PSYC MT1 (module 1-5 (p48))
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
The study of human behaviour
Psychology
Study of the nervous system
Neuroscience
Psychopharmacology is a subdiscipline of psychology, focusing on the relationship between ___ and ___
Drugs & Behaviour
Neuropsychopharmacology is a subdiscipline of neuroscience, focusing on the relationship between ___, ___ & ____
Drugs brain and behaviour
____ is a fundamental part of neuroscience and psychology
Research
Psychopharmacology is the study of drugs effects on: (4)
mood
perception
cognition
behaviour
All of which are aspects of psyc
so u could say how drugs affect our psychology
Pharmacology studies how drugs affect the ___
body
Pscyhoactive drugs affect the ___ ____
nervous system → 4 aspects of psyc
Neuropsychopharmacology is the study of how
drugs affect our nervous system function and how this change affects our psychology
psychopharmacology and neuropsychopharmacology is often mushed together (t/f)
True
_____ pharmacology refers to traditional researchers
Behavioural
Behavioural pharmacology suggest we most likely work with ___ models
animal
Psychoactive drug use is ____
ubiquitous (addictive and hard to avoid)
addiction is ___
prevalent
(blank) is an administered substance that affects physiological functioning
drug
exceptions/problem to the ‘drug’ definition (3)
supplements, food and exercise
Exogenous origin
administered outside of the body (drug)
ex. drug cream applied to skin
endogenous origin
comes from the body (not a drug)
ex. test made in body
Drugs used to achieve a specific ‘purpose’
instrumental drug use
use of a drug to simply experience the effect of the drug
recreational drug use
complication of instrumental and recreational drug use
the ‘feeling of a drug could be used for a specific purpose
ex. alch → forget
Drug names - trade names
named by brand
only one company can call it that
ex. Tylenol
Drug names: generic names
actual drug name of trade names
anyone can sell
_____ names are created by its chemical map
Chemical
amount of drug per bodyweight is called…
dose
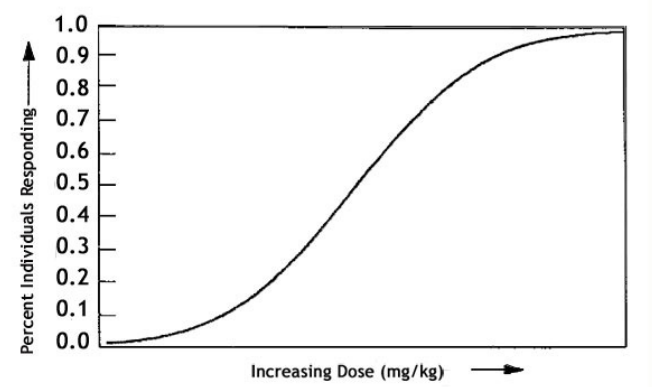
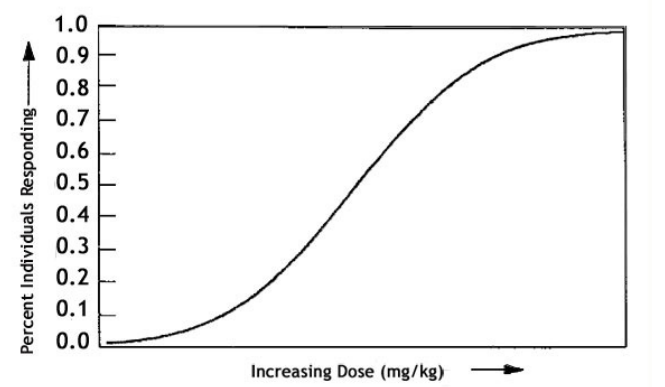
Dose-effect curves (dose-response curves ) - explain how it works
a graph that shows the relationship between the dose of a drug and the magnitude of its effect, used to determine drug potency, effectiveness, and safe dosage ranges.
potency
strength of a drug
Lower ED50 = a more ___ drug
potent
ED50
median effective dose - where 50% of participants respond
____ models are used to test toxicity rate
animals
TD50 measures …
where 50% of participants’ receive toxic effects of drug
TD50 will always be above ____
ED50
How to find Margin of saftey
TD50/ED50
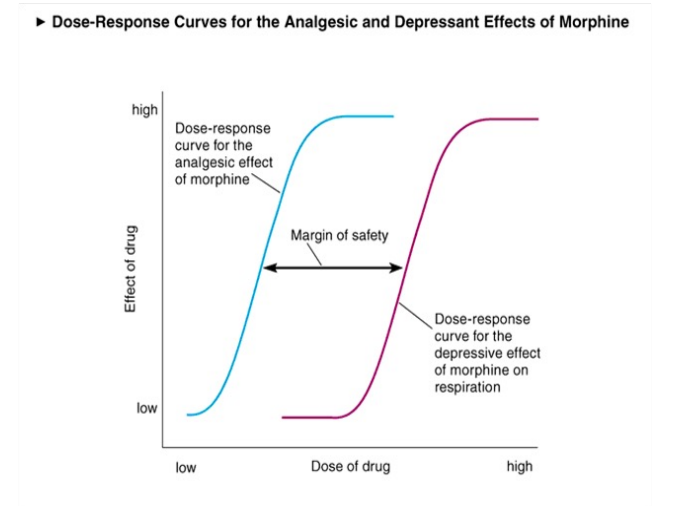
_____ ____ compares which drug is safer, higher ___ means the drug is safer because the further the margin the less likely to meet toxic effects
Therapeutic Index
TD50/ED50 = margin
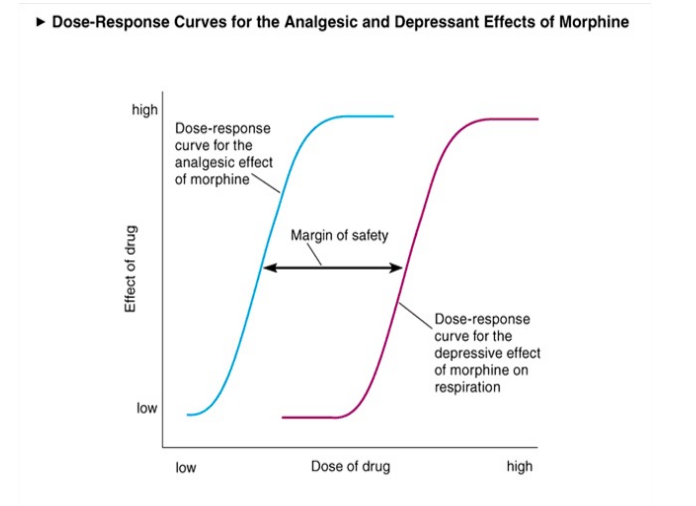
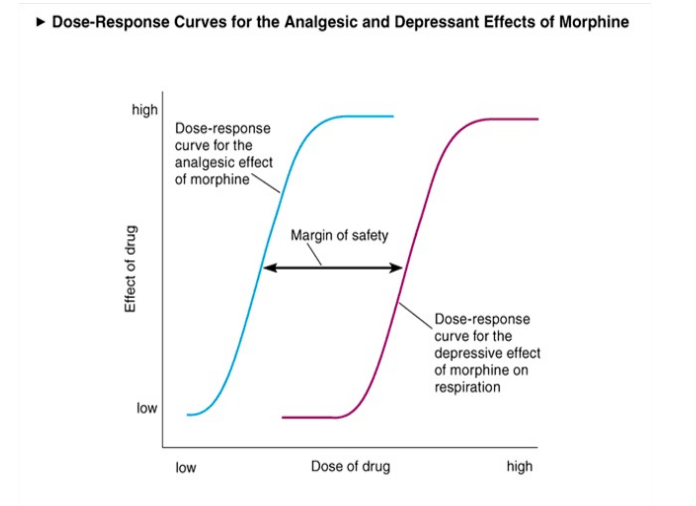
Researcher gets to choose whether the Y axis is the effect of drug or # of ___ responding
partcipants
Certain safety index
more conservative and used method to ensure drug use safety
TD1/ED99
Lethal Dose - where 50 percent of participants die to drug
LD50
Drugs physiological action on body/NS
relates to agonism and antagonism
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
How the drug moves through body (admin. to elim)
pharmacogenetics refers to
differences in genes that lead to difference in our pharmacodynamics &/or kinetics
Objective effects are ___ measured and subjective effects are ___ measured
Directly (meters seconds hear rate) , Indirectly (thoughts, feelings)

Non-experimental research
correlational research in the real world
no true variables
an issue with correlation is the ___-___ problem
third variable problem: other factors that could affect the study
research in a controlled, predictable, environment is the ___ method
experimental method - measures effect of IV on DV
Placebo can be used as control value unless a ____ already exists
treatment
treatment arms
levels of the IV
different treatment groups
ex. placebo vs experimental vs old drug (3 levels of treatment arms)
2 types of blinded procedures
single blind study - only participant doesn’t know
double blind study - researcher and participant does know which group they are in
A ___ ____ study is when everyone knows what they are given for ethical concerns
Open Label
4 reasons why animal models are used for research
understand basic mechanisms
because there are no viable alternatives
because they have high predictive value
have a number of protections in place
2 ethical considerations must be made for human research (2)
federal mandated committees review human research proposal
informed consent
Phase one of clinical trials
will not harm anyone, most pass
low dose → short term and determine most likely effects effects
treats healthy individuals if possible
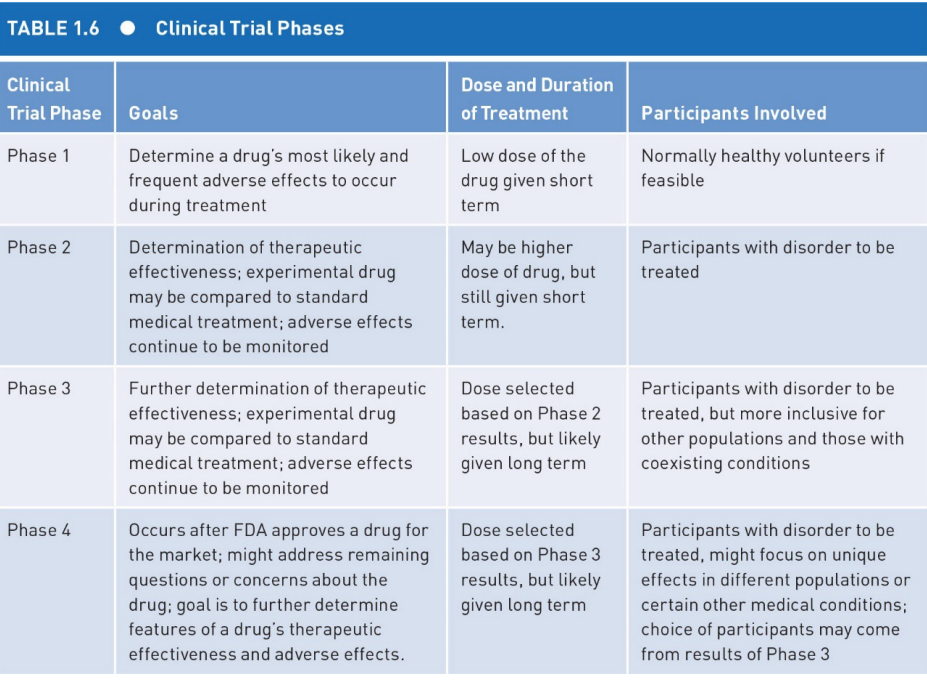
Phase 2 of clinical trials
higher dose → Sort term
Determination of therapeutic effectiveness
most do not pass but if it does will likely hit market
treats participants with disorder
phase 3 of clinical trials
dose selected based on phase 2 but given long term
brand name for market
looks to include other populations with coexisting conditions
Phase 4 of clinical trials
occurs after FDA approval
dose selected based on phase 3 but long term
hit market
still monitored to make sure there are no long term effects
human brain weighs ~_lbs
3
human brain consumes ~__ % of your energy
20
brains are slightly ____ in men than women but still huge individual variation
larger
The brain is composed of ___, ____ , ____ cells and blood vessels
neurons, glia , stem cells
stem cells can produce new cells but not ____
neurons
neurons are not replaced thus they ___ over time
degrade
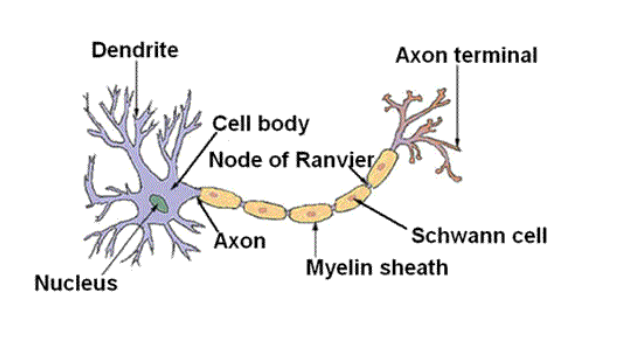
Neurons
cell that contains axons
sends AP out of axons
very quick
Glia
support cells
Neuron anatomy in order (4)
Dendrite → receives AP
Soma → Cell Body
Axon → only 1 in most cases
Terminals → end of neuron
3 types of neurons
A. Pyramidal (Projection neuron)
B. Stellate (star shaped) (lie in subcortical-area)
C. Purkinje (ton of dendrites) (lie in cerebellum)
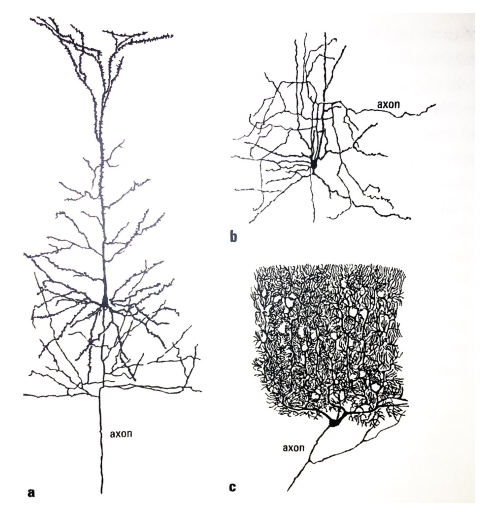
____ neurons have long axons that project to a different brain area (pyramidal)
Projection
____ have short axons that project locally
interneurons
interneurons have ____ ____ that allows for signals to be modified
multiple junctions
A→B→C→D
____ cells play a structural role and aid nervous system function
Glial
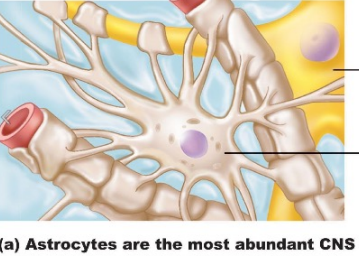
______ forms ½ of the blood brain barrier and provides ____ to the brain
they are located at _____ thus they maintain/modify _____ (same word)
most common glial cell
astrocytes , oxygen , synapses, synapses
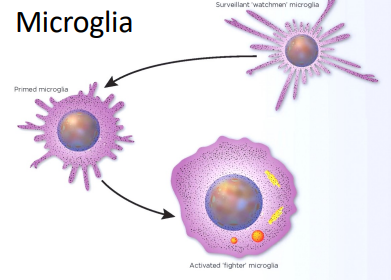
_____ aid immune system function
small cells that ____ unknown cells within the blood brain barrier
microglia, engulf
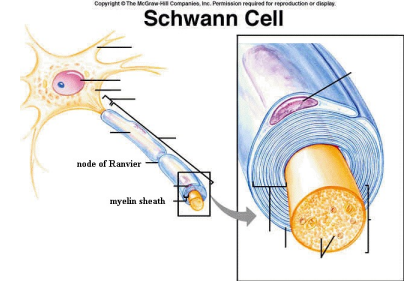
_____ cells insulate around axons
______ AP
located in the ___
myelinate only a ____ axon
Schwann
Accelerates
PNS
single
_________ speeds up AP in the CNS
can _____ several axons
oligodendrocytes , myelinate
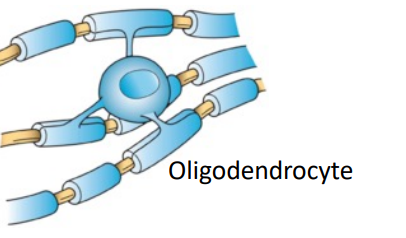
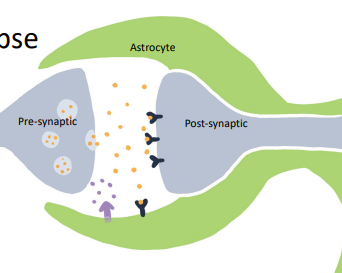
____ ____: Glia have receptors and transmitters that help to shape conditions at the synapse
Tripartite synapse
In the brain, ___ matter is the outer layer that contains cell bodies of neurons (projection and small interneurons) and ____ matter is the inner layer with ____ axons
Outer, Inner , myelinated
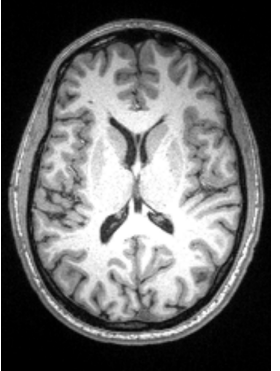
T/F does staining (paleness) decrease cell bodies
TRUE
_____ mobilize energy while _____ conserve energy (for future use), these two systems are not always ____ each other (work together)
Sympathetic , Parasympathetic , against
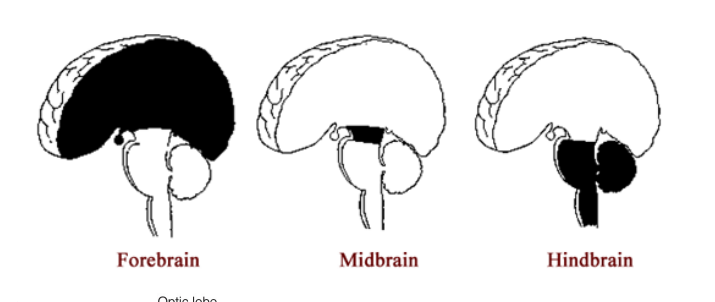
3 major divisions of the brain
forebrain
midbrain
hindbrain
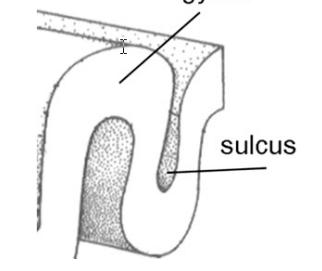
gyrus/gyri fold _____ and sulcus/sulci (fissures) fold ____
outwards, inward
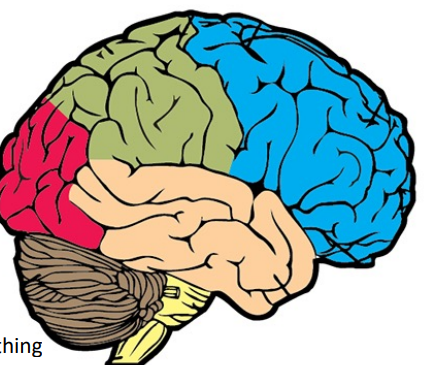
name all the lobes of the brain in photo (even brown thing)
Blue - frontal
Green - parietal
Red - Occipital
Orange - temporal
brown raisin thing- cerebellum
under the cortex are grey matter clusters called ____/____
nuclei/nucleus
The ___ is located in the hindbrain and provides basic physiological functions for survival (damage=death)
medulla
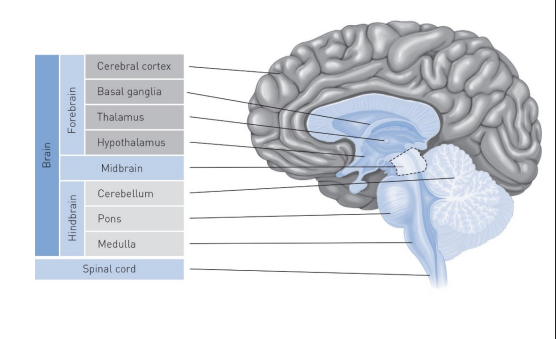
The _____ is responsible for hormonal control and SNS and PNS activity
Hypothalamus
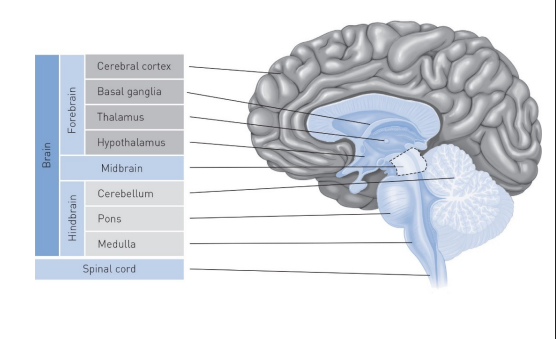
Limbic system contains the ____, responsible for emotions and the _____ which plays a key role in LTM (affected by many drugs)
Amygdala ,hippocampus
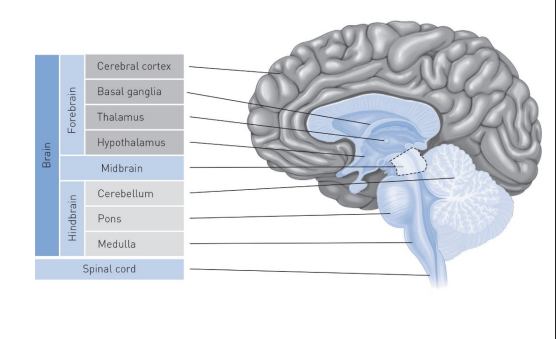
the ____ _____ is a mediating region for drug inhibition and a subsection of it is the _____ ____ which is responsible for motor learning (muscle memory)
nucleus accumbens , basal ganglia
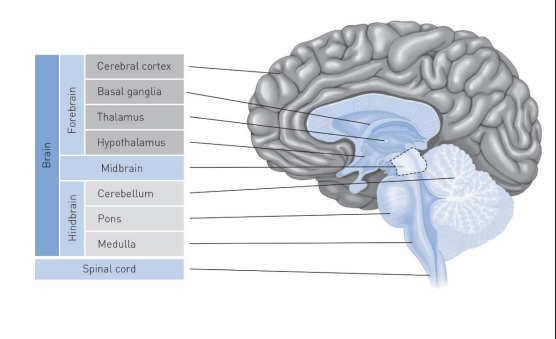
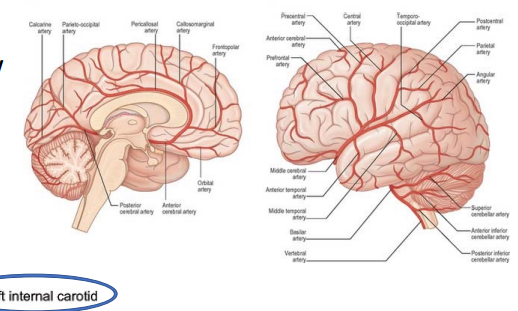
cerebral blood flow - ____ supply & no _____
limited, reserves
Blood brain barrier (4)
tightly packed
protects brain
active transport for larget molecules
drugs that cross the BBB better work better
Our primary protection for the brain is the ______ (contains periosteal and meningeal) which is the thick part of the skull and the ___ _____ which is the thin plastic wrap part
Dura mater , pia meter
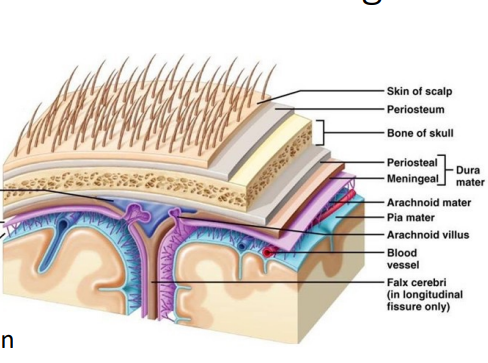
CSF is inside the ______ and helps (3)
Ventricle
support
protect
provides nutrition
DNA → ____ → ___
mRNA, protein
cell nucleus contains __ chromosomes , which are made of DNA
56, DNA
__ code for specific proteins
genes
______ : slight variations within genes, makes us unique
polymorphisms
____ is the reversible process of coding DNA to RNA
Transcription
____ is information that is carried outside our geenes
epigenetics
____ animals have a slight change in genes (at birth) (genetically modified )
Transgenic
_____ animals is the removal of genes (deactivation) (modified organisms)
Knockout
conditional knockout mice have a ____ of a gene in adulthood
removal
The ___ is the site of neural communication
synapse