Unit 7: Technology, Modernity, and Discontent (1890-1914)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What were the main factors of discontent in the world between 1890-1914?
People uprooted, poverty amid plenty, and resentment of European domination.
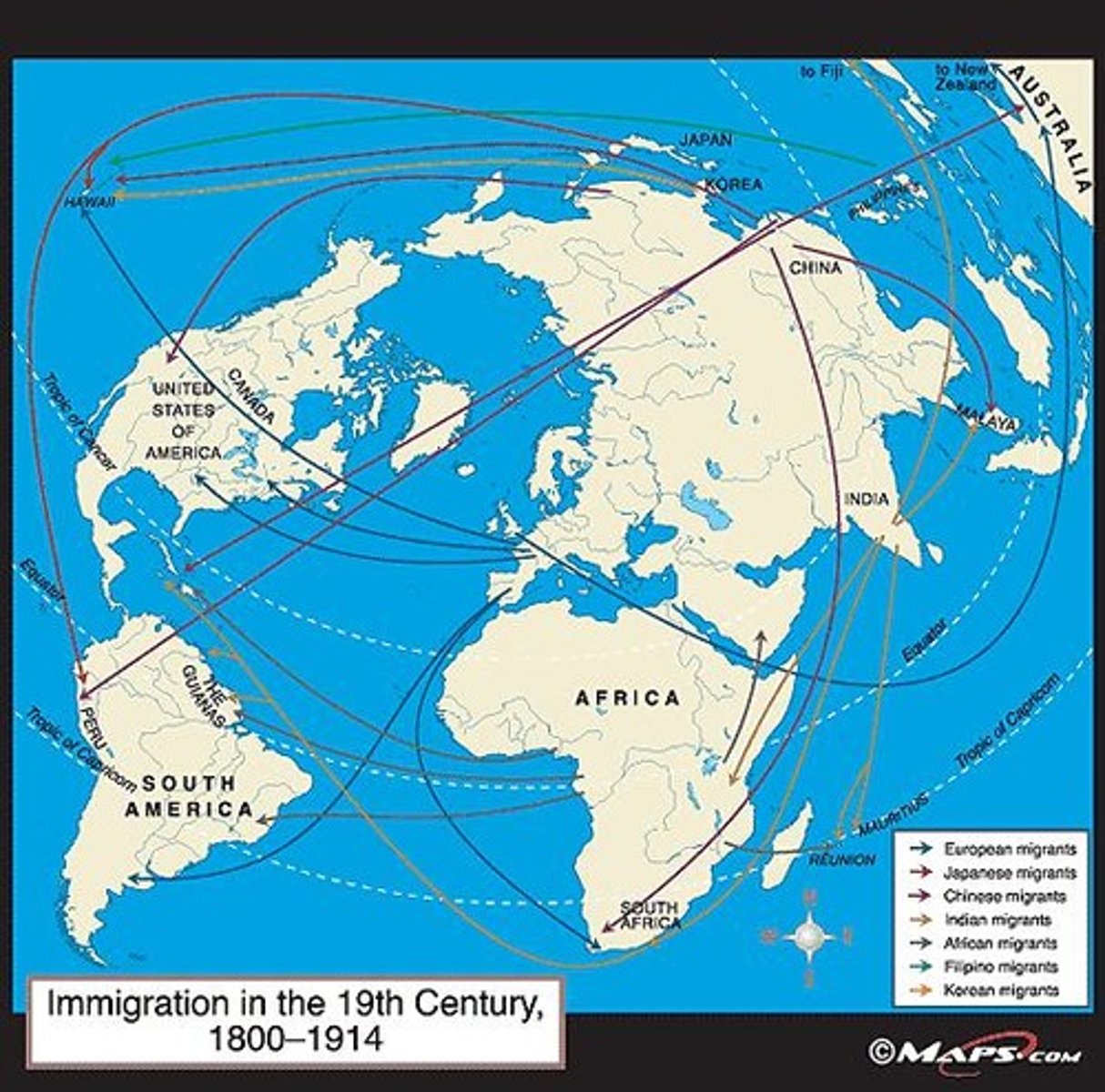
What were the primary reasons for migration during this period?
Scarcity of land and resources, industrial jobs, and temporary jobs.
What challenges did immigrants face upon arrival in urban areas?
Separation from family, potential dangers for temporary migrants, dangerous travel and work, crowded conditions, and overtaxed urban infrastructure.
What was a significant example of exploitation faced by women immigrants?
Women in China were exploited without protection.
What was the demographic impact of migration from South Asia between the 1840s and 1940s?
29 million South Asians migrated to the Malay Peninsula, Burma, Dutch Indies, East Africa, and the Caribbean.
How did the urban growth in cities like Buenos Aires reflect the promise of the city?
Buenos Aires grew from 180,000 in 1869 to 1,580,000 in 1914, promising more jobs, opportunities, and cultural hubs.
What were the European responses to African unrest against imperialism?
Responses included paternalistic views, reformist approaches, and punitive actions against rebellions.
What sparked the Anglo-Boer War and who were the main parties involved?
The conflict was between the British and Afrikaners (Dutch settlers) over gold found in Afrikaner territory.
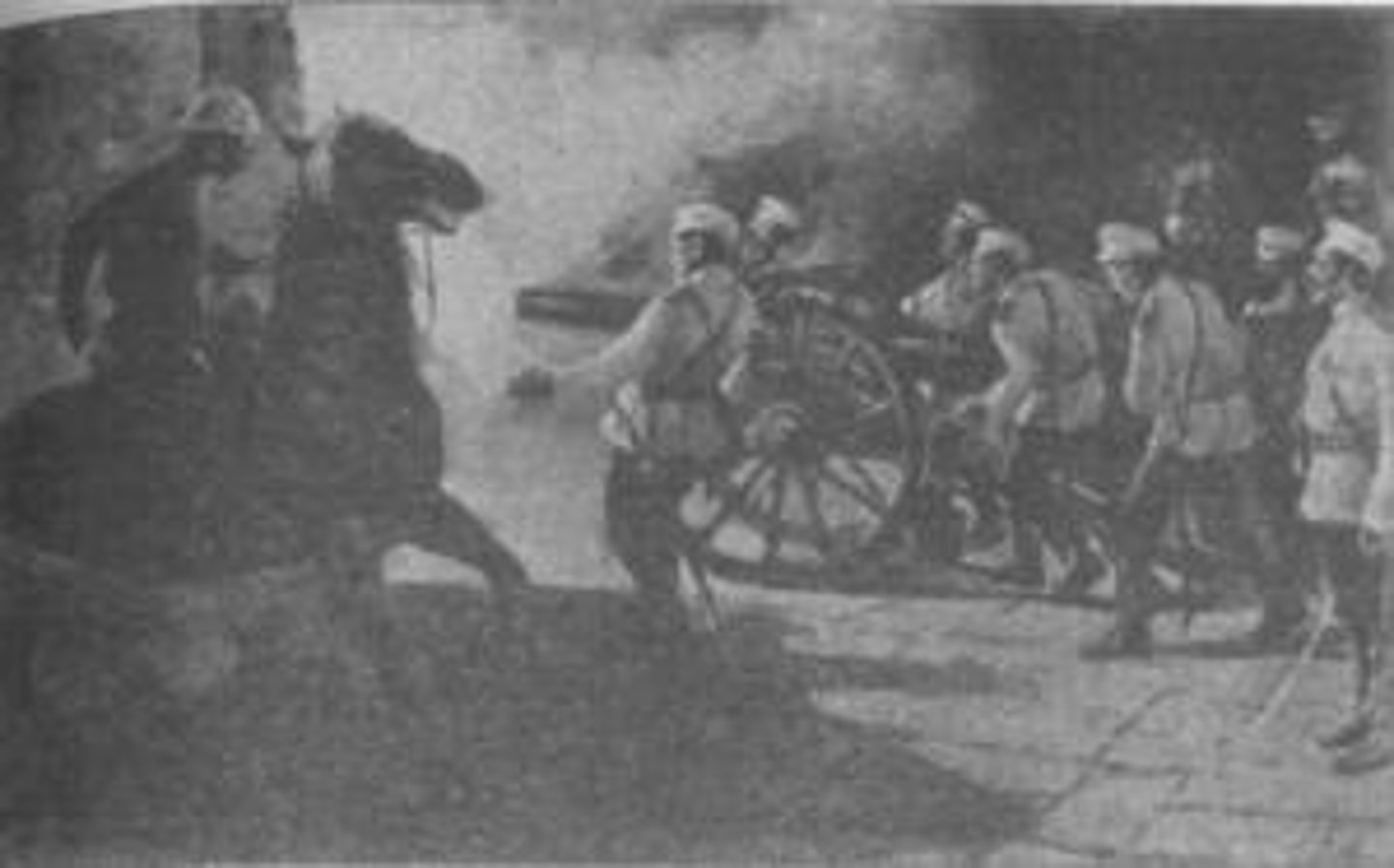

What was the Boxer Uprising and what did it oppose?
The Boxer Uprising was a rebellion against Western and Christian privileges in China, supported by the Qing dynasty.
What role did poverty play in the Boxer Uprising?
The uprising flourished in poor areas that were hard hit by drought in 1898.
What was the significance of the 'Woman Question' during this period?
It addressed how to make women equal citizens amid growing awareness of inequality and the burdens of imperial/industrial economies.
What advancements were made in women's rights during the late 19th and early 20th centuries?
Female suffragist campaigns gained momentum, leading to voting rights in several countries: local elections in Britain (1868), national elections in New Zealand (1893), and others.
What was the impact of women's suffrage movements on birth rates?
The movements led to declining birth rates as women asserted control over reproduction.
What was the outcome of the Boxer Uprising in terms of Western intervention?
Western powers intervened to stop the uprising and demanded huge war costs, leading to a strong anti-Western sentiment.
What was the role of martial arts groups in the Boxer Uprising?
Martial arts groups, known as Boxers, called for an end to Western and Christian privileges and believed in their invulnerability to weapons.
How did urbanization change the organization of cities?
Cities became organized more along class lines and saw the emergence of increasing ethnic enclaves.
What was the significance of Jacob Riis's work 'Five Cents a Spot'?
It highlighted the living conditions in tenement workshops around 1890.
What was the relationship between migration and national identity during this period?
The worldwide demographic transformation complicated national identity.
What was the impact of the Anglo-Boer War on public awareness?
The rise of war correspondents made news and atrocities visible to the public.
What was the Qing dynasty's response to the Boxer Uprising?
The Qing dynasty initially clashed with the Boxers but later sided with them to use anti-Western sentiment to maintain power.
What were some cultural promises of urban life during this period?
Cities promised better housing, infrastructure, and cultural opportunities such as libraries, museums, music, and theatre.
What were the consequences of anti-immigrant sentiment in urban areas?
Initially welcomed, immigrants faced eventual restrictions and hostility.
What does the term 'separate spheres' refer to in the context of women's rights?
It refers to the traditional division of gender roles that began to break down as women's rights movements gained traction.