26- Cerebrum & Cerebellum
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
cerebrum
-Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
-telencephalon
-diencephalon
telencephalon
what is the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system in?
diencephalon
what is the thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland in?
brainstem
oldest part and central core of brain
begins where spinal cord swells as it enters the skull
responsible for automatic survival functions
cerebellum
large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills
spinal cord
Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain
conus medullaris
end of spinal cord
cauda equina
end of spinal cord at L1/L2
rostral
toward the forehead or nose
caudal
posterior or toward the feet
coronal slice
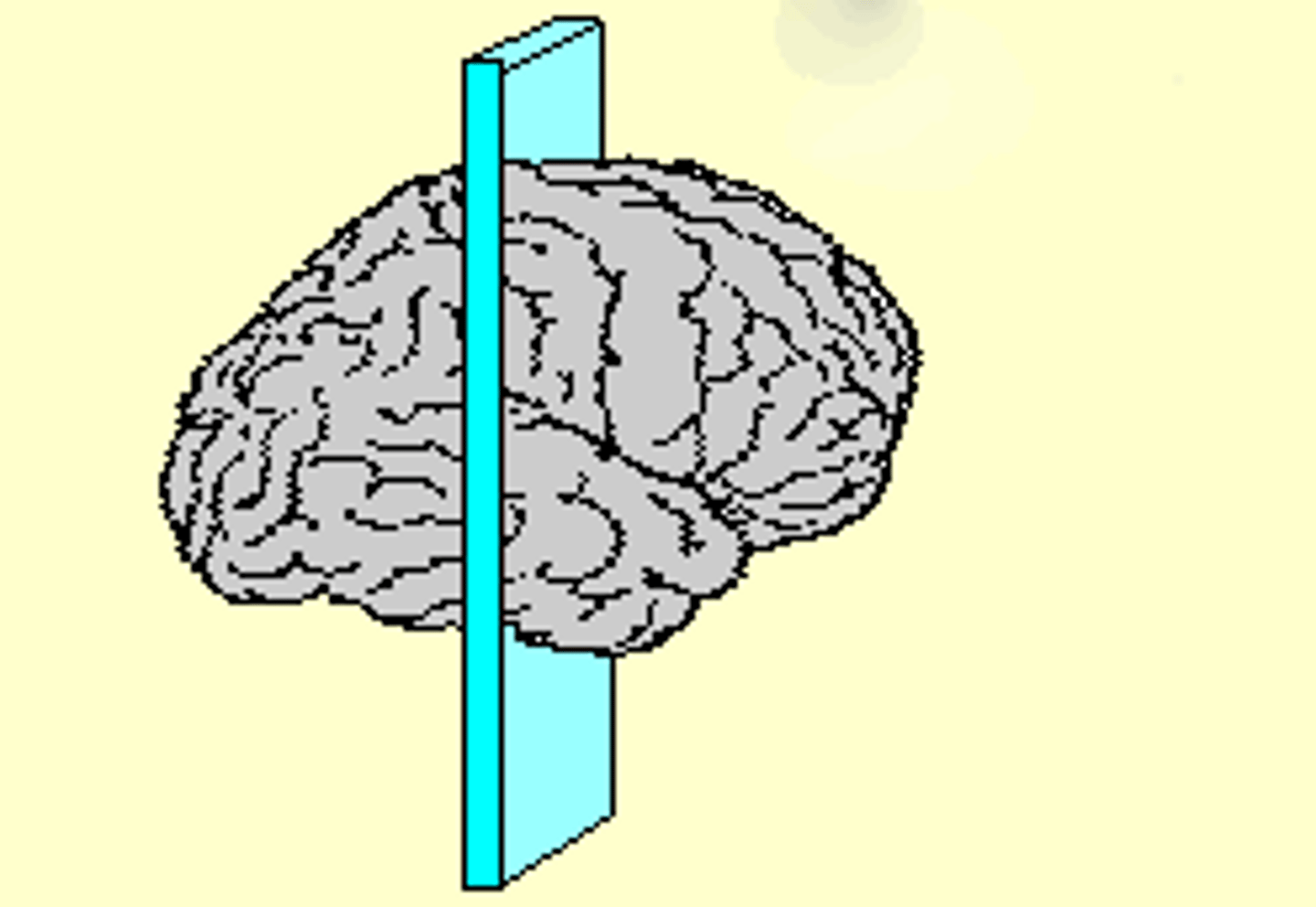
sagittal slice
horizontal slice
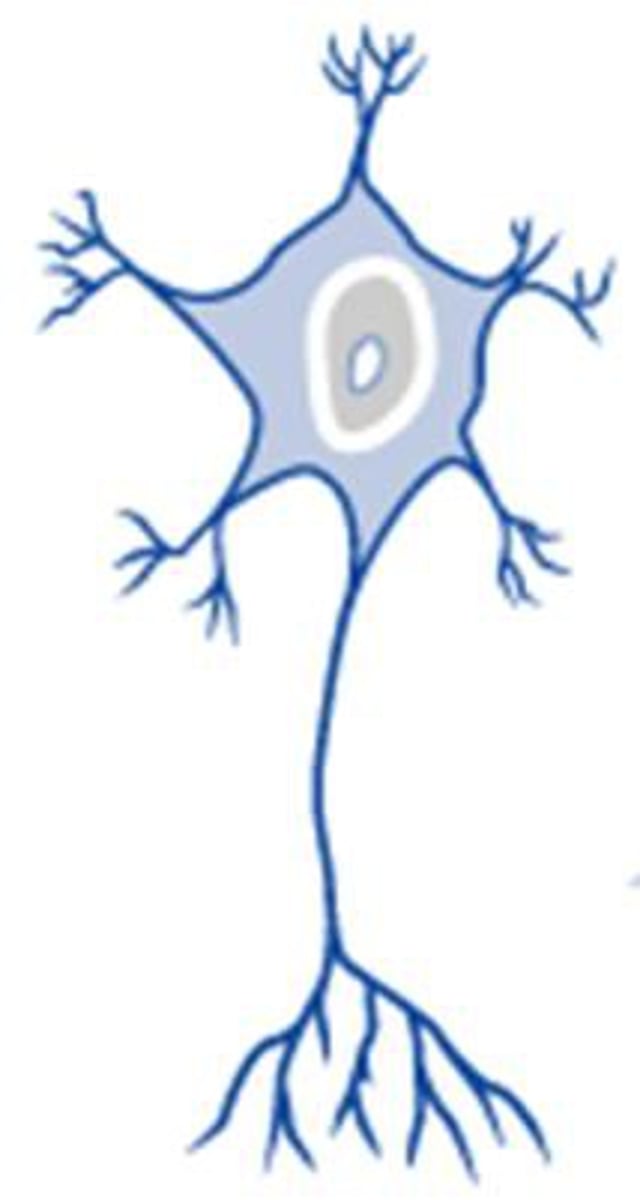
multipolar neuron
-most common
-many dendrites extend from soma
-projection and interneurons
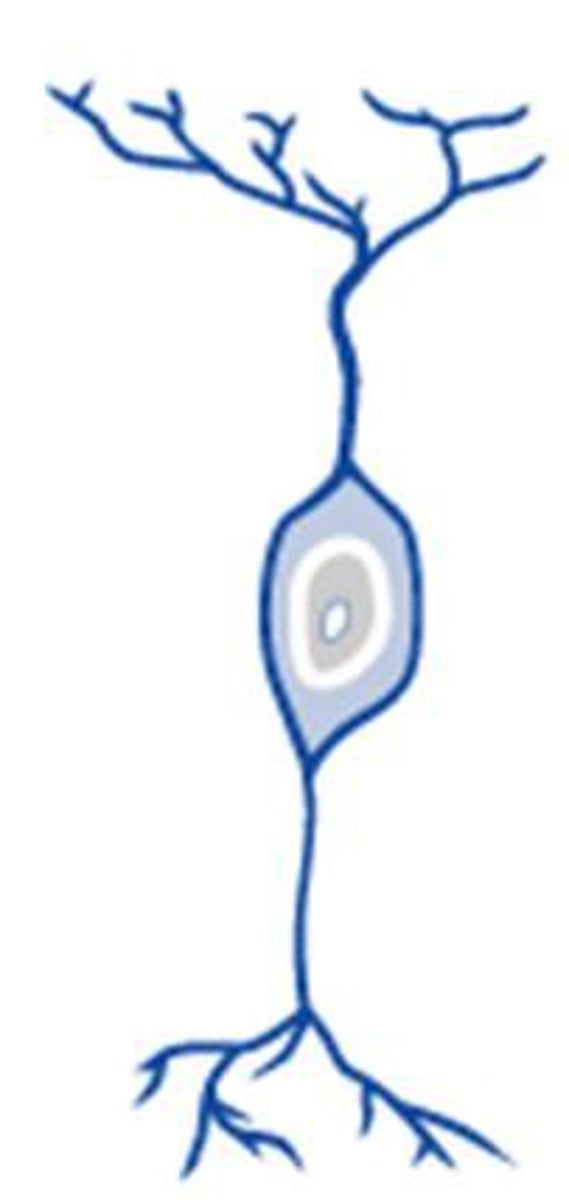
projection neuron
a neuron with a very long axon that communicates with neurons in distant areas of the nervous system
interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate inside and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
projection and interneurons
Types of multipolar neurons
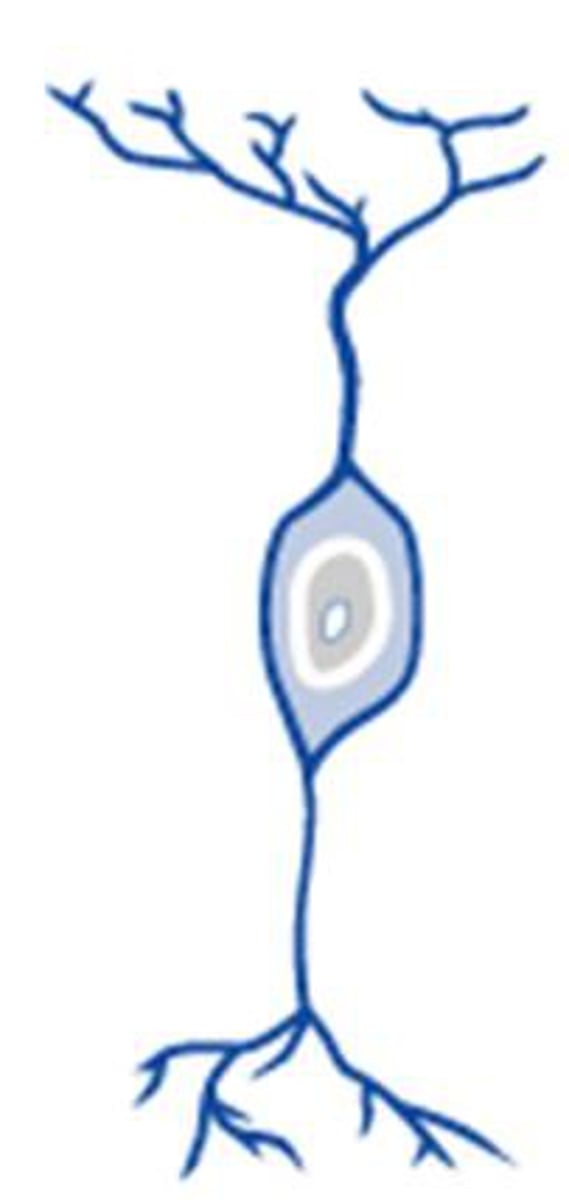
bipolar neurons
-one axon and one dendrite
-long dendrite to soma
-olfactory and retinal cells
olfactory neuron
part of the nasal mucosa; depolarize in response to odorants in the nasal cavity
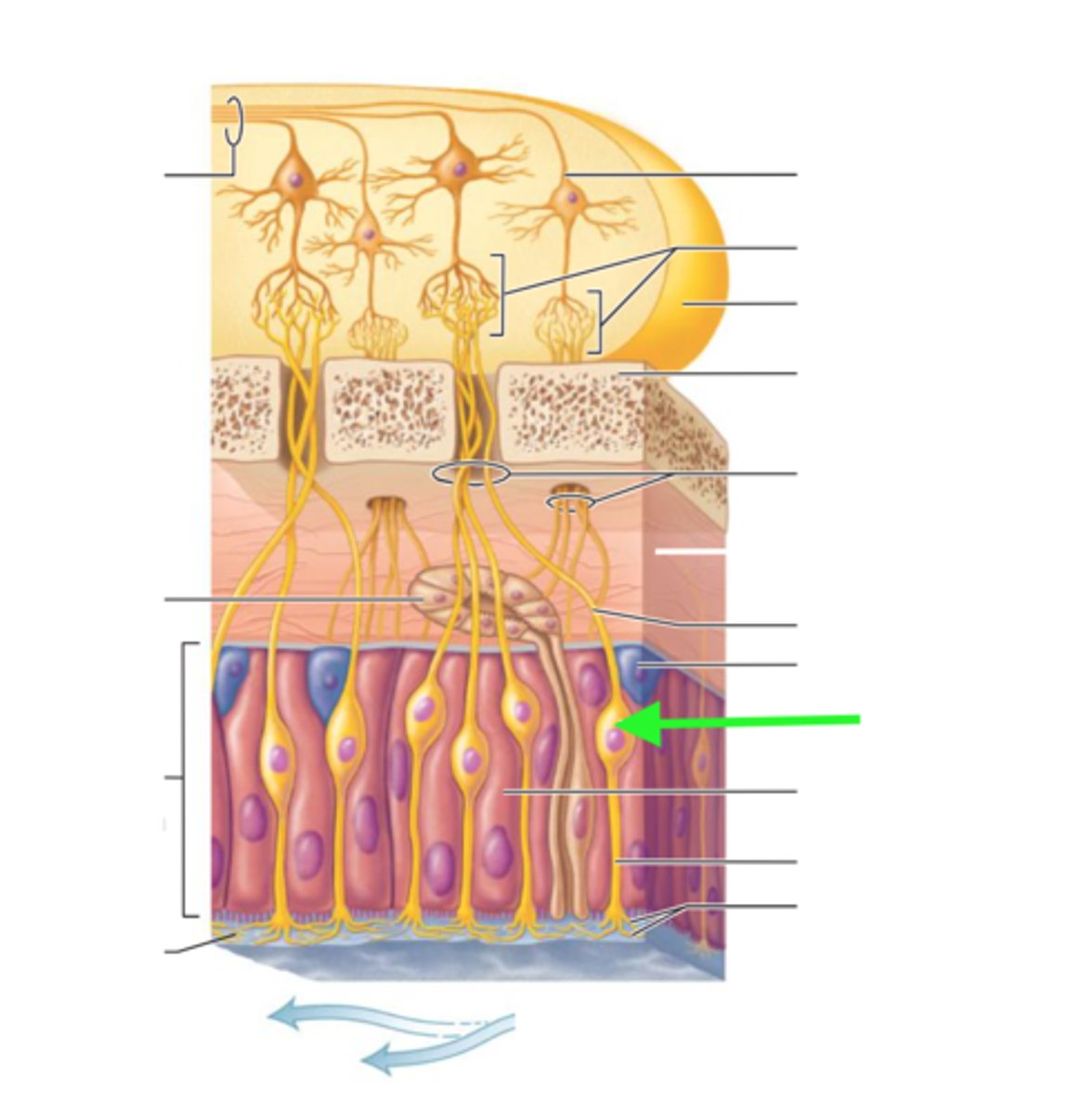
retinal cell
help communicate between photoreceptors and ganglion cells
alter sensitivity
major role in adjusting to dim or bright light
synapse with bipolar cells and bipolar cells synapse with ganglion cells
olfactory and retinal cells
Types of bipolar neurons
pseudounipolar
-The cell body is off to one side of the axon
-two axons
-sensory neurons
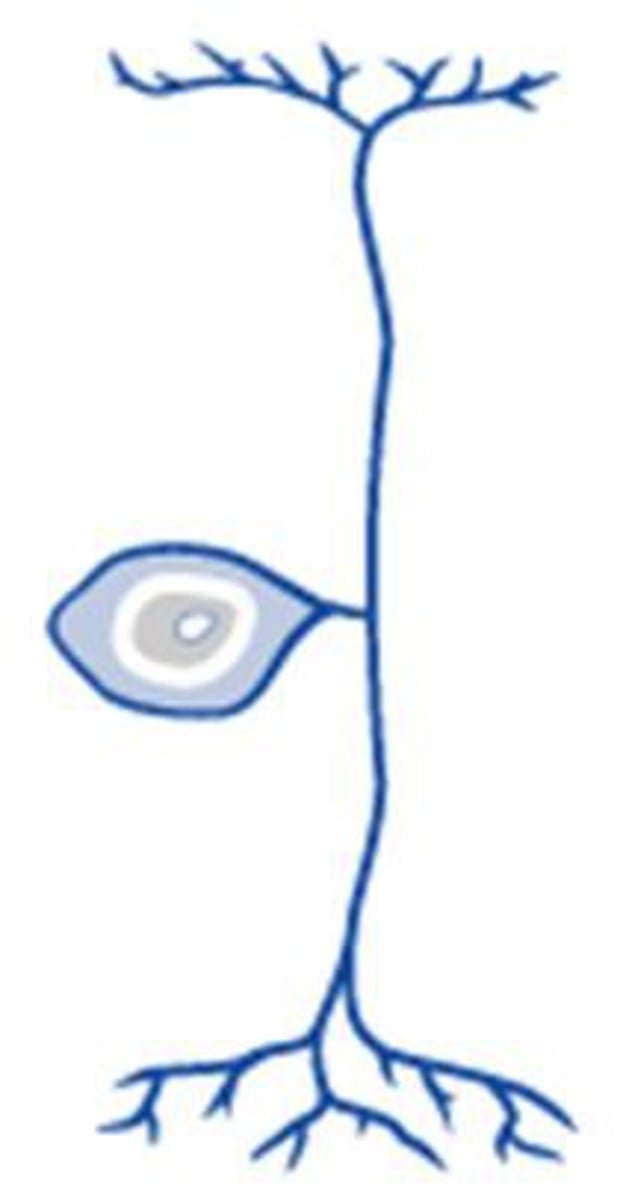
sensory neurons
-neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
-pseudounipolar neuron
astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, microglia
Glial cells of the CNS
astrocytes
-maintain blood brain barrier
-controlling levels of neurotransmitter around synapses
-regulate ion and provide metabolic support
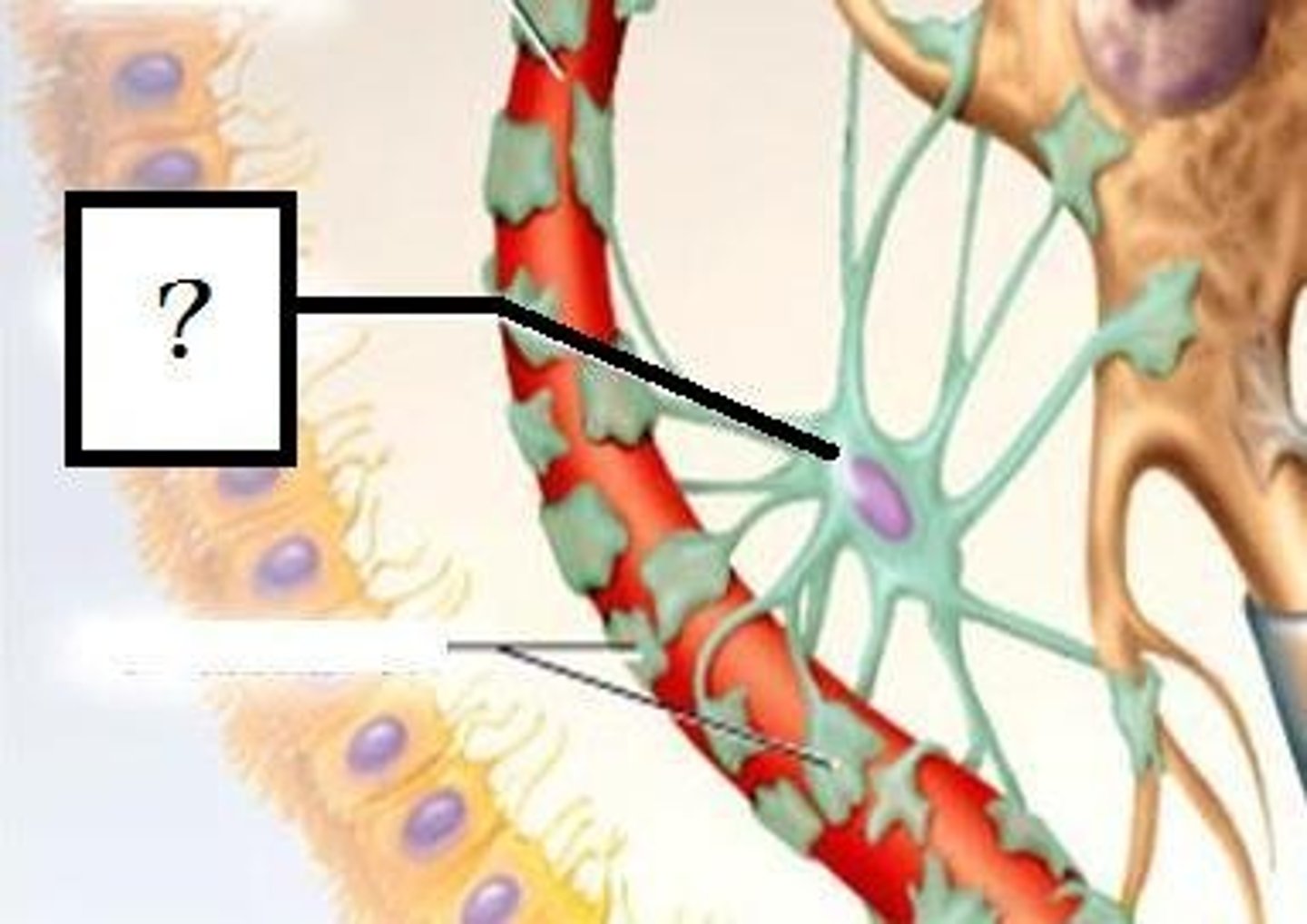
ependymal cells
-lines spinal cord & ventricles of the brain
-involved in producing CSF
oligodendrocytes
myelinate CNS axons, provide structural framework
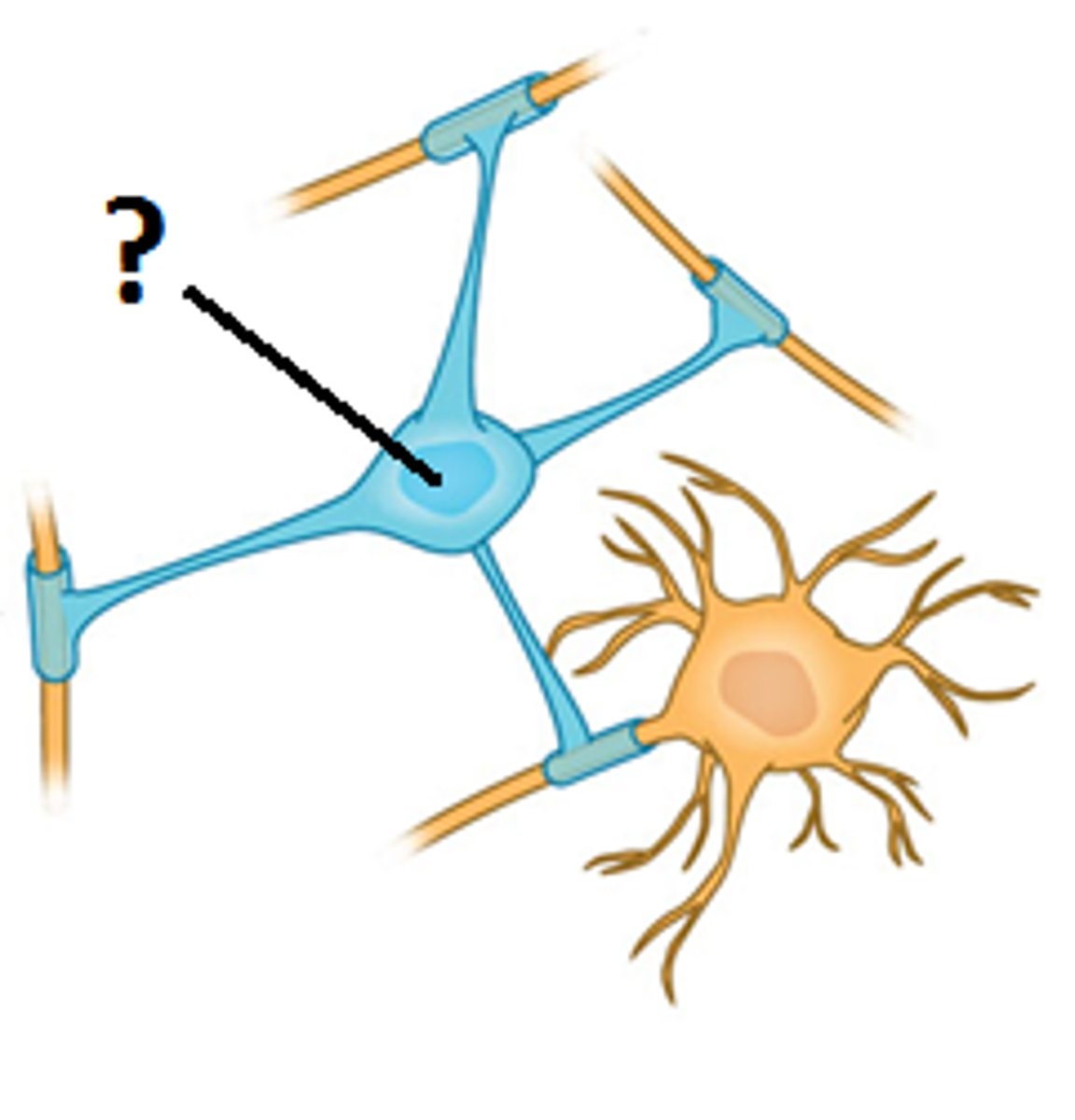
microglia
-brain's immune cells
-remove dead cells and pathogens by phagocytosis
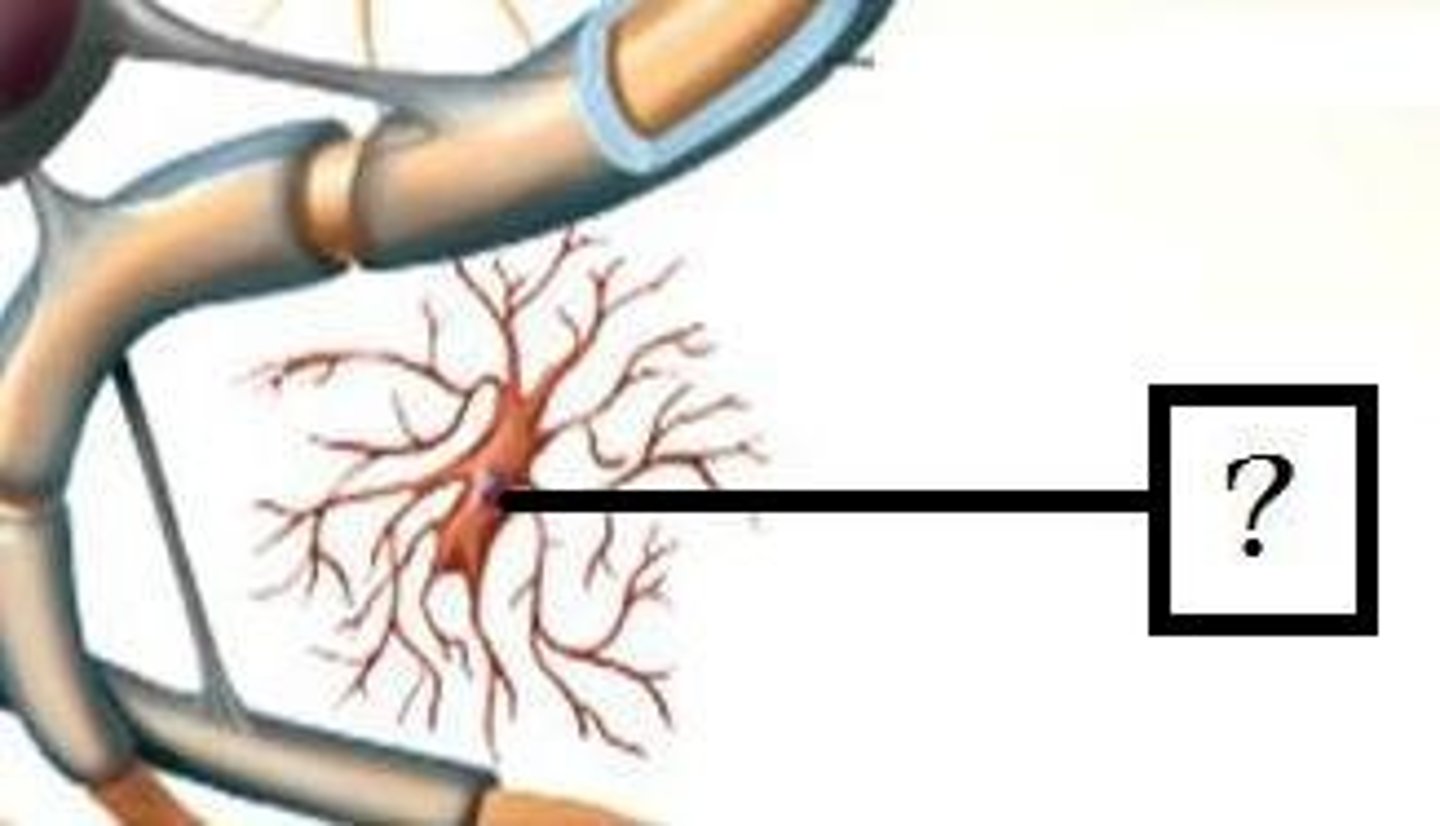
satellite cells and schwann cells
Neuroglial cells of the PNS
satellite cells
-surround neuron cell bodies in PNS
-regulate neurotransmitter levels
Schwann cells
-myelinate neurons in PNS
-maintenance and regeneration of neurons after injury
gray matter
brain and spinal cord tissue
consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and lacks myelinated axons
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
nucleus
clusters of cell bodies in the CNS
cortex
surface of the brain or cerebellum that is primarily gray matter
white matter
-nervous tissue of CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths
-bundles of axons
lipid rich nature of myelin
Why is white matter white?
tract
bundle of axons in the CNS
lemniscus
a tract that meanders through the brain like a ribbon
fasciculus
bundle of muscle fibers
column
composed of bundles of nerve fibers (axons) that transmit information up and down the spinal cord
named based on their location relative to the grey matter within the spinal cord
peduncle
a stalk-like structure that connects different parts of the brain
capsule
pathway for nerve fibers connecting the cerebral cortex with other parts of the brain and spinal cord
internal capsule
A large collection of axons that connects the telencephalon with the diencephalon.
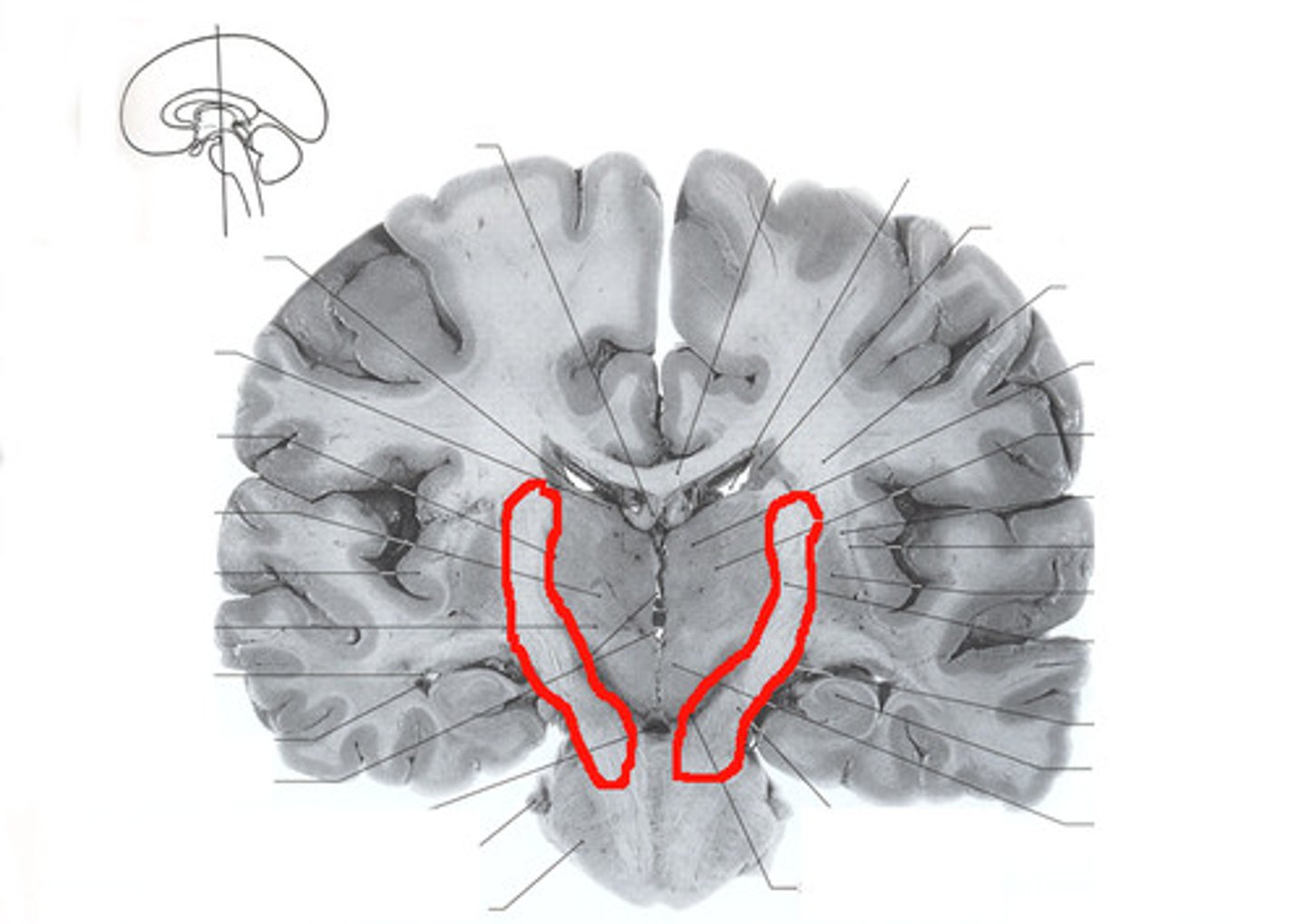
lateral ventricle
one of the two ventricles located in the center of the telencephalon
corpus callosum
communication between the two hemispheres
head of caudate nucleus
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
anterior limb of internal capsule
Bounded by the lentiform nucleus and head of the caudate nucleus
-Anterior thalamic radiation; corticopontine
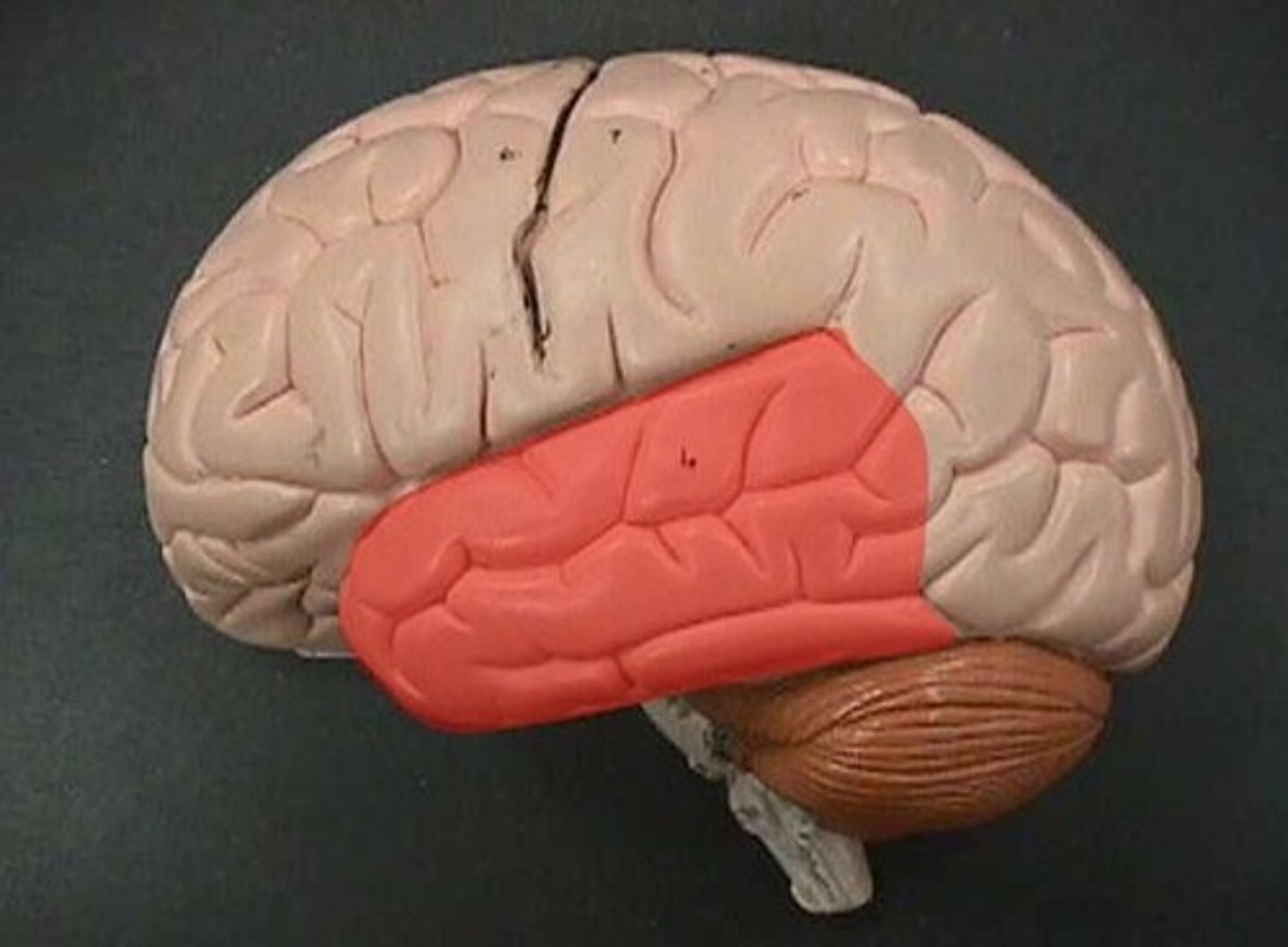
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
internal capsule
A large collection of axons that connects the telencephalon with the diencephalon.
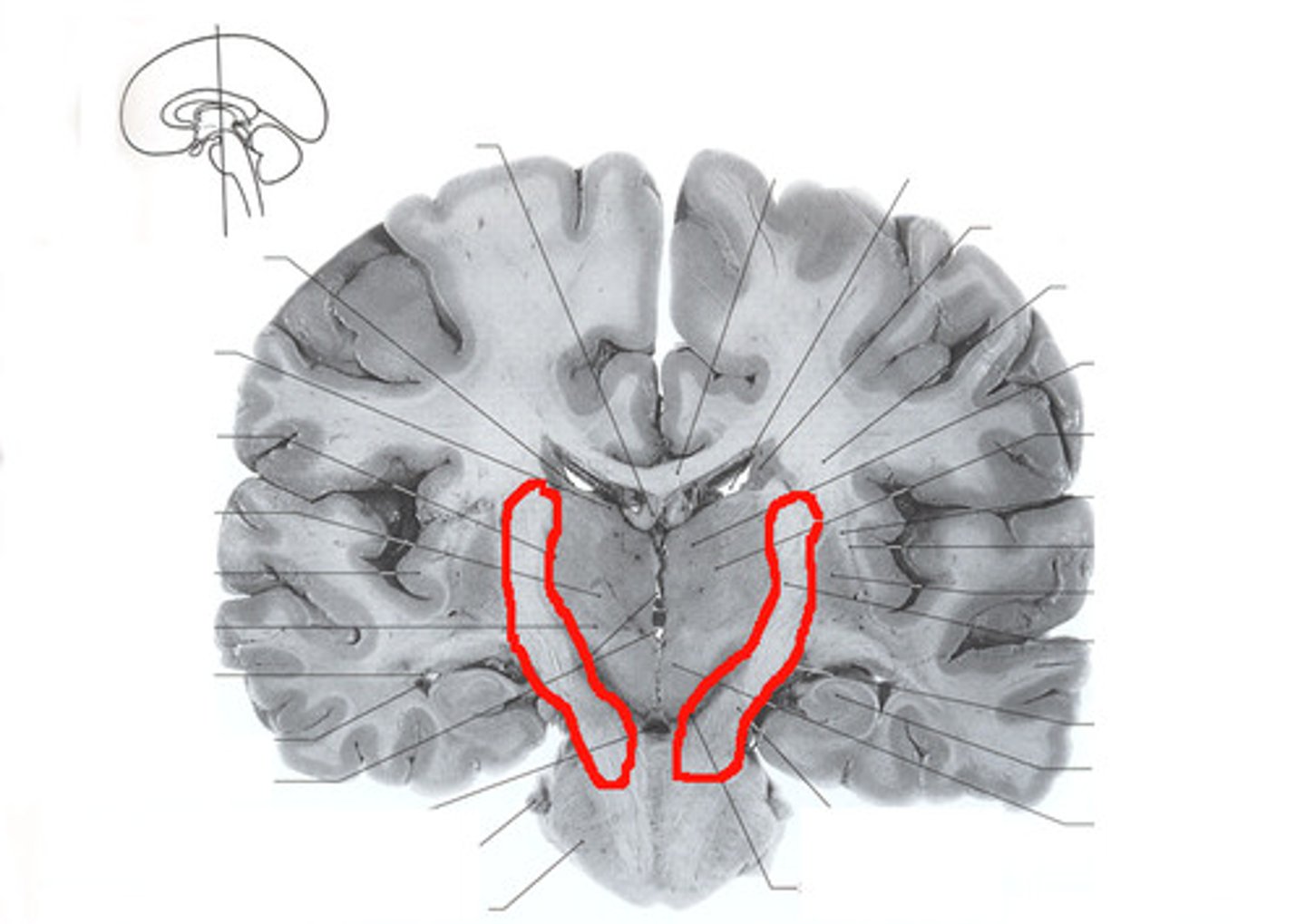
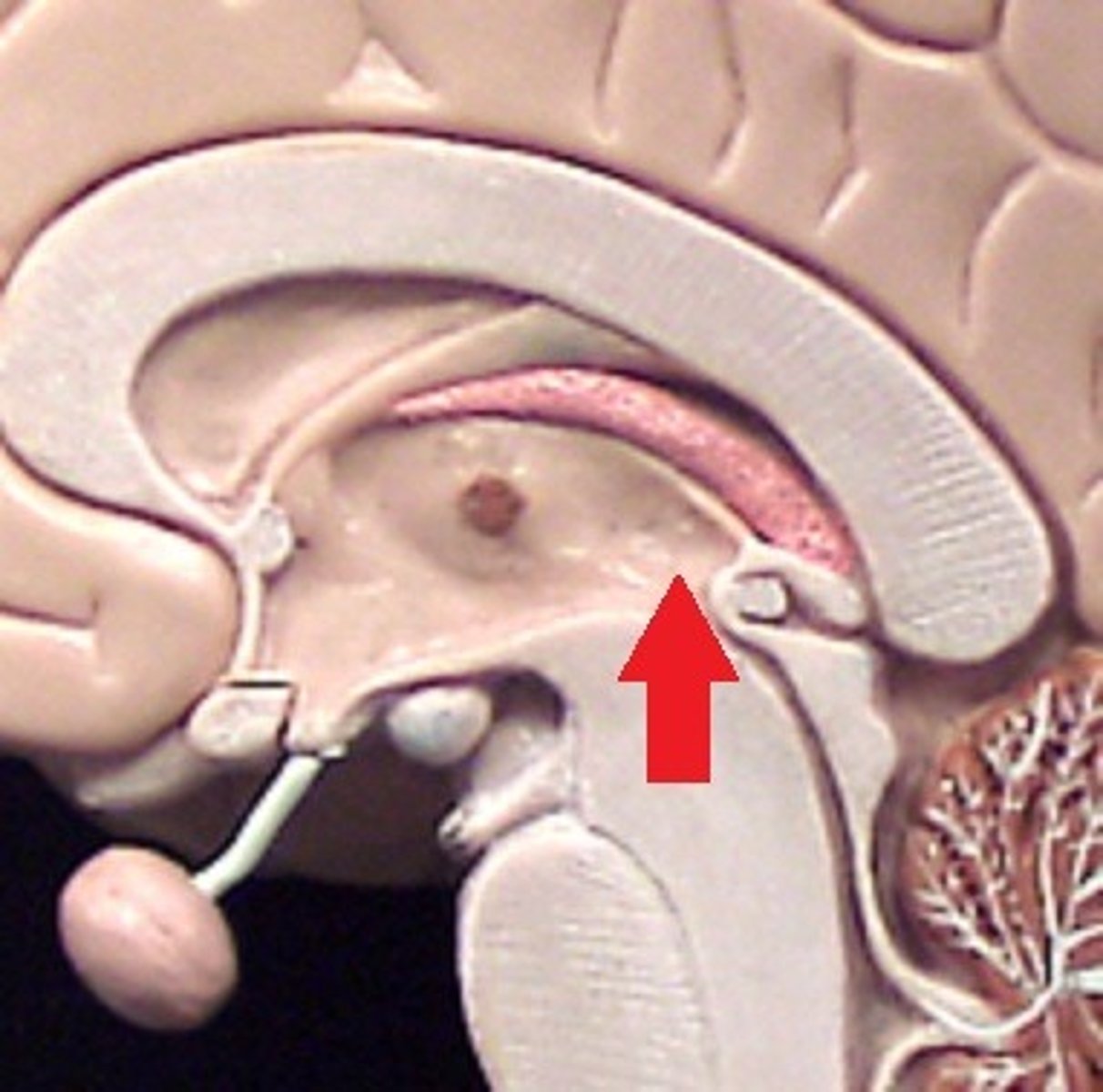
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
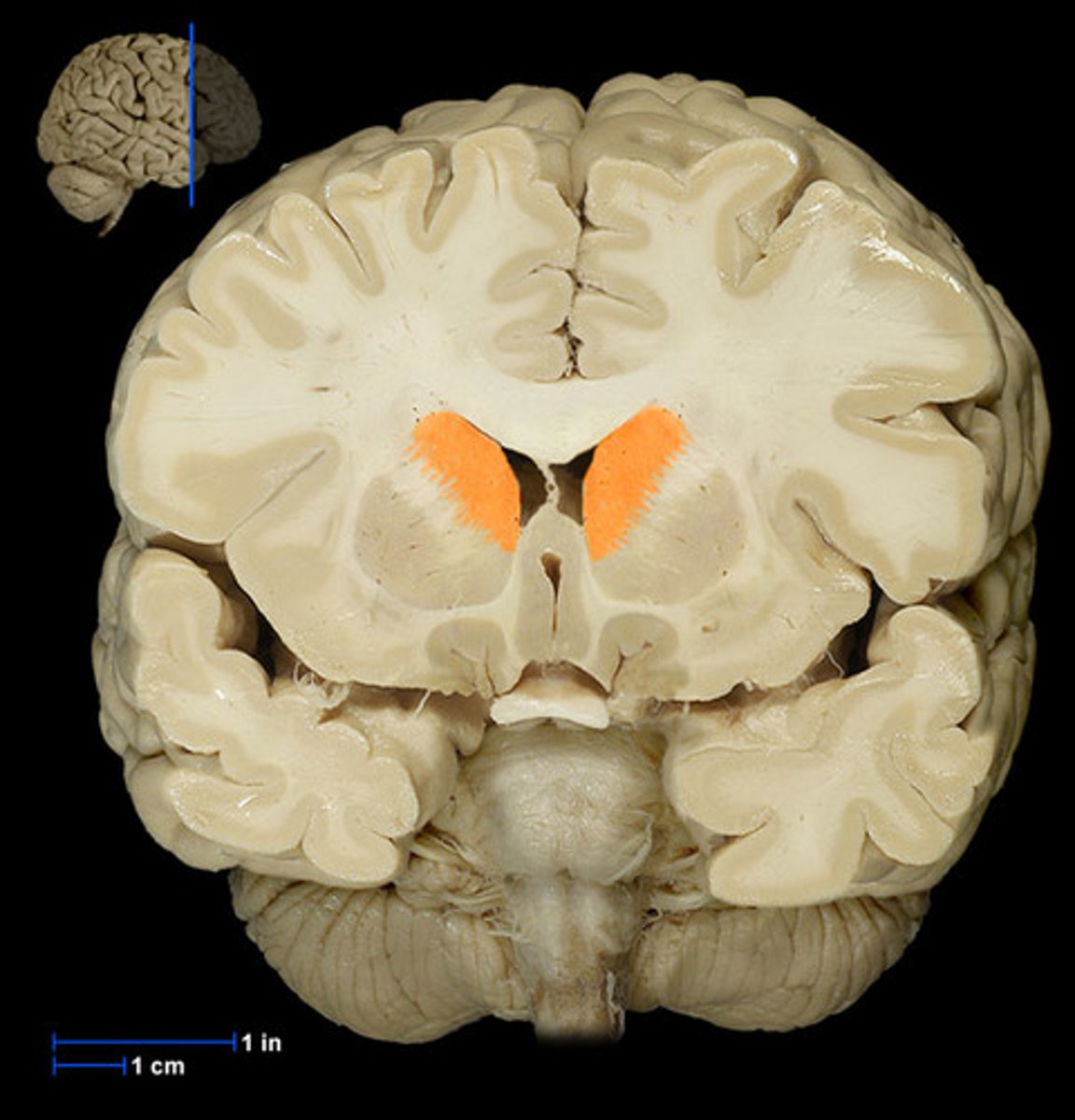
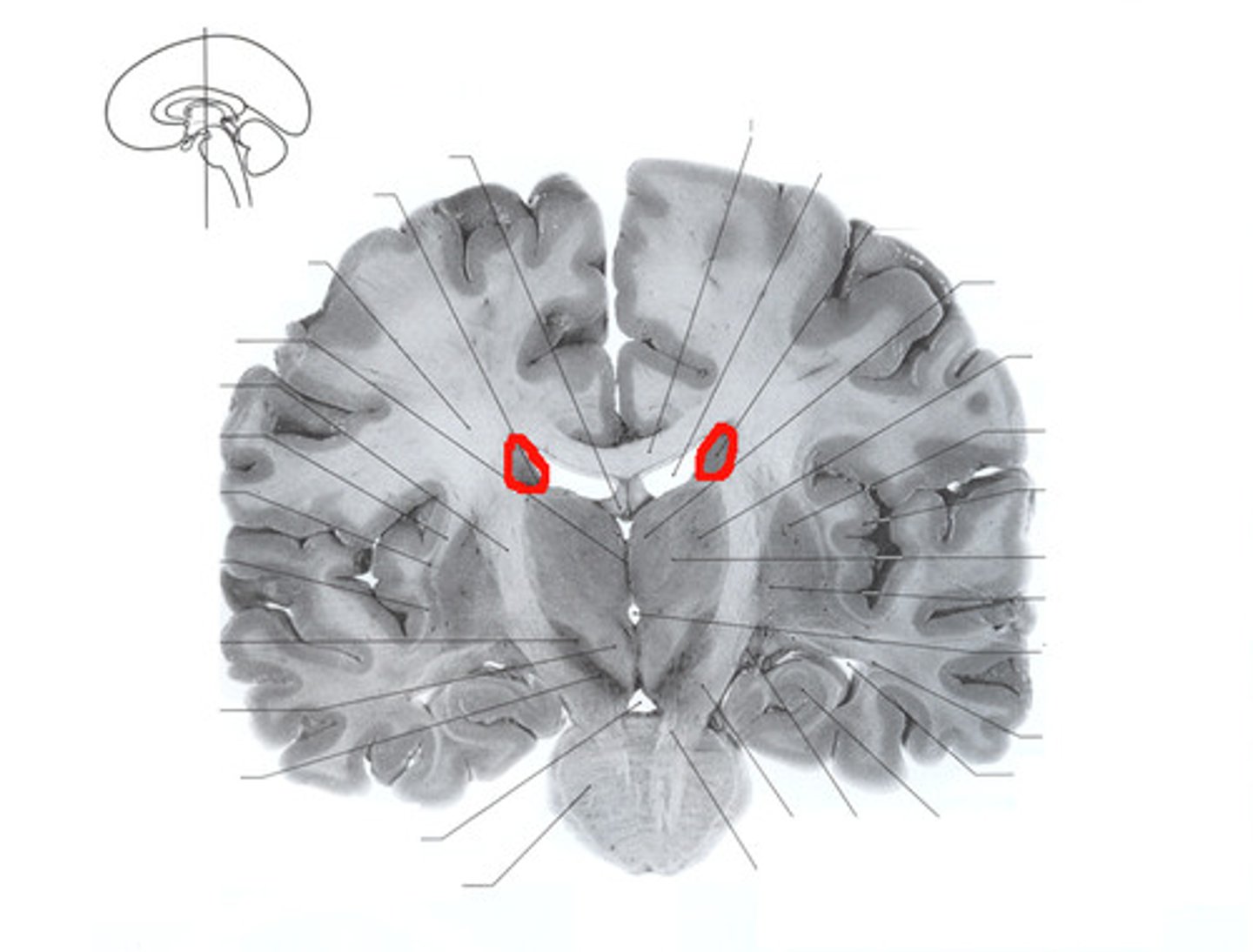
caudate nucleus
One of the basal ganglia; it has a long extension or tail.
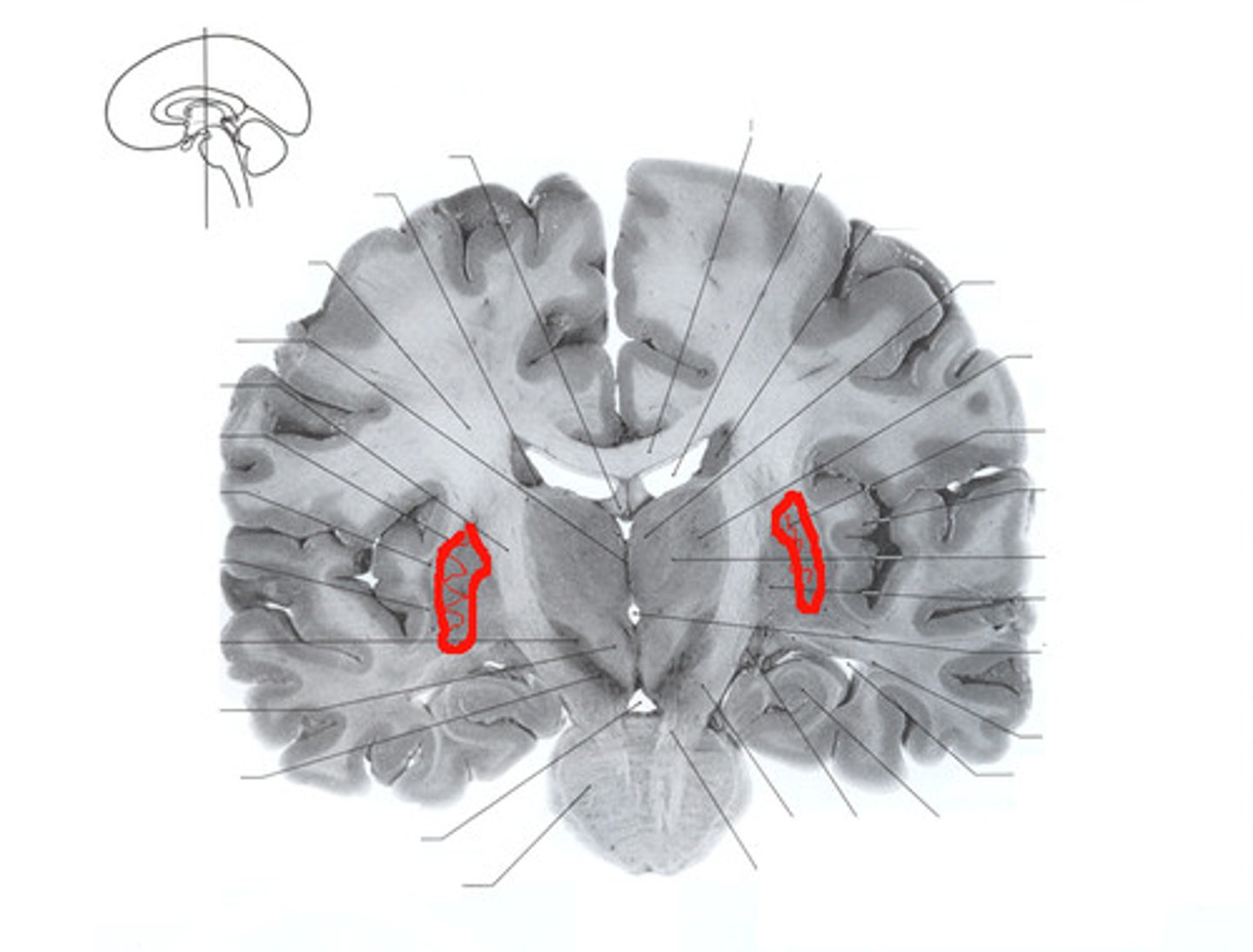
putamen
large subcortical structure, part of the basal ganglia
globus pallidus
component of the basal ganglia that connects to the thalamus which relays information to the motor areas and the prefrontal cortex
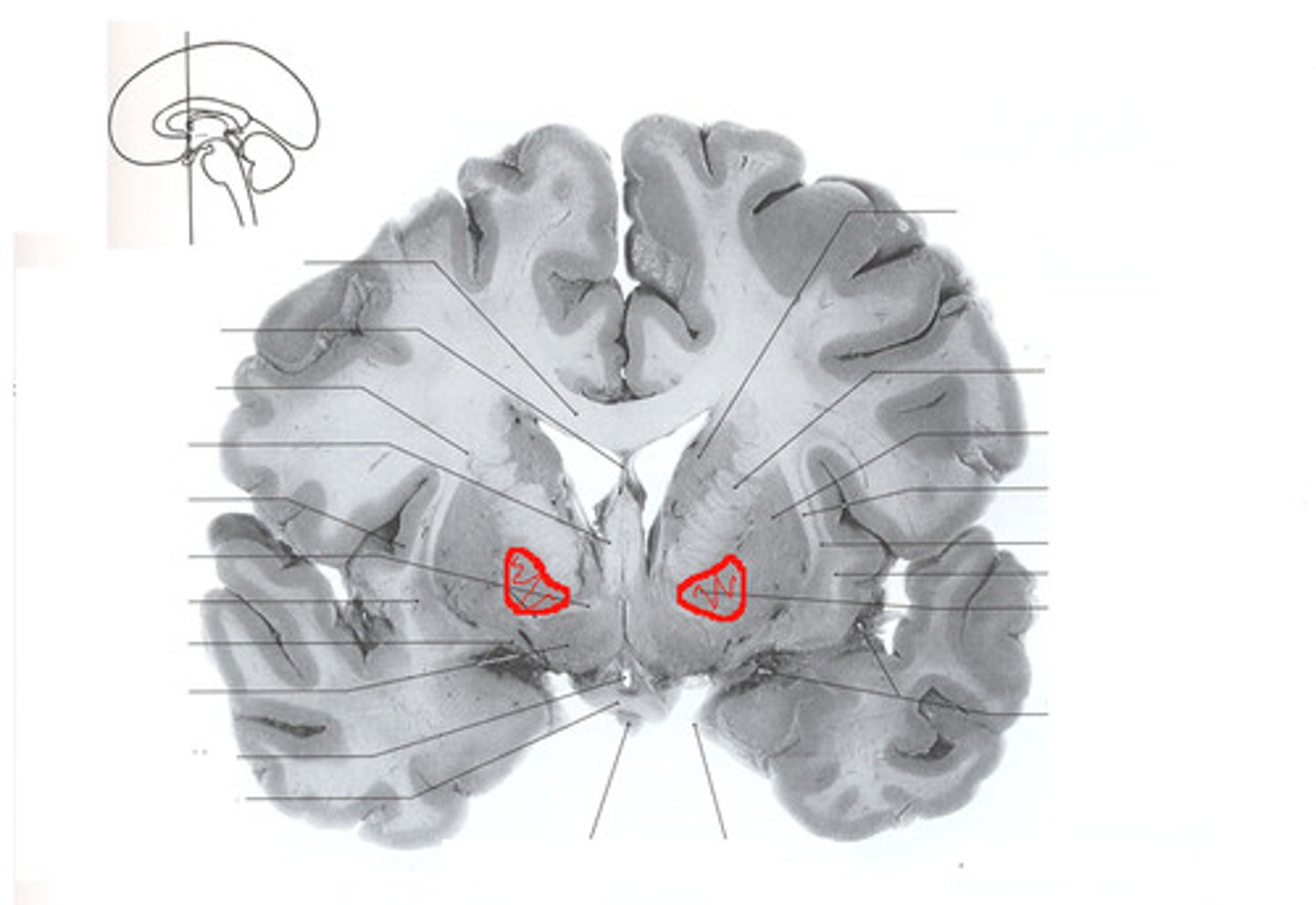
amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.
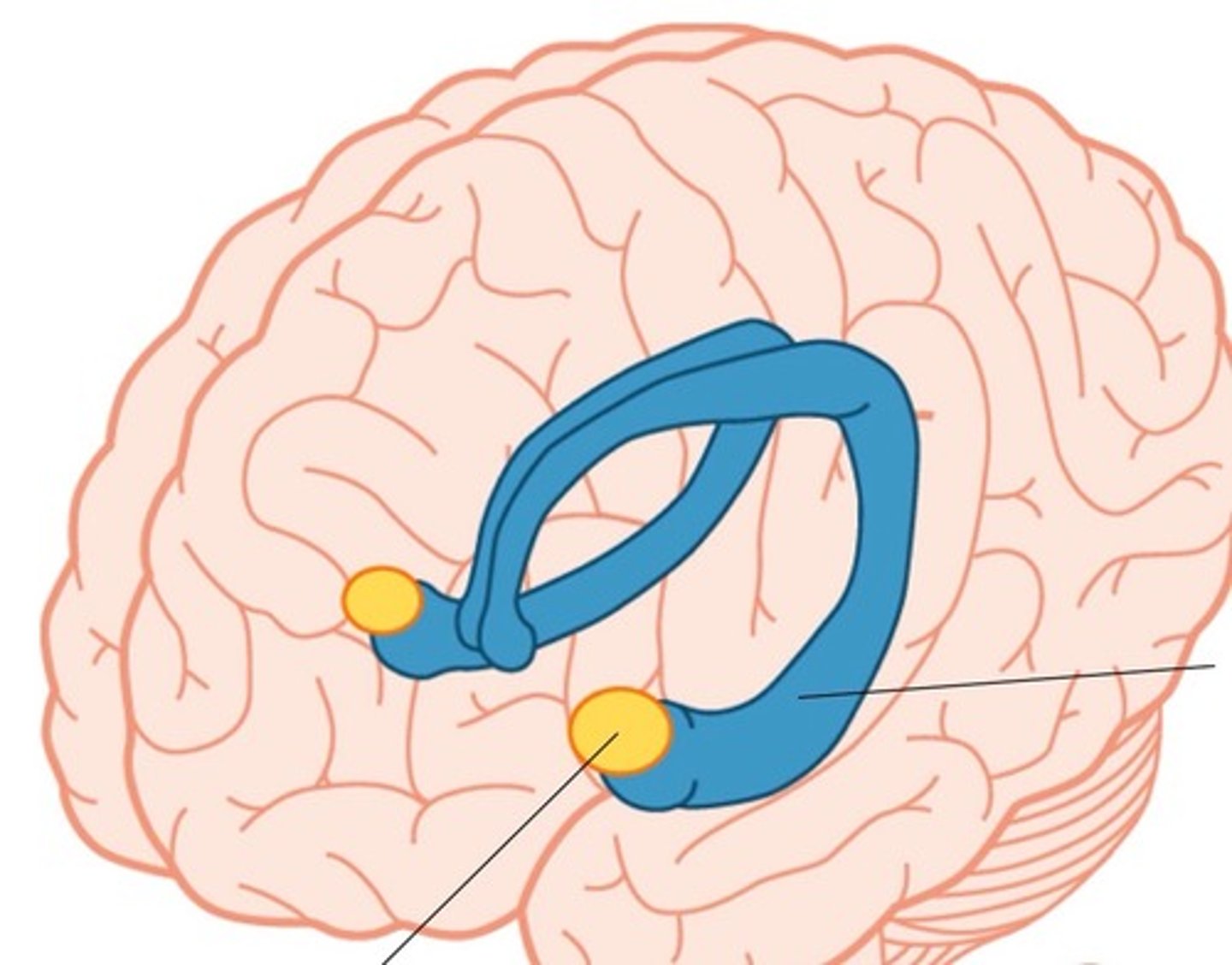
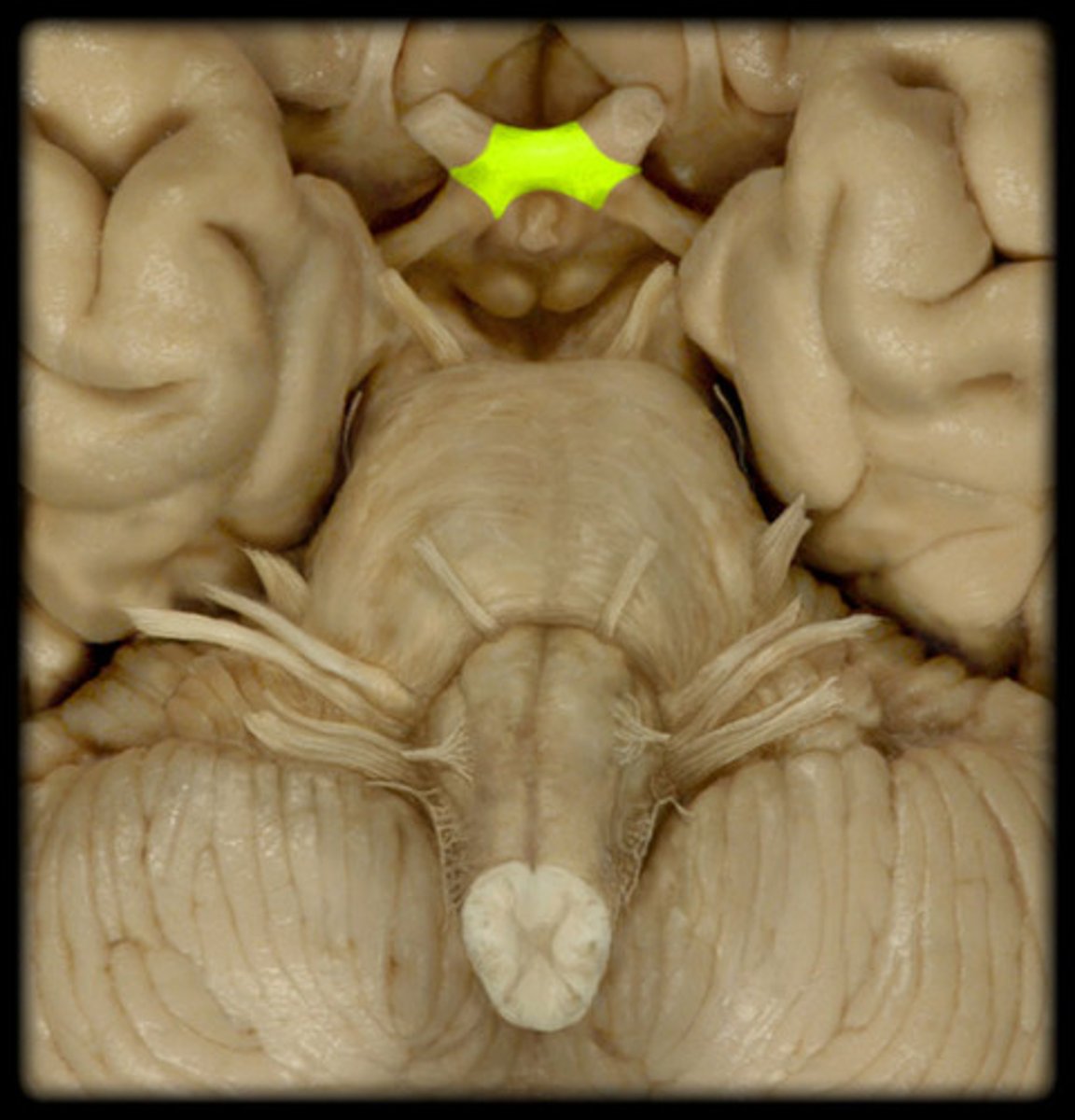
optic chiasm
point at which optic nerve fibers cross in the brain
optic tracts
nerve pathways traveling from the optic chiasm to the thalamus, hypothalamus, and midbrain
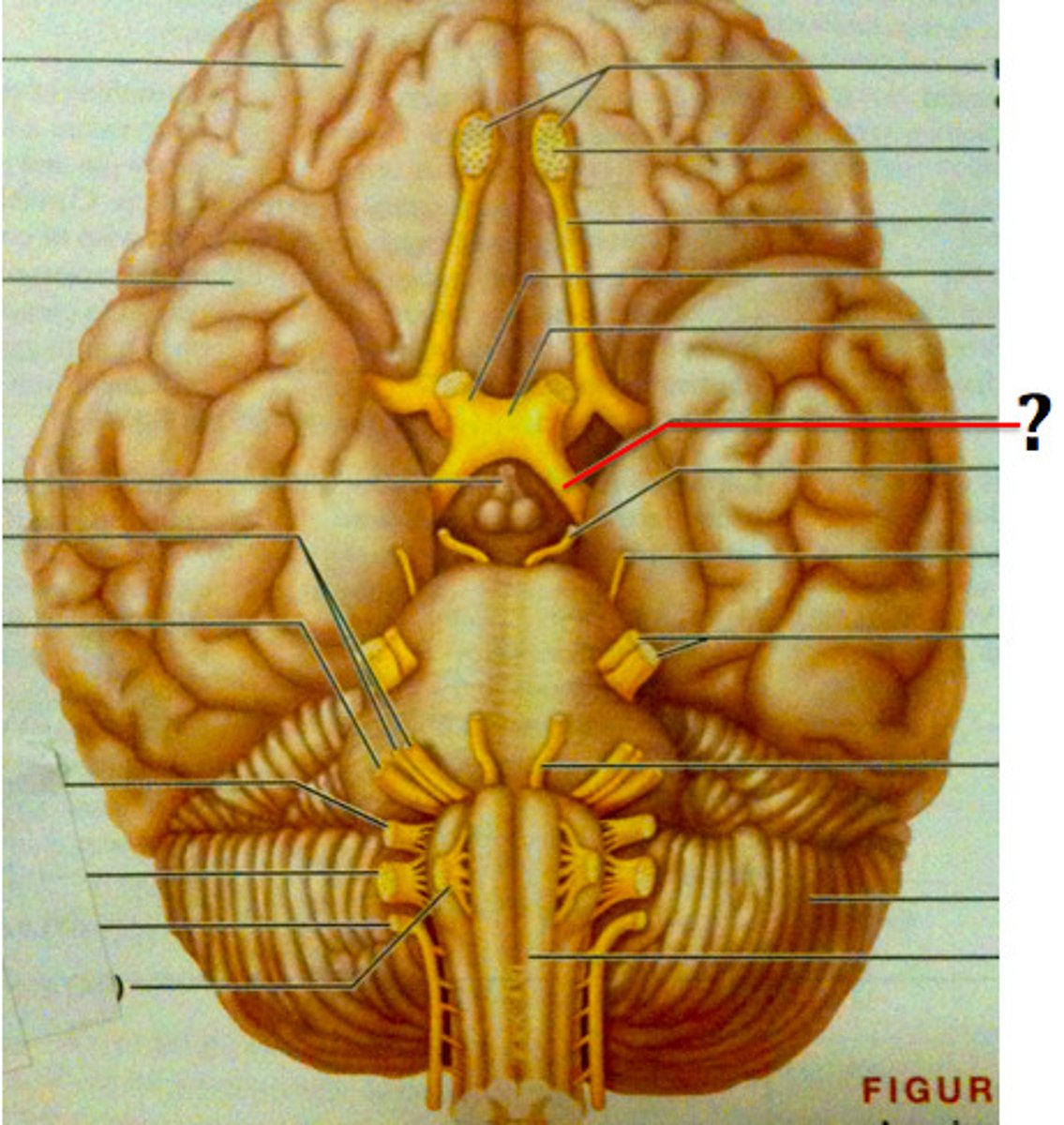
substantia nigra
An area of the midbrain that is involved in motor control and contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons
red nucleus
in midbrain
receives inputs from the cerebellum and motor cortex
sends axons to motor neurons in the spinal cord
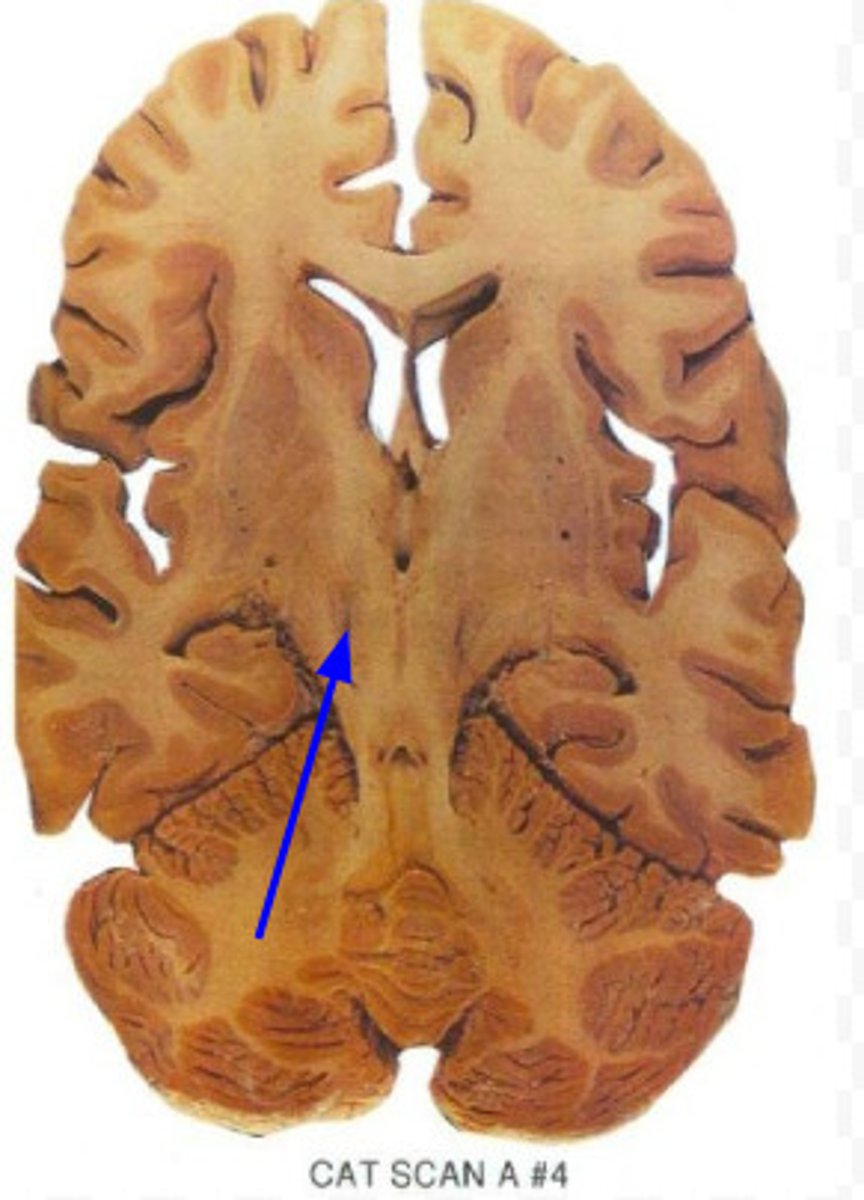
subthalamic nucleus
a small nucleus, located ventral to the thalamus, that is part of the basal ganglia
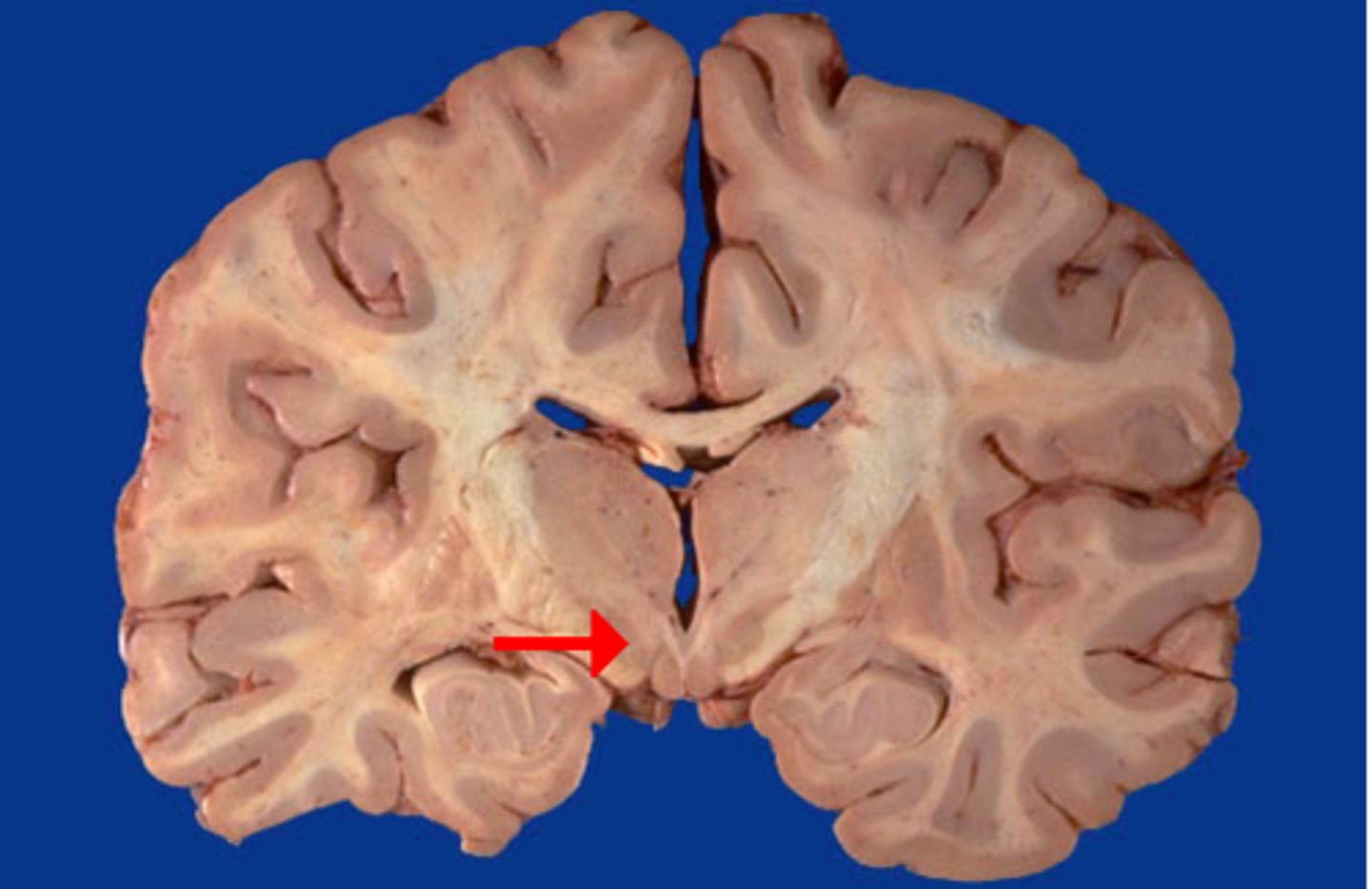
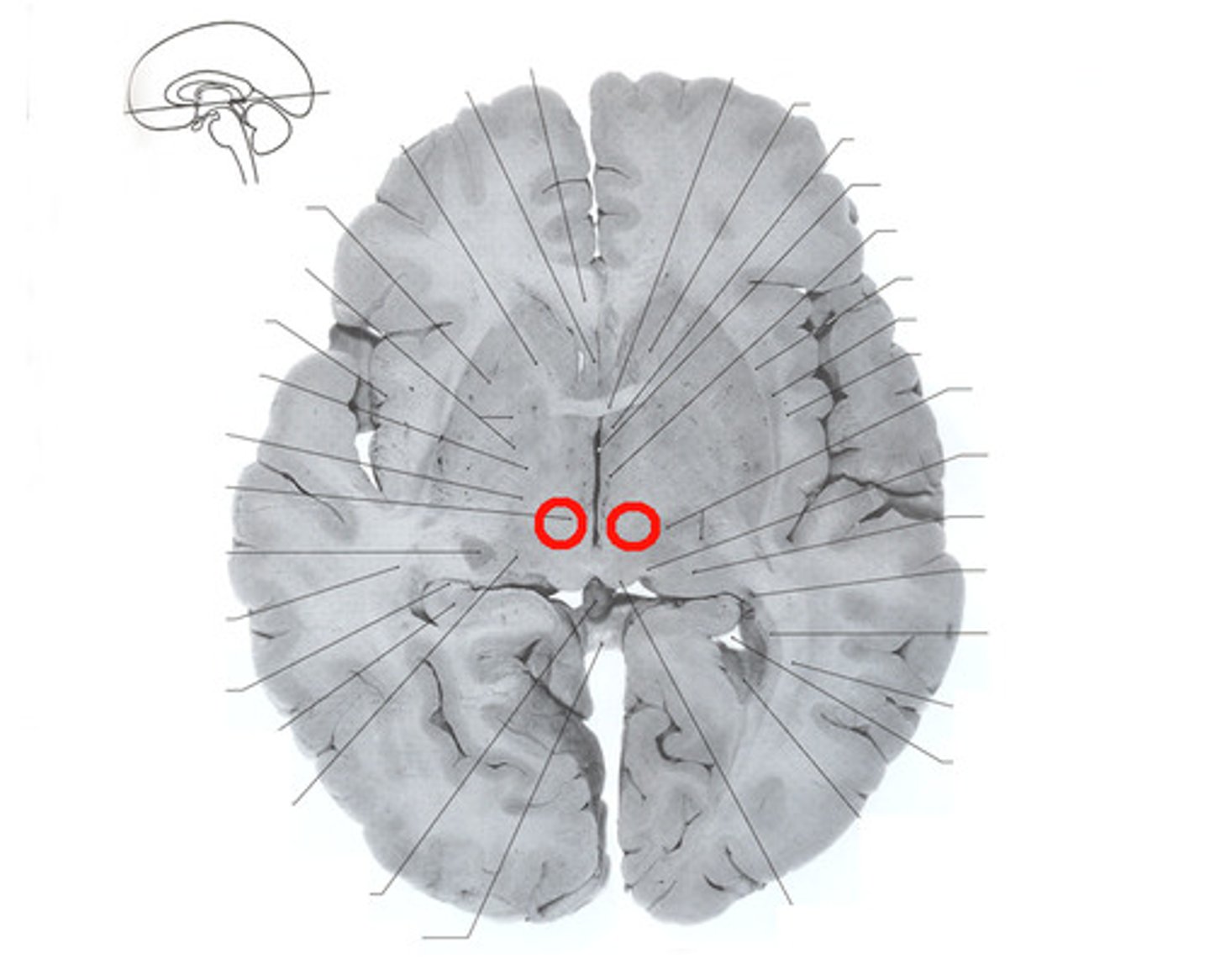
thalamus
-relay and process info
-regulate consciousness
hypothalamus
regulate homeostasis, growth, and behaviors
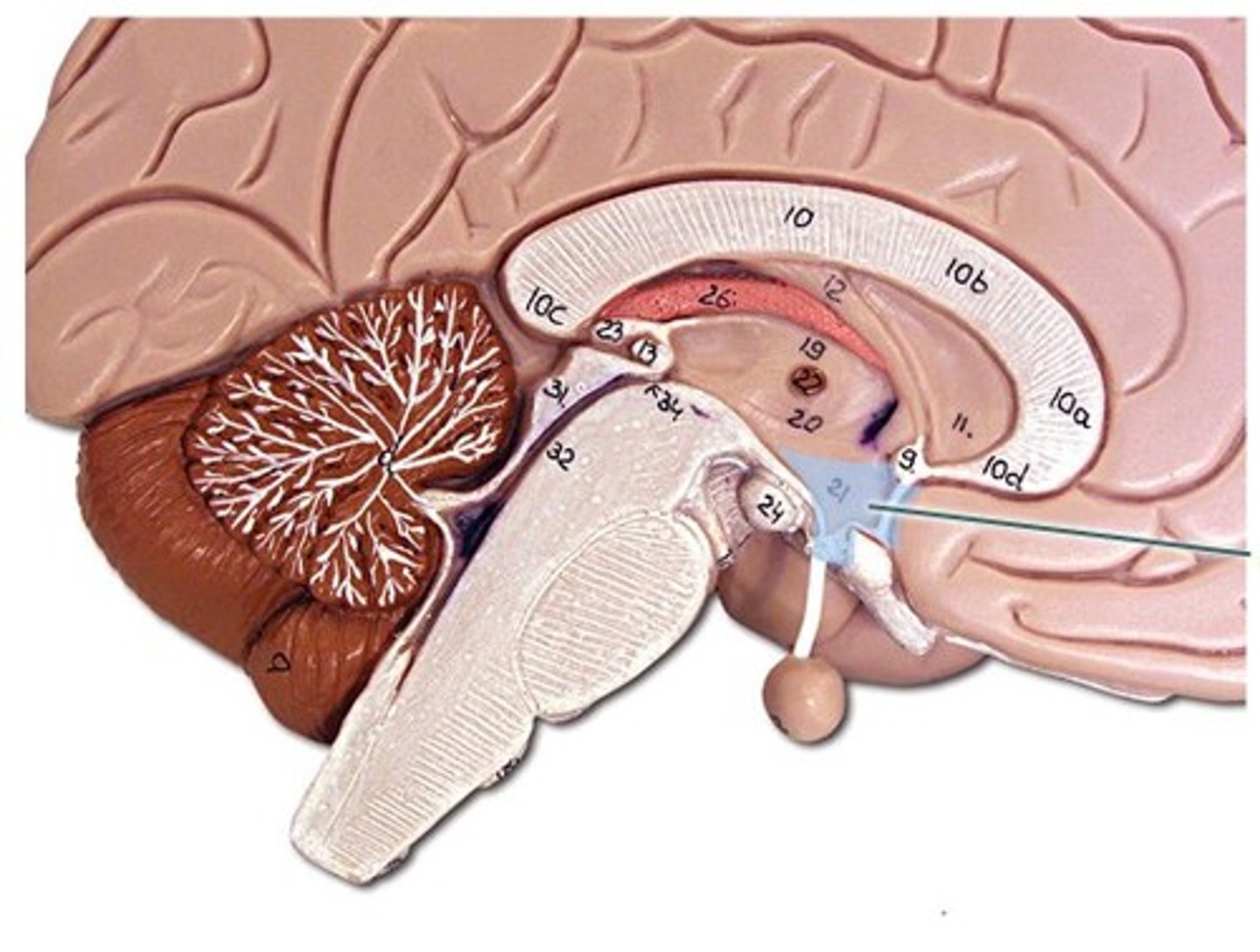
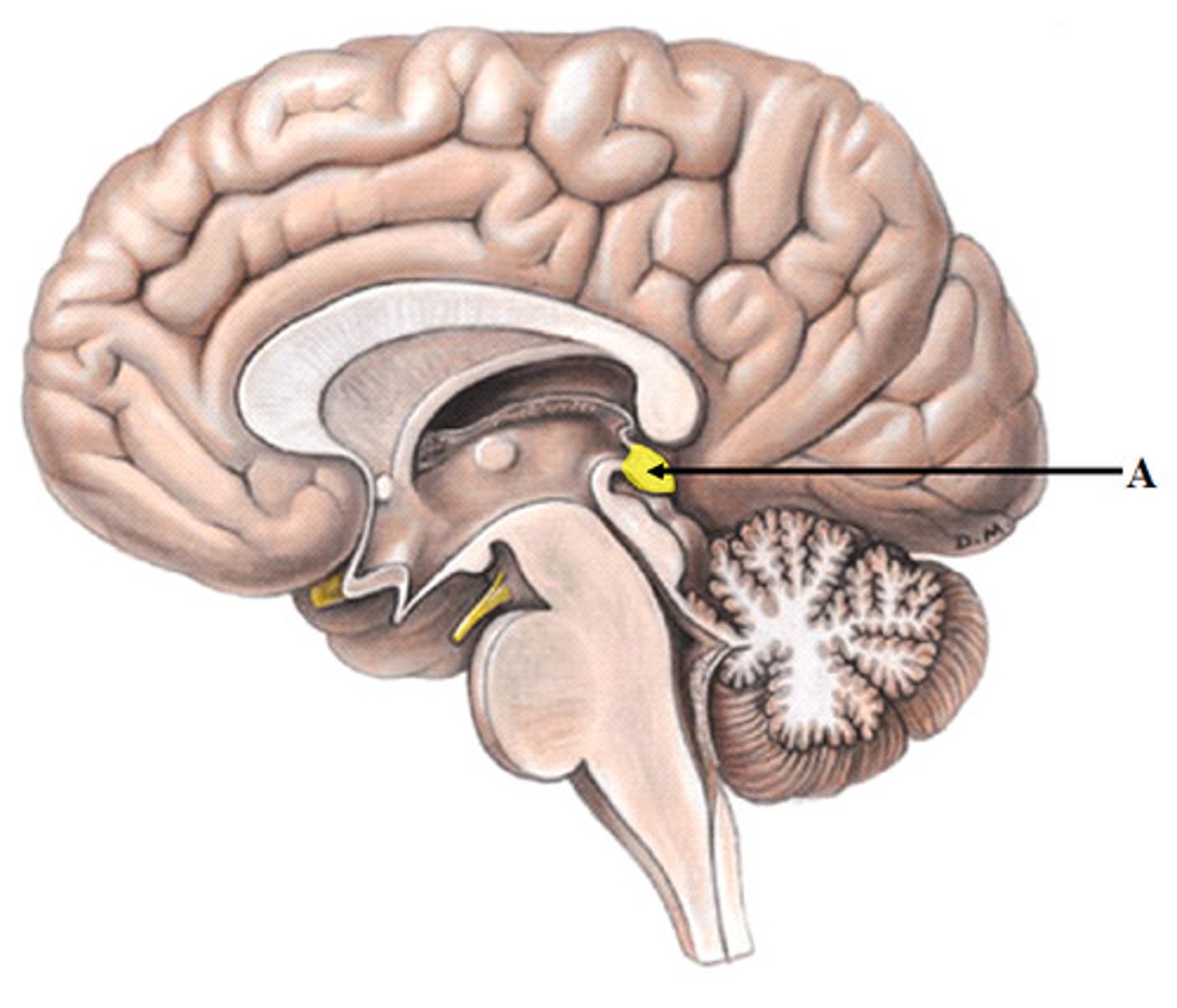
epithalamus (pineal gland)
regulates endocrine system
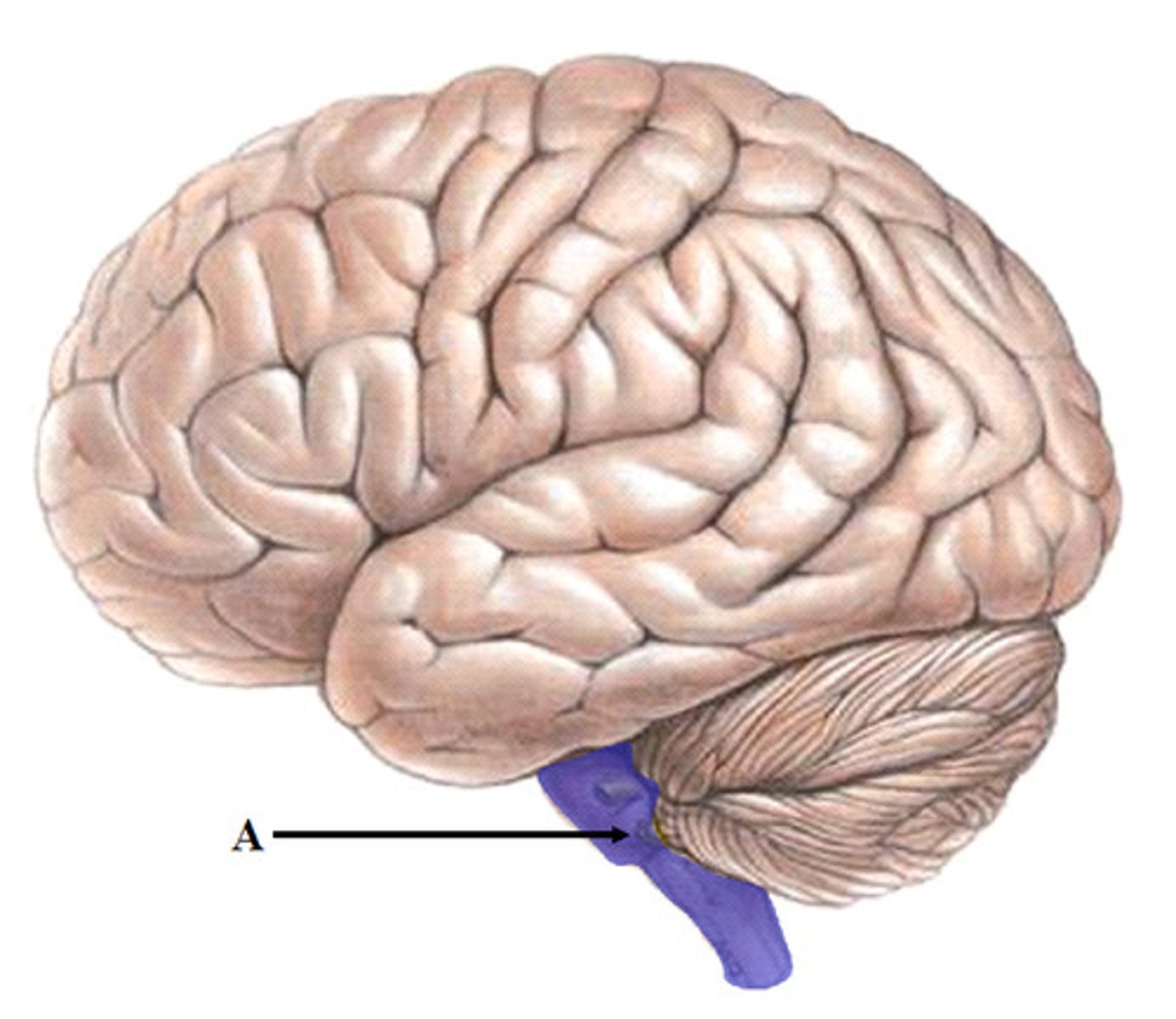
subthalamus
brain structure that regulates movement
brainstem
-midbrain, pons, medulla
-primarily white matter tracts with nuclei for some cranial nerves
midbrain
-small part of brain above the pons that integrates sensory info and relays it upward
-has cerebral peduncles
cerebral peduncles
contain fibers that carry motor output from cerebrum to other regions of CNS
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
more ascending axons that haven't exited spinal cord
Why is the cervical cord bigger?
has motor neurons for lower extremity
Why is the lumbar cord bigger?
spinal nerves are motor and sensory and cutaneous are sensory only; cutaneous are branches of spinal nerves
What is the difference between spinal nerves and cutaneous nerves?
cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
spinal roots
a bundle of axons surrounded by connective tissue that occurs in pairs, which fuse and form a spinal nerve
cutaneous nerves
Nerves that go into skin, giving off terminal branches that ascent into dermi
"Only one of the two athletes felt very good, victorious, and healthy"
How to remember cranial nerves
olfactory nerve (CN I)
Responsible for the sense of smell.
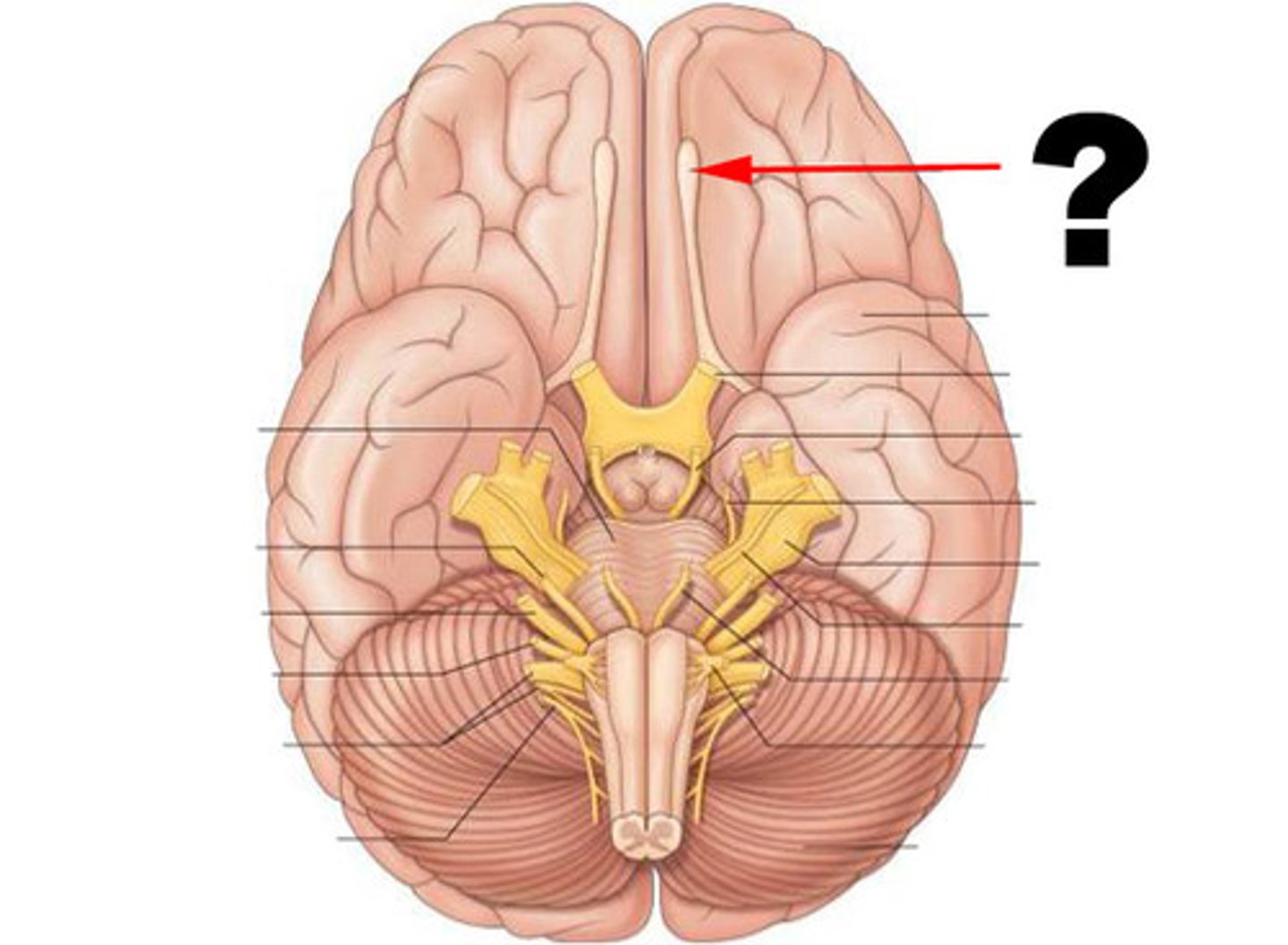
optic nerve (CN II)
sensory, vision
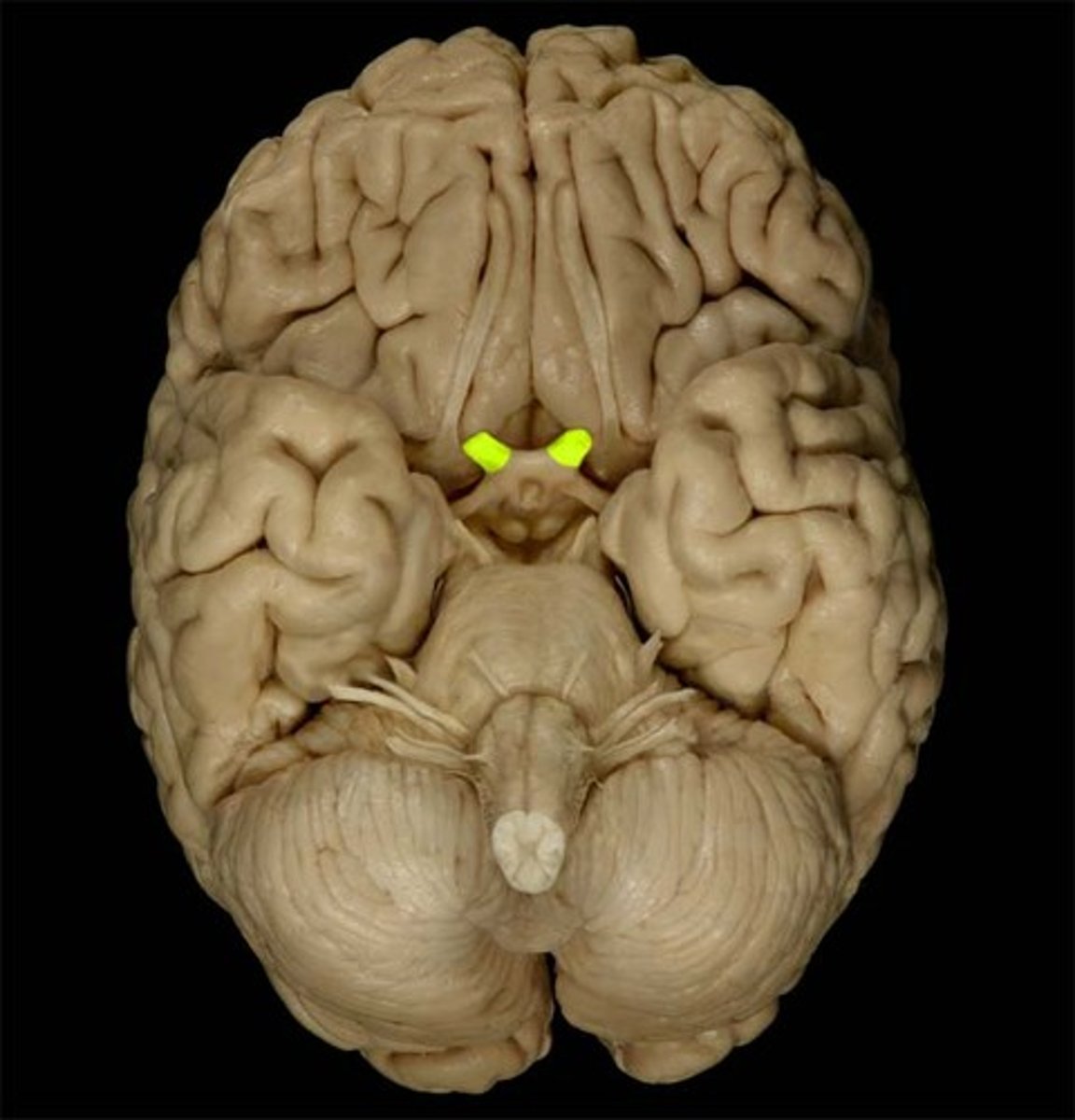
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Controls eye movement and pupil constriction.
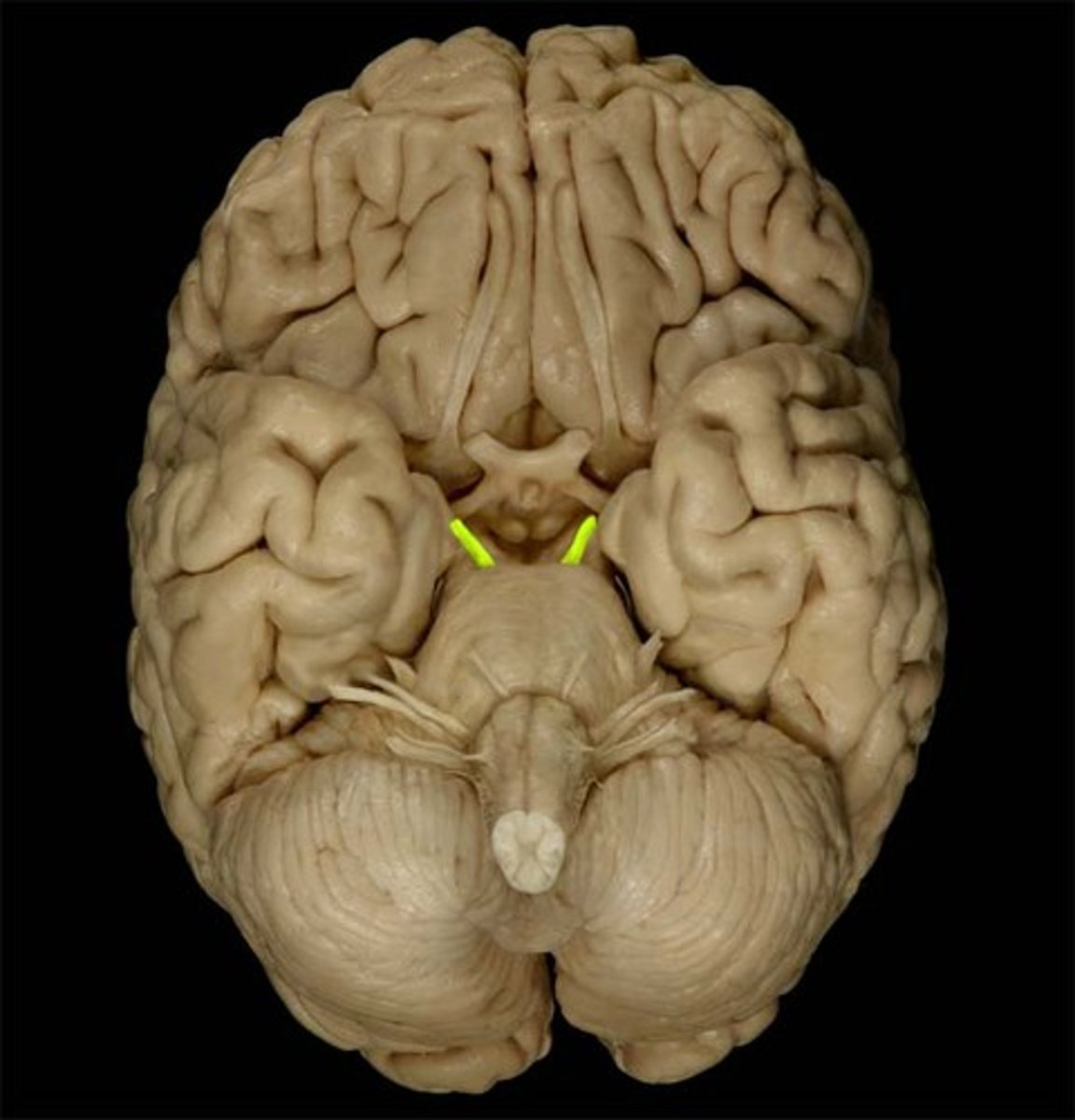
trochlear nerve (CN IV)
innervates the superior oblique muscle
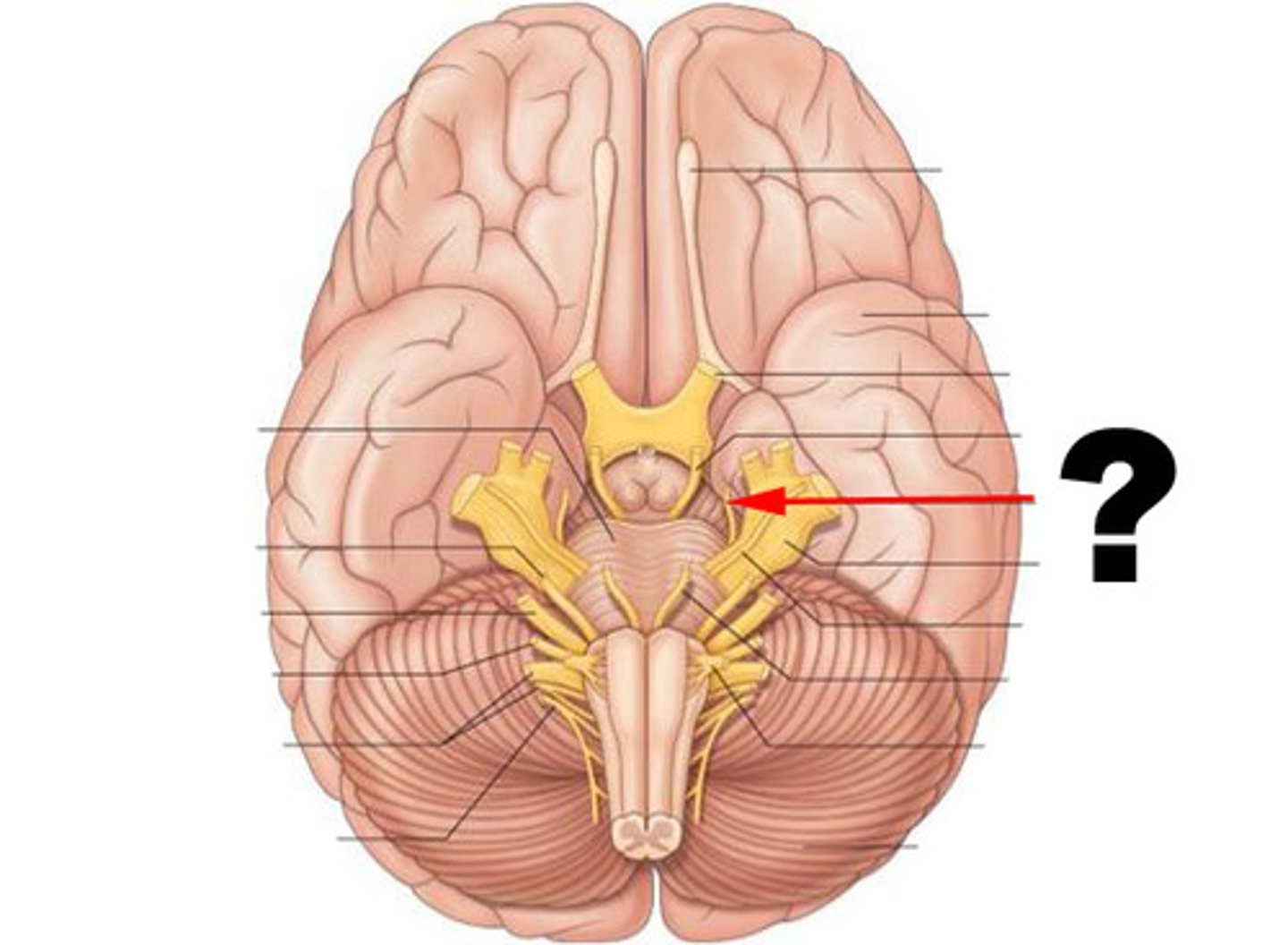
trigeminal nerve (CN V)
somatic sensory nerve to skin over mandible, temporal region, and anterior 2/3 of the tongue
sensitive to texture/irritants on the tongue and in the nasal cavity/eye
lingual nerve is the branch that controls touch for the tongue
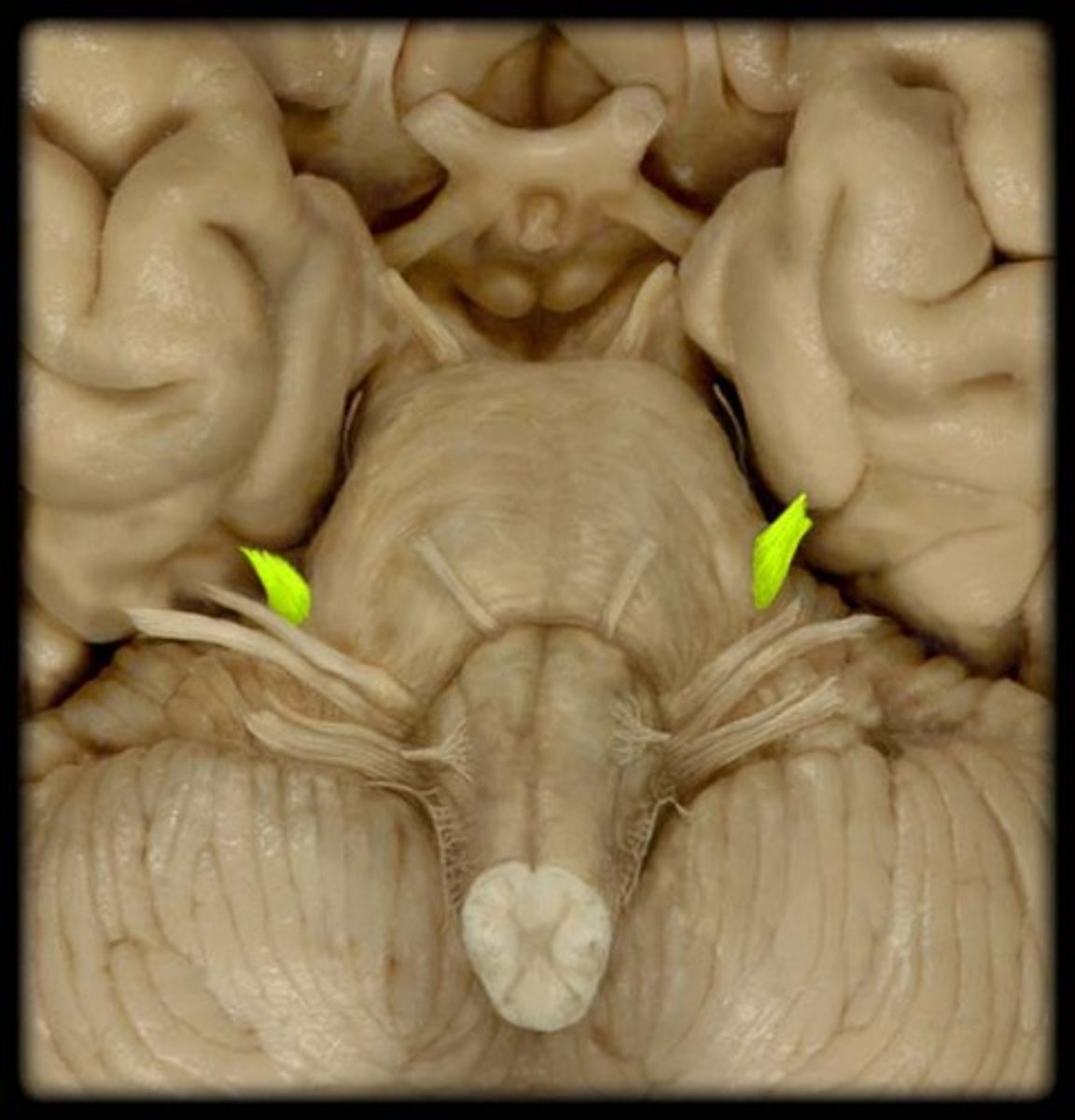
abducens nerve (CN VI)
Innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye
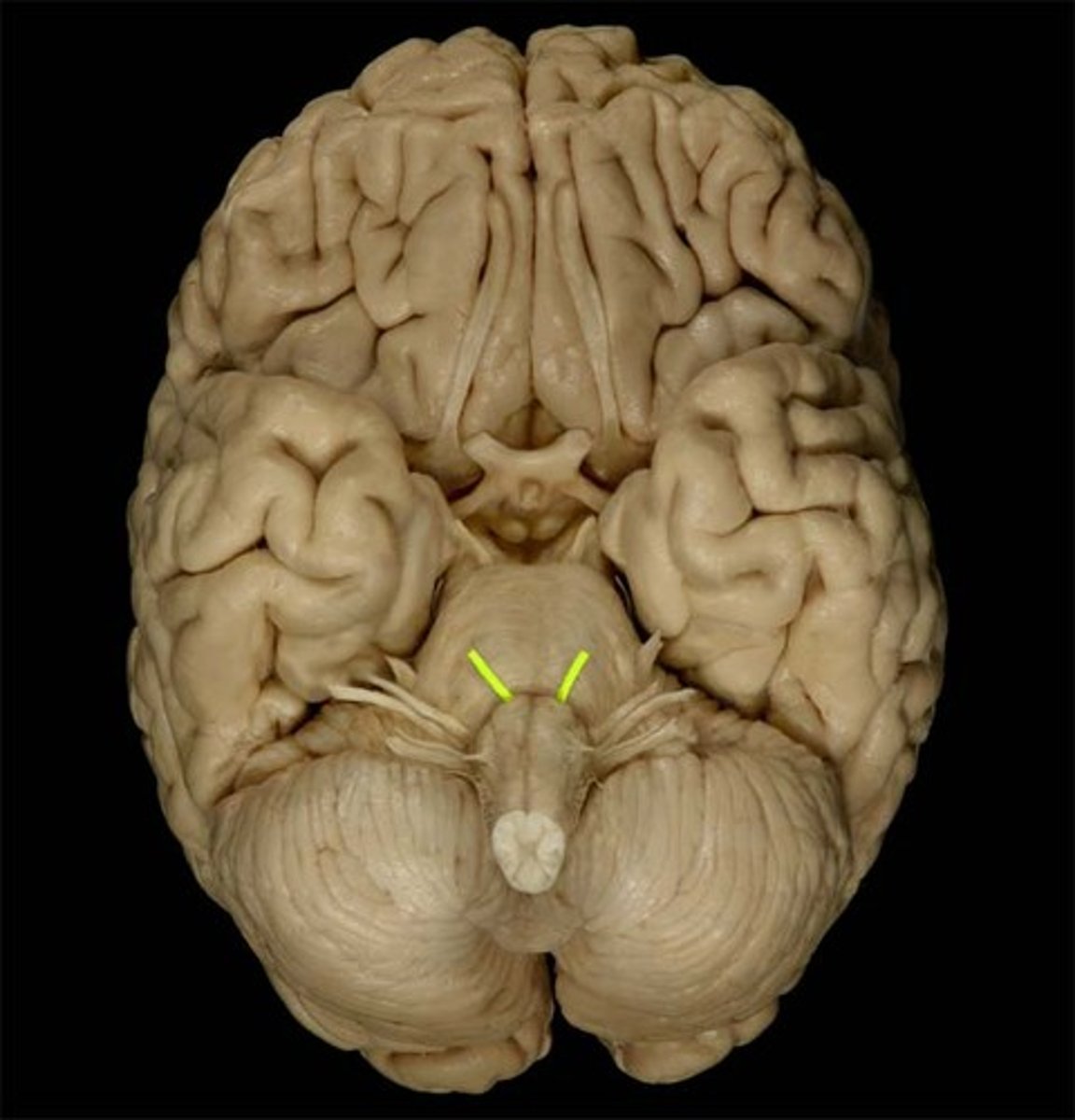
facial nerve (CN VII)
innervates muscles of facial expression
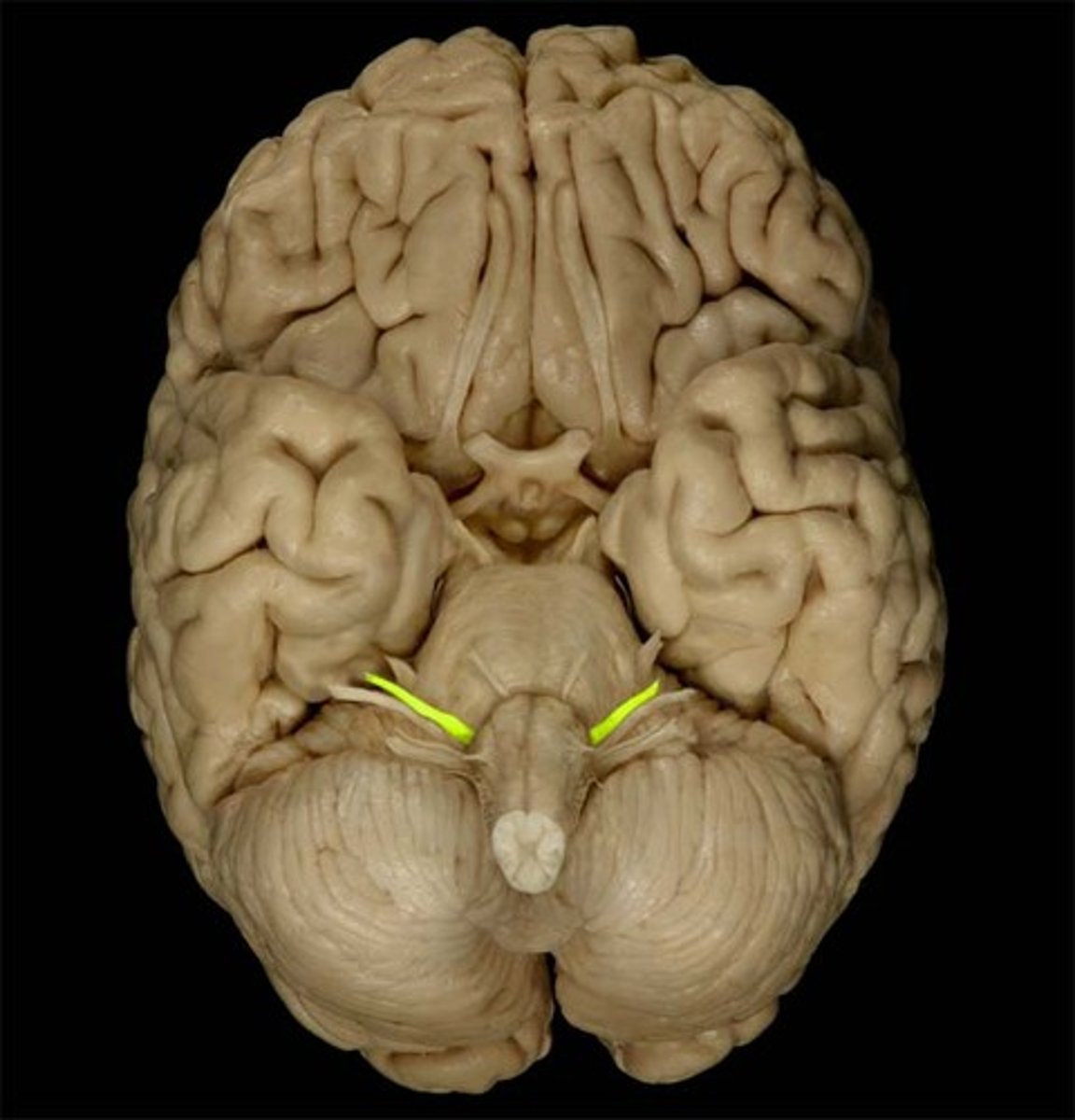
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Responsible for hearing and balance.
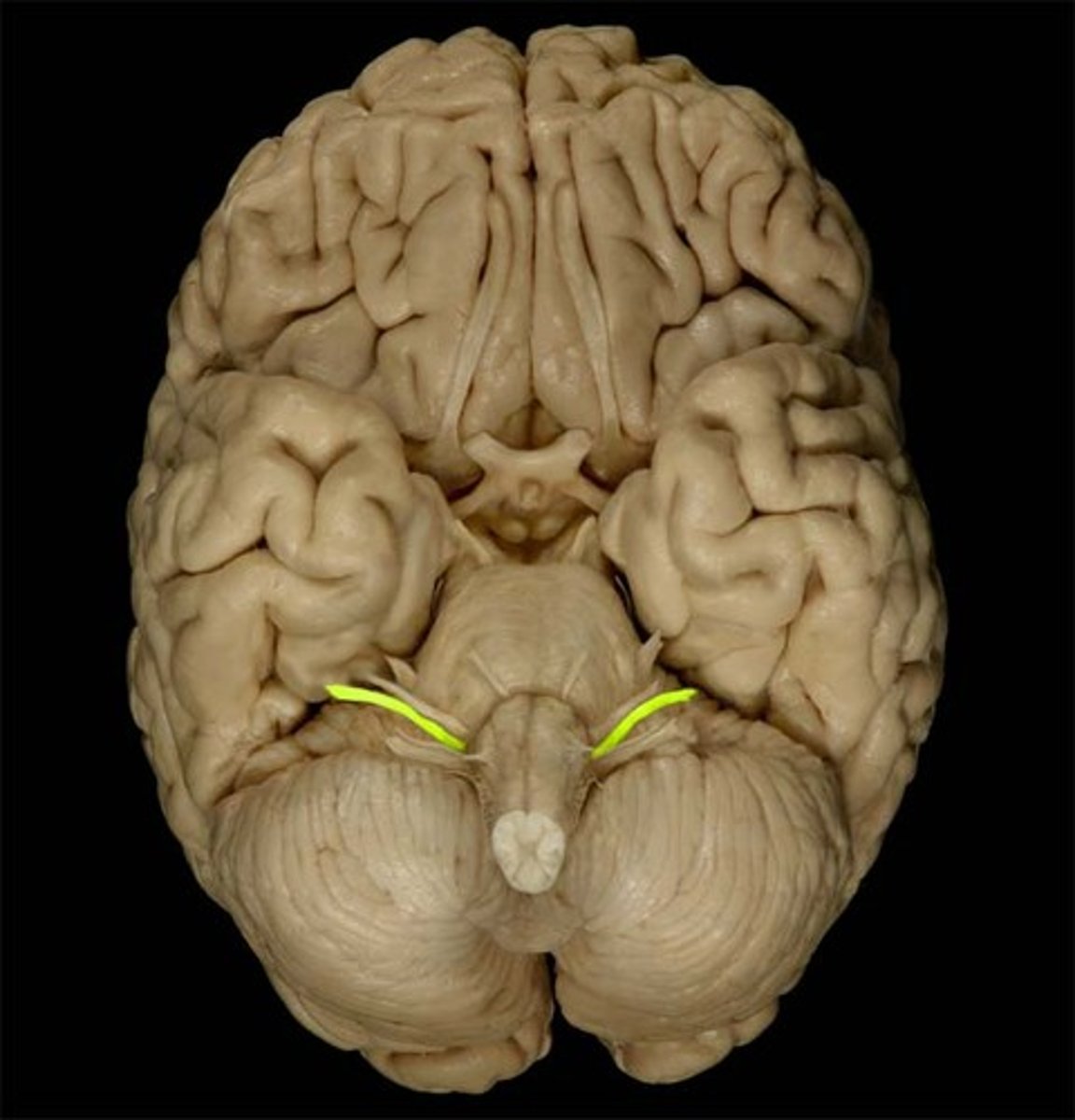
glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
general sensation and taste: posterior 1/3
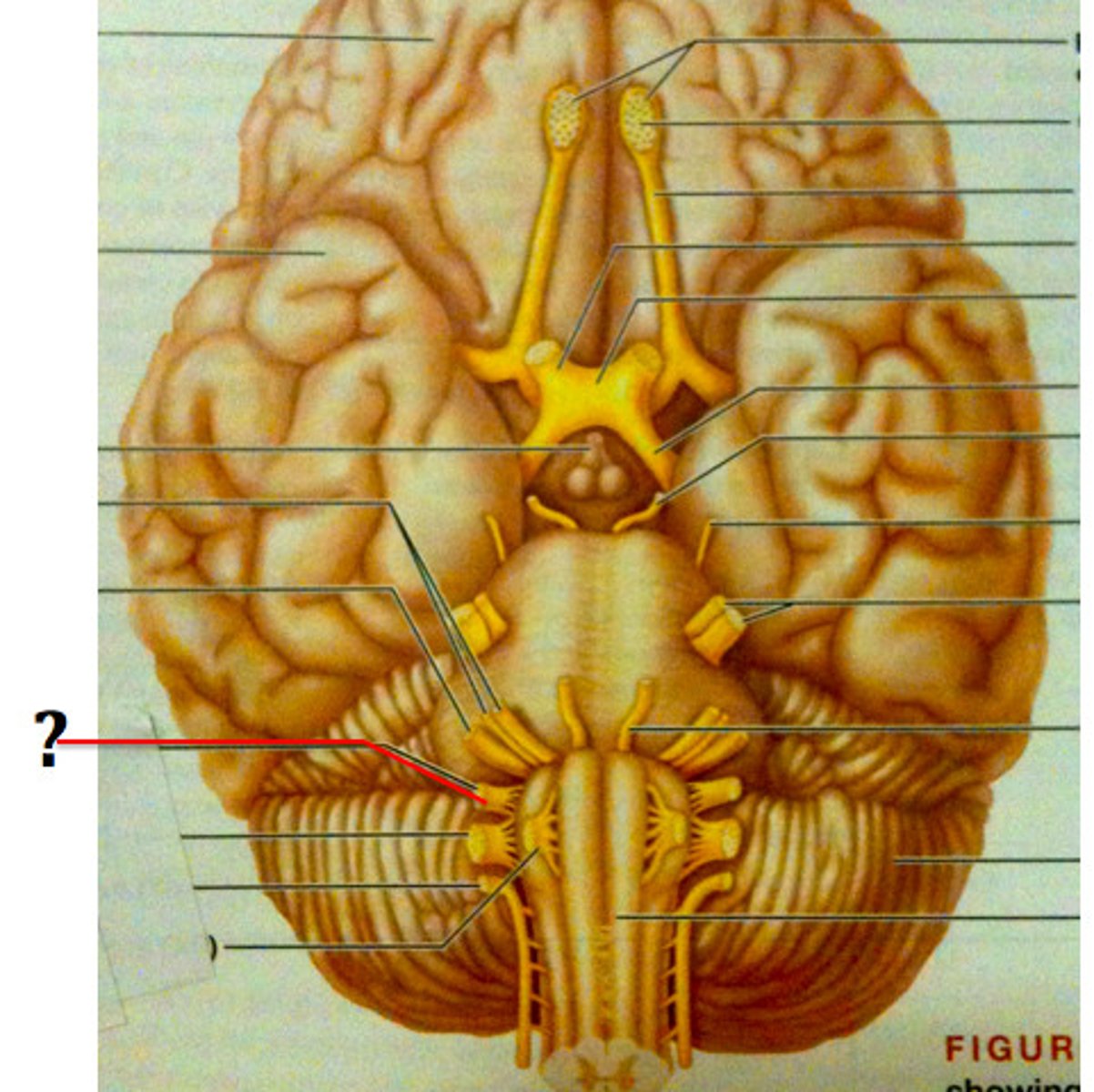
vagus nerve (CN X)
nerve that passes through jugular foramen
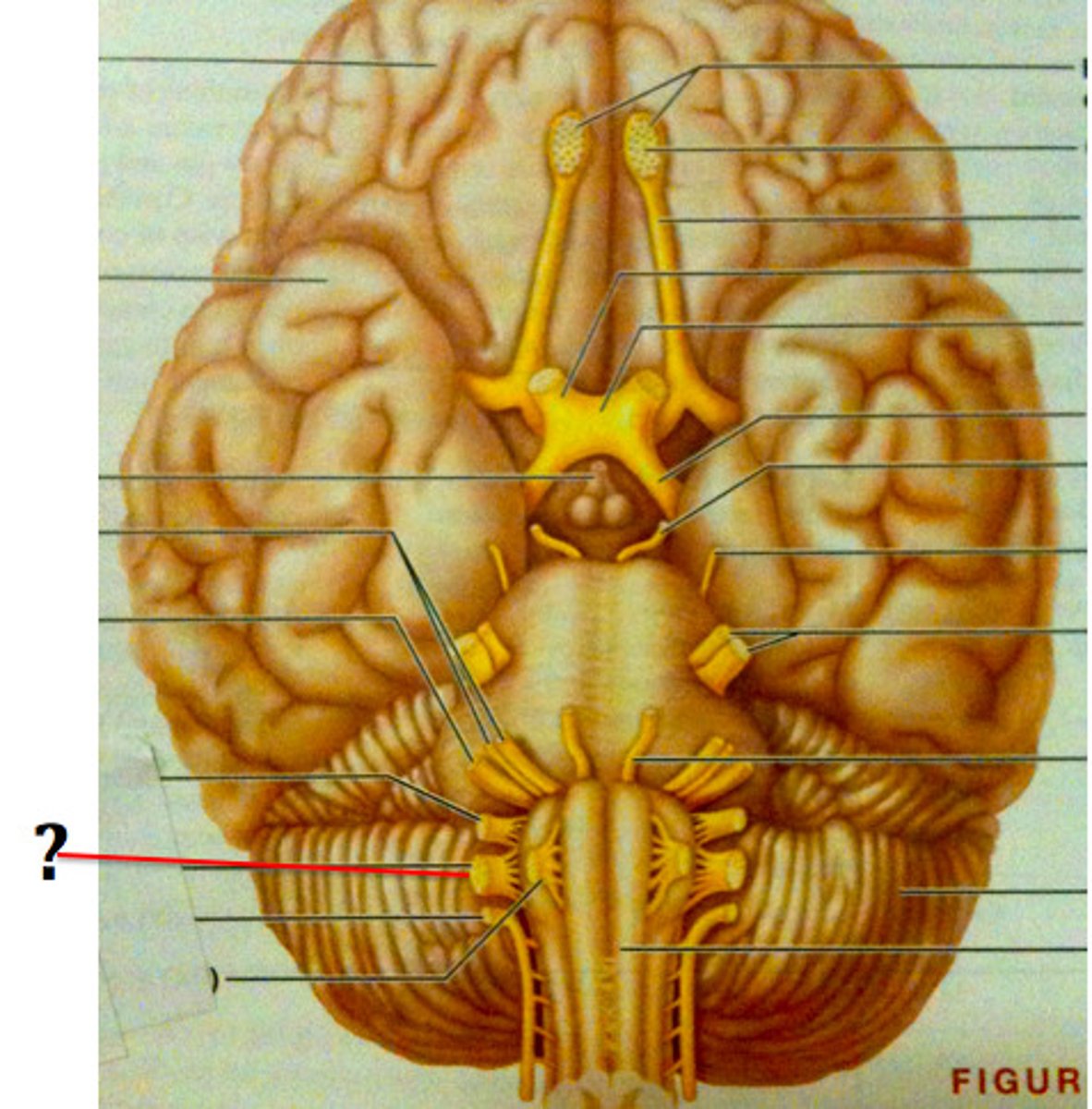
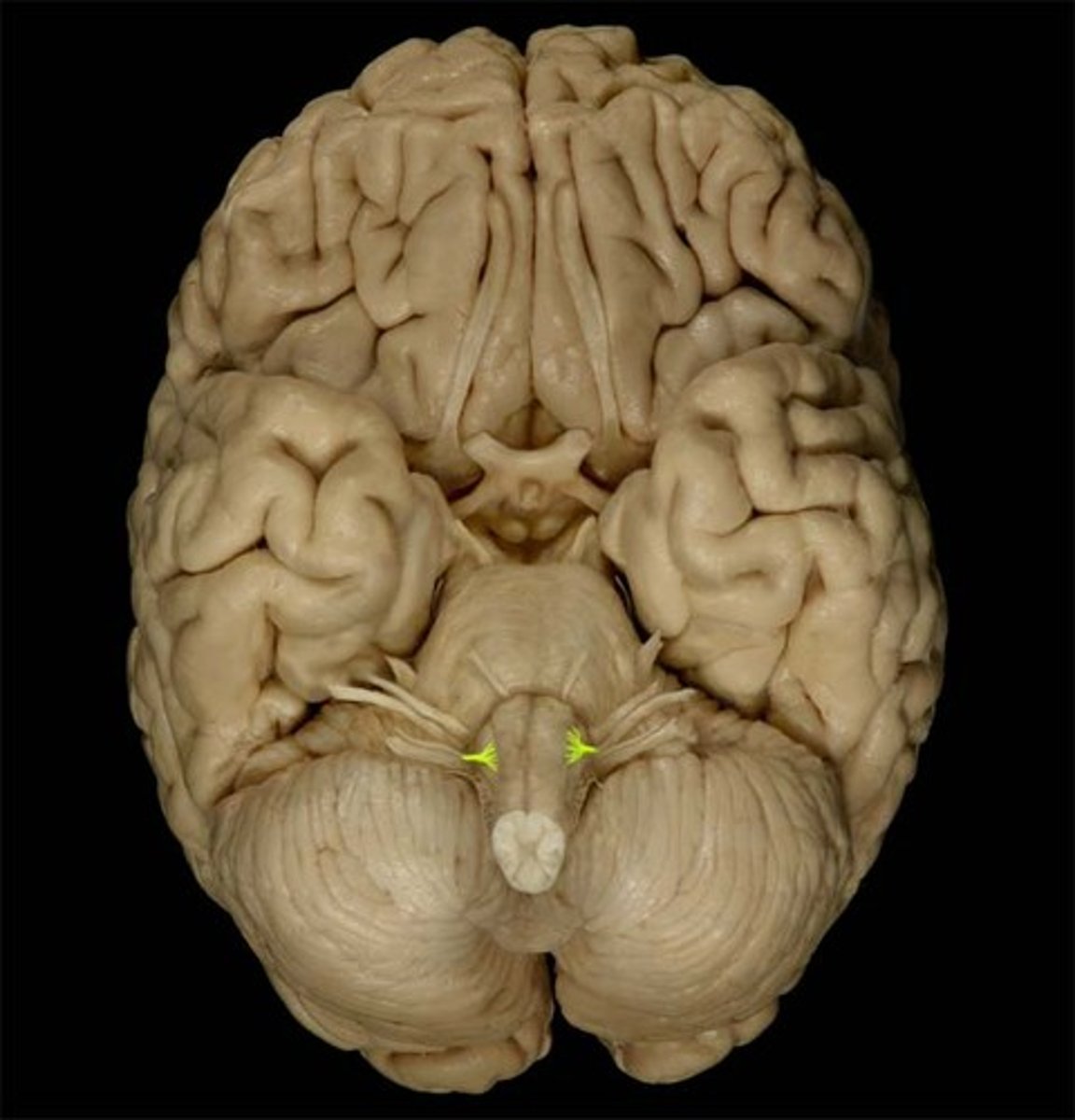
accessory nerve (CN XI)
Innervates sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
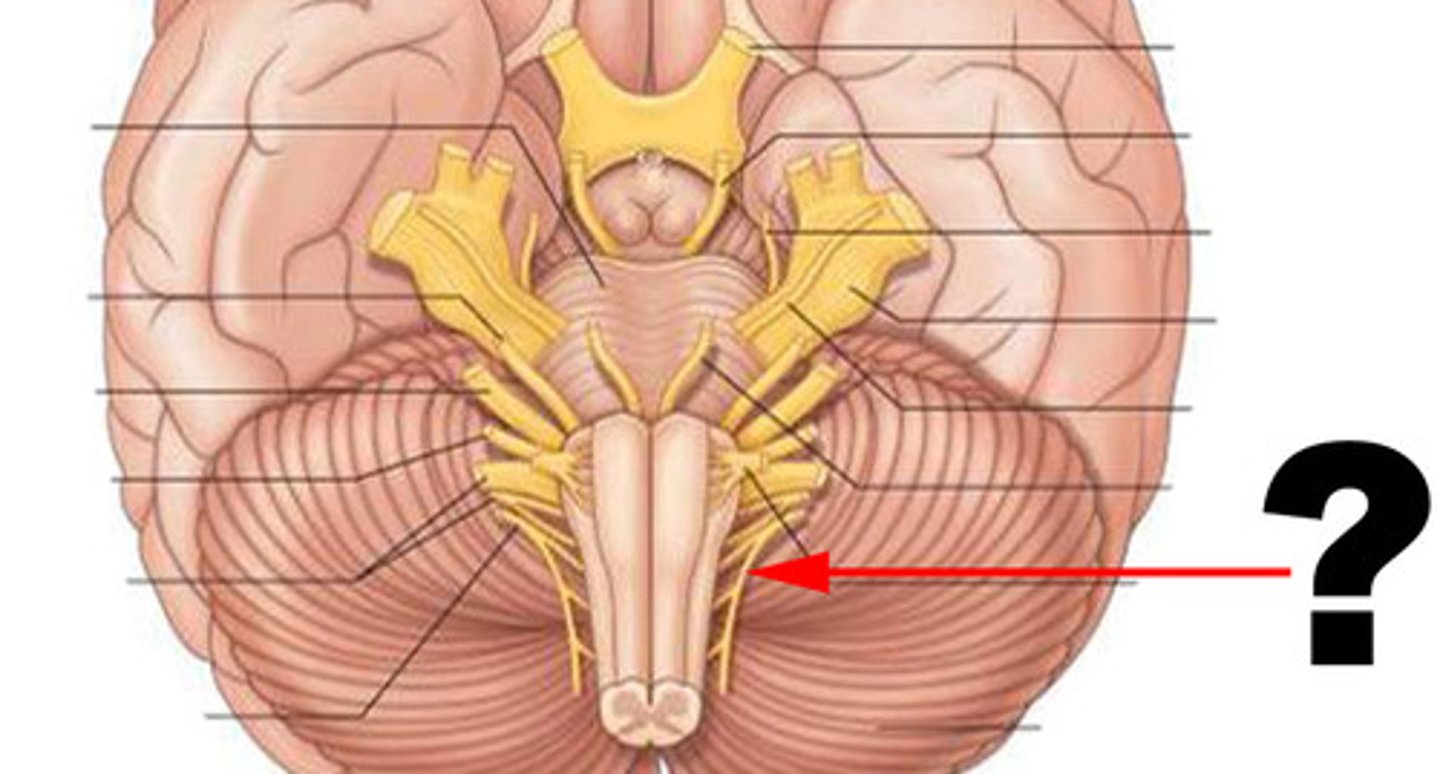
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
tongue movement
31; 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal
How many spinal nerves are there and how many of each type?
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
brainstem and sacral spinal cord
Where does the parasympathetic nervous system come from?
sympathetic nervous system
-the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
-fight or flight
T1-T12
Where does the sympathetic nervous system come from?
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
parietal lobe
region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing info about touch
occipital lobe
vision
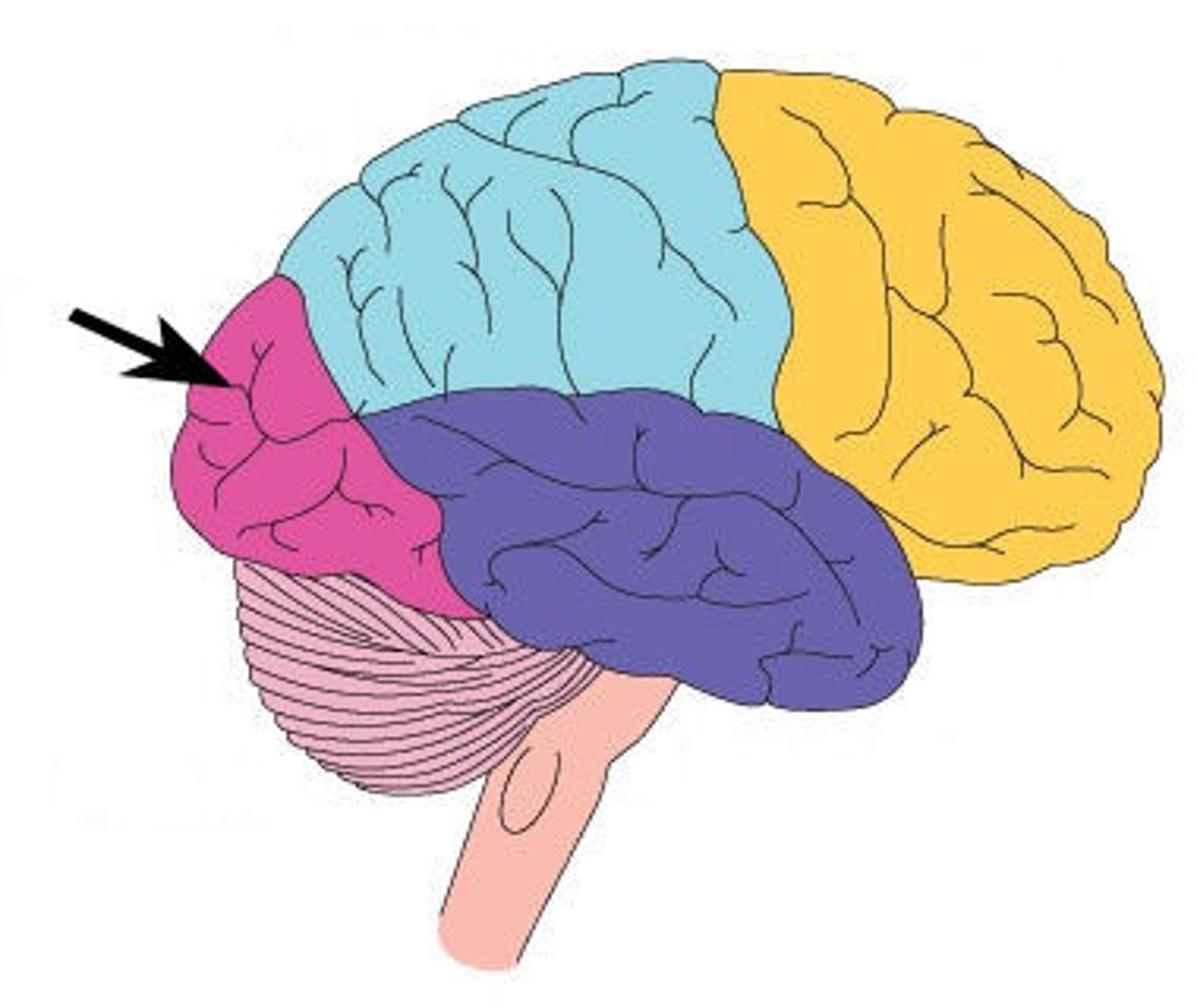
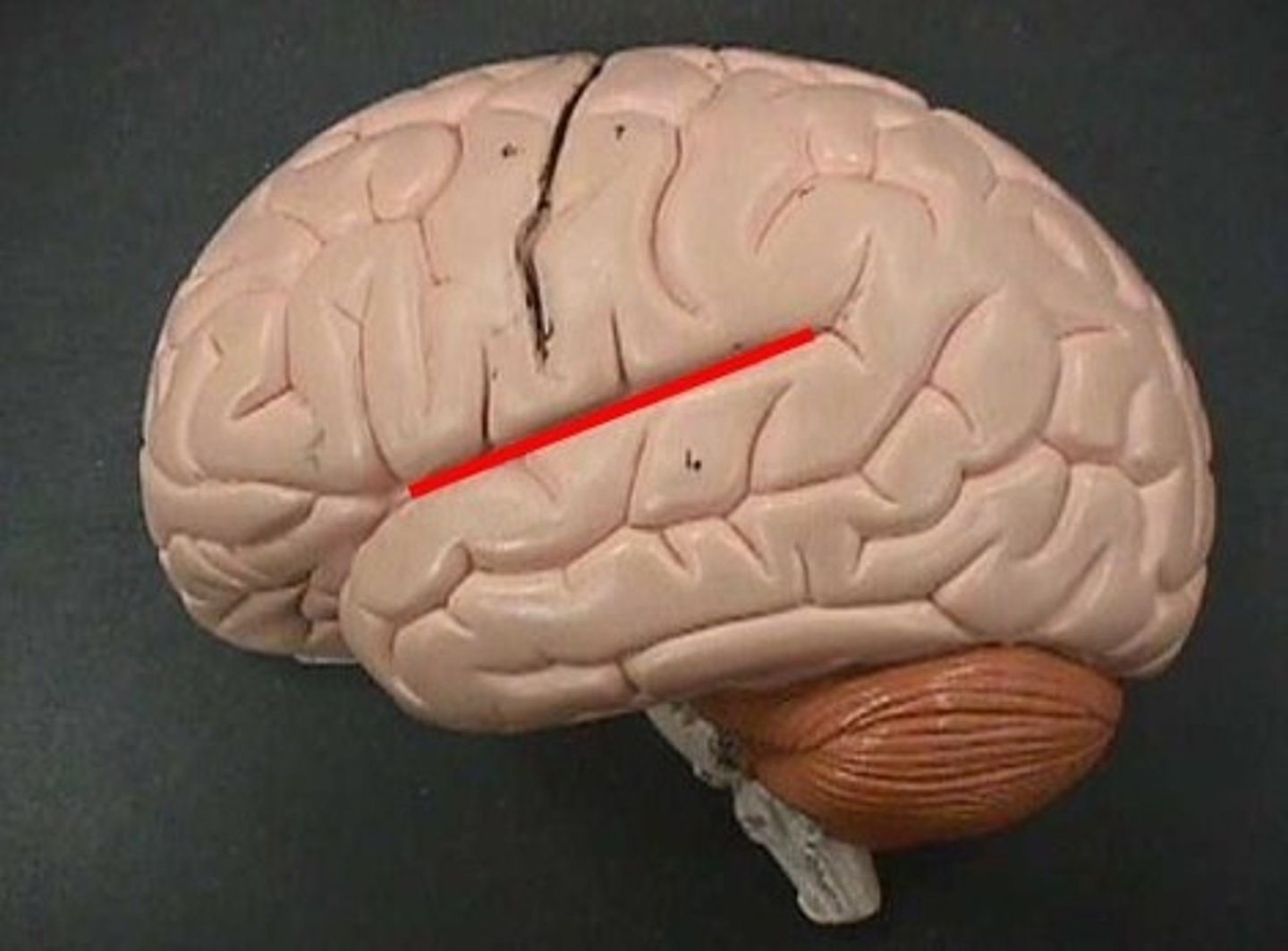
sylvian fissure
Also called lateral sulcus. A deep fissure that demarcates the temporal lobe.
cerebellum
-A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
-balance and coordination
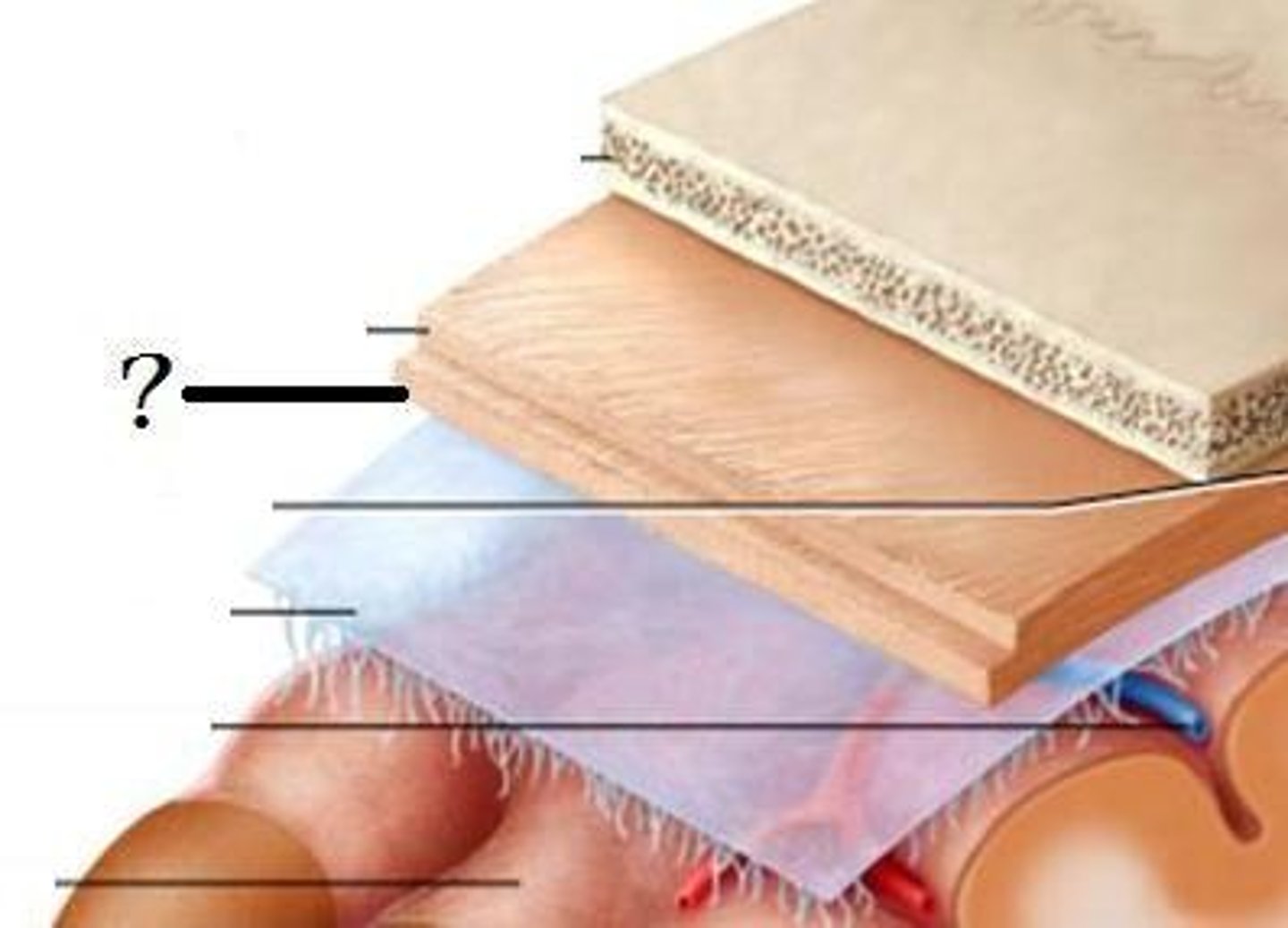
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord