X-Sectional Midterm (2)
1/376
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
377 Terms
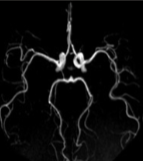
What type of view are we observing the COW at?
axial
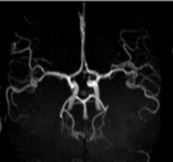
What type of view are we observing the COW at?
coronal
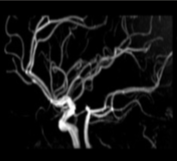
What type of view are we observing the COW at?
sagittal
Where is the abdominal cavity located?
between diaphragm and sacral promontory
What is the abdomen and pelvic cavities divided into?
4 quadrants, 9 regions
What thin membrane lines the abdominal cavity?
peritoneum
What is the outermost layer of the peritoneum called?
parietal
What is the innermost layer of the peritoneum called?
visceral
What does the peritoneum enclose?
liver, gallbladder, spleen, stomach, ovaries, majority of intestines
What does the female peritoneal cavity connect to?
exterior of reproductive system (uterine tubes, uterus, vagina)
Is the male peritoneum open or closed?
closed
What muscle of the abdominal wall flexes the trunk, flexes the L-spine and supports the abdomen?
rectus abdominis
What two muscles of the abdominal wall compresses abdominal tissue and flexes/rotates the spine?
external and internal oblique
What band of fibers serves as the central anterior attachment for the internal and external oblique muscles?
linea alba
What muscle of the abdominal wall compresses abdominal tissue?
transverse abdominis
What muscle of the abdominal wall is involved with the lateral flexion of the trunk and flexion of the hip/thigh?
psoas major
What muscle of the abdominal wall is involved with the lateral flexion of the spine?
quadratus lumborum
What 4 lobes is the liver divided into?
L, R, caudate, quadrate
What organ is divided into 4 lobes?
liver
What defines the entry/exit point in the liver for vessels?
porta hepatis
Where is the porta hepatis located?
inferomedial border of liver
What divides the left lobe of the liver into medial and lateral segments?
fissure for round ligament
What divides the caudate and left lobe of the liver?
fissure for ligamentum venosum
What holds the horizontal portions of the R and L portal veins within the liver?
transverse fissure
What is another name for the transverse fissure?
portal fissure
What serves as an imaginary line dividing the R and L lobes of the liver?
interlobar fissure
What is another name for the interlobar fissure?
main lobar fissure
What divides the liver into R and L lobes?
falciform ligament
What does the liver produce and excrete?
bile
What is the function of bile?
break down fatty acids
Besides bile, what other substances does the liver excrete?
bilirubin, cholesterol, hormones, drugs
What does the liver metabolize?
fats, proteins, carbohydrates
What does the liver convert excess glucose into?
glycogen (chains of glucose)
What does the liver store?
vitamin B12, ion/copper, other vitamins
What type of proteins does the liver produce?
meant for blood plasma (albumin; clotting)
What term defines the cleaning of blood from drugs and poisonous substances?
detoxification
Can the liver regenerate itself?
yes
What does the common hepatic artery branch into?
R + proper/left hepatic duct
In what segments of the liver is the R hepatic vein located?
5, 6, 7
In what segments of the liver is the middle hepatic vein located?
4, 5, 8
In what segments of the liver is the L hepatic vein located?
2, 3
In what segments of the liver is the IVC located?
1
What does the stomach produce?
intrinsic factor
What is the intrinsic factor required for?
absorption of vitamin B12
Where does the stomach get blood from?
splenic + gastroduodenal arteries
How many liters of gastric juices can the average adult produce daily?
2-3
How many liters of food and digestive juices can the average stomach hold?
3
What are the digestive juices of the stomach known as?
chyme
In what position is the 1st section of the duodenum?
superior
What is the 1st section of the duodenum known for?
peptic ulcer formation
In what position is the 2nd section of the duodenum?
descending
In what position is the 3rd section of the duodenum?
horizontal
In what position is the 4th section of the duodenum?
ascending
What is the 2nd section of the duodenum known for?
pancreatic and biliary drainage
What is the 4th section of the duodenum connected to?
jejunum with duodenojejunal flexure
What portion of the small bowel takes the bulk of chemical digestion and nutrient absorption?
jejunum
What is the ileum connected to?
cecum
How is the ileum connected to the cecum?
iliocecal valve
What is the longest portion of the small bowel?
ileum
What is the small bowel divided into?
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
What is the large bowel divided into?
cecum and colon
What section of the colon begins at the cecum juncture, raising along the R lateral abdominal wall to the level of the liver?
ascending
What section of the colon begins at the hepatic flexure and moves across the abdomen, ending at the spleen?
transverse
The transverse section of the colon is known to be what?
most mobile
What section of the colon begins at the splenic flexure, moving down along the L lateral abdominal wall and ending at the iliac fossa?
descending
What section of the colon connects to the rectum (in pelvic area)?
sigmoid
What are the major functions of the large bowel?
reabsorption of water, storage and elimination of poop
What does the endocrine function of the pancreas entail?
production of insulin and glucagon
What does the exocrine function of the pancreas entail?
production of digestive enzymes
For the production line of digestive enzymes in the pancreas, what would the first stop be?
main pancreatic duct
For the production line of digestive enzymes in the pancreas, what would the second stop be?
ampulla of Vater
For the production line of digestive enzymes in the pancreas, what would the third stop be?
Sphincter of Oddi
What is the main pancreatic duct also known as?
duct of Wirsung
For the production line of digestive enzymes in the pancreas, what would the last stop be?
duodenum
What portion of the pancreas is superior to its head?
tail
What leads to the Sphincter of Oddi?
common bile duct
What part of the adrenal glands produces cortisol and other hormones?
cortex
What does the cortex of the adrenal glands help control?
body’s use of fats and carbohydrates, influencing the immune system
What part of the adrenal glands produces epinephrine?
medulla
What does epinephrine do?
increase heart rate, facilitate blood flow to muscles and brain
What arteries does the medulla of the adrenal glands receive blood from?
superior, middle and inferior suprarenal arteries
Where does the suprarenal vein drain into?
IVC
What do the kidneys produce and release?
erythropoietin
What does erythropoietin do?
stimulate bones to make RBC and vitamin D, maintaining calcium absorption
What anatomical objects are found in the renal cortex?
nephrons with glomerulus, convoluted tubules
What is the function of the renal cortex?
filtration of urine
What anatomical objects are found in the renal medulla
renal pyramids with loops of Henle, collecting tubules
How many minor calyces does each kidney have?
7-14
How many major calyces does each kidney have?
2-3
What is the renal pelvis composed of?
major calyces
What are major calyces made of?
merged minor calyces
What does the renal pelvis connect to?
ureter
What is the kidney surrounded by to cushion and protect itself?
fat
What element does the spleen store?
iron
What does the spleen produce?
white blood cells
What are regions of the hip bone?
ilium, ischium, pubic
What types of pelvic muscles are there?
extrapelvic, pelvic wall, pelvic floor/diaphragm
What does the prefix “para” mean?
near
What does the prefix “peri” mean?
surrounding
What does the prefix “retro” mean?
behind