Marketing
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Purpose of market reserch
Identify what customers want.
Identify gaps in the market (market niches)
New business opportunities
Reduce the risk associated with a business Idea.
Make informed business decisions
Retain competitive advantage.
Two types of reserch
Primary
Secondary
Primary research (+examples)
Obtaining data first hand by the business to match the specific needs of the business. Examples include:
survey
questionnaire
focus group
observation
Secondary research (+examples)
Secondary research includes data from other sources Examples include:
MINTEL
internet market reports
national government reports.
Advantage and disadvantage of primary research
Advantage: accurate to the business
Disadvantage: more expensive, takes time
Advantage and disadvantage of secondary research
Advantage: cheaper, faster
Disadvantage: Less accurate for the business
Quatitative data
numerical and can be analysed statistically
Qualitative data
comes from interviews and in-depth studies, where the information gathered cannot easily be converted to data
Market segmentation
when the market is put into seperate sections - it helps businesses see what consumer they are looking for
different market segments
location
demographics
lifestyle
income
age
Product life cycle
development
introduction
growth
maturity
(product extension)
decline
Product life cycle (as a graph)
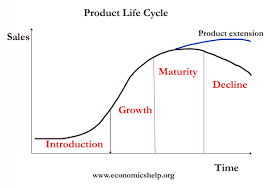
Extensions strategies
lowering prices
advertising
enhancing the product
re-packaging
repositioning the product into a different market segment
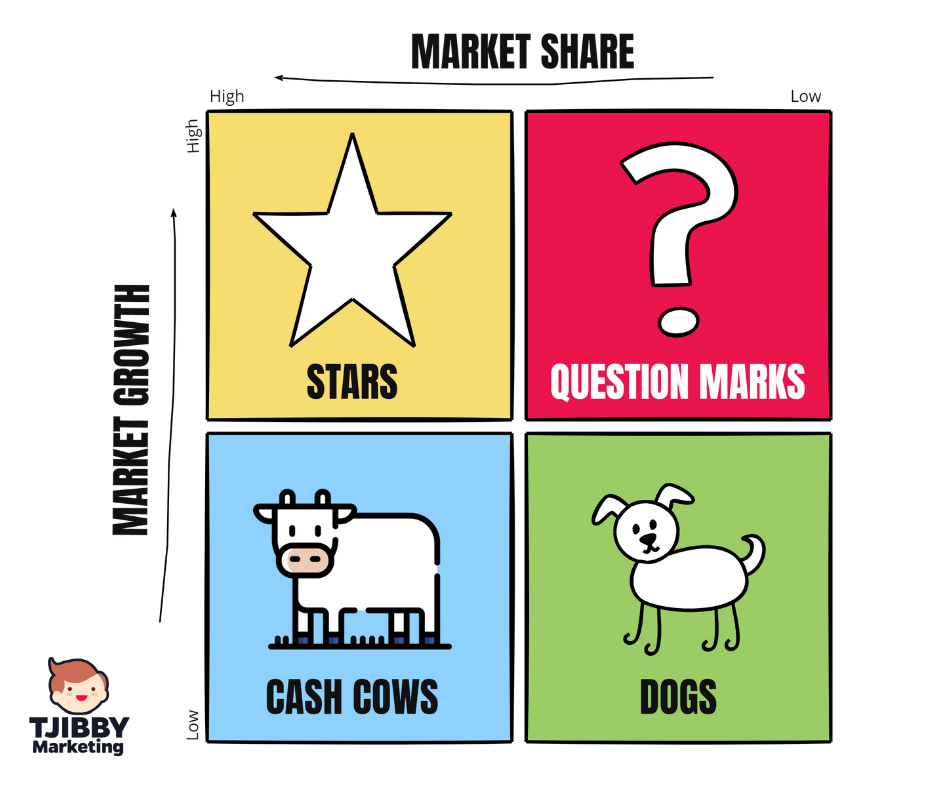
Boston matrix
Boston Matrix:The Boston Matrix, also known as the Growth-Share Matrix, is a strategic planning tool that categorizes a company's products into four quadrants based on market growth rate and market share. It classifies products as stars, cash cows, question marks, or dogs to guide resource allocation decisions.
Boston matrix (image)
Pricing strategies businesses use
Penetration pricing
Price skimming
Cost-plus pricing
Competitive pricing
Promotional pricing
Penetration pricing
pricing at a low level close to average total cost or below average total cost to allow the product to build market share. It is usually used for new products that have just entered the market.
Price skimming
normally be used when the product has significant USPs/differentiation and the product can be priced at a high level with a large profit margin
Cost-plus pricing
adding a percentage mark-up on to the average total cost of the product. This is a simple pricing strategy that does not take the market into consideration
Competitive pricing
used in markets where there is lots of competition. It involves low prices with small profit margins since to price at a higher level would involve loss of sales to competitors.
Promotional pricing
short-term discounts to the price of the product to try and encourage initial sales or increase sales for a specific period of time
Types of promotion
advertising
sponsorship
product trials
special offers
branding