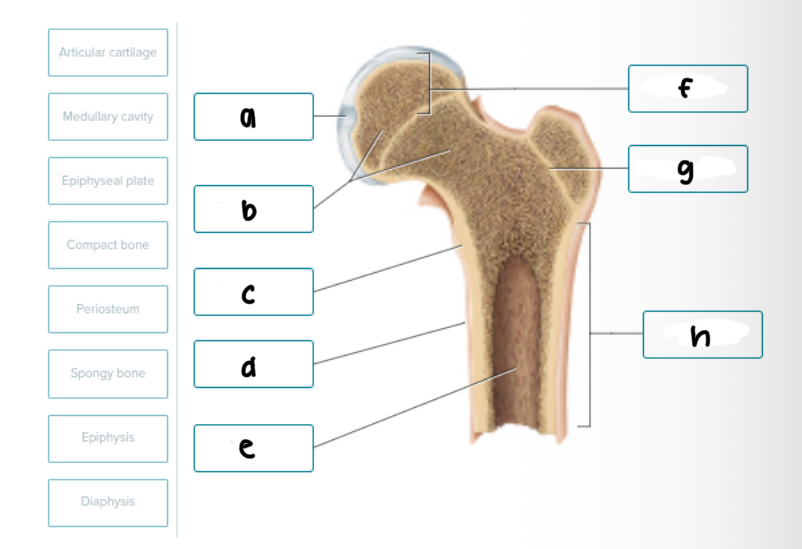
Label the Bone Structure