Bio 1 Midterm
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
How do heterotrophs get the energy they need?
by breaking down food molecules gradually and capturing their chemical energy
What starts the whole photosynthesis reaction?
Light hitting photosystem 1
Which structure in the figure represents a single thylakoid?
Structure C
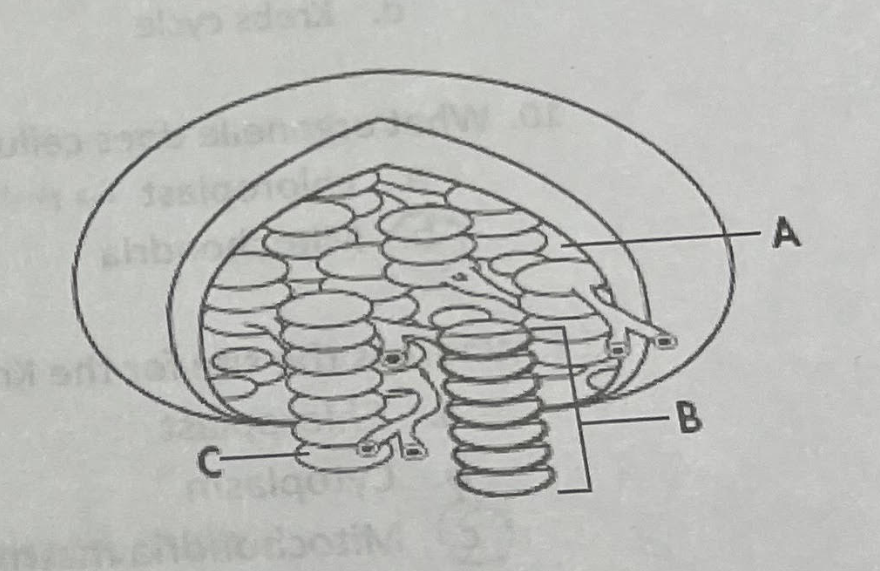
Which structure in the figure represents stroma
Structure A
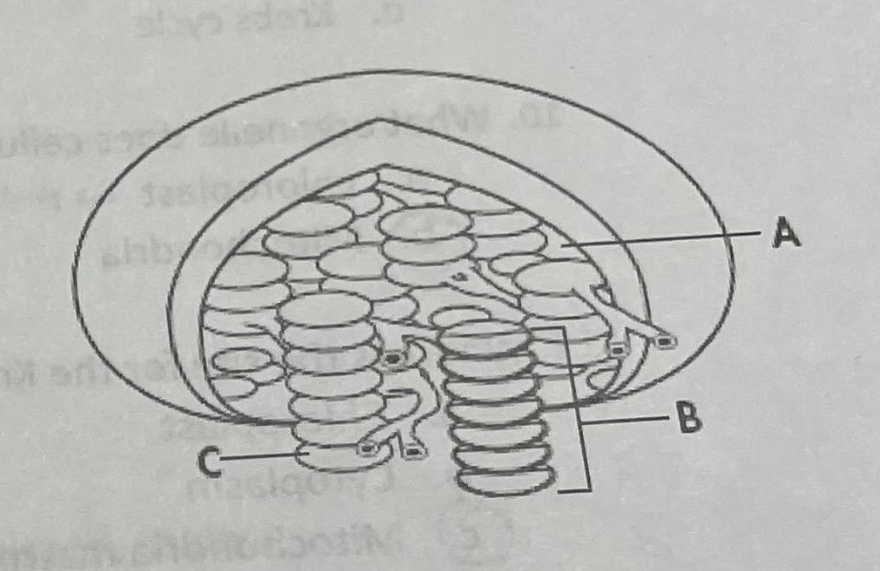
Which organelle does photosynthesis occur in?
Chloroplast
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into?
Oxygen and glucose
Light-dependent reactions take place in the ___ while the-independent reaction takes place in the ___ ?
Thylakoid membrane, stroma
In the calvin cycle one of the products is a 3 carbon molecule. What is that called?
Glucose
Which of the following is NOT a stage of cellular respiration?
Calvin Cycle
What organelle does cellular respiration occur in?
Mitochondria
Where is the site for the Krebs cycle?
Mitochondria Matrix
Where is the site for the electron transport chain?
Inner mitochondria matrix
Which of these are a product of cellular respiration?
Water
Glycolysis provides a cell with a net gain of
2 ATP molecules
The molecule that starts the Glycolysis reaction?
Glucose
Cellular Respiration in the presence of oxygen is called
aerobic respiration
The chemical formula of cellular respiration is?
C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 --> 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + ATP
The krebs cycle starts with
Pyruvic acid and yields carbon dioxide
If oxygen is NOT present, glycolysis is followed by
Fermentation
At the end of cellular respiration approximately ____ ATP are produced
38 ATP molecules
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in cellular respiration in the presence of oxygen?
Glycolysis → Krebs Cycle → Electron Transport
Lactic acid fermentation occurs in ___ cells and produces ___.
Humans, lactic acid and NAD+
Alcoholic fermentation occurs in ___ cells and produces ___.
Yeast; alcohol, CO2 and NAD+
How many phosphates does ATP have?
3 phosphates
How many phosphates does ADP have?
2 phosphates
What’s the name of this process?
Cellular Respiration
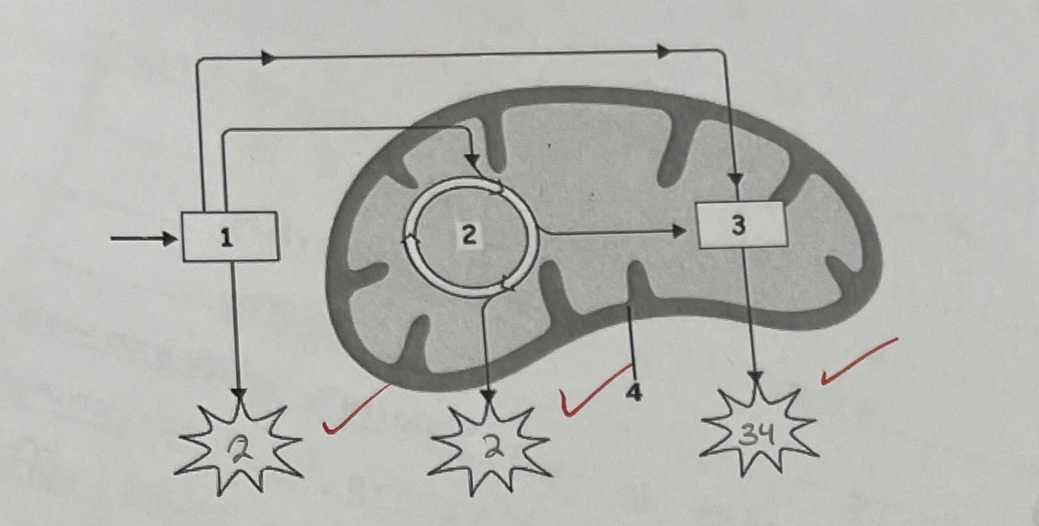
What are the 3 steps, and where do they occur?
Glycolysis → Cytoplasm
Krebs Cycle → Thylakoid Membrane
ETC → Inner Membrane
Compare and contrast dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis.
Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis are different because dehydration synthesis removes water while hydrolysis adds it. Both of these rxns are caused by enzymes.
The ____ lactase, works specifically on the ____ lactose.
Enzyme, sugar
Which of the following is true of DNA molecules?
They are the instructions for proteins and traits
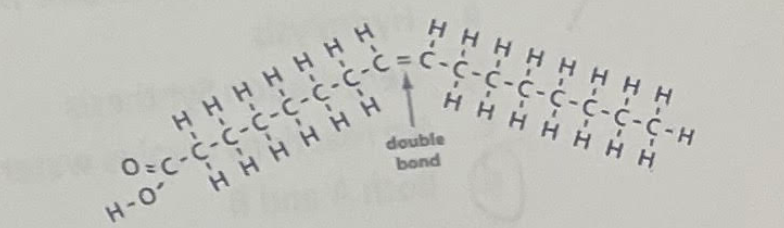
Which molecule is pictured?
Unsaturated fatty acid
Which macromolecule is used as a primary source of quick energy?
Carbohydrates
Which macromolecule is the main component of cell membranes?
Lipids
Which of the following is an example of a carbohydrate?
Glucose
Amino acid is to protein as -
Monosaccharide is to carbohydrate
Which two molecules are made only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen?
Lipids and carbohydrates
Lysosome
Digests food
Nucleolus
Makes ribosomes
Nuclear Membrane
Controls what enters and exits the nucleus
Vacuole
Stores food, water and waste
Cytoskeleton
Network of proteins that supports the cell’s shape
Golgi Apparatus
Processes and packages proteins and lipids
Ribosome
Makes proteins
Chloroplast
Carries out photosynthesis
Mitochondria
Responsible for making energy; site of cellular respiration
What is the function of the Smooth ER?
To make lipids and remove toxins
What is the function of a microtubule?
Helps to move chromosomes during cell division
What two organelles are most needed for a protein to be made and then packaged?
Rough ER and Golgi Apparatus
What two organelles are most needed for a cell to make energy?
Lysosome and Mitochondria
What two organelles are most needed for the cell to protect itself from bad bacteria?
Cell Membrane and Lysosome
What is the relationship between the nucleus and the ribosomes?
The ribosome was made in the nucleus
What is the relationship between the Golgi Apparatus and a vesicle?
The golgi body sends different nutrients in the vesicle
Which of the following is an example of an Atom?
Carbon
The smallest basic unit of matter is?
Atom
The reason plants are able to bring water molecules to the tops of trees is because the water molecules can stick to the sides of the xylem. What property of water is this describing?
Adhesion
Which of the following is an example of a compound?
Water
In a solution, the salit is considered a ____ and the water is considered a ____
Solute; Solvent
The reason that water molecules are able to stay together on the hood of a car is due to?
Cohesion
The bonds that occur between two different water molecules that keep them together are called ___
Hydrogen bonds
The chemical reaction that represents photosynthesis is 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2. What are the reactants?
H2O and CO2
What are the products of: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2?
C6H12O6 and O2
An organic compound always contains
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen
In a complete molecule, each unit is called a ___ and when they are linked together they become a ___ .
Monomer, Polymer
Hydrolysis is the process by which
Sugar molecules can be bonded together, by removing water
When two amino acids are bonded together through dehydration synthesis, ____ .
Water is removed
A polysaccharide consists of
A chain of many repeating sugars
Bears will eat large quantities of food prior to hibernation. What macromolecule will store this energy throughout the winter?
Lipids
The head of a phospholipid is ___; whereas the tail of a phospholipid is ___ .
Hydrophilic ; Hydrophobic
True or False: A protein is not a monomer.
True
What is the function of a nucleic acid
Code for building proteins
What can alter the function of a working enzyme?
Lowering the pH and increasing the body temperature
Chemical reactions that involve water are called:
Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis
Substances are changed into different substances when bonds break and form during a ____ .
Chemical Reaction
What macromolecules are the following foods part of: Eggs, seeds, and chicken.
Protein
What are all the parts of a nucleotide?
Has a Nitrogenous base, phosphate group, and is a 5 carbon sugar.
Both animal fats and plant oils are made up of glycerol and ___.
Fatty acids
There are ____ different amino acids, the human body produces ___ of them on its own.
20 , 12
The main difference between a polypeptide and a protein is that
A polypeptide has under 50 amino acids and a protein has over 50 amino acids
A disaccharide consists of two ___ .
Sugars
Which aspect of a chemical reaction is affected by enzymes?
Speed
Enzymes that help with digestion fall under what category?
Proteins
The bonds that occur between two amino acids that keep them together are called _______.
Peptide Bonds
If a protein is changed due to heat or pH this is called _______ .
Denaturation
The specific reactant that an enzyme acts on and connects with is called the _______.
Substrate
Any enzyme can work for any reaction?
False
An enzyme can only bring in one substrate at a time to break it down and not two.
True
Proteins -
CHON, Makes up enzymes
Carbohydrates -
Has the monomer of a monosaccharide
Lipids -
Responsible for insulation in animals
Nucleic Acids -
CHONP, Has the monomer of nucleotides
Enzymes -
Speeds up reactions
What are the 4 main classes of macromolecules, and their functions?
Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides; giving short term energy
Lipids - Glycerol/Fatty Acid; waterproof membranes
Proteins - Amino Acids; Control cell division + metabolism
Nucleic Acids - Nucleotides; Store information
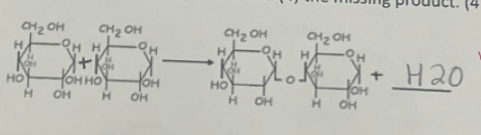
What is the name of this diagram, its importance, and what is happening in it? Pt.1
Dehydration Synthesis; It is important because it is joining two monomers to make a polymer and it’s molecule is the carbohydrate.
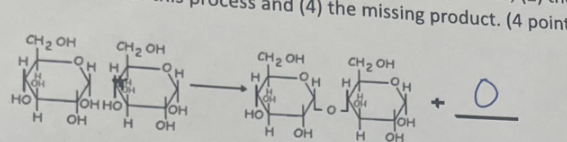
What is the name of this diagram, its importance, and what is happening in it? Pt.2
Hydrolysis; It’s importance is to add water. The biomolecules are Hydrogen, Carbon, and Hydrogen.
It is the night before a soccer game. What is the main biomolecule that you are going to want to eat and why?
Carbohydrates, because it gives you short term energy. So eat pasta.
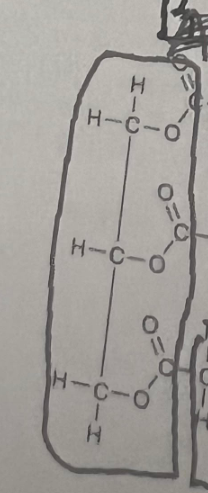
What molecule is shown in the diagram?
Glycerol Molecule
What elements are in Carbohydrates?
Carbon only
What elements are in Lipids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
Bears will eat large quantities of food prior to hibernation. What macromolecules will store this energy throughout the winer?
Nucleic Acids
What macromolecule surrounds the cell, serving as a layer of protection for the cell?
Lipids