Atomic Physics (Theory)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Charge of an electron
-1.6 x 10-19 C
Mass of electron
9.1 x10-31 kg
What does an electron orbit?
Nuclei
Who named the electron?
G.J Stoney
Who measured the charge of an electron?
Milikan
Who measured the mass of an electron
J.J Thomson
Why do we use the electron-Volt?
Joule is too large of a unit of energy at the atomic level
How to convert eV to J?
Multiply by 1.6x10-19
How to convert J to eV?
Divide by 1.6x10-19
What is GeV?
Giga-electronvolts
What is keV?
Kilo-electronvolts
What is MeV?
Mega-electronvolts
Draw a diagram of Thermionic Emission
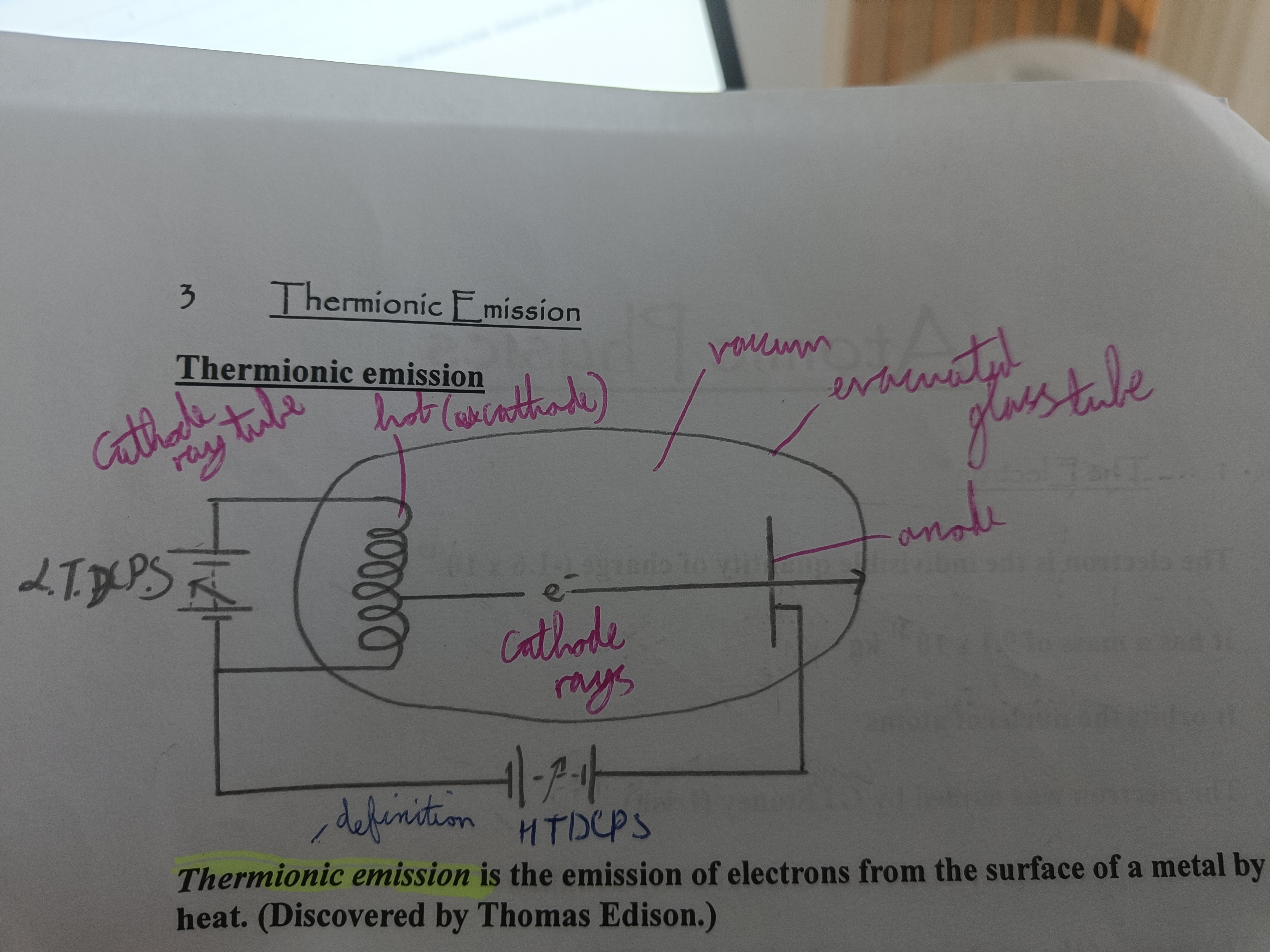
Thermionic emission (Definition)
The emission of electrons from the surface of a metal by heat
Who discovered thermionic emission?
Thomas Edison
Explain thermionic emission
Voltage from LTDCPS pushes electricity through filament which gets hot and electrons are boiled off. They're attracted to the positive of the HTDCPS and pass through the disk if there's a hole. Electrons strike glass and the kinetic energy is converted to light
What colour of light is usually emitted by thermionic emission?
Usually green light
Where must thermionic emission take place in?
Vacuum tube
Why would thermionic emission not work outside of a vacuum?
Electrons would collide with air molecules which would stop/slow them if there was air in the tube
What were beams of electrons originally known as?
Cathode rays
Where is thermionic emission used in? (4)
Televisions. Cathode ray oscilloscopes (CRO). ECG/EEG monitors. Radar displays
What is a Cathode ray oscilloscopes (CRO)?
Heart rate monitor
What is a ECG/EEG monitors?
Monitor brain waves
Draw a diagram of J.J Thomson's e/m experiment (Deflection of cathode rays in electric fields & magnetic fields)
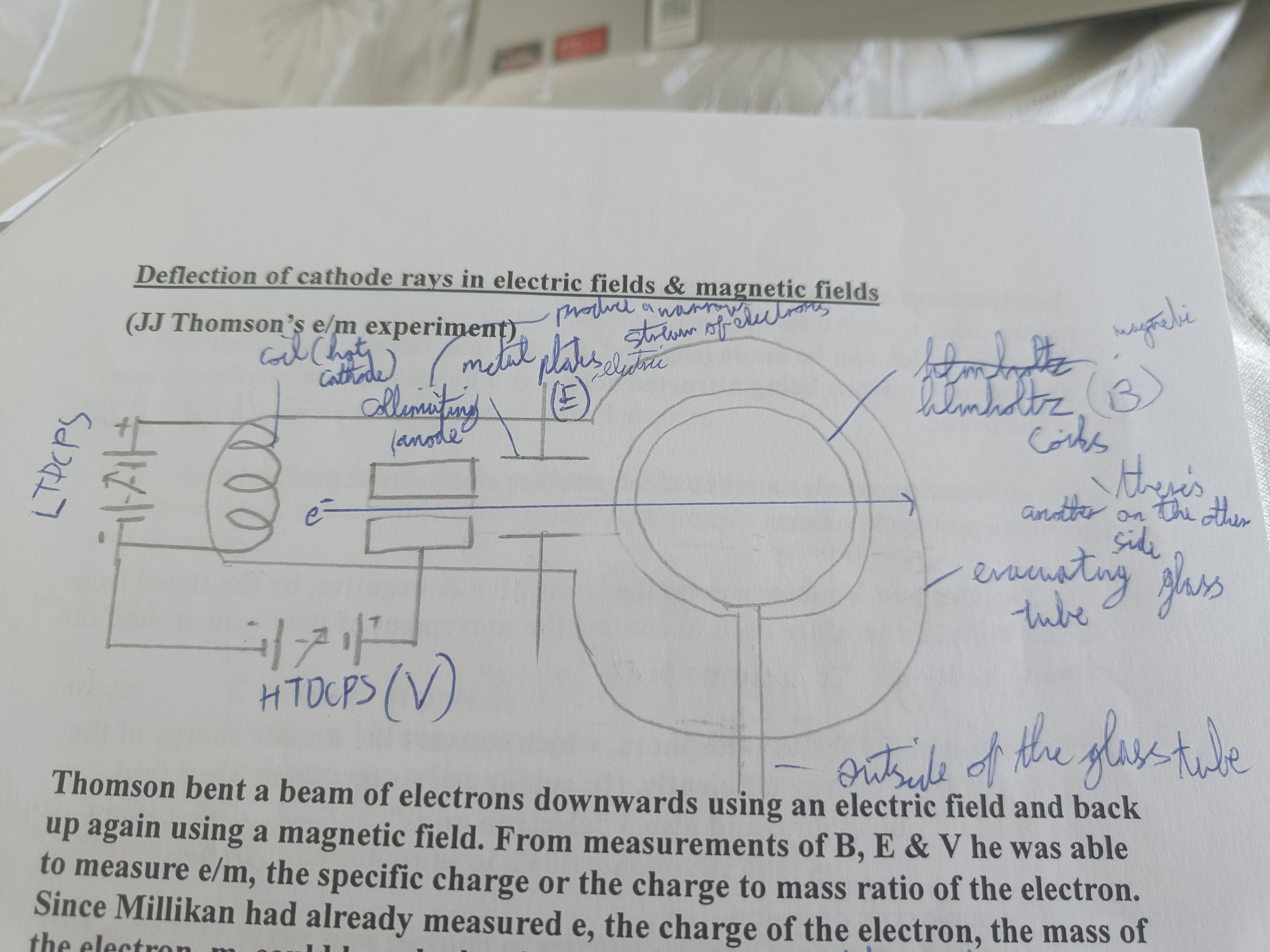
Explain Thomson's e/m experiment
Beam of electrons bent downwards with an electric field and up with a magnetic one. From B E and V he measured e/m the charge to mass ratio of the electron.
Why could J.J Thomson calculate the mass of the electron?
Milikan already measured e
Draw a cathode ray tube
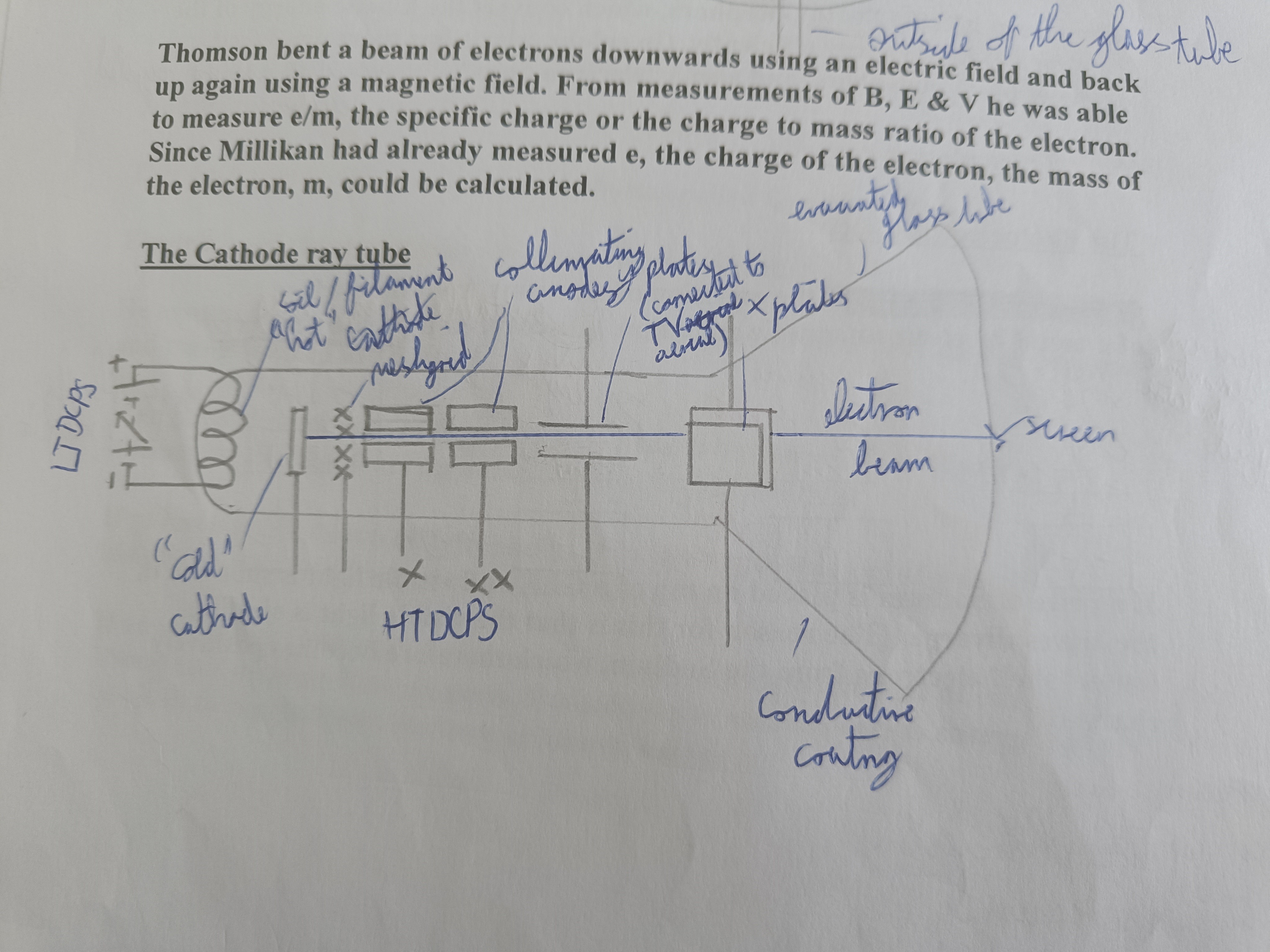
Explain the cathode ray tube
Electrons boiled off. Collimating anodes accelerate electrons across and produce a narrow beam. Screen coated with phosphors which convert the kinetic energy of the electrons to light energy
How is the brightness of the beam controlled (Cathode Ray Tube)?
Grid can be made negative to control amount of electrons being attracted across
How is the movement of the beam (pixel by pixel) controlled?
X-plates Y-plates can be made positive and negative by the signal from the aerial
How many colours in TV?
Red Green Blue
Function of conductive coating
Recycles electron
Photoelectric emission (Definition)
Emission of electrons from the surface of a metal by electromagnetic radiation of a suitable frequency
Who discovered photoelectric emission?
Heinrich Hertz
Example of black-body radiation
Stars
Formula for the energy of a photon
E = hf
What does h stand for (Formula for the energy of a photon)?
Planck's constant
What does E stand for (Formula for the energy of a photon)?
Energy of photon
What does f stand for (Formula for the energy of a photon)?
Frequency of photon
Photon (Definition)
A quantum of electromagnetic energy
Draw a diagram of a photon liberating an electron from an atom
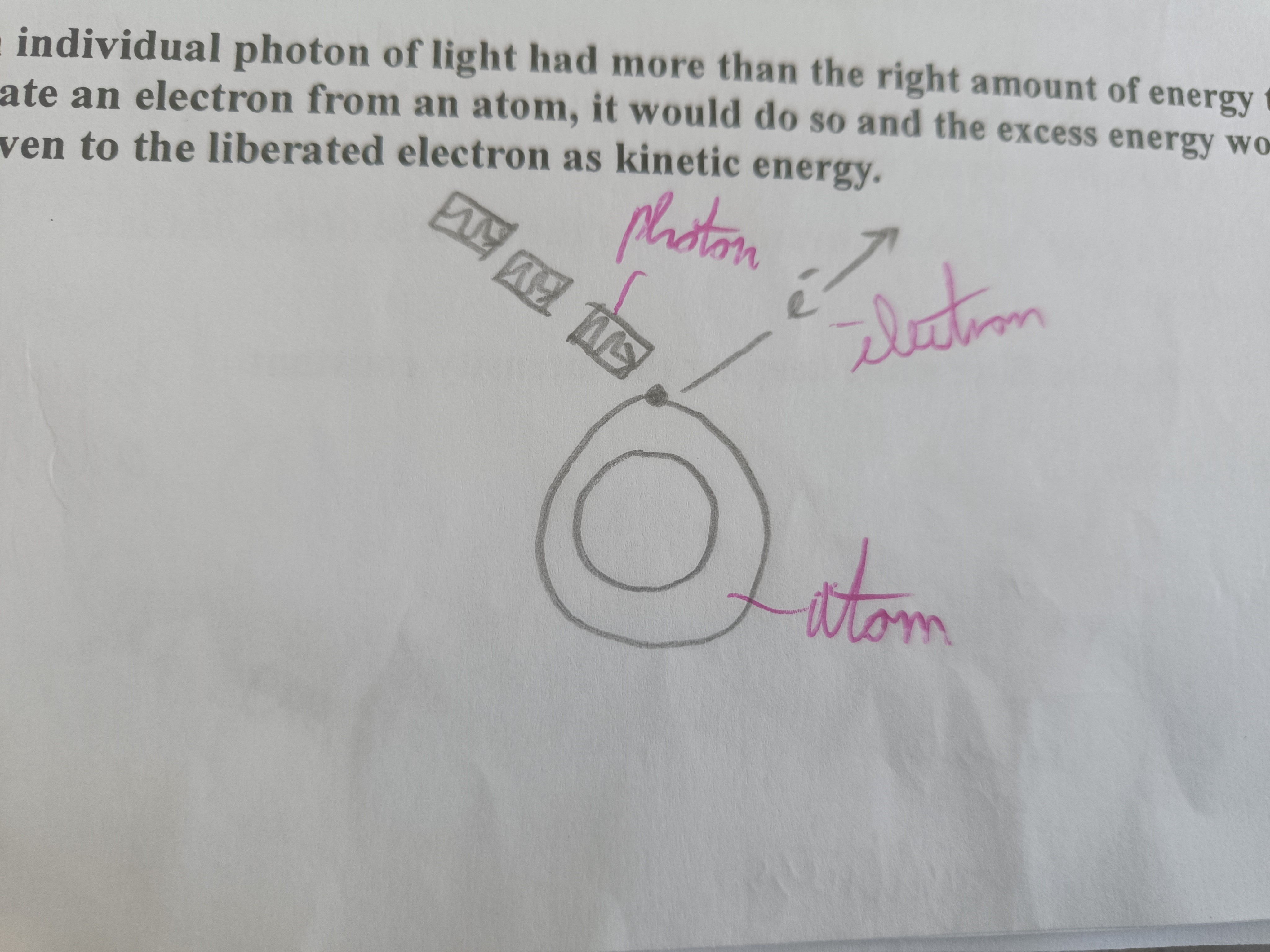
How does light travel, get emitted, get absorbed?
As photons
Explain the photoelectric effect according to Einstein
If a photon of light has less than the required energy to liberate an electron then nothing would happen. When a photon has exactly the energy required it would liberate the electron. If the photon had more energy than the required amount it would liberate the electron and the extra would be given to the liberated electron as kinetic energy
Threshold frequency (Definition)
Minimum frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to liberate an electron from the surface of a metal
Einstein's photoelectric law Formula
E = ϕ + Ek hf=hfo +1/2mv2 hc/λ = (hc/λo)+1/2mv2
What is E? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Energy of photon
What is ϕ? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Work function
What is Ek? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Kinetic energy
What is h? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Planck's constant
What is f (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Frequency of photon
What is fo? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Threshold frequency
What is m? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Mass of electron
What is v? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Velocity of electron
What is c (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Speed of light
What is λ? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Wavelength of photon
What is λo? (Einstein's photoelectric law Formula)
Threshold wavelength
What is work function in Einsteins photoelectric law?
Energy needed to kick out an outer shell electron
When are X-Rays produced?
When high-speed electrons are stopped by a dense metal target
Who discovered X-rays?
Wilhelm Röntgen
Draw a diagram of a hot cathode X-ray tube
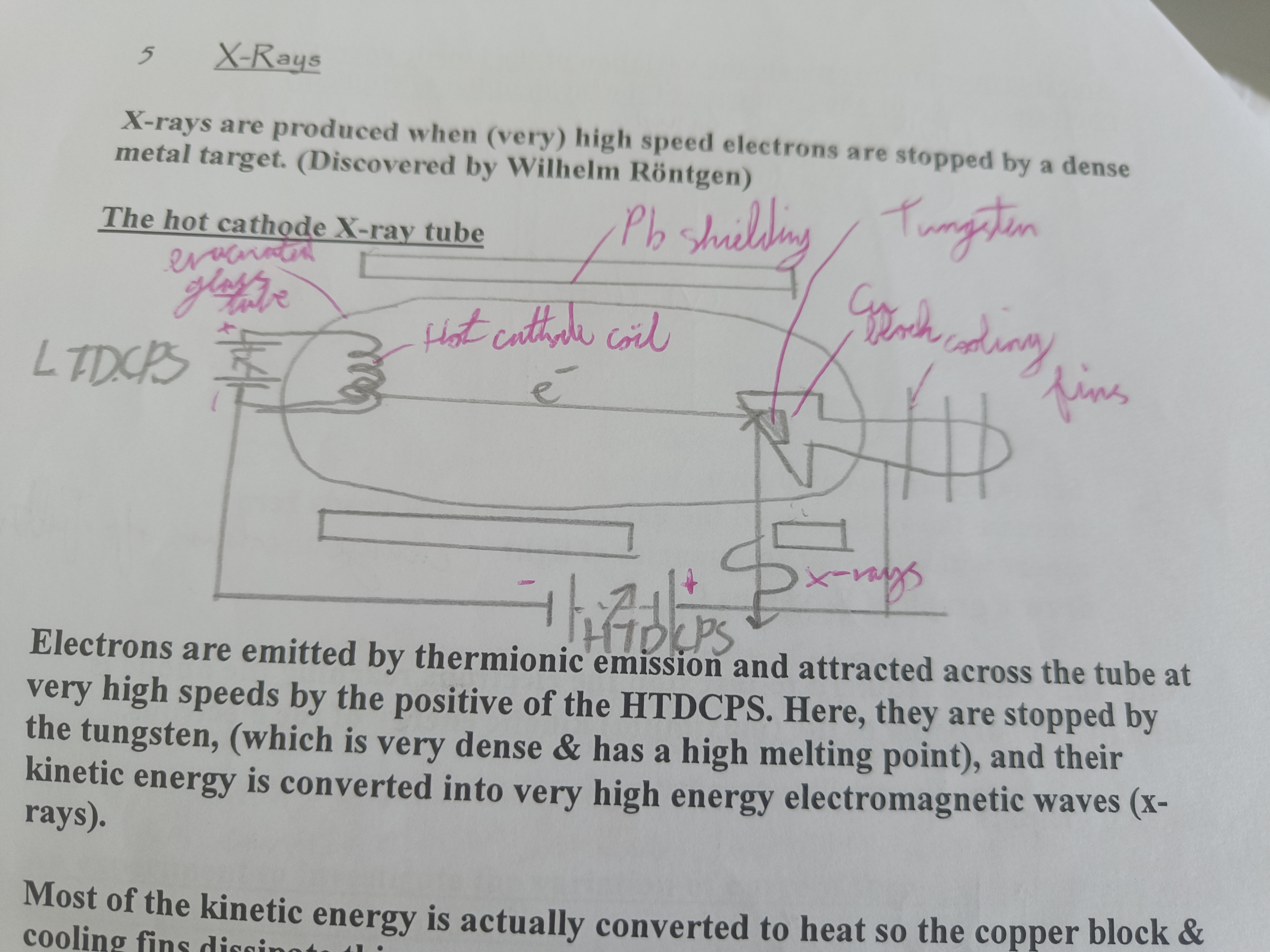
Explain a hot cathode X-ray Tube
Electrons emitted by themionic emission and attracted at high speeds to the positive of the HTDCPS. Stopped by tungsten and their kinetic energy is converted into high energy electromagnetic waves (x-rays)
Features of tungsten
Very dense. High melting point
What is most of the kinetic energy in an x-ray tube converted to?
Heat
Function of copper block and cooling fins
Dissipates heat energy
What is the number of x-rays/intensity directly proportional to?
Number of electrons
How is the number of electrons controlled in a x-ray?
Temperature of the cathode
How is the temperature of the cathode controlled in an x-ray tube?
Voltage of LTDCPS
What is the energy of an x-ray directly proportional to?
Kinetic energy of an electron
What is the kinetic energy of an electron directly proportional to in an x-ray tube?
Voltage of HTDCPS
Higher LTDCPS means what in an x-ray tube?
More x-ray rays
Higher HTDCPS means what in an x-ray tube?
More energetic x-rays
Function of lead shielding in an x-ray tube
Protects the operator
What is x-ray production the opposite of?
Photoelectric effect
Properties of x-rays (3)
Electromagnetic waves. Low ionisation. High penetration
Uses of x-rays (3)
Internal photographs of the human body. Checking for fractures in metal structures e.g. oil rig legs. Curing cancer (radiotherapy)
Hazards of x-rays (2)
Cancer. Mutations
Draw a diagram of a discharge tube
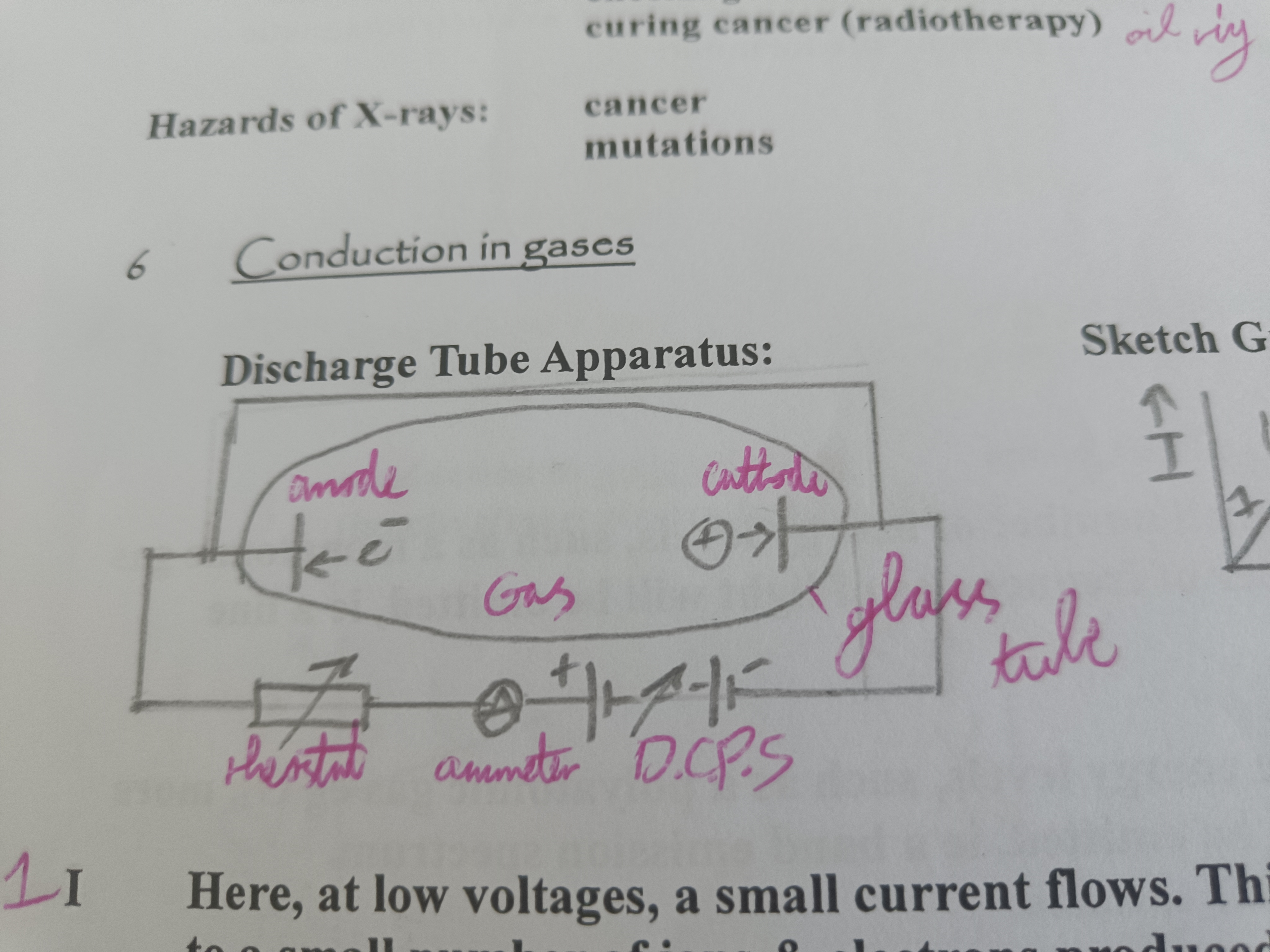
Draw a diagram of a discharge tube sketch graph
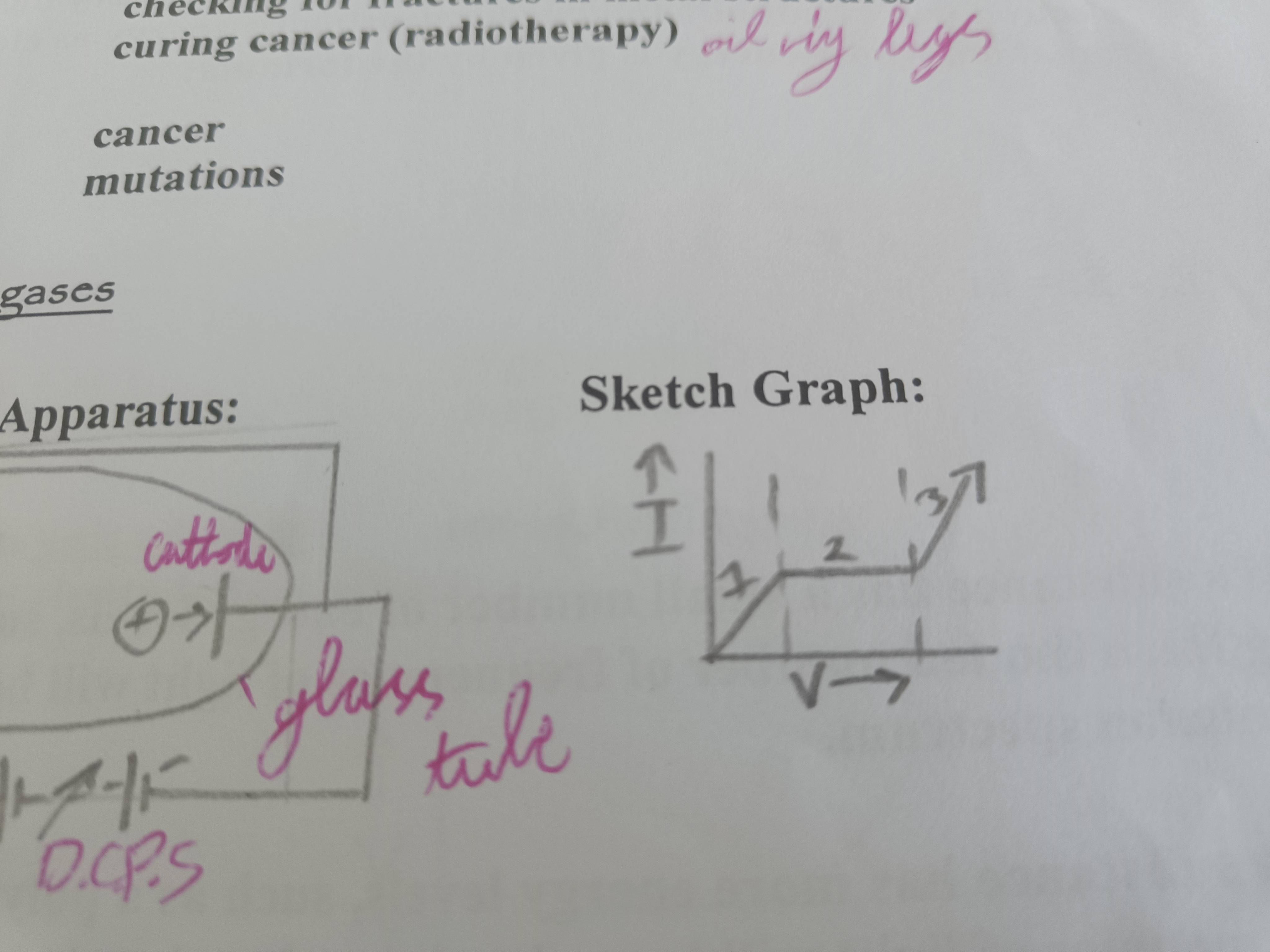
Explain a discharge tube (1 of sketch graph)
At low voltages a small current flows. Current due to ions and electrons produced by radiation. Voltage is increased more ions/electrons reach electrodes increasing the current.
Explain a discharge tube (2 of sketch graph) (Why does the graph stop increasing for some time?)
All ions/electrons produced are reaching electrodes and increasing the voltage has no effect on the current
Explain a discharge tube (3 of sketch graph)
Voltage becomes big enough that ions are travelling so fast that they create more ions by collision. These can produce even more ions increasing the voltage and the current to rise
What radiation produces ions and electrons in a discharge tube?
X-rays or cosmic radiation
What is a current in a gas called?
Discharge
What are the conditions for a gas to produce electromagnetic radiation?
Low pressure and high voltage
What happens when a gas is at a low pressure with a high enough voltage?
Gas emits electromagnetic radiation
What is the electromagnetic radiation produced by a gas called?
Glow discharge
What is a discharge tube also known as?
Fluorescent
Explain how electrons become excited
Electrons occupy lowest energy levels in atoms. However if supplied with heat or electricity electrons become excited. This is unstable and the electron falls back releasing energy as electromagnetic radiation
Formula for excited electrons
Ex-Ey=hf
What is emitted by a substance which has a small number of energy levels?
Line emission spectrum
What is a line emission spectrum?
Limited number of frequencies of light will be emitted
Example of a substance with a small number of energy levels
Monatomic gas e.g. He
What is emitted by a substance which has more energy levels?
Band emission spectrum
What is a band emission spectrum?
More frequencies of light emitted
Example of a substance with more energy levels
Polyatomic gas e.g. O2
What is emitted by a substance which has a lot of energy levels?
Continuous emission spectrum
What is a continuous emission spectrum?
Many many frequencies of light is emitted
Example of a substance with a lot of energy levels
Solids and liquids
What is the reverse of an emission spectrum?
Absorption spectrum
What are absorption spectra used for?
Identify unknown substances