MOSBY IMAGE PRODUCTION
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
What is atomic mass?
A. The number of protons
B. The number of photons
C. The number of electrons
D. The number of protons plus number of electrons
A. The number of protons
The number of x-ray waves passing a given point per unit time is called:
A. Wavelength
B. Photonic frequency
C. Urgency
D. Frequency
D. Frequency
When a predetermined level of ionization is reached in the ionization chamber, what does the machine do?
A. The unit shuts off as a result of a malfunction
B. The maximum allowable time has been reached
C. A warning light illuminates
D. The exposure is terminated
D. The exposure is terminated
What type of current is required for proper operation of the x-ray tube?
Direct current
Modern rectifiers are made of
Silicon based semiconductor
When performing a quality control test to ensure that adjacent mA stations are accurate, the results must be within this amount of one another:
A. 2% of SID
B. 4%
C. 10%
D. 5%
C. 10%
When a quality control test is performed to ensure that the same exposure factors produce consistent x-ray output, successive exposures must be within this amount of one another:
A. 2% of SID
B. 4%
C. 10%
D. 5%
D. 5% (reproducibility)
When a quality control test is performed to ensure that the collimator is providing appropriate Safety, the result must be within this amount:
A. 2% of SID
B. 4%
C. 10%
D. 5%
A. 2% of SID
When performing a quality control test to ensure that the penetrating ability of the x-ray beam is accurate, the result must be within this amount of the control panel setting:
A. 2% of SID
B. 4%
C. 10%
D. 5%
D. 5% (kVp)
The accuracy of collimation at a 60-inch SID must be:
A. ±6 inches
B. ±3 inches
C. ±2 inches
D. ±1.2 inches
D. ±1.2 inches (Collimator must be accurate to within 2% of SID; 2% of 60 is 1.2)
The accuracy of kVp at 70 kVp must be:
A. No longer than 63 kVp and no higher than 77 kVp
B. No longer than 69 kVp and no higher than 71 kVp
C. No longer than 66 kVp and no higher than 74 kVp
D. No lower than 68 kVp and no higher than 72 kVp
A. No longer than 63 kVp and no higher than 77 kVp (kVp must be within 10%)
The feature of the image intensifier that automatically adjusts kVp and mAs during fluoroscopy is the:
A. photocathode
B. electron-focusing lens
C. automatic gain control
D. Automatic exposure control
C. automatic gain control
Automatic gain control
automatically adjusts kVp and mAs during fluoroscopy. This process, also known as automatic brightness control, keeps the image constant during the exam
The energy of position is called:
A. kinetic
B. positive
C. potential
D. synthetic
C. Potential
Electrons in motion in a conductor are called:
A. potential energy
B. heat energy
C. ionizing
D. current
D. current (movement of electrons along a conductor or electric circuit)
What letters designate the first four inner shells of an atom?
A. A, B, C, D
B. W, X, Y, Z
C. N, M, L, K
D. K, L, M, N
D. K, L, M, N (closest to farthest)
Radiation may also exist as particles, such as:
A. radiation only exists as rays
B. alpha and beta particles
C. electrons and protons
D. Waves and quarks
B. alpha and beta particles (radioactive particles and are highly ionizing)
Electromagnetic radiation travels:
A. in curves
B. in straight lines
C. as waves in straight lines
D. at the speed of sound
C. as waves in straight lines
Which of the following surrounds a current running through a conductor?
A. alpha particles
B. magnetic field
C. insulator
D. circuit
B. magnetic field (surrounds an electric charge in motion (current), making electromagnetic induction possible)
Insulator
prohibits flow of e-
The unit of electric current is the:
A. volt
B. ohm
C. ampere
D. resistor
C. ampere
The unit of electromotive force is":
A. volt
B. ohm
C. ampere
D. resistor
A. volt
Electrical generating stations produce what type of current?
A. Direct
B. Altered
C. Pulsating direct
D. Alternating
D. Alternating
The x-ray machine recieves what type of current from the incoming line (comes from power company)
A. 120 watt
B. 240 DC
C. 120-Hz DC
D. 120-Hz AC
D. 120-Hz AC
Which of the following is a property of x-rays?
A. can be focused by collimators
B. possess wavelengths between 1 and 5 angstroms
C. have no effect on chemicals
D. travels in bundles of energy called photons
D. travels in bundles of energy called photons
The composition of the x-ray beam as it leaves the anode is:
heterogenous (many different energies, wavelength)
The composition of the x-ray beam comes from which energy conversions?
A. Photoelectric and compton
B. Characteristic
C. Brems
D. more than one of the above
D. more than one of the above
The primary purpose of filtering the x-ray beam is to:
A. increase contrast
B. improve safety
C. soften beam for proper imaging
D. remove short-wavelength rays
B. improve safety
Total filtration in the x-ray beam must be at least:
A. 2.5 mm lead equivalent
B. 2.5 mm aluminum equivalent
C. the same as the amount of compensating filtration
D. the same as the added filtration
B. 2.5 mm aluminum equivalent
Electron energy is converted to light in what part of the image intensifier tube?
A. input phosphor
B. output phosphor
C. photocathode
D. electrostatic lenses
B. output phosphor
Visible light is converted into an electronic image in what part of the image-intensifier tube?
A. input phosphor
B. output phosphor
C. photocathode
D. electrostatic lenses
C. photocathode
X-ray energy is converted to light energy in what part of the image-intensifier tube?
A. input phosphor
B. output phosphor
C. photocathode
D. electrostatic lenses
A. input phosphor
Three-phase, six-pulse equipment produces how much higher average photon energy?
A. 1.41%
B. 41%
C. 1.35%
D. 35%
D. 35% (The calculation of heat units three-phase, six-pulse equipment is kVp × mAs × 1.35, producing x-ray photons with 35% higher average photon energy.)
Three-phase, 12-pulse equipment produces how much higher average photon energy?
A. 1.41%
B. 41%
C. 1.35%
D. 35%
B. 41% (The calculation of heat units three-phase, 12 pulse equipment is kVp × mAs × 1.41, producing x-ray photons with 41% higher average photon energy.)
A compound's smallest component is the:
molecule
The ability to do work defines
Energy
A change in wavelength will always correspond to a change in:
A. x-ray beam speed
B. altitude
C. frequency
D. amplitude
C. frequency
The movement of electrons between objects is called:
A. electromagnetism
B. electrostatics
C. electrification
D. electrodynamics
C. electrification
The laws of electrostatics state that:
A. unlike charges attract; like charges repel
B. electrostatic charges reside on the outer surface of a conductor and are concentrated at the area of least curvature
C. only positive charges move
D. like charges attract; unlike charges repel
A. unlike charges attract; like charges repel
Home
Opposing voltage created in a conductor by passing alternating current through it describes:
A. electromagnetism
B. electrodynamics
C. self-induction
D. mutual induction
C. self-induction
The simplest type of current, this voltage (and accompanying current) flows as a sine wave, begins at zero, peaks at full value at the crest of the wave, returns to zero, reverses, and again peaks on the inverse portion of the cycle at the trough. This describes:
single phase
Voltage wave forms are created 120 degrees out of phase with one another. This describes:
3-phase
The x-ray circuit depends on a constant source of power, has power coming into the radiology department may vary, keeps incoming voltage adjusted to the proper value, and usually operates automatically but may be manually adjusted on older equipment. This is the:
A. line voltage compensator
B. phototimer
C. autotransformer
D. ionization chamber
A. line voltage compensator
Select all of the following that are condition(s) necessary for the production of x-rays:
1. Source of electrons
2. Acceleration of electrons
3. Sudden stoppage of electrons against target material
4. Rotating anode
1, 2, 3
Source of electrons, Acceleration of electrons, Sudden stoppage of electrons against target material
This device is also known as a variable transformer:
A. autotransformer
B. step-up transformer
C. step-down transformer
D. x-ray generator
A. autotransformer (provides for a variation of kVp)
This device is placed in the circuit between the autotransformer and the high-voltage transformer:
A. ionization chamber
B. rectifier
C. prereading voltmeter
D. cathode
C. prereading voltmeter (foresees and indicates the kilovoltage that will be flowing through the tube once the exposure is made)
This device is wired in the circuit between the autotransformer and the high-voltage transformer:
A. timer
B. rectifier
C. step-down transformer
D. cathode
A. timer
When an AEC is used, the backup timer:
A. protects the patient from overexposure
B. prevents the x-ray tube from overheating
C. replaces the radiographers professional judgement
D. more than of the above
D. more than of the above (The backup timer protects the patient from overexposure and prevents the x-ray tube from overheating)
The operating portion of this device consists of silicon-based n-type and p-type semiconductors:
rectifier
Full-wave rectification produces
A. direct current
B. alternating current
C. pulsating direct current
D. pulsating alternating current
C. pulsating direct current
Following single-phase full-wave rectification, the waveform contains two pulses per cycle, or:
A. 60 pulses per second
B. 120 pulses per second
C. 2 pulses per second
D. 360 pulses per second
B. 120 pulses per second
The voltage actually used in three-phase, six-pulse units is about:
A. 99% of the kVp set on the control panel
B. 96% of the kVp set on the control panel
C. 87% of the kVp set on the control panel
D. 50% of the kVp set on the control panel
C. 87% of the kVp set on the control panel (3p6p ripple 13%: 100-13=87% of kVp)
The voltage actually used in three-phase, 12-pulse units is about:
A. 99% of the kVp set on the control panel
B. 96% of the kVp set on the control panel
C. 87% of the kVp set on the control panel
D. 50% of the kVp set on the control panel
B. 96% of the kVp set on the control panel (ripple 4%; 100-4=96%)
When going from single-phase to three-phase or high-frequency machines, kVp values may be:
A. decreased 12% to 16%
B. increased 10% to 20%
C. decreased 20% to 25%
D. increased only slightly
A. decreased 12% to 16%
This is wired between the rectifier and the x-ray tube:
A. prereading voltmeter
B. milliammeter
C. transformer
D. semiconductor
B. milliammeter
The target angle allows for a:
A. larger actual focal spot and a smaller effective focal spot
B. smaller actual focal spot and a larger effective focal spot
C. grid-controlled assembly to be added
D. smaller anode to be used
A. larger actual focal spot and a smaller effective focal spot (The larger the actual focal spot, the greater the heat capacity; the smaller the effective focal spot, the greater the radiographic image sharpness.)
What supports and protects the x-ray tube, restricts leakage radiation during exposure, and provides electrical insulation?
A. glass envelope
B. vacuum
C. tube housing
D. grid-controlled cathode
C. tube housing
The increase in brightness caused by acceleration of the electrons in the image intensifier is called:
A. flux gain
B. minification gain
C. total brightness gain
D. image gain
A. flux gain
Because the output phosphor is smaller than the input phosphor, there is an increase in brightness, called:
A. flux gain
B. minification gain
C. total brightness gain
D. image gain
B. minification gain
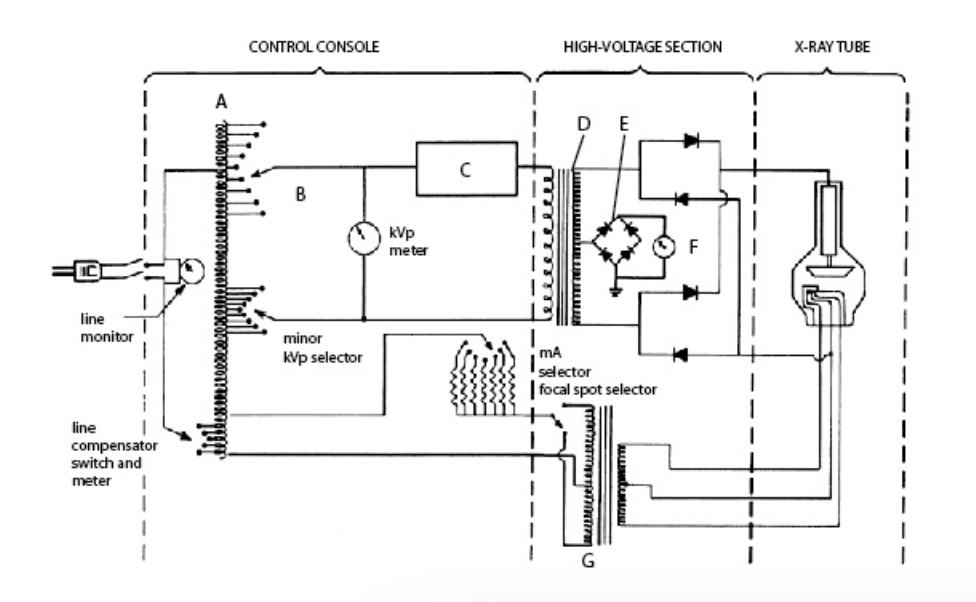
In this diagram, B is the:
A. mA meter
B. timer
C. kVp select
D. step-down transformer
C. kVp select (major kVp selector, set on the transformer)
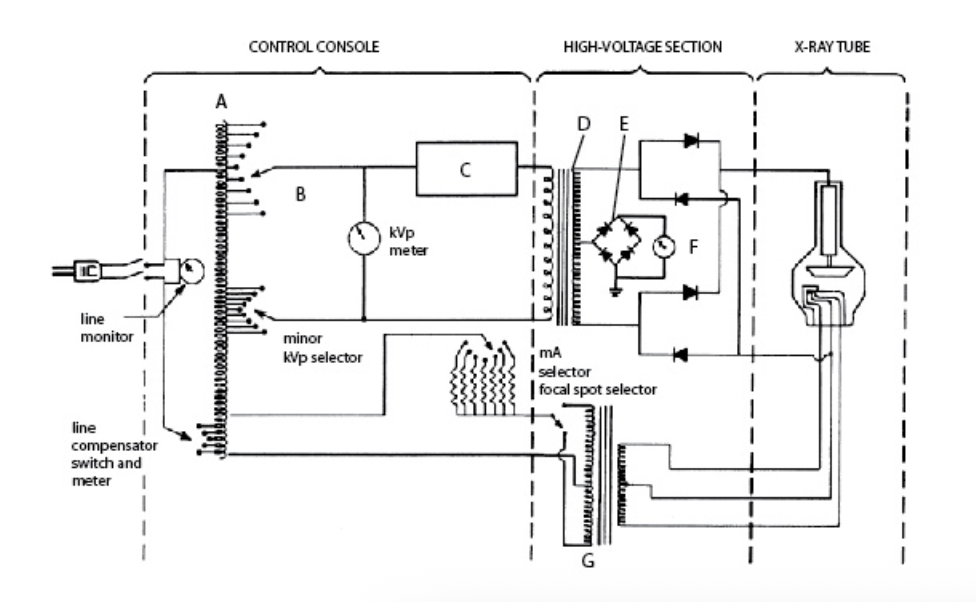
In this diagram, C is the:
A. mA meter
B. timer
C. kVp select
D. step-down transformer
B. timer
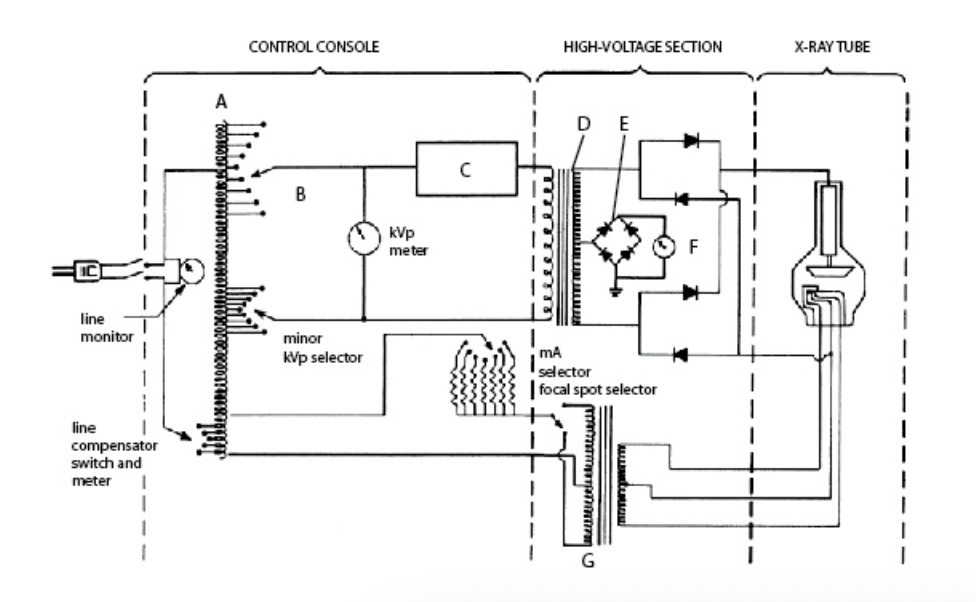
In this diagram, F is the:
A. mA meter
B. timer
C. kVp select
D. step-down transformer
A. mA meter
Which of the following is equivalent to the speed of light in a vacuum?
1. 3 × 108 meters per second
2. 3 × 1010 cm per second
3. 186,000 miles per second
1, 2, 3
In a full-wave rectification circuit, the:
A. negative wave of alternating current is suppressed
B. positive wave of alternating current is suppressed
C. negative wave of alternating current is changed into a second positive wave
D. positive wave alternating current is changed into a second negative wave
C. negative wave of alternating current is changed into a second positive wave
The photocathode of the image intensification tube will convert:
A. x-ray photons into visible light
B. electrons into visible light
C. visible light into electrons
D. electrons into x-ray photons
C. visible light into electrons
By increasing the mA control on the operating console of the x-ray machine, the radiographer can increase the:
A. number of electrons boiled off the filament
B. length of time that electrons take to cross the tube
C. energy of the electrons crossing the gap
D. wavelength of the x-rays produced
A. number of electrons boiled off the filament
The x-ray tube manufacturer's warm-up procedure should be followed to:
A. prevent excessive evaporation of the filament
B. allow for slow heating of the filament
C. cause localized melting of the target
D. allow for even expansion of the target
D. allow for even expansion of the target
In an x-ray tube circuit with four rectifiers, how much will exposure output decrease if one of the rectifiers fails?
A. 25%
B. 50%
C. 75%
D. 100%
B. 50%
Which of the following devices permits the radiographer to vary the kilovoltage in the x-ray circuit?
A. autotransformer
B. induction motor
C. rectifier
D. prereading kilovoltmeter
A. autotransformer
The function of the autotransformer(variable transformer) is to
vary the voltage going to the primary coil of the step-up transformer
The increased brightness of an image resulting from accelerated electrons traveling across to the output phosphor is called:
A. minification gain
B. brightness gain
C. flux gain
D. electrostatic gain
C. flux gain
Rotating anodes can tolerate higher instantaneous heat loads than stationary anodes because:
A. rotating anodes are thicker than stationary anodes
B. heat is distributed over a larger area in rotating anodes
C. rotating anodes are made of materials that can withstand greater heat loading
D. none of the above
B. heat is distributed over a larger area in rotating anodes
How many kilovolts equal 70,000 volts?
A. 7
B. 70
C. 700
D. 7000
B. 70 (70,000 divide by 1000)
X-ray photons have no:
1. energy
2. electric charge
3. mass
2, 3 (x-ray photons are bundles of energy with no mass or charge)
Electron flow from negative to positive is:
A. electric current
B. electromotive force
C. potential difference
D. resistance
A. electric current
Compared with conventional radiography, computed radiography exhibits:
A. poorer visualization of bone and soft tissue
B. narrower exposure latitude
C. better visualization of soft tissue and bone
D. less detail
C. better visualization of soft tissue and bone
In computed radiography, each pixel corresponds to a shade of gray representing an area in the patient known as a(n):
A. pathology
B. detector element
C. voxel
D. artifact
C. voxel
A backup timer is used in automatic exposure devices to:
A. control minimum response time of the equipment
B. limit exposure in case of equipment failure
C. allow longer time exposure for extremely large patients
D. control tissue density altered by pathology
B. limit exposure in case of equipment failure
A digital image may be printed on to film using a:
A. high resolution dot matrix printer
B. photon transfer imager
C. flux capacitor
D. laser camera
D. laser camera
The amount of darkness on a radiograph is primarily controlled by:
A. kVp
B. scatter radiation
C. collimation
D. milliampere-seconds
D. milliampere-seconds
Which of the following grid errors will result in an image that shows normal IR exposure in the middle but decreased IR exposure on the sides and may follow removal and replacement of the grid?
A. upside-down grid
B. off-focus grid
C. lateral decentering
D. grid-focus decentering
A. upside-down grid
Which of the following grid errors will result in an image that shows decreased IR exposure across the entire radiograph?
A. upside-down grid
B. off-focus grid
C. lateral decentering
D. grid-focus decentering
B. off-focus grid
Grid frequency is described as the:
A. height of the lead strips divided by the distance between the lead strips
B. distance between the lead strips divided by the height of the lead strips
C. number of lead strips per inch or centimeter
D. SID at which the grid may be used
C. number of lead strips per inch or centimeter
Grid conversion factor (Bucky factor) is described as the:
A. height of the lead strips divided by the distance between the lead strips
B. distance between the lead strips divided by the height of the lead strips
C. number of lead strips per inch or centimeter
D. amount of exposure increase necessary to compensate for the absorption of image-forming rays and scatter in the cleanup process
D. amount of exposure increase necessary to compensate for the absorption of image-forming rays and scatter in the cleanup process
When kVp is decreased, which of the following happens?
A. receptor exposure increases
B. contrast decreases
C. spatial resolution decreases
D. contrast increases
D. contrast increases because there is increased photelectric interaction
When kVp is increased, which of the following happens?
A. brightness decreases
B. contrast increases
C. spatial resolution increases
D. scale of contrast lengthens
D. scale of contrast lengthens (because there is more uniform penetration of the part by shorter-wavelength rays)
The poorest spatial resolution would be produced by which of the following sets of exposure factors?
A. 60 mAs, 80 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID (object-to-image distance)
B. 30 mAs, 92 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
C. 120 mAs, 92 kVp, 20-inch SID, 4-inch OID
D. 15 mAs, 100 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
C. 120 mAs, 92 kVp, 20-inch SID, 4-inch OID
(Source-to-image distance (SID), rather than mAs or kVp, is a controlling factor in recorded detail. Shorter SID results in poorer recorded detail)
The lowest contrast would be produced by which of the following sets of exposure factors?
A. 60 mAs, 80 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
B. 30 mAs, 92 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
C. 120 mAs, 92 kVp, 20-inch SID, 4-inch OID
D. 15 mAs, 100 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
D. 15 mAs, 100 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID (Higher kVp results in lower contrast)
The lowest patient dose would be administered by which of the following sets of exposure factors?
A. 60 mAs, 80 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
B. 30 mAs, 92 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
C. 120 mAs, 92 kVp, 20-inch SID, 4-inch OID
D. 15 mAs, 100 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID
D. 15 mAs, 100 kVp, 40-inch SID, 4-inch OID (lowest mAs and highest kVp)
Which of the following statements is true?
A. High kVp = high contrast = short-scale contrast = few gray tones
B. Low kVp = high contrast = short-scale contrast = few gray tones
C. When kVp is increased, there is an increase in the number of photoelectric interactions that occur.
D. When kVp is decreased, there is an increase in the number of Compton interactions that occur.
B. Low kVp = high contrast = short-scale contrast = few gray tones
Which of the following statements is true?
A. High kVp = high contrast = short-scale contrast = few gray tones
B. Low kVp = low contrast = long-scale contrast = many gray tones
C. When kVp is increased, there is an increase in the number of Compton interactions that occur.
D. When kVp is decreased, there is an increase in the number of Compton interactions that occur.
C. When kVp is increased, there is an increase in the number of Compton interactions that occur.
How does beam restriction affect contrast?
A. decreases contrast
B. longer scale of contrast
C. shorter scale of contrast
D. no effect on contrast
C. shorter scale of contrast because it reduces the amount of scatter produced, beam restriction results in increased contrast.
mAs controls the:
A. quality of x-rays produced at the anode.
B. quantity of x-rays produced at the cathode
C. quantity of x-rays produced at the filament
D. quantity of x-rays produced at the anode.
D. quantity of x-rays produced at the anode.
As mAs is increased, receptor exposure:
A. decreases
B. increases
C. remains the same
D. inreases in the same amount
D. inreases in the same amount (directly proportional)
The relationship between mAs and density is governed by what law or rule?
A. ohm’s law
B. Reciprocity law
C. inverse law
D. power equation
B. reciprocity law
As kVp increases, a greater potential difference exists between:
A. tube and patient
B. anode and cathode
C. photoelectric and compton interactions
D. kVp and mAs
B. anode and cathode
As kVp increases, there is an increased production of:
A. long wavelengths
B. low-energy waves
C. short wavelengths
D. electrons
C. short wavelengths (As kVp increases, there is an increased production of high-energy, short-wavelength radiation)
The relationship between kVp and receptor exposure is:
A. indirect
B. directly proportional
C. direct but not proportional
D. inverse
C. direct but not proportional
What new kVp is needed to double receptor exposure if the original kVp is 100?
A. 85
B. 90
C. 105
D. 115
D. 115 (The relationship between kVp and IR exposure is governed by the 15% rule—an increase in kVp of 15% will double IR exposure; therefore, if the original kVp is 100, a kVp of 115 is required to double the IR exposure.)
What new kVp is needed to halve IR exposure if the original kVp is 80?
A. 75
B. 60
C. 68
D. 72
C. 68 (According to the 15% rule, a decrease in kVp of 15% will halve IR exposure. Because 15% of 80 is 12, the new kVp should be 68.)