Microbial dynamics
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Define microbial dynamics
Microbial dynamics: Study microbial population changes and interactions including how microbes grow, reproduce,die and interact with each other and their environment over time and space.
Meaning of growth
Growth
Def: orderly increase in sum of all components of organism
Cell x is consequences of growth.
In unicellular organisms growth leads to increase number of individuals making population or culture
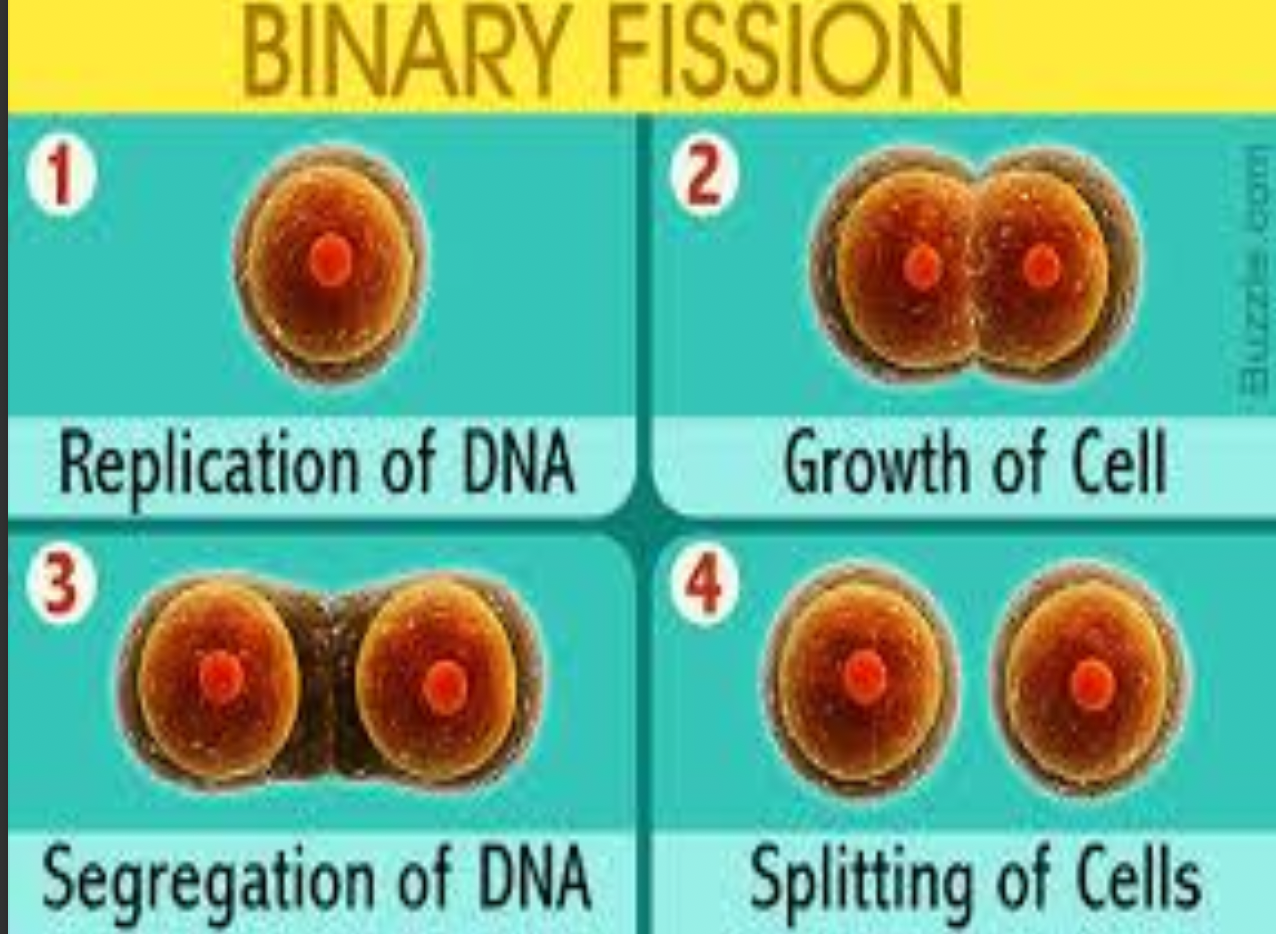
Describe bacterial reproduction by binary fission (mitosis)
Binary fission steps
Nuclear material divides
Transverse septum originates from plasma memb and cell wall divides cell into 2 parts
2 daughter cells receive identical set of chromosome
Daughter cells separate and may be arranged singly, pair, clumps or chains
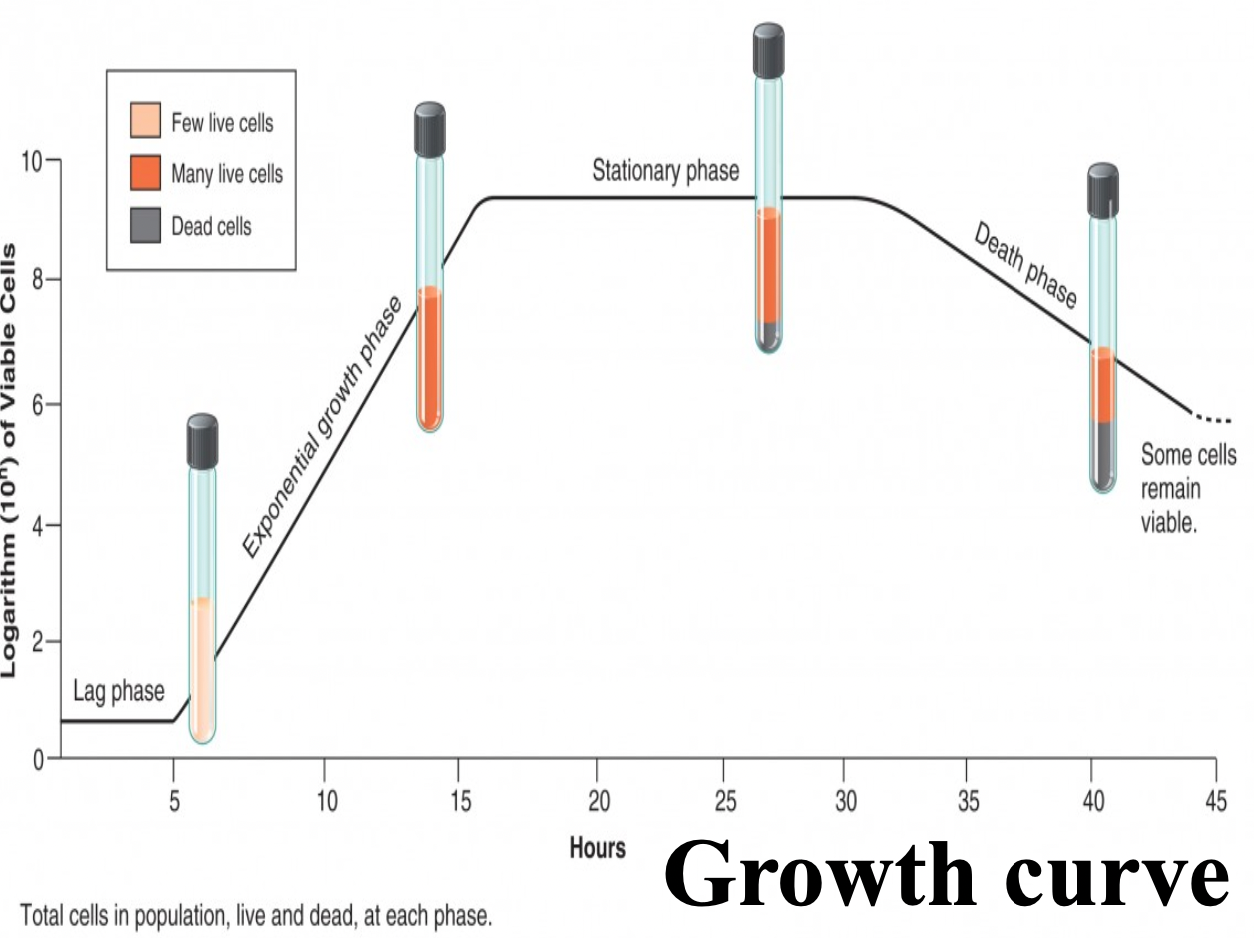
Growth curve : Def , the 4 growth phases and total count vs viable count
Growth curve: Growth curve indicates multiplication and death of bacteria
Bacteria passes through 4 phases : Lag, Log, Max stationary , Decline/ Death phase
Bacterial count is used in examination of water and milk
Total count vs viable count…
Total count = Living + Dead bacteria
Viable count = Living only
Growth phase : Lag Phase features
Increase in cell size but not multiplication
Enzymes formed and accumulate until present in concentration that permits growth to start
Antibiotic have little effect at this stage (it targets enzyme not growth)
Growth phase : Logarithmic (Log) Phase features
Cells multiply at max rate by binary fission division
Continues till…
1 or more nutrient in medium become exhausted
Toxic metabolic products accumulate and inhibit growth
Nutrient oxygen becomes limited for aerobic organisms
Antibiotics act better at this stage → kill bacteria, stop bacteria x
Growth phase : Maximal stationary phase features
Due to nutrient exhaustion or toxic products accumulation death of bacteria starts and growth cease completely
Count remains stationary as multiplication rate = death rate
Importance: Production of exotoxins (alive bacteria), antibiotics, metachromatic granules and spore formation take place in this phase
Growth phase : Decline/Death phase features
In this phase progressive cell death
However some living bacteria use product breakdown of dead bacteria as nutrient and remain
Maintenance of cells in the exponential phase
Cells can be maintained in exponential phase by transferring them repeatedly into fresh medium of identical composition while they are still growing exponentially → called continuous culture