11-Thermodynamics Terms & Definitions
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
how can you calculate change in Energy? (delta E)
delta E = work (w) + heat (q)
*w and q are NOT state functions and DO depend on the pathway, not just the final and initial states
what are the three laws of thermodynamics?
Law 1: Conservation of Energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed, but only converted from one form to another
Law 2:
The entropy (disorder) of the universe is always increasing
Law 3:
For a perfect crystal that's been cooled to absolute zero (0 K or -273 C), its entropy is close to (or approaches) 0
how do you calculate the difference in enthalpy in a reaction?
delta H = total H products - total H reactants
what is the enthalpy of formation?
the delta H of a chemical reaction of forming 1 mol of a single substance from its parent elements at 298 K (25 C) and 1 atm
what is the enthalpy of formation (ΔH f) of any element in its standard state?
0 kJ/mol
what does a negative and positive q mean?
-q: heat is transferring to the surroundings and being lost by the system (exothermic)
+q: heat is transferring to the system from the surroundings (endothermic)
what is the equation that relates work, pressure, and volume?
w = -PΔV
P=system's internal pressure
ΔV= system's internal change in volume
what does +w and -w mean?
+w: surroundings are doing work on a system (think squeezing a balloon)
-w: the system has done work on the surroundings (think a balloon expanding, pushing on its surroundings)
heat transfer due to direct contact via molecular agitation within a material
conduction
heat transfer due to the motion of a fluid
convection
heat transfer via electromagnetic radiation
radiation
the amount of heat required to raise 1 g of liquid water by 1 degree C
calorie (cal)
-this is also called water's specific heat, and is equal to 4.19 J
the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1 gram of a certain substance by 1 degree C or 1 K
specific heat (C)
-this can be different for a substance depending on what phase it's in
the "calorie" used on nutrition labels and it equals 1,000 calories, or 1 kilocalorie
Calorie (C)
technique used to measure how much heat is produced by a chemical reaction, in other words, that chemical reaction's heat transfer
calorimetry
what is the bomb calorimeter equation?
q = -CcalorimeterΔT
q= amount of heat the reaction produces
Ccalorimeter= calorimeter's specific heat
ΔT=the temperature change caused by the reaction
When measuring q for a specific amount of substance, what equation must we use?
q = mcΔT
q= amount of heat the reaction produces
c= calorimeter's specific heat
ΔT=the temperature change caused by the reaction
m= substance's mass
diagrams that show how a substance changes from a solid to a liquid to a gas, as temperature is raised
heat curves
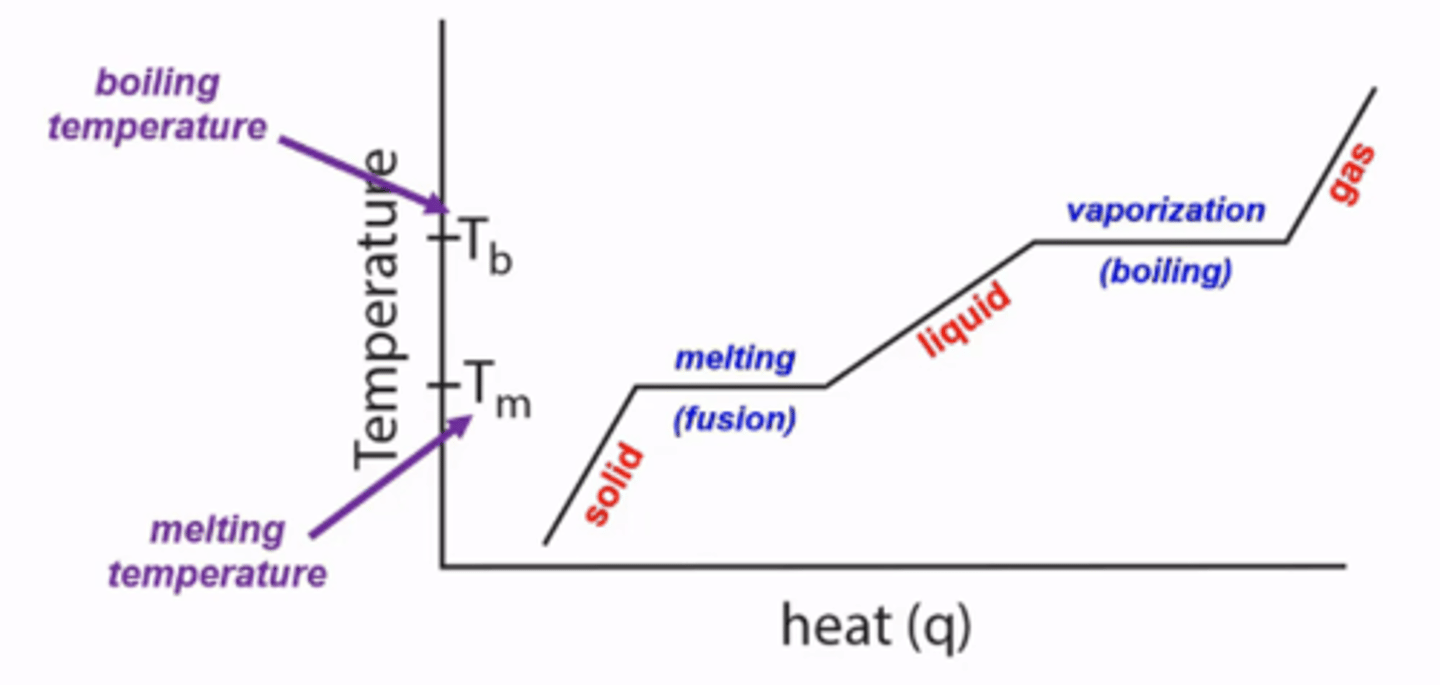
how do you calculate the amount of heat required for a specific amount of a specific substance to traverse a heat curve during a phase change?
fusion (solid->liquid):
q=(m)(ΔHfusion)
vaporization (liquid->gas):
q=(m)(ΔHvaporization)
what are the entropies of any element in its standard state at 298 K and 1 atm?
Snaught is NOT zero kJ/mol
-also, S values for substances cannot EVER be negative! but delta S can either be positive, negative, or zero
which of the phase changes create disorder?
fusion, vaporization, and sublimation (they're also endothermic because they consume heat, +ΔH)
which of the phase changes create order?
crystallization, condensation, deposition (they're also exothermic because they give off heat, -ΔH)
what does Hess's law state?
if you add multiple reactions together, then the new overall reaction's ΔH is equal to the combined sum of all the individual reaction's ΔH's
how do you use Hess's law?
this is the technique where they give you a bunch of ΔH's for different reactions and you put them together in different ways for the target reaction
how do you calculate bond enthalpies in order to figure out ΔHrxn?
making bonds = exothermic
breaking bonds =endothermic
1. draw the lewis structures of each molecule involved
2. write down the ΔH value for each bond in the structure
3. use formula ΔH = ΔHbond broken - ΔHbonds formed
what is the Gibb's free energy equation used for?
to determine whether a reaction is spontaneous or not
what is the Gibb's free energy equation?
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
ΔG+, reaction is not spontaneous
ΔG-, reaction is spontaneous
make sure units match!
what is the difference between ΔG and ΔGnaught?
ΔGnaught is the change in Gibb's free energy under standard conditions (298 K, 1 atm, 1 M)
when is a reaction spontaneous at low temperatures?
when ΔH-, ΔS-, and -TΔS+
when is a reaction spontaneous at high temperatures?
when ΔH+, ΔS+, and -TΔS-
how can you relate ΔG and ΔGnaught?
ΔG = ΔGnaught + RTln(Q)
R: ideal gas constant 8.314 J/mol-K
Q: reaction quotient
(don't memorize)
*when ΔGnaught =0, rxn is under equilibrium under standard conditions, but not necessarily all conditions
how can you mathematically relate ΔGnaught to K (rate constant)?
ΔGnaught = -RTln(K)
K: rate constant