a level chemistry
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
what are the charges and masses of a proton, neutron, electron?


what is an isotope?
atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons and different masses
why do isotopes have similar chemical properties?
same electronic structure/same number of electrons
what is relative isotopic mass?
the mass of an isotope compared with 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
what is relative atomic mass?
the weighted mean mass of one atom compared to 1/12th of the mass of one atom of carbon-12
what is relative molecular mass?
the average mass of a molecule compared to 1/12th of the mass of one atom of carbon 12
formula for zinc and gold ions
Ag+, Zn2+
how do you calculate the relative atomic mass of an element?
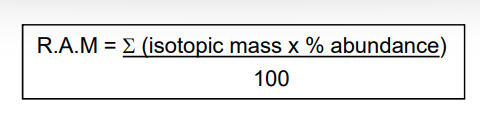
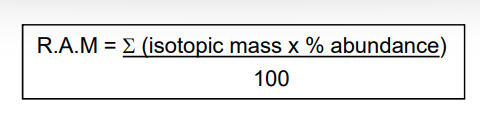
what does isoelectronic mean?
atoms and ions that have the same number of electrons
what do covalent compounds not contain?
covalent compounds don’t contain ions → exist as molecules with a small number of atoms bonded together
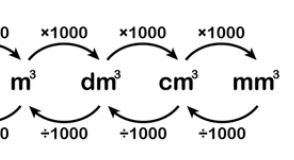
conversions (m3)

what is a mole?
the amount of substance which contains as many elementary particles as there are atoms in exactly 12g of carbon-12
what is avogadro’s constant?
6.02×1023
how to calculate number of particles
number of particles = moles x avogadros constant
what is molar mass?
the mass in (g) of one mole of susbtance (gmol-1)
for which molecules do we multiply the ram by 2?
diatomic elements (HNFOICB)
equation for number of moles
moles = mass/mr
how do you deduce the molecular formula from empirical formula?
mass of molecular/mass of empirical
then multiply each number by that answer
equation for reacting volumes
n = volume/24 or 24,000
what is the definition for molar gas volume?
the volume per mole of gas molecules at a stated temperature and pressure
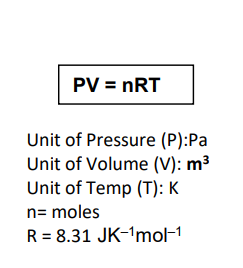
equation for ideal gas
pV = nRT

how do we go from K to celcius?
-273
equation for reacting solutions
n=cV/1000
name the vessel you make a standard solution with?
volumetric flask
how and with what should you weigh solids?
weigh by difference on a balance (top pan)
how do you know you have correctly filled a volumetric flash or pipette?
bottom of the meniscus touches the fill line
what are the two ways to prepare a standard solution?
dissolving a solid in distilled water
diluting a known conc of an existing solution with distilled water
how to calculate new diluted concentration
origjnal concentration x original volume/new diluted volume
equation for % uncertainty
number of readings x uncertainty on equipment/quantity measured x 100
equation for % yield


equation for atom economy
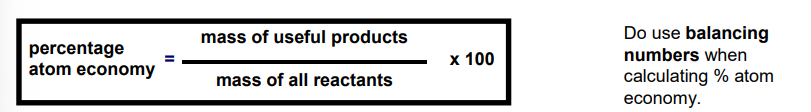

table of ions you need to know
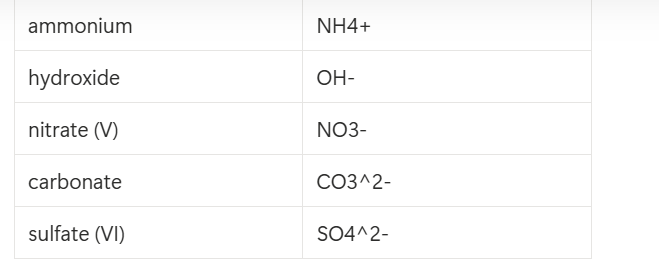

diatomic elements


state symbols expected to know at room temperature
H2, O2, N2, Cl2 are all gases
metals are all solids (mercury exception)
most ionic substances formed in water are also aqueous
most acids (HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, H3PO4) are also aqueou
what is a covalent bond?
the strong electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms
what is a dative covalent bond?
a covalent bond where only one of the bonded atoms donates both electrons being shared
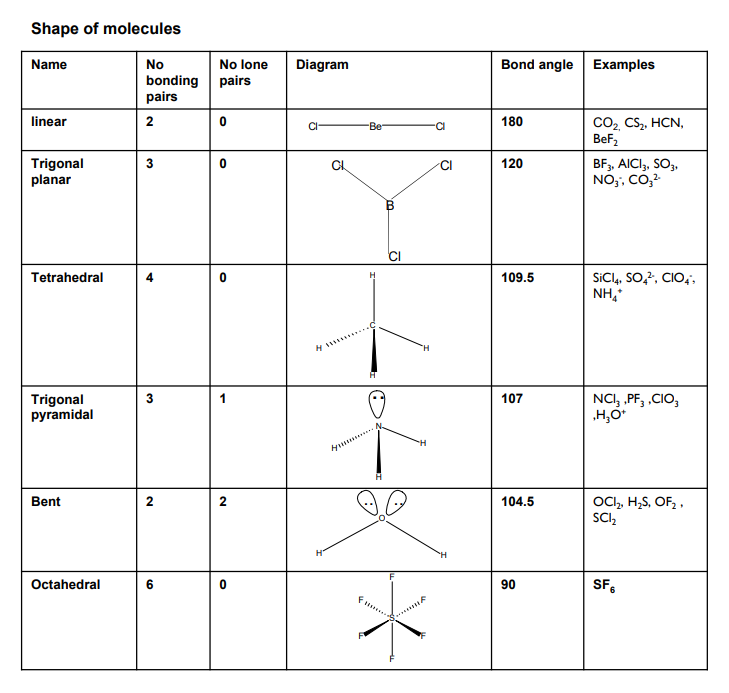
shapes of molecules

how can the strength of an induced dipole-dipole interaction increase?
the number of electrons in the molecule or atom increases
the surface contact of the molecules or atoms increases
what is electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond.
what are the factors that affect electronegativity?
increases across a period as the number of protons increases and the atomic radius decreases because electrons in the same shell are pulled in more
decreases down a group because distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons increases and the shielding of inner shell electrons increases
what are the features of a polar molecule?
difference in electronegativity
unsymmetrical
lone pair of electrons around central atoms
why can’t symmetrical molecules be polar?
dipoles will cancel each other out and there will be no overall permanent dipole
why do the boiling points increase as you go down group 7?
increasing number of electrons in the bigger molecules causing an increase in the size of the induced dipole–dipole interactions (making them stronger) between the molecules.
why is X a polar molecule but Y is not?
X is an unsymmetrical molecule so the dipoles cancel out
Y is a symmetrical molecule so the dipoles do not cancel out
describe permanent dipole-dipole forces
occurs between polar molecles
stronger than IDDI
asymmetrical
occurs in addition to IDDI
explain how permanent dipole-dipole forces arise between xy molecules
x is more electronegative than y so permament dipole forms
the x in one molecule is attracted to the y in another molecule
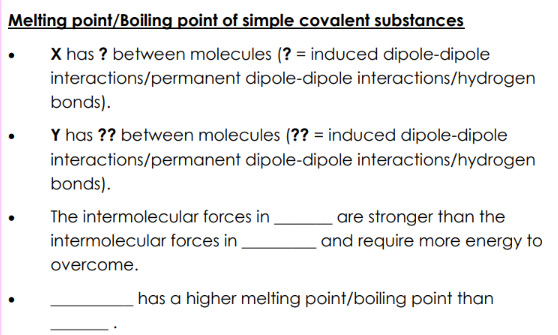
difference in m.p/b.p between simple covalent molecules (size)
X has more electrons than Y so has more/stronger induced dipole-dipole interactions between molecules
that require more energy to overcome.
difference in m.p/b.p between simple covalent molecules (same size but one is branched)
X is more branched than Y
As the branching increases the surface contact decreases
Induced dipole-dipole forces between molecules are weaker so less energy required to overcome.
melting point/boiling point of simple covalent substances

melting point for ionic substance and metallic substance


how induced dipole-dipole forces arise


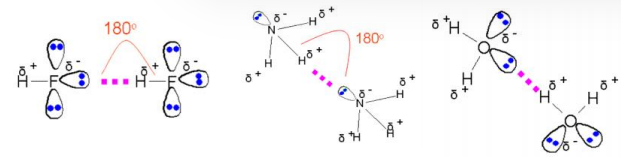
what is hydrogen bonding?
an intermolecular bonding between molecules containing NOF and the H atom of -NH, OH, HF
there is a large electronegativity difference between the H and the NOF
occurs in addition to IDDI
strongest intermolecular bonding
what are the two anomalous properties of water and explain them?
higher melting/boiling point than expected
H2O has strong hydrogen bonds holding the water molecules together
alot of energy is needed to overcome the intermolecular forces
solid is less dense than the liquid (ice floats on water)
hydrogen bonds hold the H2O molecules in an open lattice structure
draw hydrogen bonding in water and ammonia

what is a metallic bond?
the strong electrostatic attraction between cations and delocalised electrons
properties of simple covalent materials


properties of giant covalent lattices


properties of giant ionic substances


properties of giant metallic substances


structure, bonding and particles of substances


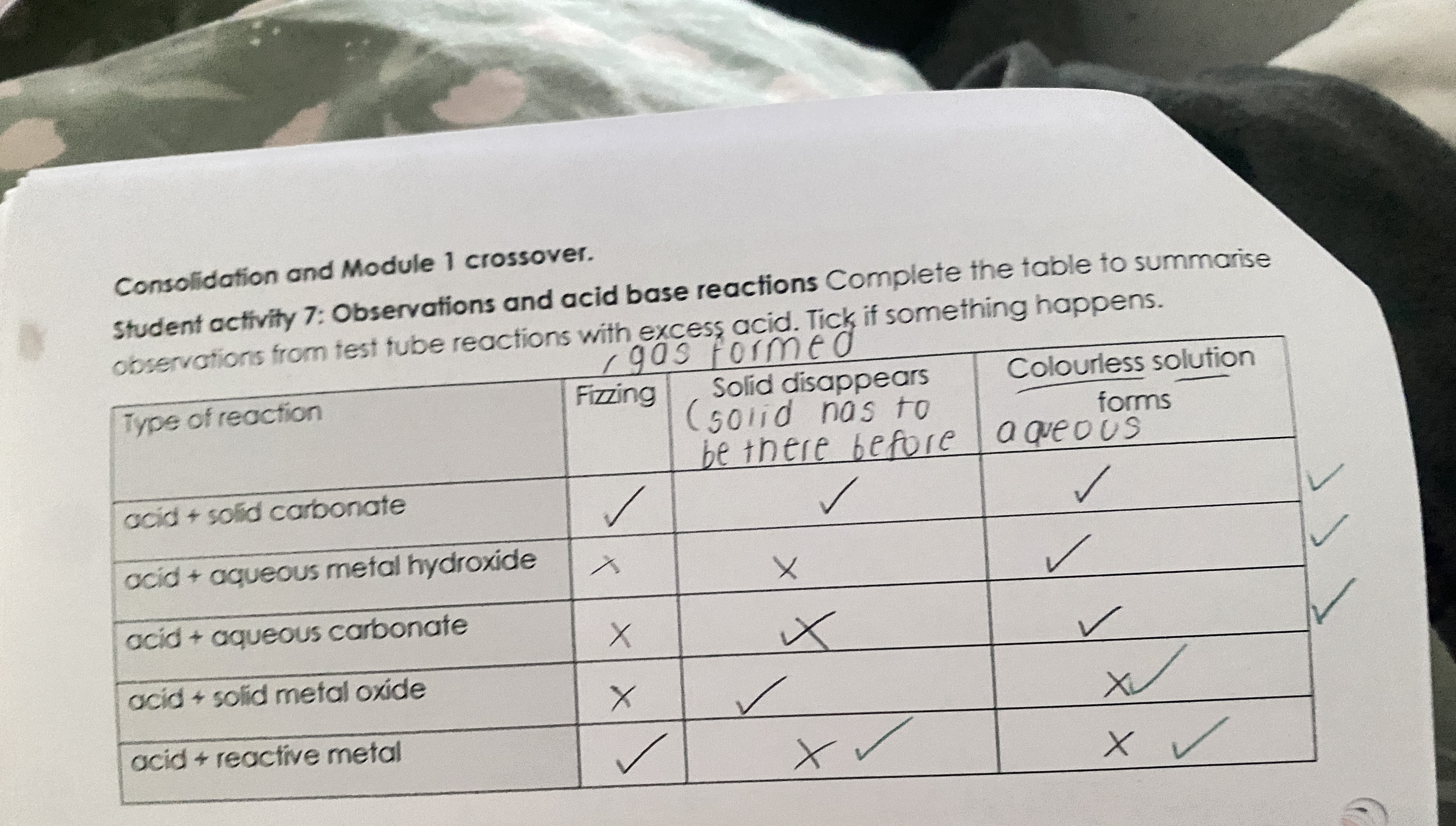
what do acids do?
releases H+ ions in aqueous solutions (proton donors)
what do alkalis do?
release OH- in aq solutions
what do bases do?
react with acids to form salts (neutralisation)
what is a strong acid?
proton donors that completely dissociate in aq solutions
what is a weak acid?
proton donors that partially dissociate in aq solutions
what are bases?
proton acceptors
what does acid + alkali make?
salt + water
what does acid + metal oxide make?
salt + water
what does acid + metal carbonate
salt + water + carbon dioxide
what does acid + ammonia make?
ammonium salt
how do you write an ionic equation?
solids liquids and gases cannot be separated into ions → so stay the same in the ionic equation
cancel out ions that are the same
how do you prepare a 250cm3 standard solution?


observations and acid base reactions

what is oxidation?
loss of electrons and decrease in oxidation number
what is reduction?
gain of electrons or decrease in oxidation number
rules of oxidation


how to name using roman numerals


what is disproportionation
same element is oxidised and reduced
maxiumum amount of electrons each shell can have


what is an orbital?
a region around the nucleus that can hold two electrons with opposite spins
write the subshells in order of increasing energy
spdf
how many orbitals does an s subshell have?
1
how many orbitals does an p subshell have?
3
how many orbitals does an d subshell have?
5
how many orbitals does an f subshell have?
7
how do you calculate the number of electrons of each subshell?
multiply by 2
what are the subshells in each shell?


what are the subshells in increasing energy (electronic configuration)
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 4d, 4f
what are the 3 rules for determining electronic configuration?
subshells filled in order of increasing energy, lowest energy levels are filled first
an orbital cannot contain more than two electrons and then only if they have opposite spins
the orbitals of a subshell must be occupied singly and with parallel spin before being occupied in pairs
short hand electronic configuration
Ne - 10
Ar - 18
Kr - 36
what is the electronic configuration of chronium and copper?
this creates either a full or half full 3d orbital which gives the atom increased stability
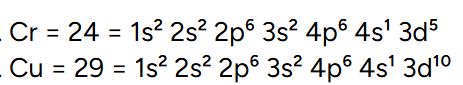
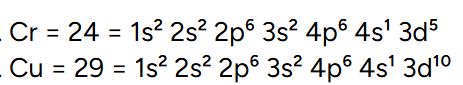
what is the rule for transition metal ions?
4s always lost before 3d
how is the periodic table separated into blocks?
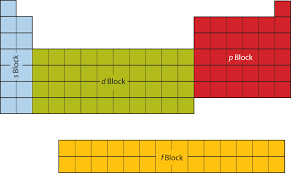

why is Fe considered a d block element?
because its highest energy electron is found in the d subshell
describe the structure of the periodic table
elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic (proton) number
elements are arranged in vertical columns called groups → each element in a group has atoms with the same number of outer-shell electrons / elements in the same group have similar chemical properties
elements are arranged in horizontal rows called periods → the number of the period gives the number of the highest energy electron shell in an element’s atoms
define periodicity
repeating trends in physical and chemical properties across a period
what is first ionisation energy?
the energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms of an element to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions
write the formula for first ionisation energy


how does atomic radius affect ionisation energy?
The greater the distance between the nucleus and outer electrons, the less the nuclear attraction
The larger the atomic radius, the lower the ionisation energy
how does nuclear charge affect ionisation energy?
The more protons there are in the nucleus of an atom, the greater the nuclear attraction
The greater the nuclear charge, the larger the ionisation energy