Polymorphism
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
“Object” ref var
Object o;
a reference of type Object can be used to store any object
can be used to acquire polymorphic behaviours
.equals method in Object class
compares the content of two objects of the same class (logical equality)
can be manipulated to work for any pairs of any kind of objects
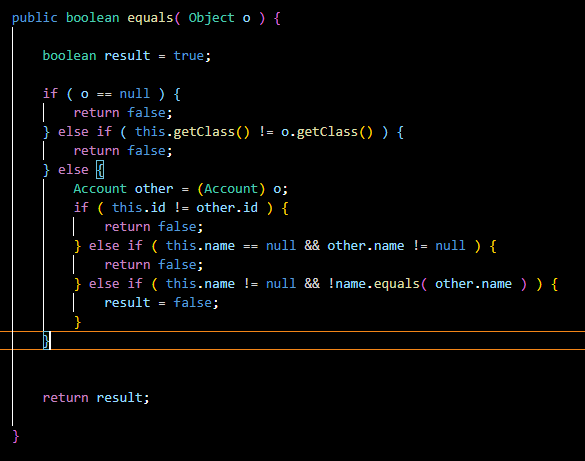
(kind of) general recipe of the .equals method
(this is for the Account class made in lecture)
check if the given obj is ull
check if the given obj and “this obj” is of the same class
***type cast the obj to be Account (Account other = (Account)o)
for each instance var, ensure that they are equal
for prim types, use ==
for ref types (most notably String) use equals method
check null again, this time for the instance ref vars (like String)
instanceof
Suppose you have a statement “s instanceofT T”
returns false if the val of s == null
returns true if the class of obj s is compatible with the type T at runtime, so either:
T is a class, and s is an instance of T or an instance of a subclass of T
T is an interface, and s is an instance of a class that implements T
before typecasting (vv important for .equals method and other methods that compare objs with each other ), ALWAYS:
PRECEDE with the “instanceof” operator

whenever an element is removed from the “generic” data structure, the reference must be ____
cast to the original type of the object.
advantage and drawback of generic data structures
advantage: a single implementation can be used in a variety of contexts
drawback: the type of the return value of the access methods (getters) is Object, consequently requiring type casting back to its proper specialized type THUS we need Generics
Generics
a concept unique to java
introduces CLASS parameters (whereas we only had parameters for methods before)
see keyword in image → <T> reps the Type of objs to be stored in the class (Pair in this case)

the body of a parametized class

type declaration involving a parametized class
now, typecasting would not be necessary for the generic data structure known as Pair, so the type validation step done at compile-tiime would not be sacrificed but it can enjoy the advantage of being a generic data structure
a Pair declared with Pair<Integer> can only store Integer objs
helps detect errors at compile time

defining a generic type cont’d (for Pair class)
now the first item and the second item in the pair do not have to be the same type
