FIN 463 Final
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
CH #6: PV of annuities-DCF valuation Conceptual Terms
CH #6: PV of annuities-DCF valuation Conceptual Terms
Annuity
Equal stream of cash flows per regular interval
for a definite number of periods
Ordinary/regular/deferred annuity vs. Annuity Due
Ordinary/regular/deferred annuity – An equal stream of cash
flows per period for a definite number of periods arising at the
END of each period. (0 on excel)
Annuity due – an equal stream of cash flows per period for a
definite number of periods arising at the BEGINNING of each
period. (1 on excel)
Ordinary/regular/deferred annuity vs. Annuity Due Examples
Ordinary annuity: mortgages, car loans, stock dividends, and bond dividends
Annuity Due: rent, lease agreements, subscription fees, insurance premiums,
Discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation:
The process of determining the PV of future cash flows to establish their worth today (at period 0). DCF is widely used to determine the value (PV) of assets such as bonds and stocks.
Unless specifically otherwise stated, we always assume …
annuities arise at END of each period (ordinary/regular/deferred annuities). Therefore, if a question is silent on when the annuity arises, always assume it is ordinary annuity.
Unlike zeros (zero-coupon bonds) which don’t pay
periodic interest (coupons), coupon (straight or plain
vanilla) bonds pay …
periodic (semi-annual) interest income
Irregular CFs
A stream of cash flows that varies every period. Each cash
flow is a single or lump sum amount
Perpetuity
A equal stream of cash flows per a regular
period for indefinite (unending) number of periods.
Examples of perpetuities are
Consols (consolidated stocks)
Preferred stocks
A growing perpetuity is …
an annuity that is growing at a constant rate per period forever
Delayed annuities
Annuities that do not start in period 1
What is the golden rule with annuities
The PV of perpetuity (and annuity) gives the PV one period before the first payment
Pure discount loans
The principal amount is repaid at some future
date, without any periodic interest payments
Ex: pay-day loans and Treasury bills
issued by the government
requires only a single lump-sum payment at the end of the term
Interest only or non-amortizable loans
The borrower pays interest only each period and repays
the principal (amount borrowed) loan at the maturity date.
This is similar to straight/coupon/plain vanilla bonds
When the interest-only period ends, you'll need to repay the remaining balance, usually in a lump sum
Amortized loans
Amortization - process of providing for a loan to be paid off
by making regular principal reductions.
Borrower pays a fixed amount per period (annuity) which
consists of interest charges and a portion of the principal
loan.
amortized loans do not have lump sum payments
Partial amortization or balloon loans
Periodic payments do not fully payoff (amortize) the loan hence
the word partial
A balloon or lump sum payment is required at the end of the
specified term to repay the remaining principal balance
(borrower is biting the bullet)
The last payment in a partially amortized loan is called balloon payment: A large lump-sum payment
CH #6: PV of annuities-DCF valuation Formulas
CH #6: PV of annuities-DCF valuation Formulas
FV of annuity (FVA) Formula
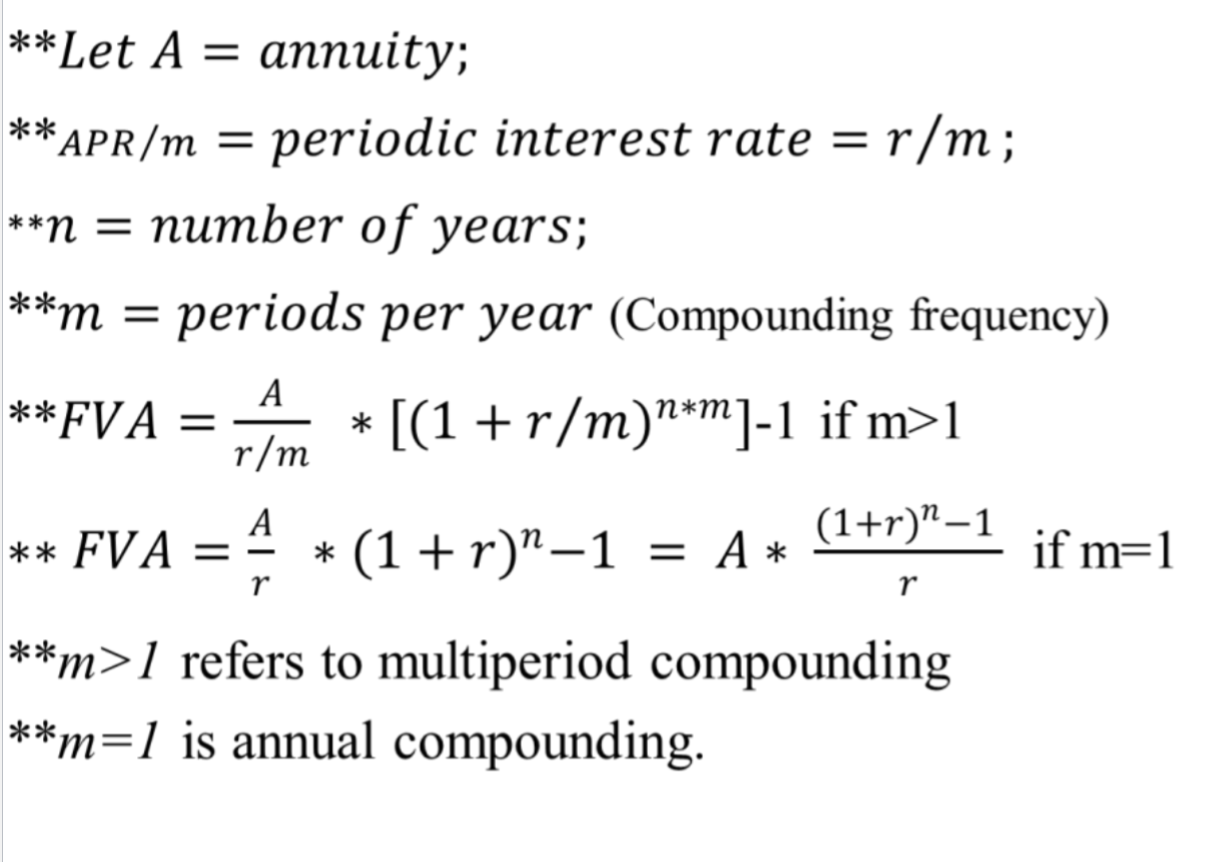
PV of annuity (PVA) Formula
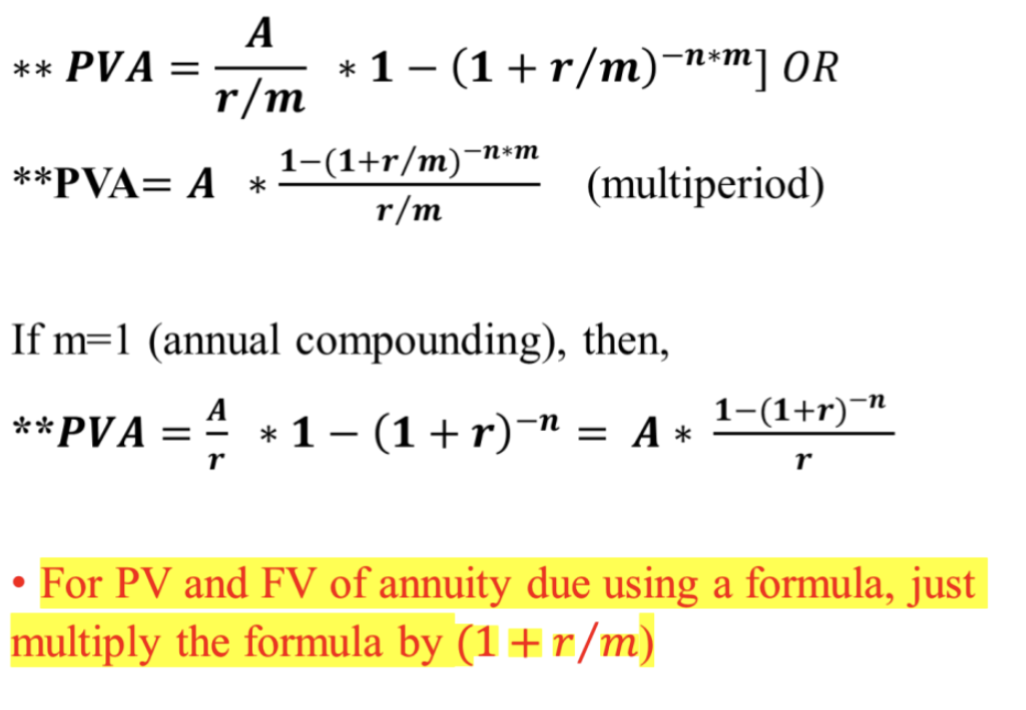
PV of a perpetuity Formula
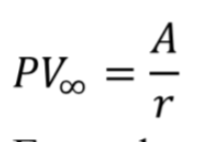
PV of a growing perpetuity Formula
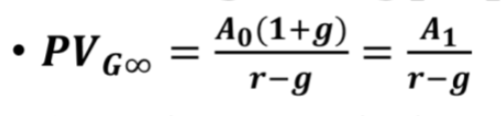
PV of a growing annuity with a definite life Formula
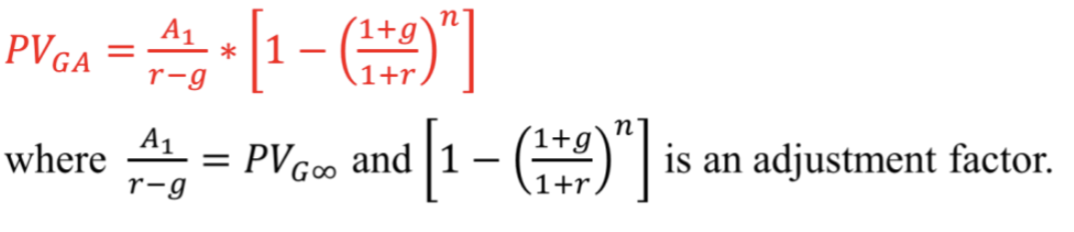
Delayed annuity formula
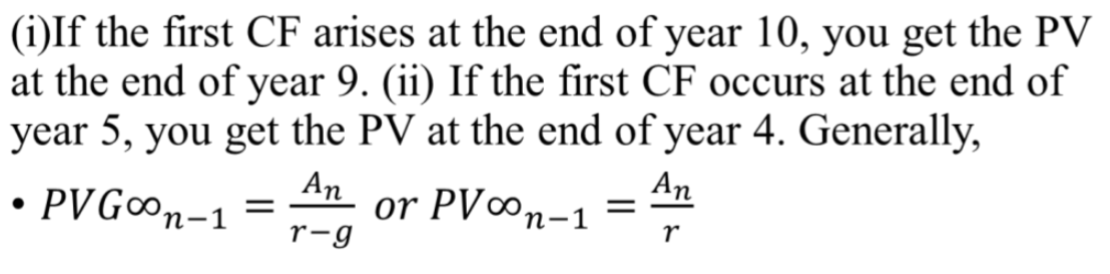
CH #6: PV of annuities-DCF valuation HW Questions
CH #6: PV of annuities-DCF valuation HW Questions
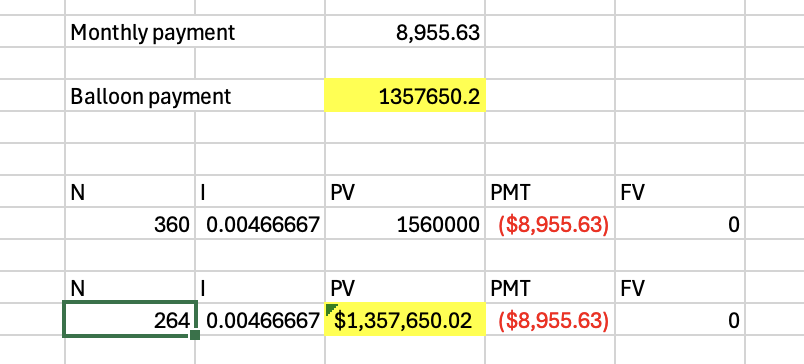
Q1: You have just arranged for a $1,560,000 mortgage to finance the purchase of a large tract of land. The mortgage has an APR of 5.6 percent, and it calls for monthly payments over the next 30 years. However, the loan has an eight-year balloon payment, meaning that the loan must be paid off then. How big will the balloon payment be?
1,357,650.02
Q2: The Maybe Pay Life Insurance Company is trying to sell you an investment policy that will pay you and your heirs $32,000 per year forever. Suppose a sales associate told you the policy costs $477,000. At what interest rate would this be a fair deal?
6.71%

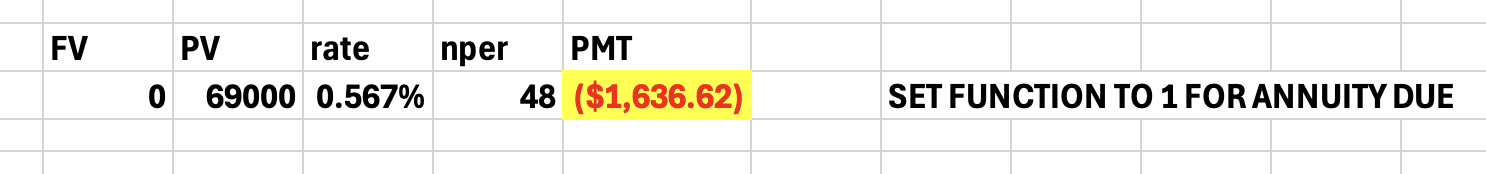
Q3: You want to buy a new sports car from Muscle Motors for $69,000. The contract is in the form of a 48-month annuity due at an APR of 6.8 percent. What will your monthly payment be?
1,632.62
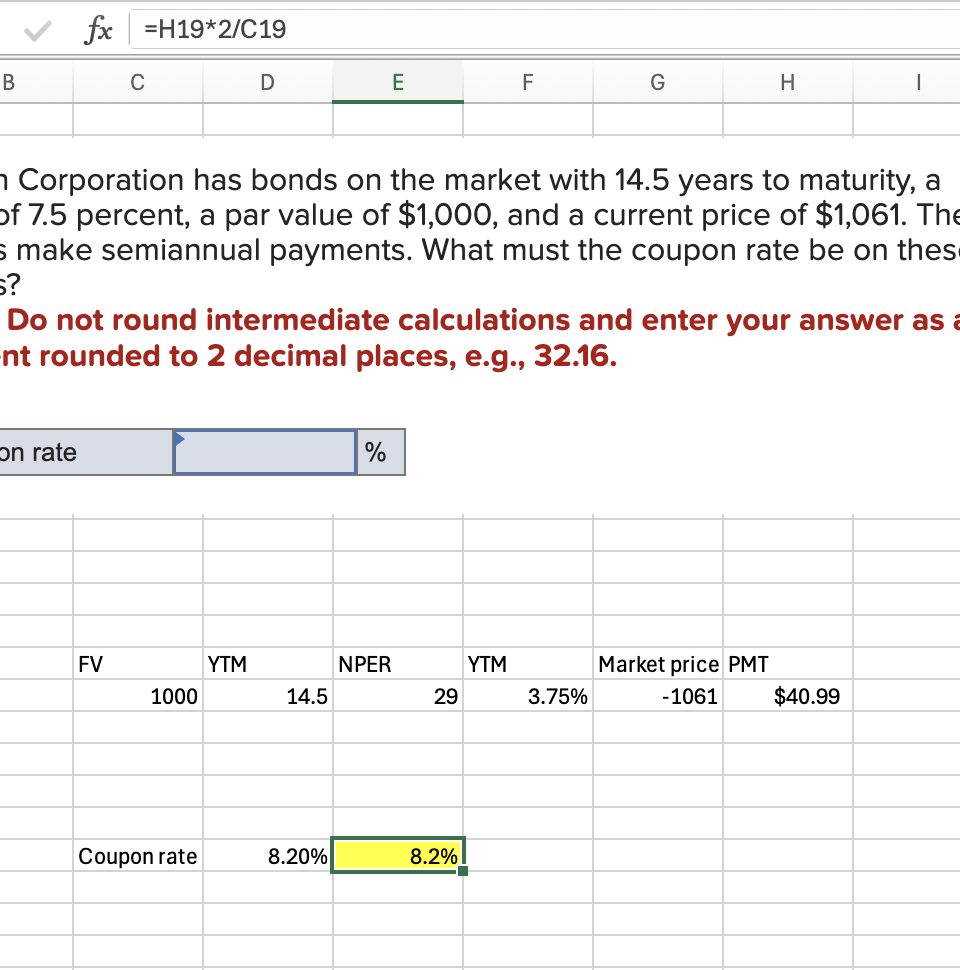
Q4: Redan Corporation has bonds on the market with 14.5 years to maturity, a YTM of 7.5 percent, a par value of $1,000, and a current price of $1,061. The bonds make semiannual payments. What must the coupon rate be on these bonds?
8.2%

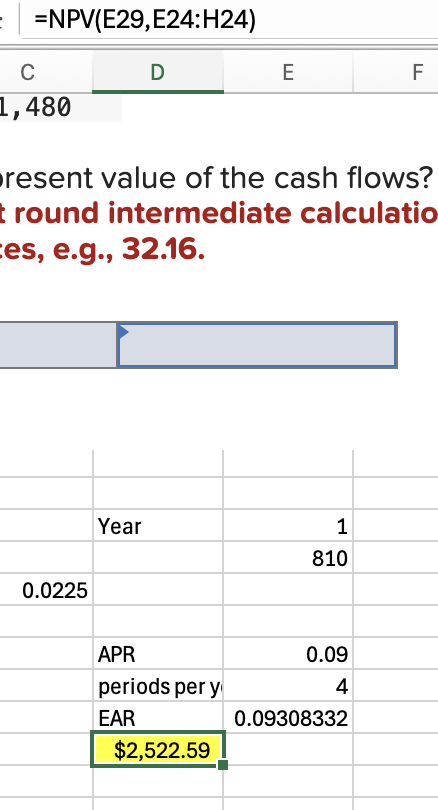
Q5
2522.59
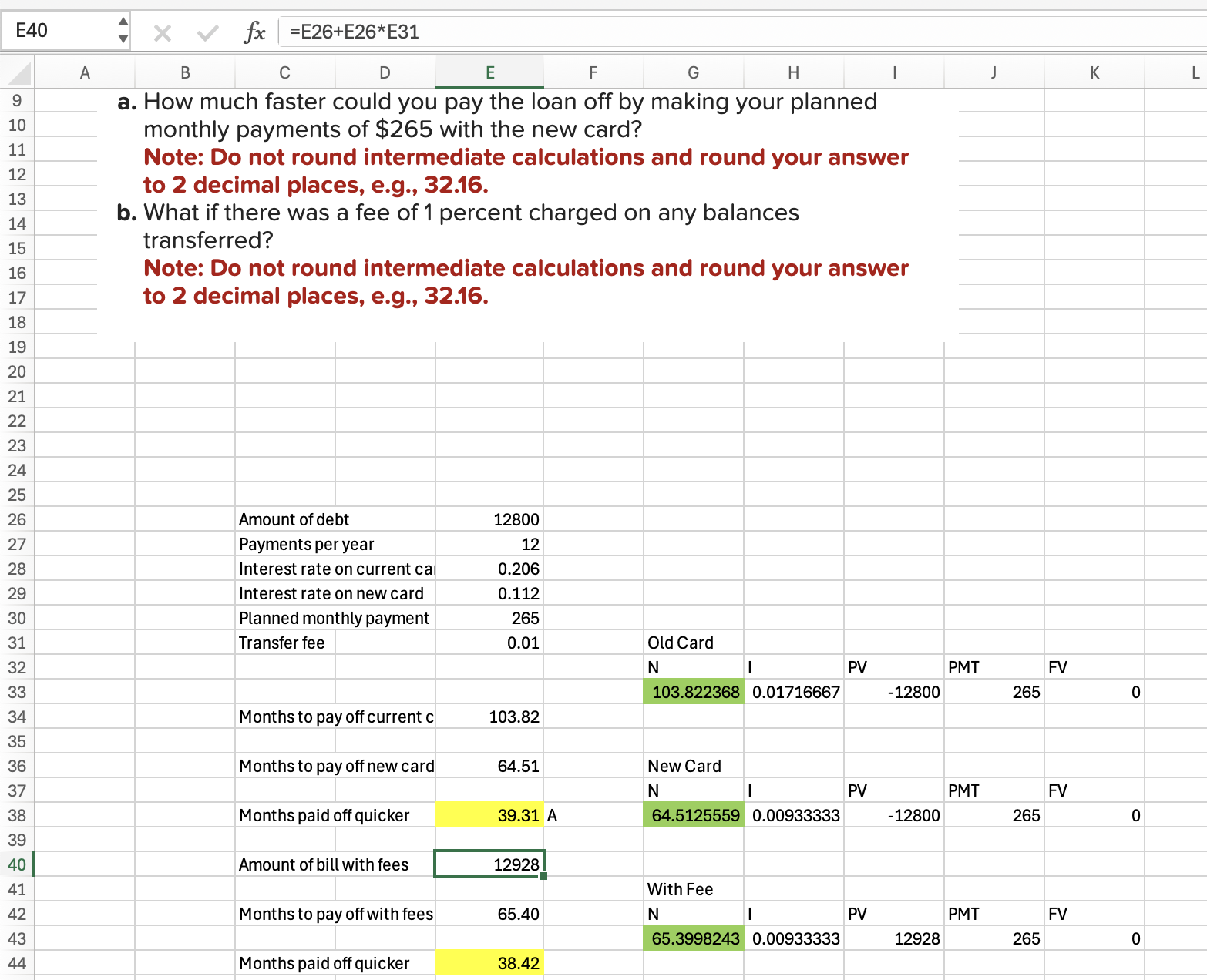
Q6
Without Fee: 39.31
With 1% Fee: 38.42

Q7
$3,898.11
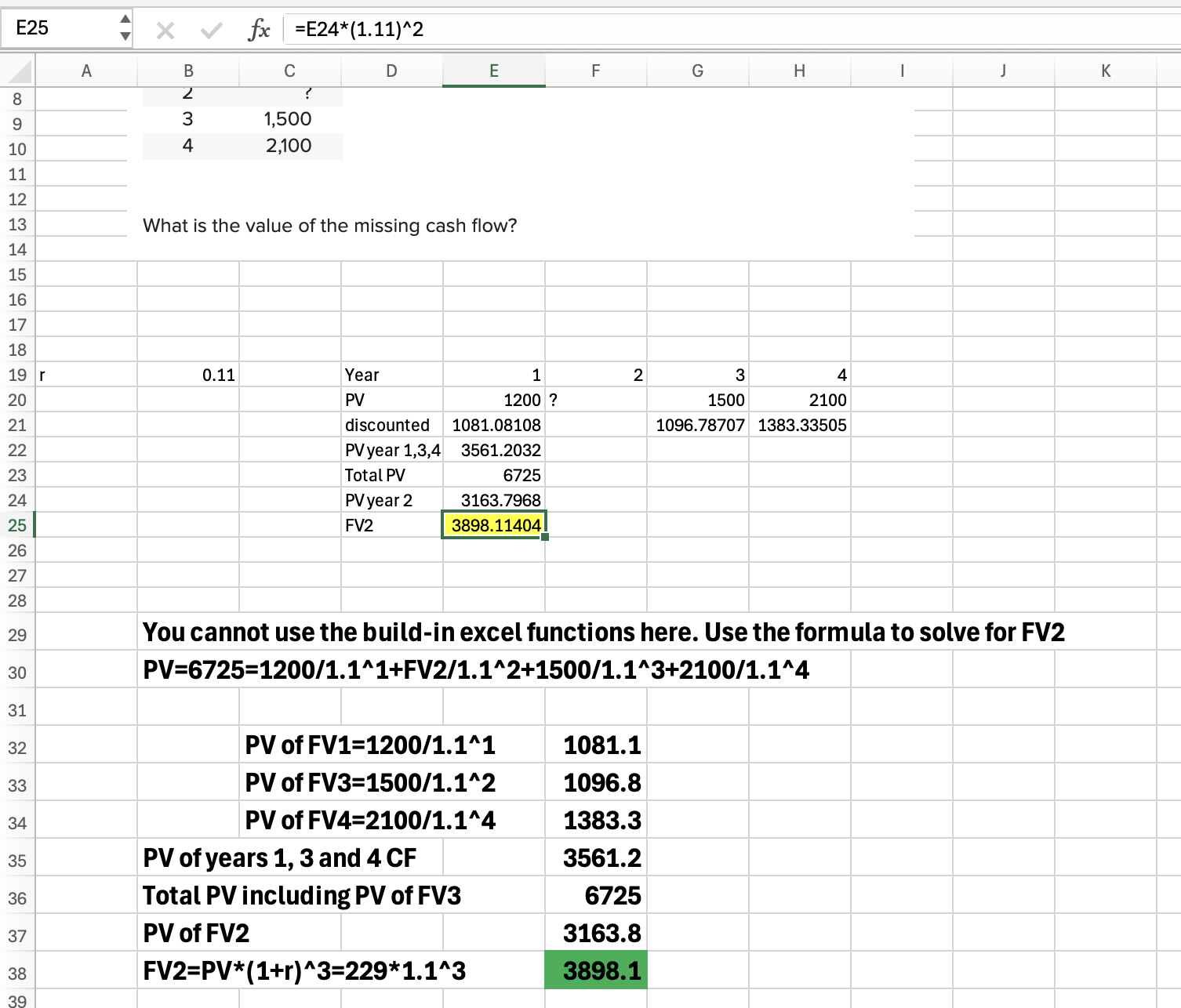
Q8: McCabe Corporation is expected to pay the following dividends over the next four years: $16, $12, $11, and $6.50. Afterward, the company pledges to maintain a constant 5 percent growth rate in dividends forever. If the required return on the stock is 12 percent, what is the current share price?
97.78
=E41/(1.12), F41/(1.12)^2, etc
THEN
=Sum all math
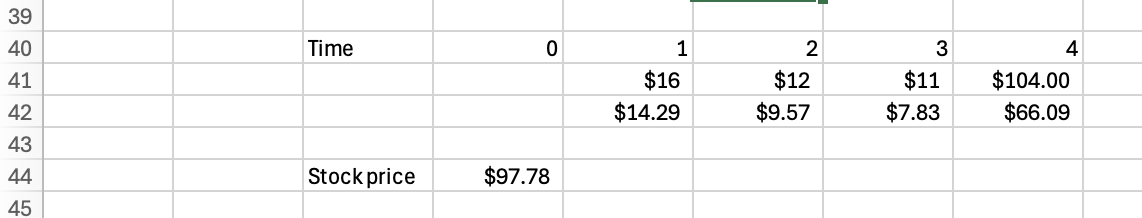
Q9: Chen Corporation issued 15-year bonds two years ago at a coupon rate of 9.1 percent. The bonds make semiannual payments. If these bonds currently sell for 103 percent of par value, what is the YTM?
8.74%
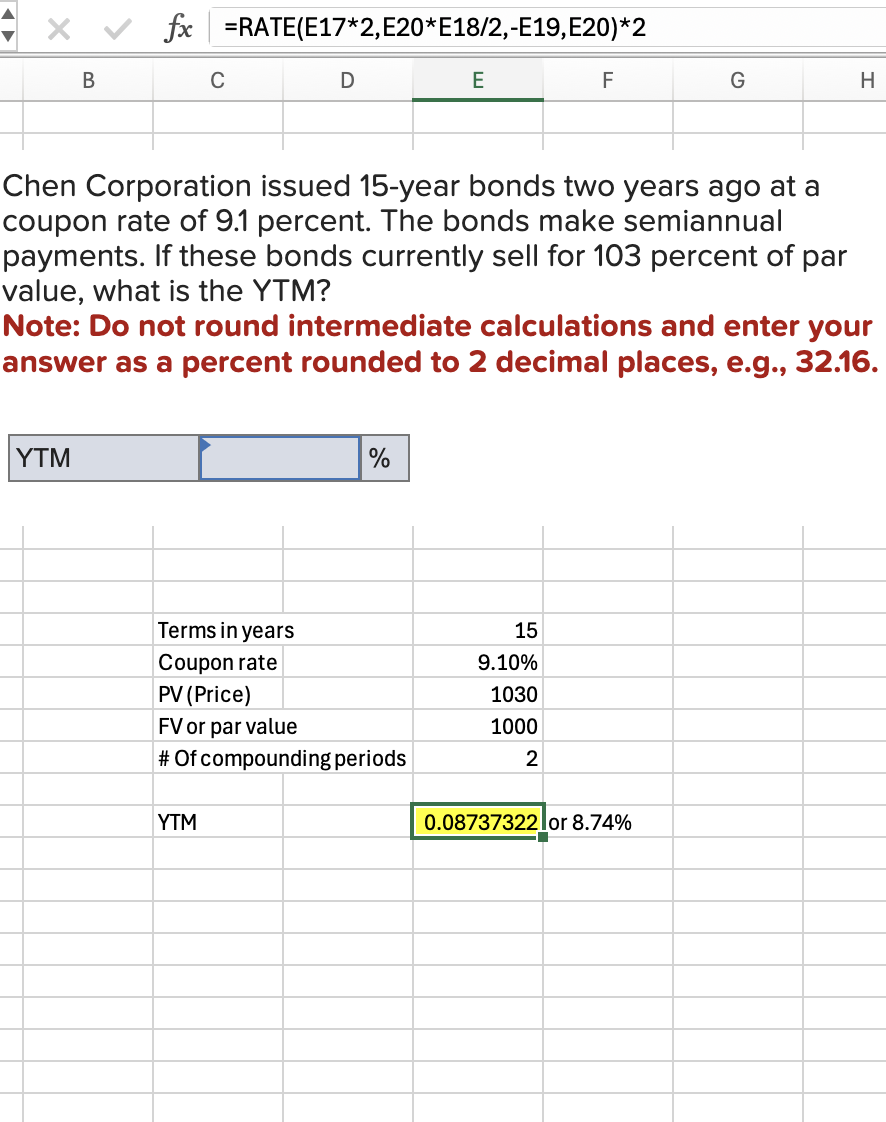
Q10: Metallica Bearings, Incorporated, is a young start-up company. No dividends will be paid on the stock over the next nine years because the firm needs to plow back its earnings to fuel growth. The company will pay a dividend of $15 per share 10 years from today and will increase the dividend by 5 percent per year thereafter. If the required return on this stock is 10.5 percent, what is the current share price?
111.04
Value after 9 years: =15/(0.105-0.05)
THEN
=that value/(1+0.105)^9

Q11
385667.63
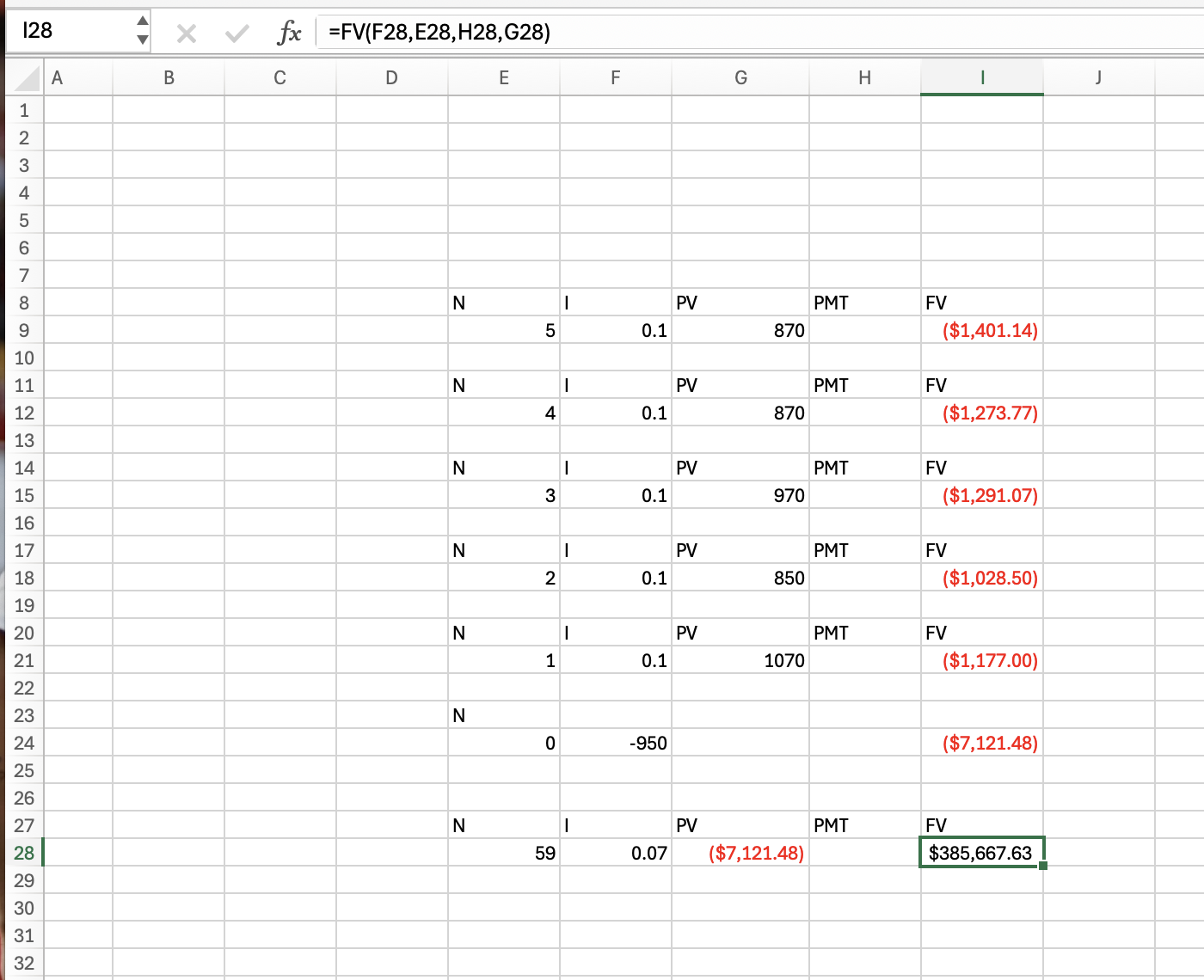
Q12: Avacado Farms just paid a dividend of $3.00 on its stock. The growth rate in dividends is expected to be a constant 4 percent per year indefinitely. Investors require a return of 11 percent for the first three years, a return of 9 percent for the next three years, and a return of 7 percent thereafter. What is the current share price?
88.96
Discounted: Step 1: =D21*(1+0.04)^1, =E21*(1+0.04)^2
PV: Step 2: =D29/(1.11)^1, =E29/(1.11)^2
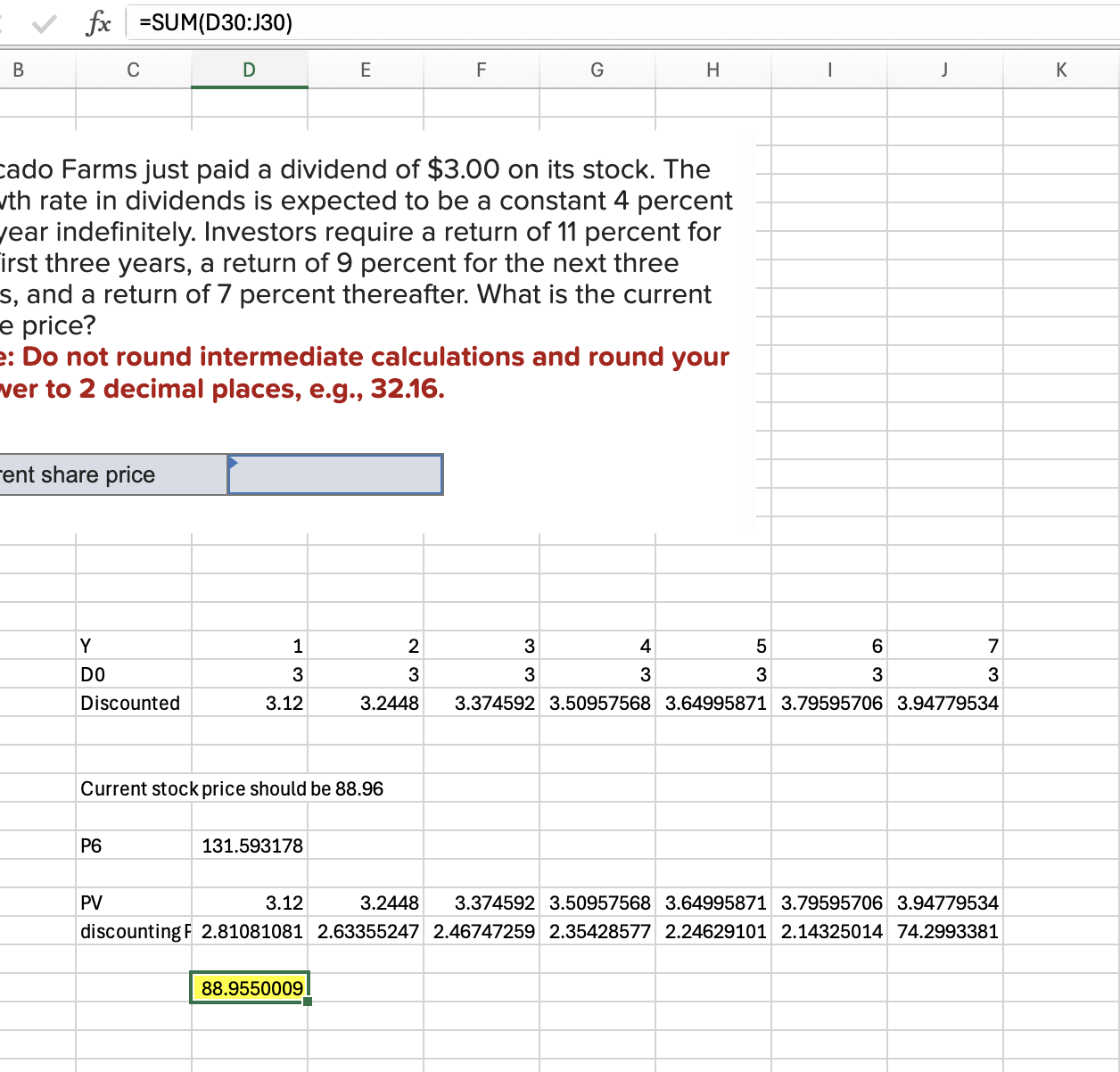
Q13: Red, Incorporated, Yellow Corporation, and Blue Company each will pay a dividend of $2.55 next year. The growth rate in dividends for all three companies is 3 percent. The required return for each company’s stock is 5 percent, 8 percent, and 11 percent, respectively. What is the stock price for each company?
Red: 127.5
Yellow: 51
Blue: 31.875
Math for Red: =2.55/(0.05-0.03)
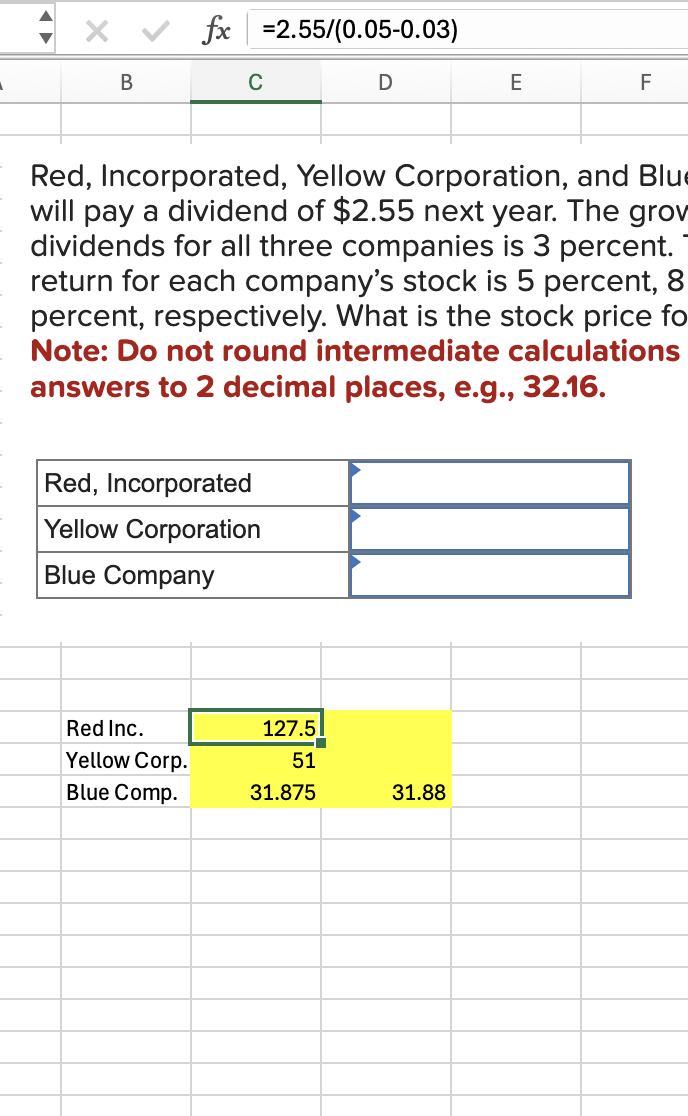
Q14: You have successfully started and operated a company for the past 10 years. You have decided that it is time to sell your company and spend time on the beaches of Hawaii. A potential buyer is interested in your company, but he does not have the necessary capital to pay you a lump sum. Instead, he has offered $700,000 today and annuity payments for the balance. The first payment will be for $290,000 in three months. The payments will increase at 1.2 percent per quarter and a total of 25 quarterly payments will be made. If you require an EAR of 9 percent, how much are you being offered for your company?
7,037,407
Step 1 APR: =NOMINAL(E32,4)
Step 2: Quarterly discount rate=E35/4
Step 3: PV Quarterly Payment
Step 4: PV = Lump sum today + PV Quarterly payment
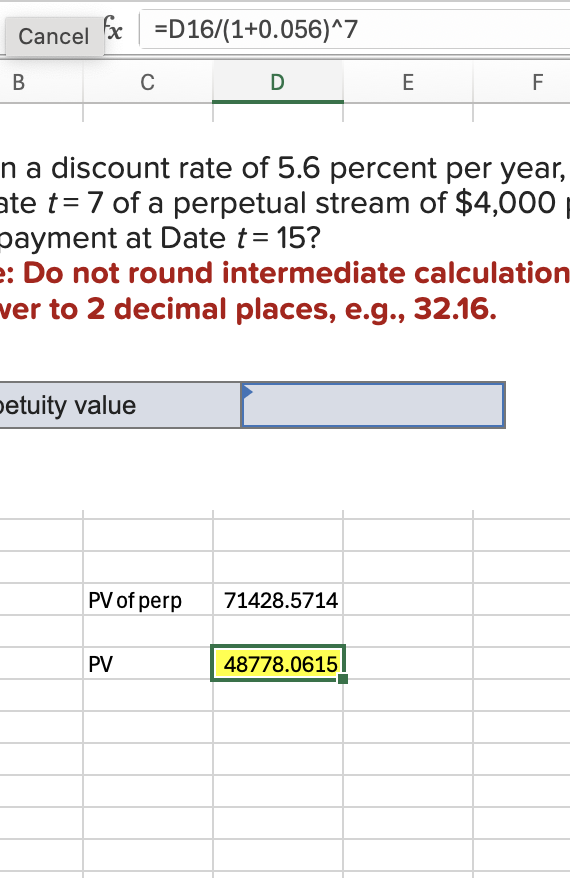
Q15: Given a discount rate of 5.6 percent per year, what is the value at Date t = 7 of a perpetual stream of $4,000 payments with the first payment at Date t = 15?
48,778.06
Step 1: PV of perp = =4000/0.056
Step 2: PV = =D16/(1+0.056)^7

Q16
APR: 1,106.38
EAR: 2271876.75

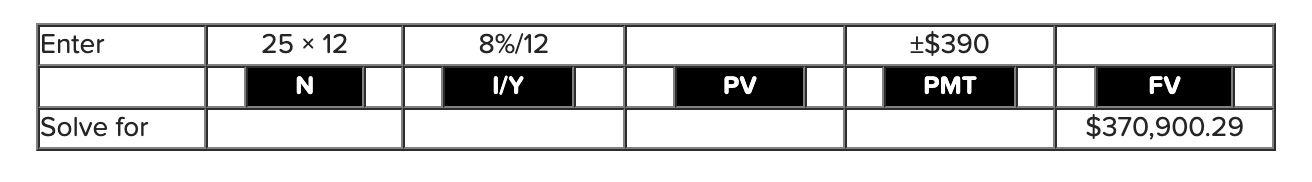
Q17: You are planning to make monthly deposits of $390 into a retirement account that pays an APR of 8 percent compounded monthly. If your first deposit will be made one month from now, how large will your retirement account be in 25 years?
370900.29
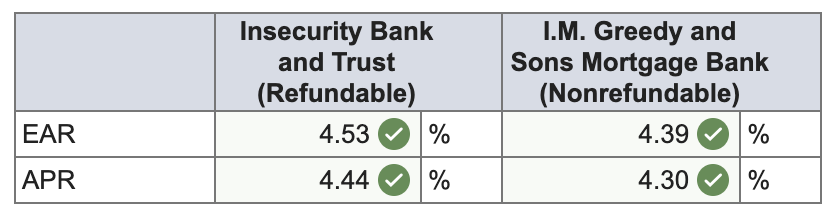
Q18: Two banks in the area offer 25-year, $250,000 mortgages at 4.3 percent and charge a $3,500 loan application fee. However, the application fee charged by Insecurity Bank and Trust is refundable if the loan application is denied, whereas that charged by I.M. Greedy and Sons Mortgage Bank is not. The current disclosure law requires that any fees that will be refunded if the applicant is rejected be included in calculating the APR, but this is not required with nonrefundable fees (presumably because refundable fees are part of the loan rather than a fee). What are the EARs on these two loans? What are the APRs?
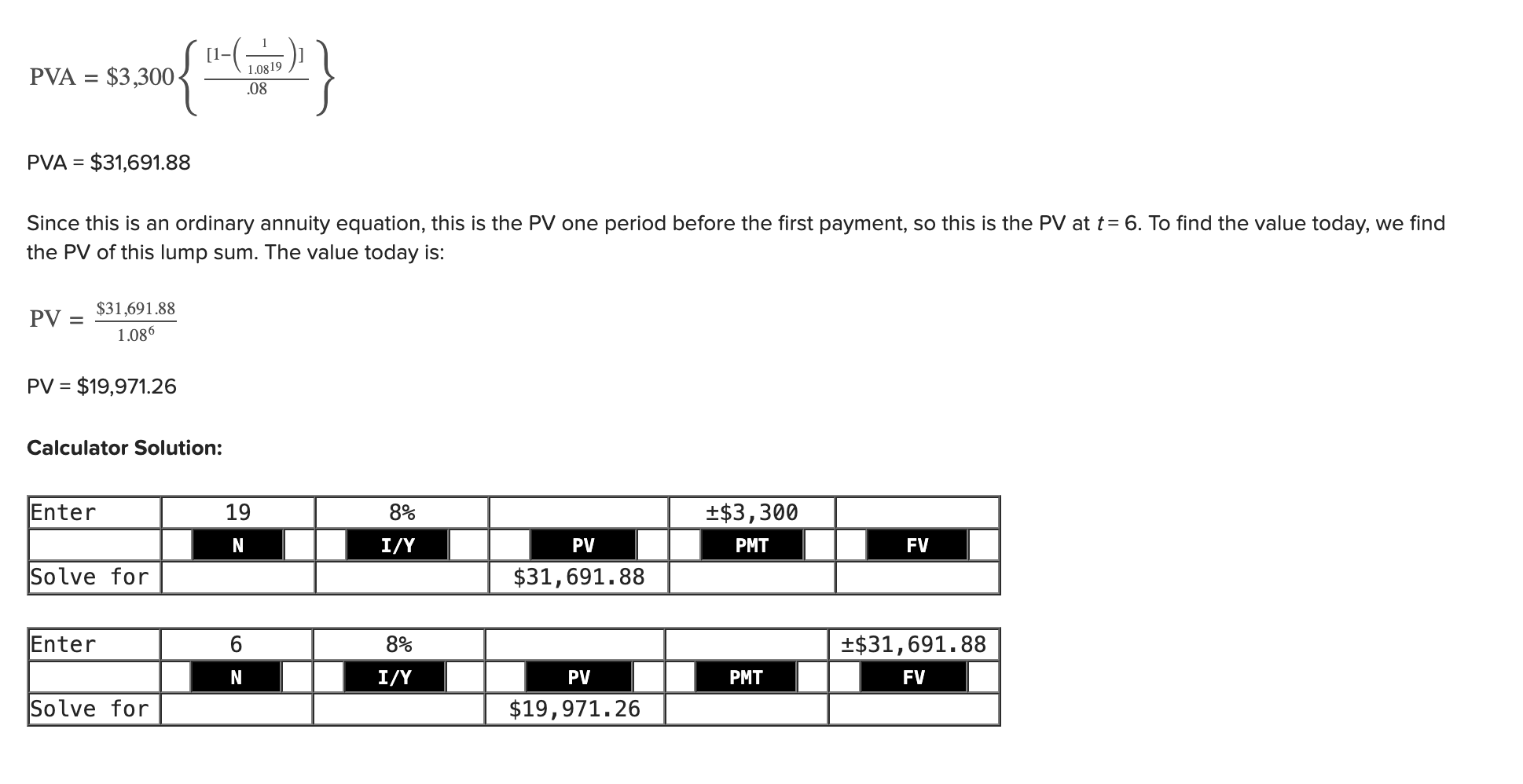
Q19: What is the value today of $3,300 per year, at a discount rate of 8 percent, if the first payment is received 7 years from today and the last payment is received 25 years from today?
19,971.26

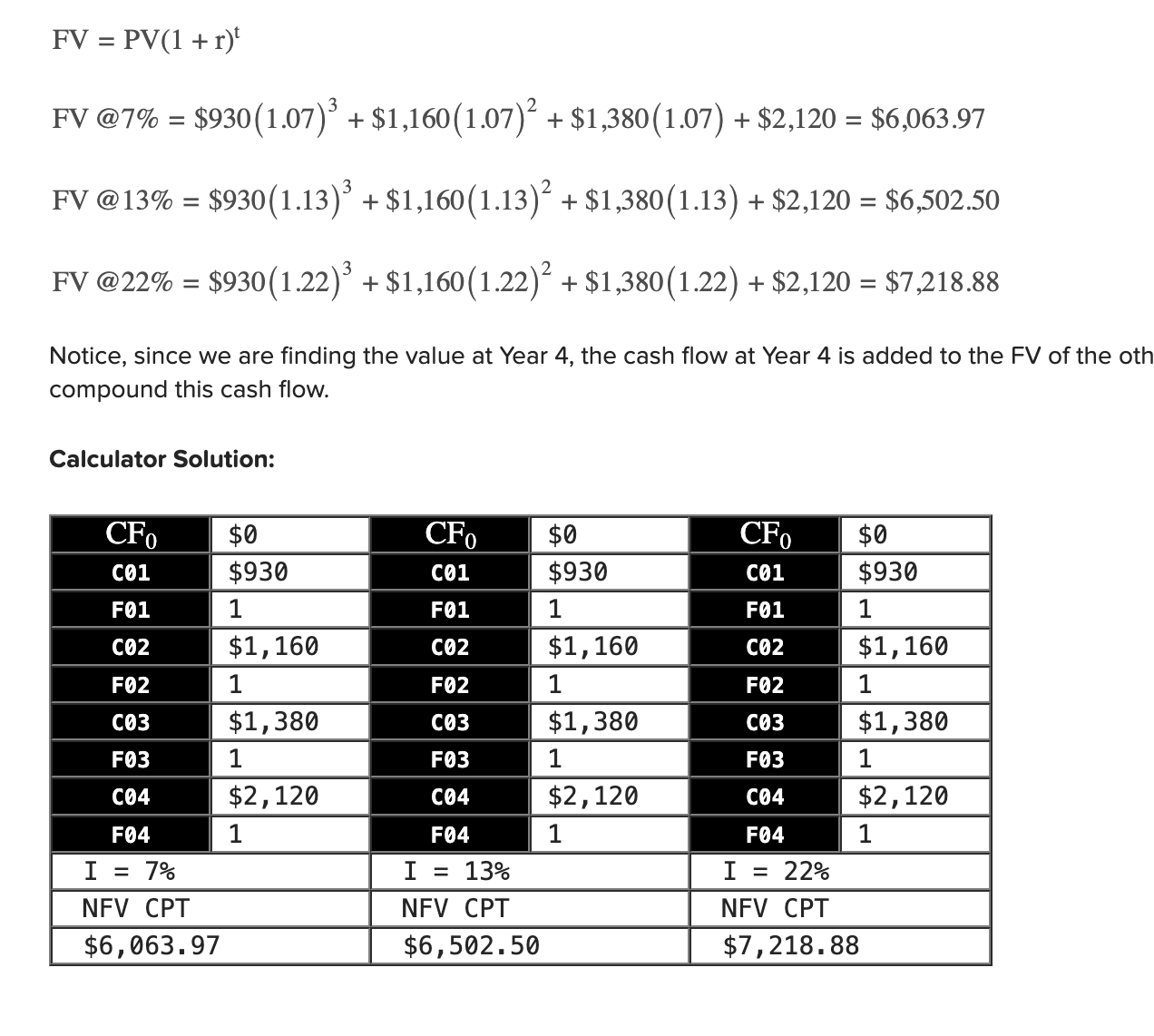
Q20
7%: 6063.97
13%: 6502.49
22%: 7218.88
Q21: The Maybe Pay Life Insurance Company is trying to sell you an investment policy that will pay you and your heirs $29,000 per year forever. If the required return on this investment is 5.3 percent, how much will you pay for the policy?
547,169.81

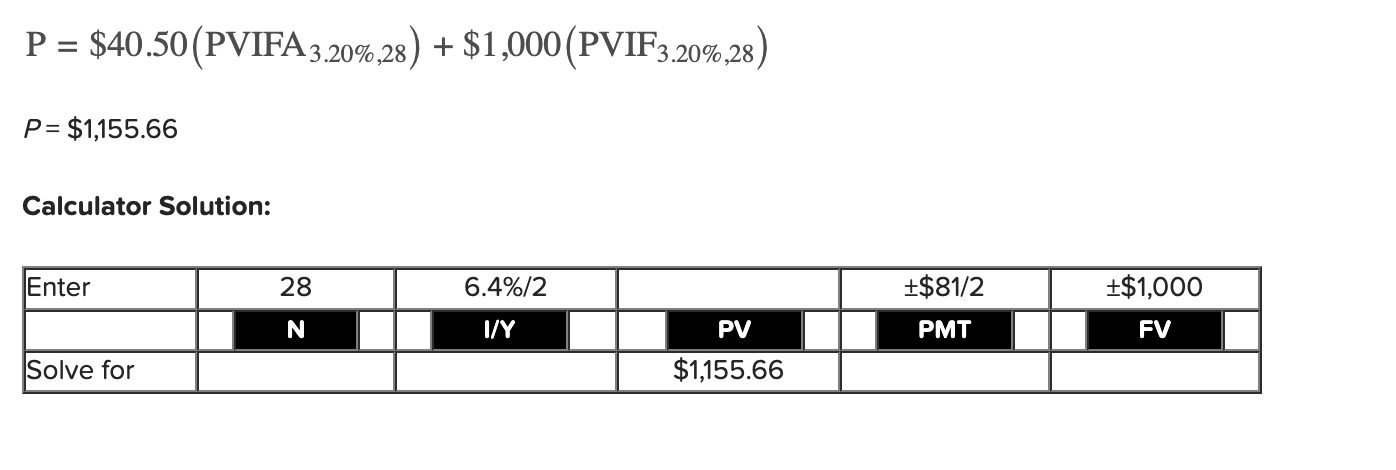
Q22: Elkus Company issued 15-year bonds a year ago at a coupon rate of 8.1 percent. The bonds make semiannual payments and have a par value of $1,000. If the YTM on these bonds is 6.4 percent, what is the current bond price in dollars?
1,155.66
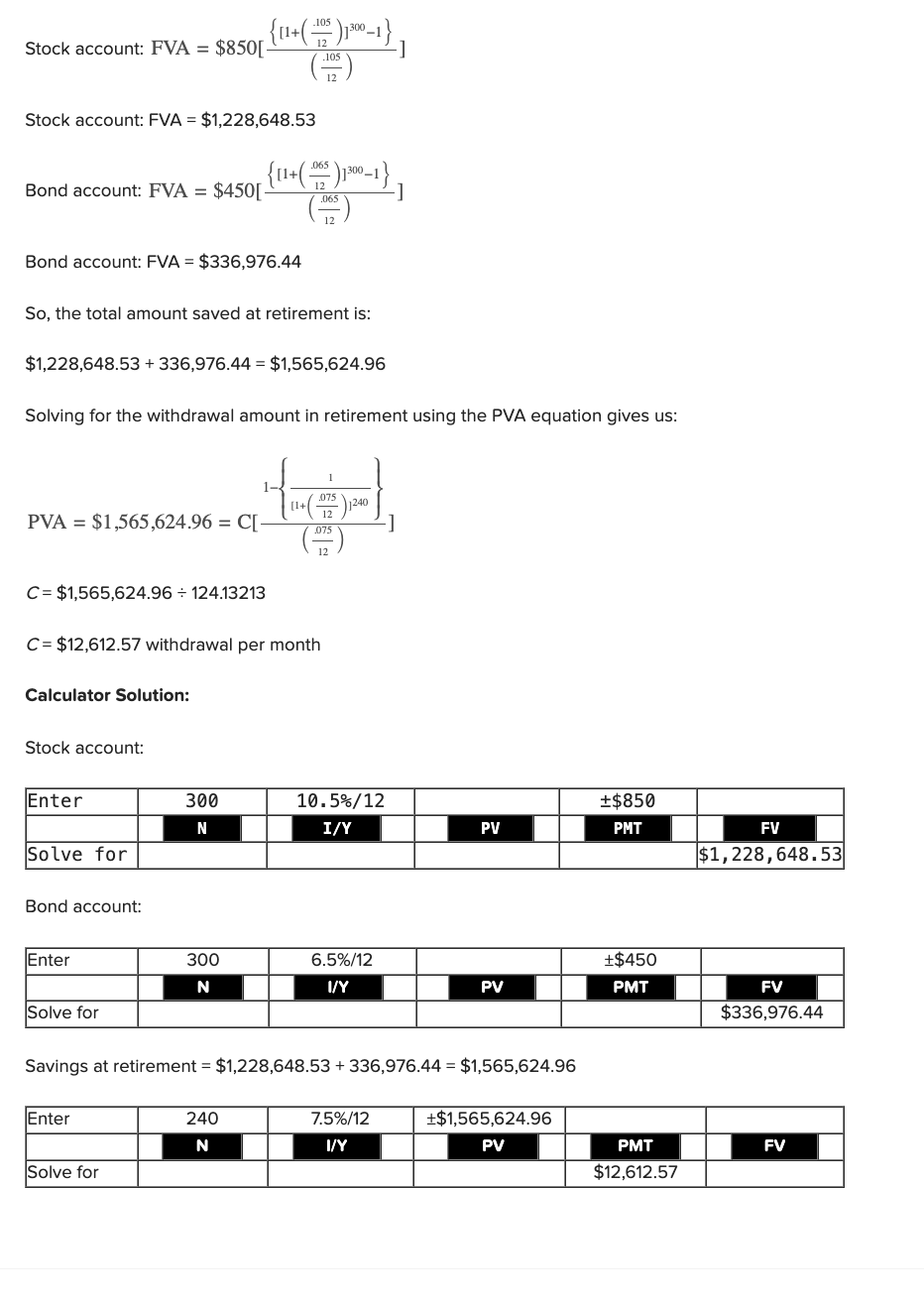
Q23: You are planning to save for retirement over the next 25 years. To do this, you will invest $850 per month in a stock account and $450 per month in a bond account. The return of the stock account is expected to be 10.5 percent, and the bond account will return 6.5 percent. When you retire, you will combine your money into an account with a return of 7.5 percent. How much can you withdraw each month from your account assuming a 20-year withdrawal period?
12,612.57
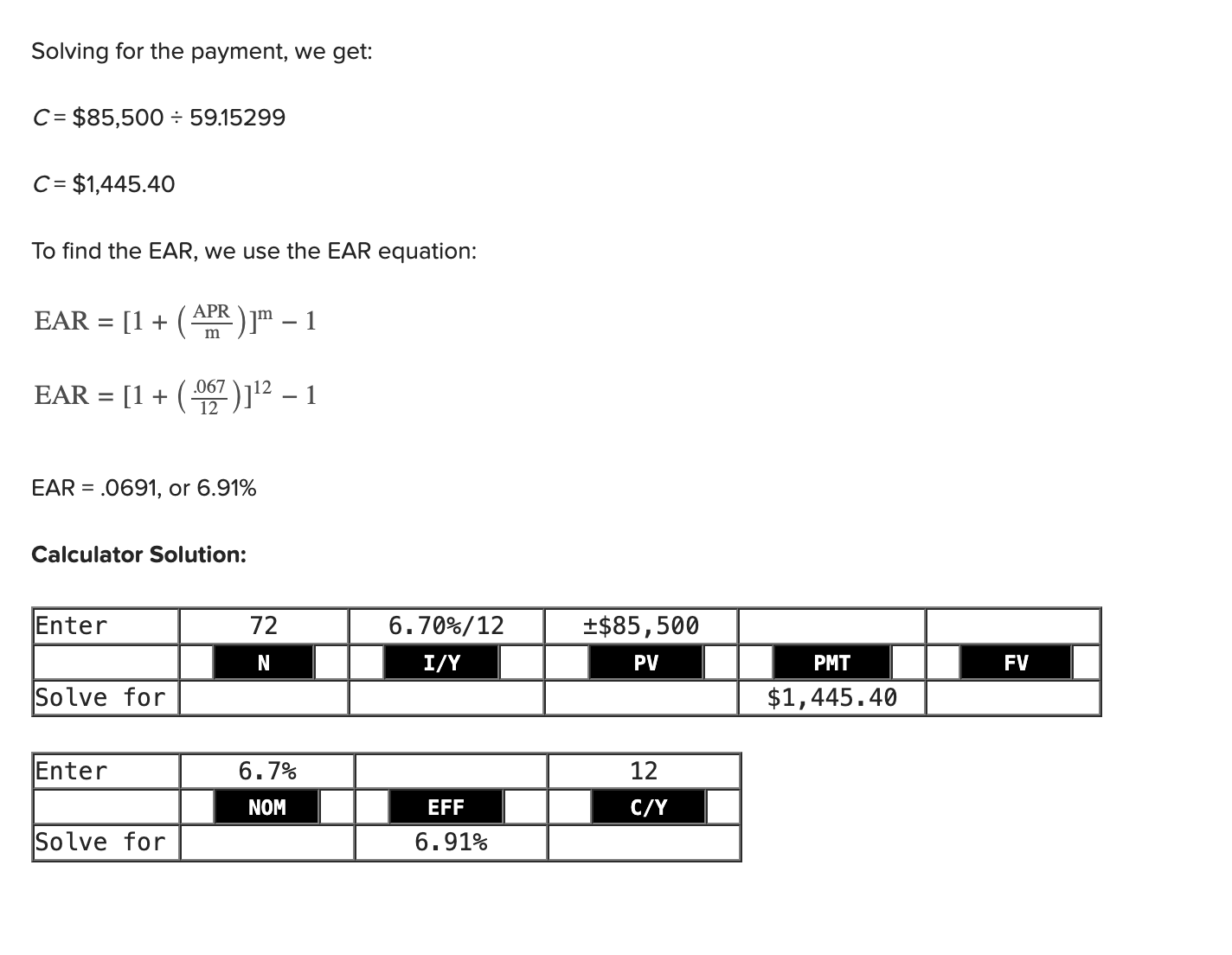
Q24: You want to buy a new sports coupe for $85,500, and the finance office at the dealership has quoted you an APR of 6.7 percent for a 72-month loan to buy the car.
What will your monthly payments be?
What is the effective annual rate on this loan?
Monthly payment: 1,445.40
EAR: 6.91
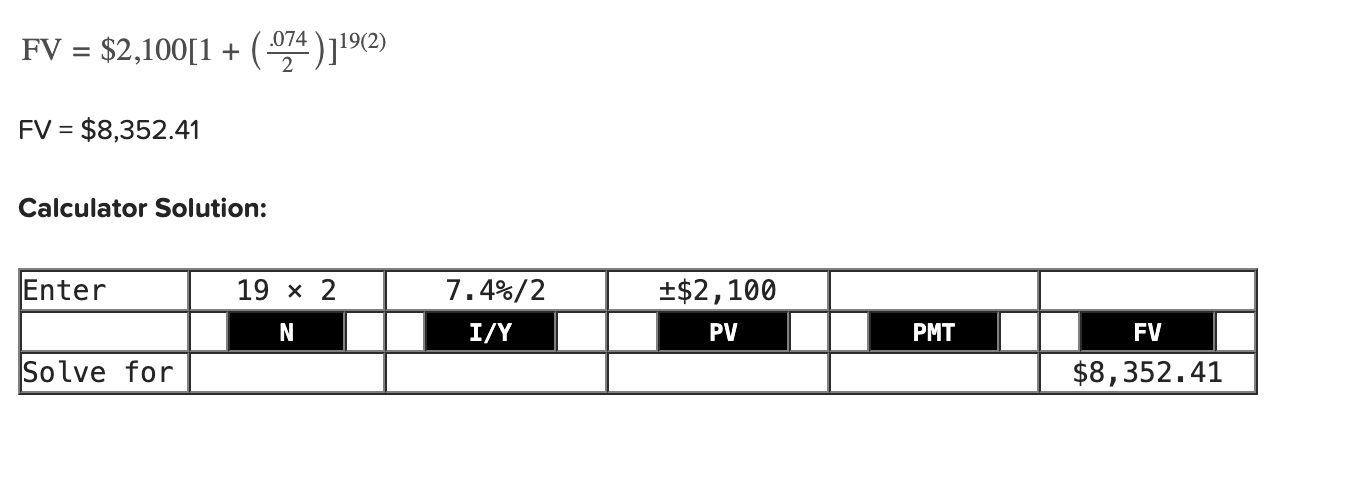
Q25: What is the future value of $2,100 in 19 years at an APR of 7.4 percent compounded semiannually?
8,352.41
CH #6: PV of annuities-DCF valuation Excel Questions
CH #6: PV of annuities-DCF valuation Excel Questions
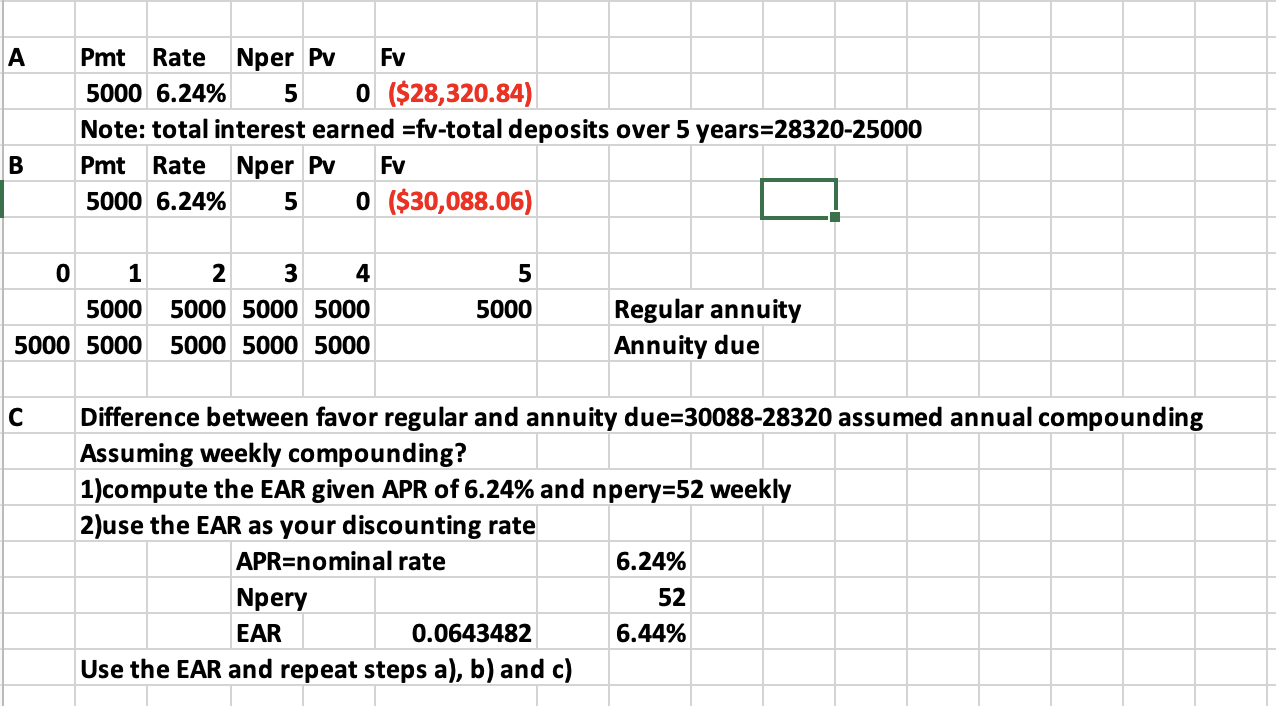
Q1: Suppose you plan to save $5000 each year and expect to earn 6.24% rate of return.
a)What will be the value of the savings at the end of five years?
b) What would be the FV if the savings were made at the beginning of each year?
c) What is the difference between FV in (a) and (b) if interest is compounded weekly?
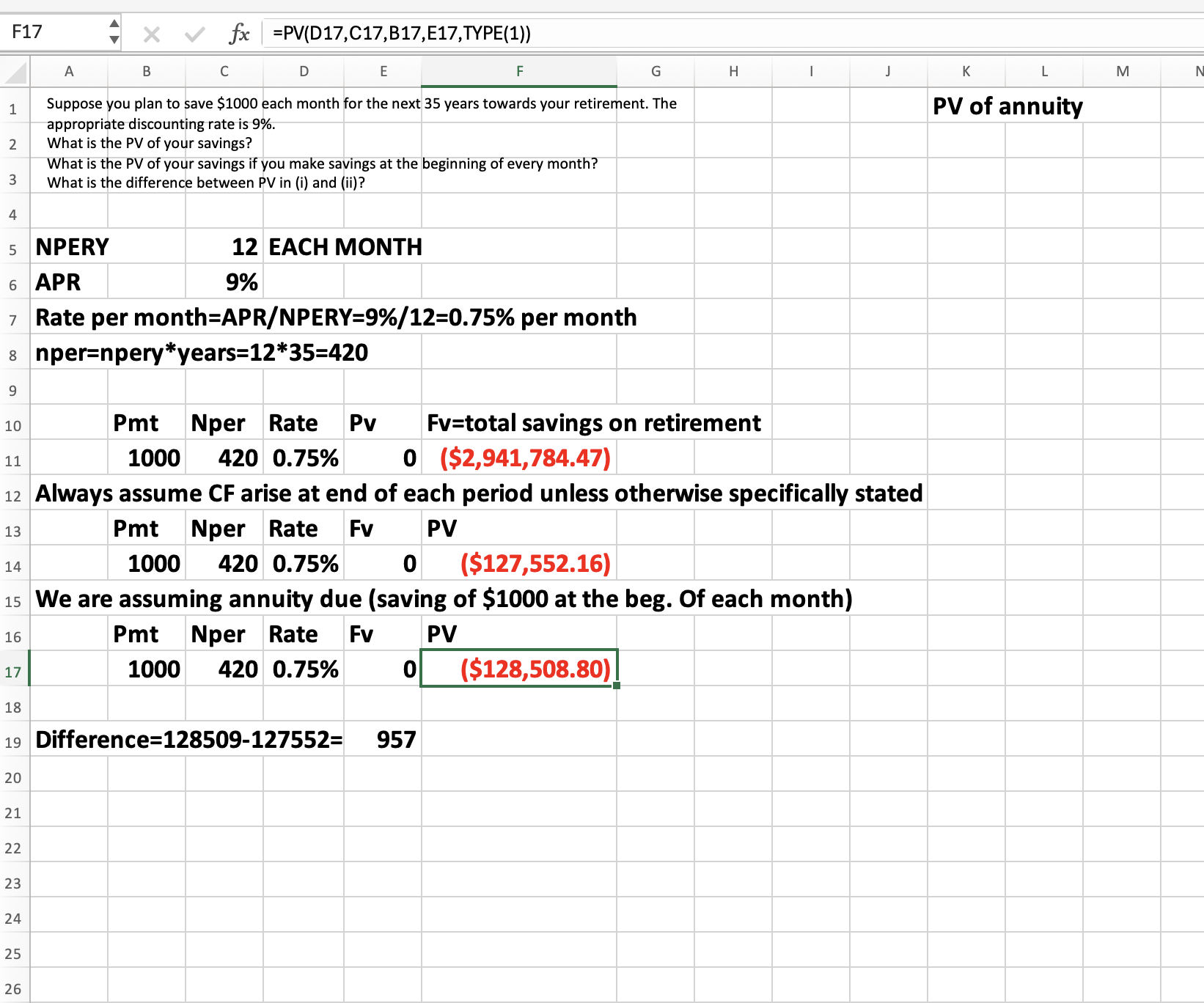
Q2: Suppose you plan to save $1000 each month for the next 35 years towards your retirement. The appropriate discounting rate is 9%.
a) What is the PV of your savings?
b) What is the PV of your savings if you make savings at the beginning of every month?
c) What is the difference between PV in (i) and (ii)?
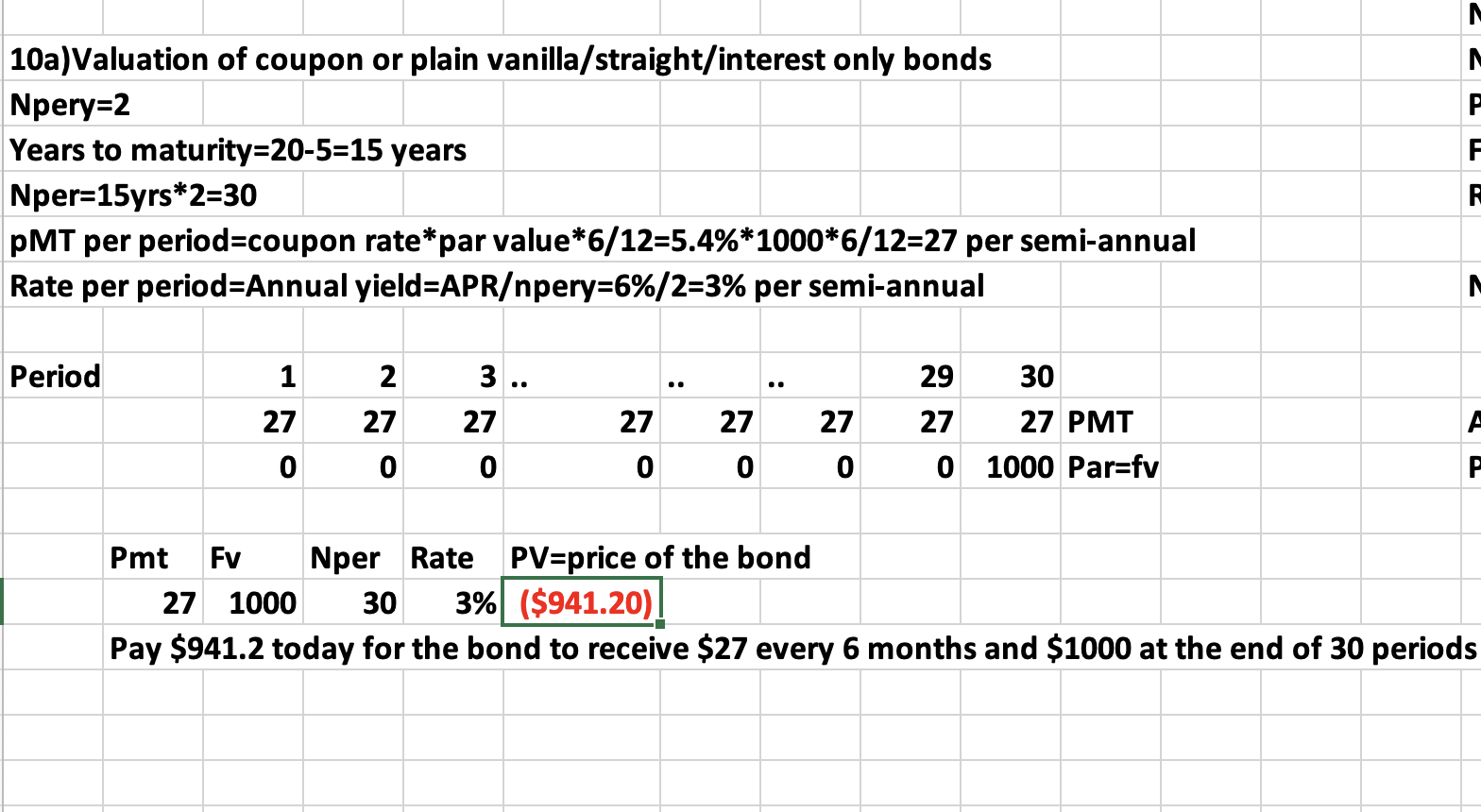
Q3: A 20-year, 5.4%, $1000 par bond was issued 5 years ago. The YTM is 6%. Interest is paid semi-annually. What is the
*Coupon=PMT=interest per semi-annual
*number of periods (nper) to maturity
*periodic YTM
*FV
*PV=price of the bond
Q4: Rivers wants to buy a $32,000 car. He makes a down payment of $7,000 to the car dealer and finances the rest. He also agrees to pay $483.32 per month for the next 5 years.
What
a)Interest should the dealer quote Rivers? (APR)
b)Is the EAR?
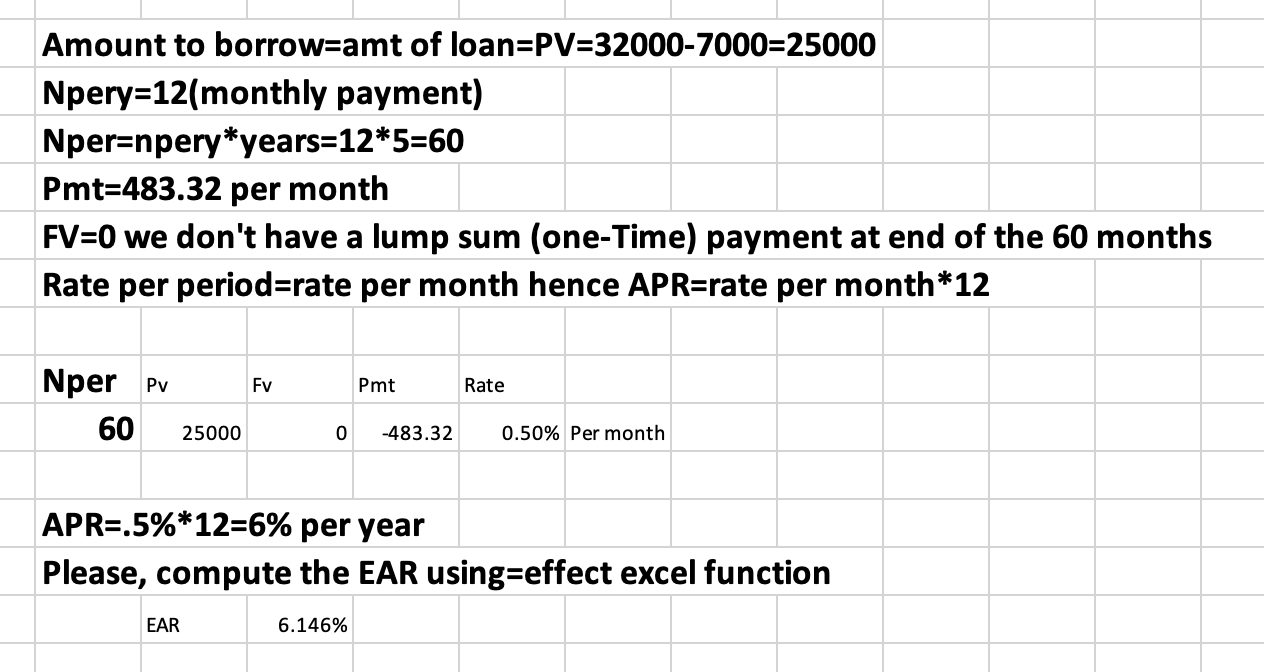
Q5: Suppose you take $300,000 business loan at 4.5% repayable in 5 years. What is your monthly payment?
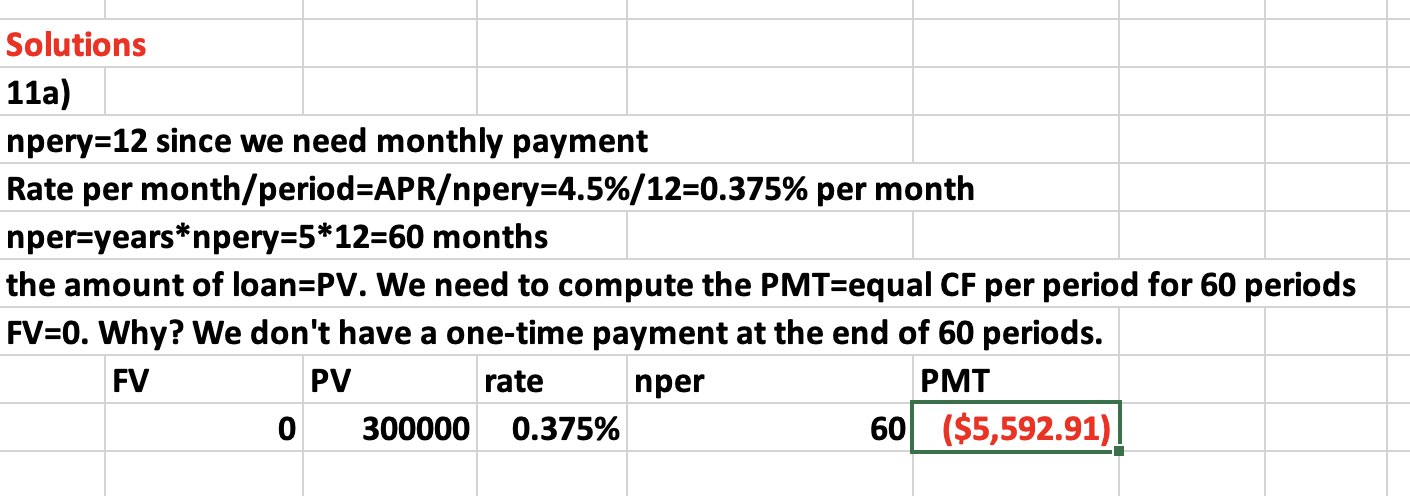
Q6: Kiki Inc. has a 4.4%, 10-year coupon bond with a maturity or par value of $1000. The bond is trading at 98.411. Interest is compounded semi-annually. What is the yield to maturity or market interest rate?
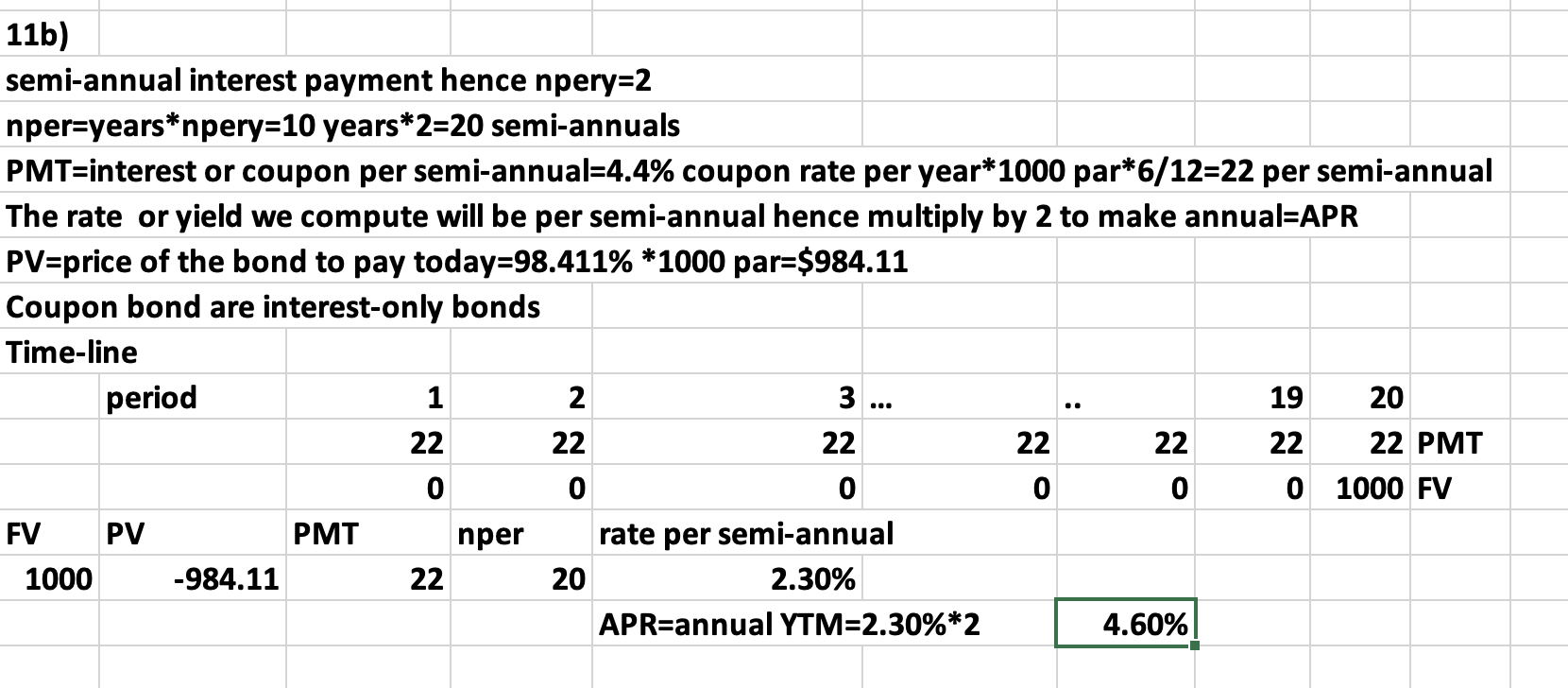
Q7: A bond with a maturity value of $1000 is currently trading at 90. The market interest rate is 6.2% compounded semi-annually. Interest payments is at 4% (coupon payments) of the par value. How many years does the bond has to maturity?
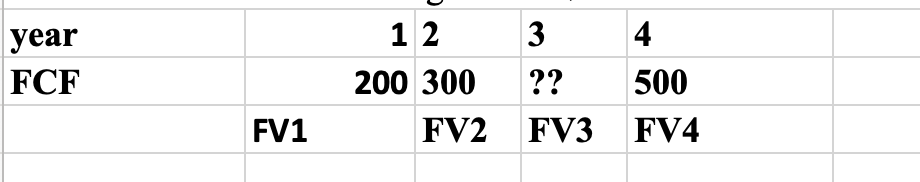
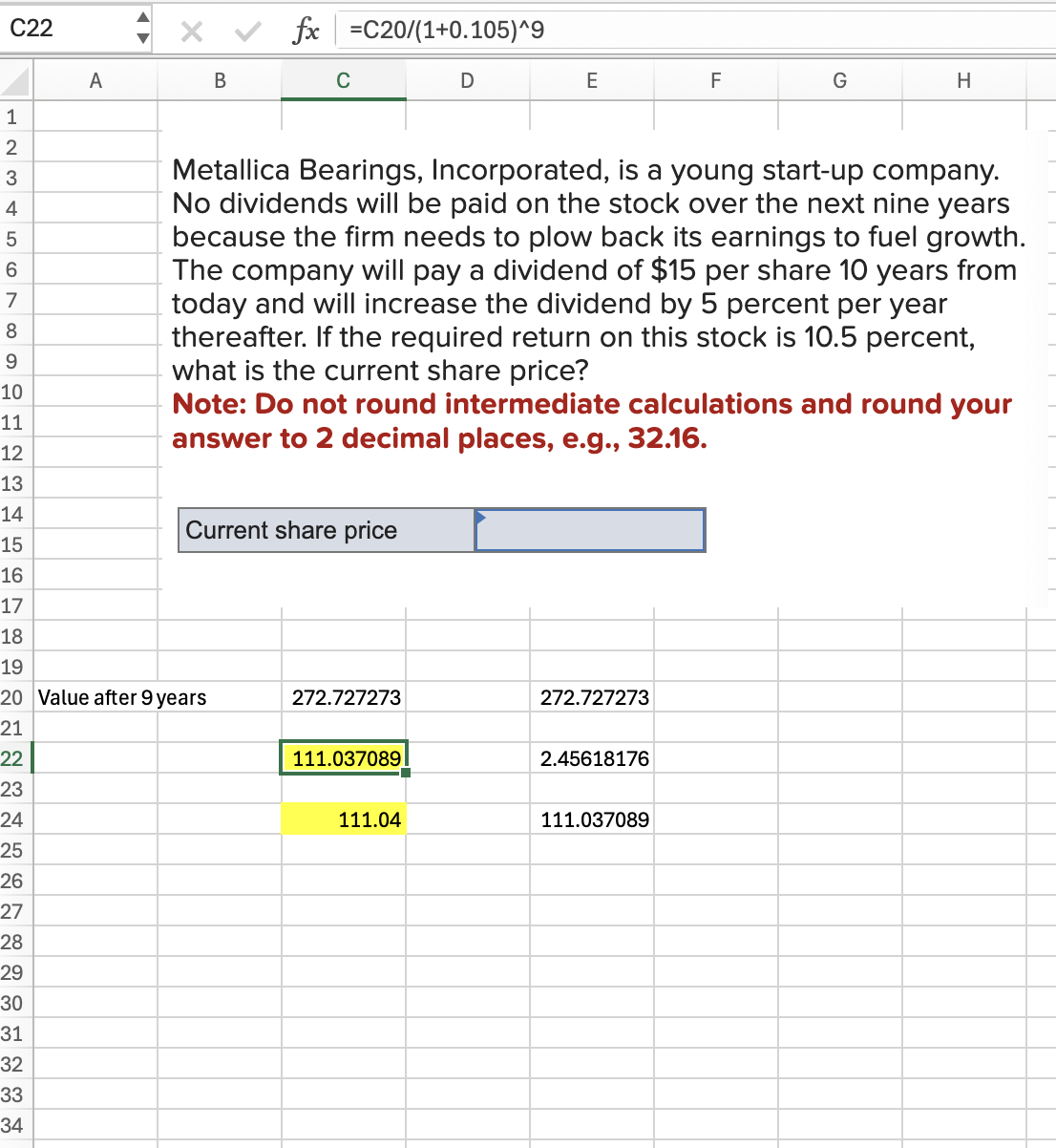
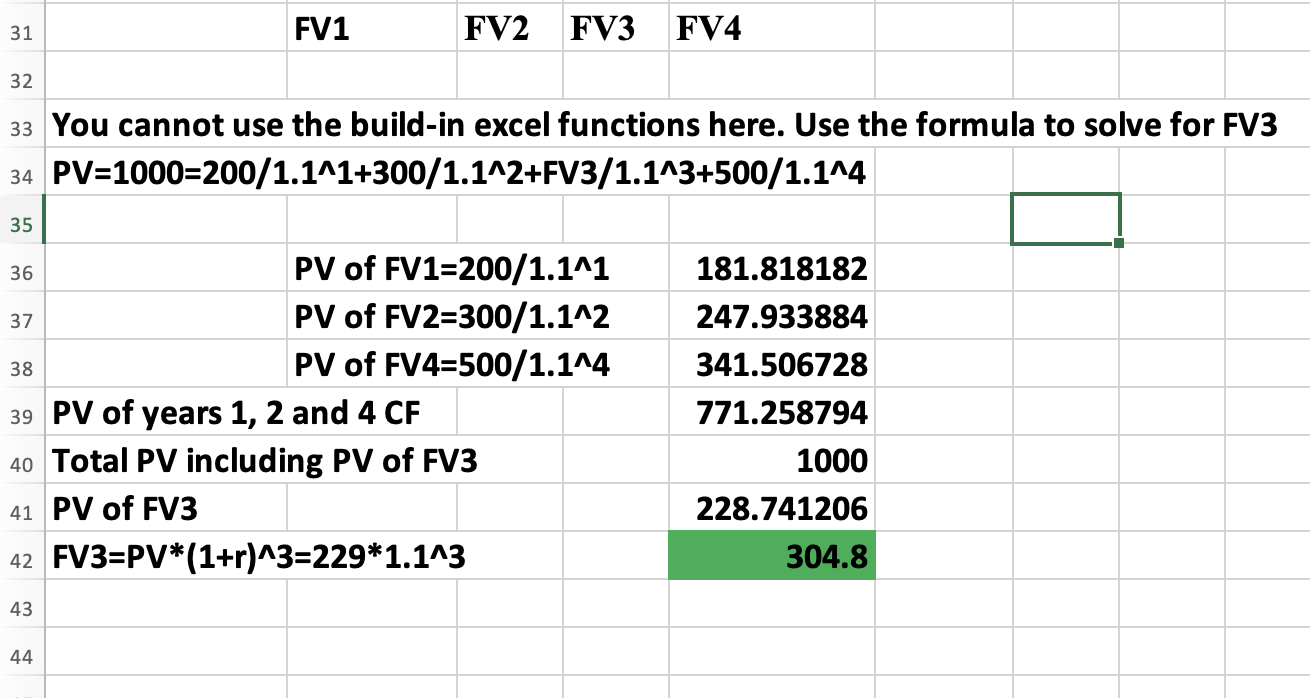
Q8: The PV of the following FCF is $1000. What is the value of the missing FCF? Assume rate=10%
304.45

Q9:
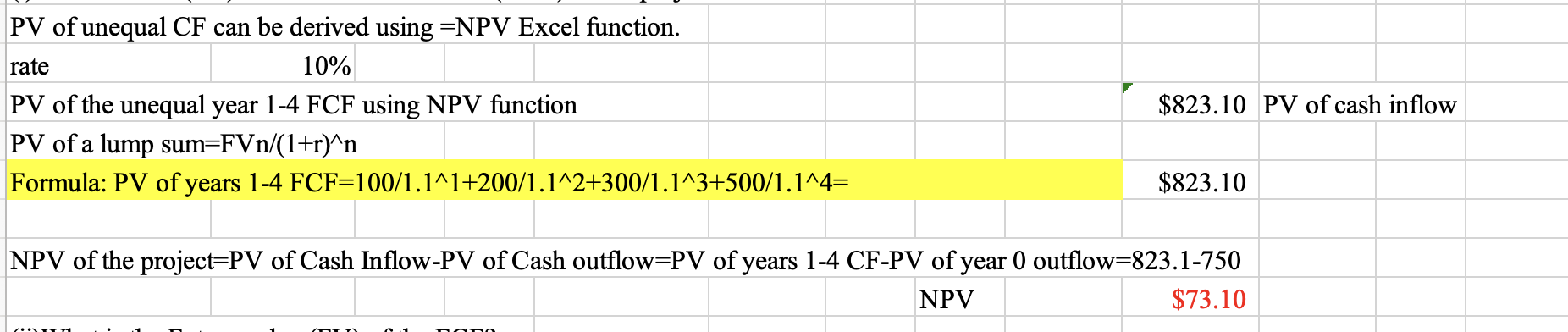
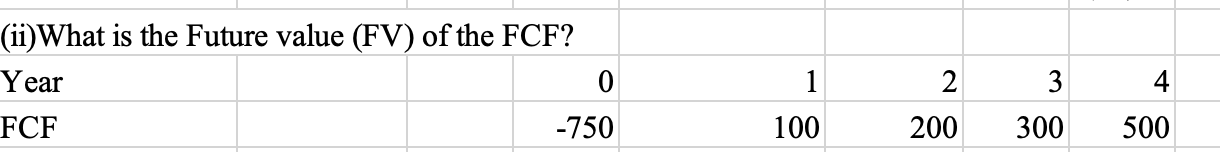
Q10:


Q11:
304.45
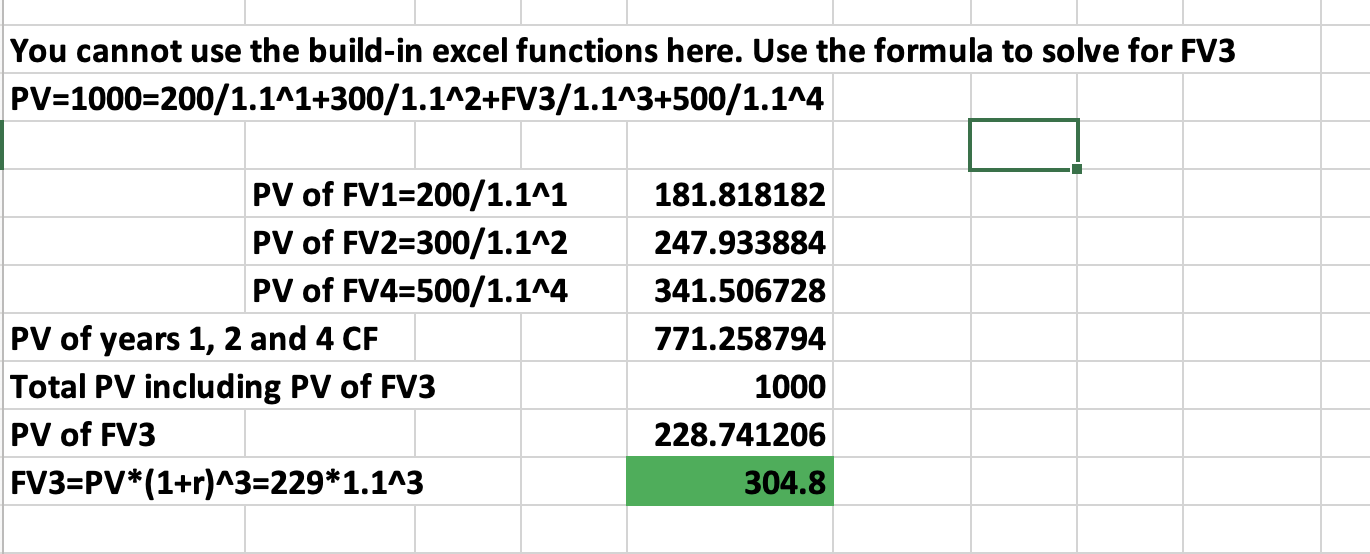
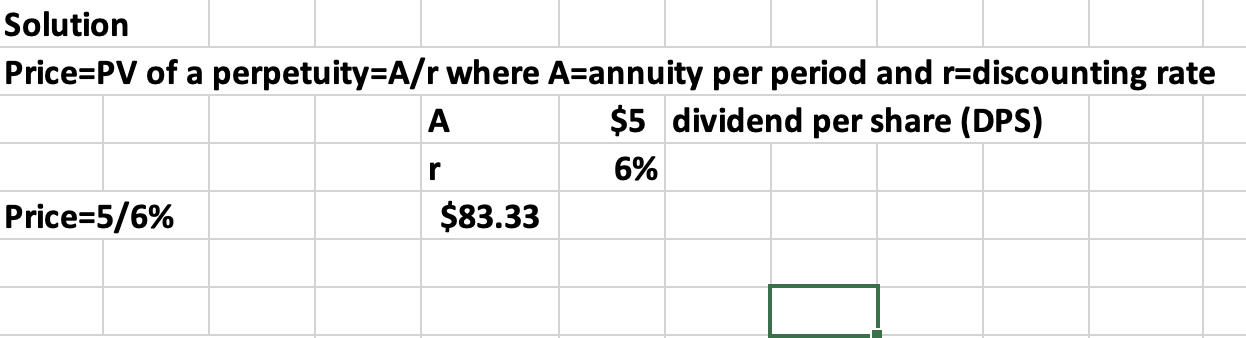
Q12: A preferred stock pays 5.00 per year indefinitely. If investors require 6% returns on their investment, what is the price (PV) of each preferred stock?
Q13: Forever Life Insurance Company is selling a perpetuity contract that pays $2,000 monthly. The contract currently sells for $250,000. Compute the monthly rate of return and APR

Q14: A firm just paid a dividend of $2.00 per share. The dividend is then expected to grow at 4% per year indefinitely. Common shareholders required rate of return is 12%. What is the current price (PV) of the stock?

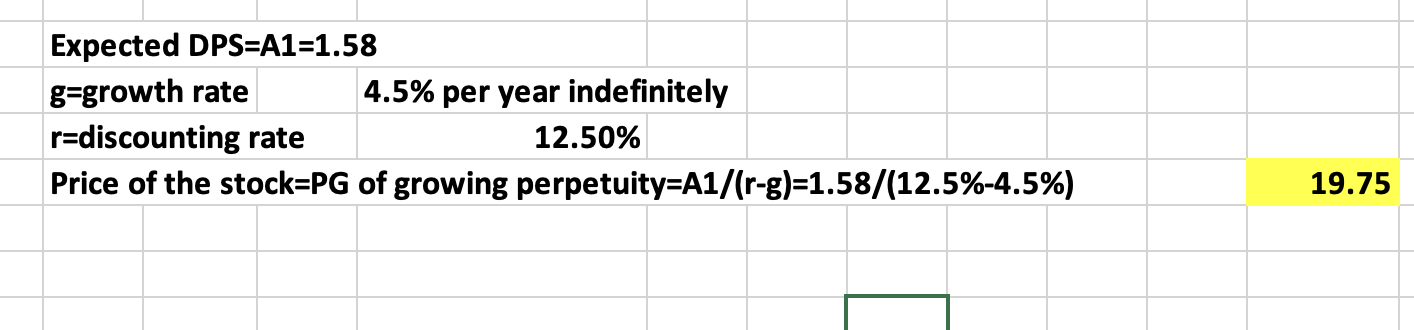
Q15: You are holding a stock of Interface Corp. The firm expects to pay you $1.58 dividend at the end of the year. The dividend is then expected to grow at 4.5% per year indefinitely. The cost of equity capital (shareholders required rate of return) is 12.5%. What is the current price of the stock?
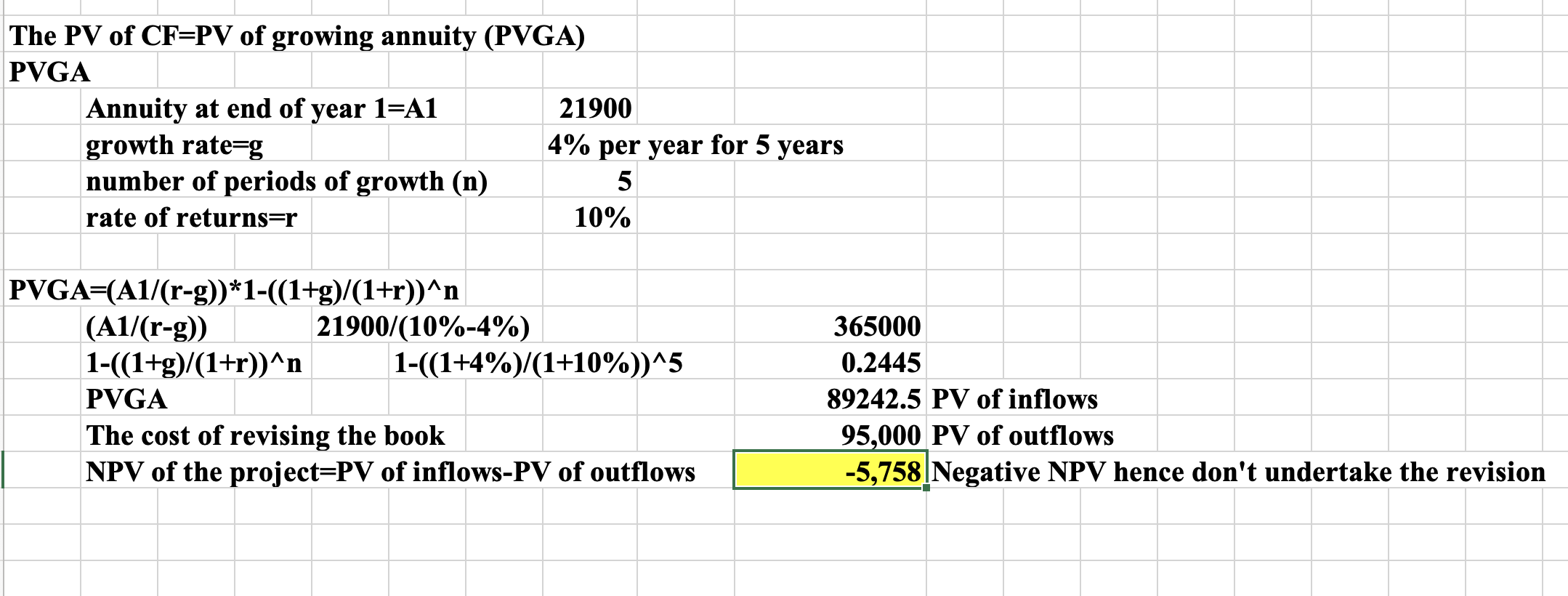
Q16: SCP is trying to decide whether to revise its popular textbook Finance Made Simple. It has estimated that the revision will cost $95,000. Cash flows (CF) from increased sales will be $21,900 the first year. These CF will increase by 4% per year. The book will go out of print five years from now. The initial cost is paid now and CFs are received at the end of each year. If the company requires a return of 10 percent for such an investment, what is the value today of the future CFs?
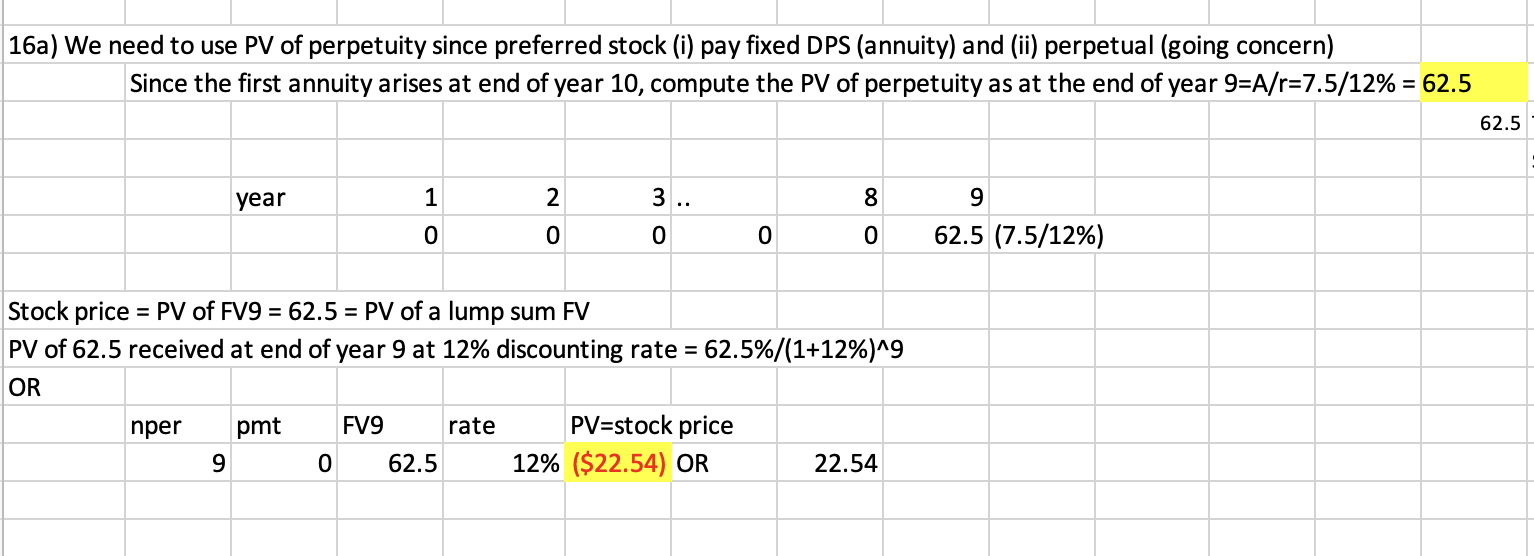
Q17: A preferred stock will pay $7.5 dividends starting 10 years from now (n=10). What is the price of the stock given 12% required rate of return?
22.54
Q18: A firm common stock just paid a dividend of $2. The dividend will increase by $4 per year for the next 4 years after which the growth rate will be 5% per year indefinitely. Given a 10% return, how much would you pay for the stock today?

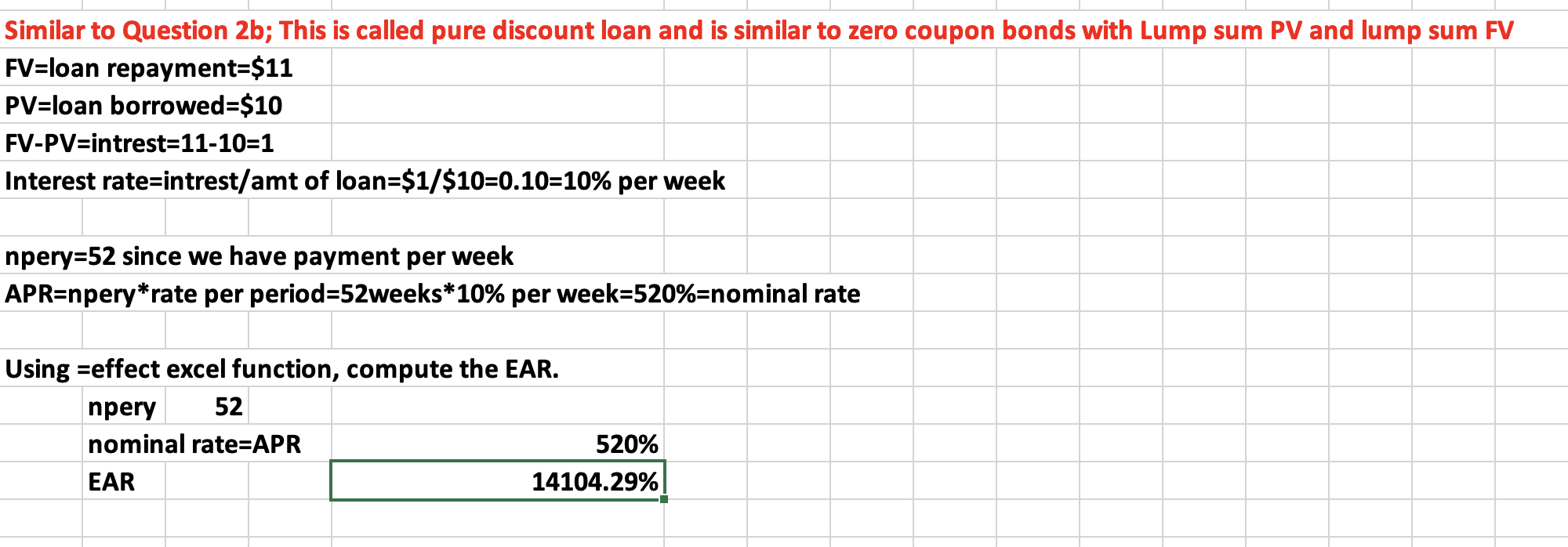
Q19: Friendly’s Quick Loans, Incorporated, offers you “ten for eleven or I knock on your door.” This means you get $10 today and repay $11 when you get your paycheck in one week (or else).
What is your periodic (weekly) interest rate?
What is your APR?
What is your EAR?
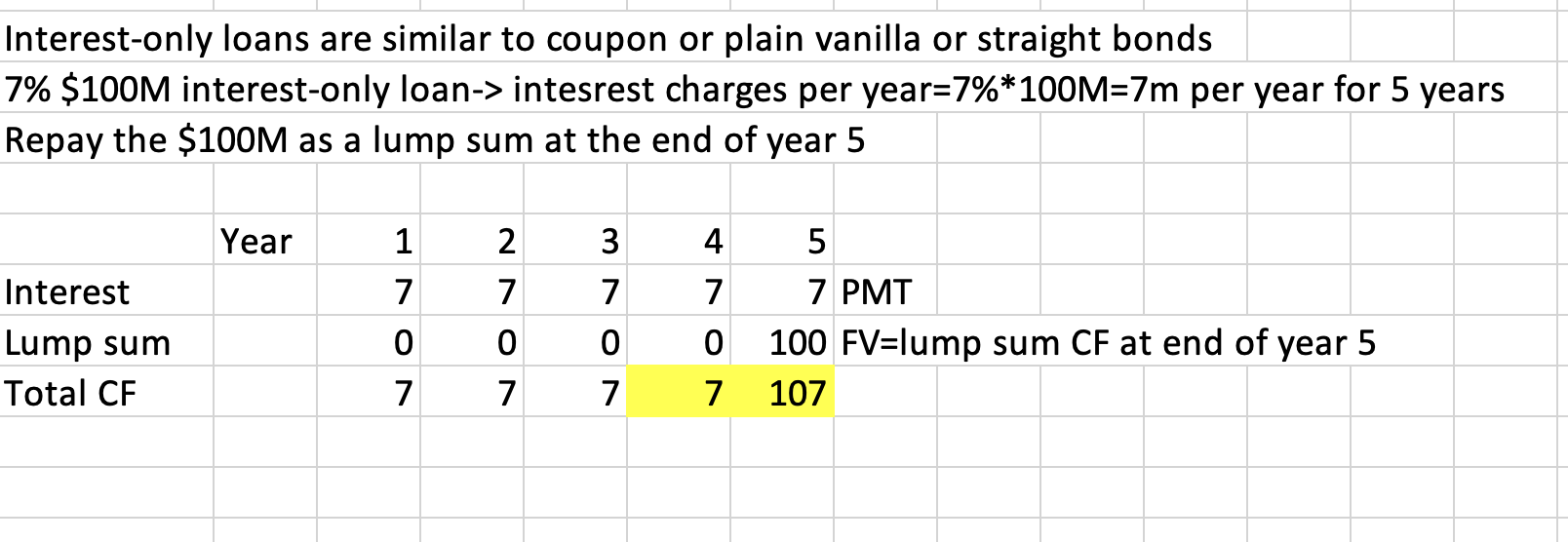
Q20: Consider a 5-year, interest-only loan with a 7% interest rate. The principal amount is $100M. Interest is paid annually. How much is payable at the end of year 4 and at the end of year 5?
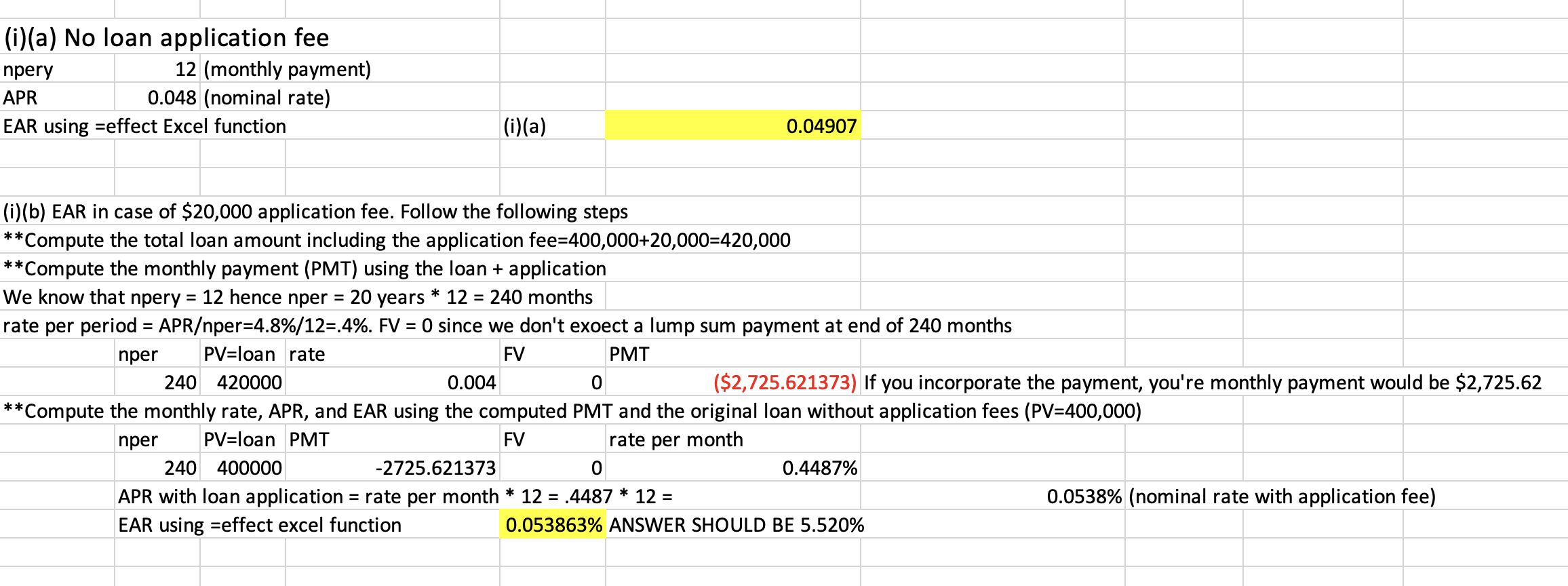
Q21: Your dad has a 20 year $400,000, 4.8% (APR) house mortgage. He makes monthly mortgage payment. What is the
(i) EAR (a) assuming no loan application fees (b) $20,000 loan application fee
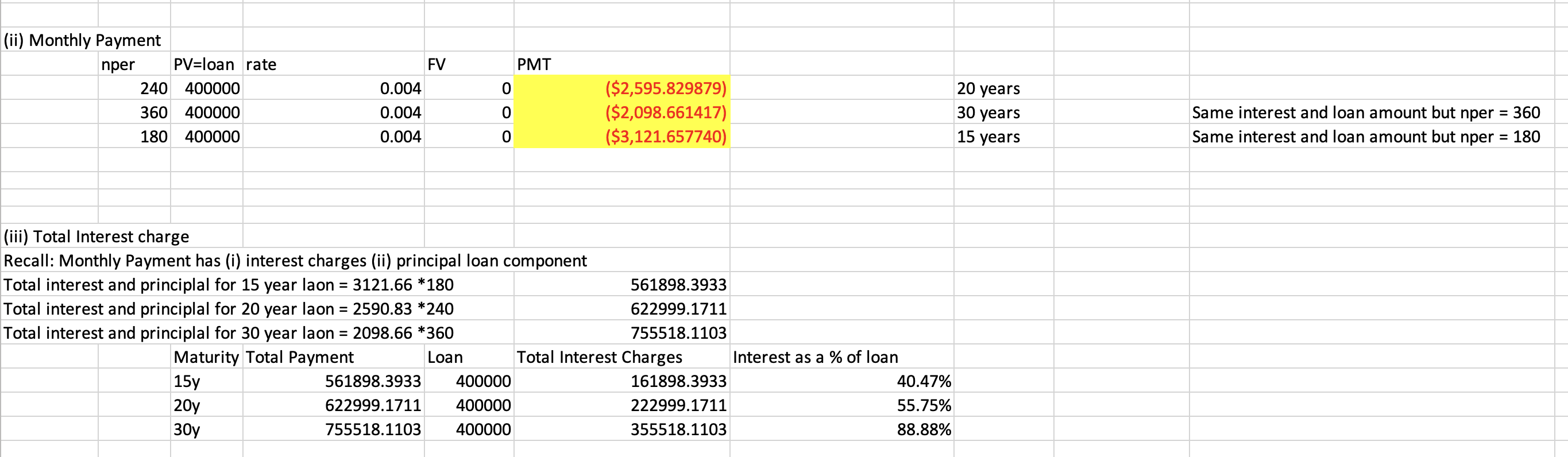
Q22: Your dad has a 20 year $400,000, 4.8% (APR) house mortgage. He makes monthly mortgage payment. What is the
(ii) Monthly payment
(iii) Total interest charges by the time the loan is repaid
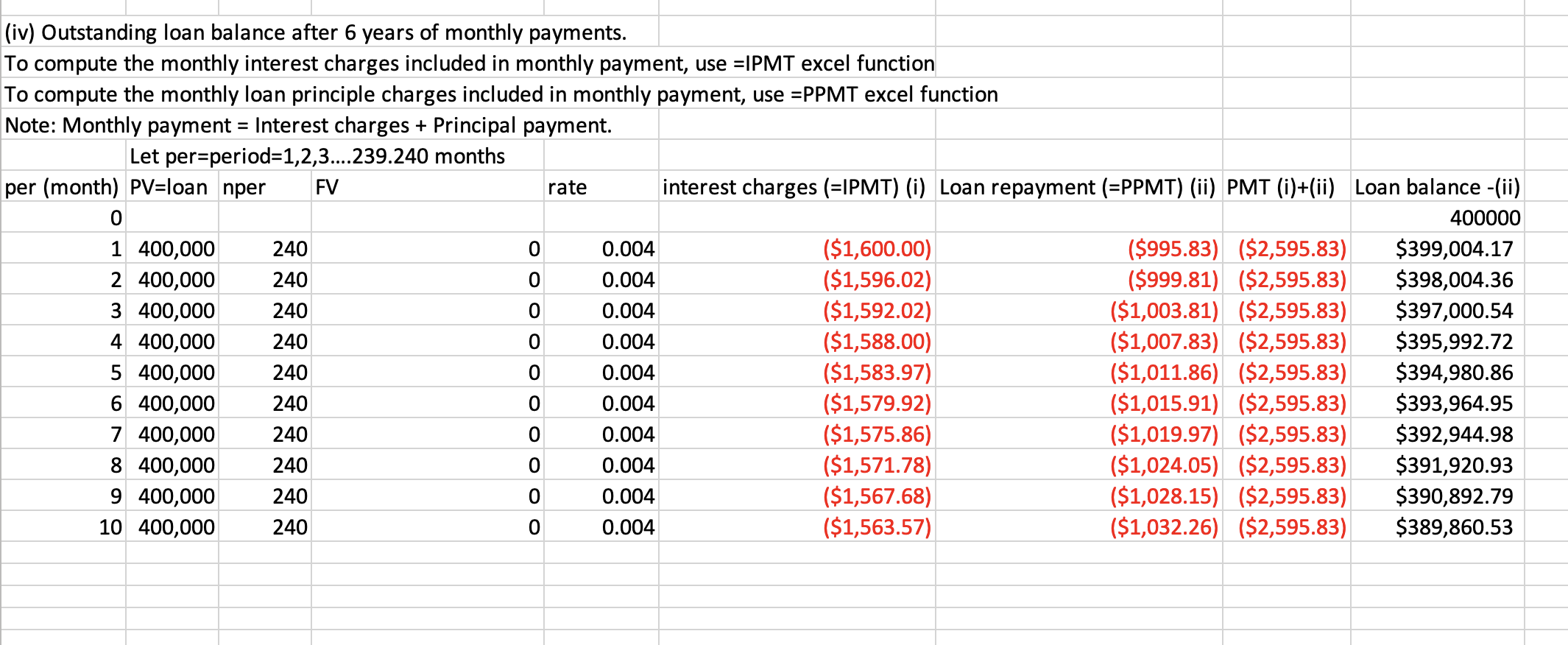
Q23: Your dad has a 20 year $400,000, 4.8% (APR) house mortgage. He makes monthly mortgage payment. What is the
(iiii) Interest charges and outstanding loan balance in the 3rd month
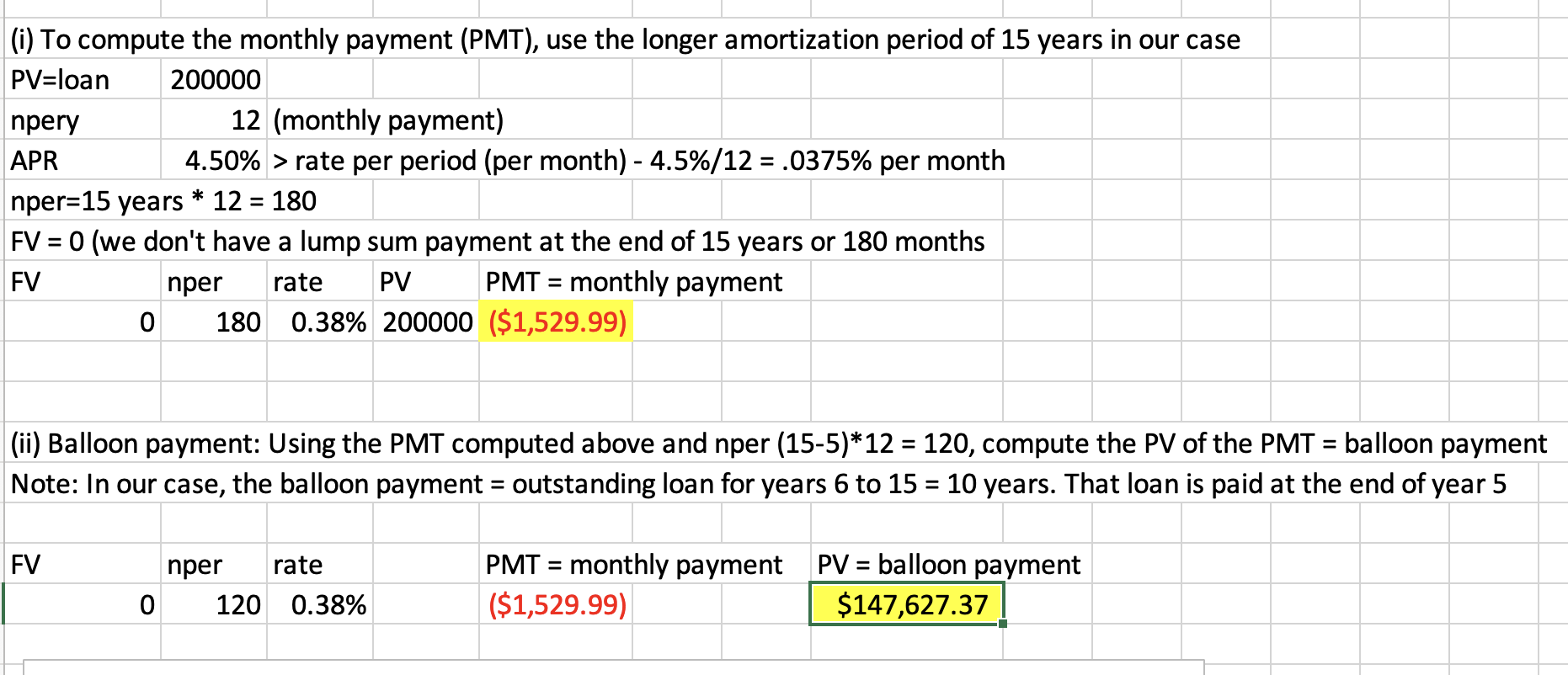
Q24: Suppose you have a 5-year balloon mortgage of $200,000 with 15-year amortization. The interest rate (APR) is 4.5%. What is the amount of:
(i)Monthly payment
(ii)Balloon payment
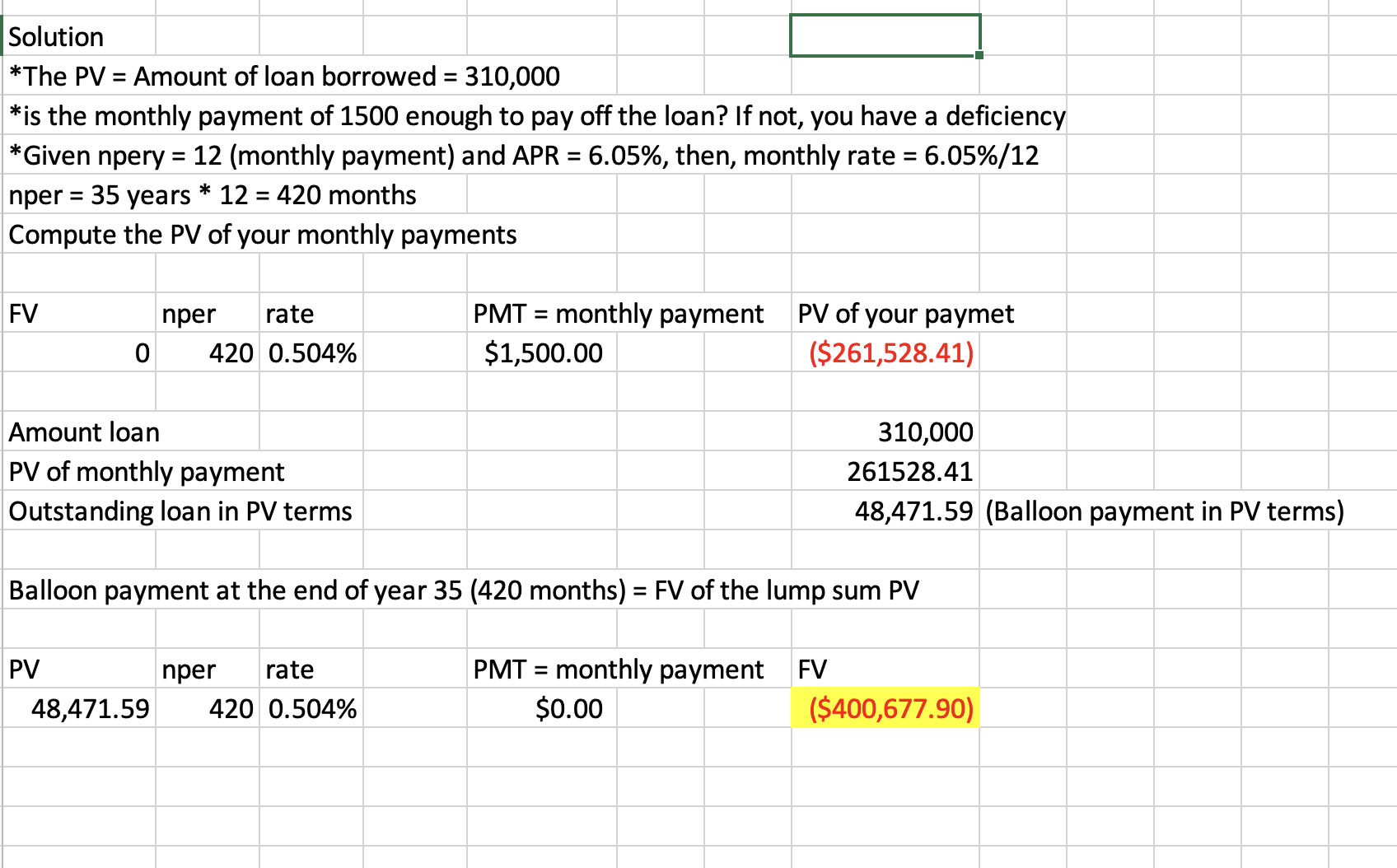
Q25: You need a 35-year, fixed-rate mortgage to buy a new home for $310,000. Your mortgage bank will lend you the money at an APR of 6.05 percent. However, you can only afford monthly payments of $1,500, so you offer to pay off any remaining loan balance at the end of the loan in the form of a single balloon payment. How large will this balloon payment have to be for you to keep your monthly payments at $1,500?
CH #9: NPV and other investment (project) appraisal criteria Conceptual Terms
CH #9: NPV and other investment (project) appraisal criteria Conceptual Terms
Capital Budgeting or Long-term investment
Involves allocating capital (financial resources)
to long-lived projects. It includes acquisitions of other firms, product lines, and subsidiaries and divestments (disposal of loss-making or high-risk projects, product lines, subsidiaries, etc.
Process of capital budgeting
-Generate alternative ideas/proposals/projects from inside and outside of the firm
-Evaluate each alternative: Gather information and evaluate the viability of each alternative ideas
-Plan the capital budget: Analyze the fit of the proposed projects with the company’s strategy
-Monitoring and post-audit: Compare expected and realized results and explain the deviations
Categories of capital projects
Replacement projects
2. Expansion projects
3. New products and services
4.Regulatory, safety, and environmental (mandated) projects
Replacement projects
Existing assets are replaced with similar assets. Example: A
manufacturing company replacing equipment on an assembly line
Expansion projects
Increase the size of the business. Example: Wal-Mart opening a new retail outlet
New products and services
These projects involve more uncertainties but higher rewards.
They require detailed analysis. Example: Apple’s initial introduction of the iPhone or Uber.
Regulatory, safety, and environmental (mandated) projects
There are generally mandatory projects, but the company may have choices on how to satisfy requirements. If sufficiently costly, shutdown is an alternative.
Issues relating to capital budgeting and value maximization
-What is the amount (size) of future cash flows?
-When will the future cash flows arise? (Timing)
-How uncertain are future cash flows? (risk)
Net present value (NPV)
An asset's current market value or price equal to the present value
of future cash flows. NPV is the market value (Total PV of future cash flows) less the capital invested (cost of acquiring the asset). NPV measures the project’s contribution to shareholders’ wealth. The increase in shareholders’ wealth is equal to NPV per share. That is why we always prefer the highest NPV projects.
Mutually Exclusive Projects
Only ONE of several potential projects can be chosen since
projects are substitutes for each other and serve similar purposes. They compete for scarce
capital resources.
Example: Should I buy a Toyota OR a Ford? You can’t buy both since they serve the same purpose
Independent Projects
These projects serve different purposes. Accepting or rejecting one project does not affect the decision on the other projects. Therefore, all viable projects can be accepted subject to
availability of capital (assuming there is no capital rationing). This requires establishing a MINIMUM acceptance criterion for all projects.
Examples: Concurrent construction of a new business school building and football stadium
What are the various project appraisal methods?
Net Present Value (NPV)
The Profitability Index (PI) or Benefit-cost ratio
The Payback Period (PBP) Method
Discounted Payback Period (DPBP)
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The Average Accounting Rate of Return (AAR)
NPV Appraisal Method
The total PV of future cash flows is less than the initial cost or
capital. NPV is the estimate of how much the firm's value and shareholders’ wealth change with the project's adoption. It estimates the value added (destroyed) if the NPV is positive (negative)
Decision Criteria:
-For a single (stand-alone) project, accept if NPV>0 (increases wealth); otherwise, reject.
-For mutually exclusive projects, accept the one with a higher NPV
NPV=PV of cash inflows-PV of cash outflows
Advantages & Disadvantages of NPV Appraisal Method
Advantages of NPV: See the features of a good project appraisal method or investment
rules.
The NPV method is always superior to all other rules or project appraisal methods
The Profitability Index (PI) or Benefit-cost ratio Appraisal Method
Decision Criteria:
-For independent projects, Accept a project if PI>1 (NPV>0). Reject if PI<1 (NPV<0)
-For mutually exclusive projects, accept the project with a higher PI
-If there is a conflict between NPV and PI in ranking mutually exclusive projects, NPV ranking
prevails. Why? It is consistent with shareholder value maximization.

PI Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
• Most helpful when available investment funds are limited (capital rationing)
• Easy to understand and communicate to investors and managers (bang for dollars)
• Correct decision when evaluating independent projects
Disadvantage:
• It ignores the size or scale of the project.
Payback Period (PBP) Appraisal Method
PBP shows the number of periods (years) it takes to
recover or recoup the initial capital invested in a project from non-discounted cumulative cash
flows. The shorter the PBP, the better since receiving cash as early as possible improves the
firm's liquidity.
Decision Criteria: For mutually exclusive projects, accept the one with a shorter PBP
PBP Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
Simple to use and still popular with large firms making small decisions (such as
investment in a small warehouse, paying a tune-up for a truck, etc.) at the tactical levelBias for short PBP promotes the firm’s liquidity (alleviates the firm’s liquidity problems )
Disadvantages:
No discounting of cash flows (ignores the time value of money). It assumes the FCFs before the cutoff are discounted at a zero discounting rate (WACC=0).
Does not use all cash flows of the project (ignores cash flows after PBP)
Bias toward short-term (liquid) projects with shorter PBP (The firm is a going concern)
Discounted Payback Period (DPBP) Appraisal Method
This is similar to PBP, but it uses discounted
cash flows (PV of cash flows) to compute PBP. DPBP is the number of periods (years) it takes to
recover the project’s initial capital outlay from the accumulated discounted cash flows. The
shorter the DPBP, the better the project.
Decision Criteria: For mutually exclusive projects, accept the one with the shortest DPBP
DPBP Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
Simple to use and communicate, just like the PBP
The time value of money is accounted for
If the project pays back on a discounted basis, it has a positive NPV (assuming no large
negative cash flows after the cut-off period).Disadvantages:
Ignores cash flows beyond the payback period
No decision criteria other than whether a project pays back (The arbitrary cut-off DPBP may eliminate projects that would increase firm value)
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Appraisal Method
IRR is the discounting rate that equates NPV to zero.
IRR is the expected compound return when all intervening cash flows in the project can be reinvested at the IRR, and the investment will be held until maturity. It is similar to the yield to
maturity (YTM) of the bond
Decision Criteria:
For a single project, accept if the IRR>discounting rate; otherwise, reject.
For mutually exclusive projects, accept the project with a higher IRR.
IRR Advantages & Disadvantages
Advantages:
-Easy to understand (Involves computation of the project’s rate of return)
-Considers the time value of money
-Considers all project’s cash flows
Disadvantages:
General problems affecting the ranking of independent and mutually exclusive projects.
These are
a) Investing or financing problem
b) Multiple IRR problems due to non-conventional cash flows
2) Problems specific to the ranking of mutually exclusive projects. These are
c) Scale or size problems
d) Cash flow timing problem
IRR financing or investing problem
Investing projects start with cash outflow in period 0, followed by cash inflows in subsequent
periods. (Pay out money and then receive money). In this case, accept the project when
IRR>discounting rate.Financing projects start with cash inflow in period 0, followed by cash outflows in subsequent
periods. In this case, accept the project when IRR<discounting rate. (Receive and then pay out
money