Dopamine synthesis, regulation and physiology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is dopamine?
neurotransmitter synthesised in both the CNS and peripheral tissues
How does dopamine work?
exerts its effects by binding to GPCRs, mediating a wide range of physiological and behavioural functions.
Draw a neurotransmitter
Diagram.
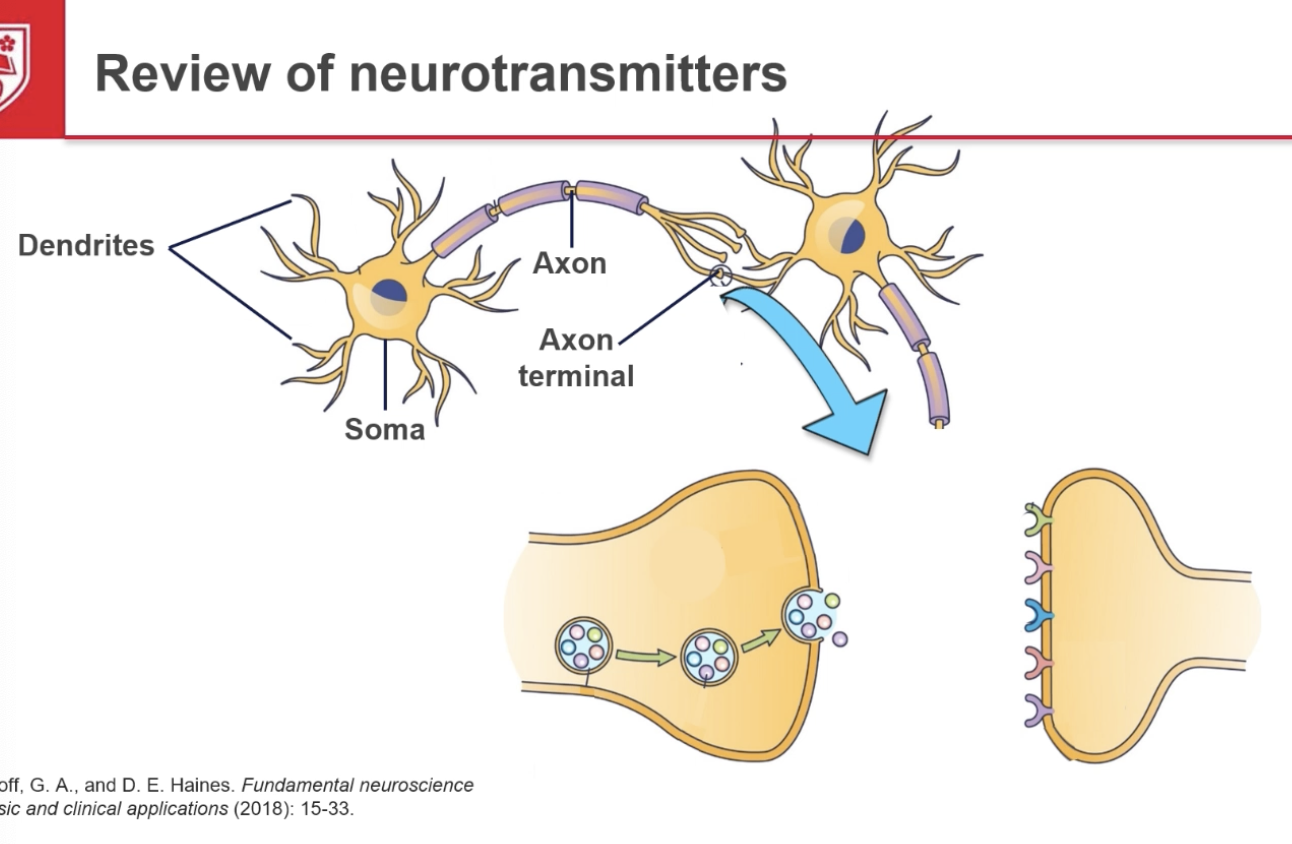
What are the classes of neurotransmitters?
ester, amino acids, monoamines, peptides and others.
What type of neurotransmitter is dopamine?
catecholamine
Give examples of excitatory neurotransmitters
Give example of inhibitory neurotransmitter
Give example of ‘dual’ (excitatory and inhibitory) neurotransmitter
What two transmitters can be derived from dopamine?
noroadrenaline and adrenaline
What does dopamine regulate?
movement, motivation, reward and cognition
Dopamine deficit
a state where the brain has insufficient amounts of dopamine, a neurotransmitter and hormone that plays a crucial role in movement, reward, motivation, and other functions. It can be linked to various health conditions, including Parkinson's disease, depression, and ADHD.
Dopamine reward-seeking experiment (Lever)
Animal trained to work to receive a reward. Once trained, they reliably press the lever to receive the reward. Dopamine antagonists such as pimozide can be given to the animal which decreases desire for reward so lever is pressed less.
Dopamine reward-seeking experiment (Intracranial self-stimulation)
Animals would press a lever repeatedly to receive a brain electrical stimulation in the septal area of the brain specifically (mesolimbic pathway)
What is micro dialysis?
technique used to measure dopamine levels in the brain's extracellular fluid, providing insights into its function and dysregulation in various conditions. It's a minimally invasive method that allows for real-time monitoring of neurotransmitters like dopamine, including their metabolites.This technique is valuable in neuroscience research and clinical applications, helping to understand the role of dopamine in different brain functions and disorders.
What are different areas of the brain involved in with dopamine? (i.e., amygdala, nucleus accumbens, hippocampus, cortex)
amygdala is emotion, nucleus accumbent is motivation, hippocampus is memory, cortex is attention.
How does reinforcement work?
activates the mesolimbic pathway which causes dopamine to be released and individual to feel pleasure which reinforces behaviour so more likely for it to be repeated due to strong positive associations between behaviour and outcome.