Diseases of the Cornea and Corneal Refractive Surgery - Anterior Segment & Ocular Disease Fall 2025
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
cornea
The _____ is responsible for 75% of the refractive power of the eye
avascular
The cornea is a (vascular/avascular) structure
comes from the AH and the tear film
Where do the nutrients of the cornea come from if it is an avascular structure?
highest
The cornea has the (highest/lowest) conc of nerves in the body
the first division of the trigeminal nerve
The subepithelial and deeper stromal corneal nerves are supplied by what?
11.5mm vertical and 12mm horizontal
Corneal diameter?
540 micometers
Avg corneal thickness?
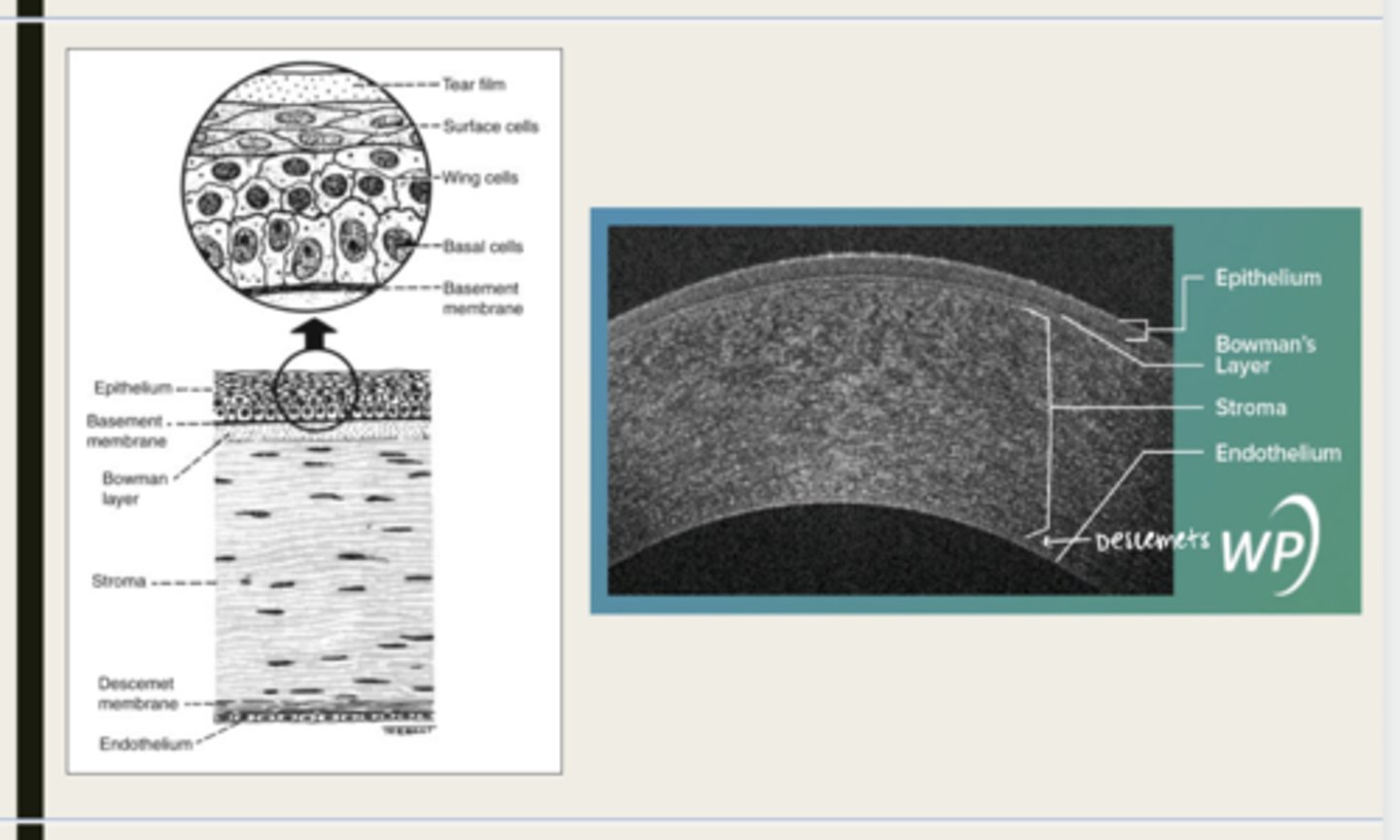
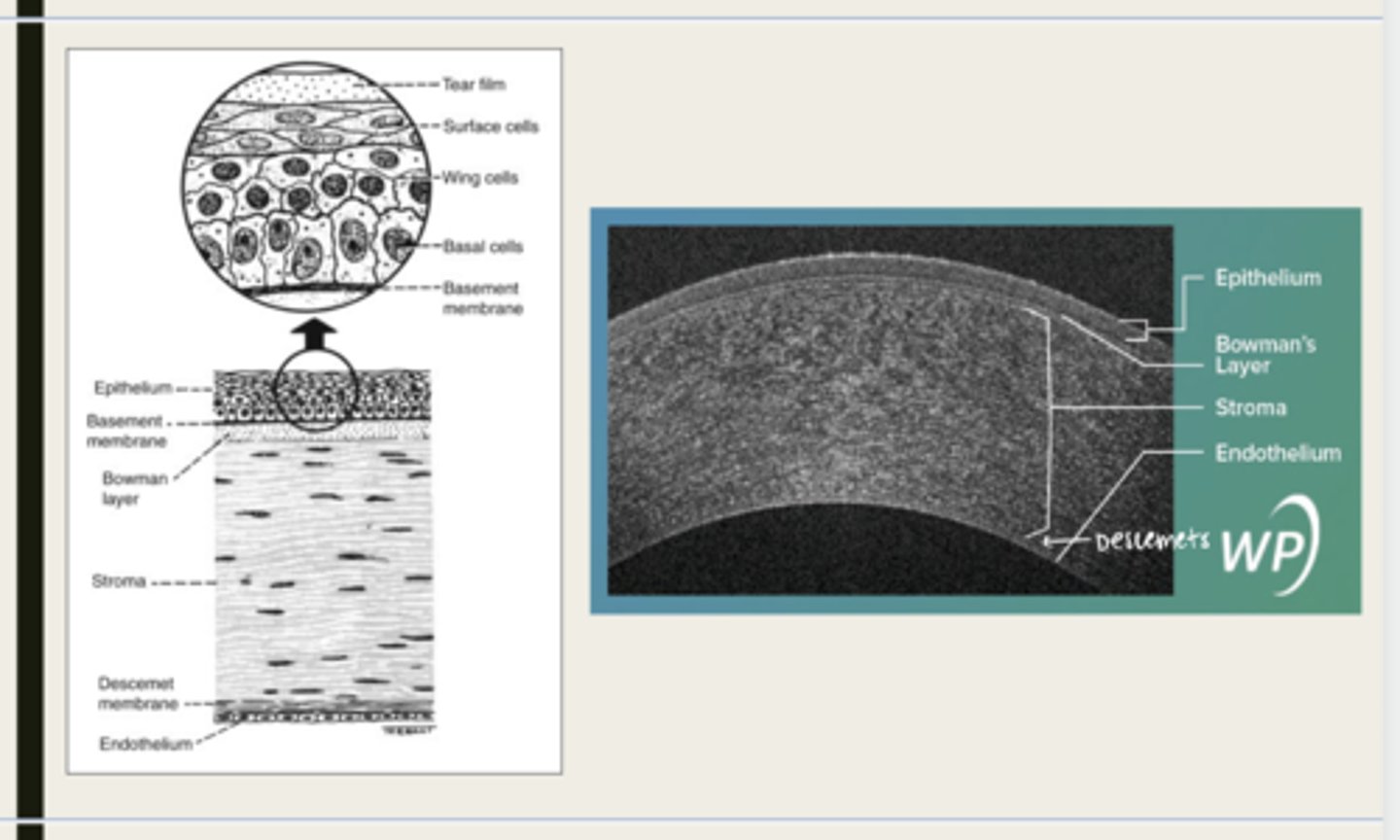
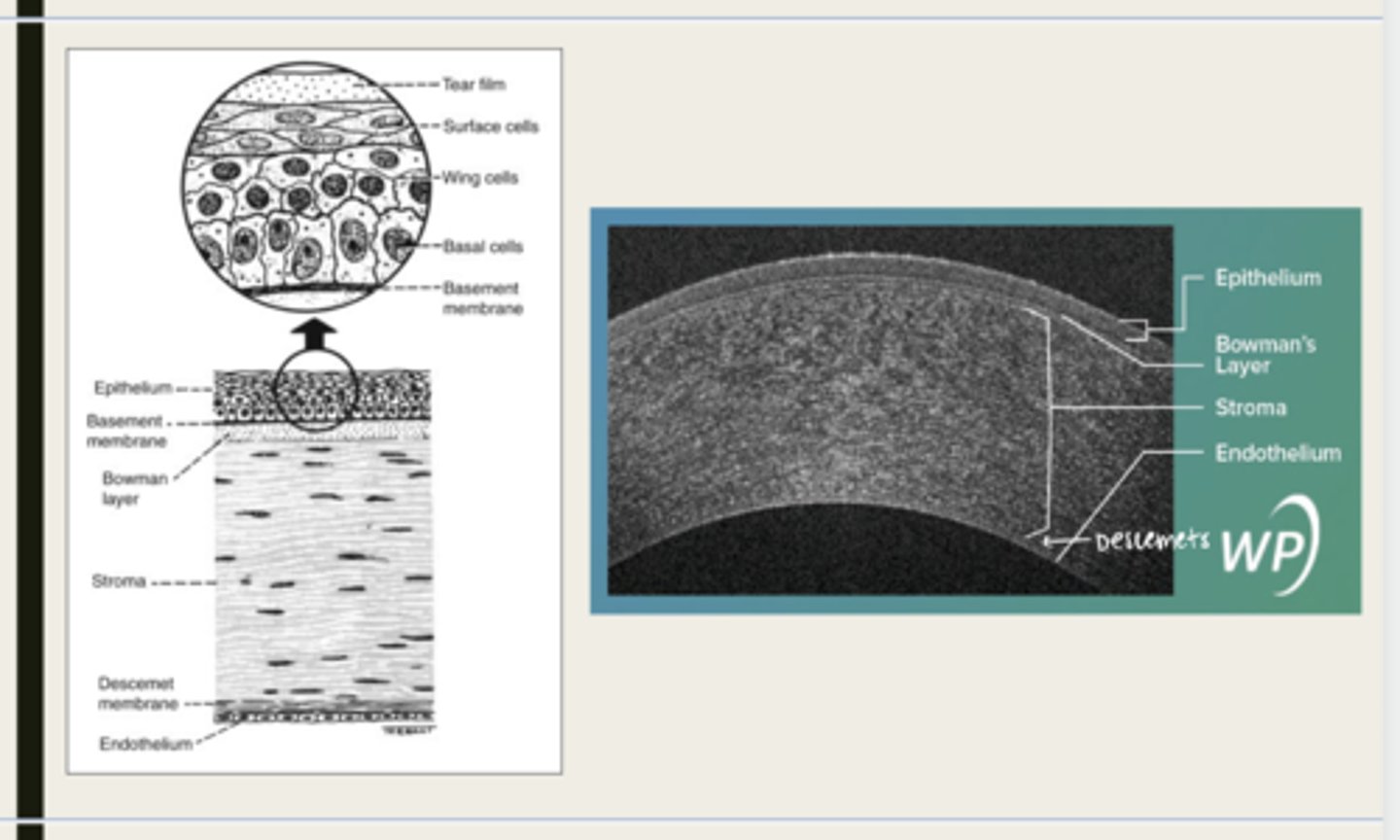
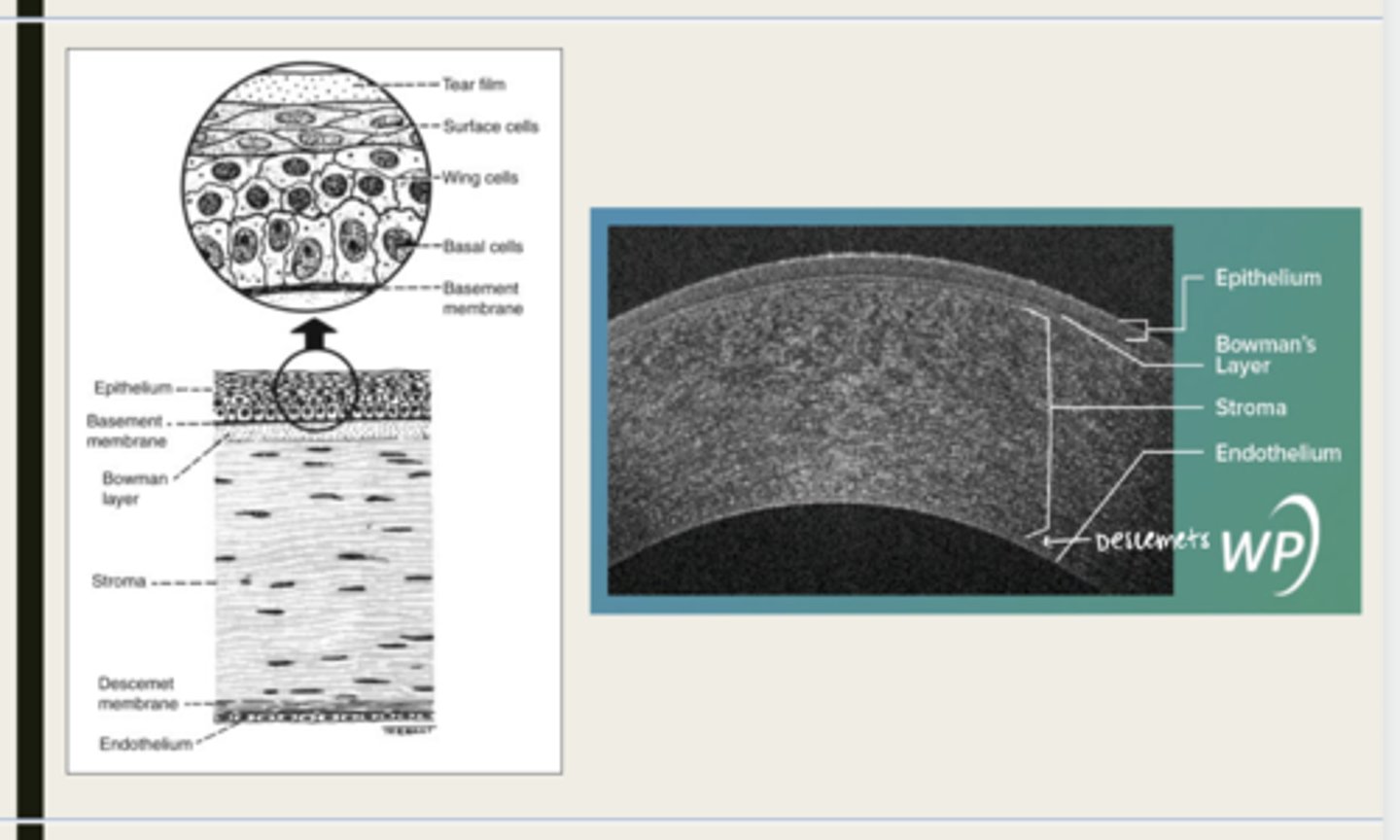
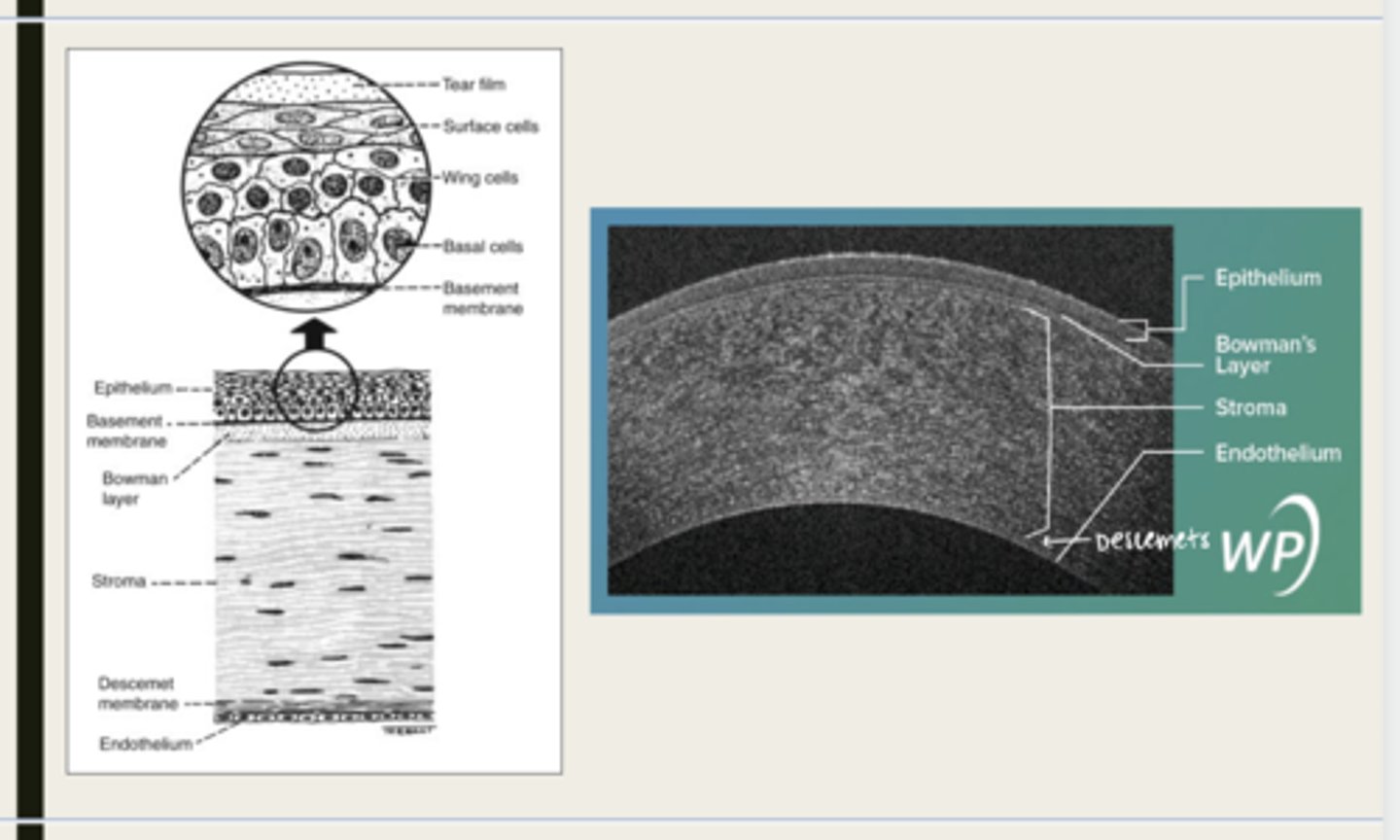
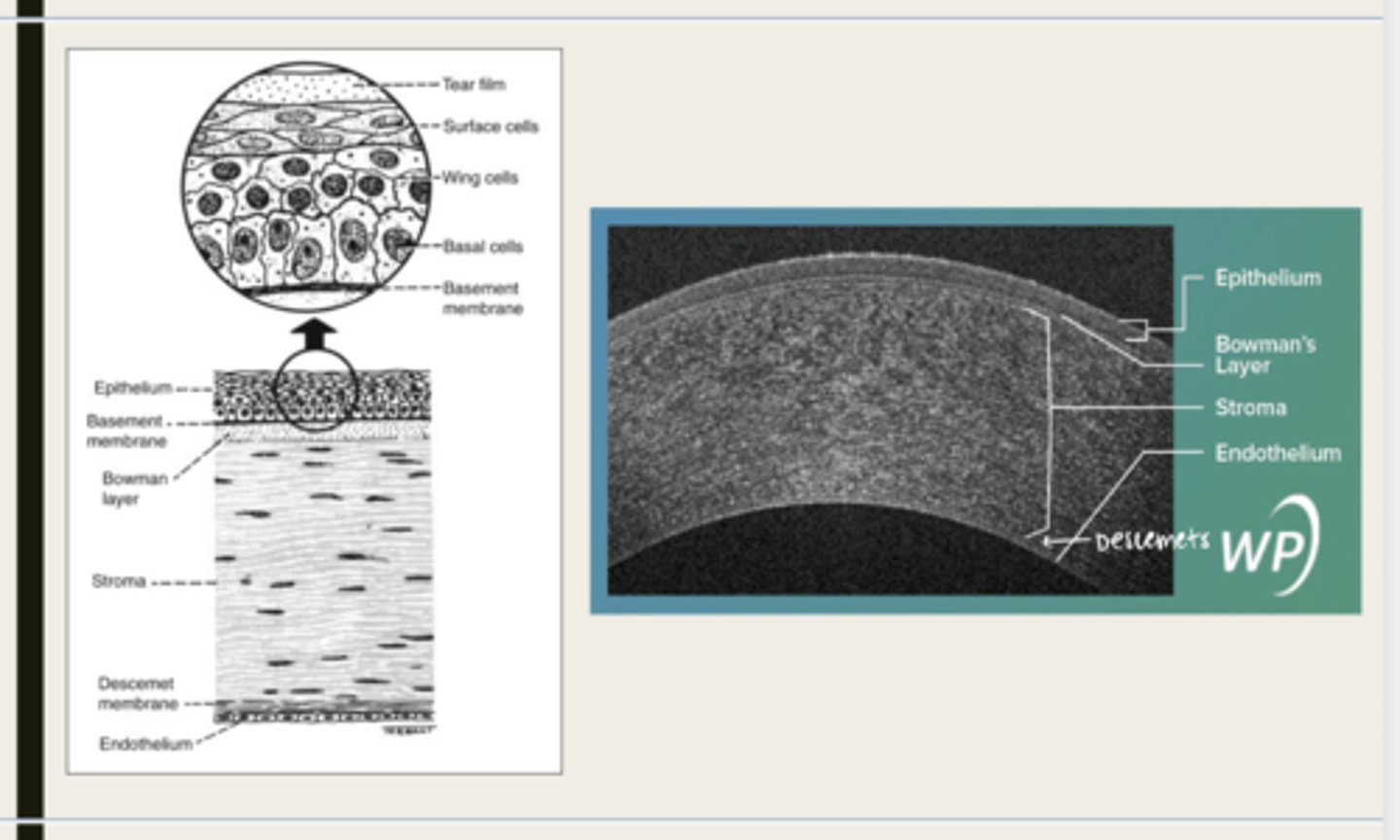
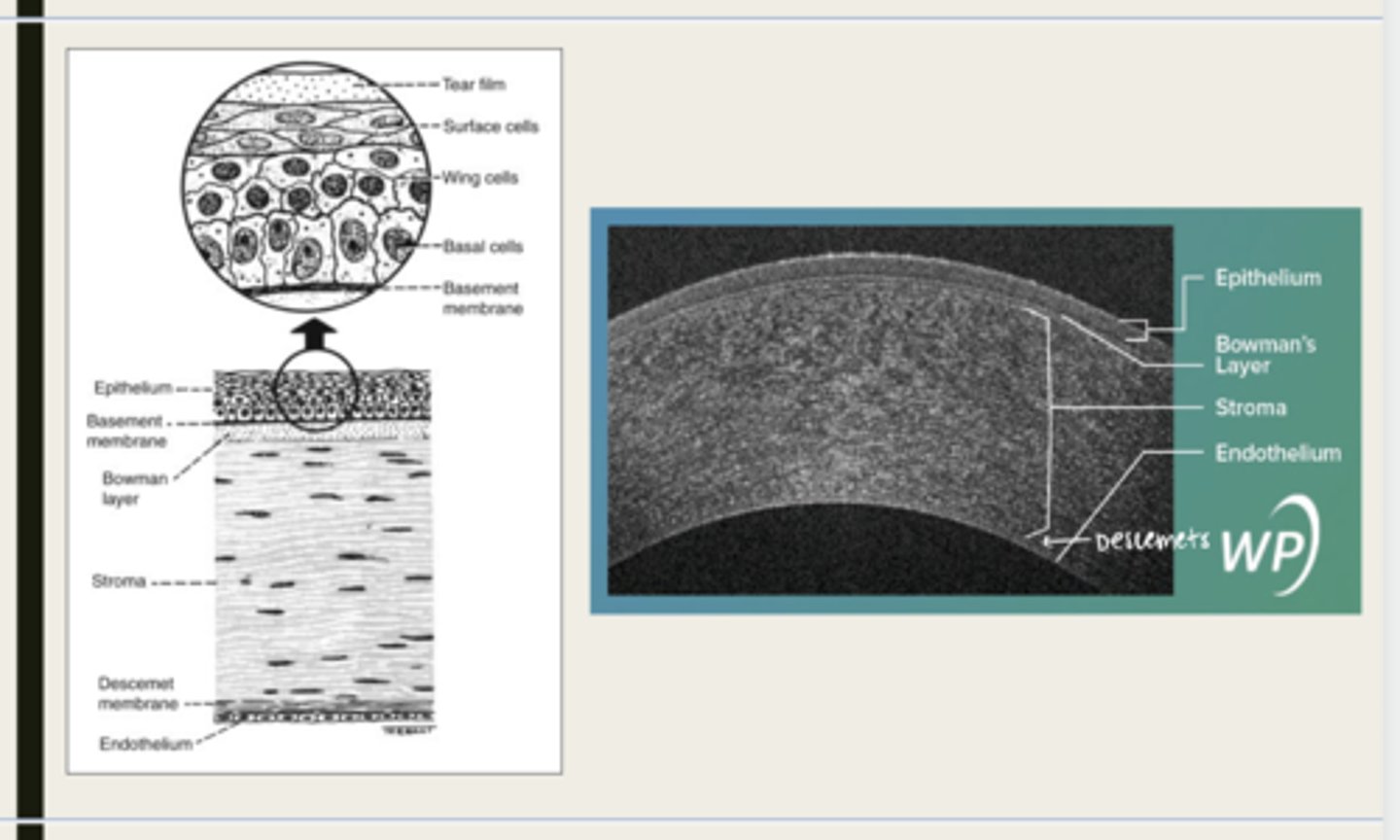
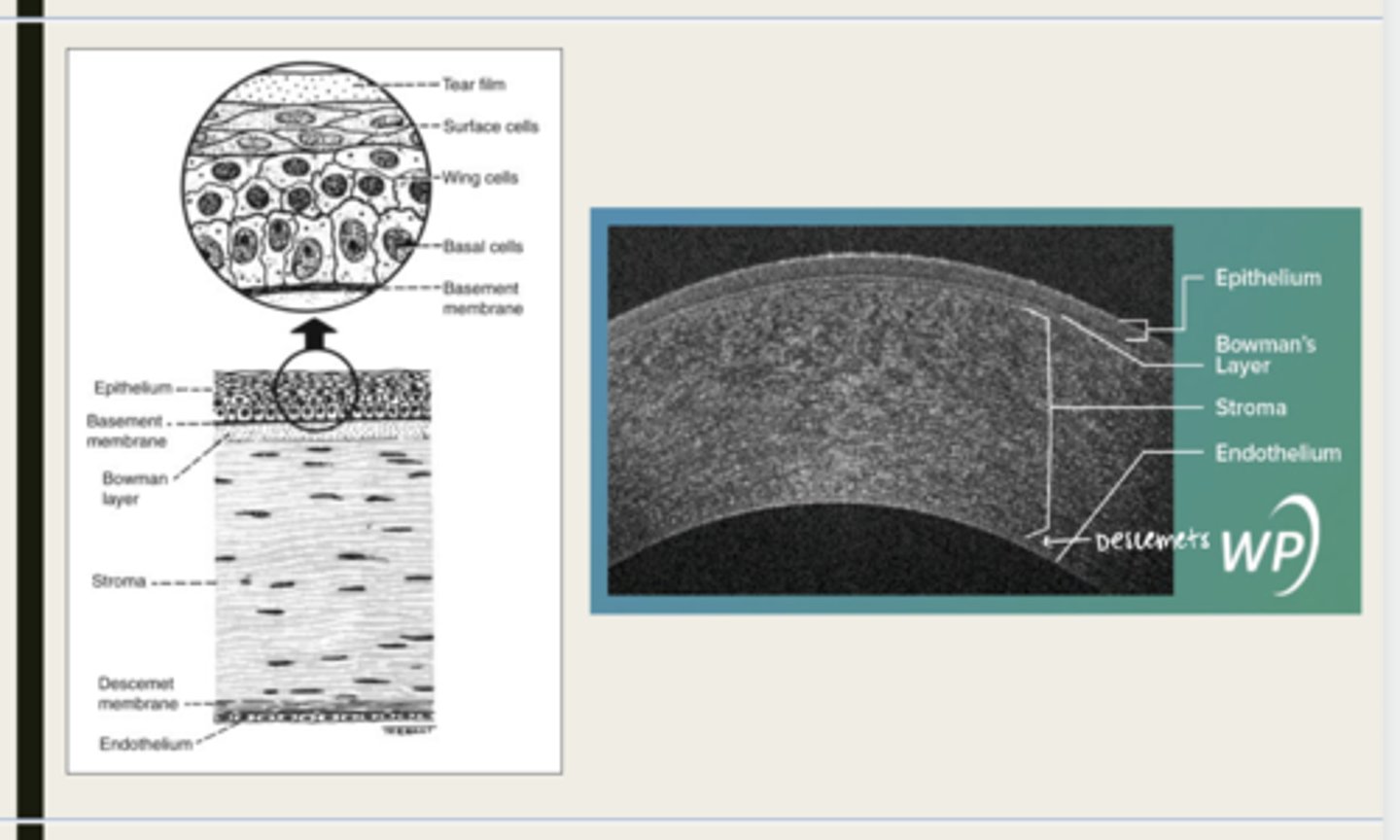
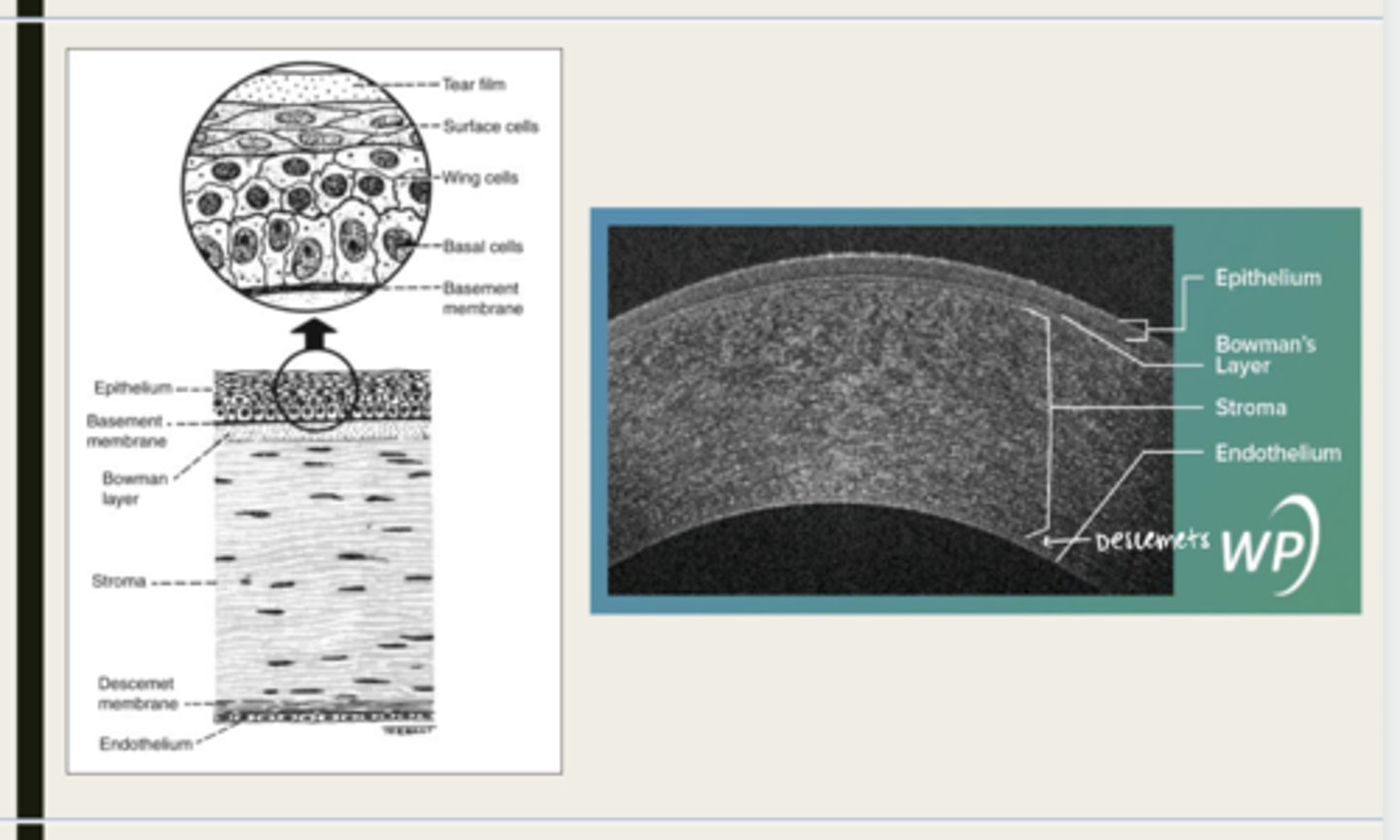
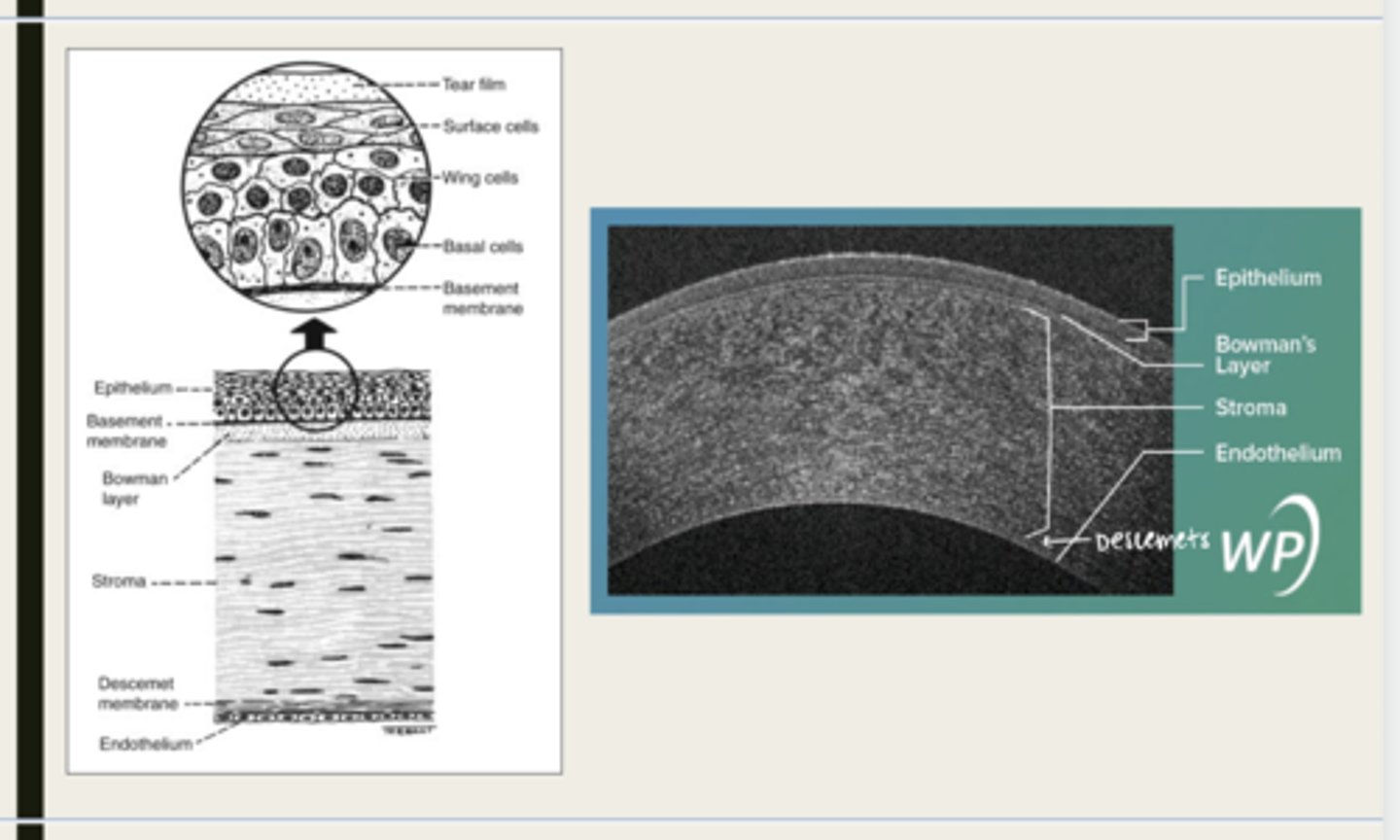
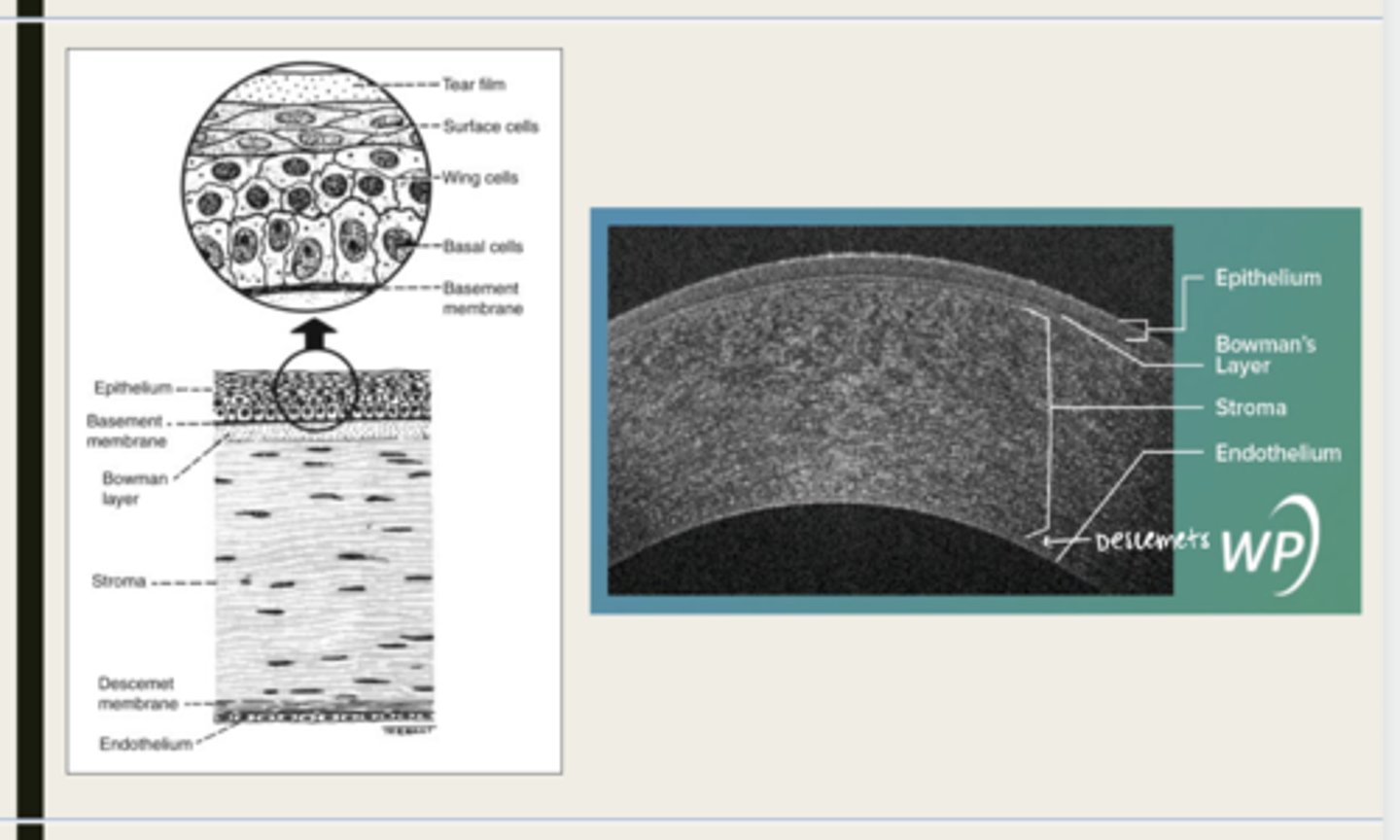
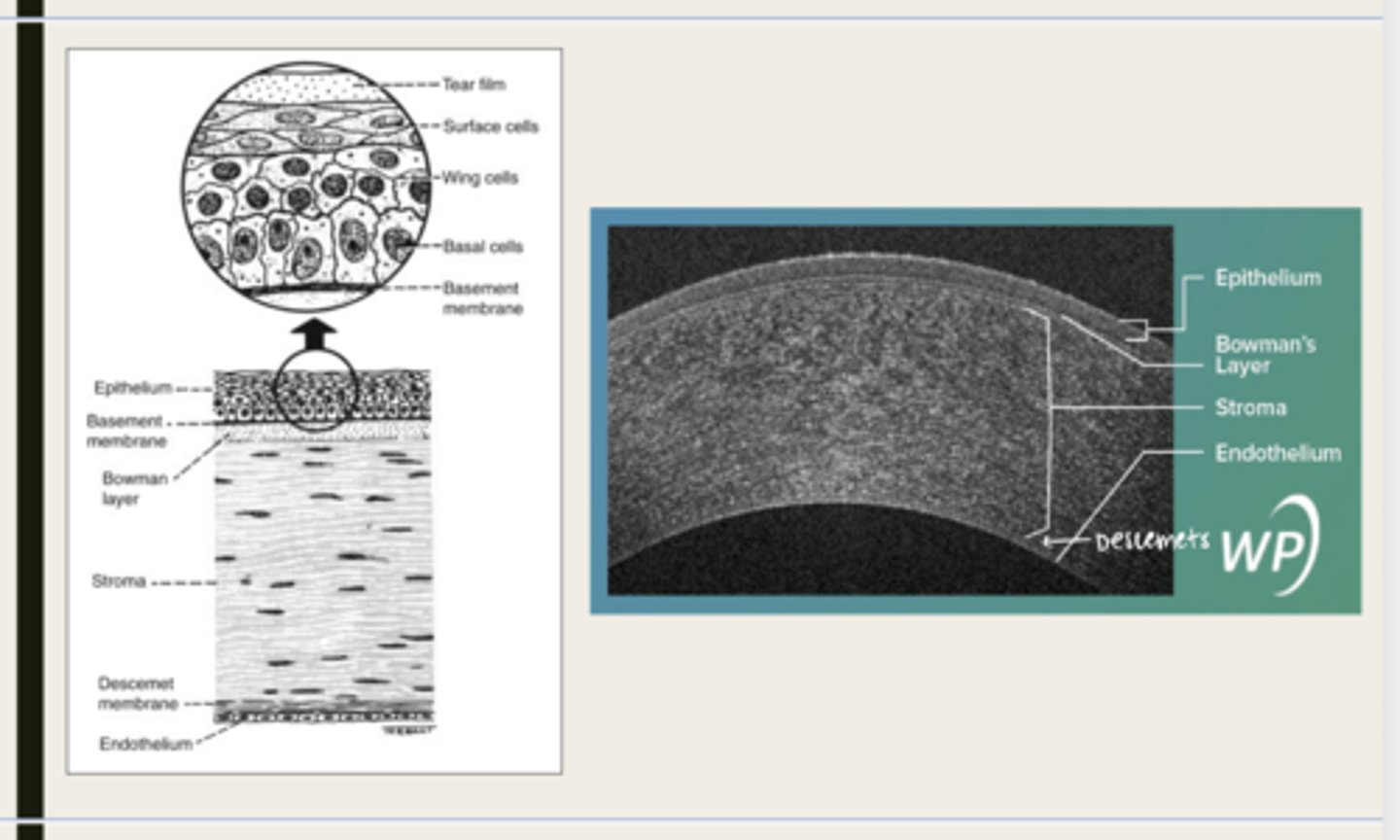
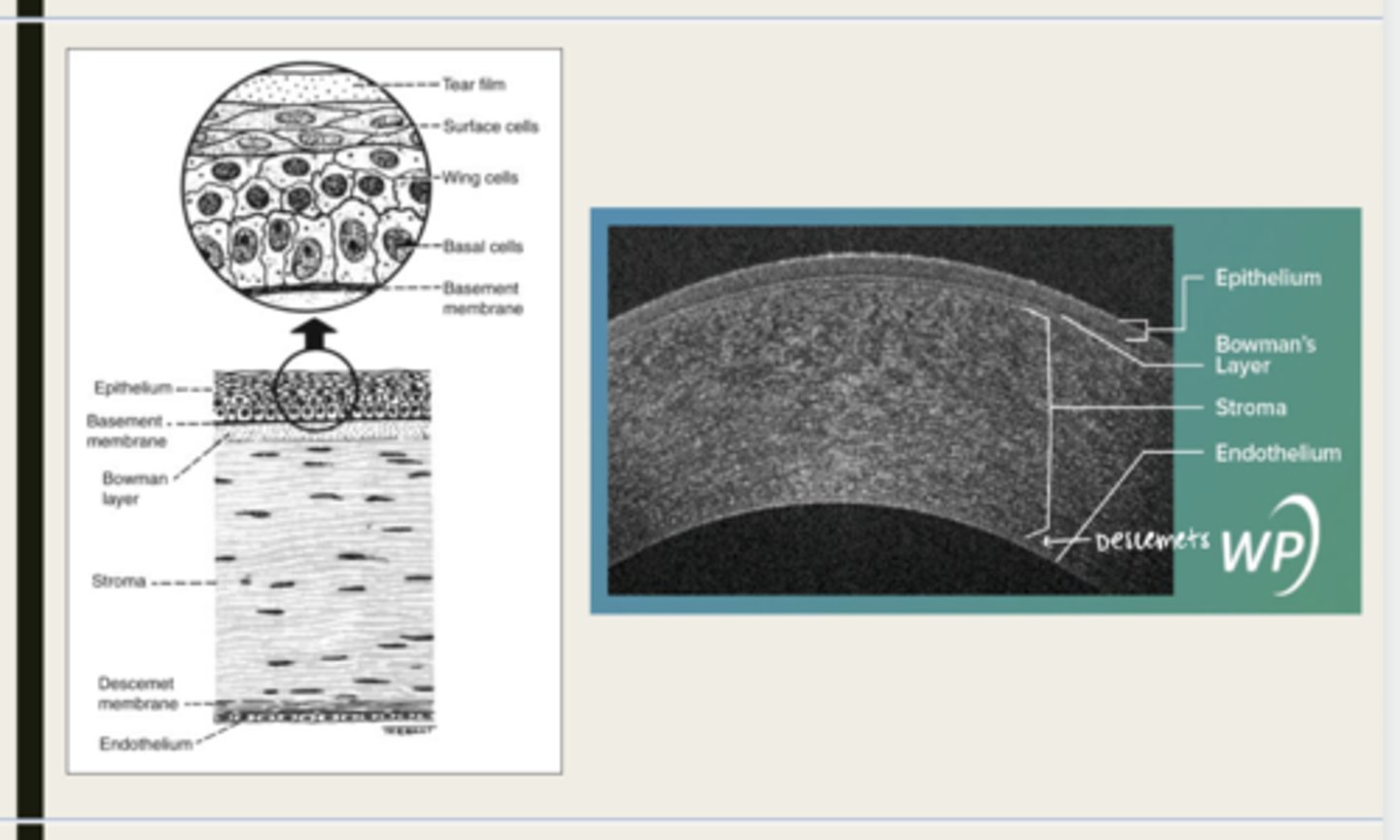
-epithelium
-Bowman's
-stroma
-Descemet membrane
-Endothelium
What are the 5 layers of the cornea?
stratified squamous
The epithelium of the cornea is made up of _______ cells
nonkeratinized
The epithelium of the cornea is (keratinized/nonkeratinized)?
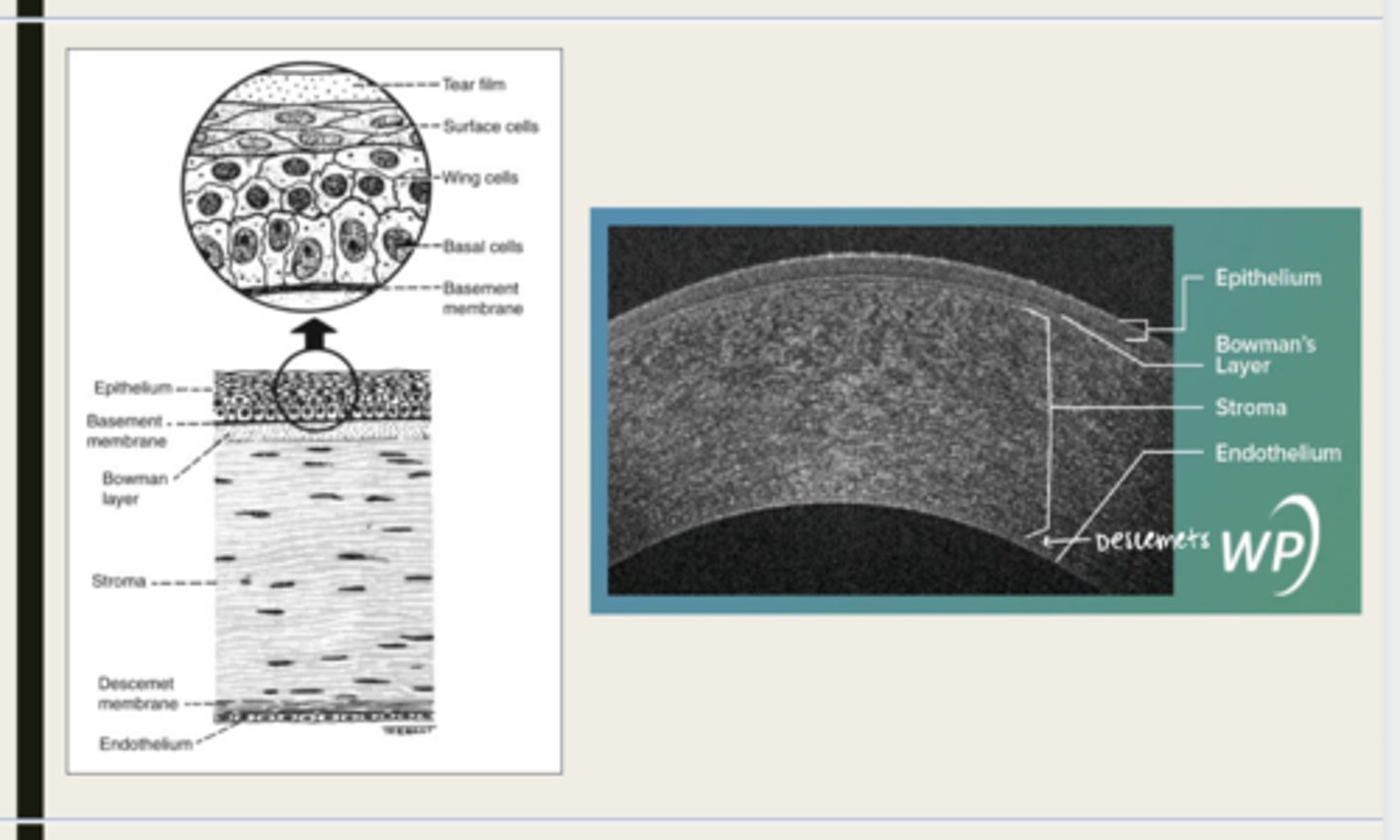
-basal cells
-wing cells
-squamous surface cells
-microplica and microvilli
What cells is the corneal epithelium composed of?
adhesion of the mucin layer of the tears to the cornea
What do the microvilli and microplica of the corneal epithelium assist in?
in the limbus
Where are corneal stem cells located?
yes
Will the corneal epithelium regenerate after trauma?
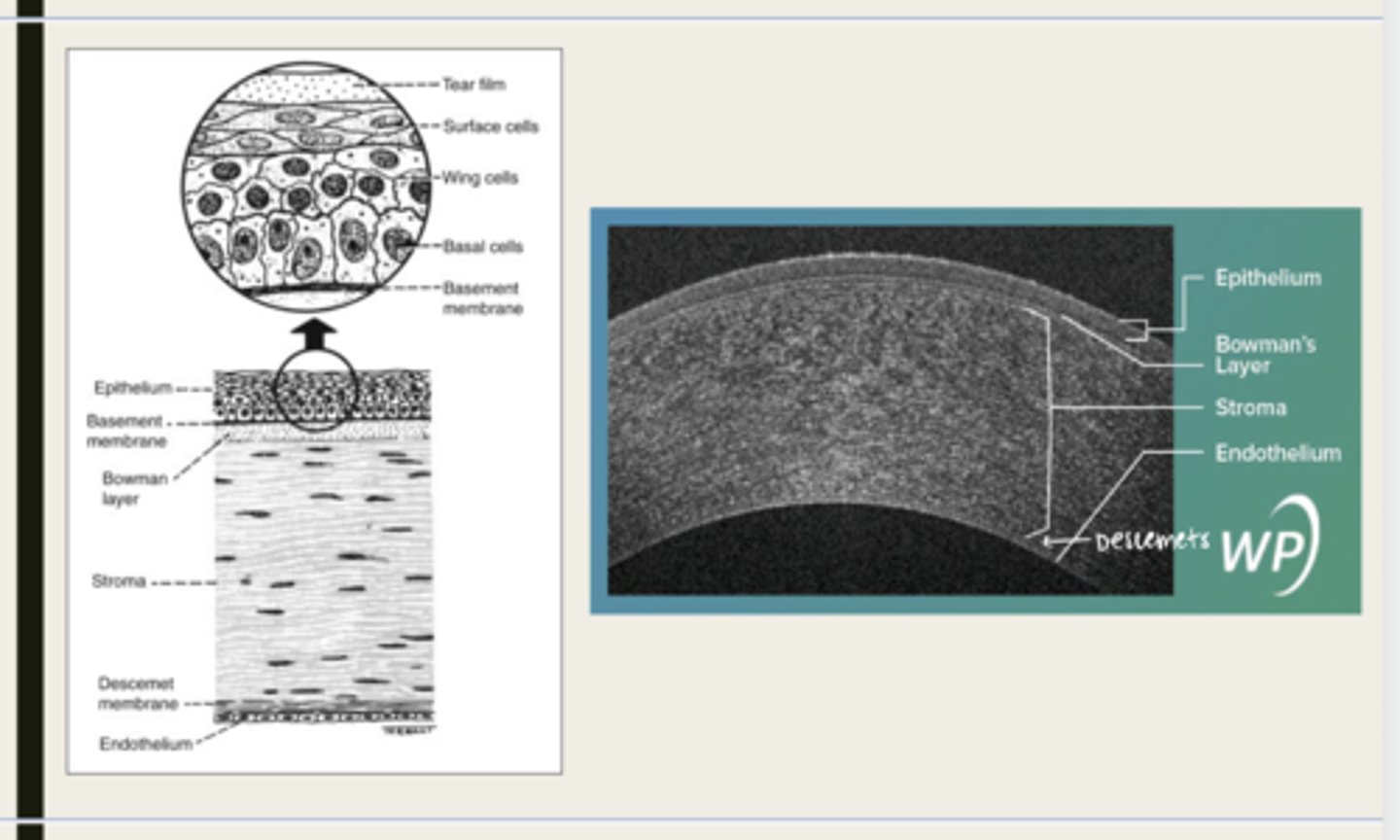
Bowman layer
acellular superficial layer of the stroma
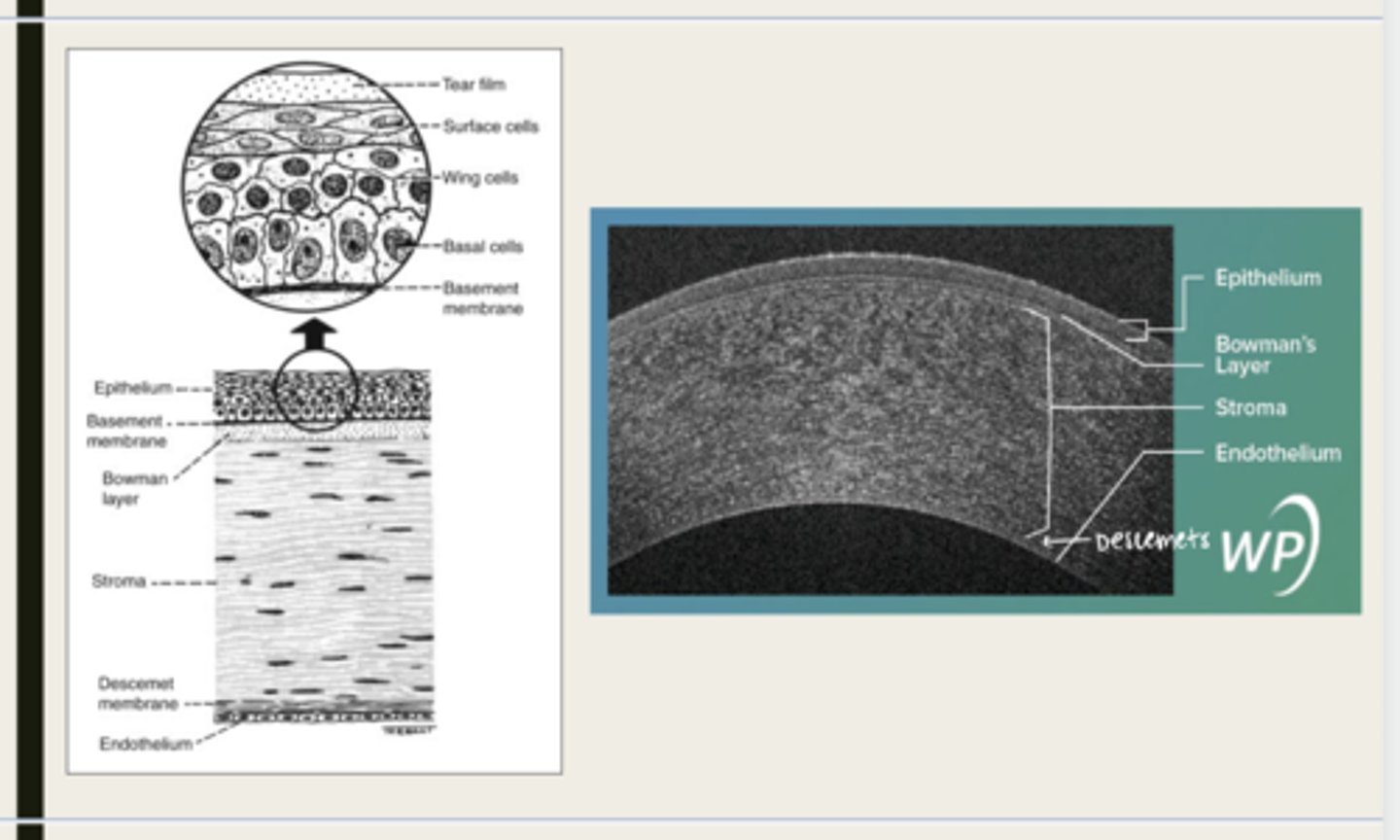
collagen fibers
What is Bowman layer of the cornea composed of?
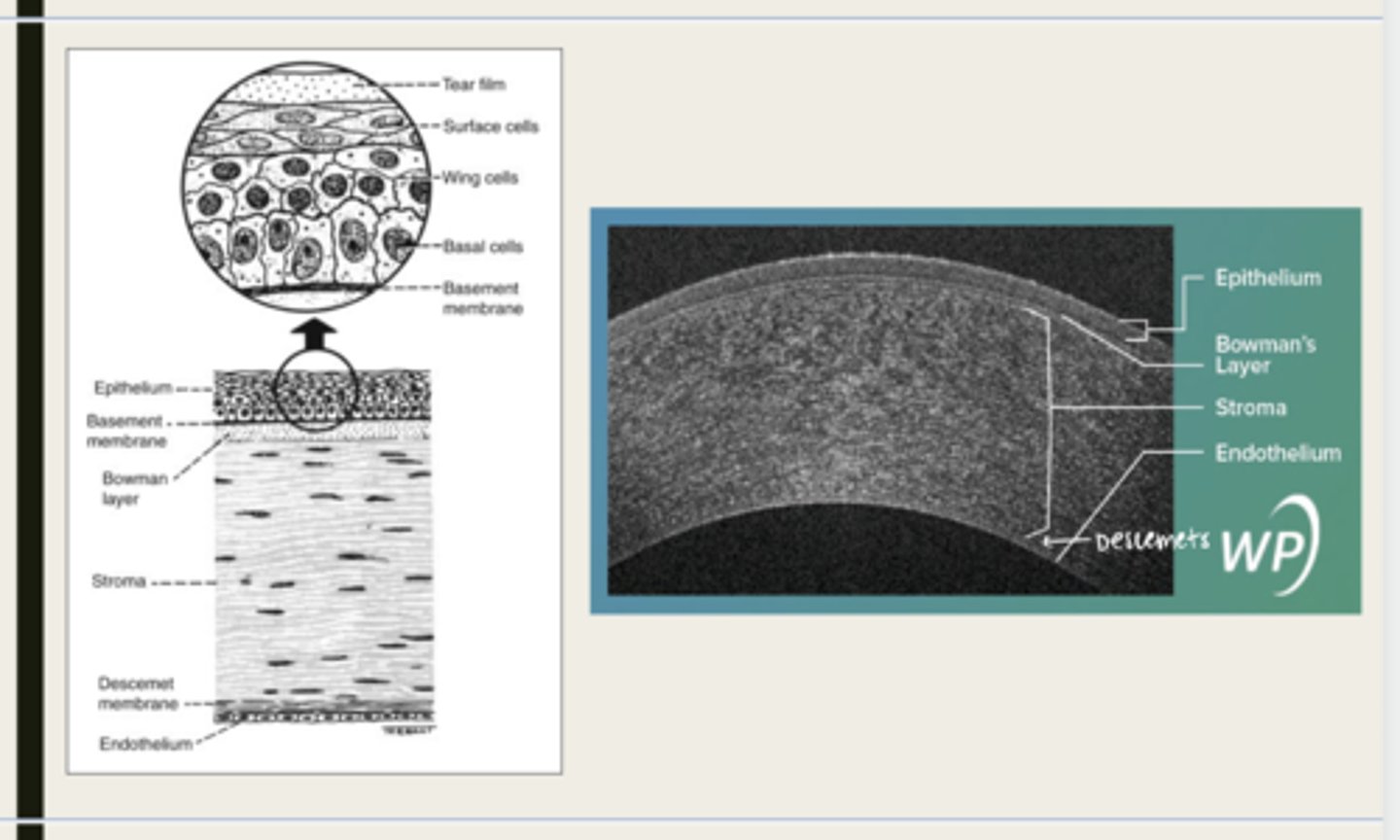
stroma
What makes up 90% of the corneal thickness?
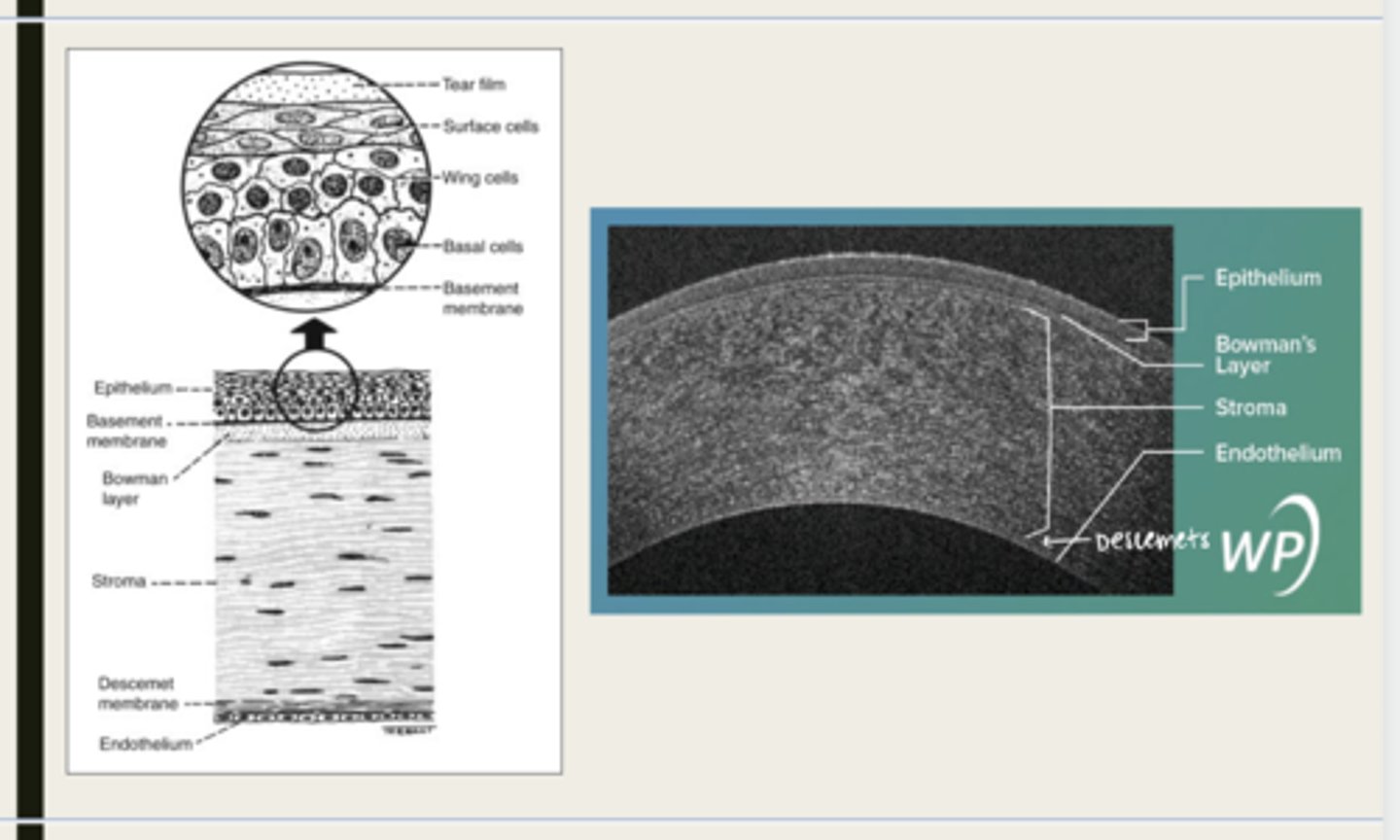
regularly orientated layers of collagen fibrils
What is the corneal stroma composed of?
regular orientation and spacing of collagen
What allows the cornea to remain clear?
no
Will the corneal stroma regenerate following trauma?
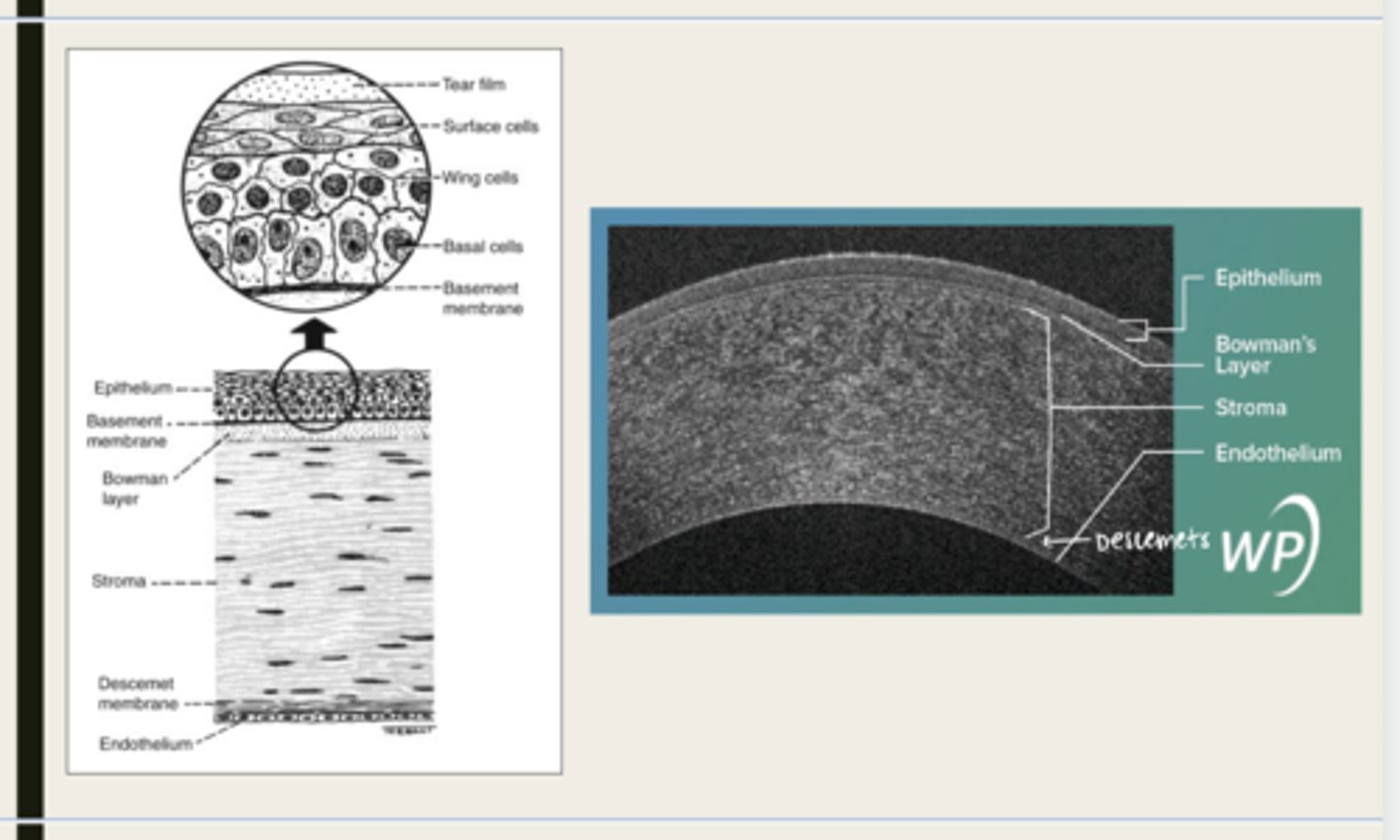
Descemet membrane
What layer is composed of fine latticework of collagen that is distinct from the stroma?
2 bands
How many bands in Descemet membane?
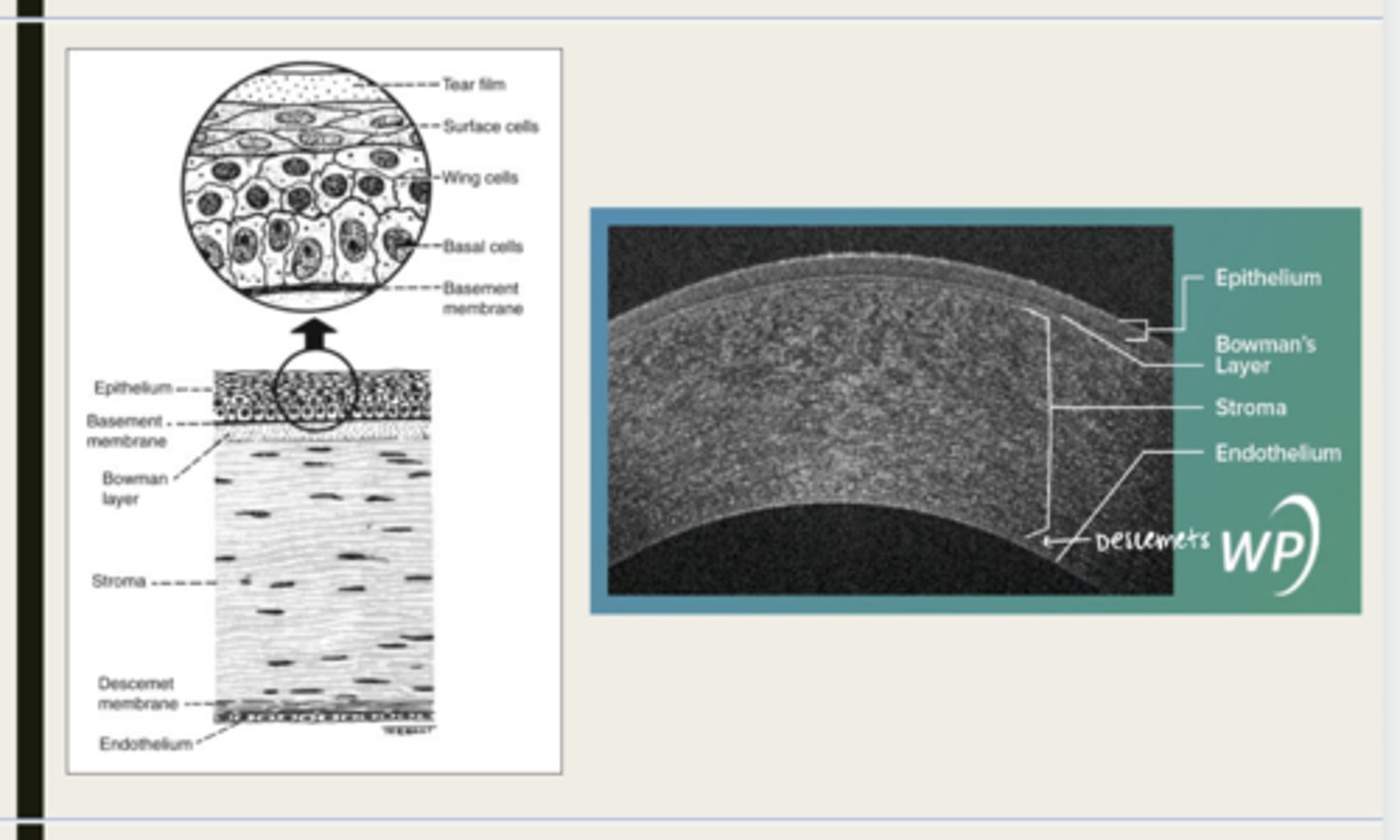
One develop in utero and one that is laid throughout life and serves as a basement membrane for the endothelium
When do the 2 bands of Descemet membrane develop?
endothelium
monolayer of hexagonal cells that are responsible for deturgescence of the cornea
corneal edema and hazing
What are the consequences to corneal endothelium pathology?
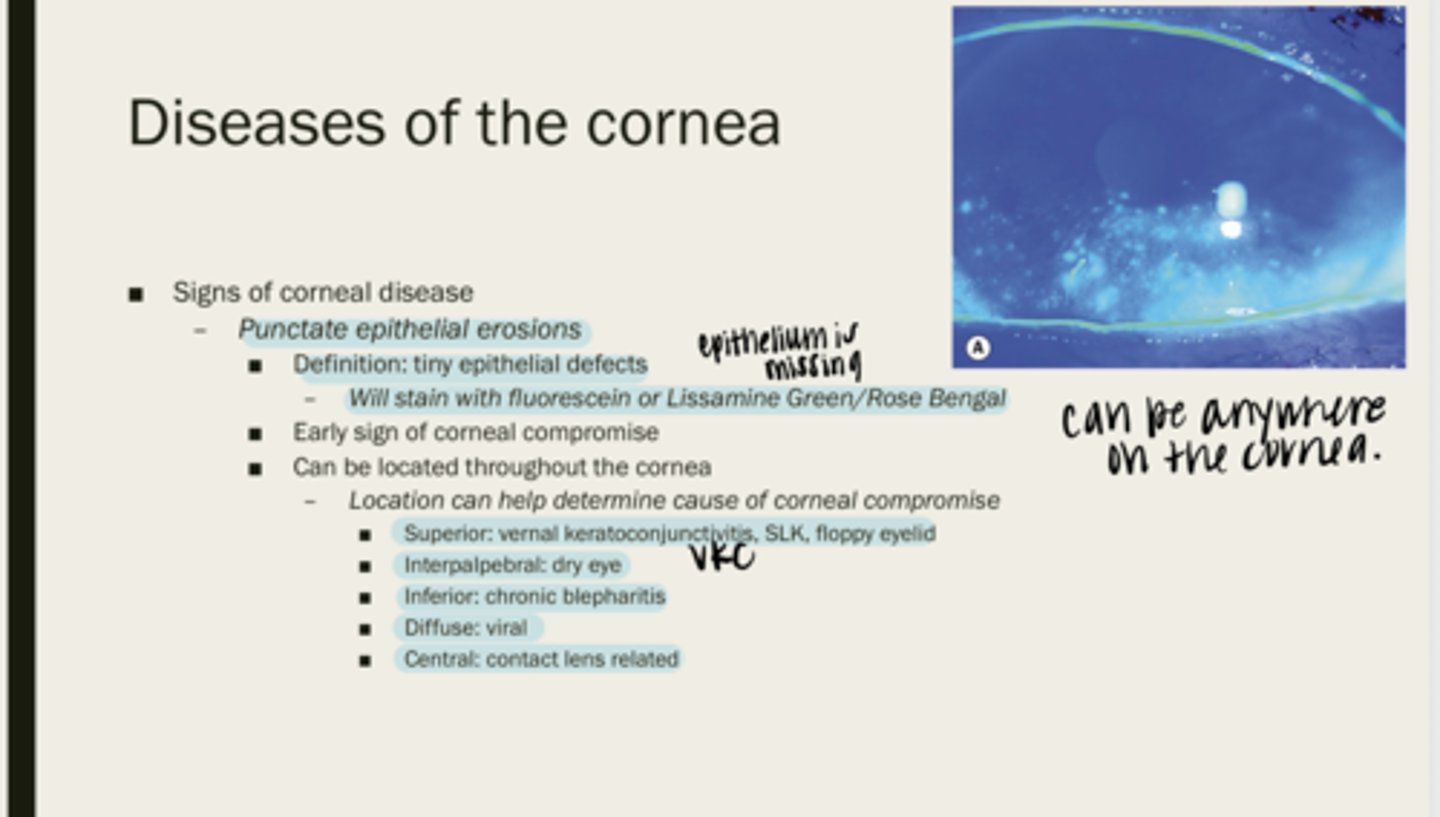
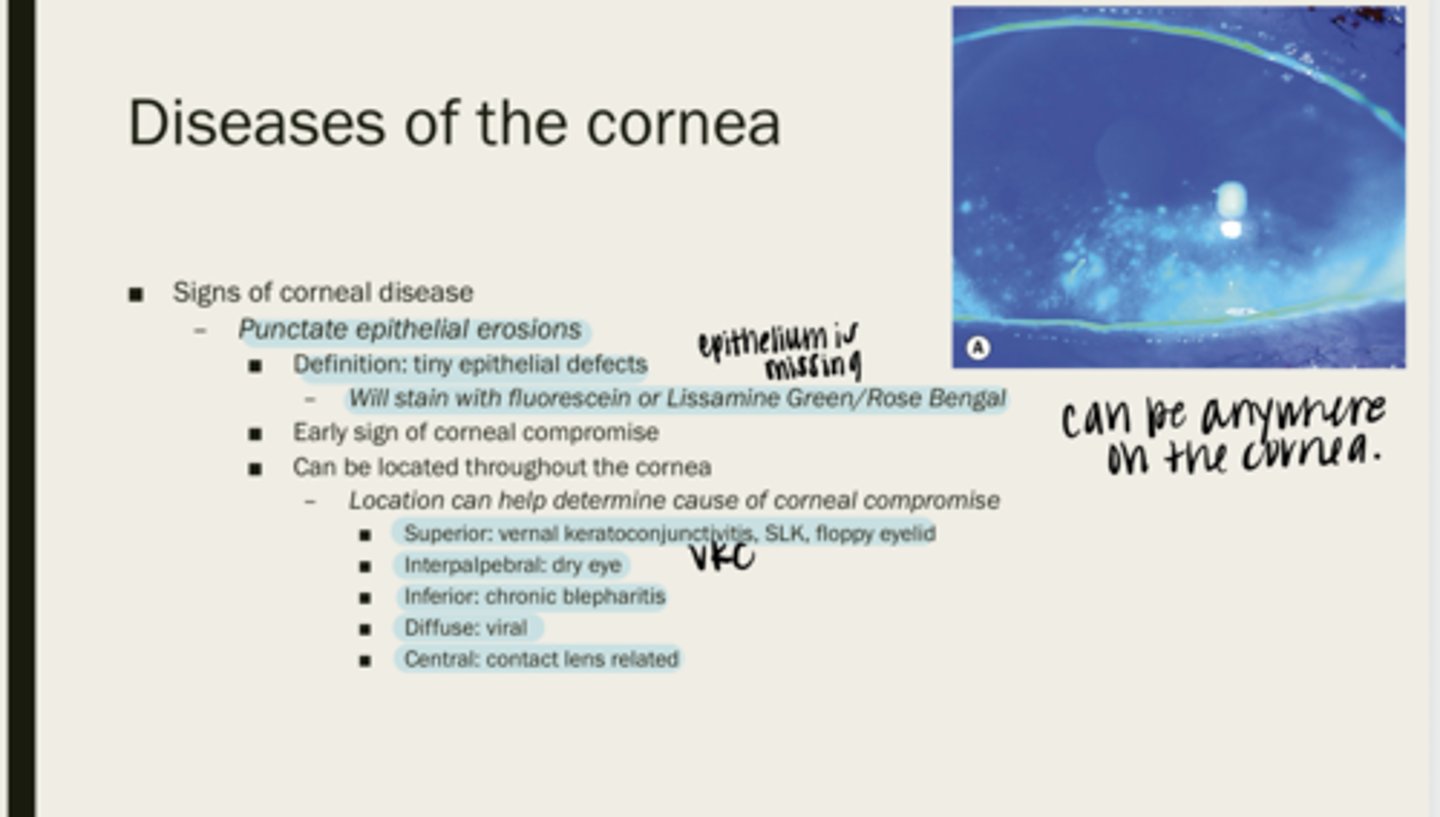
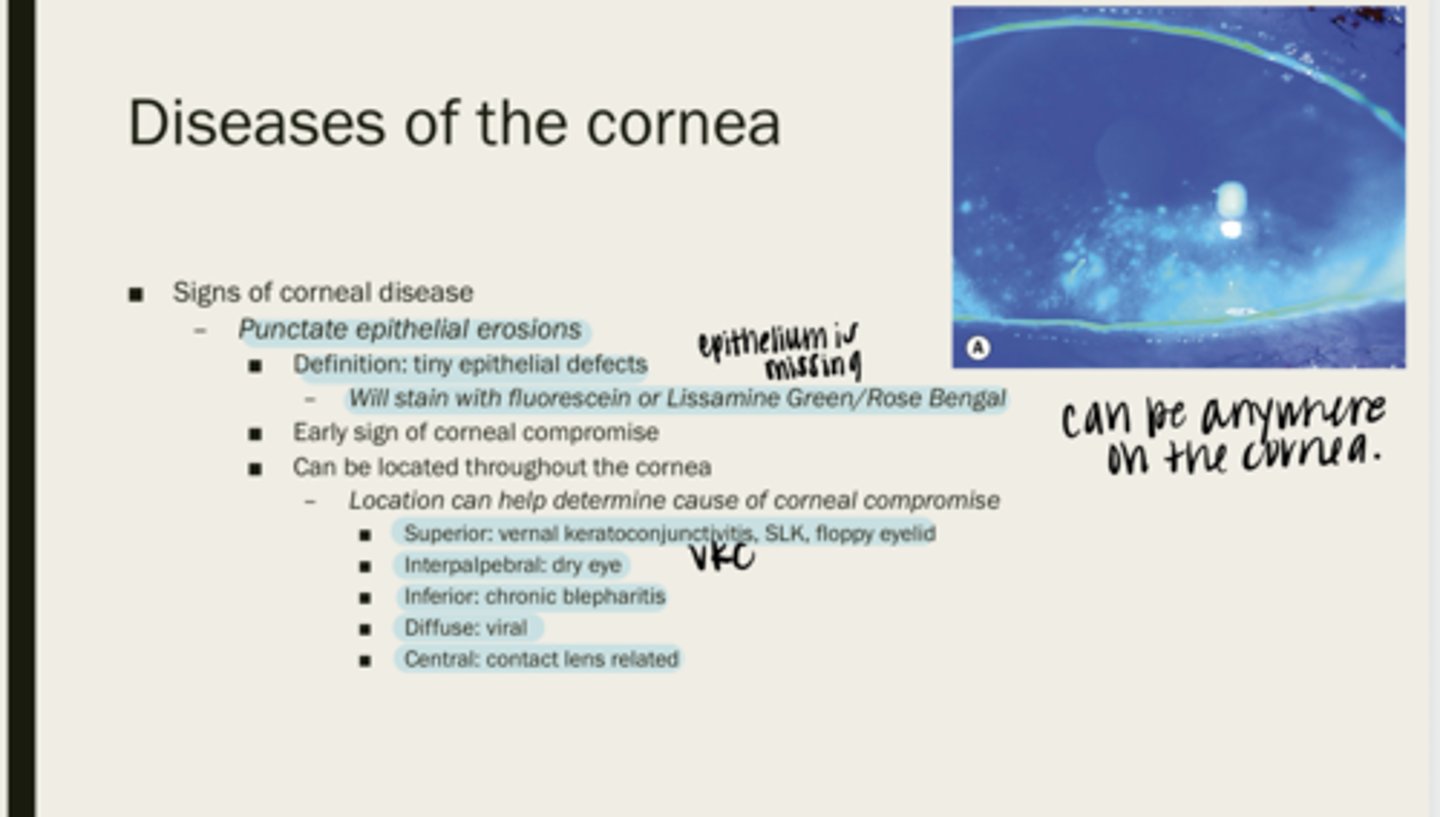
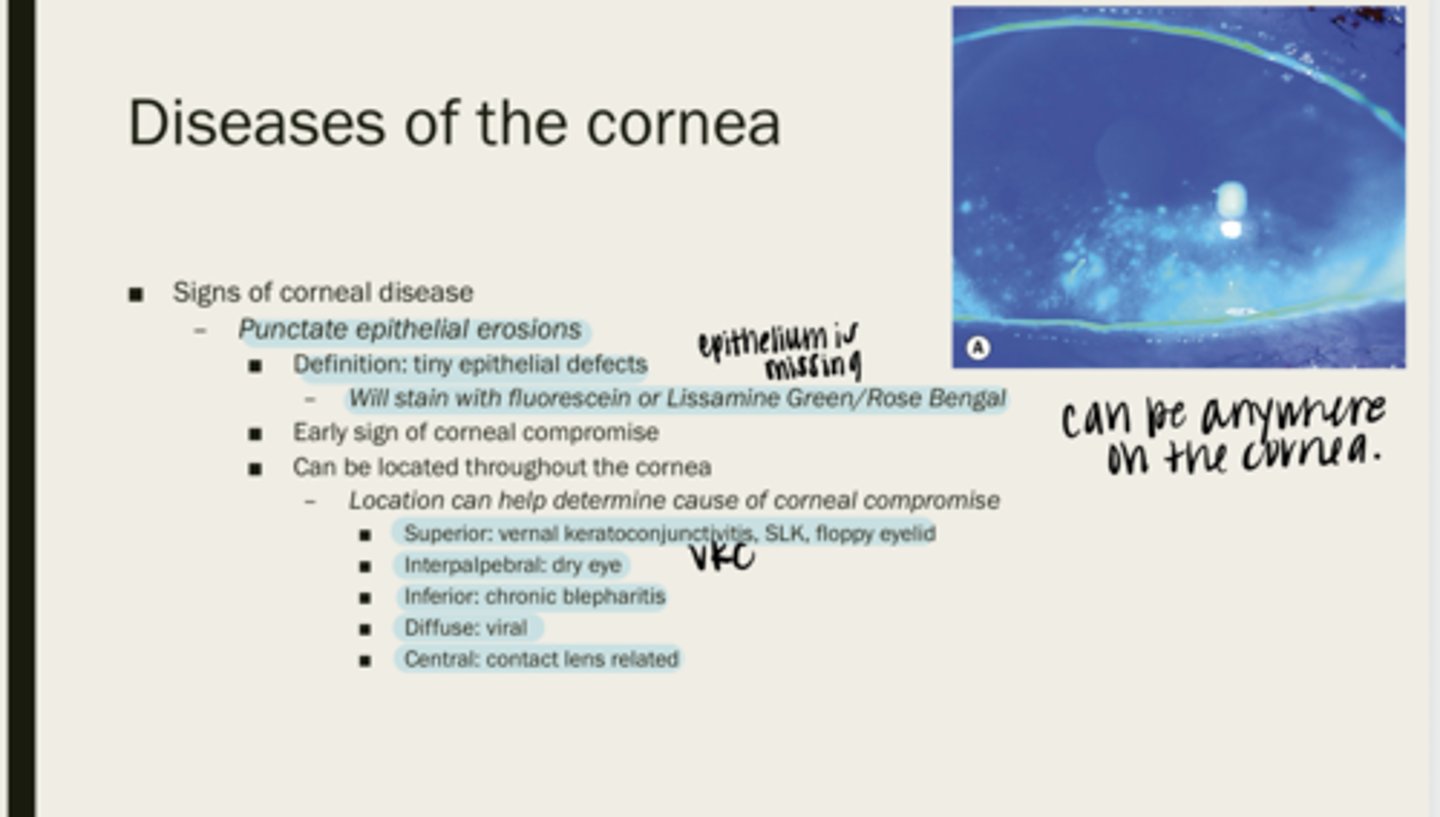
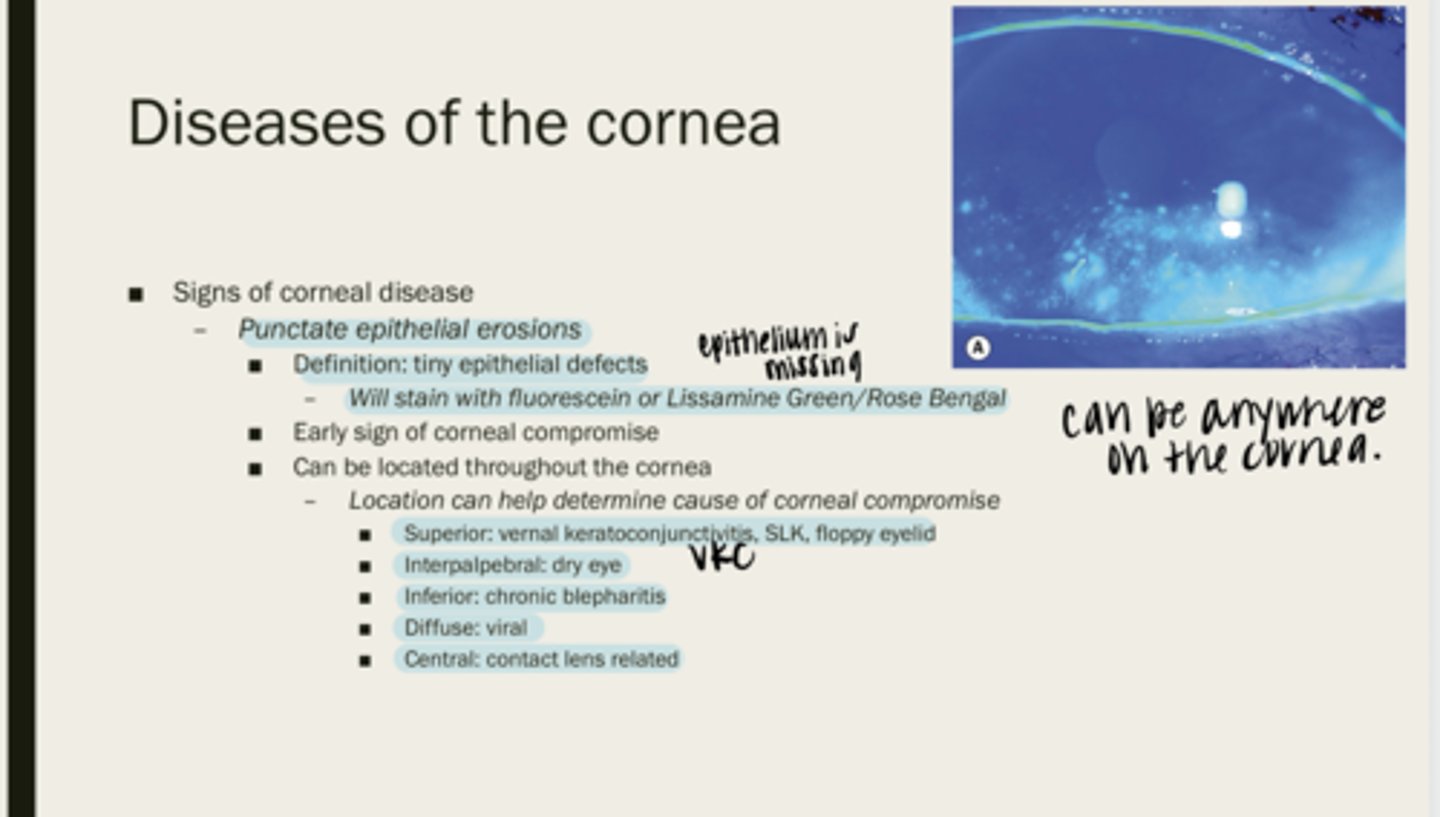
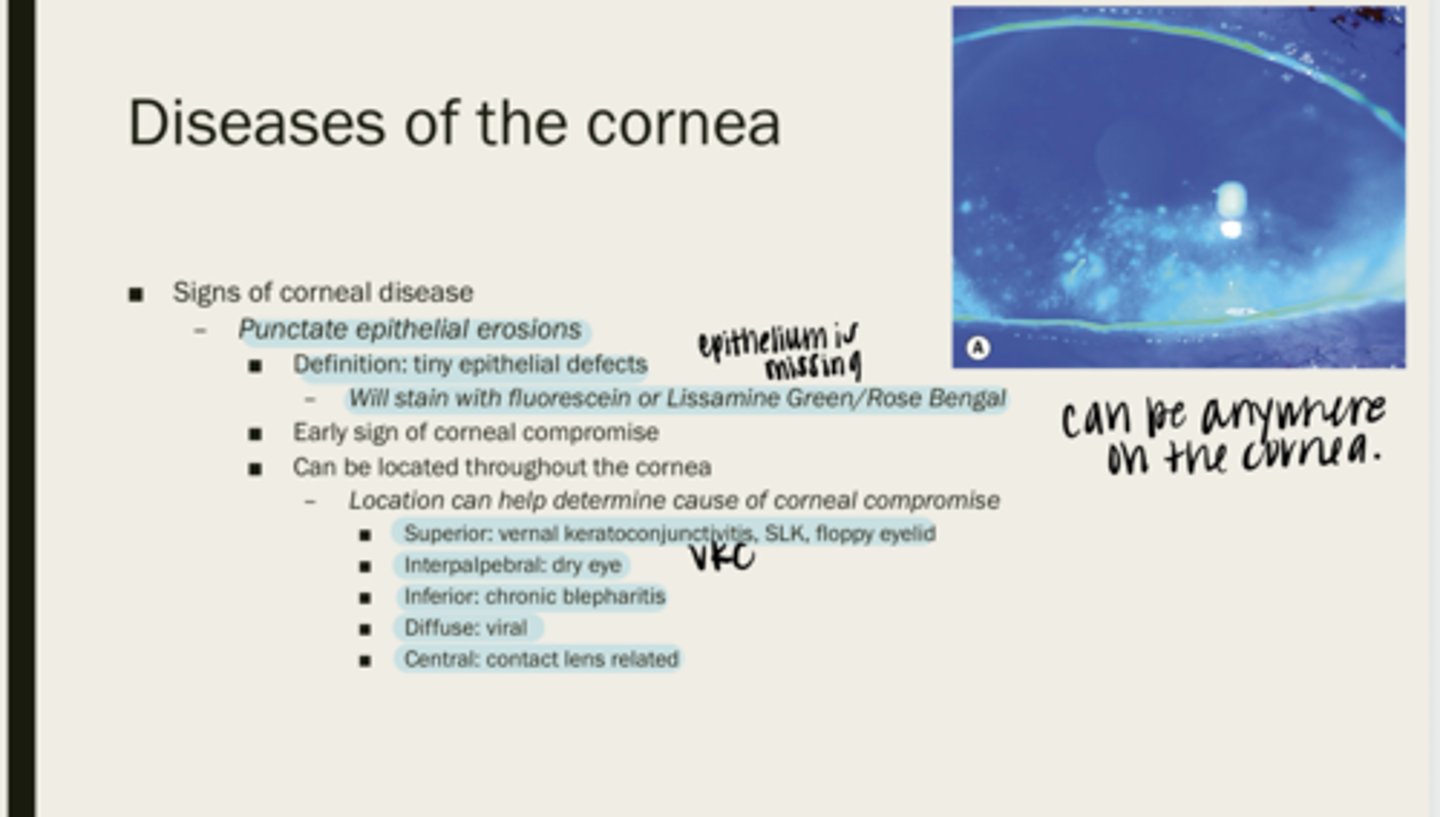
punctate epithelial erosions
tiny epithelial defects
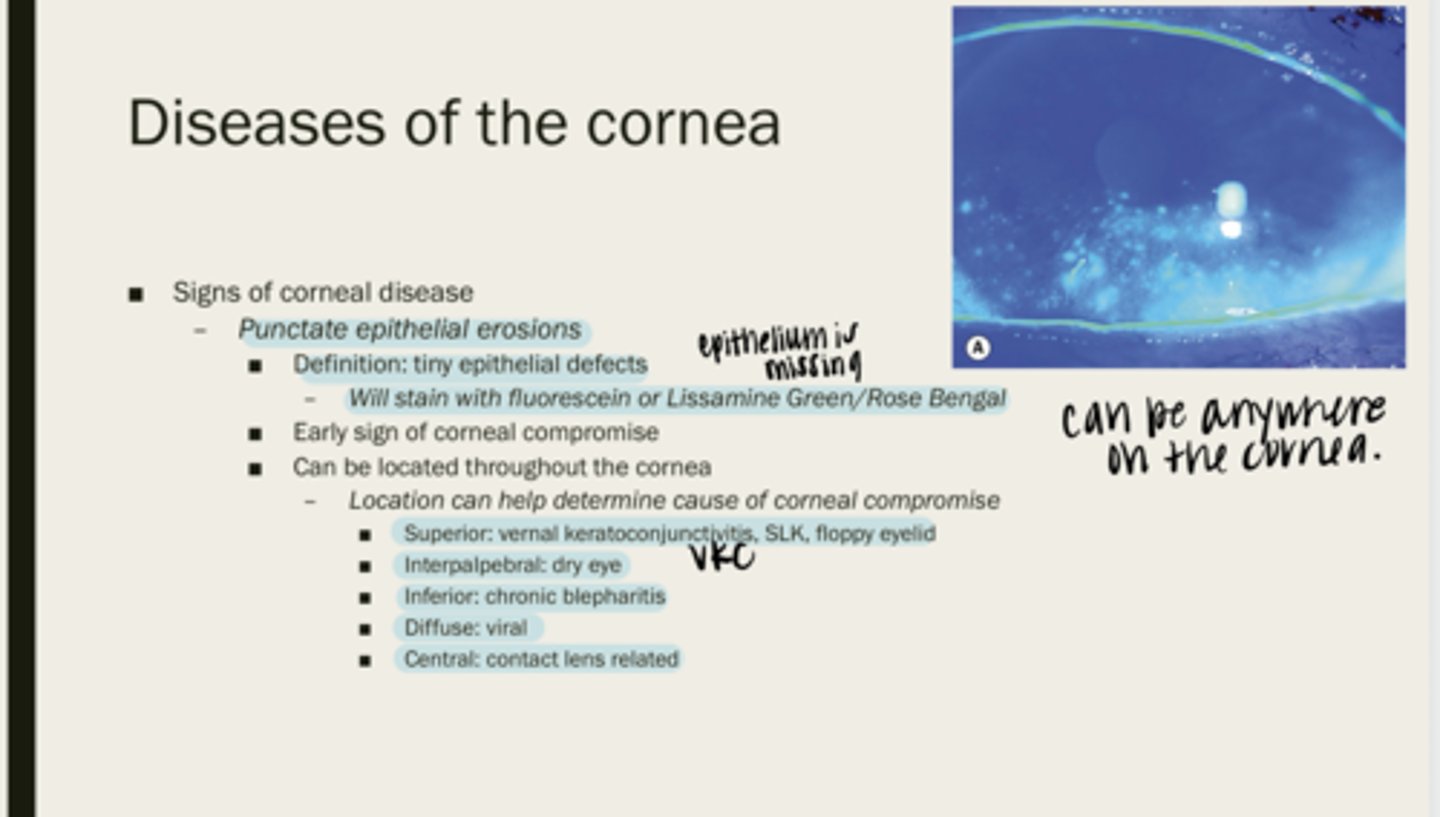
fluorescein or lissamine green/rose bengal
What will PEEs stain with?
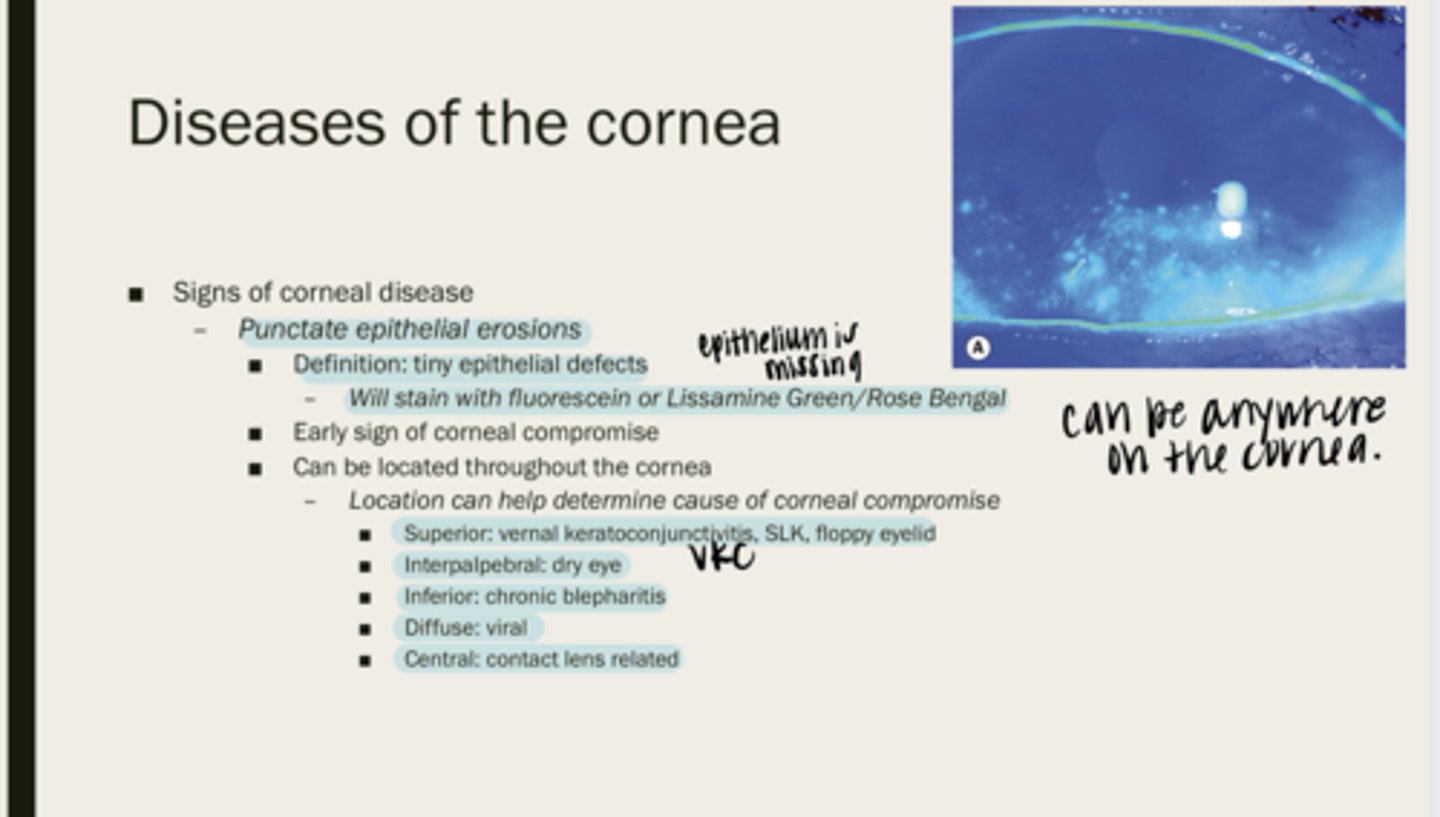
corneal compromise
What are PEEs an early sign of?
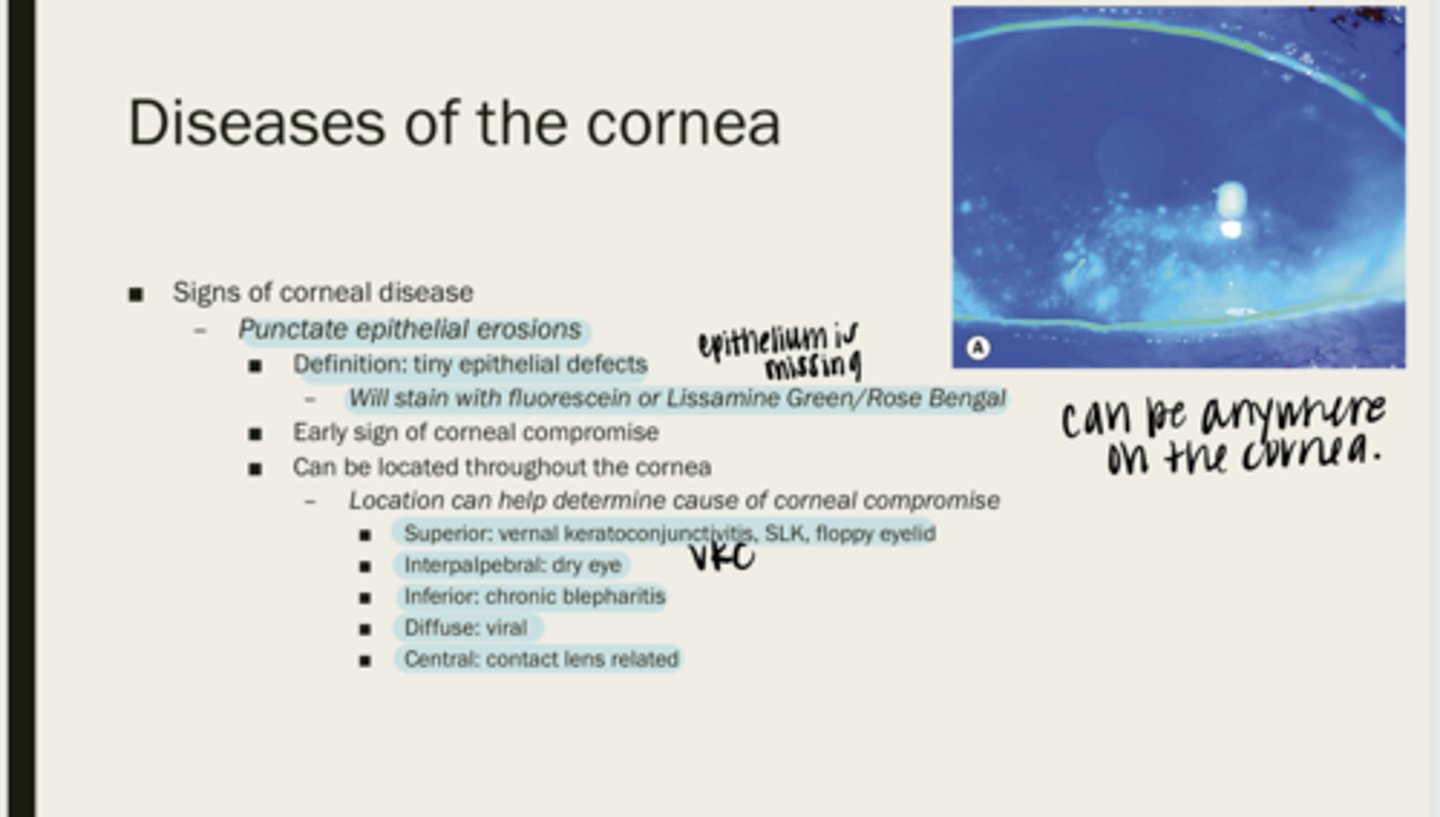
throughout the cornea
Where are PEEs located?
VKC, SLK, floppy eyelid
Superior PEEs can be indicative of what diseases?
dry eye
Interpalpebral PEEs can be indicative of what diseases?
chronic blepharitis
Inferior PEEs can be indicative of what diseases?
viral
Diffuse PEEs can be indicative of what diseases?
contact lens related
Central PEEs can be indicative of what diseases?
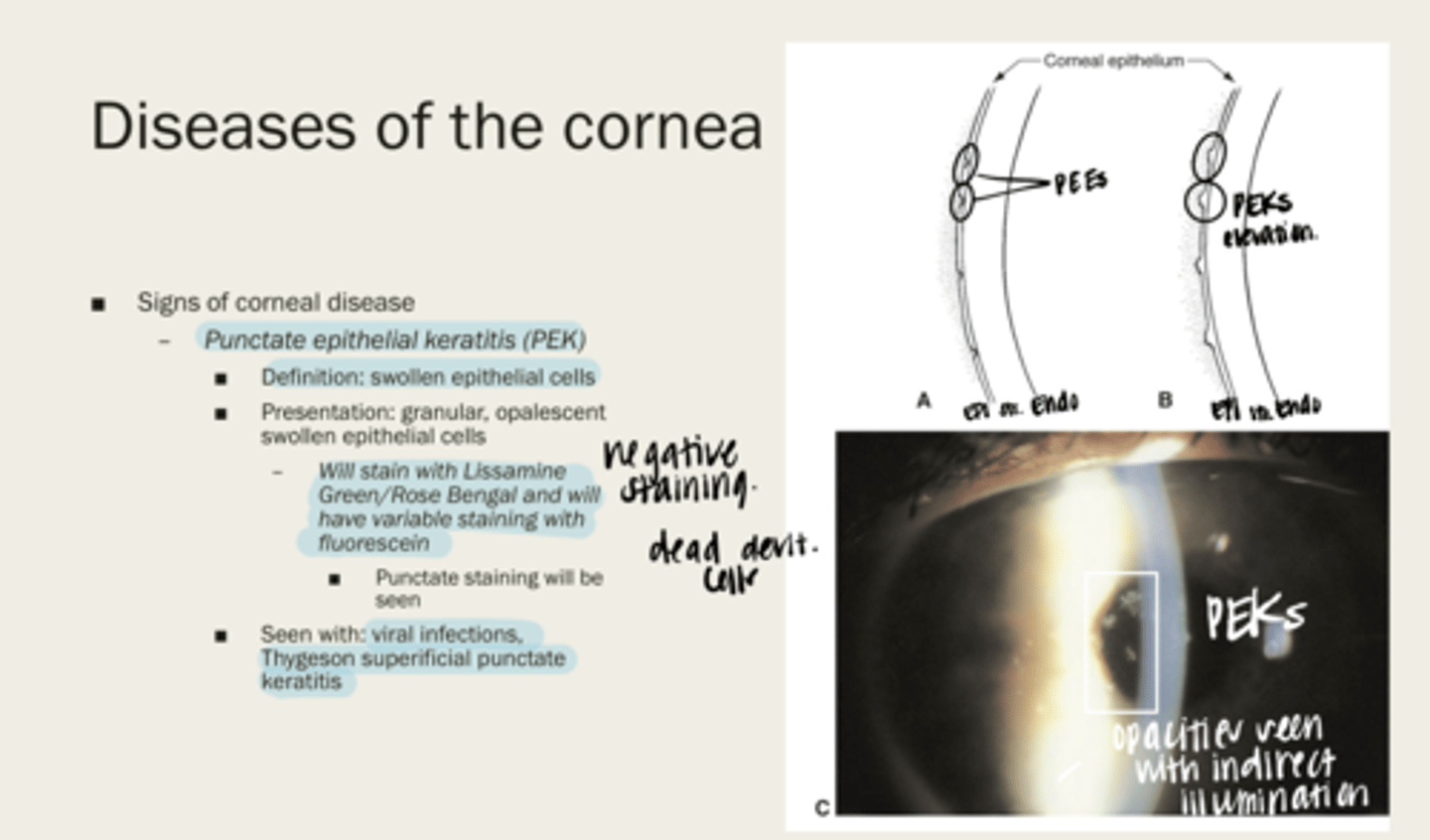
punctate epithelial keratitis (PEK)
swollen epithelial cells
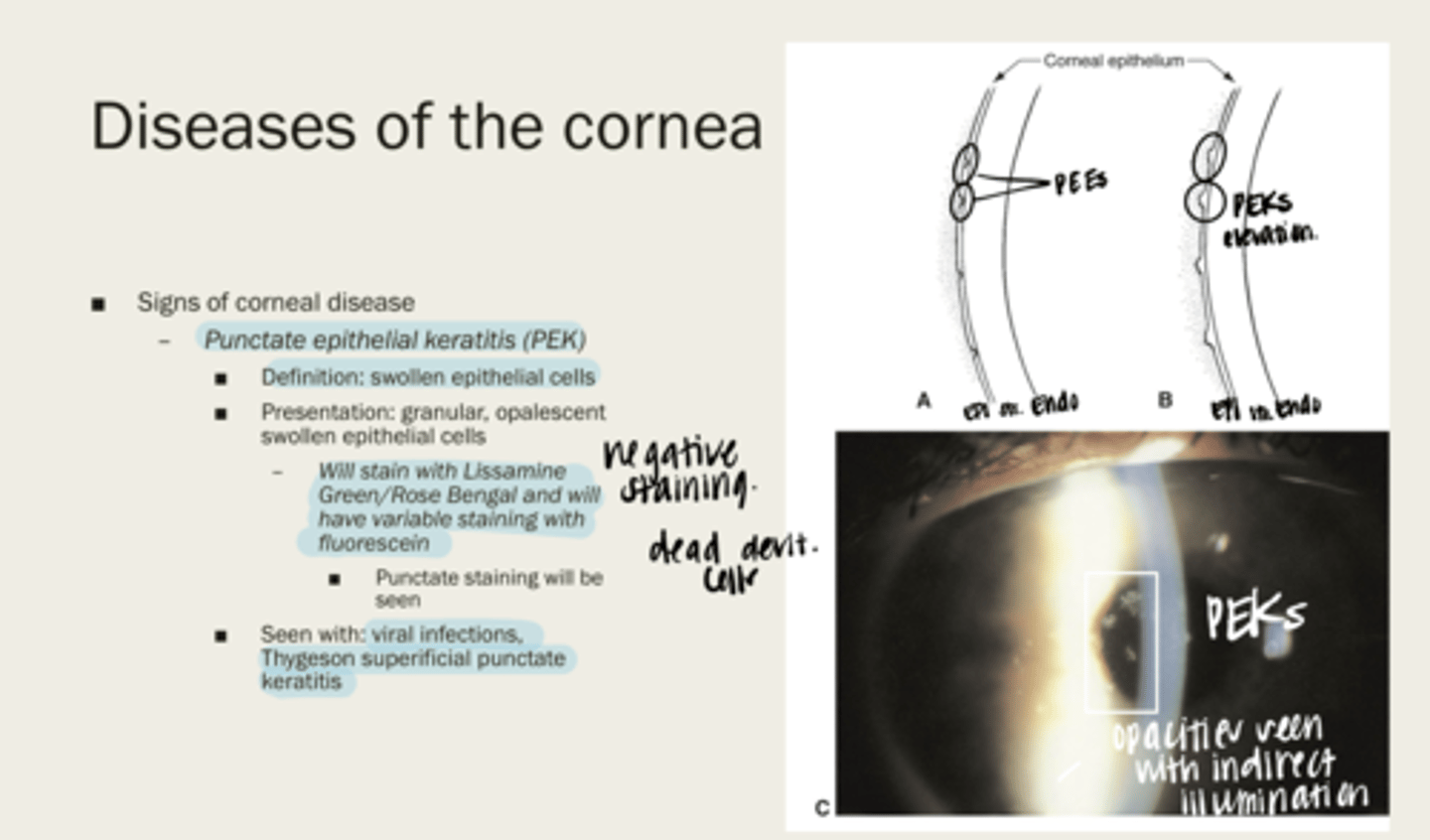
-granular
-opalescent swollen epithelial cells
What is the presentation of punctate epithelial keratitis (PEK)?
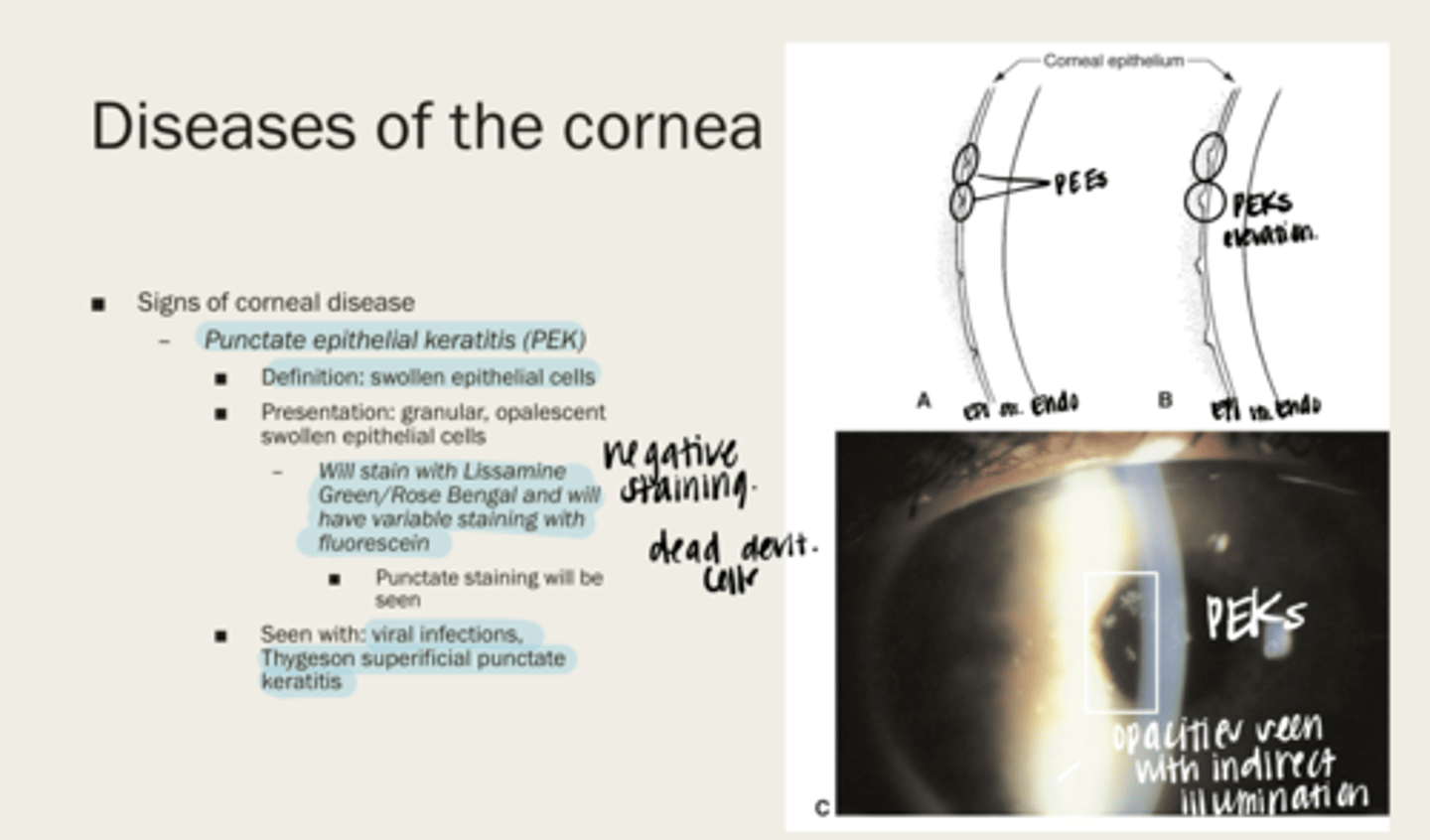
-Lissamine Green/Rose Bengal
-variable staining with fluorescein
What will punctate epithelial keratitis (PEK) stain with?
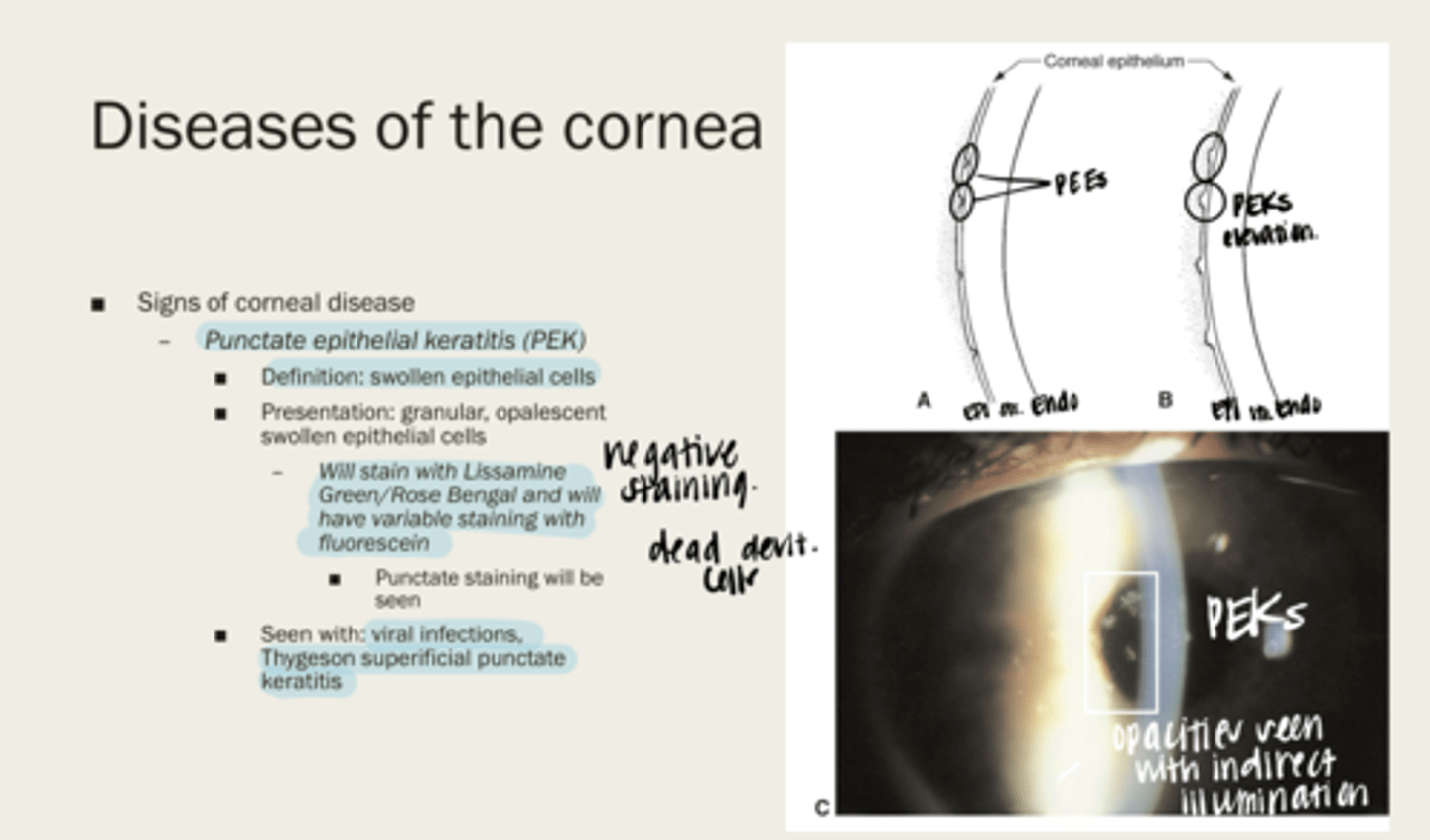
-viral infections
-Thygeson superficial punctate keratitis
When will punctate epithelial keratitis (PEK) be seen?
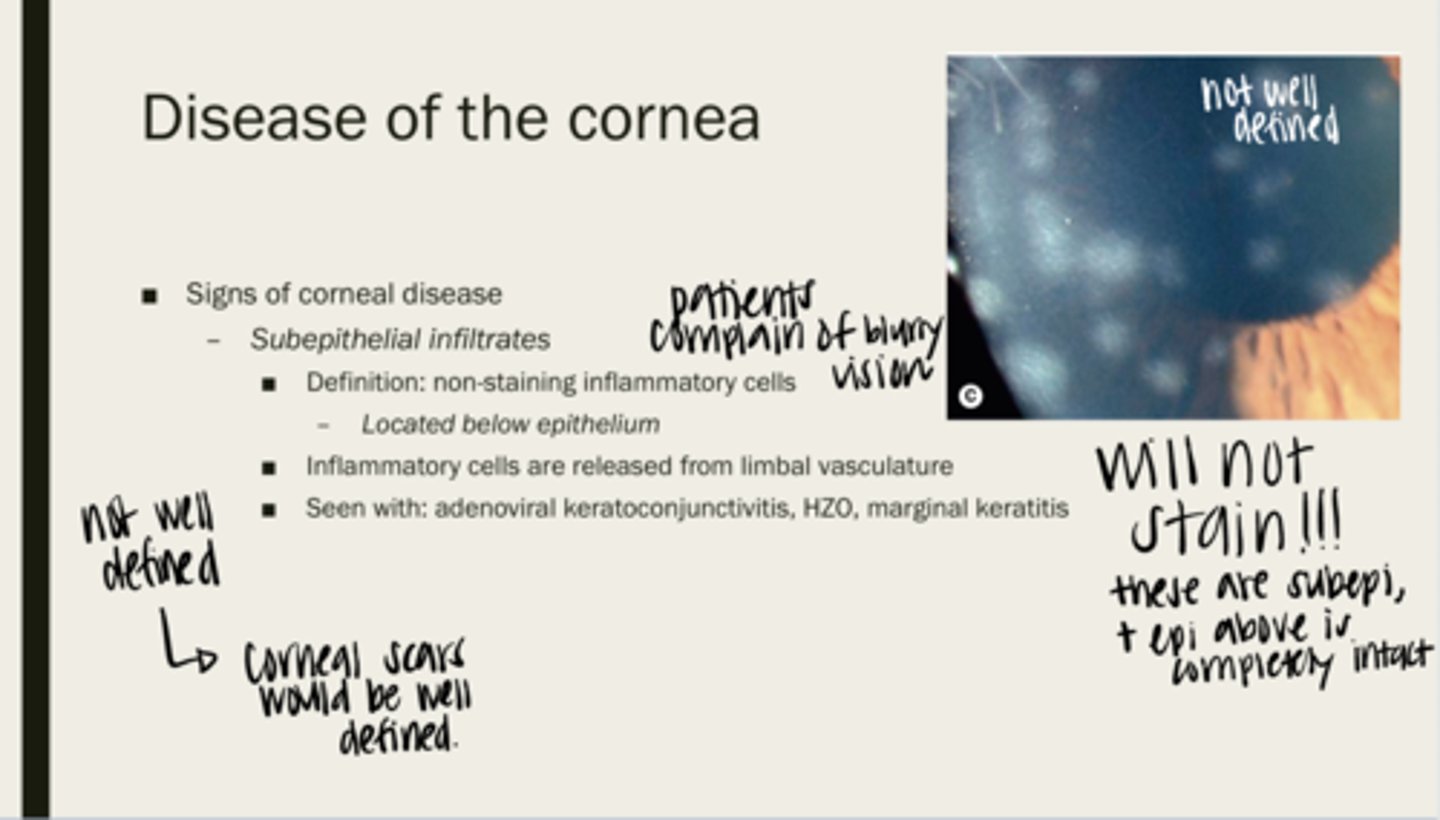
subepithelial infiltrates
non-staining inflammatory cells
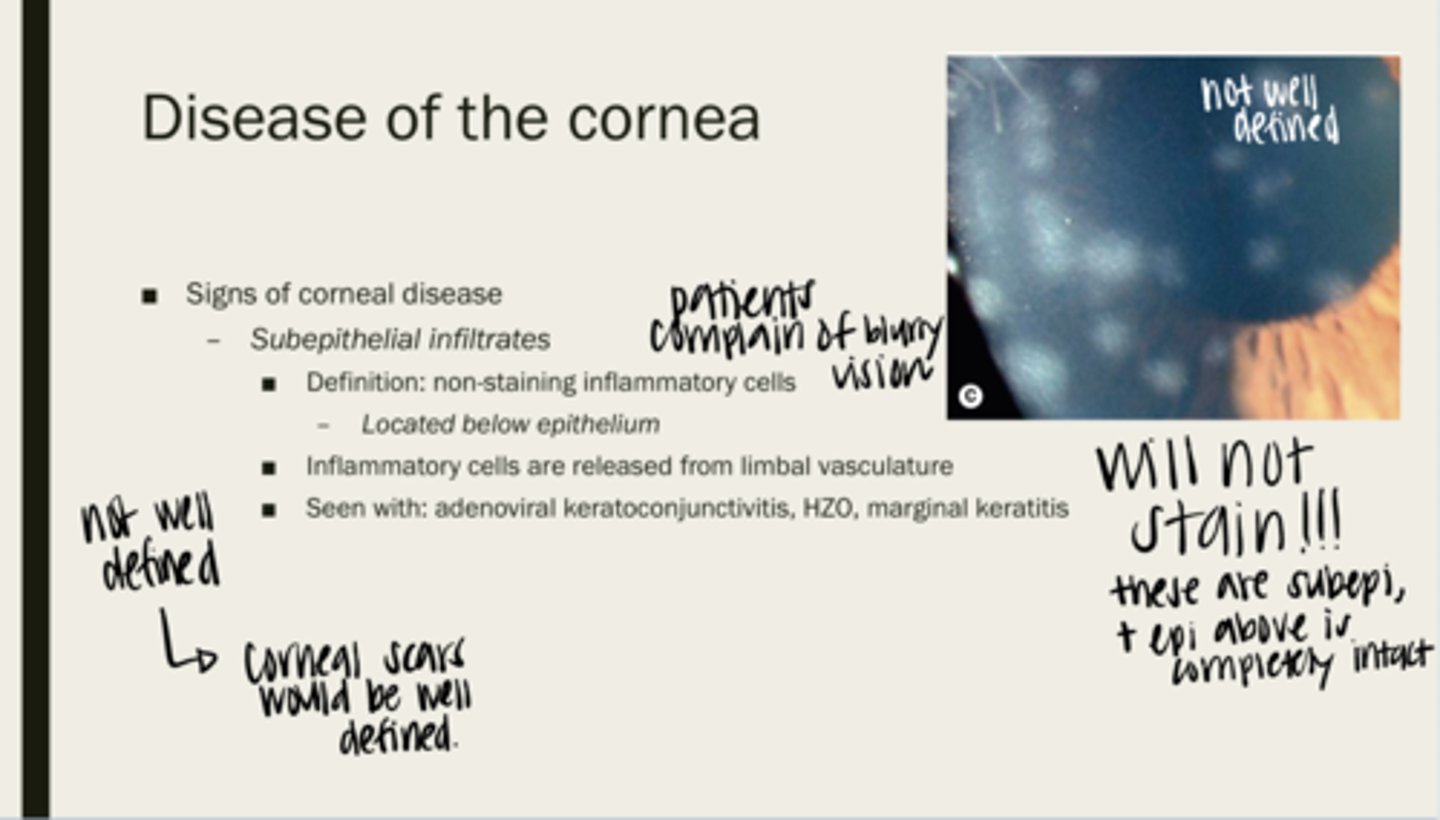
below the epithelium of the cornea
Where are subepithelial infiltrates located?
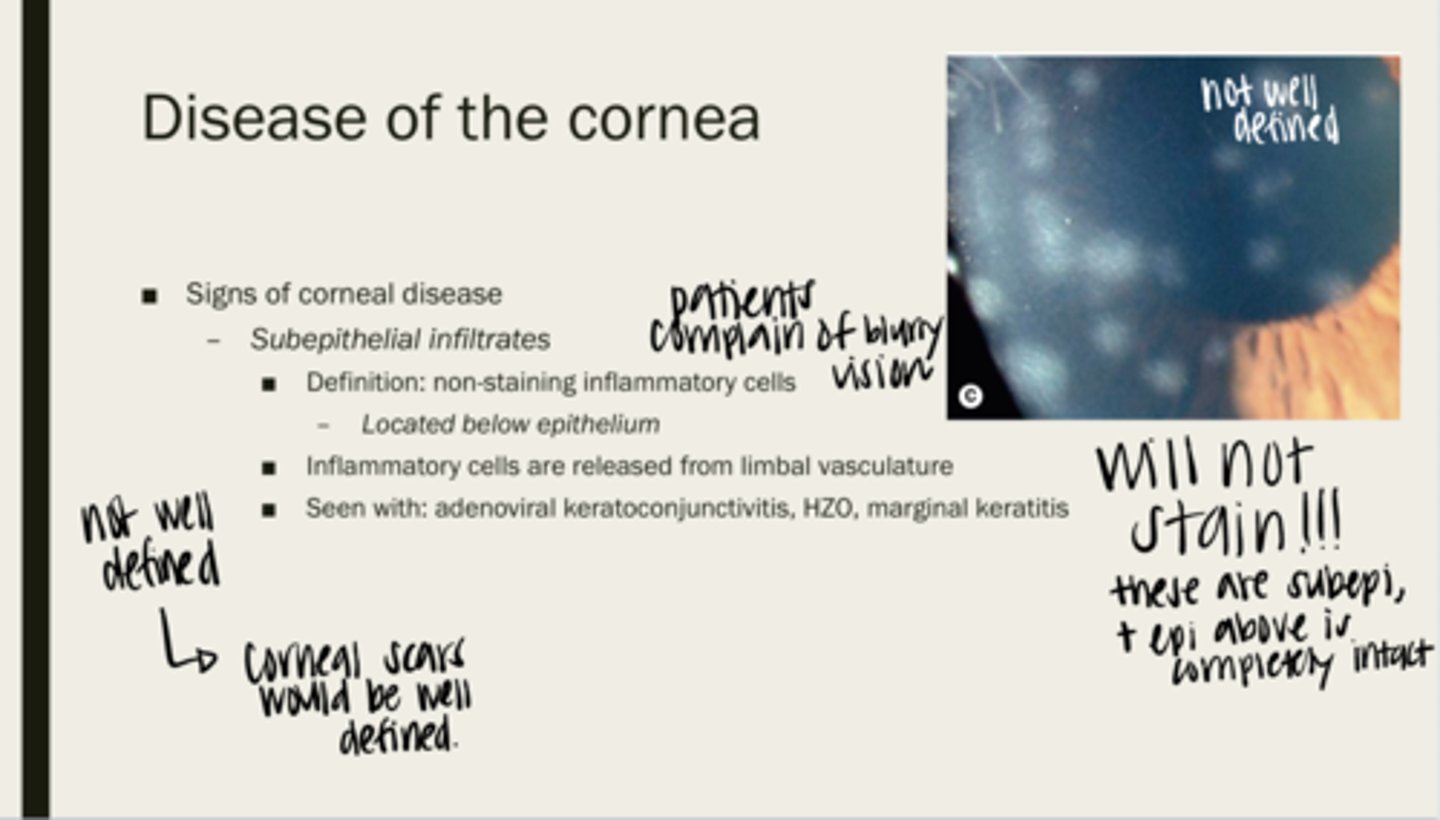
limbal vasculature
Where are inflammatory cells released from?
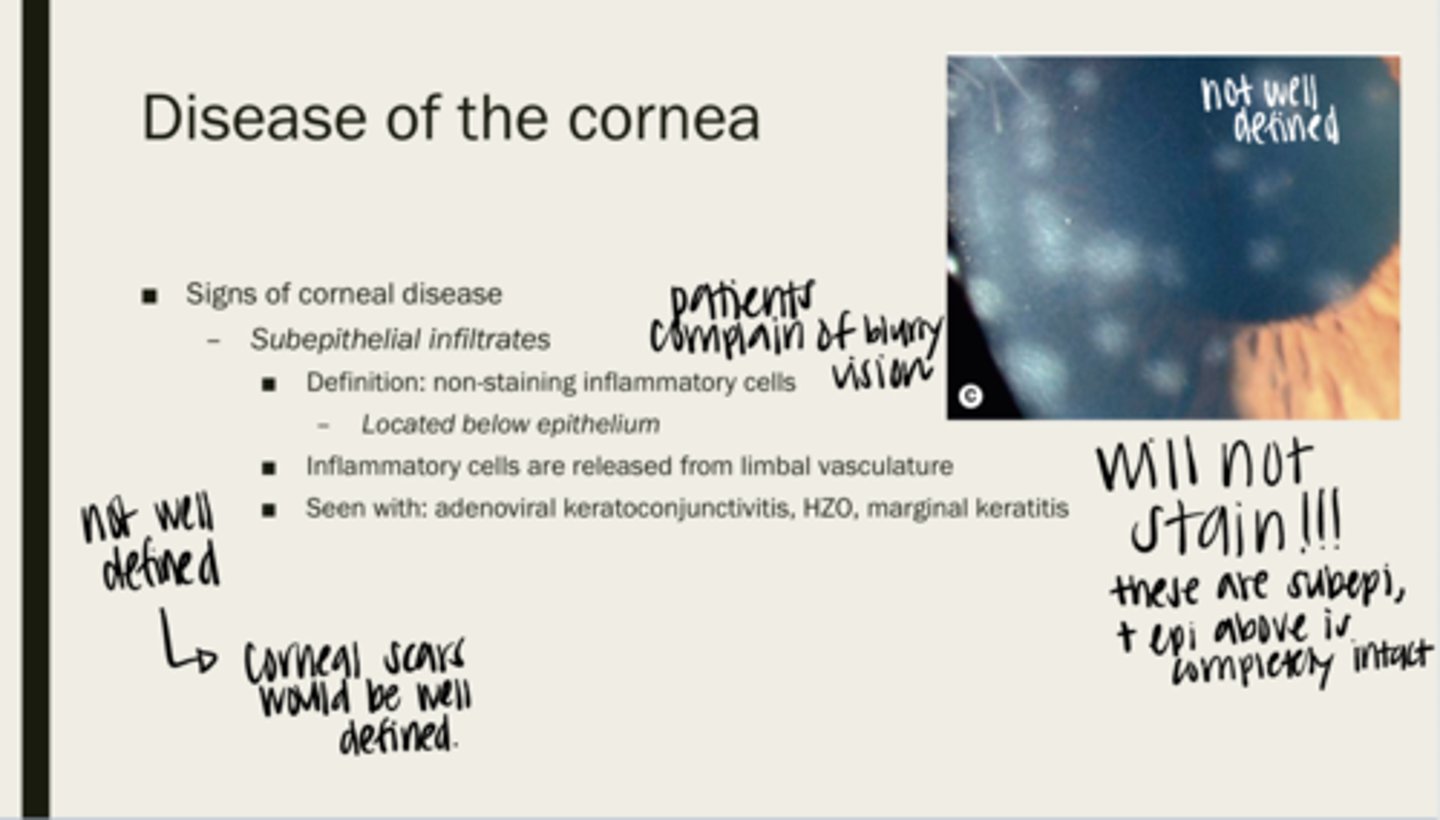
adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis, HZO, marginal keratitis
What are subepithelial infiltrates seen with?
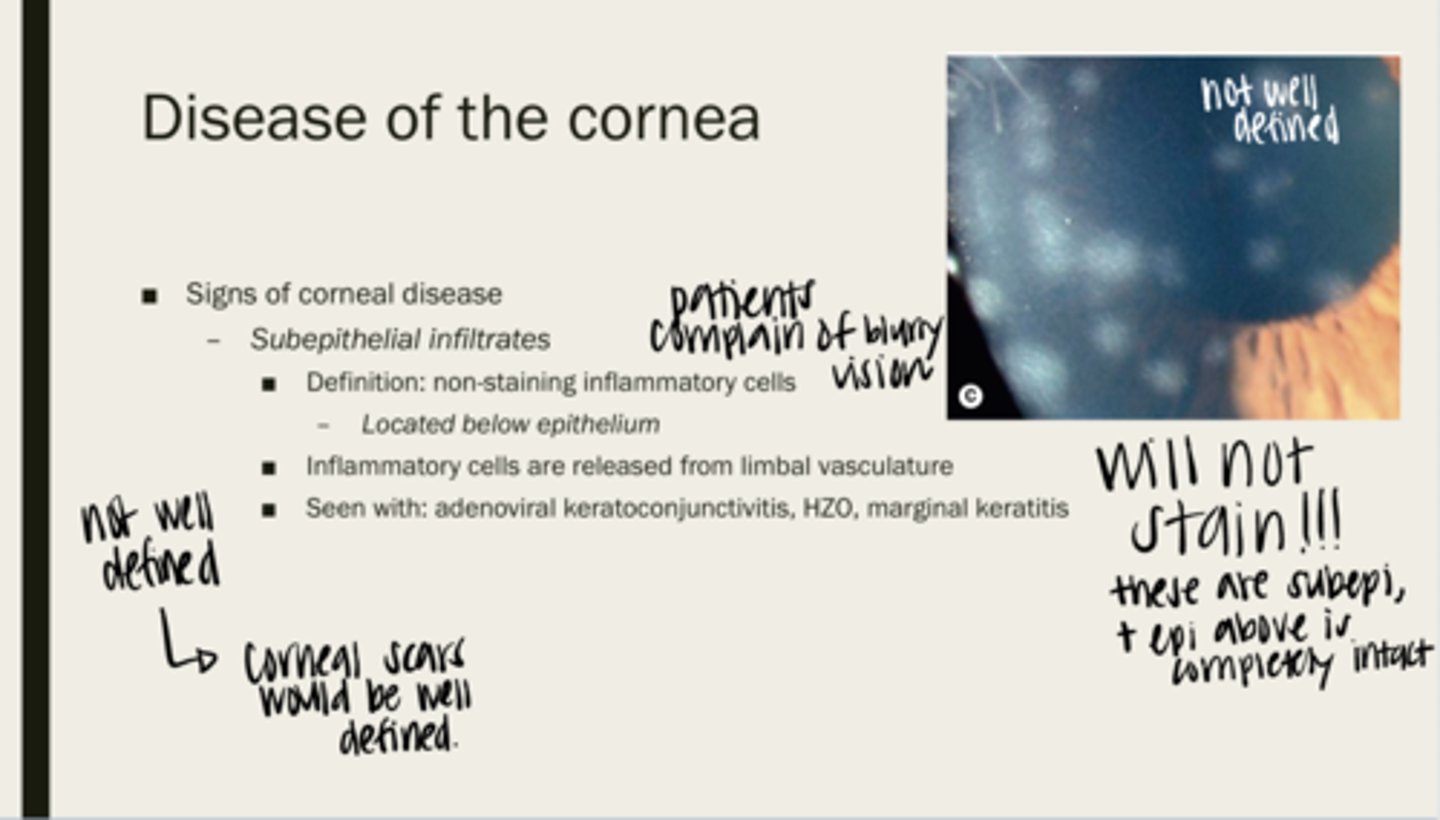
no -- they do not stain because they are under the epithelium. The epithelium is not intact
Will subepithelial infiltrates stain?
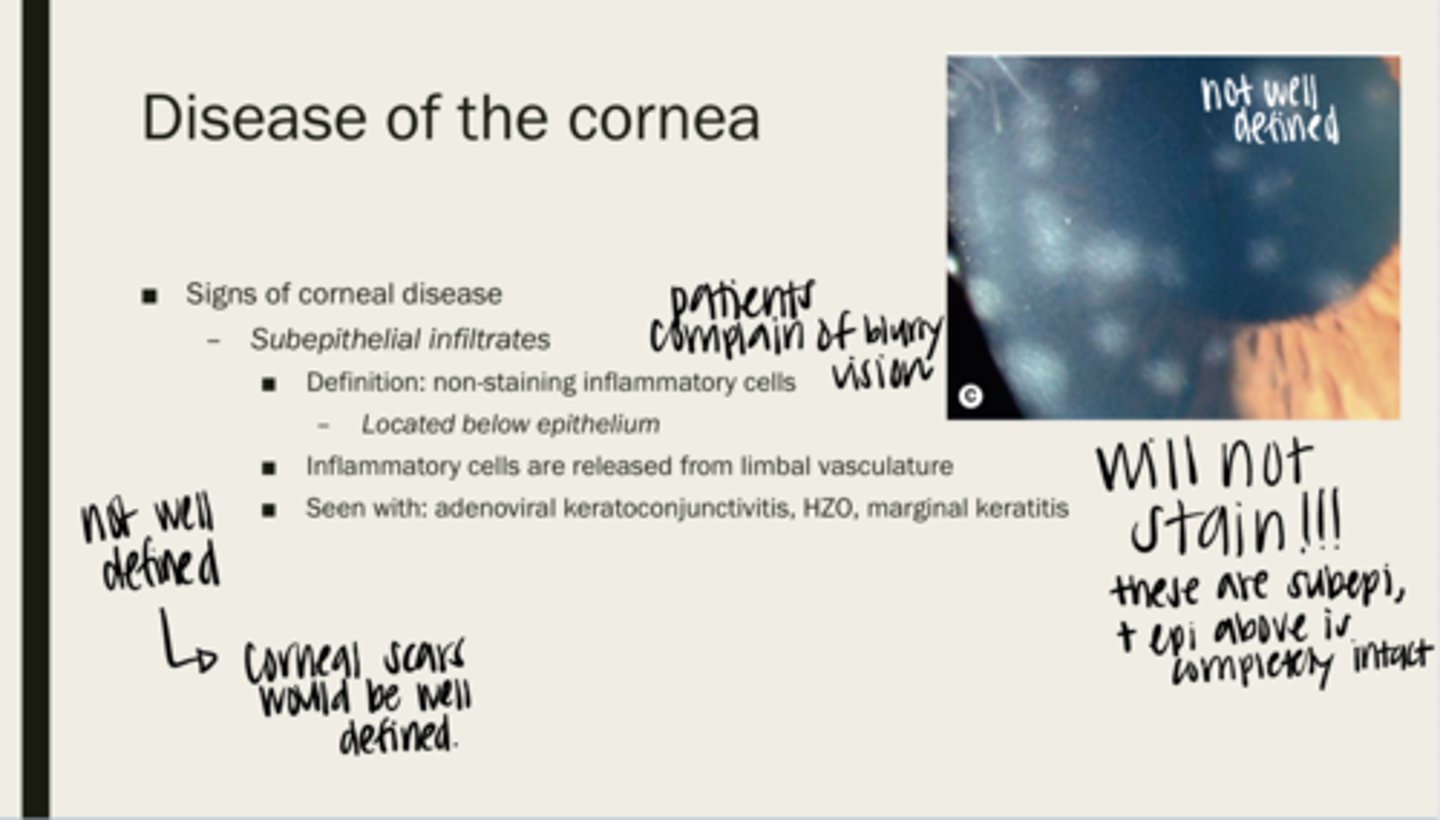
-infiltrates are not well defined
-corneal scars are well defined
Are epithelial infiltrates well defined? How are you able to tell them apart from corneal scarring?
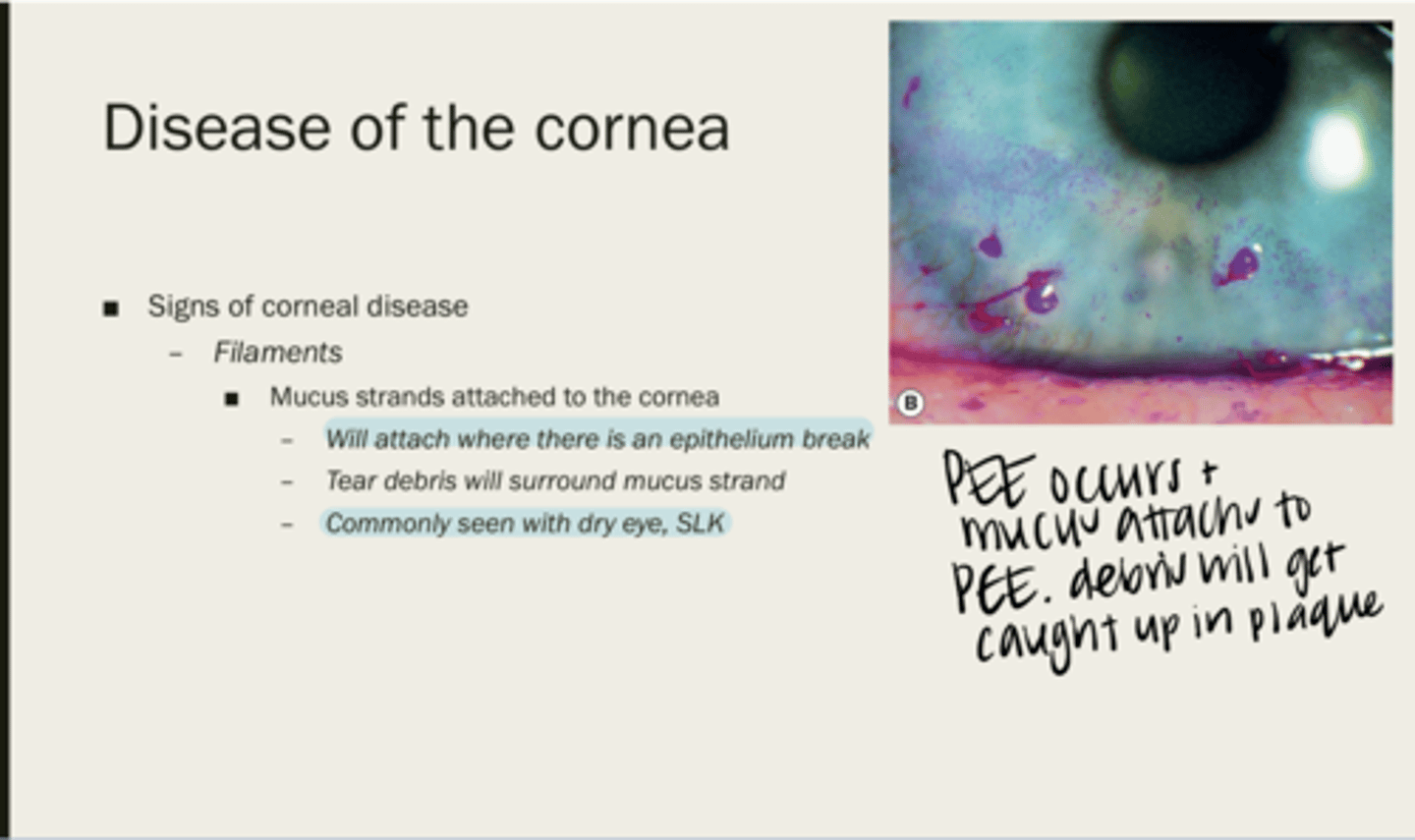
filaments
mucus strands attached to the cornea
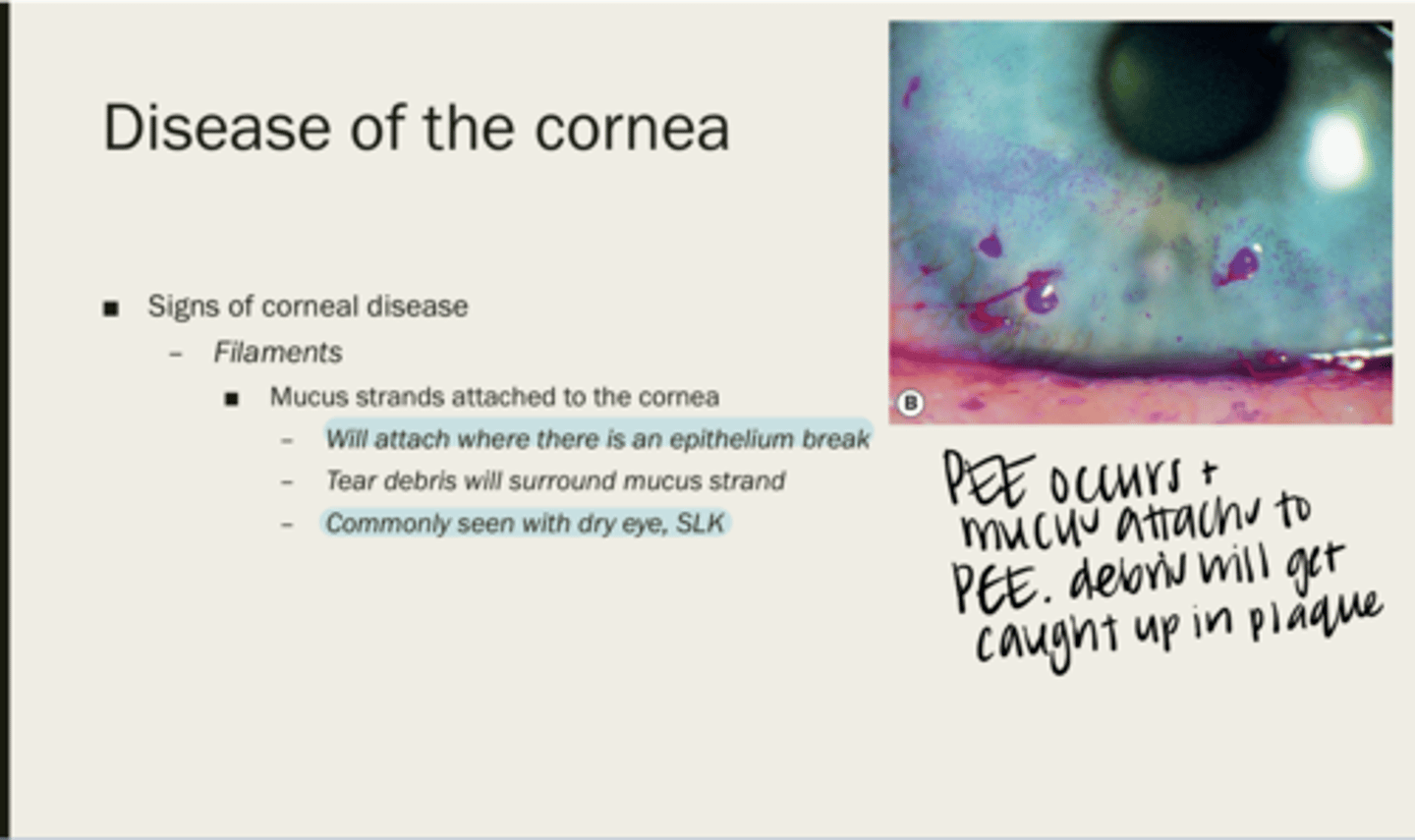
where there is an epithelium break
Where will filaments attach?
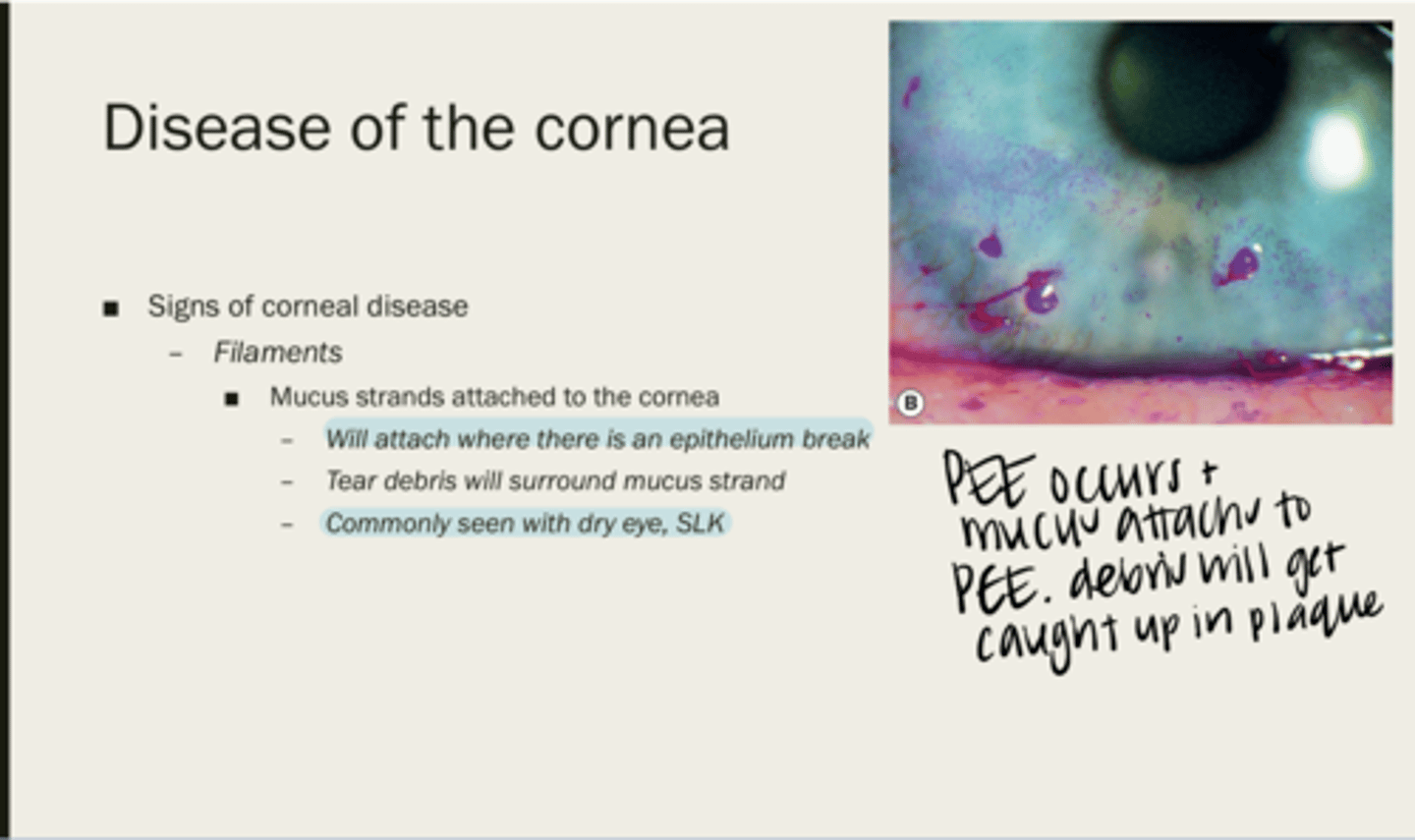
tear debris
What will surround a mucus strand?
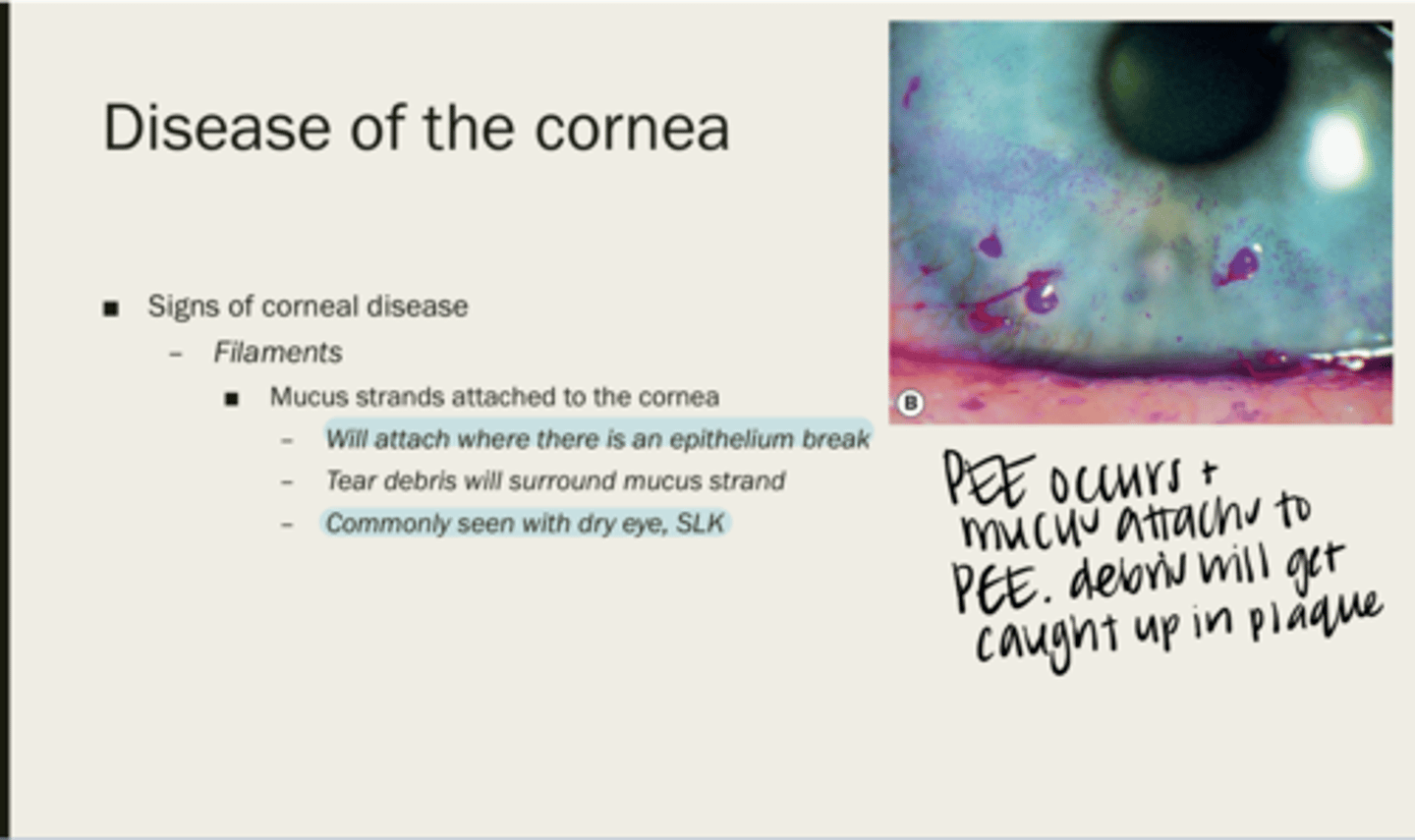
with dry eye, SLK
When are filaments usually seen?
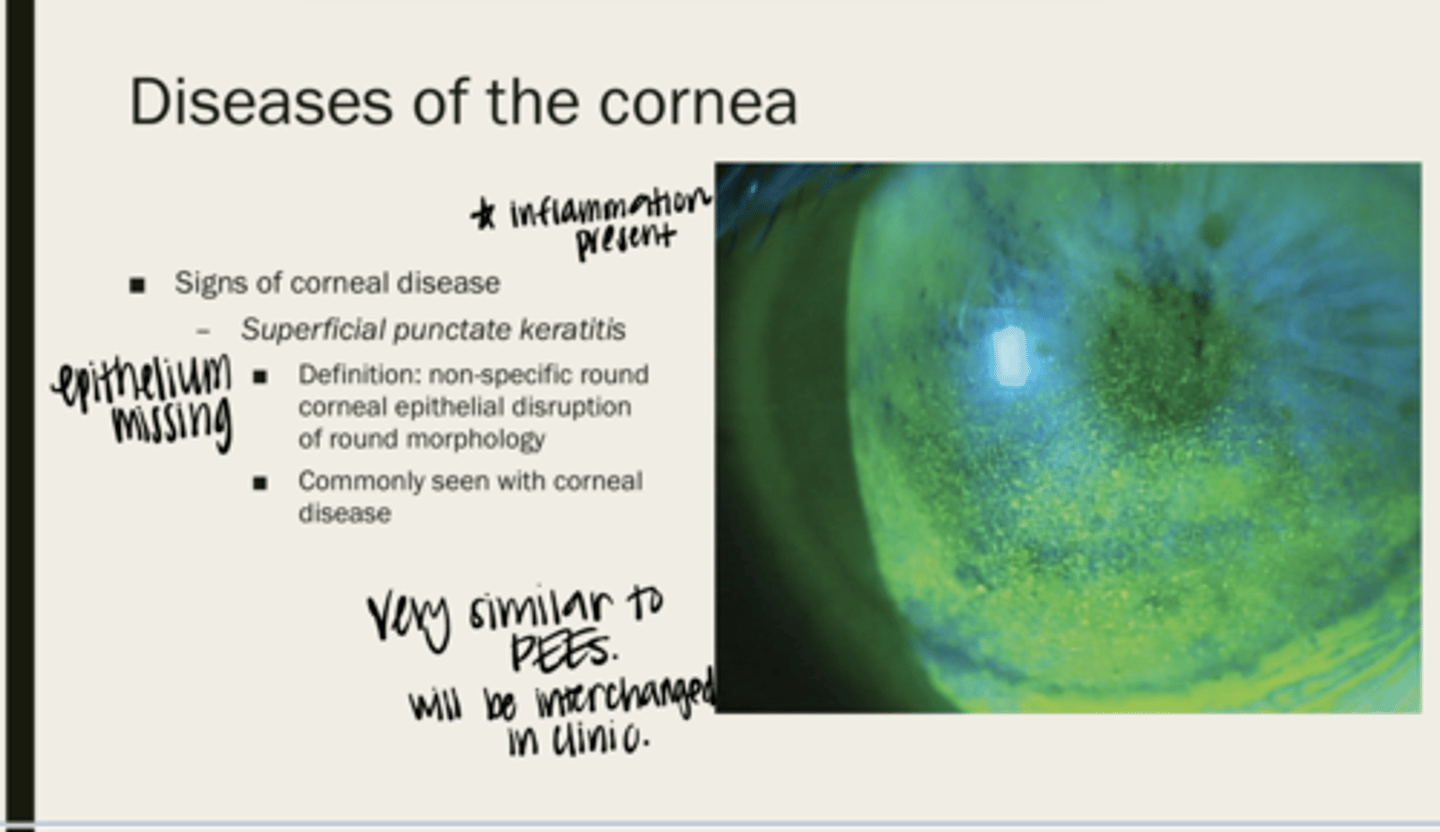
superficial punctate keratitis (SPK)
non-specific round corneal epithelial disruption of round morphology
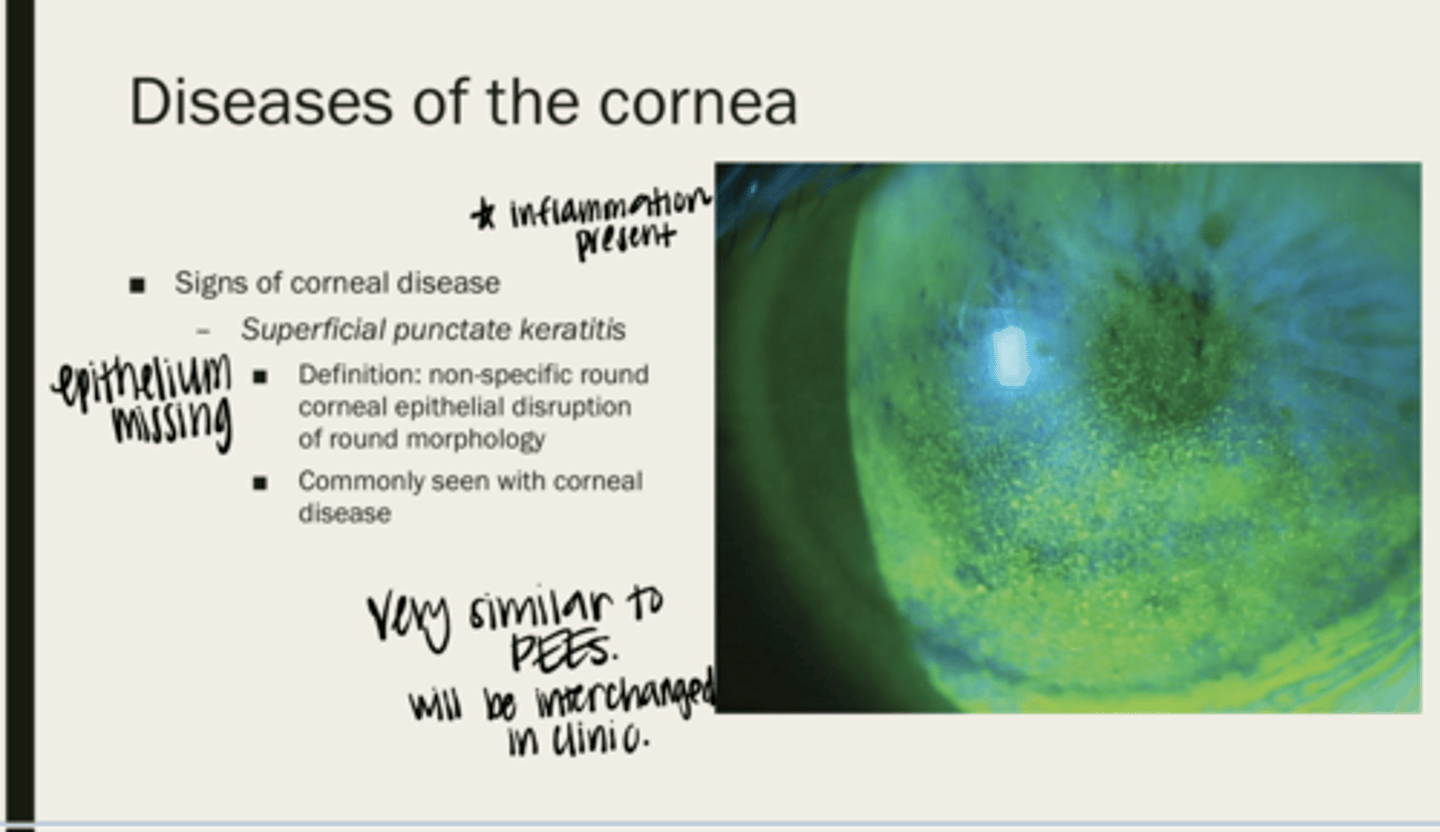
corneal disease
What is superficial punctate keratitis (SPK) seen with?
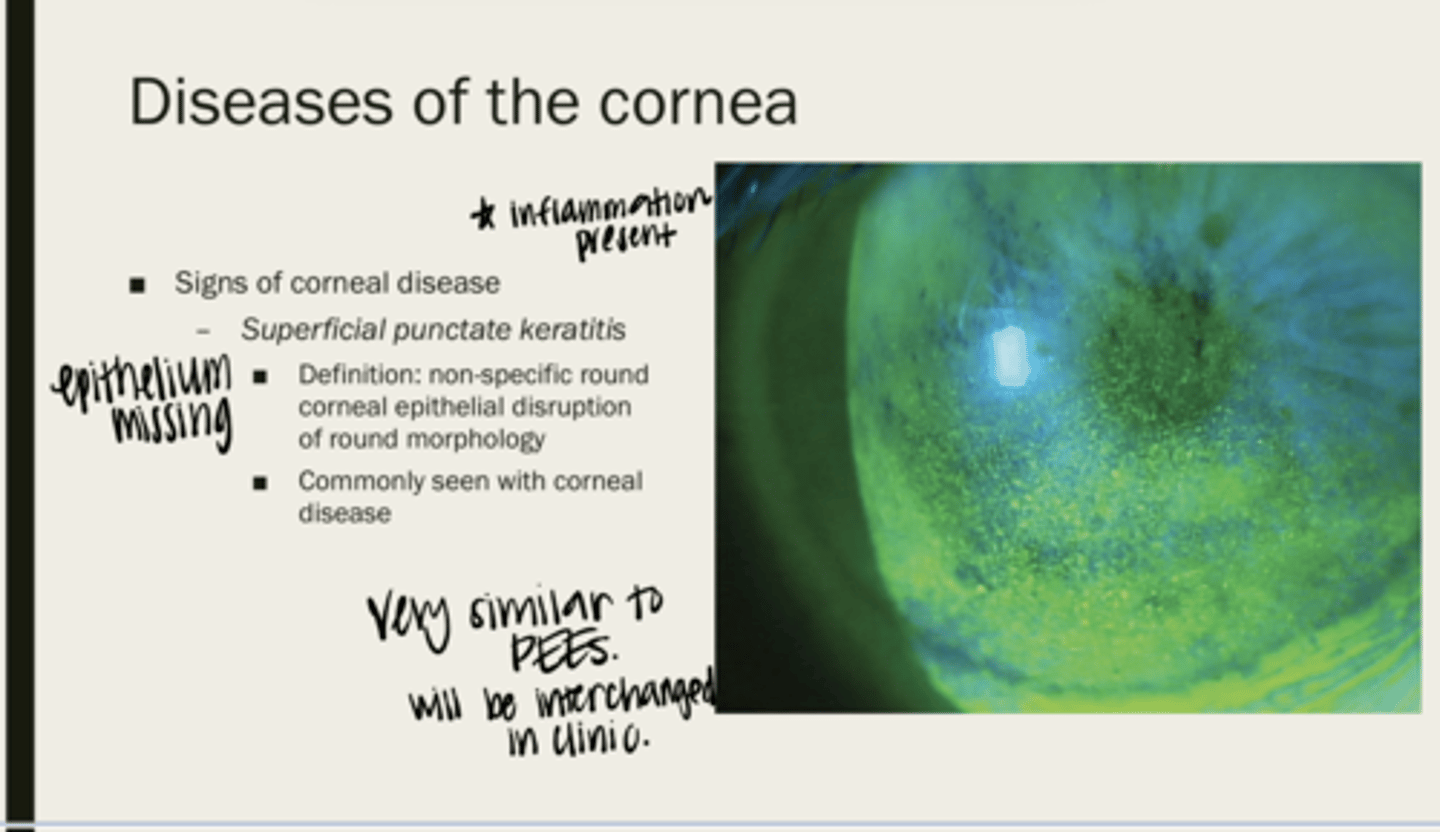
SPK - inflammation present, PEE - no inflammation present
What is the main difference between SPK and PEEs?
no
Will you be able to tell the difference between SPK and PEEs on slit lamp examination?
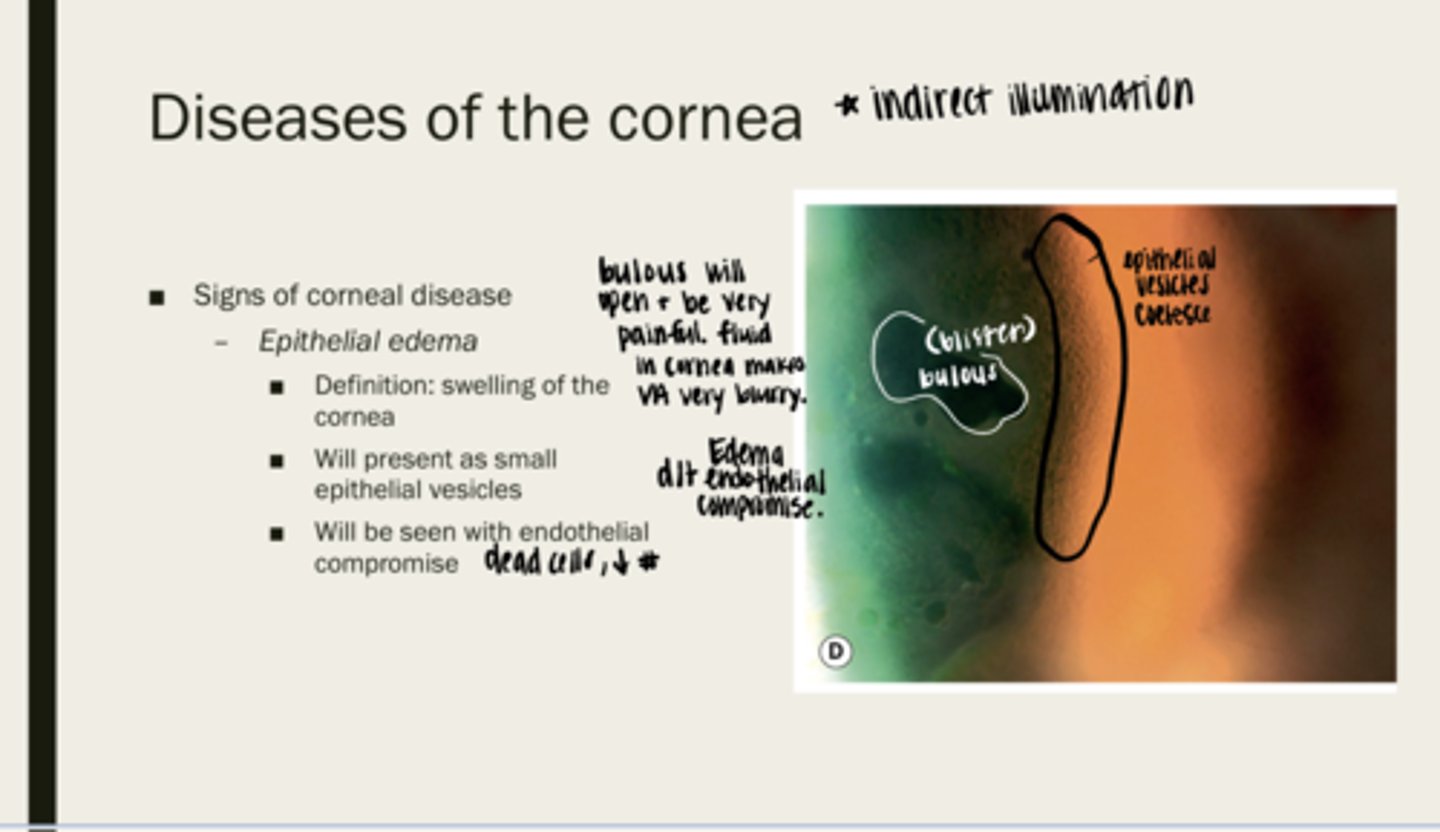
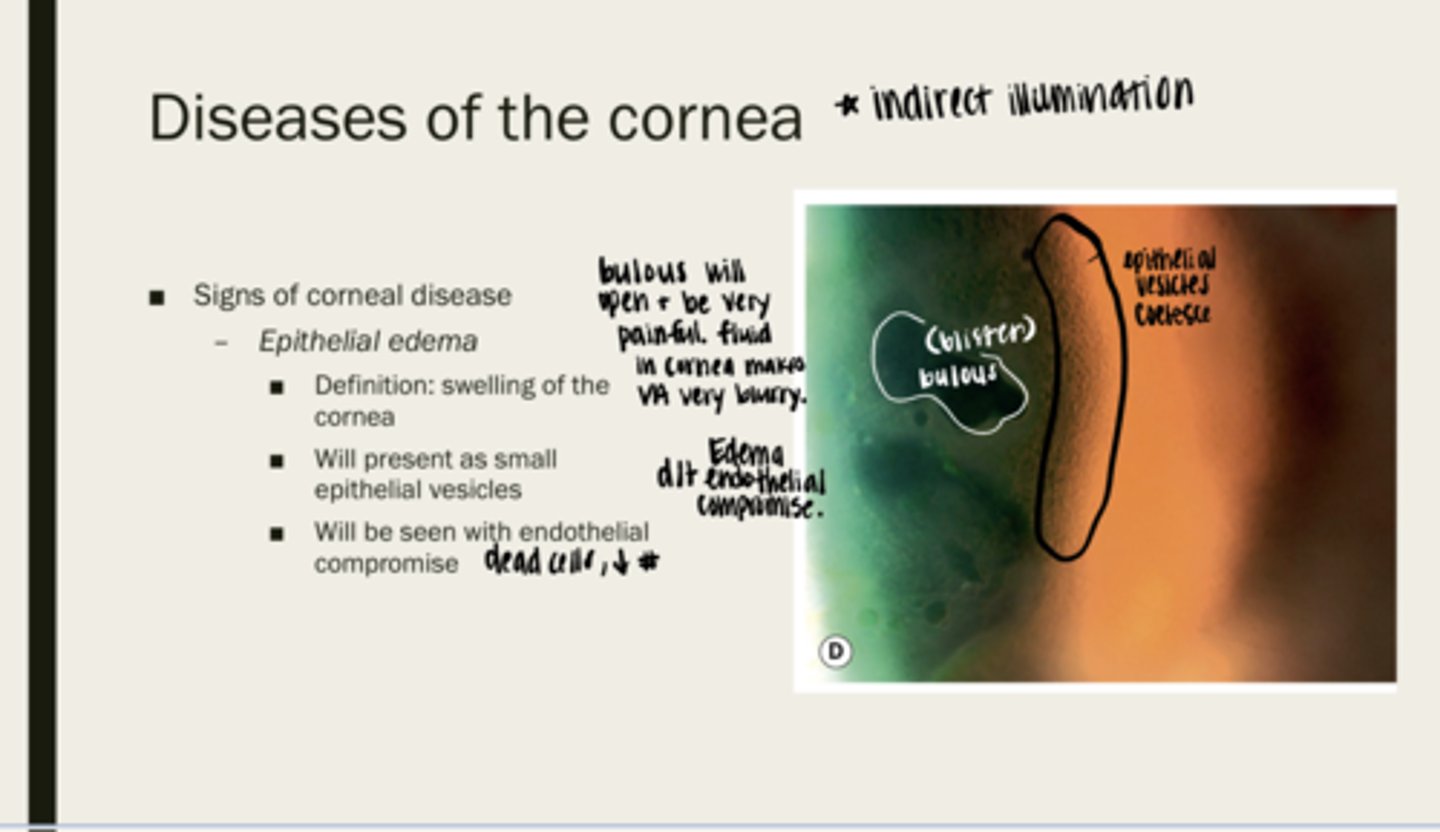
epithelial edema
swelling of the cornea
epithelial vesicles (bullous blistering)
What will epithelial edema present as?
endothelial compromise (dead cells or decreased number)
What will epithelial edema be seen with?
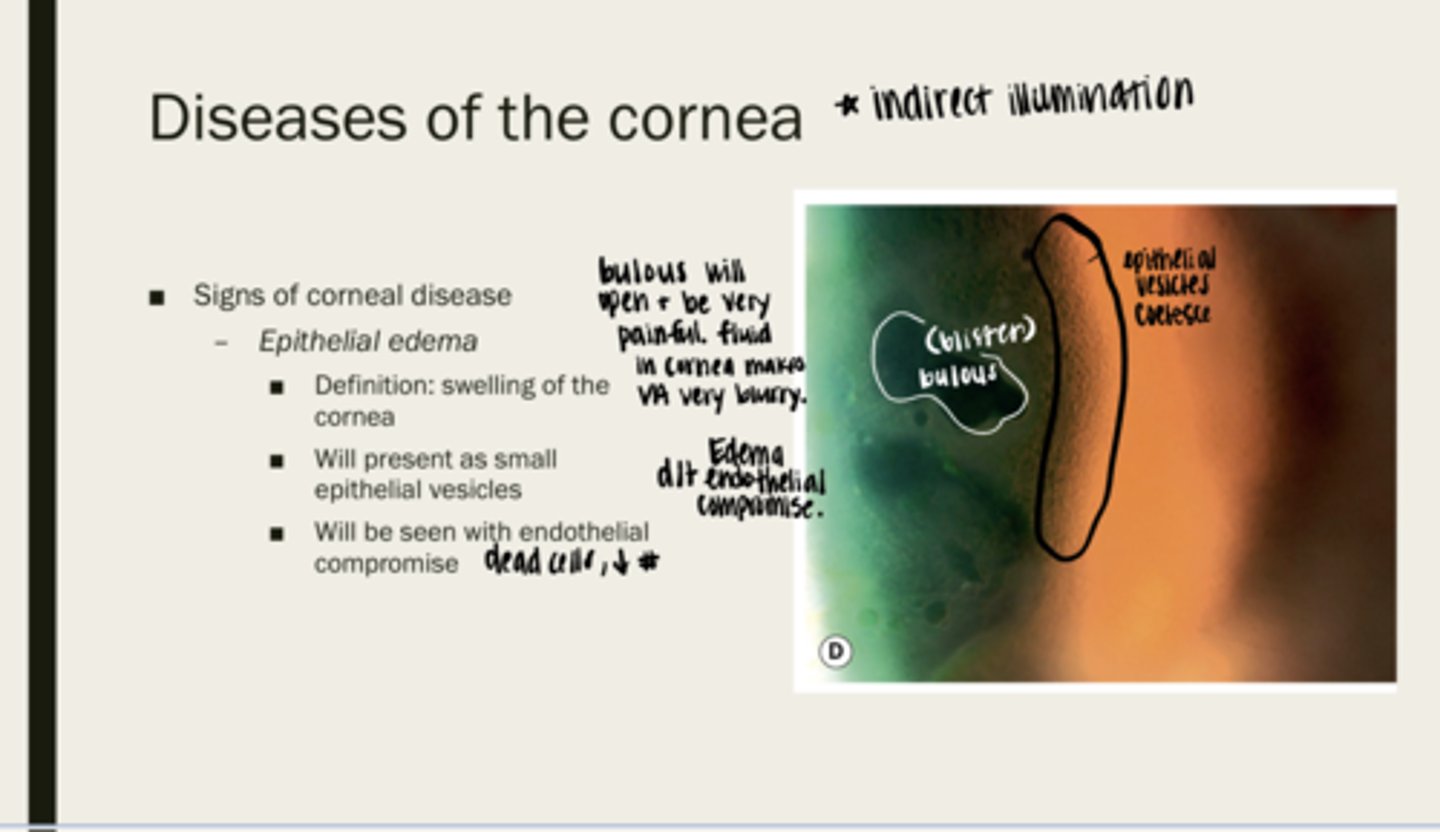
yes -- cornea is very innervated
Are the bullous (blisters) that are caused by epithelial edema painful?
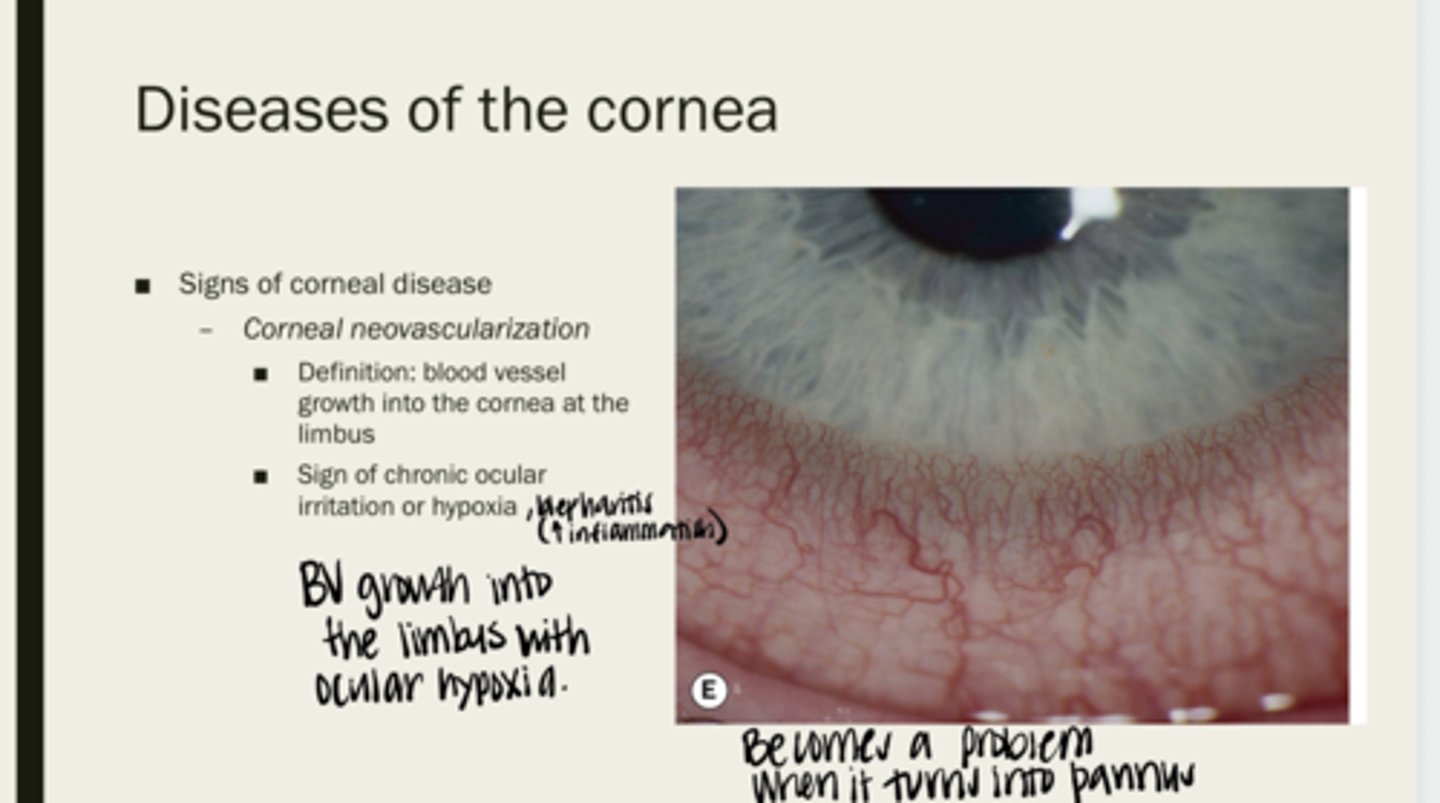
corneal neovascularization
blood vessel growth into the cornea at the limbus
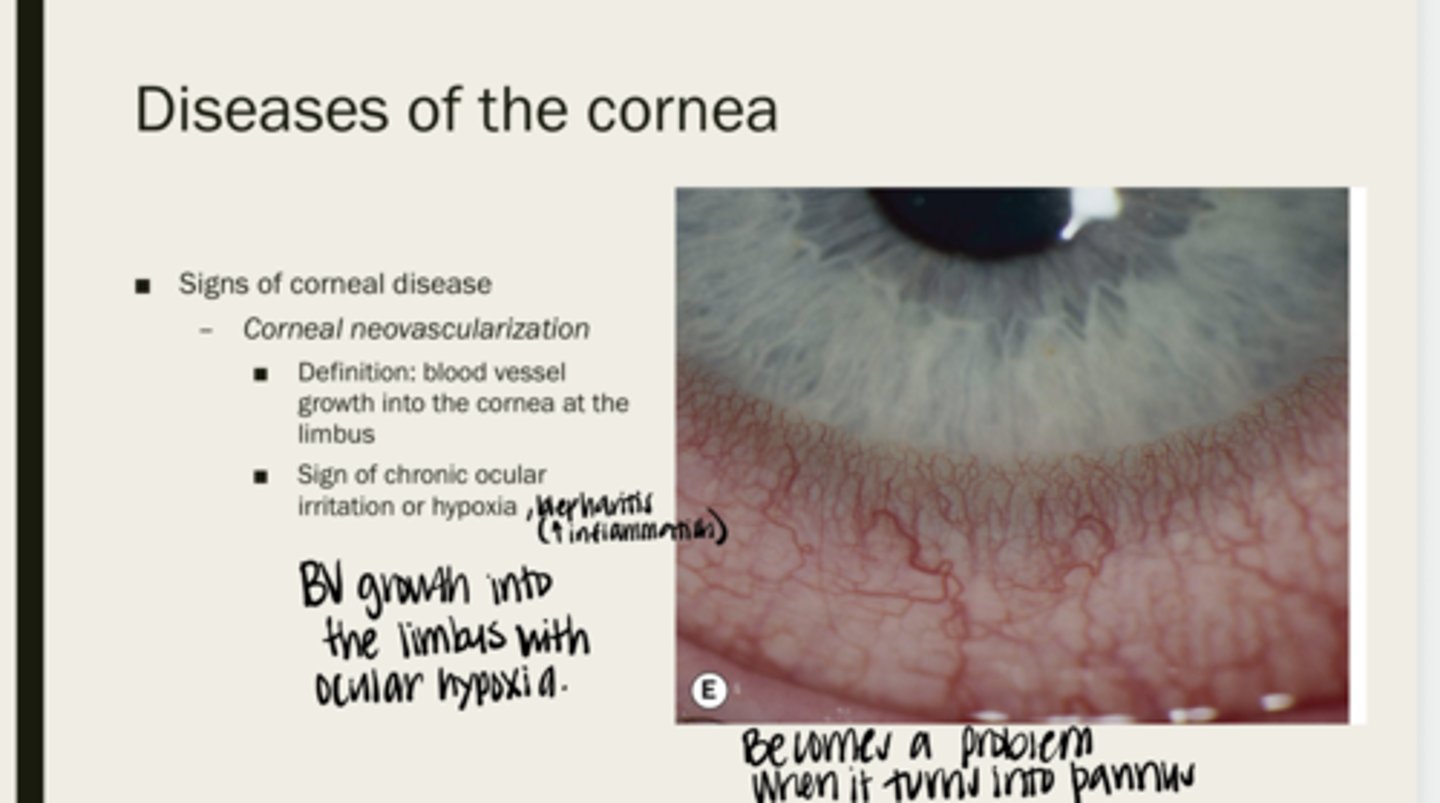
corneal irritation or hypoxia
What is corneal neovascularization a sign of?
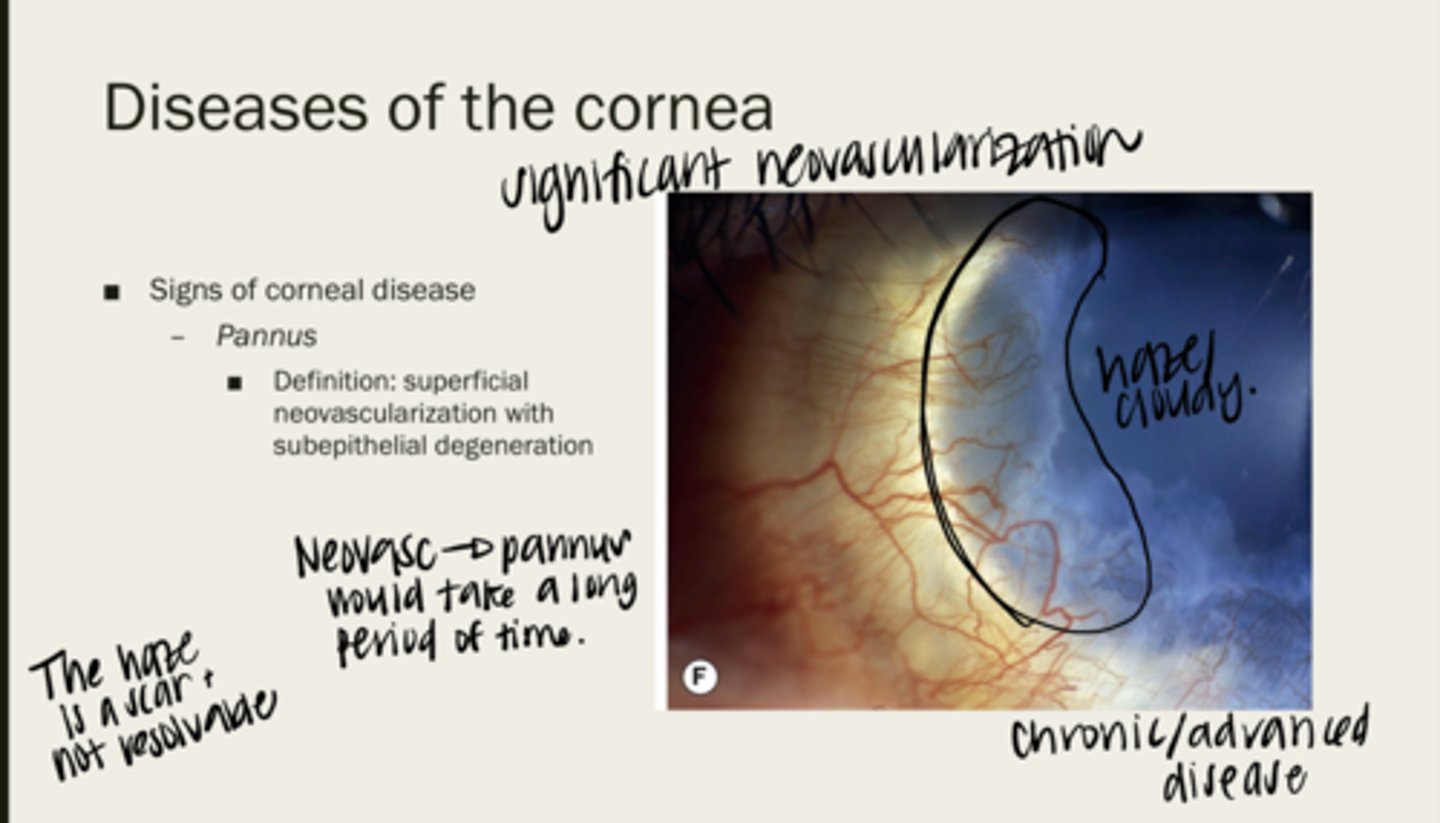
pannus
superficial neovascularization with subepithelial degeneration
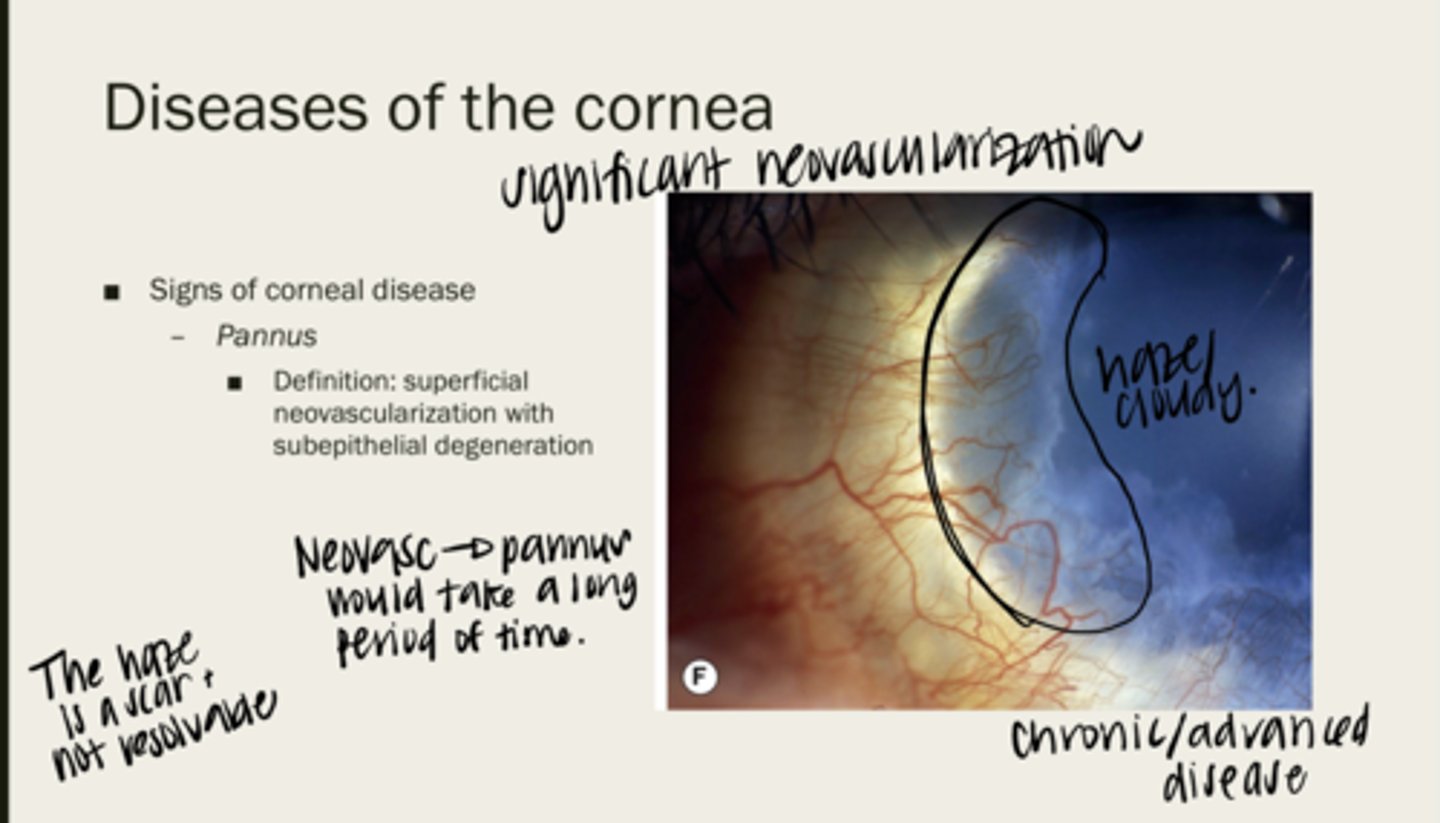
no -- it is a scar
Is pannus resolvable?
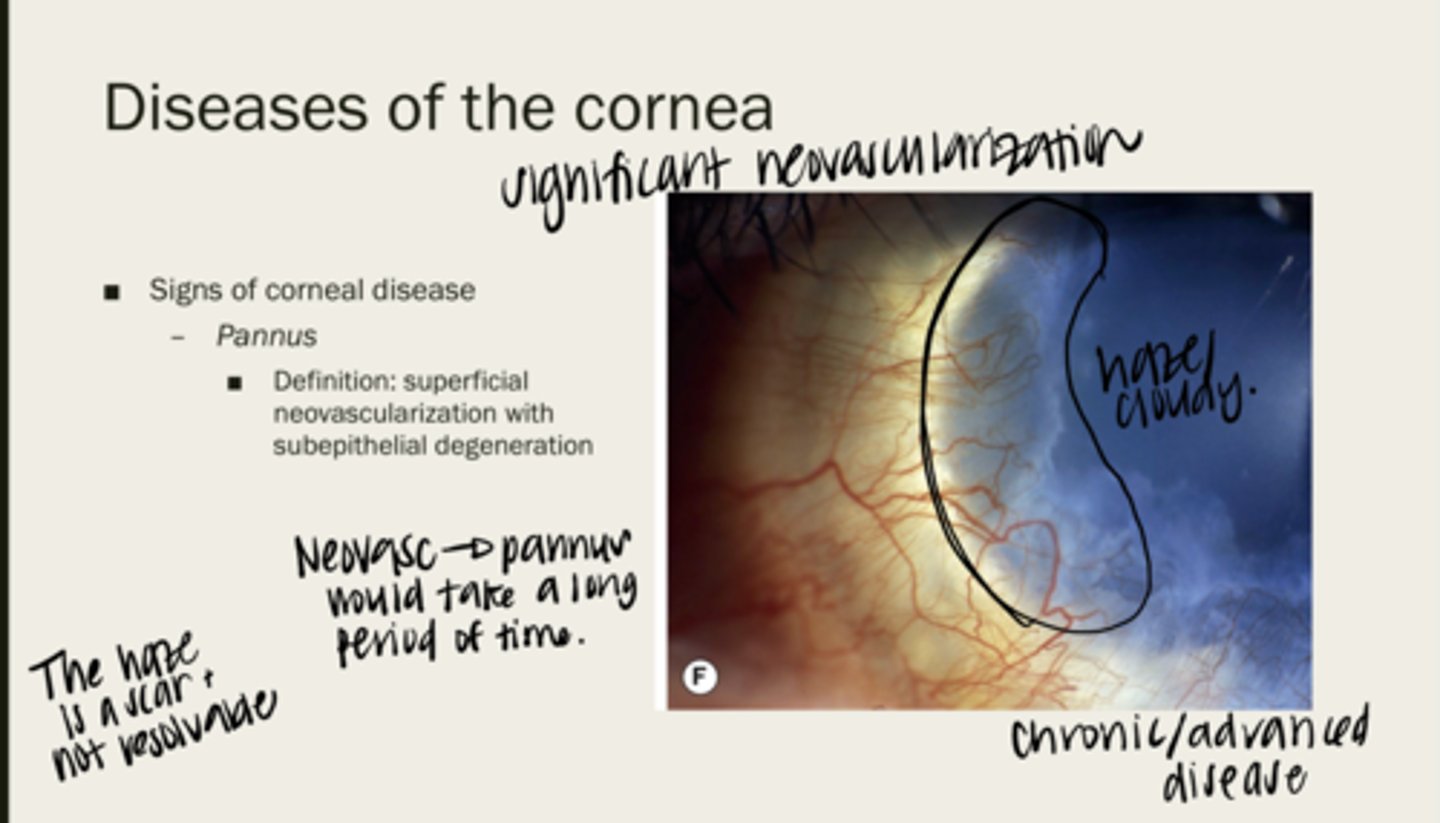
no -- takes a long time for pannus to present
Will pannus be acute onset?
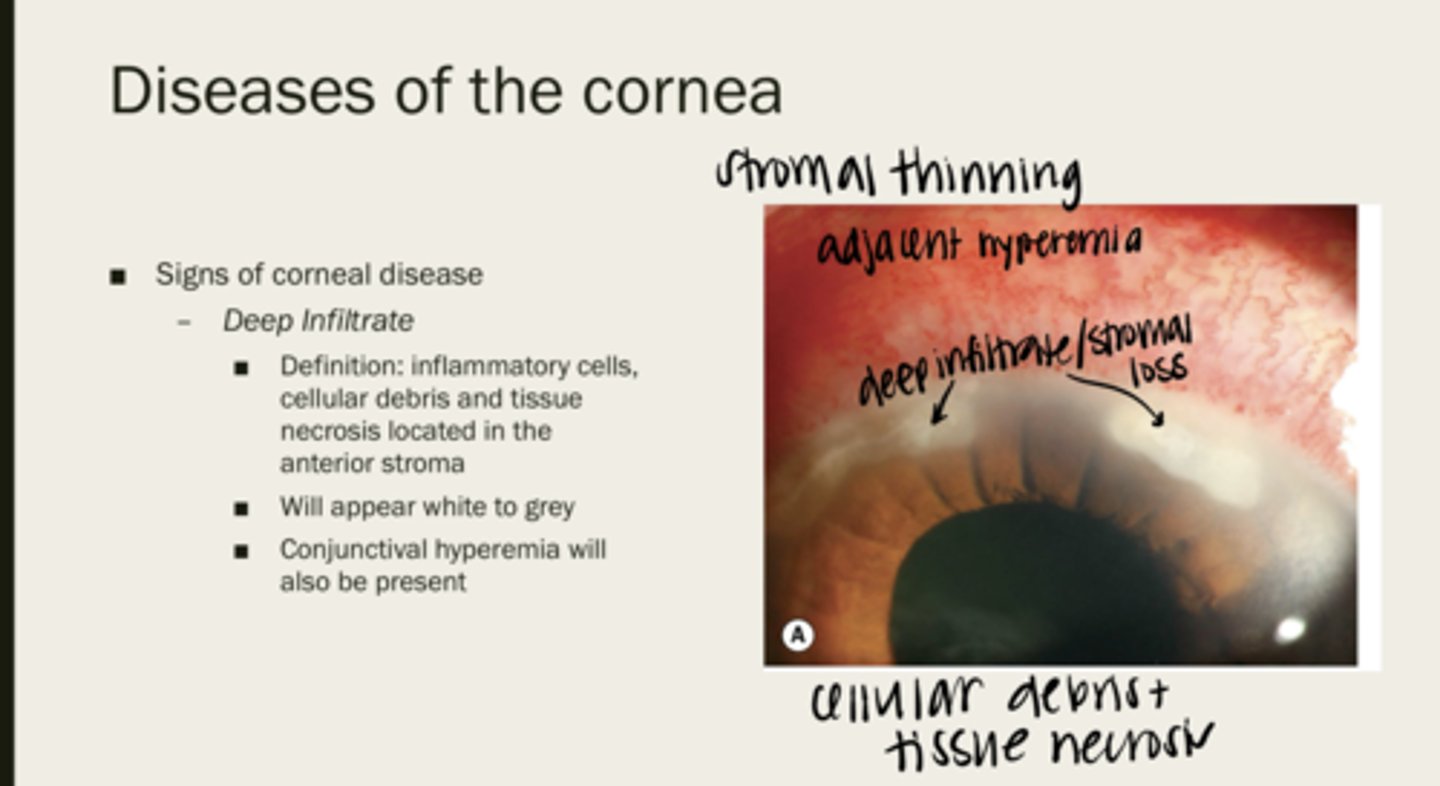
deep infiltrate
inflammatory cells, cellular debris, and tissue necrosis located in the anterior stroma
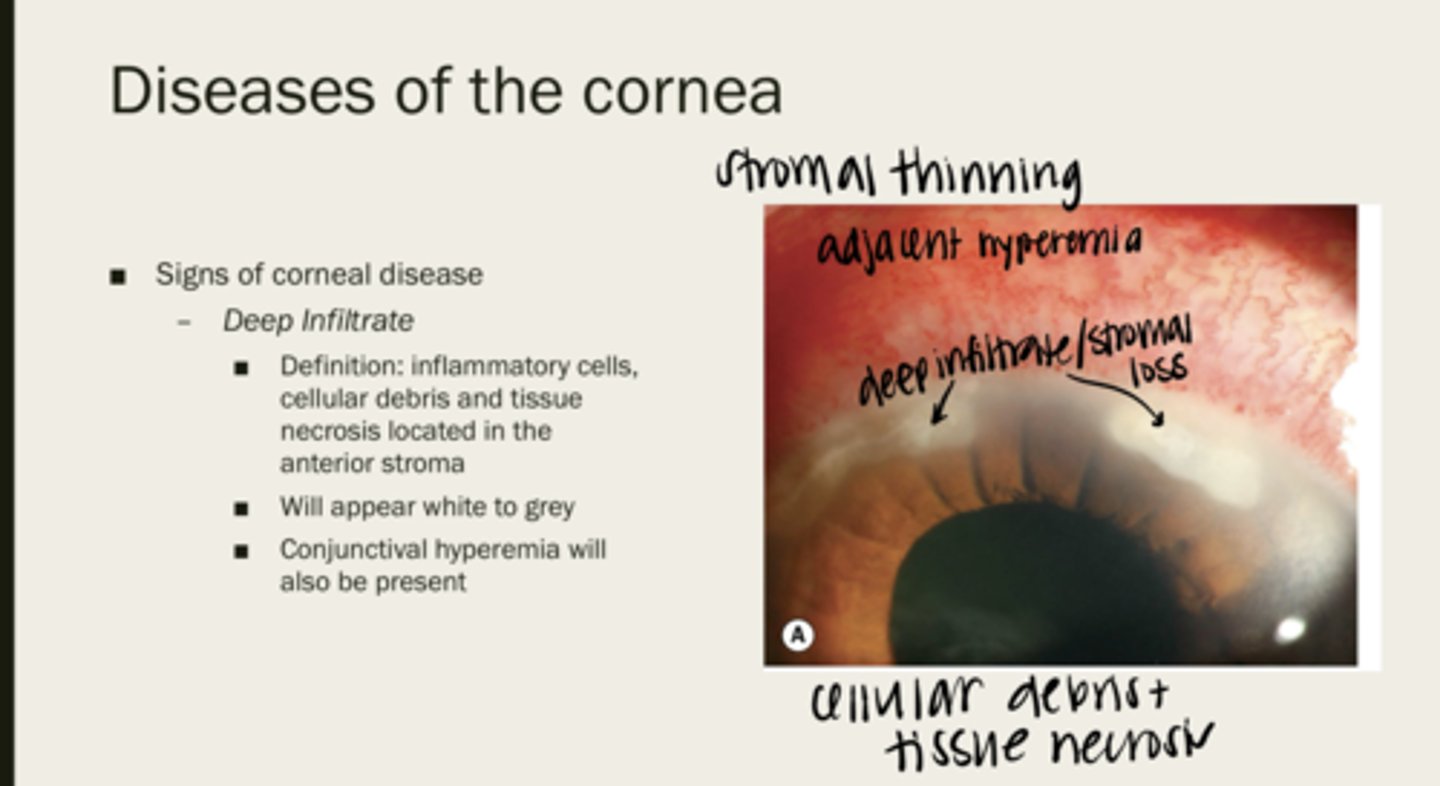
white/grey
How will deep infiltrates of the corneal stroma appear?
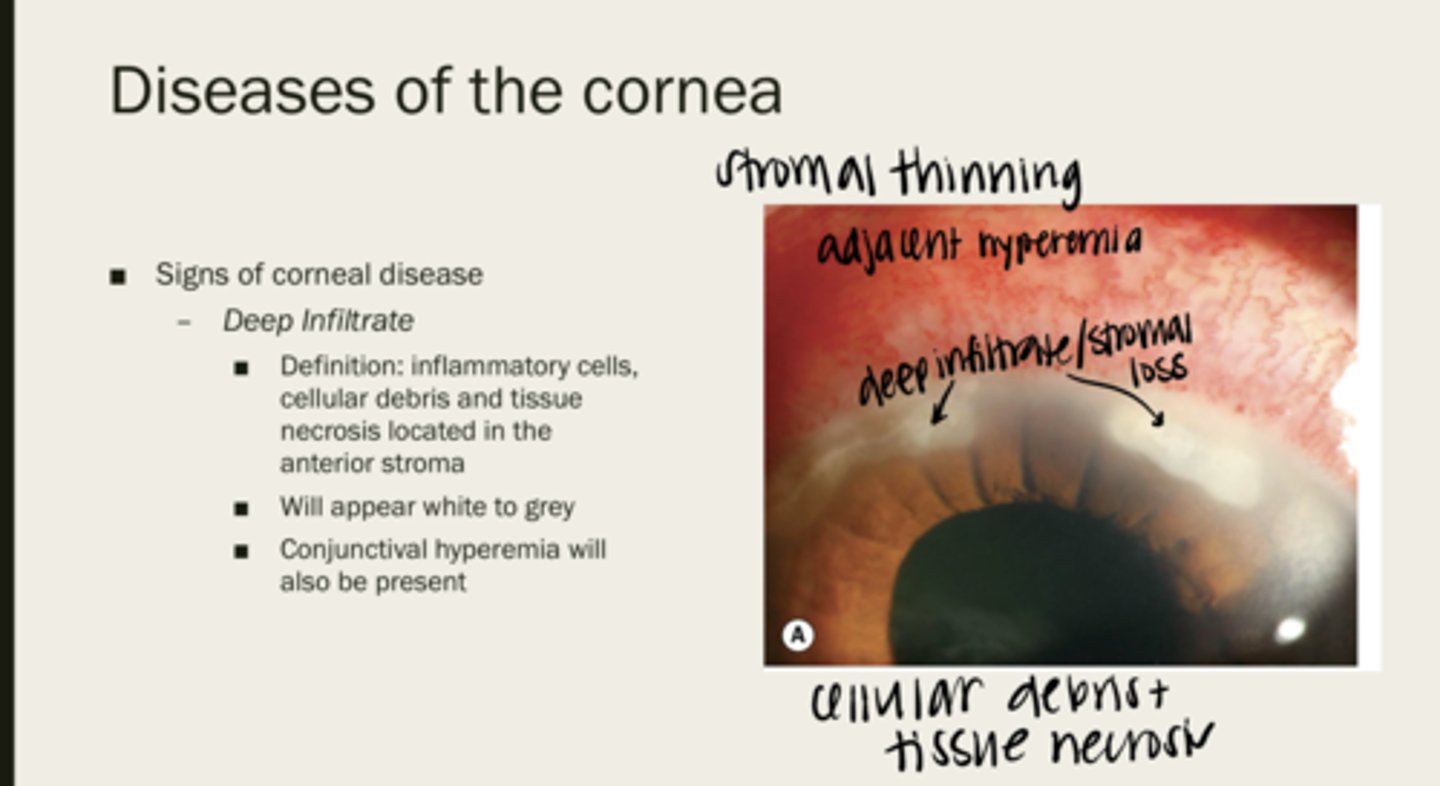
conj hyperemia
What will also be present with deep infiltrates?
ulceration
excavation of corneal tissue with epithelial defect

deep infiltrate
Ulceration is seen with what?

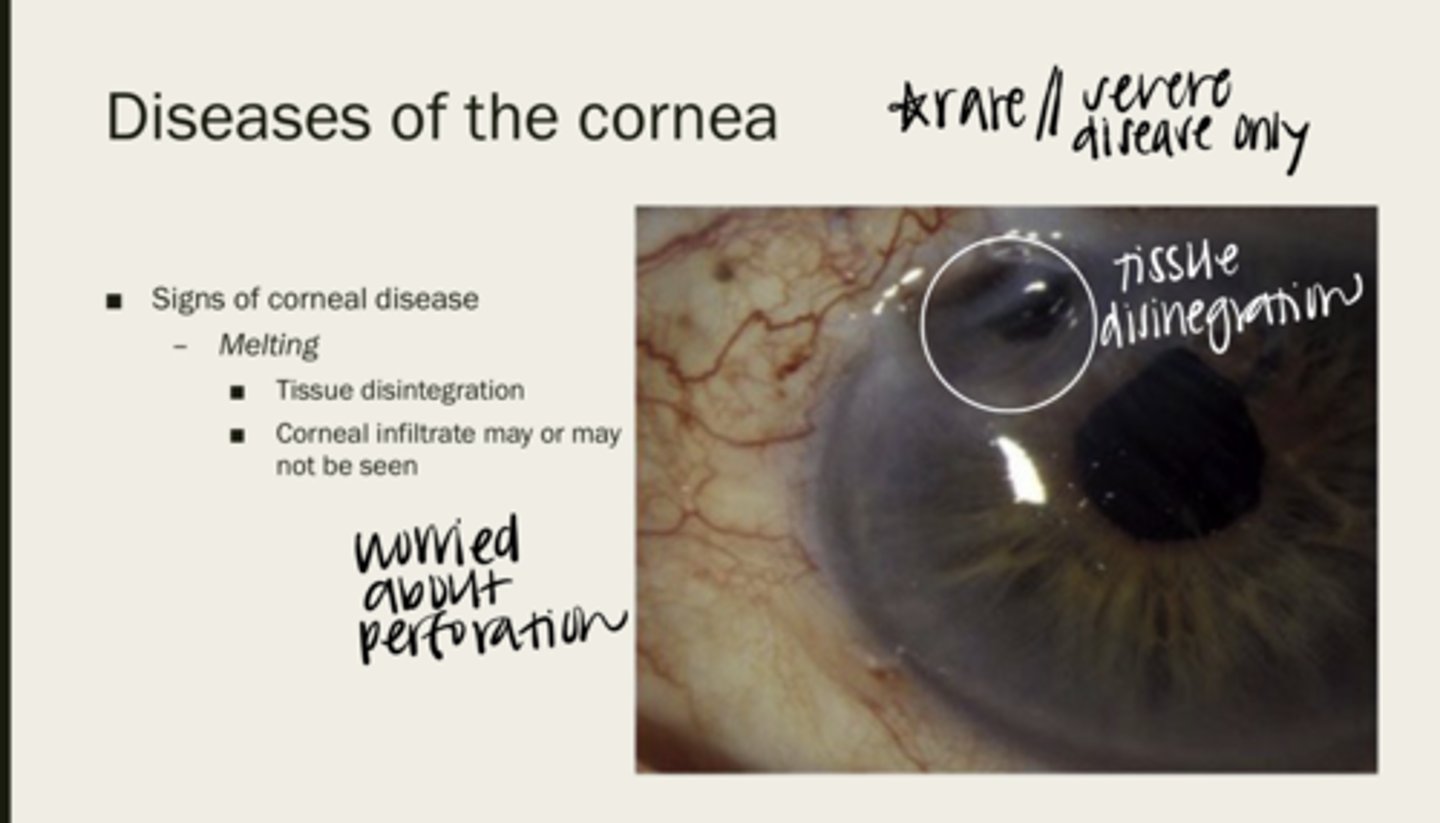
melting
corneal tissue disintegration
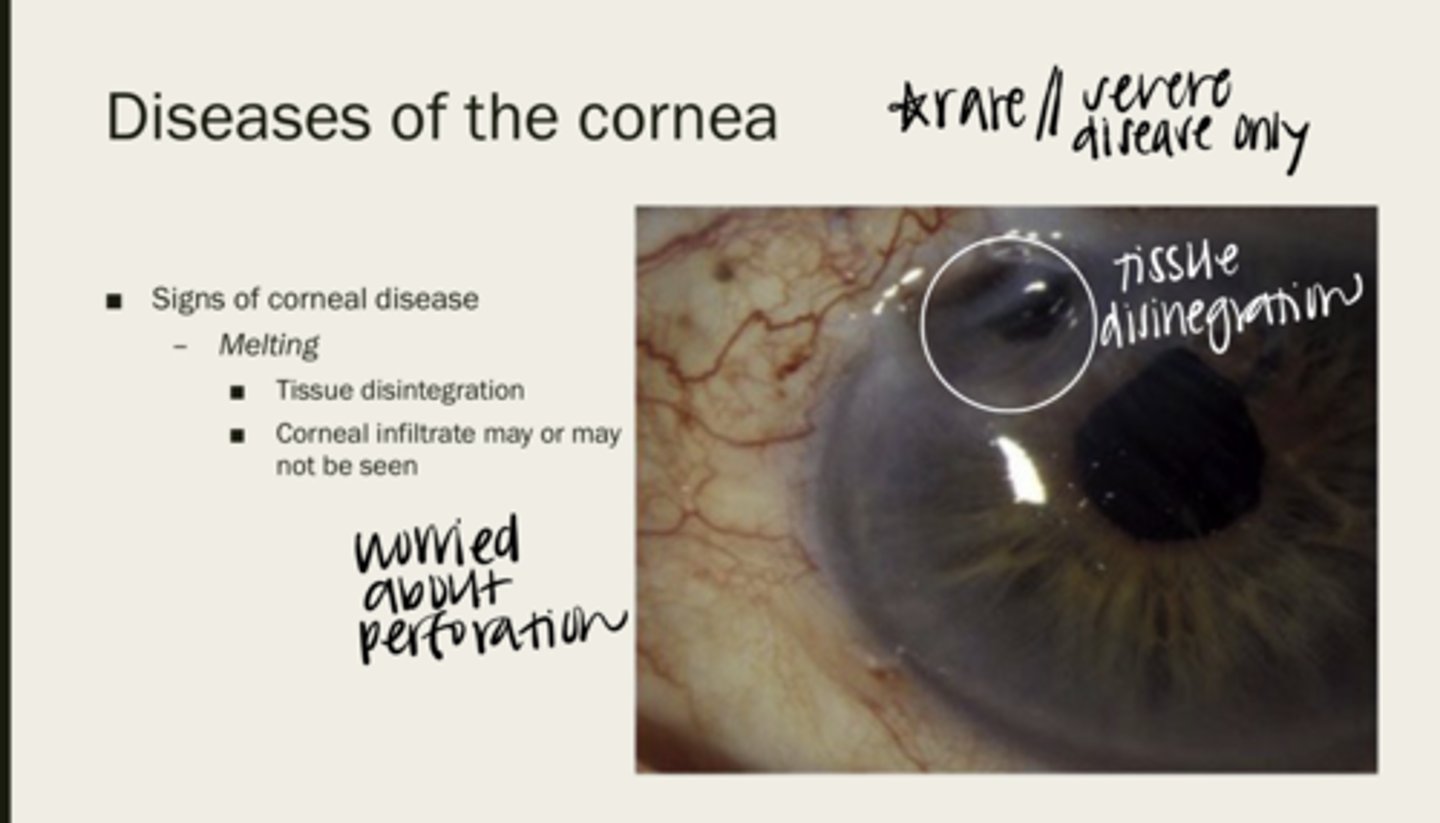
maybe or maybe not
Will a corneal infiltrate be seen with corneal melting?
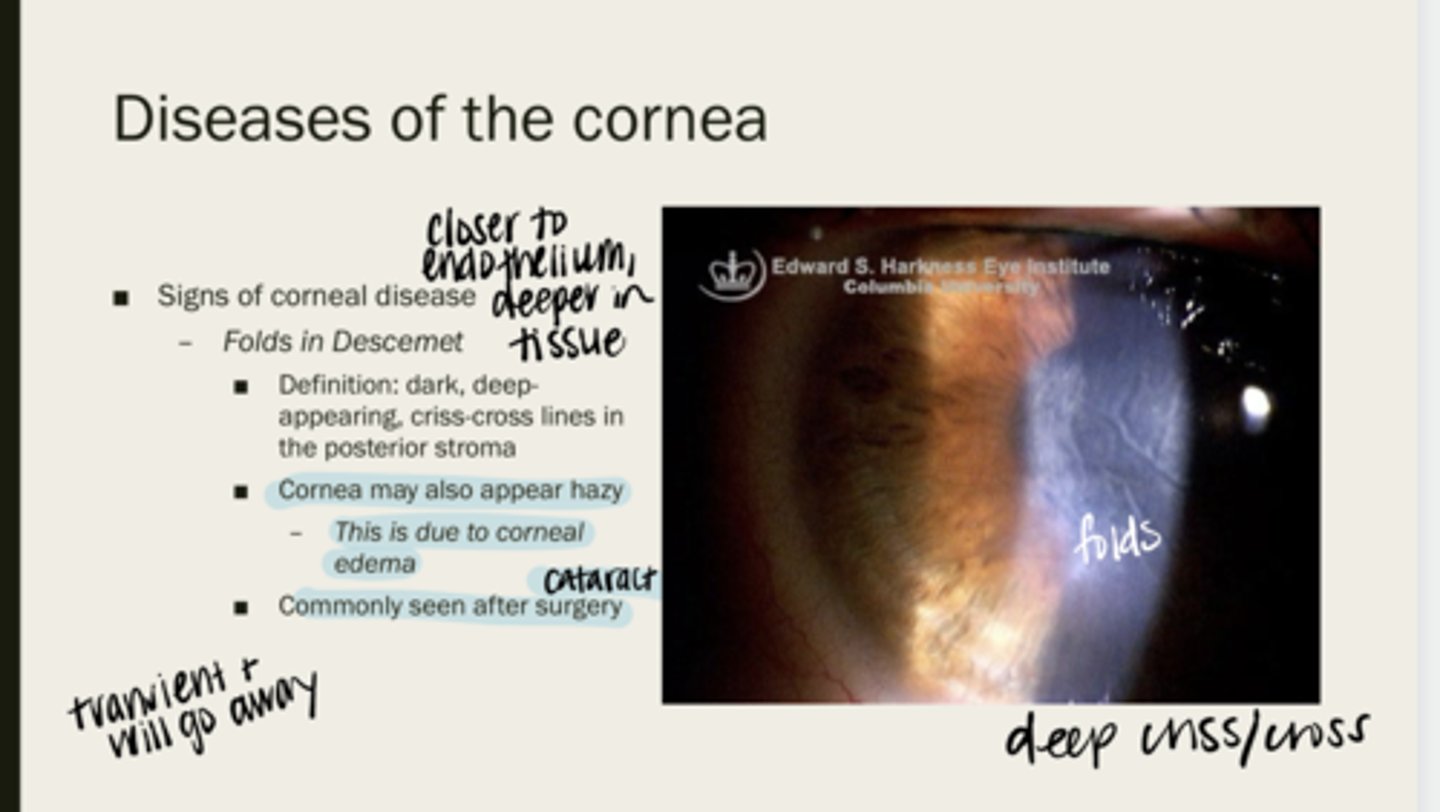
Folds of Descemet
dark, deep-appearing, criss-cross lines in the posterior stroma
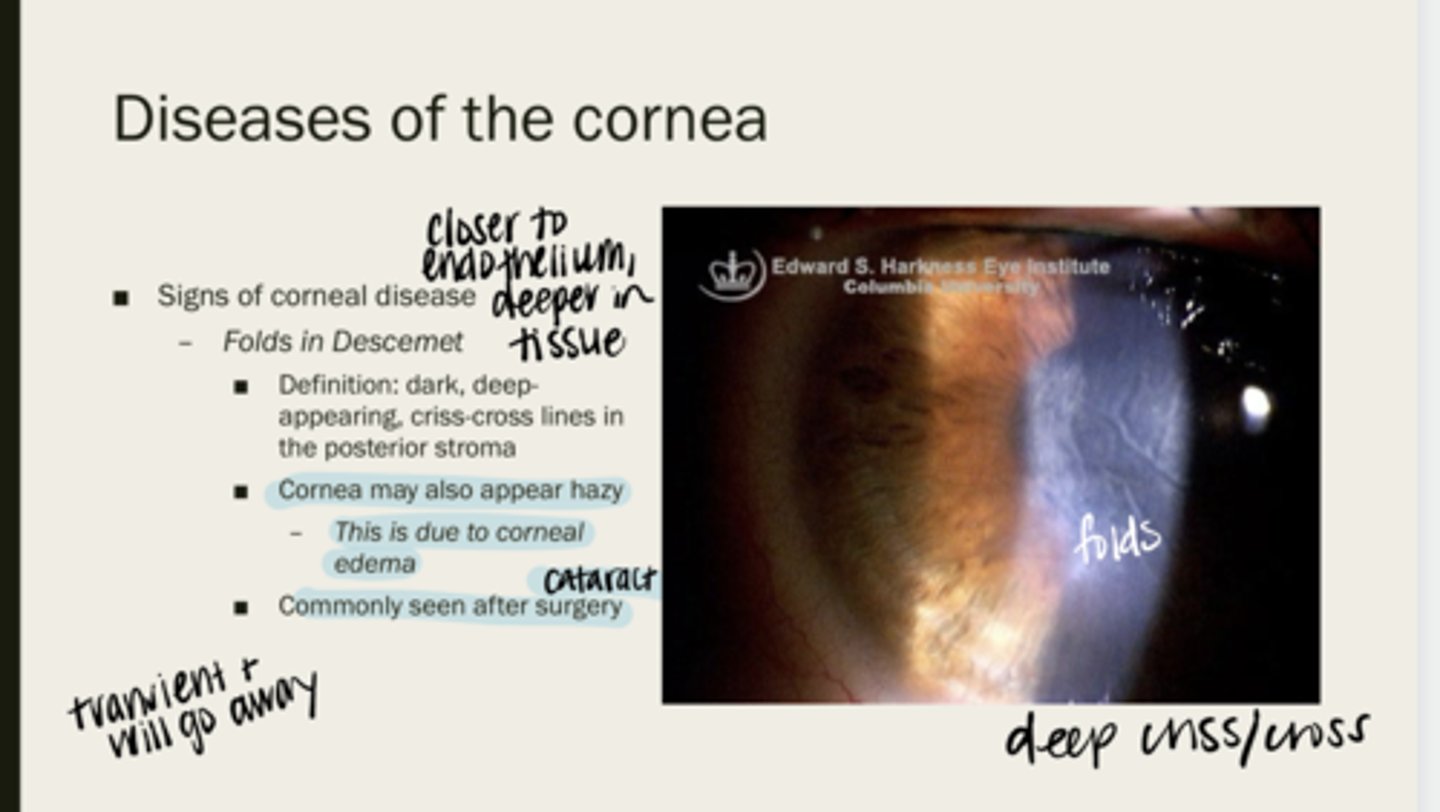
cornea may appear hazy due to corneal edema
When folds of Descemet are present, will the cornea be completely clear? Why?
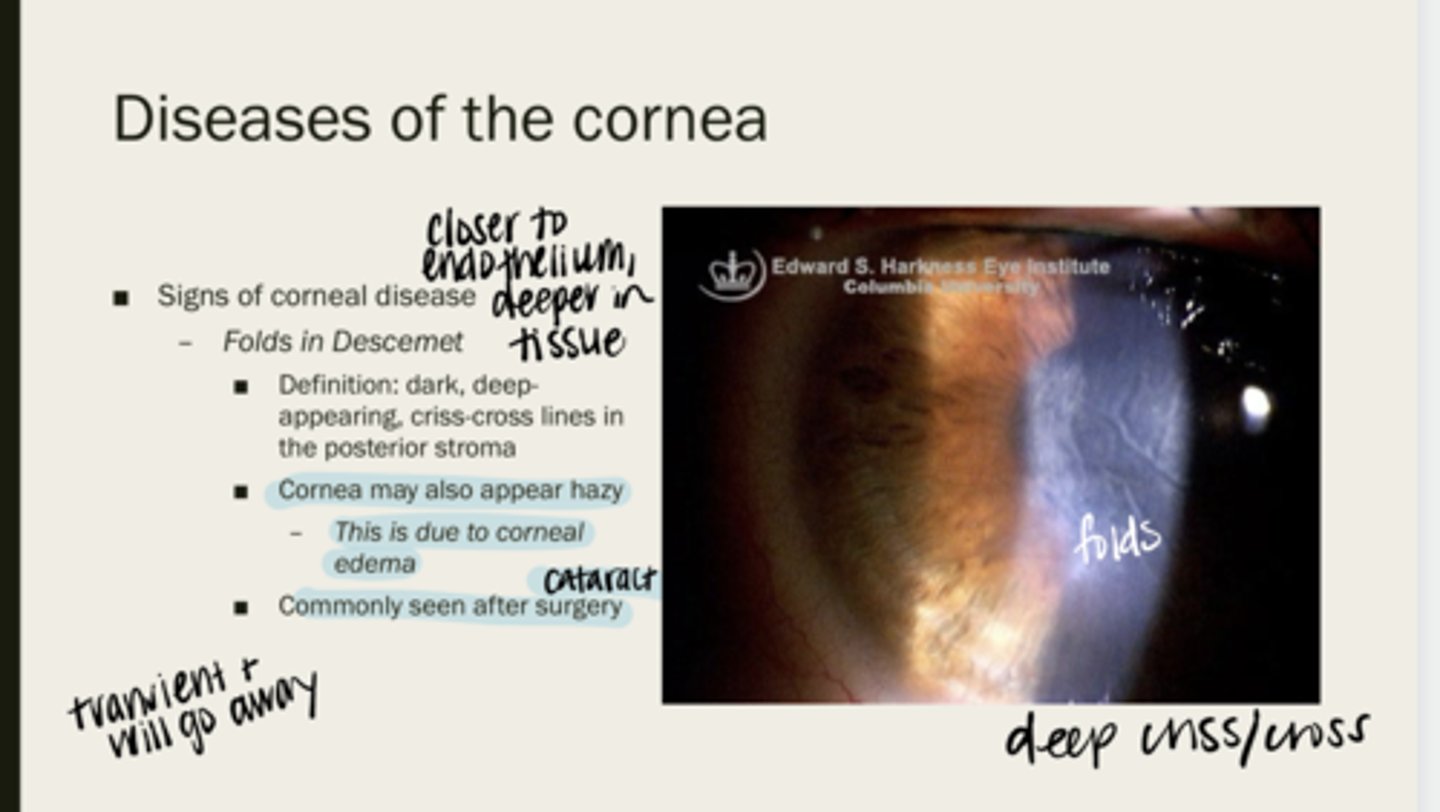
after cataract sx
When are folds in Descemet membrane typically seen?
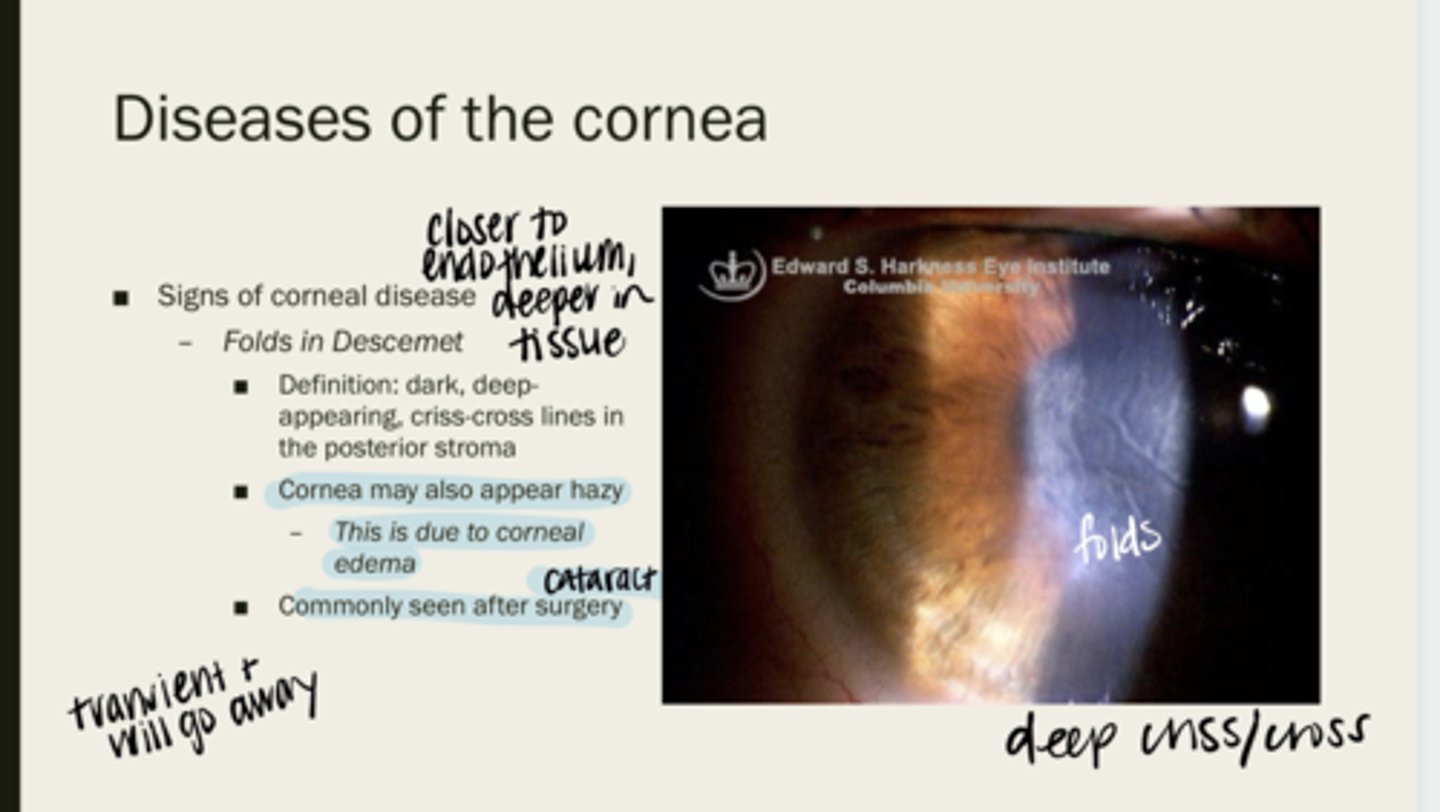
yes -- they are transient and go away with time
Will Descemet folds go away over time?
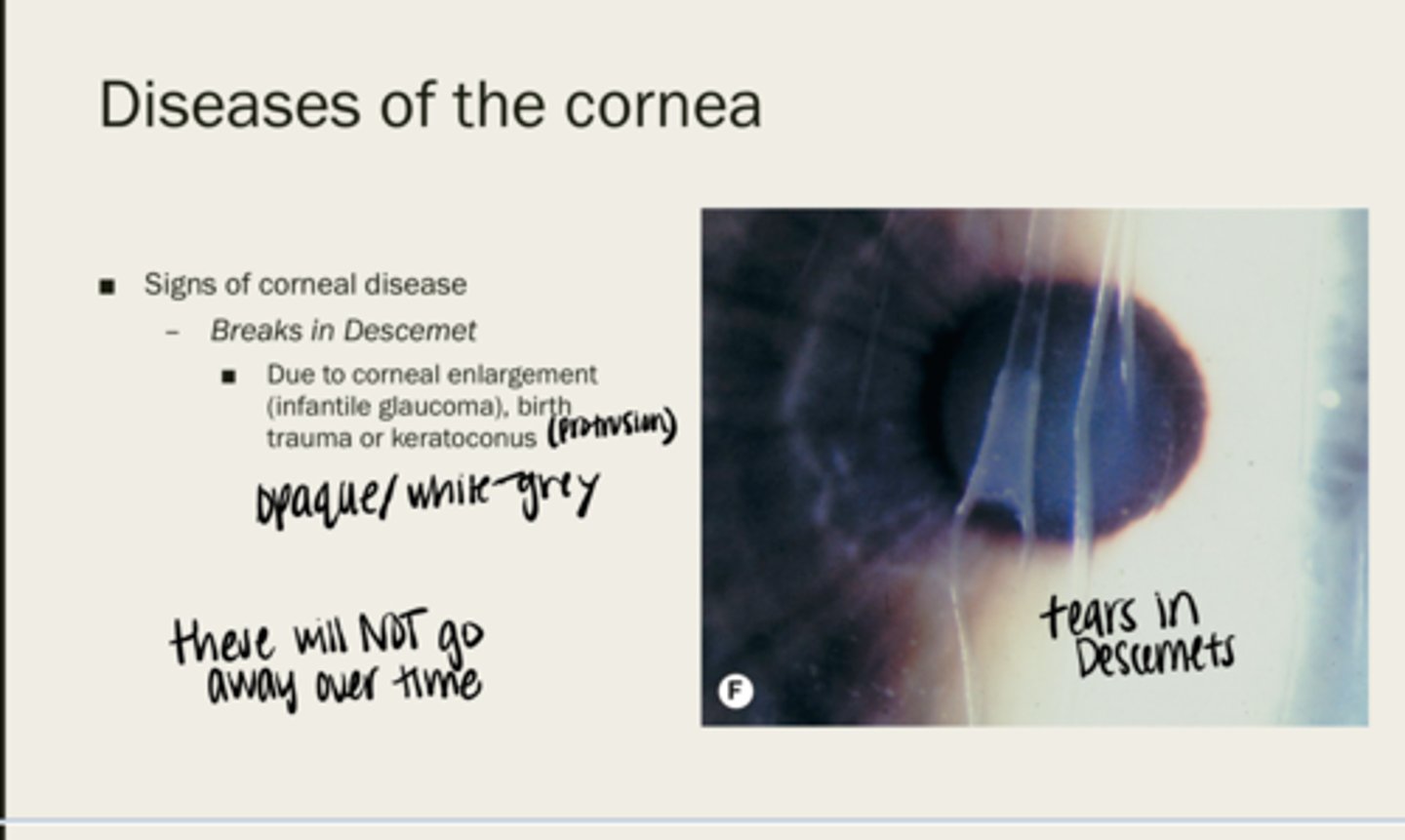
Breaks in Descemet membrane
due to corneal enlargement (infantile glaucoma), birth trauma, or keratoconus
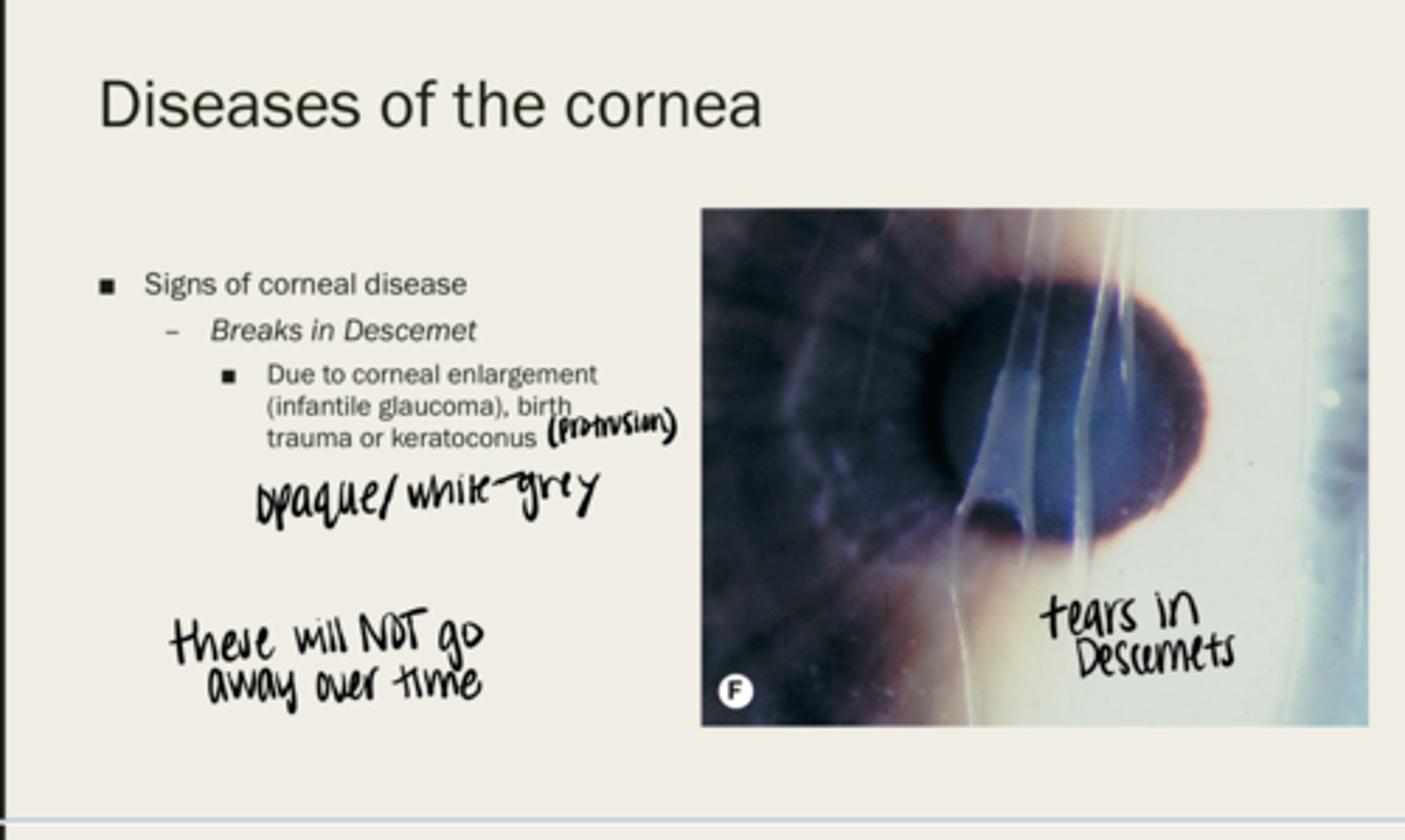
-opaque
-white/grey
What color will breaks in Descemet membrane be?
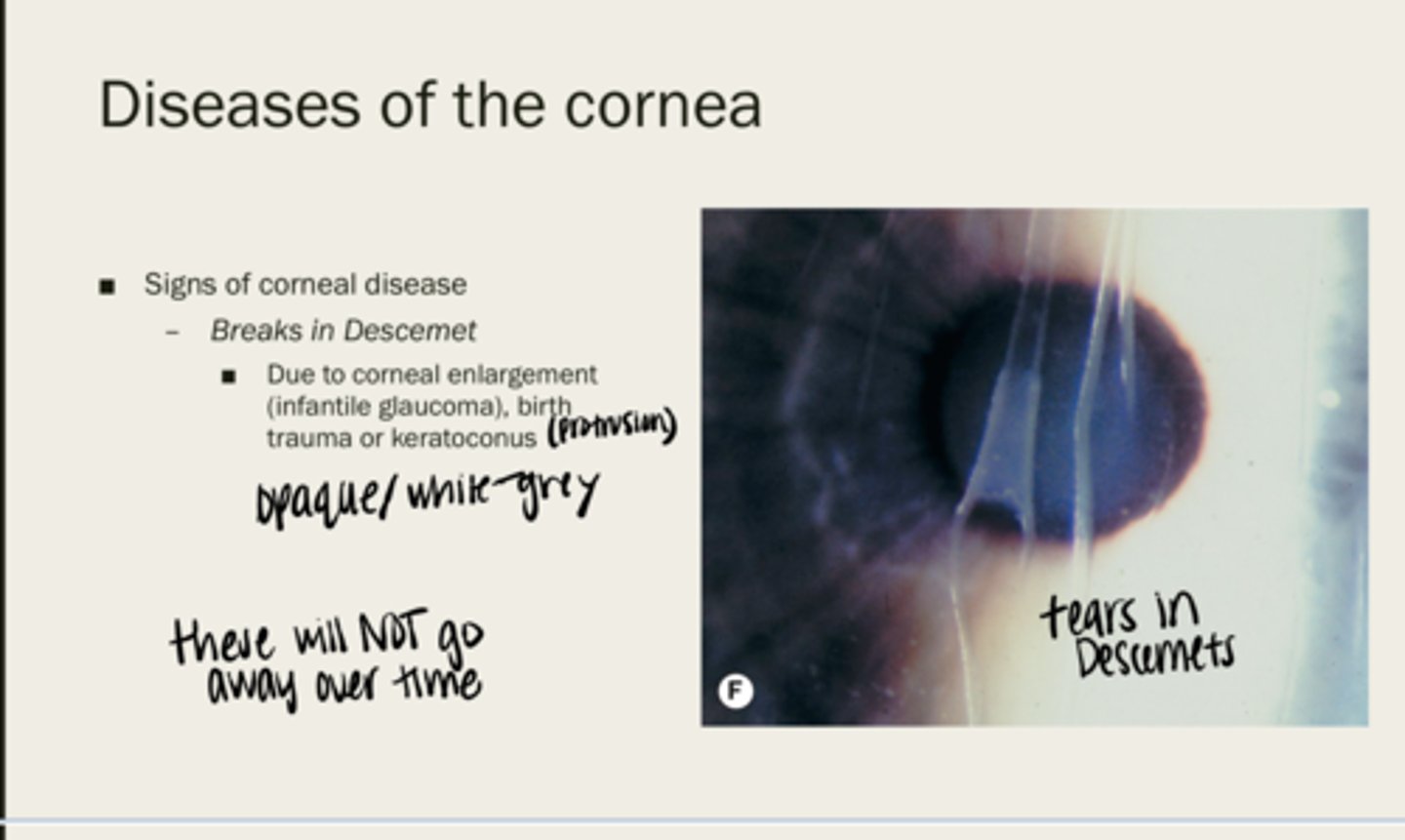
no -- these do not go away
Will breaks in Descemet membrane go away over time?
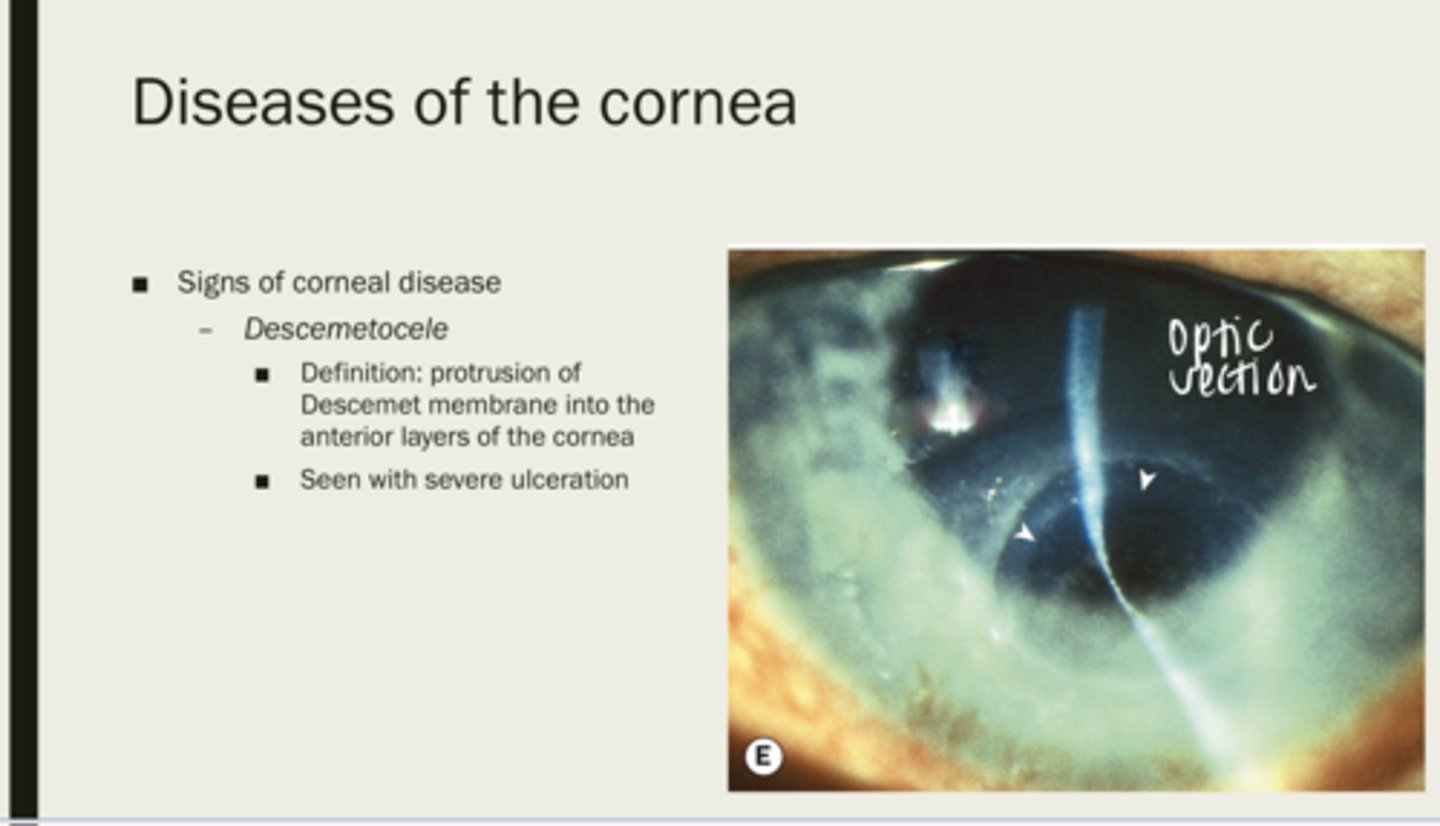
descemetrocele
protrusion of Descemet membrane into the anterior layers of the cornea
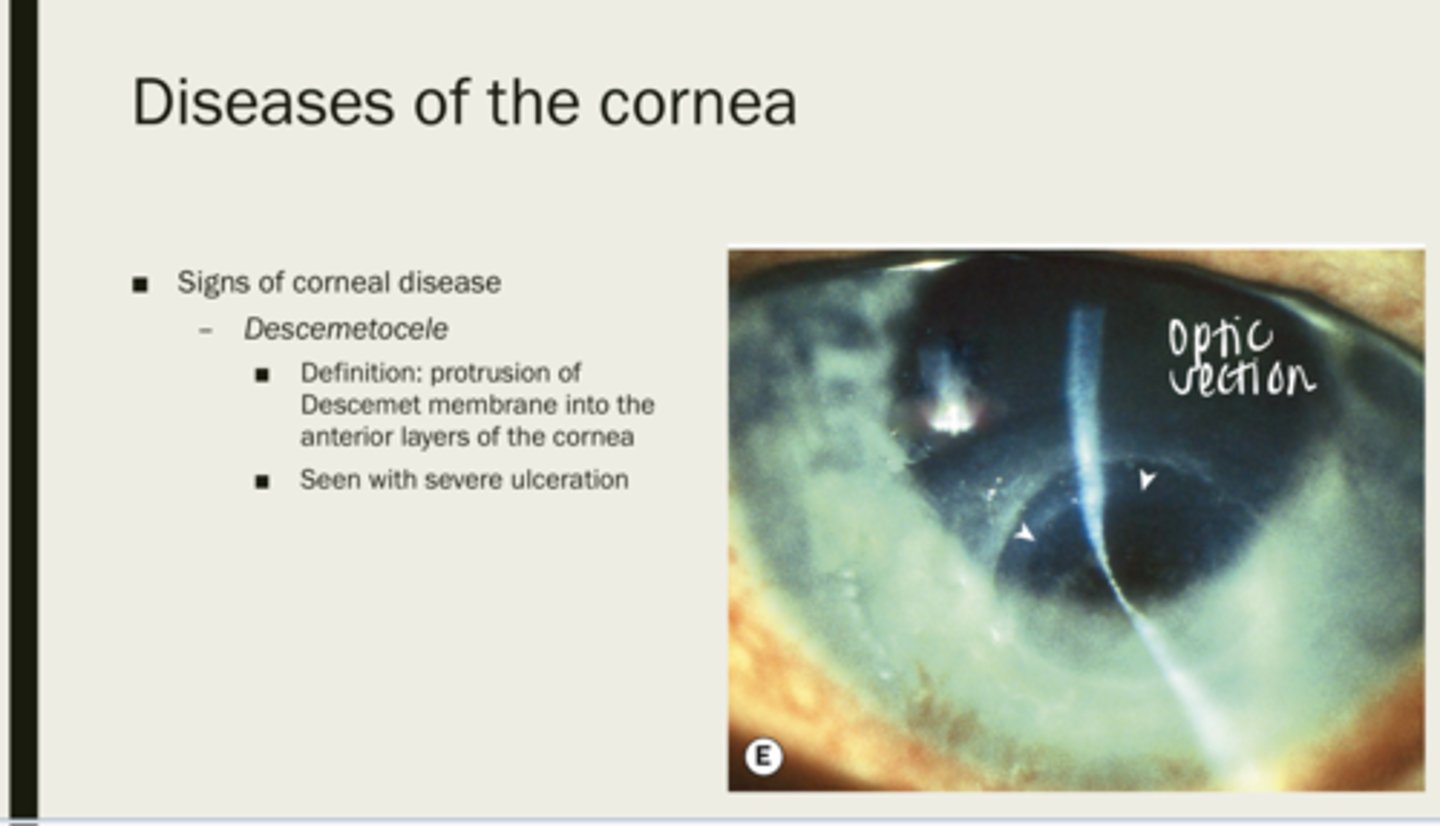
severe ulceration
What is descemetrocele seen with?
corneal dystrophy
group of slowly progressive usually bilateral corneal opacification that may cause a decrease in vision and discomfort
only one
A corneal dystrophy will typically affect _____ layer of the cornea
center, periphery
A corneal dystrophy will start in the _____ of the cornea and migrate to the _____ of the cornea
no -- this is a white eye condition
Are corneal dystrophies inflammatory?
yes, majority are autosomal dominiant
Are corneal dystrophies genetic?
younger patients
What population do corneal dystrophies occur in?
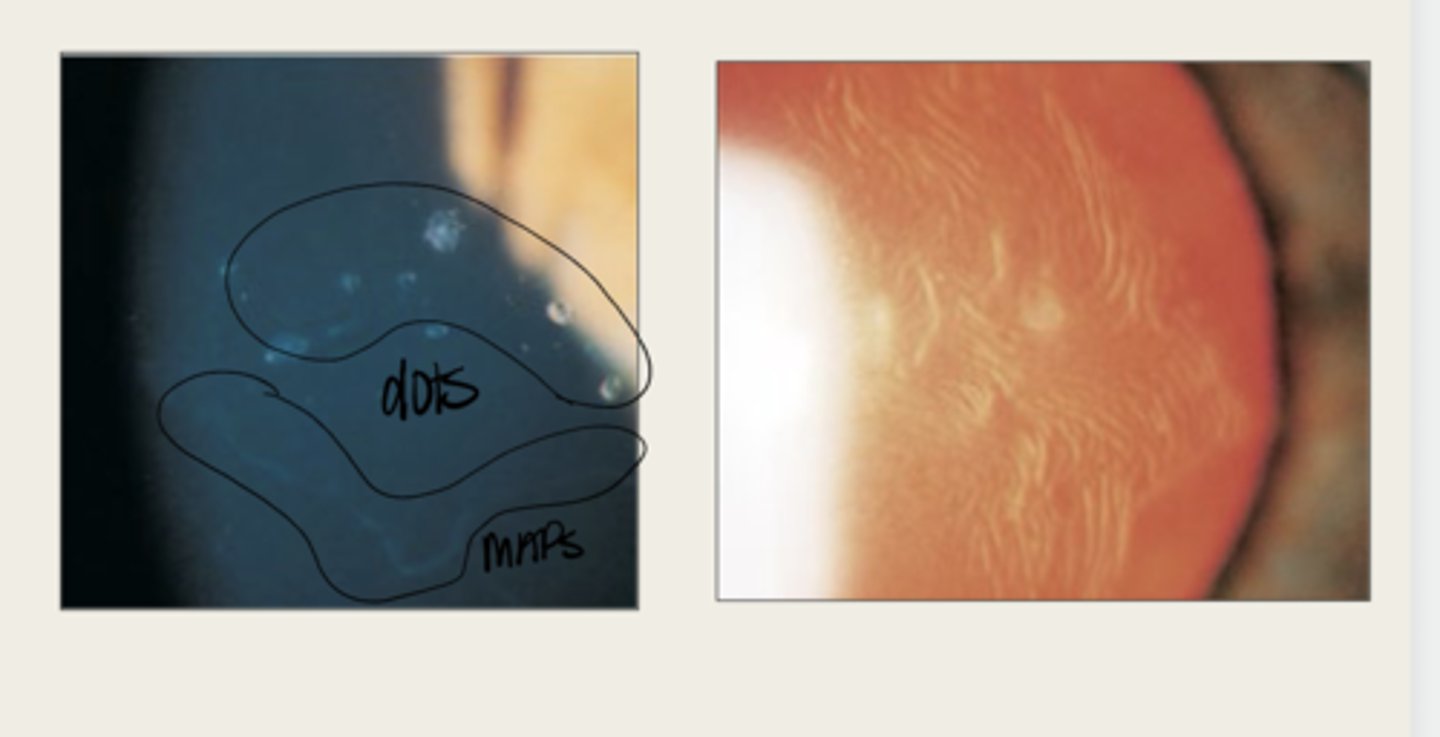
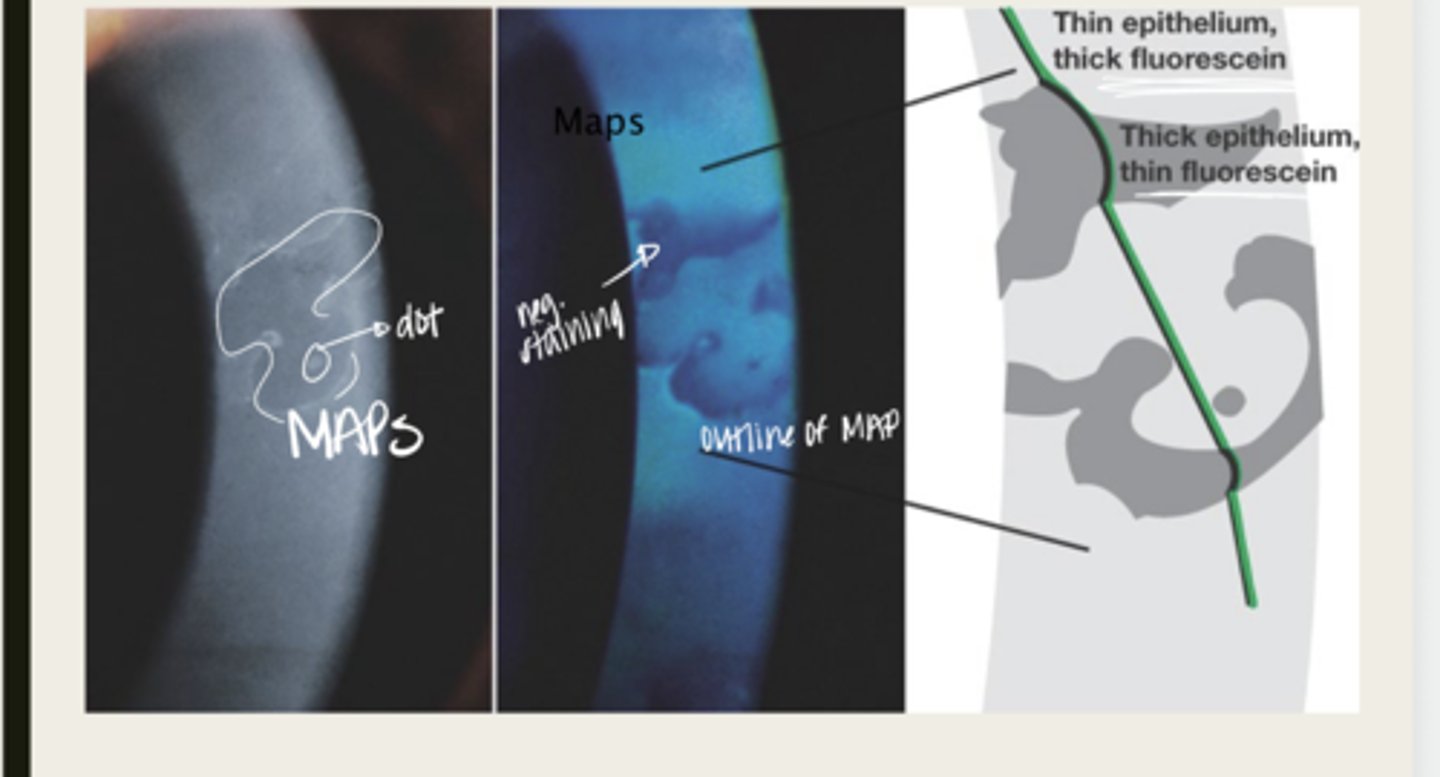
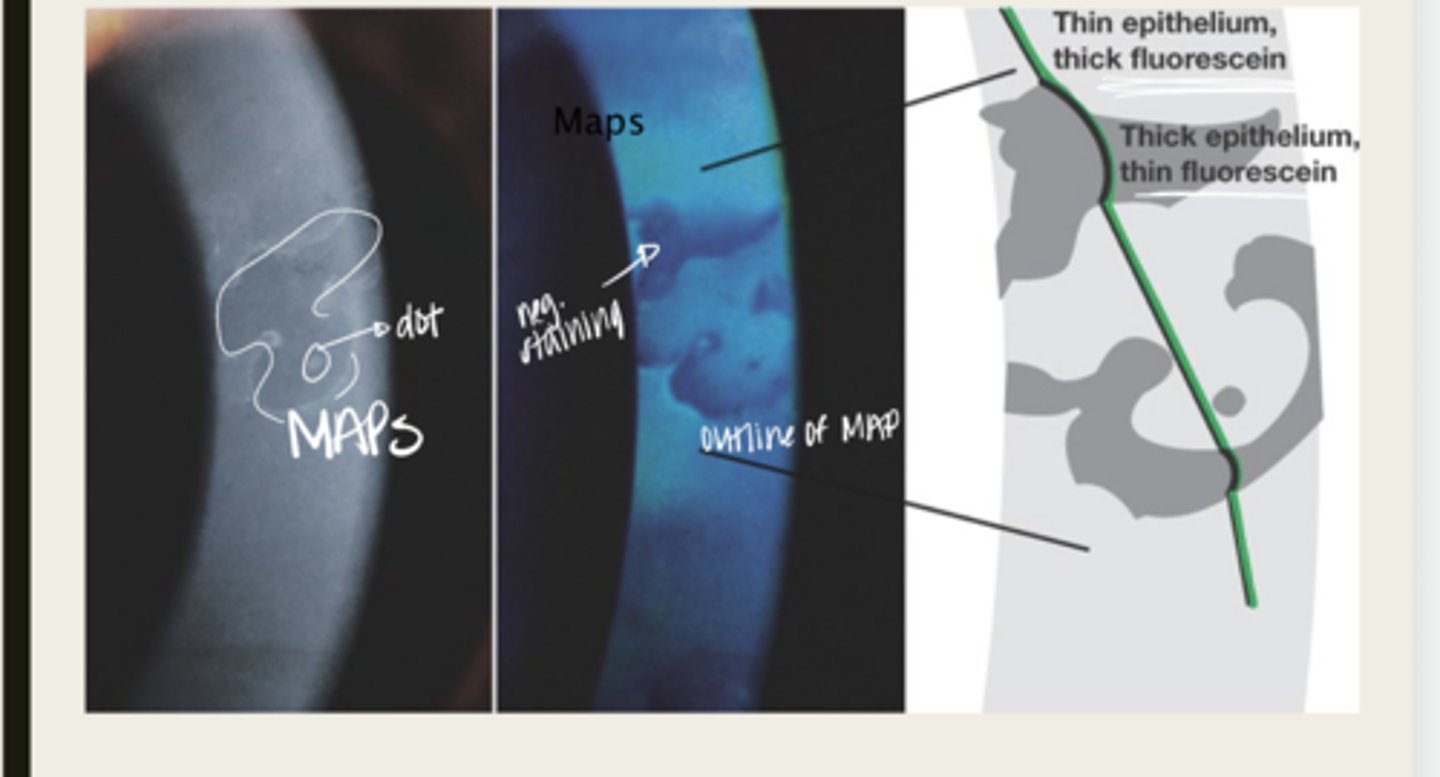
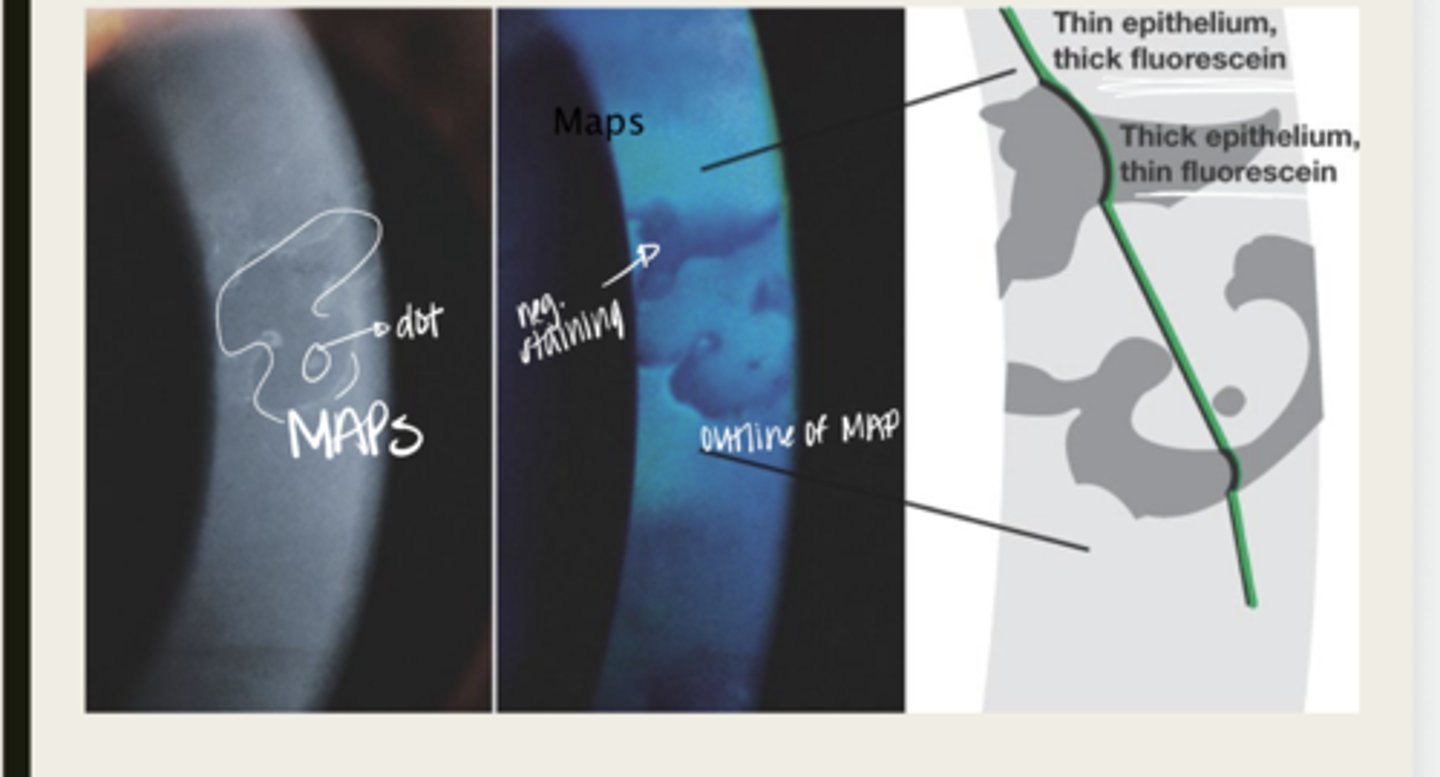
Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy (Cogan or Map Dot Fingerprint)
What is the most common corneal dystrophy?
40%, 70% of the population over 50+
What proportion of the population does Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy affect?
2nd decade of life
What is the onset of Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
females
Is Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy more common in males or females?
no clear pattern -- can be d/t trauma and some consider it more of a DEGENERATION
What is the inheritance pattern of Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
synthesis of an abnormal basement membrane
What is the pathophysiology of Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
faulty adhesions between the basement membrane and the epithelium of the cornea
What is the cause of Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
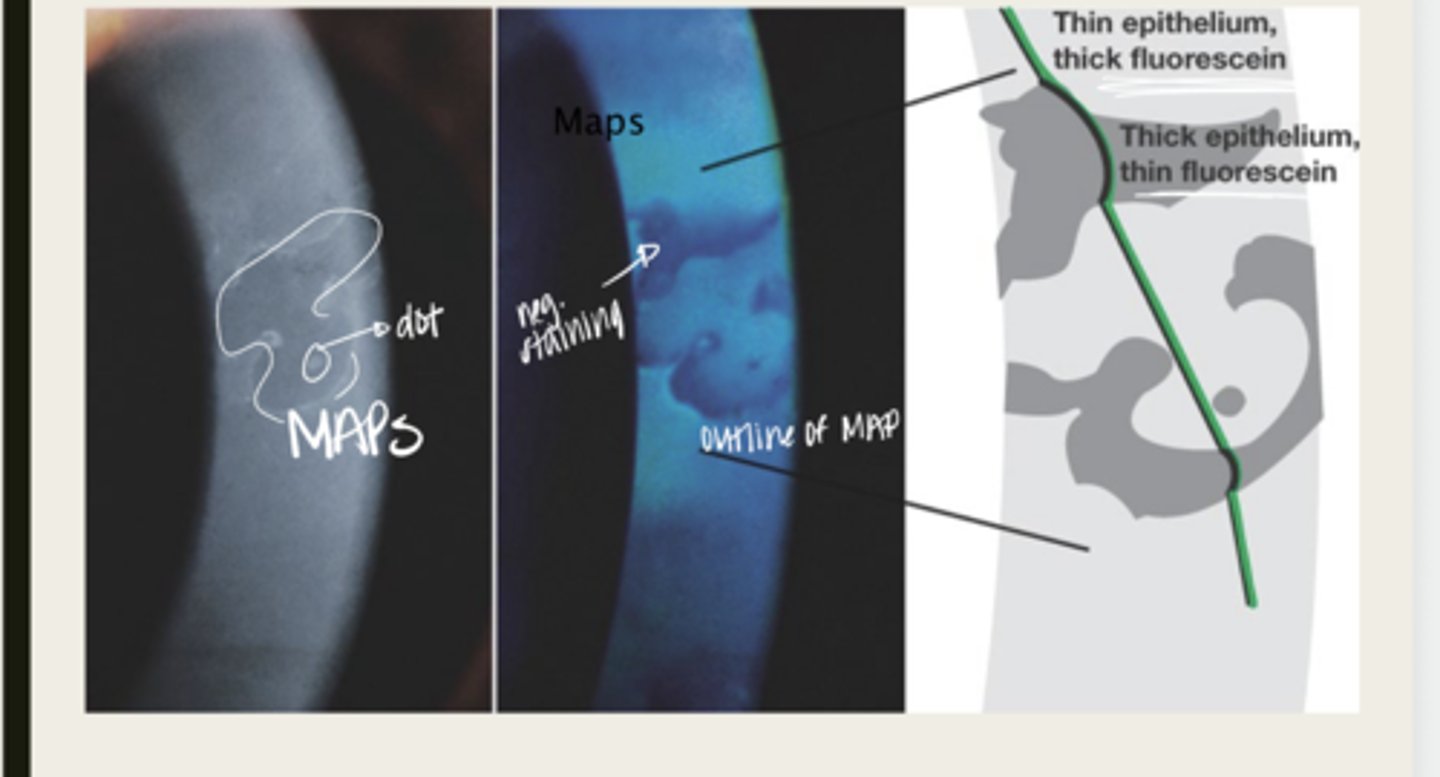
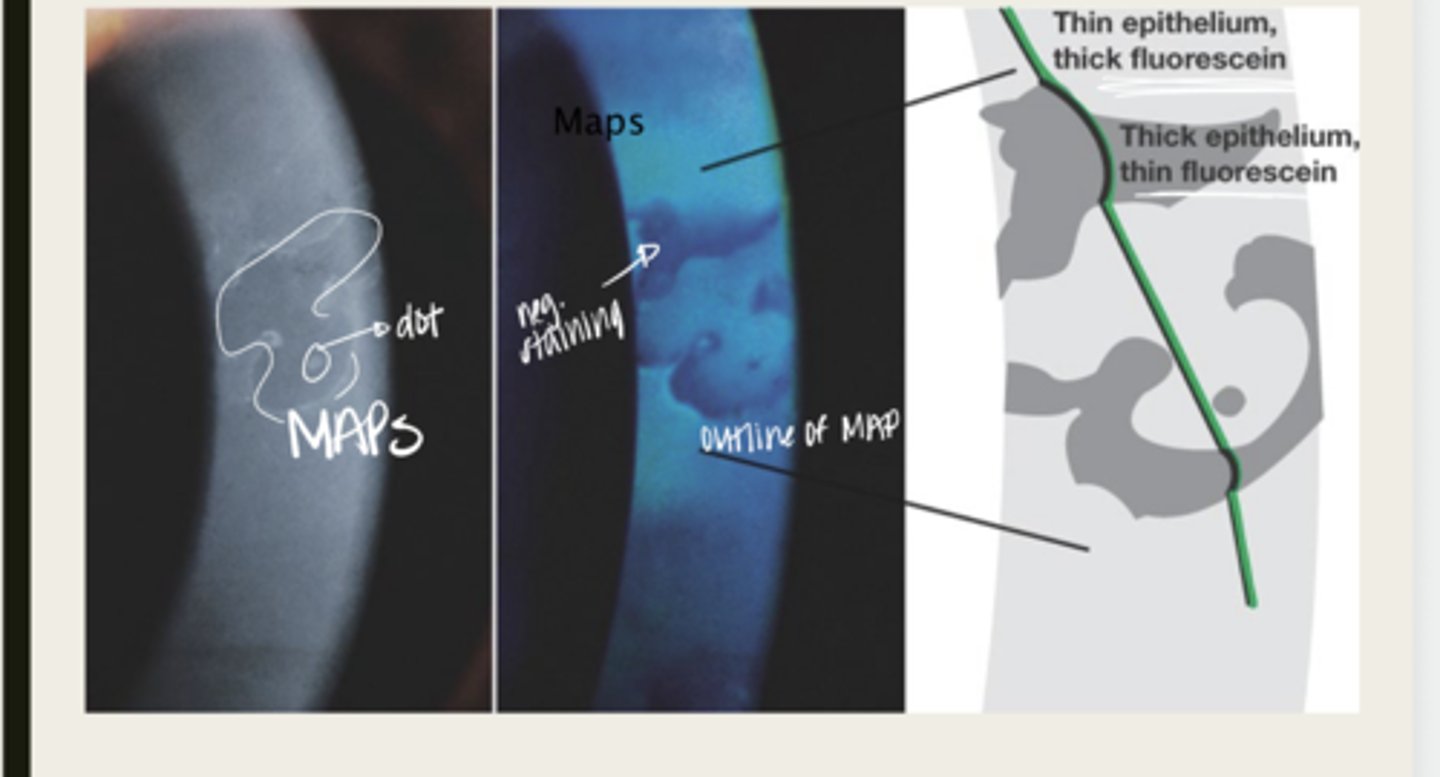
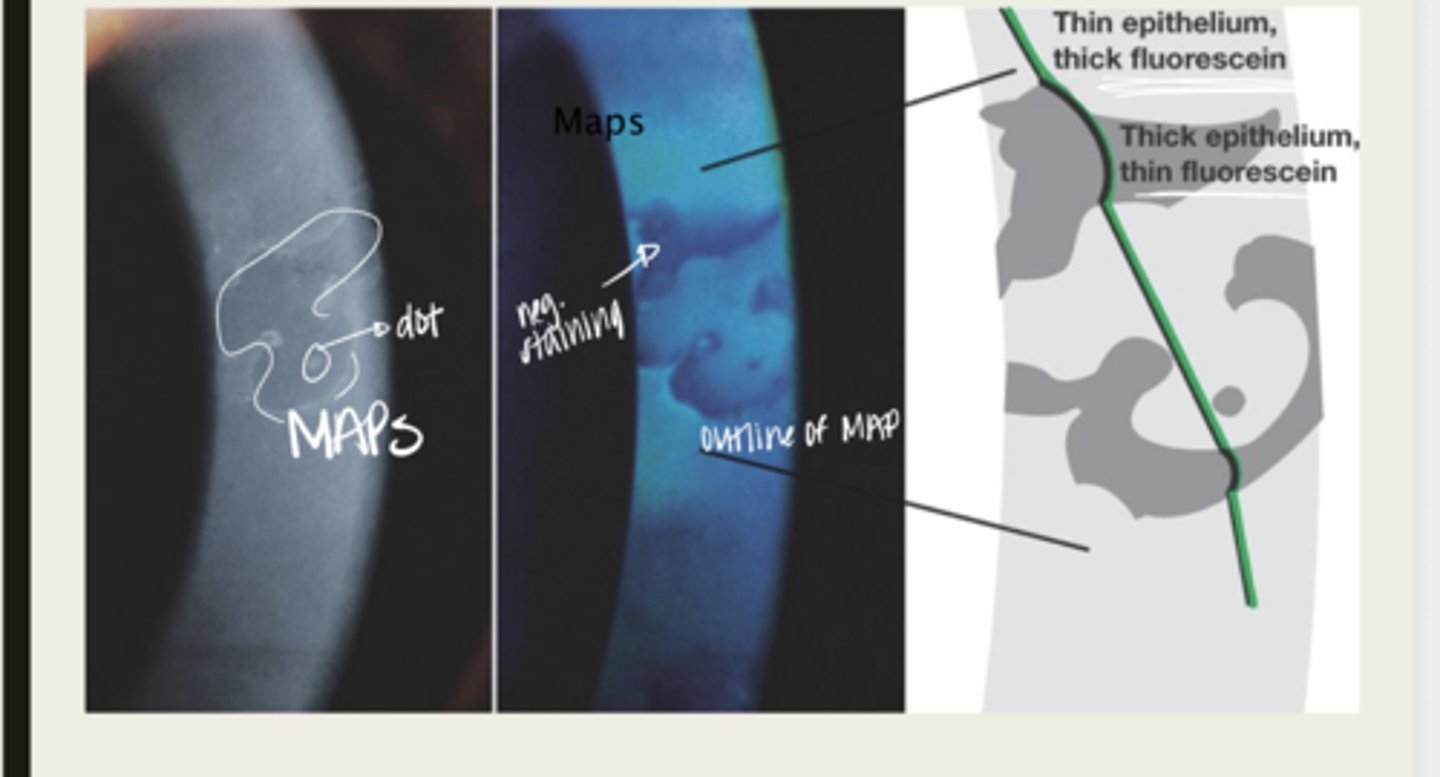
Causes the epithelial tissue to heap up
In Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy, the basement membrane extends into the epithelium and causes what?
map
The elevated tissue of Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy will give the classic sign of a what?
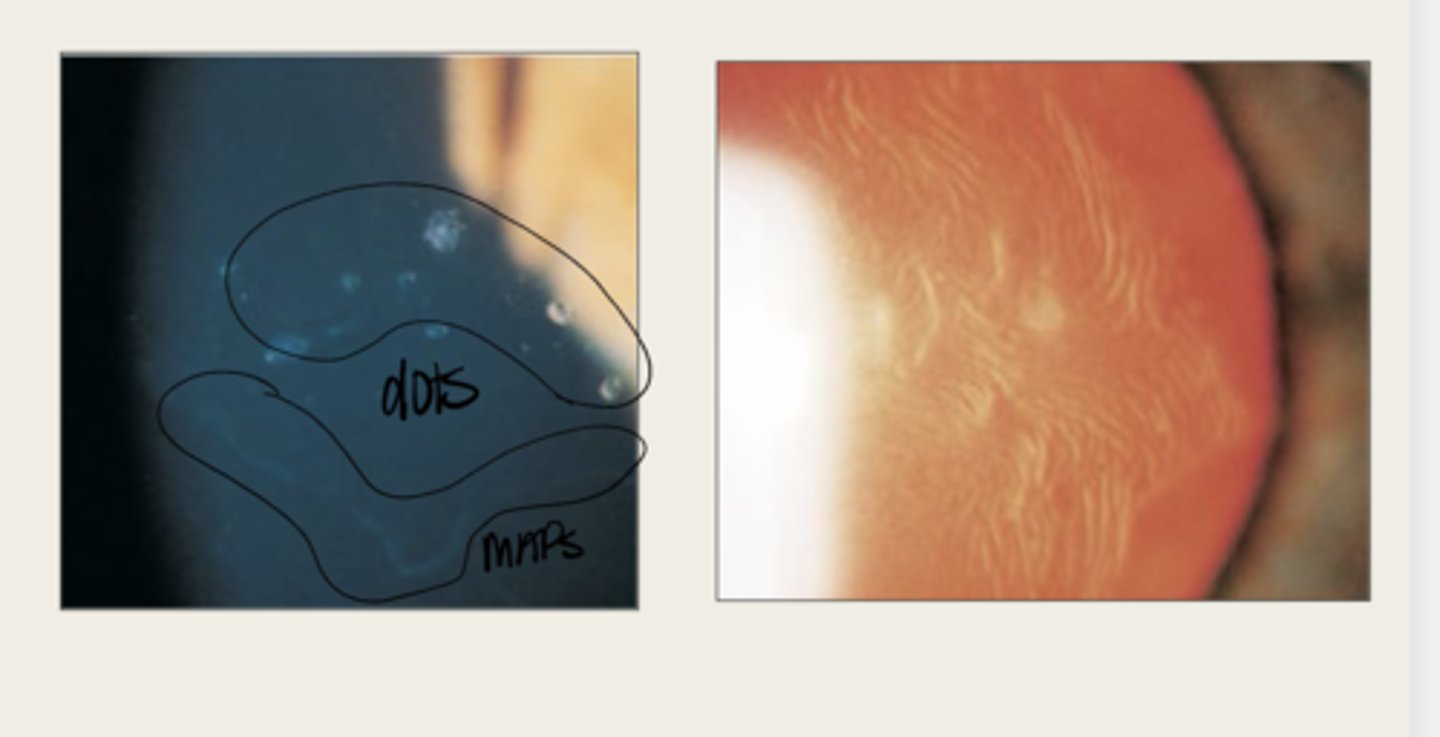
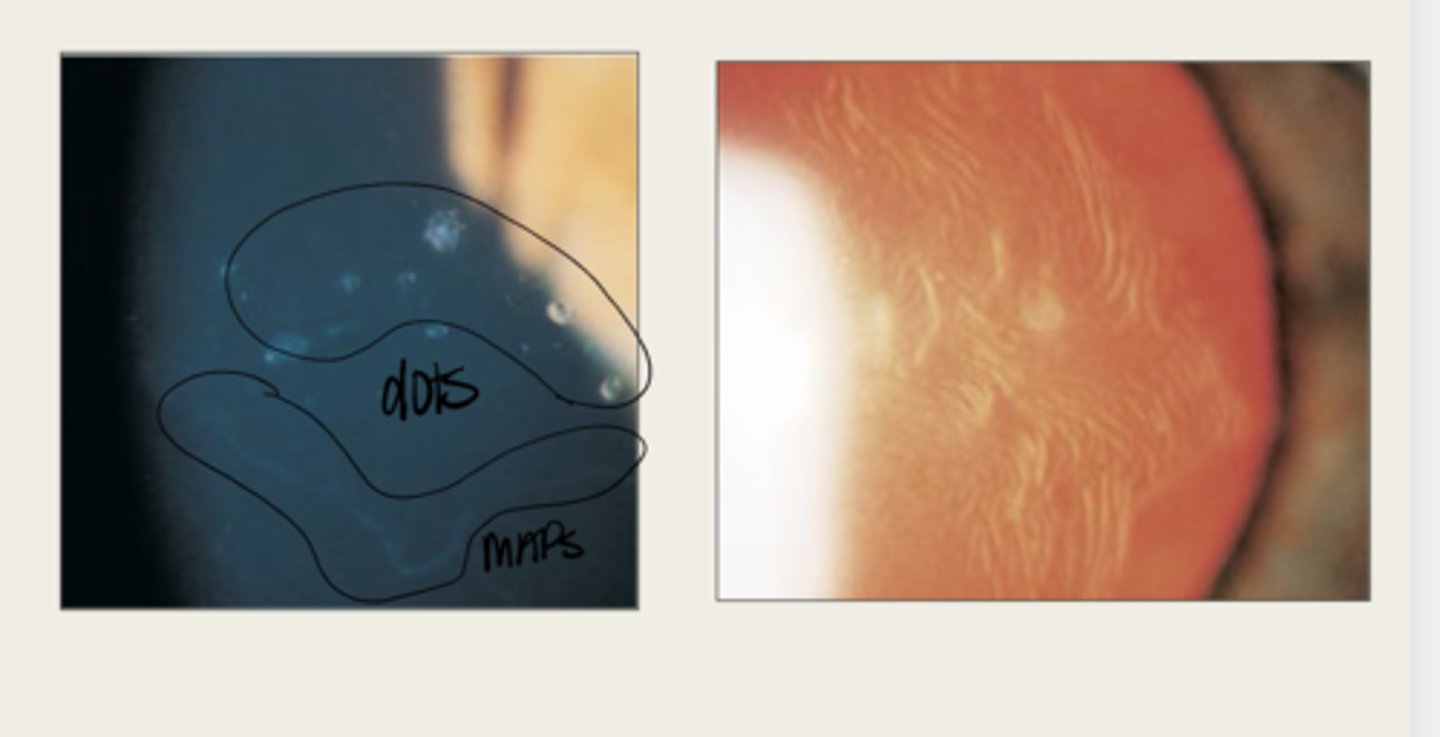
develops dots and other cystic changes
Migrated cellular material becomes trapped and develops what in Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
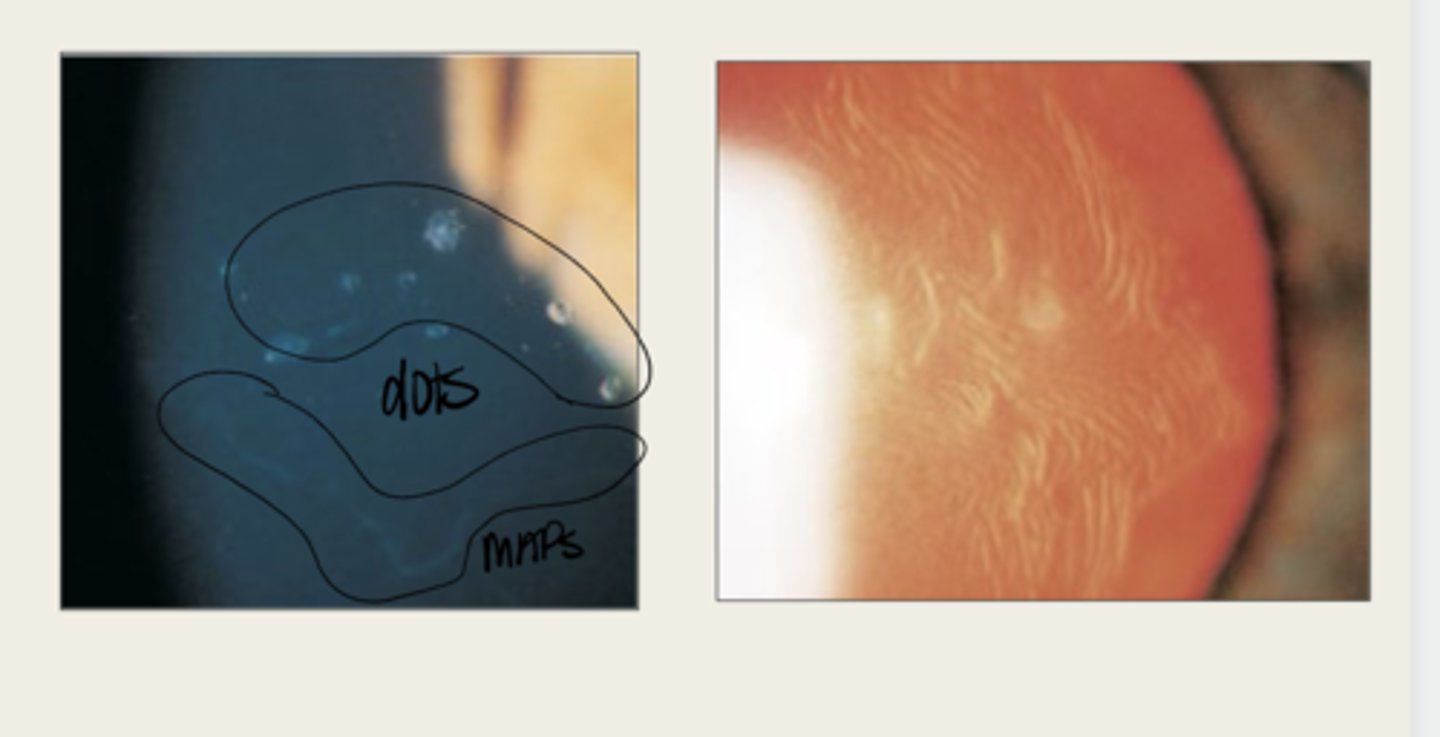
will develop into fingerprints
Adjacent rows of thickened and elevated epithelium will develop into what in Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
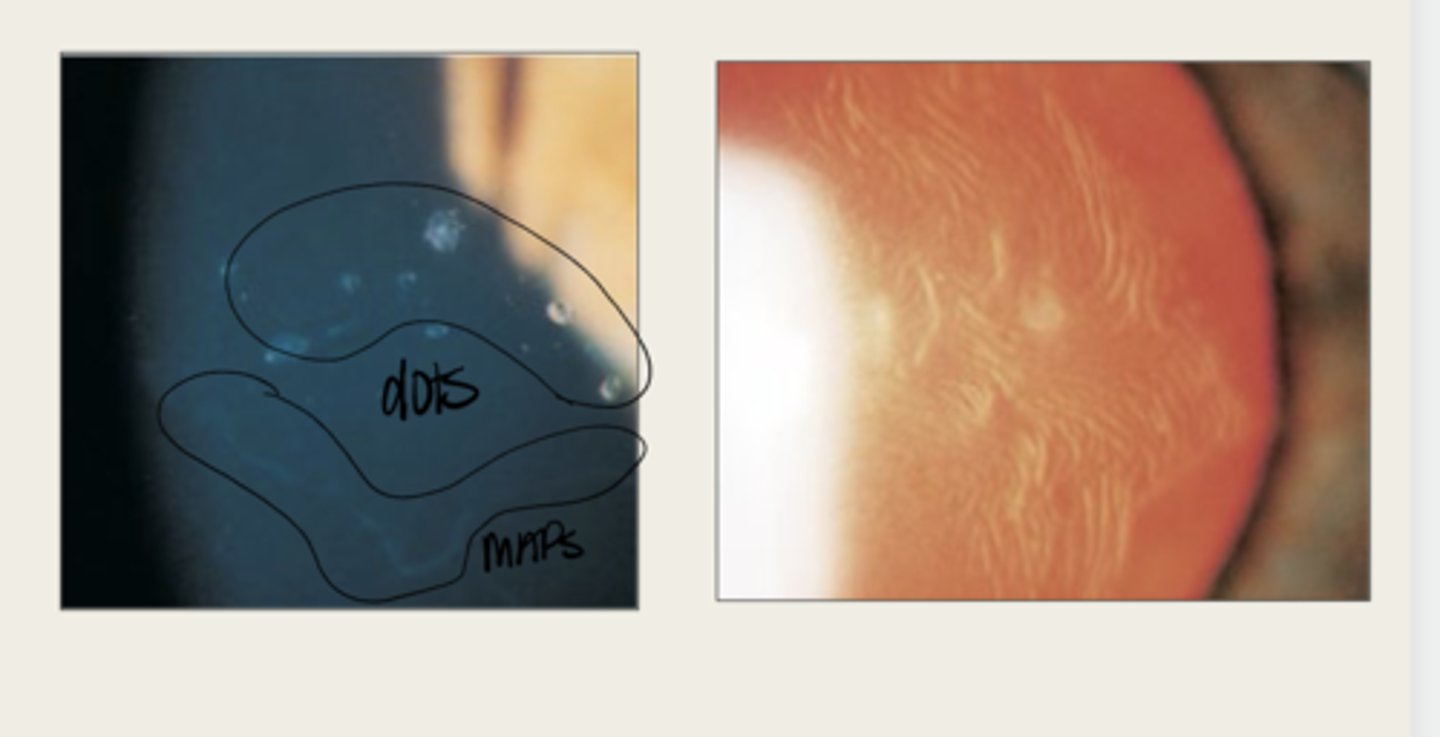
-asymptomatic
-blurred vision worse in the AMs
-diplopia
-dry eye
-FB sensation
What are the symptoms of Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
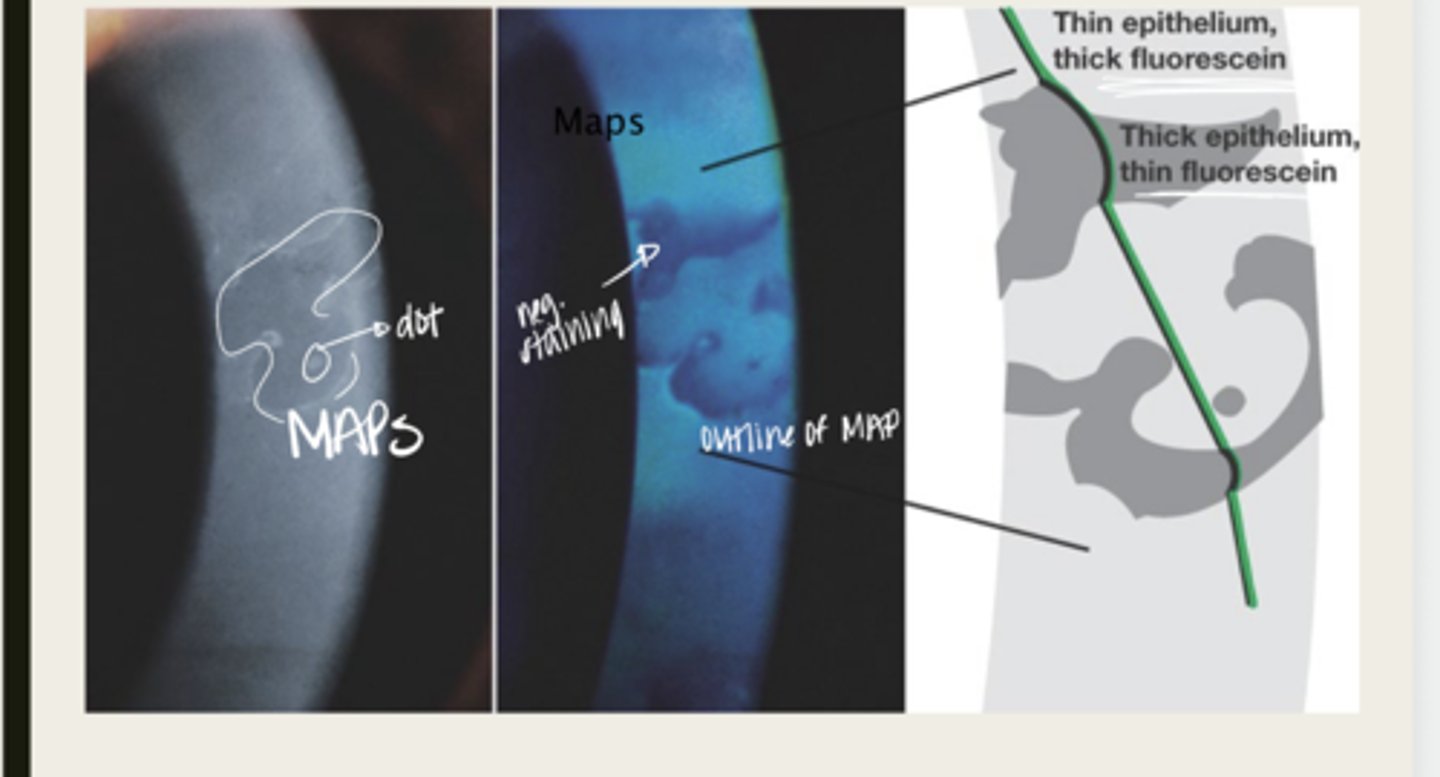
maps, dots, fingerprints
What is the presentation of Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
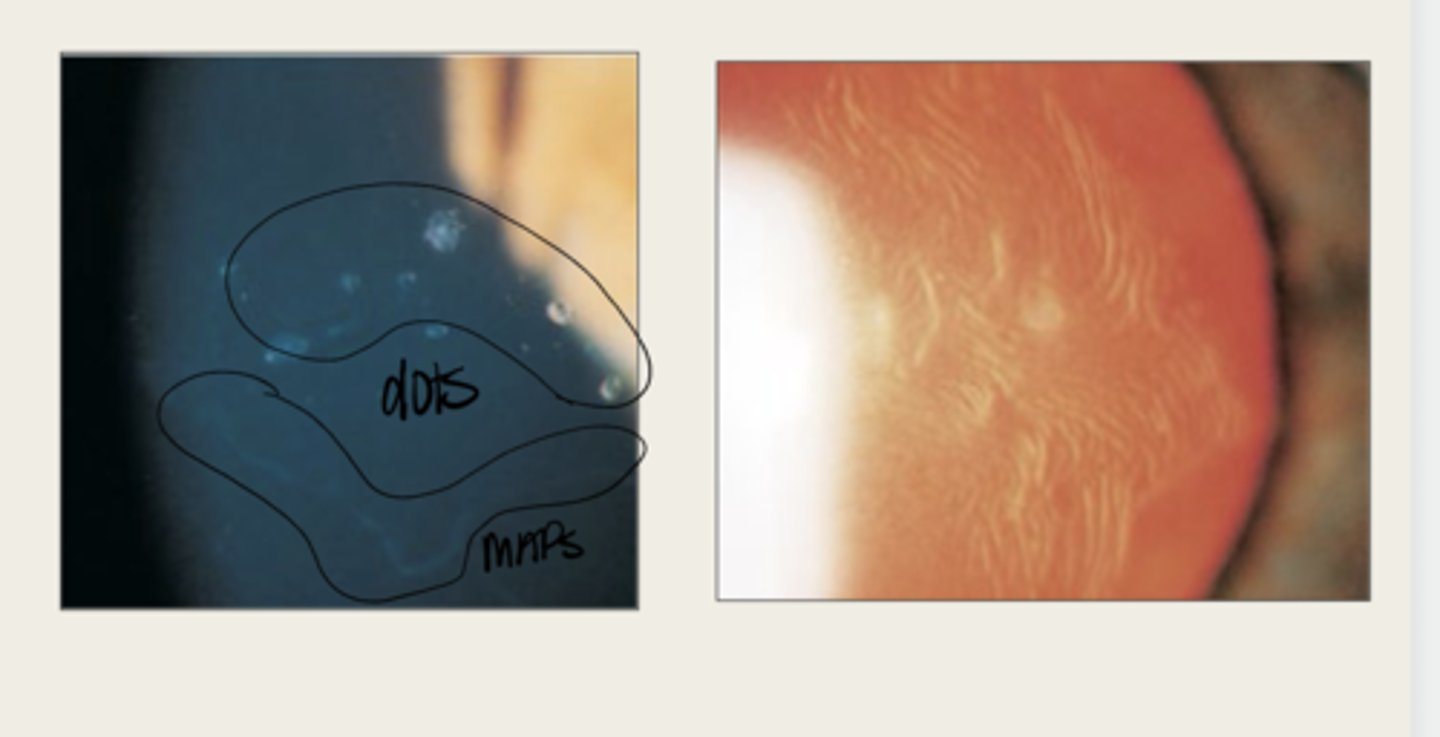
large geographic lesions
What do the maps of Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy appear as?
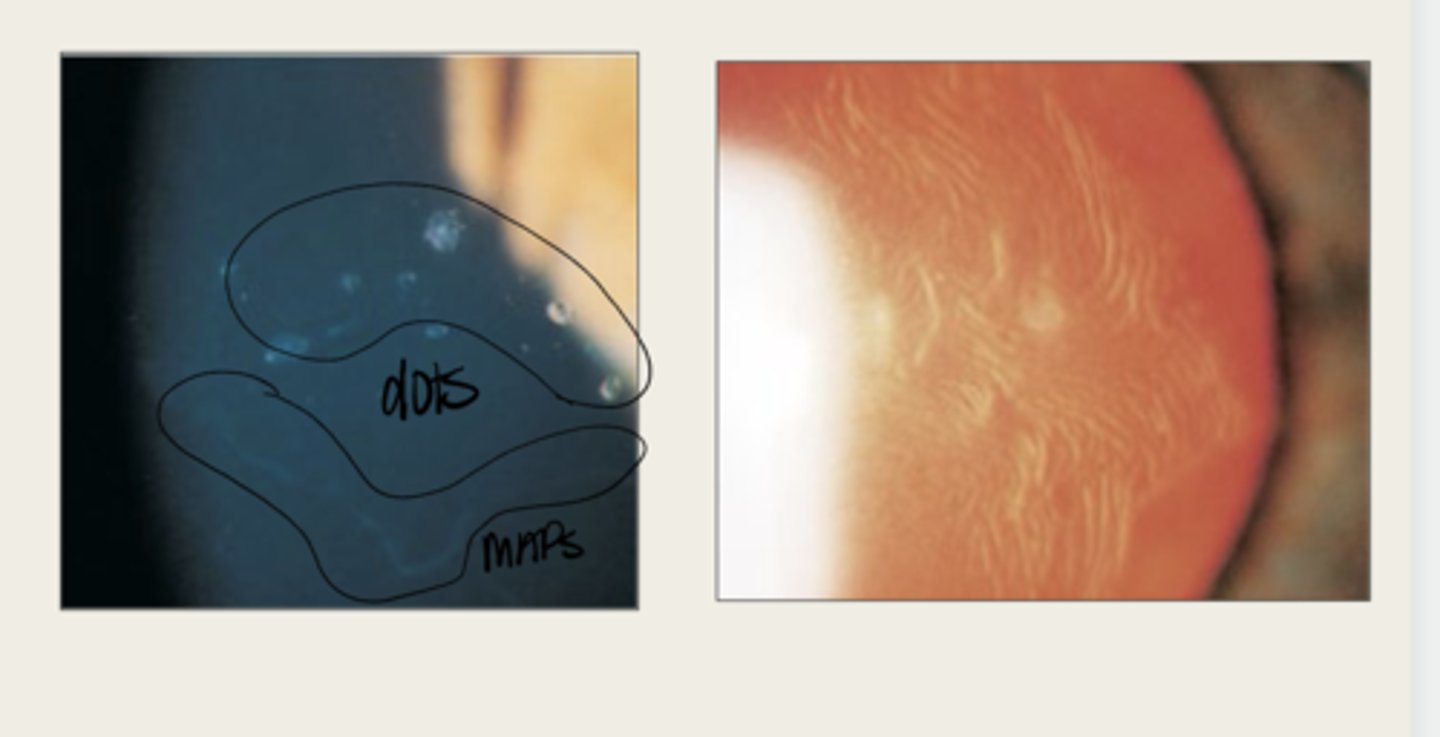
line (in isolation)
What do the fingerprints appear as in Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
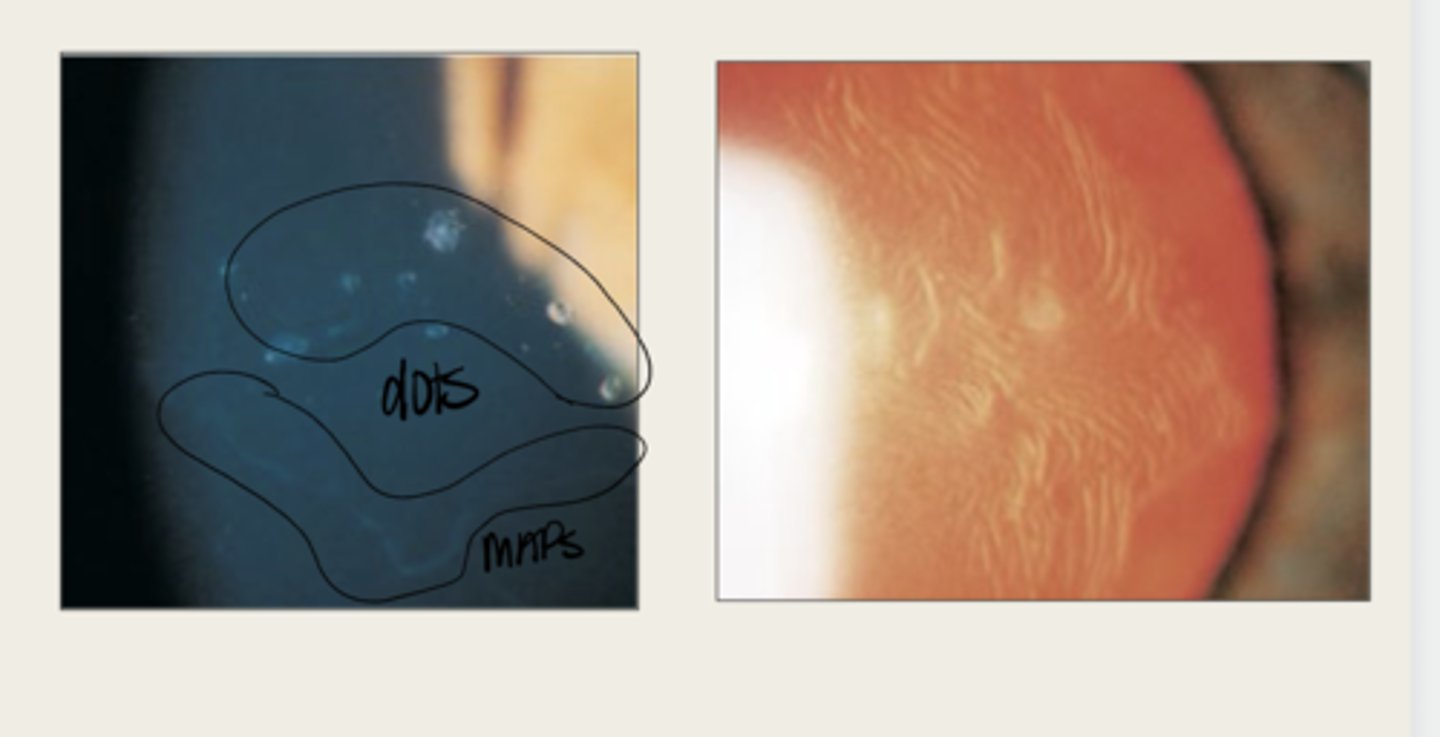
negative staining -- elevated epithelium
Lesions in Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy will have (positive/negative) staining?