bio unit 2 vocab
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
polar/polarity
difference in electronegativity
hydrophilic
tendency to mix with water
hydrophobic
tendency to repel water
h-bonds
attraction between positive H atoms and negative N, O, F atoms
attraction between molecules that is strong without sharing electrons
capillary action
movement of liquid without gravity
cohesion
attraction of identical molecules
adhesion
attraction of dissimilar molecules
surface tension
surface of liquid uses cohesion to resist external force
heat capacity
the heat energy needed to raid temp by 1°C
organic
from a living organism
functional group
group of atoms in molecules that are responsible for a characteristics
hydroxyl (OH makes substance more soluble) carboxyl (COOH make amino fatty acids) carbonyl (CO found in every sugar) phosphate (PO4 in nucleic acids) amino (NH2 make all proteins)
monomer
type of molecule that bond to make a chain
polymer
the chain of monomers
hydrolysis reaction
chemical reaction when water is added to a molecule making two separate molecules
dehydration reaction
chemical reaction where water is removed from two molecules to make one molecule
lipid (wax/oils)
C H O P
no distinct monomer/polymer
saturated fatty acid has no double bond in carbon chain (straight)
unsaturated fatty acid has double bond in carbon chain (bent)
stores long term energy, hydrophobic
carbohydrates (fruits, breads)
C H O
monomers called monosaccharides (glucose, fructose) and polymers called polysaccharides (glycogen, chitin, cellulose)
1,2,1 carbon hydrogen oxygen ratio
stores short term energy, supports structure, hydrophilic
proteins (meats, cheese)
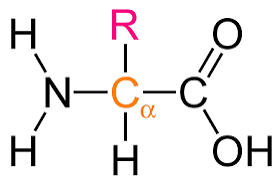
monomers called amino acids (with amino, carboxyl, R, H, and central C groups) and polymers called polypeptides (collagen, keratin)
C, H, O, N, S
transport cells, supports structure, chemical reaction speed, cell communication, immunity, growth, homeostasis
nucleic acids (dna cell fluid)
monomers called nucleotides (phosphate pool, 5 carbon (sugar), and nitrogen base) and polymers called nucleic acids (DNA/RNA)
C, H, O, N, P atoms
stores and transmits genetic information, hydrophilic
water bonds
intermolecular forces are polar covalent bonds, intramolecular forces are the h bonds
properties of water
less dense in solid form, very high heat capacity, universal solvent, capillary action, polar with negative o
what elements make up all living things
C H O N P
carbon versatility
form single double and triple bonds
practice drawing amino acid