ANAPHY: U3.1 Cells
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Cells
building blocks of all living beings
nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane
3 main regions of cells
Function of the nucleus
control center of the cells and contains DNA
3 Regions of the Nucleus
Nuclear membrane, nucleolus, chromatin
Nuclear pores
part of the nuclear membrane that allows material exchange with the rest of the cell
Nucleolus
non-membrane bound organelle taking part in synthesis of ribosomes, including processing of rRNA and assembly of them into ribosome subunits
Mitosis, stress response, cell cycle regulation
what other cellular processes nucleus is involved in
DNA and proteins
what chromatin is composed of
Plasma membrane
barrier for cell contents
phospholipids, protein, cholesterol, glycoproteins
what the plasma membrane is composed of
microvilli
finger-like projections that increase surface area for absorption
tight junctions, desmosomes & hemidesmosomes, gap junctions
type of membrane junctions
Cytoplasm
material outside the nucleus and within the bounds of the plasma membrane
cytosol, organelles, inclusions
what cytoplasm contains
Cytosol
fluid that contains other elements
Organelles
metabolic machinery of the cell
Inclusions
non-functioning units
Ribosomes
organelle made of protein and RNA where protein synthesis occurs
cytoplasm and rough endoplasmic reticulum
where are ribosome located in the cell
endoplasmic reticulum
fluid-filled tubules for carrying substances
rough endoplasmic reticulum
ER with ribosomes where building materials of the cellular membrane are formed
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
functions in cholesterol synthesis and breakdown, fat metabolism, and detoxification of drugs
golgi apparatus
modifies and packages proteins
types of packages produced by the golgi apparatus
secretory vesicles, cell membrane components, lysosomes
mitochondria
provide ATP for cellular energy, change shape constantly, and carry out reactions using oxygen to break down food
lysosomes
contain enzymes that digest non-usuable materials (waste) within the cell
peroxisomes
sacs of oxidase enzymes which detoxify harmful substances, break down free radicals, replicate by pinching in halves
radicals
atoms that block electrons that can cause mutations in the cell (cancer)
cytoskeleton
network of protein structures that extend throughout the cytoplasm; provides cell with an internal framework
microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
types of cytoskeleton
centrioles
rod-shaped, microtubule-made organelle that directs the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division
cilia and flagellum
types of cellular projections
cilia
moves materials across the cell surface; uses back and forth beating for movement
flagellum
propels the whole cell; uses propeller-like motion for movement
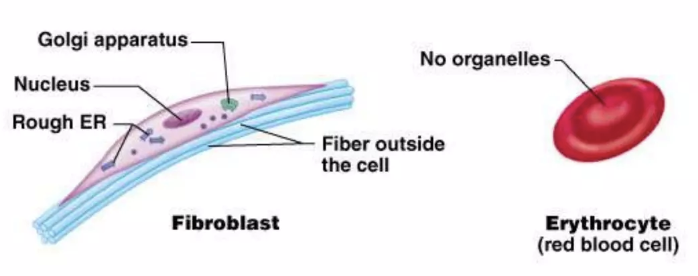
fibroblast and erythrocyte
cell(s) that connects body parts
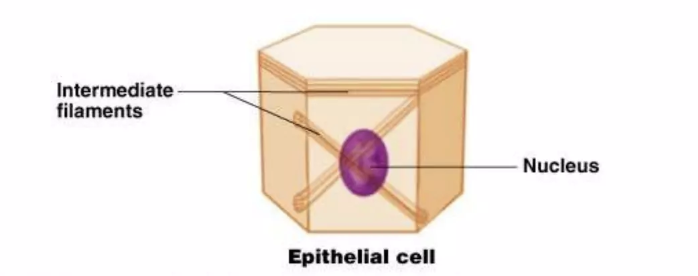
epithelial cells
cell(s) that cover and line body organs
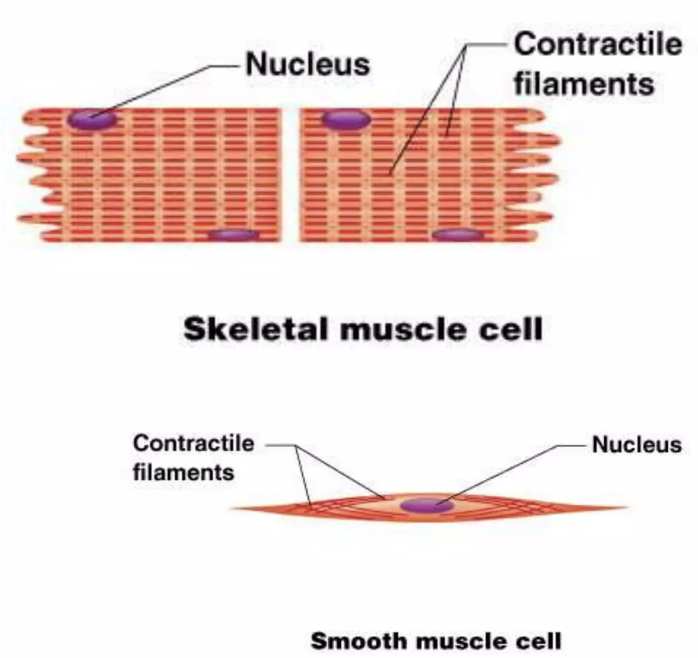
skeletal and smooth muscle cells
cell(s) that move organs and body parts
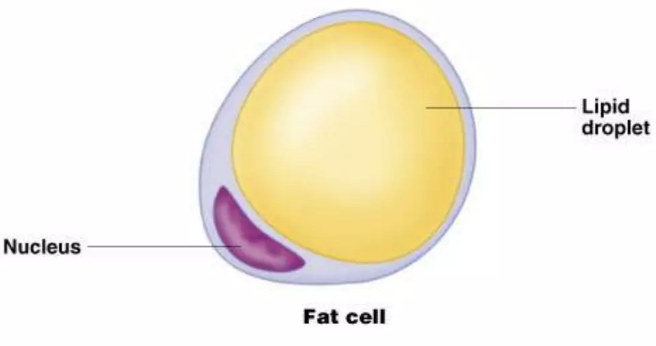
fat cell
cell(s) that stores nutrients
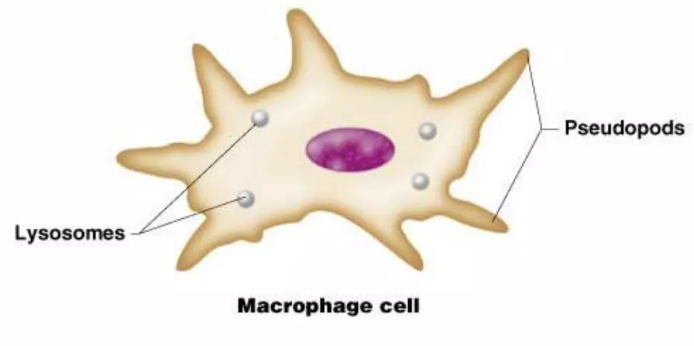
microphage cell
cell(s) that fight disease
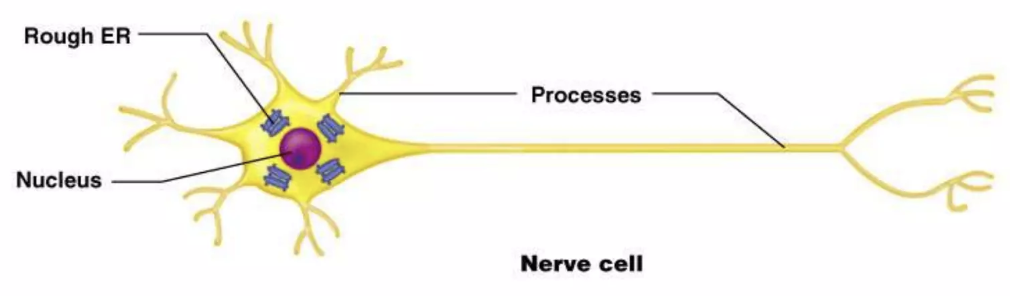
nerve cell
cell(s) that gathers info and controls body functions

ovum and sperm
cell(s) of reproduction
membrane transport
movement of substance in and out of the cells
passive and active transport
2 types of membrane transport
passive transport
type of transport in which no energy required
active transport
metabolic energy required
solution
homogenous mixture of two or more components
solvent
dissolving medium
solutes
components in smaller quantities within a solution
intracellular fluid
nucleoplasm and cytosol
interstitial/extracellular fluid
fluid on exterior of the cell
selective permeability
property of the plasma membrane which allows some materials to pass while excluding others
diffusion
particles distribute themselves evenly within a solution; move from a high to low concentration gradient
simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
types of diffusion
simple diffusion
solutes are lipid-soluble materials or small enough to pass through membrane pores
osmosis
highly polar water easily crosses the plasma membrane
facilitated diffusion
substances require a protein carrier for transport
filtration
water and solutes are forced through membrane fluid or hydrostatic pressure
too large, unable to dissolve, move against concentration gradient
why substances are not able to pass by diffusion
solute pumping and bulk transport
forms of active transport
solute pumping
how amino acids, some sugars, and ions are transported; ATP energizes protein carriers since substances are usually move against concentration gradients
exocytosis and endocytosis
types of bulk transport
exocytosis
moves materials out of the cell
endocytosis
extracellular substances are engulfed by being enclosed in a membrane vesicle
phagocytosis and pinocytosis
types of endocytosis
phagocytosis
cell “eating”
pinocytosis
cell “drinking”
interphase and cell division
major periods of the cell life
interphase
cell grows and carries on metabolic processes
cell division
cell replicates itself to produce more cells for growth and repair
nucleus
mitosis is the division of the ___
cytoplasm
cytokinesis is the division of the ___
interphase
“stage” of mitosis where no cell division occurs and the cell carries out normal metabolic activity and growth
prophase
mitotic stage in which centromeres migrate to the poles
metaphase
mitotic stage in which spindle from centromeres attach to chromosomes that are aligned in the center of the cell
anaphase
mitotic stage in which daughter chromosomes are pulled toward the poles
telophase
mitotic stage in which daughter nuclei begin forming; cleavage furrow begins to form
act as enzymes and build materials for cells
function of proteins
tRNA, rRNA, mRNA
types of RNA
transfer RNA
transfers appropriate amino acids to the ribosome for building the protein
ribosomal RNA
helps form the ribosomes where proteins are built
messenger RNA
carries instructions for building a protein from nucleus to ribosome
transcription
transfer of info from DNA’s base sequence to complimentary base sequence of mRNA
translation
base sequence of nucleic acid is translated to an amino acid sequence