MICR 270 Module 2: Branches of the Immune System
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MICR 270 Module 2 Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Innate Immune System
The first line of defense. Non-specific and relies on pattern recognition. Responds to all pathogens the same way. Comprised of immune barriers, pattern recognition, inflammation, and phagocytosis.
Physical Barriers
Skin: Largest organ.
Mucous Membrane: cilia and mucous covers body cavities to trap and sweep away pathogens.
Chemical Barriers: Tears and saliva contain antimicrobial substances like lysozyme. Gastric acid in the digestive tract.
Cellular Barriers
Neutrophils
Macrophages
Dendritic Cells
NK cells
Components of the Soluble Barrier
The Complement System
Cytokines
The Complement System
>30 soluble proteins that complements the efficiency of other systems. (Inflammation, Phagocytosis, MAC)
Complement system activation.
Three pathways: Classical, Lectin, Alternative. Activated through signaling cascades and forms the membrane attack complex (MAC).
Inflammation and the Complement System
Complement proteins bind complement receptors on immune cells signaling the release of chemotactic factors. Chemotactic molecules attract immune cells to the site of infection.
Phagocytosis and the Complement System
C3b proteins mark pathogens to be phagocytosed (opsonization).
The Membrane Attack Complex
Destroys extracellular invaders and creates holes in pathogens leading to cell lysis and death. A deficiency in the complement system would lead to longer periods of infection.
Cytokines
Proteins that are secreted by immune cells that have affinity for cytokine receptors. They act through autocrine and paracrine signaling and by binding to receptors, they induce changes in gene expression. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and anti-inflammatory cytokines maintain equilibrium in the body.
Signs of the Inflammatory Response
Pain, Redness, Swelling, Heat, Loss of Function.
Steps of the Inflammatory Response
Breech
Vasodilation
Permeabilization
Extravasation
Phagocytosis
Breech (1)
Pathogen crosses physical barriers and enters the body (injury)
Vasodilation (2)
Vessels increase in diameter and permeability through vasoactive and chemotactic molecules. responsible for redness and heat.
Permeabilization (3)
Capillary permeability increases followed by vasoconstriction of the surrounding area. Exudate (filled with complement proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines) builds up forming an edema. The accumulation of fluid causes swelling.
Extravasation (4)
Immune cells are recruited by chemotaxis. Neutrophils attach to epithelial cell walls (margination) then migrate into the tissue at the site of infection (diapedesis)
Phagocytosis (5)
Phagocytes engulf pathogens. If the infection persists, the adaptive immune system is engaged.
Pattern Recognition Receptors
Recognize repeated patterns in pathogens to initiate the innate immune response. Many families exist.
PAMPs
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns. Are expressed on the cell surface or the surface or interior. The patterns are specific to each pathogen and different molecules are indicative of different groups.
DAMPs
Danger/Damage Associated Molecular Patterns. Are released by cells undergoing necrosis. Indicate damage to the host cell. Can include molecules in places they are not supposed to be (DNA outside the cell).
TLRs
Toll-like receptors. A class of PRR that is expressed on the plasma membrane of the endosomal/lysosomal membrane. They induce the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and costimulatory molecules when activated. They increase phagocytic ability.
TLR activation process
DAMP/PAMP mediated activation
Antigen presented via MHC
Costimulatory molecules enhance and stabilize the antigen presentation
Naive T-cells bind MHC via TCRs
Phagocytosis Steps (5)
Attachment
Pathogen attaches to pseudopodia
Ingestion
pathogen is ingested, a vacuole is formed
Fusion
Vacuole fuses with a lysosome and macromolecule + bacteria are degraded
Digestion
Pathogen is digested by lysosomal enzymes
Release
The digested products are released via exocytosis
Adaptive Immunity
The second line of defense. Includes specific and diverse responses.
Cells of Adaptive Immunity
B cells
humoral immunity
T cells
Cell mediated immunity
Antigen Presenting Cells
APCs present antigens to TH causing them to differentiate into TH1 or TH2 . TH1 is cell mediated and activates CTLs that will eliminate cells displaying the antigen in their MHC class I. TH2 activates B cells triggering their differentiation into plasmacytes.
Antibodies
“Immunoglobulins”. Are “Y” shaped proteins that are specific to a singular epitope. They are responsible for:
Neutralization
Opsonization
Complement Activation
Effector Cell Activation
Surface antibodies vs. soluble antibodies
Surface antibodies are membrane bound to B cells. Soluble antibodies circulate in the blood and are secreted by plasmacytes.
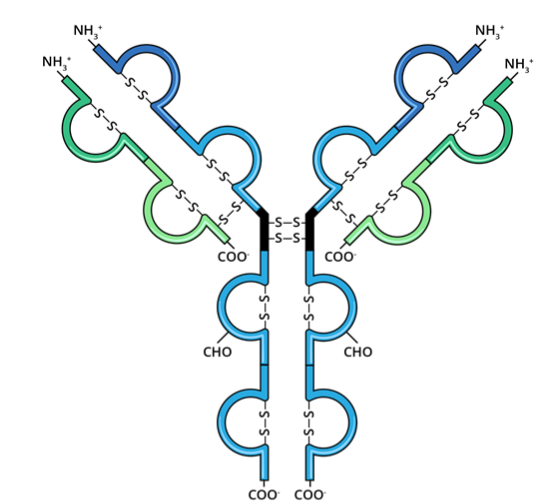
Antibody structure
Light Chain
Heavy Chain
Antigen Binding Region (variable)
Fc Region (constant, binds to Fc receptors)
Antibody Classes (5)
IgM
IgA
IgG
IgE
IgD
IgM
Pentamer, activates the complement, the first antibody formed.
IgA
Dimer, found in mucosal membranes, the first line of defense.
IgG
Monomer, opsonization by coating pathogens, can cross the placental barrier.
IgE
Monomer, involved in allergic reaction and parasite immunity.
IgD
Monomer, found on the surface of B cells in large quantities, not really sure what it does…