Chapter 25 (6.1.1) Aromatic compounds
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
properties of benzene
colourless
sweet smelling
highly flammable
liquid
found naturally in crude oil and cigarette smoke
carcinogen
evidence to disprove Kekule’s model
1) lack of reactivity of benzene. does not undergo electrophilic addition reactions, does not decolourise bromine under normal conditions
2) the lengths of the c-c bonds. the lengths of the c-c bonds in benzene were between the lengths of a single and a double bond
3) hydrogenation enthalpies. was expected to have an enthalpy change of hydrogen 3x that of cyclohexene but had a lower enthalpy change instead. actual structure of benzene is more stable than the Kekule model
main features of delocalised model of benzene
planar, cyclic, hexagonal hydrocarbon
each C atom has one electron in a p-orbital at right angles to the plane of the bonded C and H atoms
adjacent p-orbital electrons overlap sideways to form a ring of electron density = system of pi-bonds
6 delocalised electrons
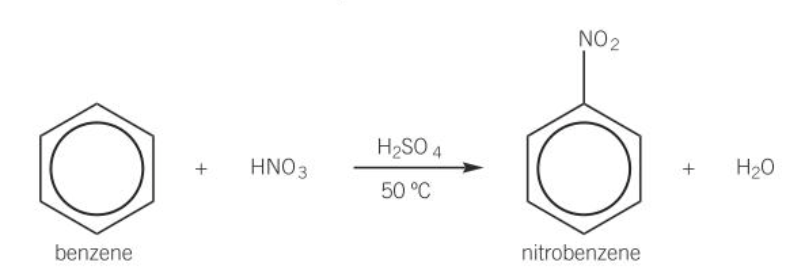
nitration of benzene
benzene + HNO3 = nitrobenzene + H2O
H2SO4 catalyst
50°C
electrophilic addition
diagram of nitration of benzene
uses of nitrobenzene
preparation of dyes, pharmaceuticals, pesticides
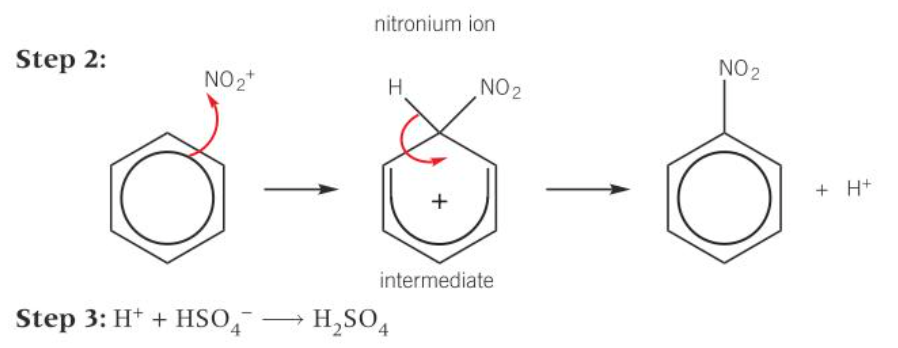
mechanism for nitration of benzene
1) HNO3 + H2SO4 = NO2+ + HSO4- + H2O
2) benzene = unstable intermediate = nitrobenzene + H+
3) H+ + HSO4- = H2SO4
diagram of mechanism for nitration of benzene
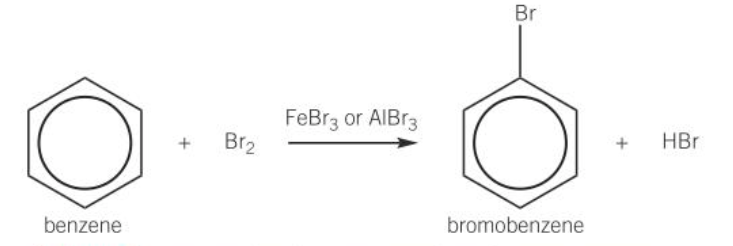
examples of halogen carriers
AlCl3, FeCl3, AlBr3, FeBr3
diagram of bromination of benzene
mechanism for bromination of benzene
1) Br2 + FeBr3 = FeBr4- + Br+
2) Br++ benzene = unstable intermediate = bromobenzene + H+
3) H+ + FeBr4- = FeBr3 + HBr
diagram of mechanism for bromination of benzene
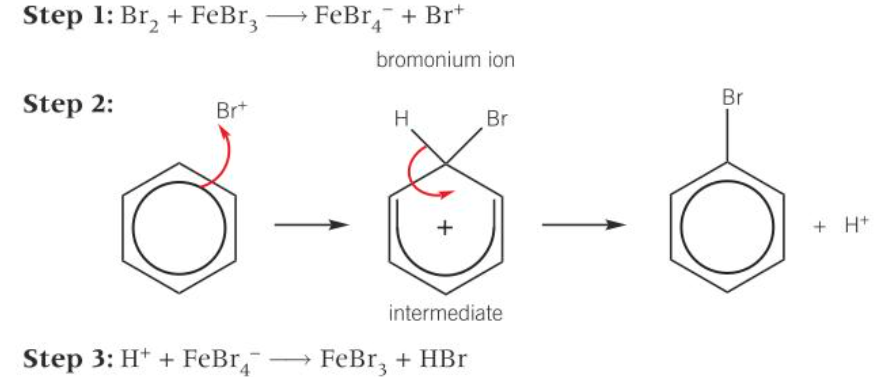
diagram of alkylation of benzene
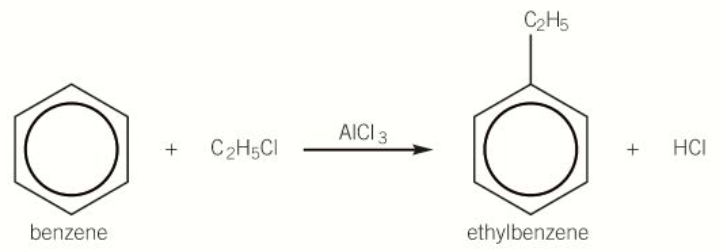
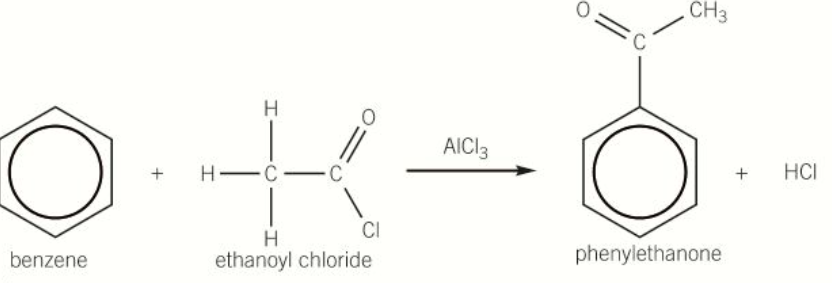
diagram of acylation of benzene
why does benzene not react with bromine unless a halogen carrier catalyst is present
1) benzene has delocalised pi-electrons spread above and below the plane of C atoms in the ring structure
2) electron density around any two C atoms in benzene ring is less than that in a C=C in an alkene
3) there is insufficient pi-electron density around any C atoms in polarise the Br
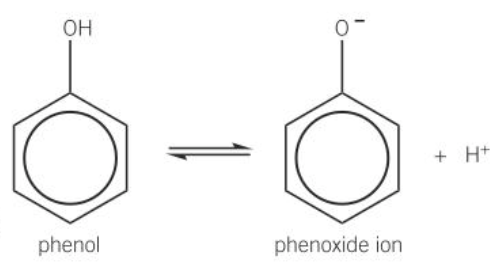
why are phenols classified as weak acids
phenol is less soluble in water due to the presence of the non-polar benzene ring
when dissolved in water phenol partially dissociates a phenoxide ion and a proton
diagram of partial dissociation of phenol
comparing acid dissociation of alcohols with phenols and carboxylic acids
ethanol does not react with NaOH (strong base) or Na2CO3 (weak base)
phenols and carboxylic acids react with solution of strong bases
only carboxylic acids are strong enough acids to react with Na2CO3
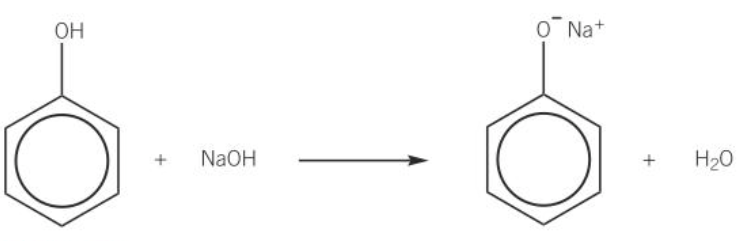
how to distinguish between a phenol and a carboxylic acid
Na2CO3 + carboxylic acid produces CO2(g)
diagram of reaction of phenol with NaOH (aq)
bromination of phenol
phenol + 3Br2 = 2,4,6-tribromophenol + 3HBr
white precipitate formed
decolourises bromine water (orange = colourless)
RTP
nitration of phenol
phenol + HNO3 = 2-nitrophenol + 4-nitrophenol
RTP
why is phenol more reactive than benzene
lone pair of electrons from the oxygen p-orbital of the -OH group being donated into the pi-system of phenol
the electron density of the benzene ring in phenol is increased
the increased electron density attracts electrophiles more strongly than with benzene
activation with benzene
-NH2 in nitrobenzene activates the benzene ring as the ring reacts more readily with electrophiles
positions 2 or 4
deactivation with benzene
-NO2 deactivates the benzene ring as the ring reacts less readily with electrophile
position 3
ortho
position 2
meta
position 3
para
position 4
examples of 2- and 4- directing groups
-NH2 or -NHR, -OH, -OR, -R or C6H5, -X
examples of 3- directing groups
RCOR, -COOR, -SO3H, -CHO, -COOH, -CN, -NO2, -NR3+