BSC 196 Biology Unit 3: Key Concepts and Definitions
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
plant hierarchical organization
organs, tissues, and cells
roots stems and leaves
root and shoot system above ground
shoot system
major site of CO2 and light uptake
root and shoot system below ground
root system
major site of mineral and water uptake
roots
anchor, absorb, and store carbohydrates
primary root first to emerge and forms lateral roots
root hairs increase the root surface area
taproot system
large central dominant root and sprouts lateral roots
anchors plant in soil
fibrous root system
thick bunch of thin roots
prevents erosion
adventitious roots
root adaptation
same functions as lateral roots but develop from aerial tissues
prop roots
root adaptation
roots that grow partially in the air and partially in the ground
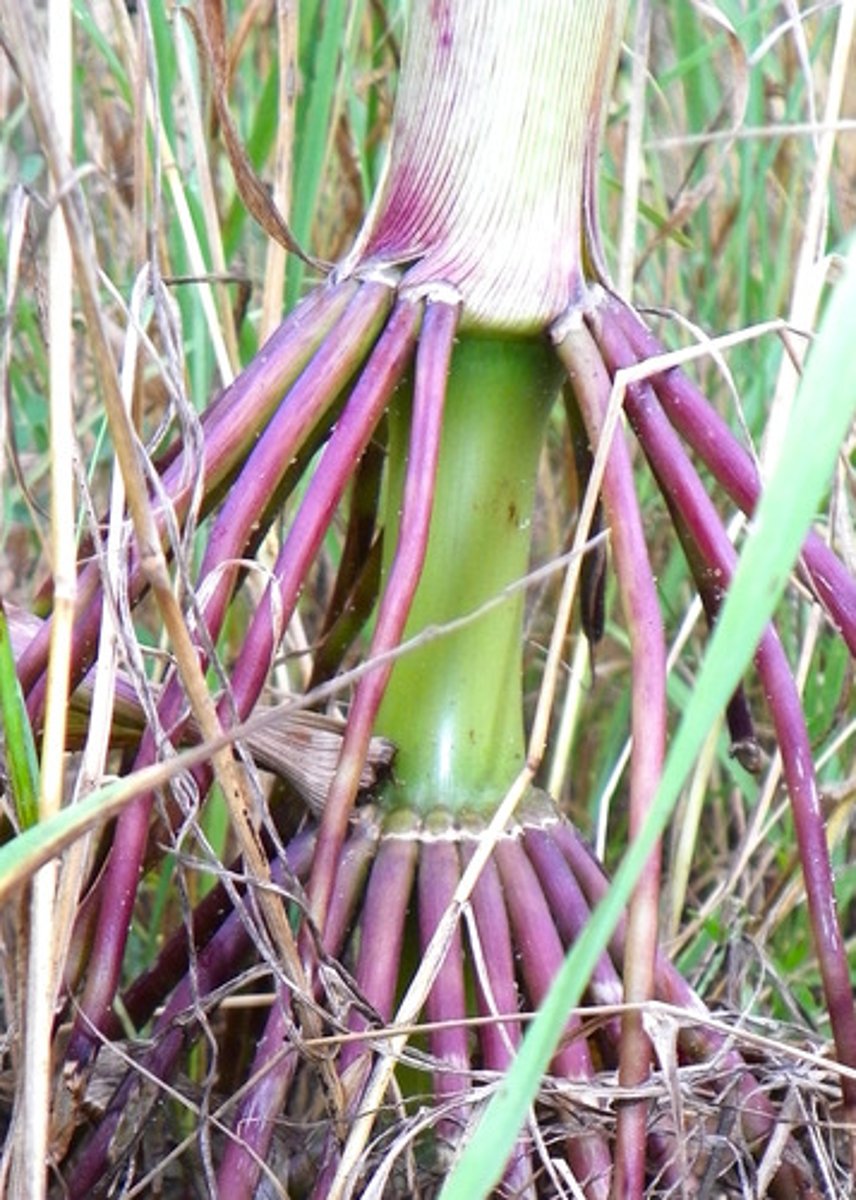

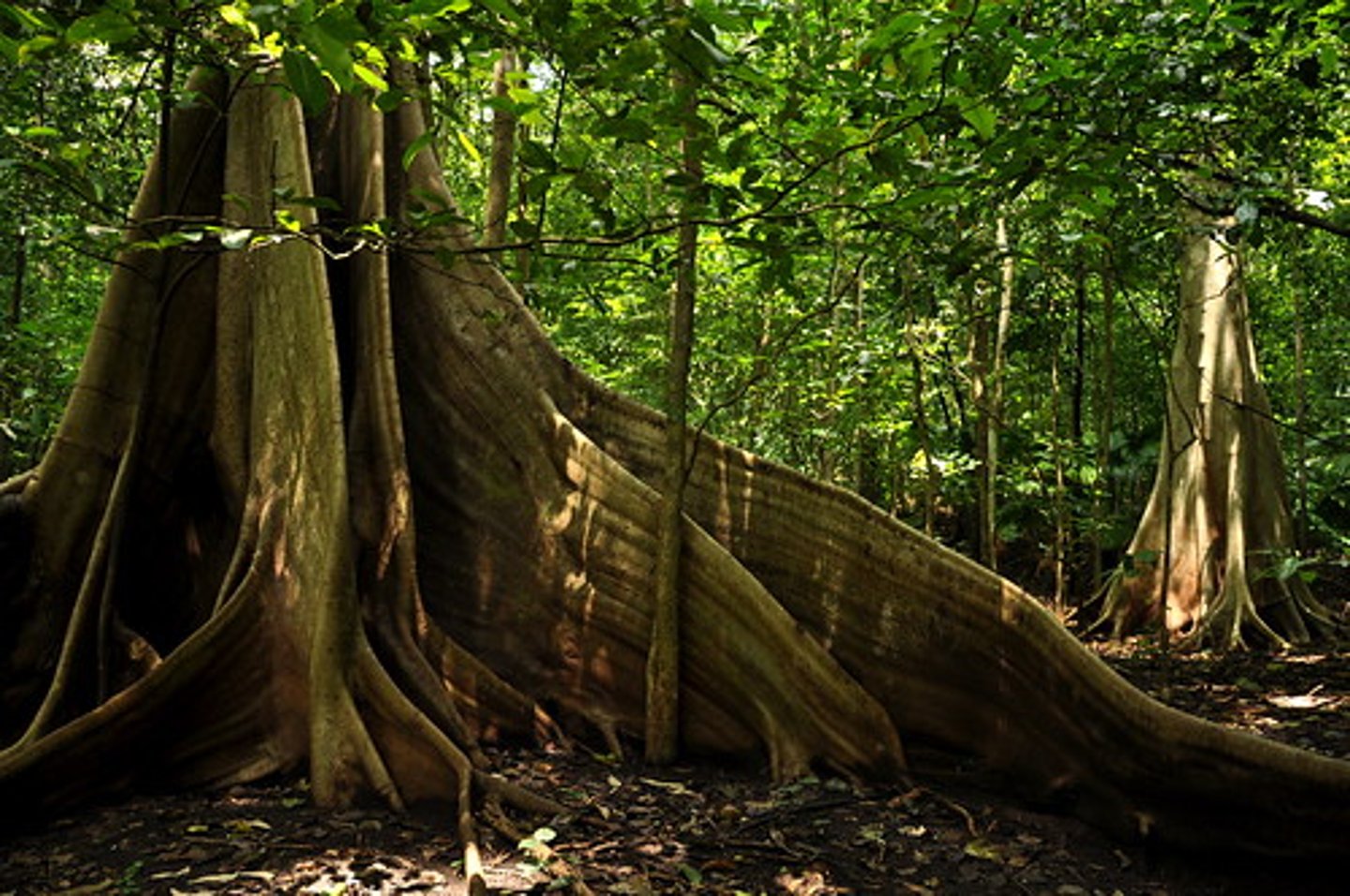
buttress roots
root adaptaion
large, above ground roots that provide stability in tropical trees
increase nutrients around trees

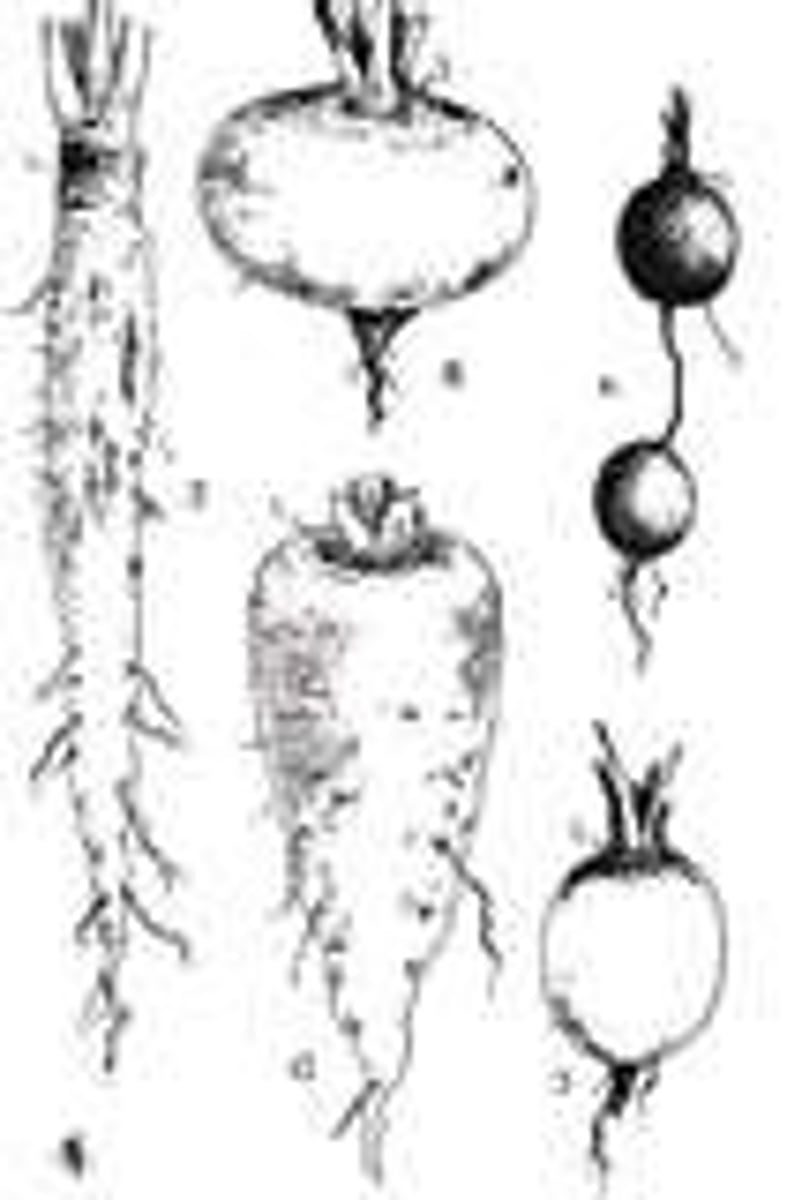
storage root
stores plant food in the form of starchy carbohydrate
also a tap root
potato, carrot, cassava

stems
organ bearing leave and buds
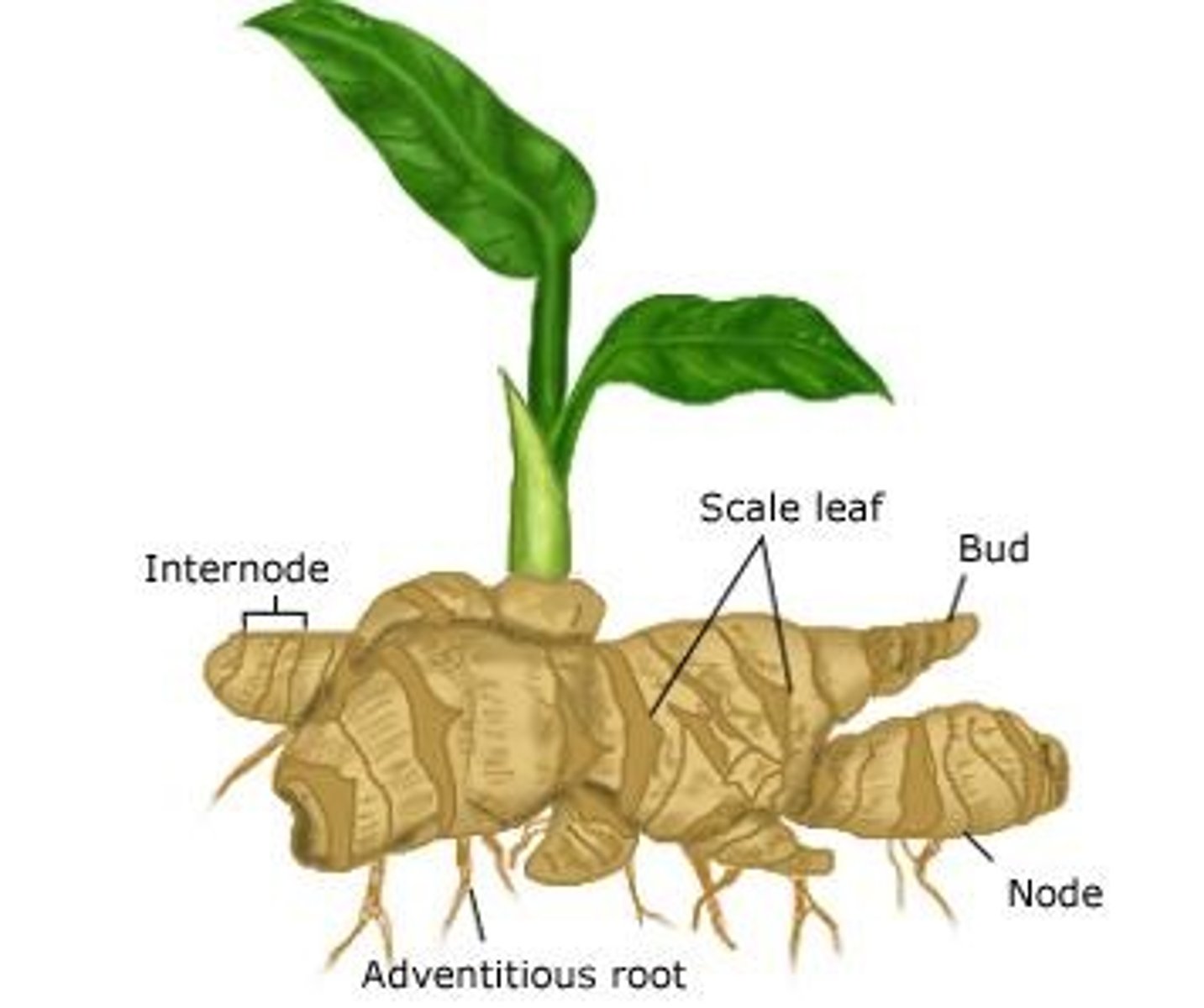
nodes
points where leaves are attached to stem
internodes
the stem segments between nodes
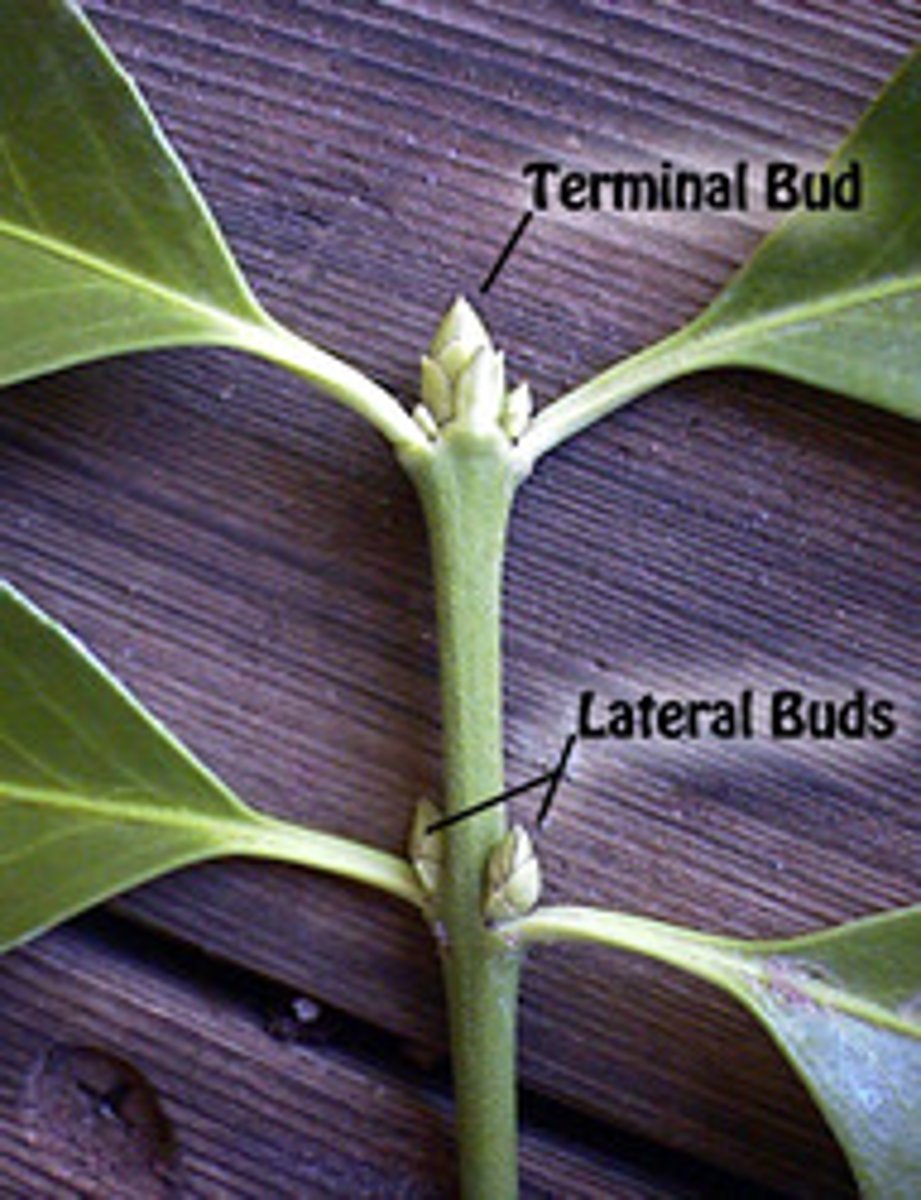
buds
apical- elongation of the stem
axillary- goes on to form lateral branch or flower cluster

rhizomes
horizontal underground stems
stolons
"runners"
asexual reproduction
mother plant produces daughter plants
tubers
the thick, fleshy parts of underground stems, potatoes
asexual reproduction
potatoes
leaves
flattened blade attached to petiole (stalk) petiole attaches to node
main photosynthetic organ (most are specialized for it)
intercept light
exchange gases
dissipate heat
defend from herbivores and pathogens
simple leaf
single undivided blade
compound leaf
single blade is separated into leaflets
are not separate leaves
argued to be important defense against pathogens
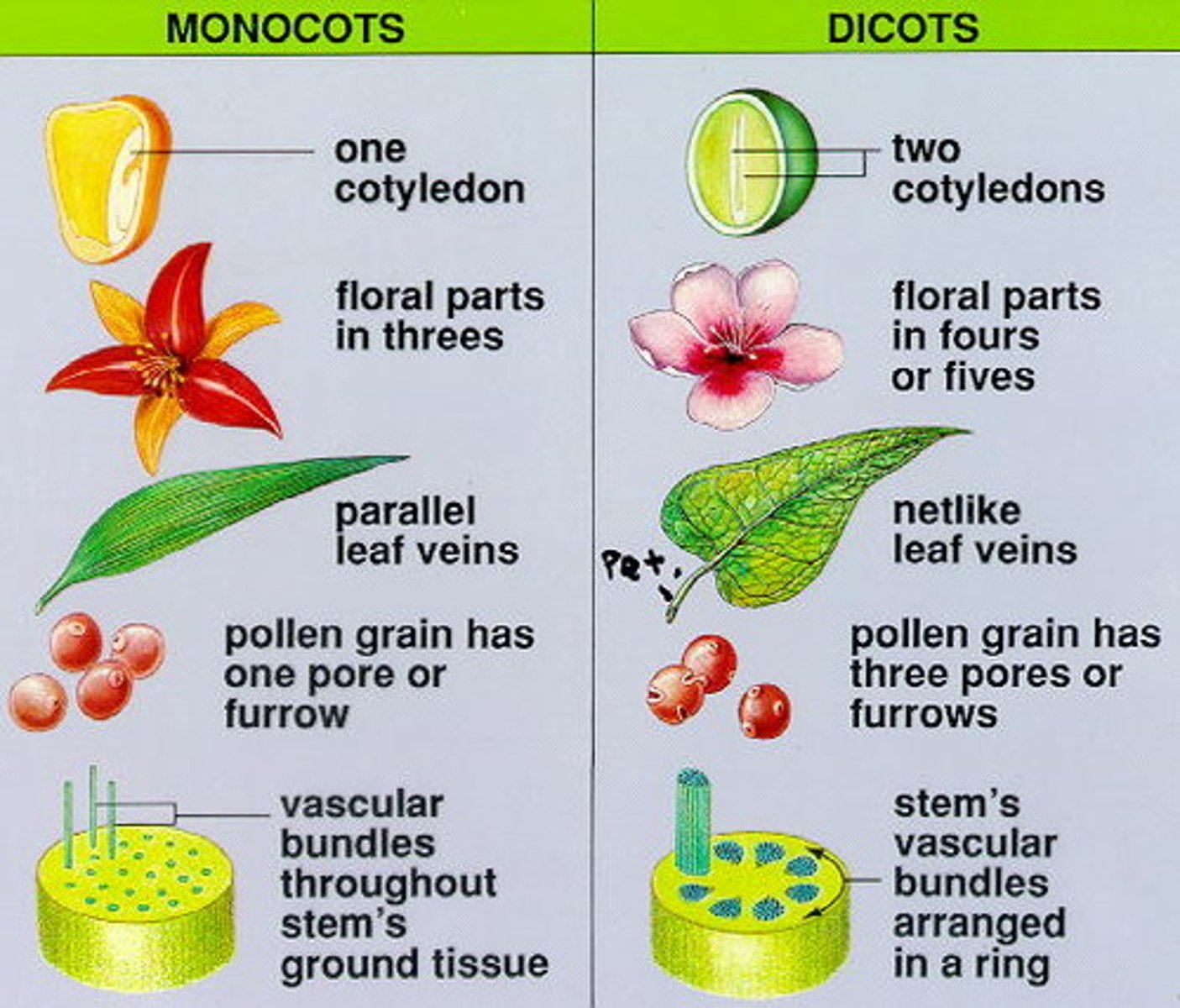
monocots
have one cotyledon (seed leaf)
parallel veins
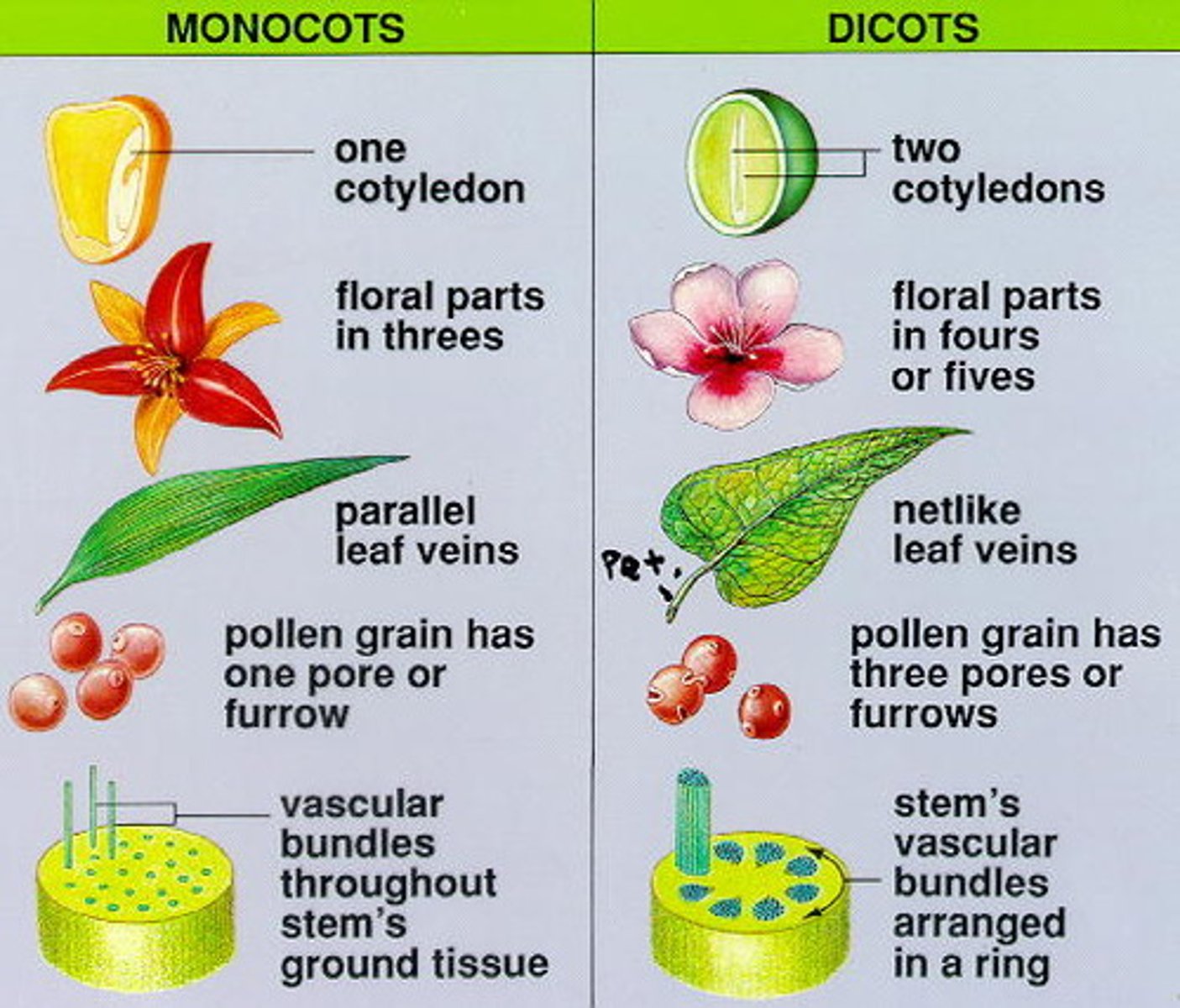
eudicots
have two cotyledon (seed leaf)
branching veins
tendrils
leaves that are adapted to attach to a supporting structure
storage leaves
Present on bulbs which have a short underground stem and modified leaves that store food
onions
3 main basic tissue types
Dermal - blue
Vascular - purple
Ground - yellolw
dermal tissue system
in non woody plants tissue is the epidermis
has a waxy coating (cuticle) to help prevent water loss
in woody plants periderm replaces the epidermis in older regions of stems and roots
vascular tissue system
transports resources and provides mechanical support
xylem conducts water and dissolved minerals upward from roots to shoots and dead at maturity and a one way system
phloem transports sugars from where they are made (primary leaves) to where they are needed (growth/storage) and a two way system
ground tissue system
primary growth
lengthens roots and stems and leaves
apical meristems
secondary growth
increases a plant's width or thickness
lateral meristems
vascular cambium
adds layers of vascular tissue called secondary xylem (wood) and secondary phloem
cork canbium
meristem that produces cork on the outside and produces periderm
morphogenesis
the development of body form and cell organization
cell differentiation
cells with same genes become different from one another
cell elongation
process directly responsible for growth with a water intake around 90%
Unequal expansion perpendicular to cellulose microfibrils supporting cell
pattern formation
development of specific structures in specific locations
depends on gene expression
cell fate is determined by final position
plant development- flowering
involves phase change from vegetative ti reproductive growth
indeterminate vegetative meristem to determinate reproductive meristem
combination of environmental cues and internal signals
ABC hypothesis
A model of flower formation identifying three classes of organ identity genes that direct formation of the four types of floral organs.
A- seplas
B- petals
C- stamens and carpals
Resource Aquisition and transport in plants
diffusion, active transport, and bulk flow act together
natural selection in vascular plants favored
taller plants, flat appendages (stems and leaves), multicellular branching roots and efficient transport
xylem and phloem allows for long distance resource
Adaptations for acquiring resources:stems
Stems for water and nutrient transport and providestructural support for leaves
finite resources
trade off between growing tall and branching out
Adaptations for acquiring resources:leaves
Generally, positive correlation between water availability and leaf size
phyllotaxy
arrangement of leaves on a stem, important for light capture
self-pruning
nonproductive shaded leaves undergo programmed cell death and drop
low light conditions
horizontal leaves capture more sunlight
sunny conditions
vertical leaves are less damaged by sun and allow light to reach lower leaves
Adaptations for acquiring resources: roots
roots respond to local changes in conditions to maximize nutrient uptake
increase surface area for absorbing water and minerals
mycorrhizae
roots and hyphae of soil fungi form mutualistic associations
soil horizons
Layers of soil
topsoil
top layer of soil, most important layer
consists of mineral particles, living organisms and humus(decaying organic material)
b horizon
less organic matter
C horizon
partially broken down rock
soil solution
water and dissolved minerals in the pores between soil particles
half water half air
loams
most fertile topsoils and contain equal amounts of sand, silt, and clay
balances aeration
soil properties: composition
include cations and anions
cations adhere to negatively charged soil particles reducing leaching from soil, are displaced from soil particles by other cations during cation exchange, and are taken up by plant roots
most particles are anions as well as many nutrients, they do not bind with soil particles and can be lost from the soild by leaching
soil properties: organic components
humus prevents clay particle packing and retains water but is porous, increases soils cation exchange capacity, and acts as mineral nutrient reservoir
soil management
use of plowing methods and fertilization to prevent or reduce soil depletion and erosion for agriculture and settlements
agriculture
depletes mineral content of soils, taxes water reserves,
ands encourages erosion
sustainable agriculture
conservation-minded, environmentally safe, and profitable
irrigation issues
huge drain on water resources, especially in arid regions
primary source of irrigation water are underground reserves
irrigation solutions
Drip irrigation - slow release of water directly at plant root
erosion solution
Planting trees as windbreaks
Including perennials in crop rotations,
Using cover crops,
Terracing hillside crops,
Cultivating in a contour pattern,
Practicing no-till agriculture
resource incorporation into plants
essential elements
17 essential elements , researchers use hydroponic systems that are stacked to determine which elements are essential
essential macronutrients
9 essential ones and required in relatively large amounts
essential micronutrients
8 essential ones and required in relatively small amounts
dead plants
provide energy needed by soil-dwelling microorganisms
living roots
their secretions support microbes in near root environment
rhizosphere
layer of soil closely surrounding the plant's roots
rhizobacteria
bacteria in the rhizosphere or in close association with plant roots
depend on nutrients secreted by plant and in return helps enhance plant growth
produce chemicals, antibiotics, and absorb toxic metals
endophytes
nonpathogenic bacteria living between hostplants cells
depend on nutrients secreted by plant and in return helps enhance plant growth
produce chemicals, antibiotics, and absorb toxic metals
nitrogen cycle
series of natural processes that transform nitrogen and nitrogen-containing compounds
Ammonium process in plants
Nitrifying bacteria oxidize ammonia (NH3) to nitrite (NO2-)
Different nitrifying bacteria oxidize NO2- to NO3-
Plant enzymes convert NO3- to ammonium
nitrogen fixation
the conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonia
legume nitrogen fixation
along legume roots are swelling called nodules
nodules are composed of plant cells infected by nitrogen fixing rhizobium bacteria
bacteroid
A form of the bacterium Rhizobium contained within the vesicles formed by the root cells of a root nodule.
legume nitrogen fixation steps
chemical signals attract bacteria and an infection thread forms
Bacteroides form
growth continues and a root nodule forms
the nodule develops vascular tissue
the mature nodule grows to be many times the diameter of the root
crop rotation
takes advantage of the agricultural benefits of symbiotic nitrogen fixation
one-year legumes planted and the other year non legumes planted
Ectomycorrhizae
A type of mycorrhizae in which the mycelium forms a dense sheath, or mantle, over the surface of the root. Hyphae extend from the mantle into the soil, greatly increasing the surface area for water and mineral absorption.
arbuscular mycorrhizae
microscopic fungal hyphae extend into the root and penetrate cell wall but not plasma membrane
Epiphytes
an alternative nutritional strategy
grow on another plant and obtain water and mineral from air and rain
do not tap into hosts for nutrition (not parasites)
parasitic plants
an alternative nutritional strategy
absorb water, sugars, and minerals from their living host plant
carnivorous plants
alternative nutritional strategies
photosynthetic but obtain nitrogen by killing and digesting mostly insects
key features of angiosperms
double fertilization, flowers, fruits
angiosperm male
pollen develops from microspores within the microsporangia (pollen sacs) of anthers
microspore undergoes mitosis to produce generative and tube cell
pollen grain
structure that contains the entire male gametophyte in seed plants
angiosperm female gametophyte
within ovule 2 integuments surround megasporangium except gap (micropyle)
pollination
transfer of pollen from anther to stigma
double fertilization
2 sperm reach female gametophyte
one sperm fertilizes egg, forming zygote
one combines with two polar nuclei forming food storing endosperm
seed development
seed develops after fertiloization
surrounding ovary develops into fruit
in germination embryo develops into new sporophyte
endosperm development
endosperm stores nutrients for use by seedling
some eudicots food reserves exported to cotyledons (seed leaves)
embryo development
first miotic division splits the zygote into basal and terminal cell
basal cell
produces a multicellular suspensor, which anchors the embryo to the parent plant
terminal cell
gives rise to most of the embryo
cotyledons form and the embryo elongates
seed dormancy
Seed dehydrates and enters a state of dormancy until conditions are favorable for germination
breaking this often requires specific enviornmental cues like temperature, rain , and fire
germination and seedling development
depends on imbibition (the uptake of water due to low water potential of the dry seed)
radicle
embryonic root
emerges first and developing roots system anchors plant
flowering
Flowers of a given plant species are synchronized to appear at a specific time of the year to promote outbreeding
triggered by a combination of environmental cues and internal signals
fruits
mature ovary of a flower
protects enclodes seeds and aids in dispersal by wind or animals
some fruits ovary dries out and some remain fleshy