Chem 215 - Exam 1
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Jones
- creates carboxylic acids
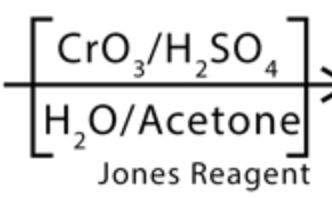
Carboxylic acid
-forms from primary alcohols with water
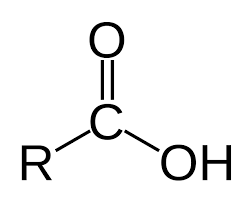
Aldehyde
- forms from primary alcohols without water
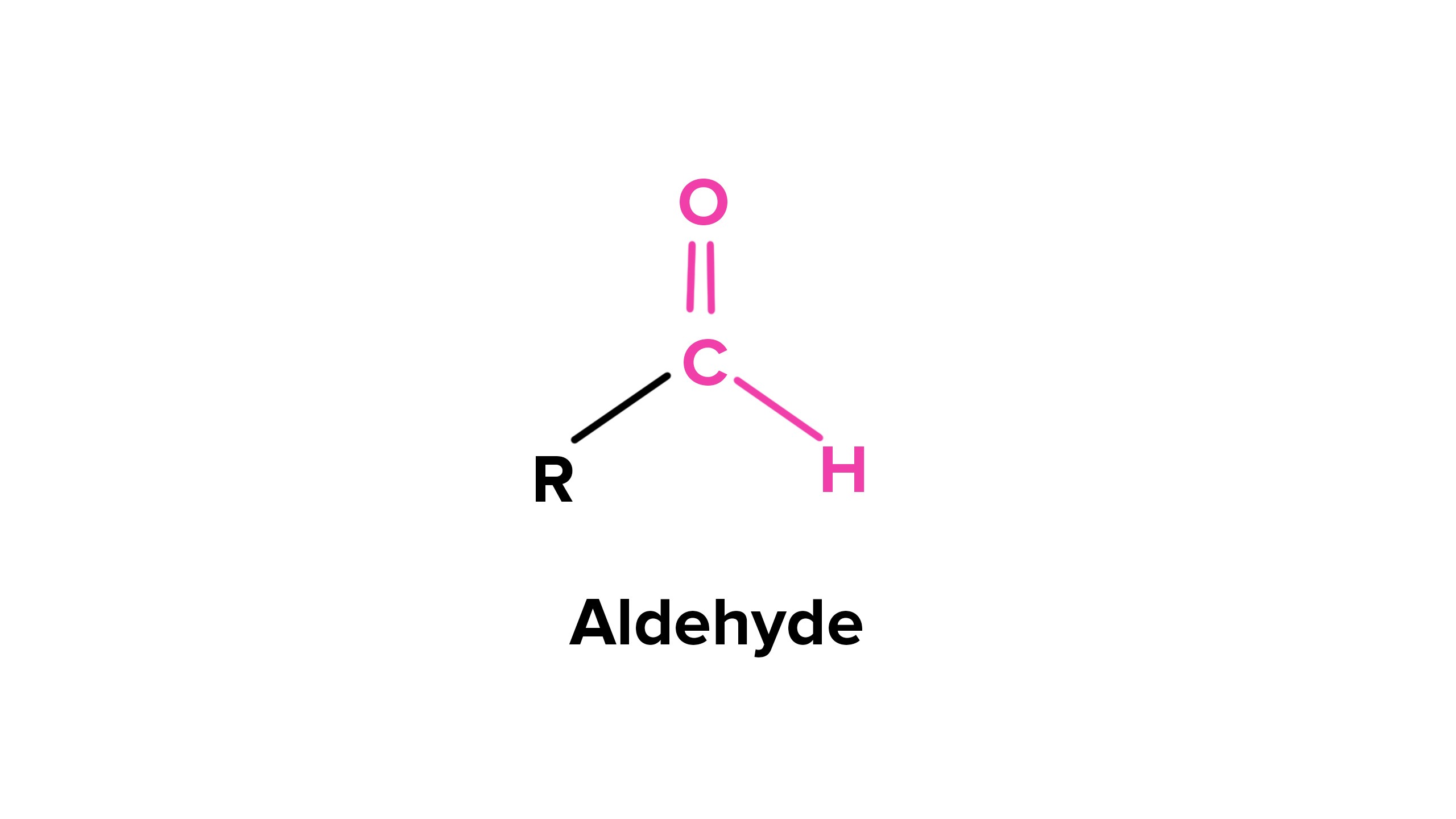
ketone
-forms from secondary alcohols
PCC
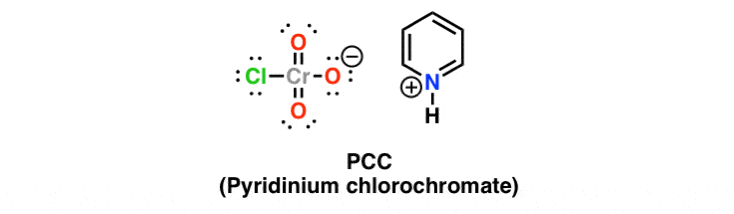
PDC
swern oxidation
Hydroboration
- anti-markonikov addition of H2O
Regio: anti-markonikov
Stereo: Syn
Adds: -OH and -H
Common reagents: BH3 or B2H6
Common solvent: H2O2, NaOH
Hydration
- markonikov addition of H2O
Regio: Markonikov
stereo: syn and anti
Adds: -OH and -H
Common reagents: H2O
Common solvents: H2SO4
Halogenation
anti-addition reaction
Regio: none
stereo: anti
adds: Br2, Cl2, I2, F2, etc.
Halohydrin
anti-additon reaction
regio: none
stereo: anti
adds: -OH and -X
common reagents: Br2+H2O , NBS + H2O, Br2+ROH, NBS + ROX
Hydrohalgenation
-addition to alkene
regio: Markonikov
stero: syn and anti
adds: -H and -X
Common reagents: HCl, HBr, HI
Dihydroxylation
Regio: none
stereo: syn
adds: -OH and -OH
Reagent: OSO4 or KMnO4
2nd step: NaOH,H2O or Na2SO3,H2O
Ozonolysis
Regio: none
Stereo: syn
common reagent: 1. O3
Common solvents: 2. Zn or 2.H2O2 or CH3CH3S
Epoxidation
regio: none
stereo: syn
common reagent: RCOOOH
Hydrogenation
- reduction reaction
regio: none
stereo: syn
adds: -H and -H
common reagent: H2
common solvent: Pd/ C
alkynes: H2 will add until fully saturated
Poised Catalyst
-reduction reaction
regio: none
stereo: syn
adds: -H and -H
common reagent: H2
common solvent: pd/BaSO4 w Pbo OR pd/CaCO3 w pbo or quinaline
Dissolving Metal
-reduction reaction
regio: none
stereo: anti
adds: -H and -H
common reagents: Na,Li or K
Common solvent: NH3
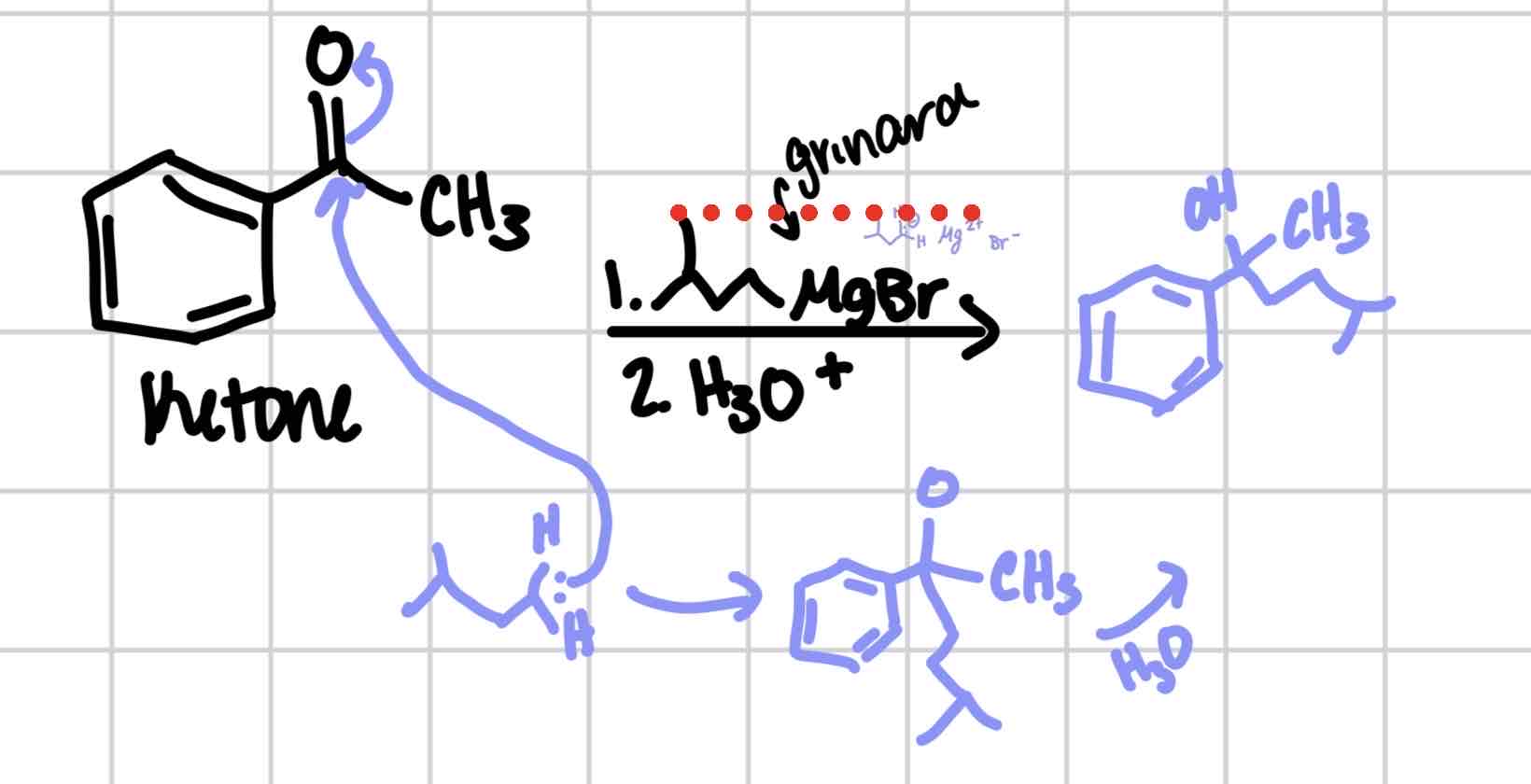
Grignard
Ketone → tertiary alcohol
Aldehyde → secondary alcohol
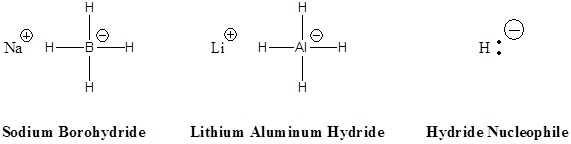
Hydride nucleophile
Ketone → secondary alcohol
Aldehyde → primary alcohol
solvents for NaBH4: CH3OH, H3O+,
solvents for LiAlH4: H3O+, H2O
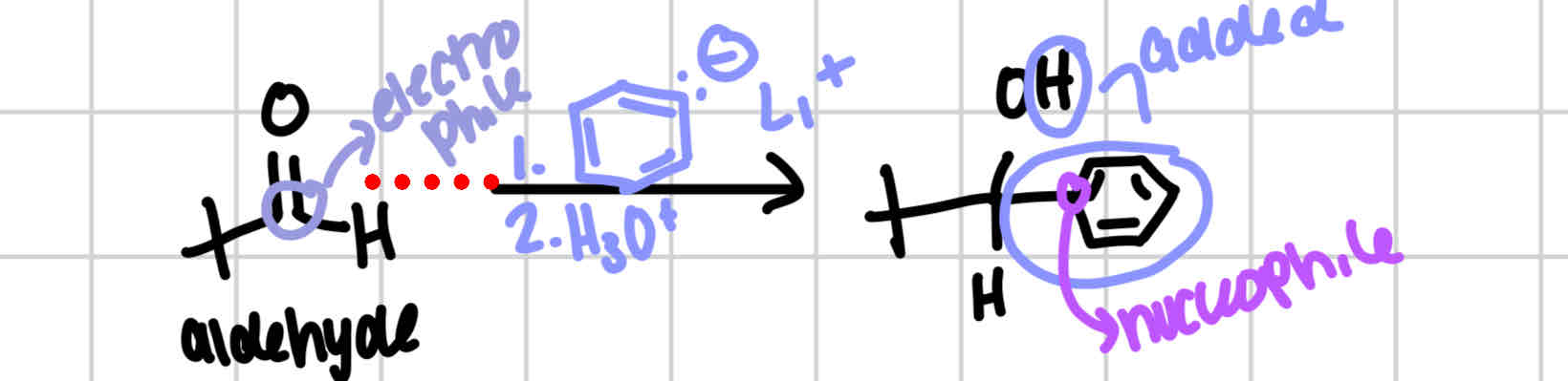
Organolithium
Ketone → tertiary alcohol
Aldehyde → secondary alcohol
Epoxide opening with weak nucleophiles
- nucleophile reacts to most substituted carbon
-examples: Br2 or H-Br
-H-Br forms alcohol
epoxide opening with strong/basic nucleophiles
-OCH3 reacts to least substituted carbon
-requires a workup (H3O+)
-example: NaOCH3/CH3OH
-forms alcohol
addition of weak nucleophiles to aldehydes
additon of weak reversible nucleophiles
specific acid catalyst mechanism
general acid catalyst mechanism
condensation reactions of hemis
condensation reaction of hemis mechanism via sn1
condensation reaction of hemiaminal
mechanism of condensation of hemiaminal
hydrolysis reactions
mechanism of hydrolysis
intramolecular substitution reactions