Cardiovascular Fitness
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
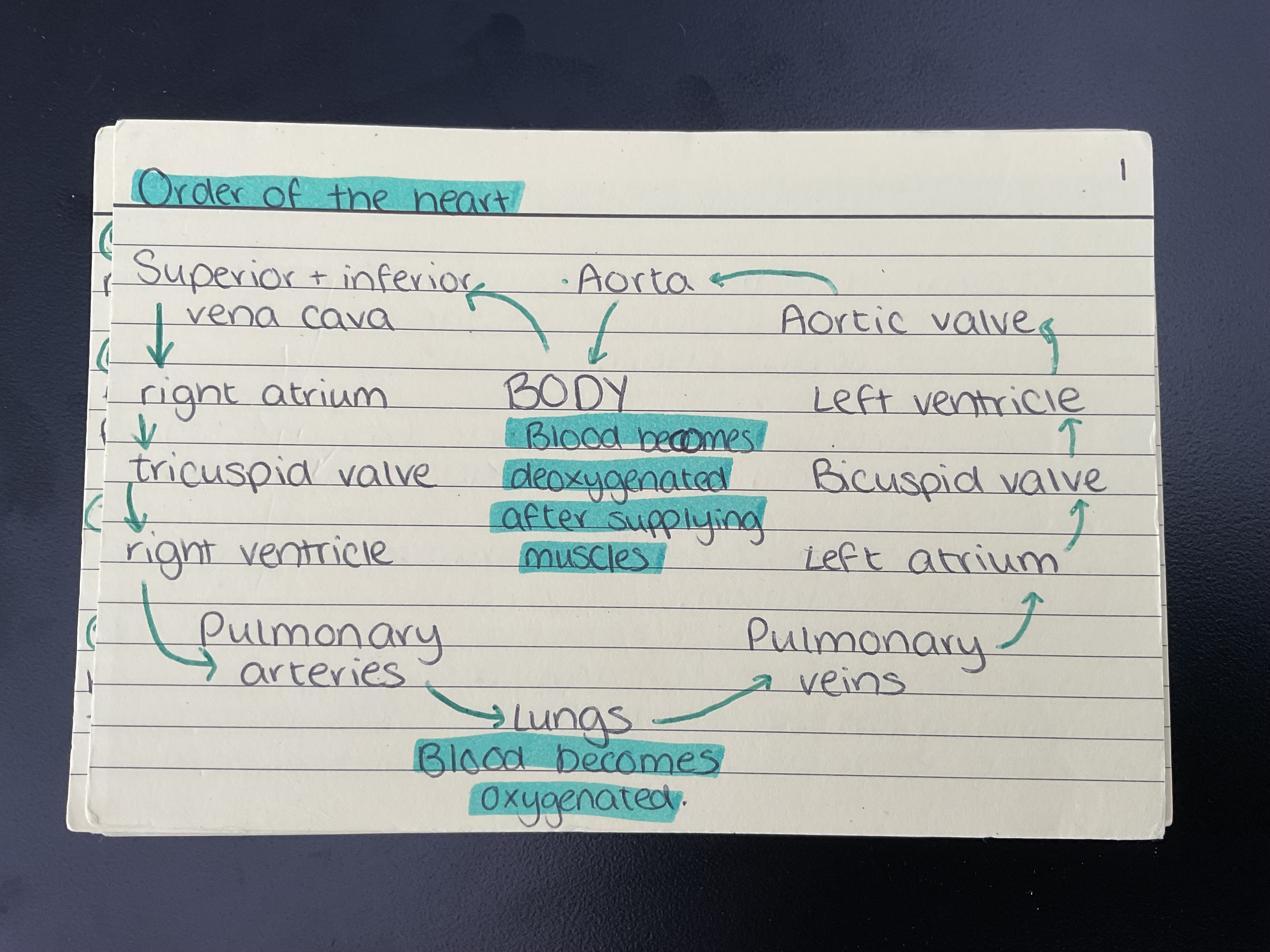
Order of the heart
Cardiac Conduction System
Specialised cells in the wall of heart sends electrical impulses to the cardiac muscle → contraction
Beat starts in heart muscle (myogenic) with an electrical signal in sinoatrial node
Electrical impulse spreads through heart in a wave of excitation
Impulse spreads through atria walls, causing them to contract to force blood into the ventricles
Impulses passes through the atrioventricular node found in the atrioventricular septum
AVN delays transmission of impulse for approx. 0.1 second to enable the atria to fully contract
Impulse passes down through some specialised fibres (Bundle of His), located in septum
Bundle of His branches out into 2 Bundle branches, then into small branches (purkinje fibres), spread throughout the ventricles causing them to contract
Neural Control Mechanism
Sympathetic nervous system - heart go faster
Parasympathetic nervous system - returns heart to resting level
Consist of central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (nerve cells that transmit to and from the CNS)
Two systems are co-ordinated by the cardiac control centre (medulla oblongta) - detects CO2 levels
Chemoreceptors
Found in carotid arteries and aortic arch
Sense chemical changes. Detect increases in CO2 in blood
Increase concentration of CO2 in blood stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, heart beating faster
Baroreceptors
Contain nerve endings that respond to the stretching of the arterial wall (blood pressure)
Increase blood pressure ← → Decrease in heart rate
When exercising, they are restricted and do not slow the heart rate down
Proprioceptors
Muscles, tendons and joints provide information about body position and movement
When detecting movement/exercise, receptors send an impulse to the SAN to increase heart rate
Parasympathetic system stimulates the SAN to increase heart rate
Cardiac hypertrophy
Thickening of the muscular wall of the heart
Bradycardia
Resting heart rate is below 60 beats per minute
Stroke Volume
Amount of blood pumped out of heart per beat
Starling’s law
Increased stroke volume means that overall cardiac output will increase
Cardiac output
Amount of blood pumped out of the heart per minute
Stroke volume x beats per minute