Microscopic anatomy of the urinary system:
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
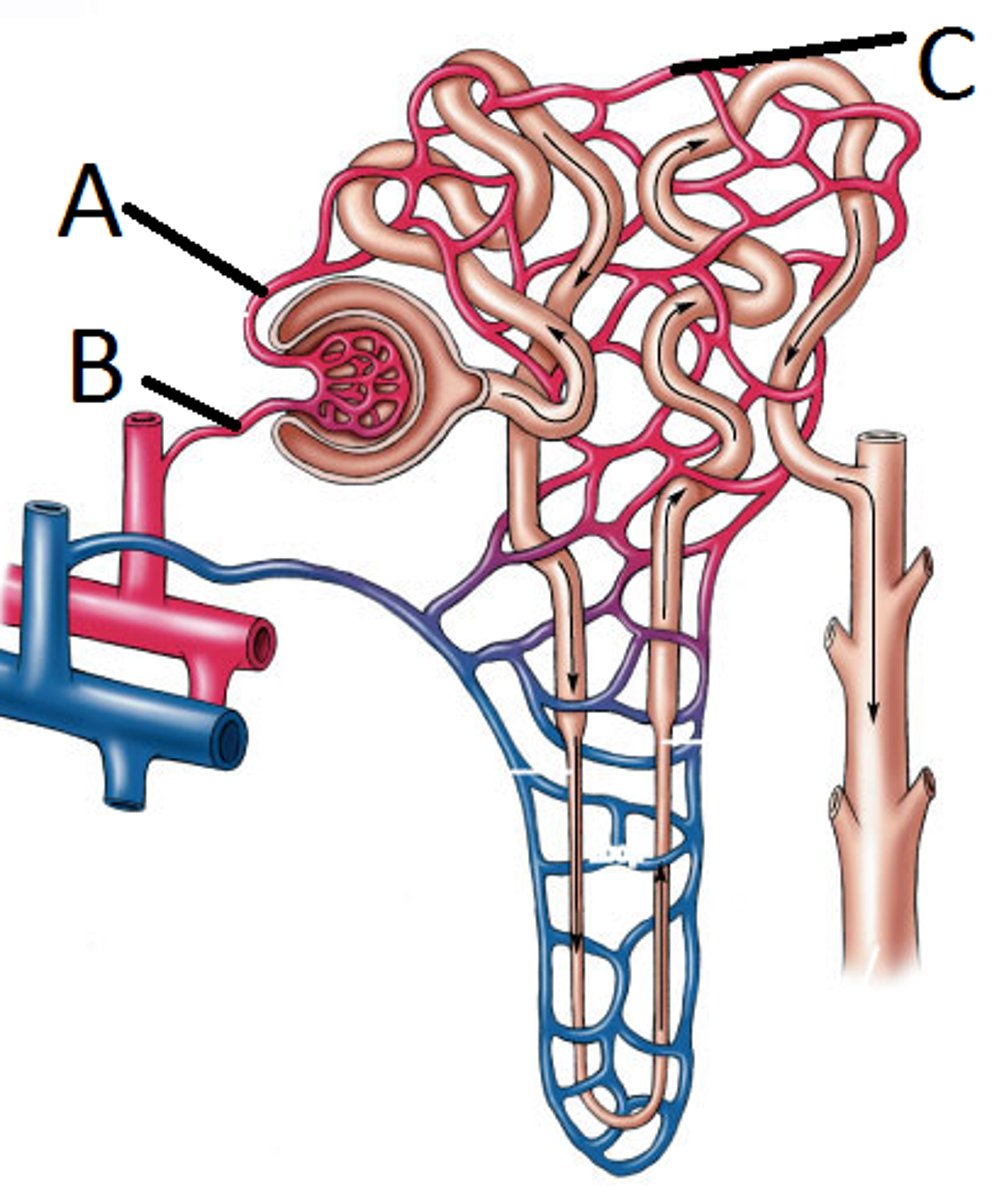
Afferent arteriole
(B). A small blood vessel that carries blood to the glomerulus in the kidney. (supplies)

Glomerulus
(A). A network of capillaries located at the beginning of a nephron that filters blood to form urine.
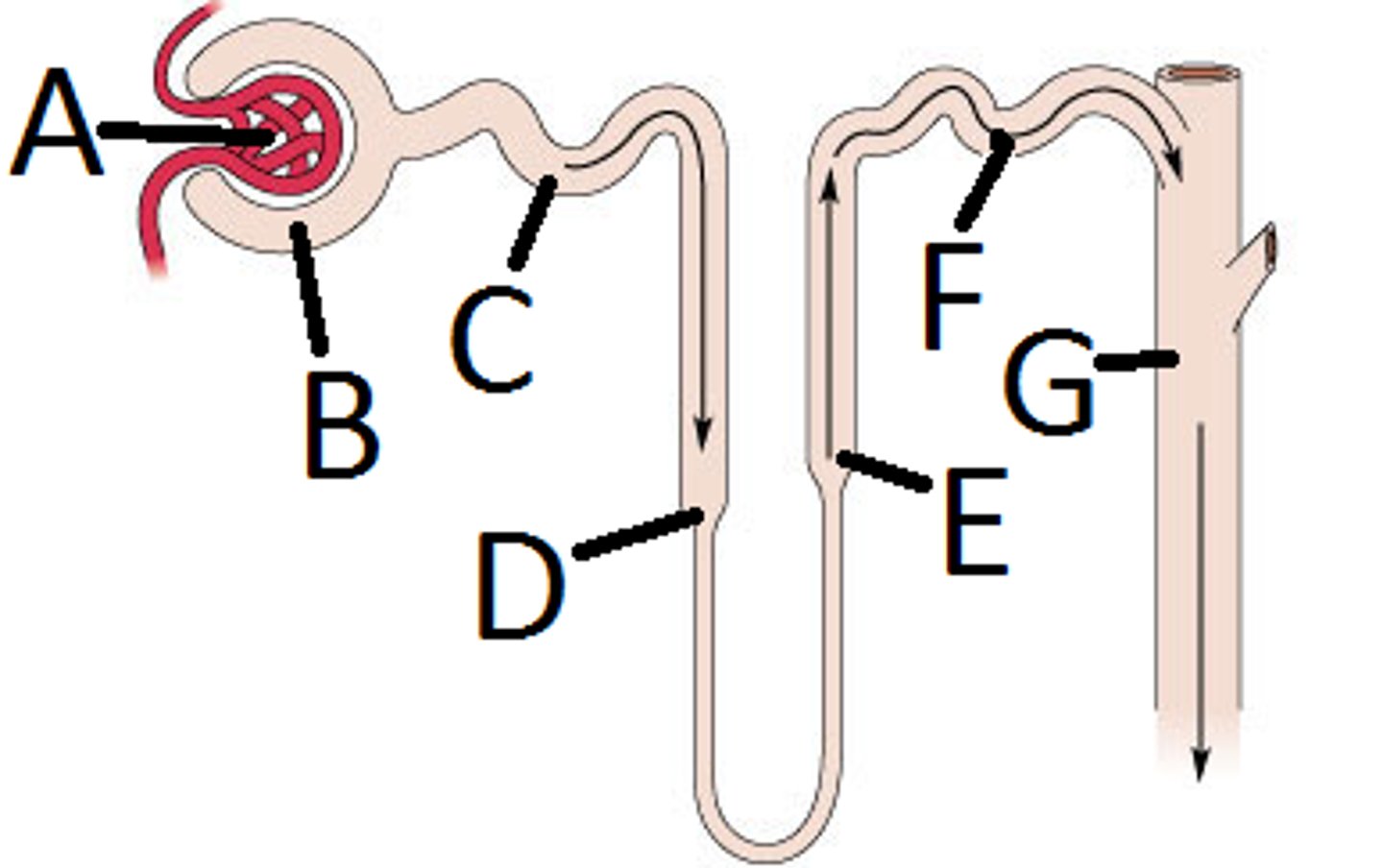
Efferent arteriole
(A) A small blood vessel that carries blood away from the glomerulus. (drains)

Peritubular capillary blood vessels
(C) Small blood vessels that surround the nephron tubules and facilitate the exchange of substances.
Bowman's capsule
A cup-like sac that encases the glomerulus and collects the filtrate from blood.
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
The first segment of the renal tubule where reabsorption of water, ions, and nutrients occurs.
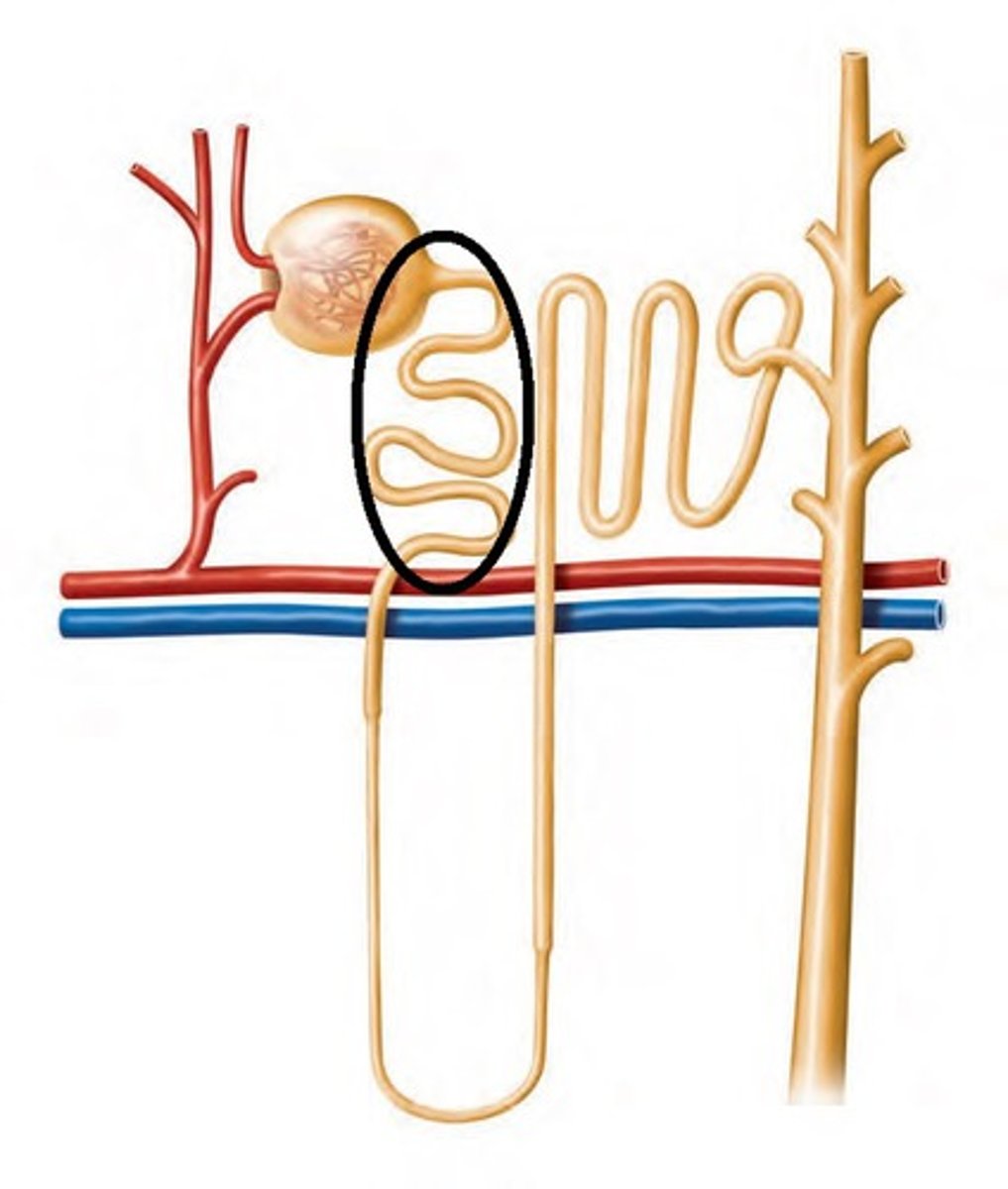
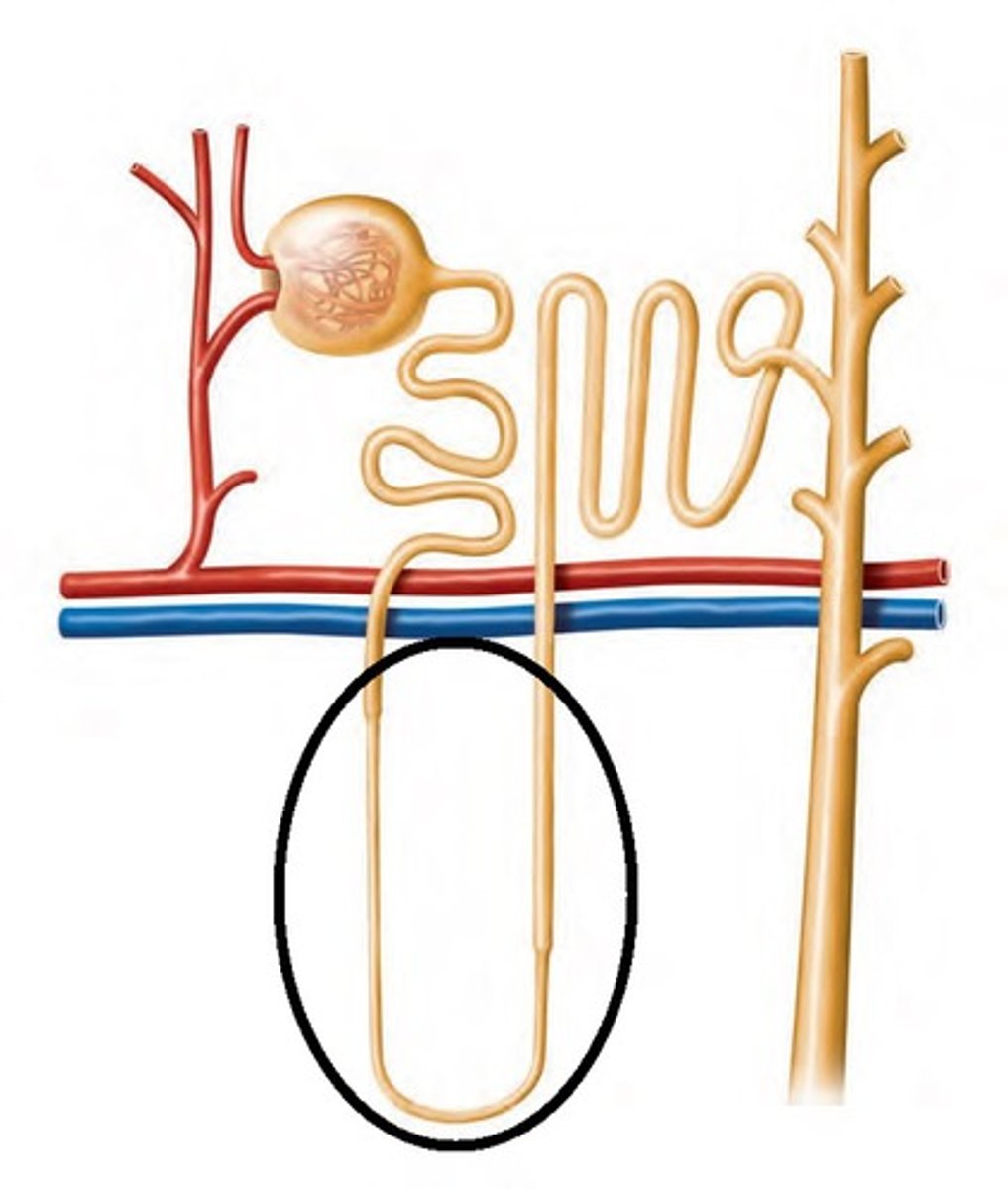
Loop of Henle
A U-shaped portion of the nephron that concentrates urine and conserves water.
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
The segment of the nephron where further reabsorption and secretion occur, leading to the collecting duct.

Collecting duct
A tube that collects urine from multiple nephrons and transports it to the renal pelvis.
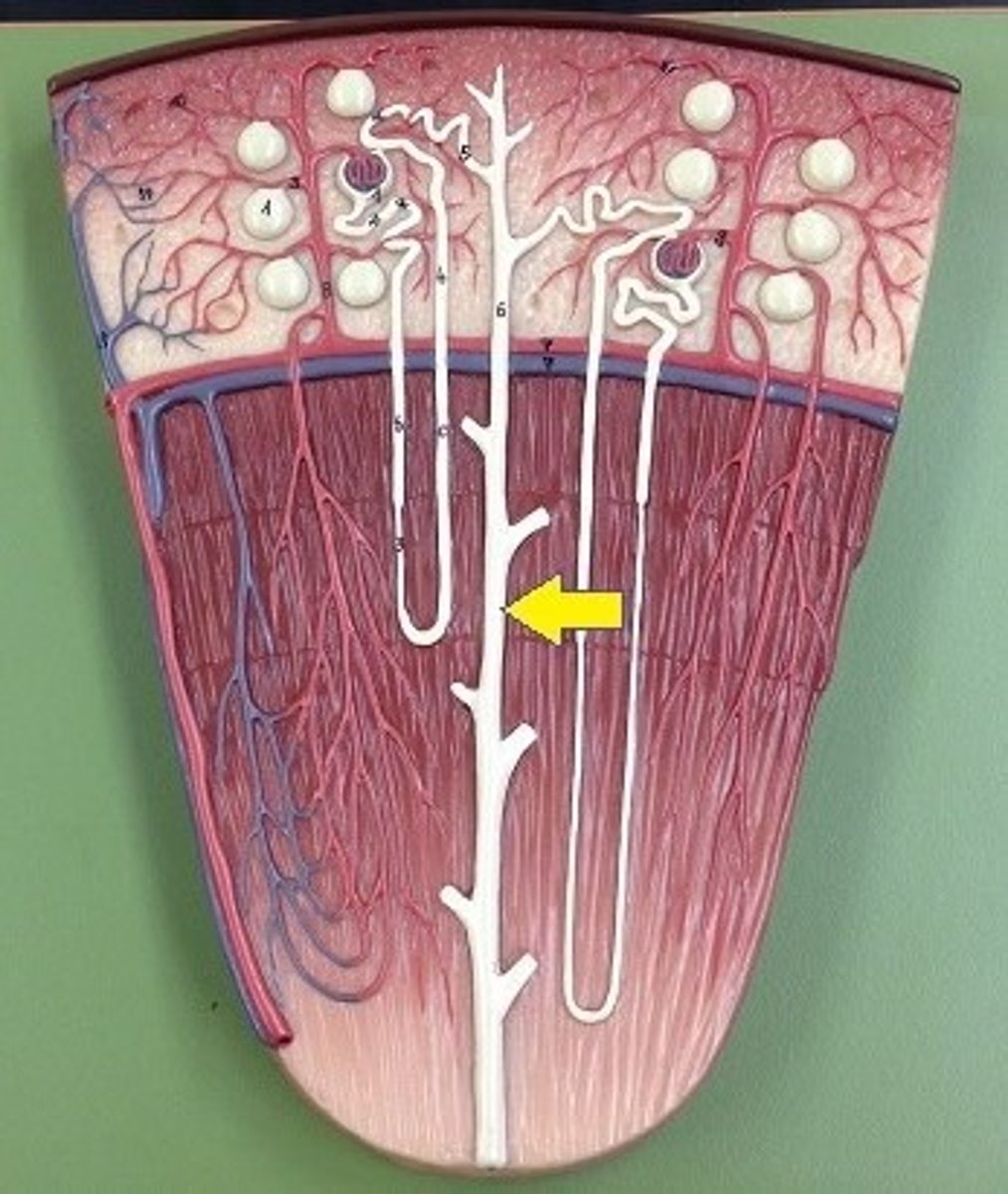
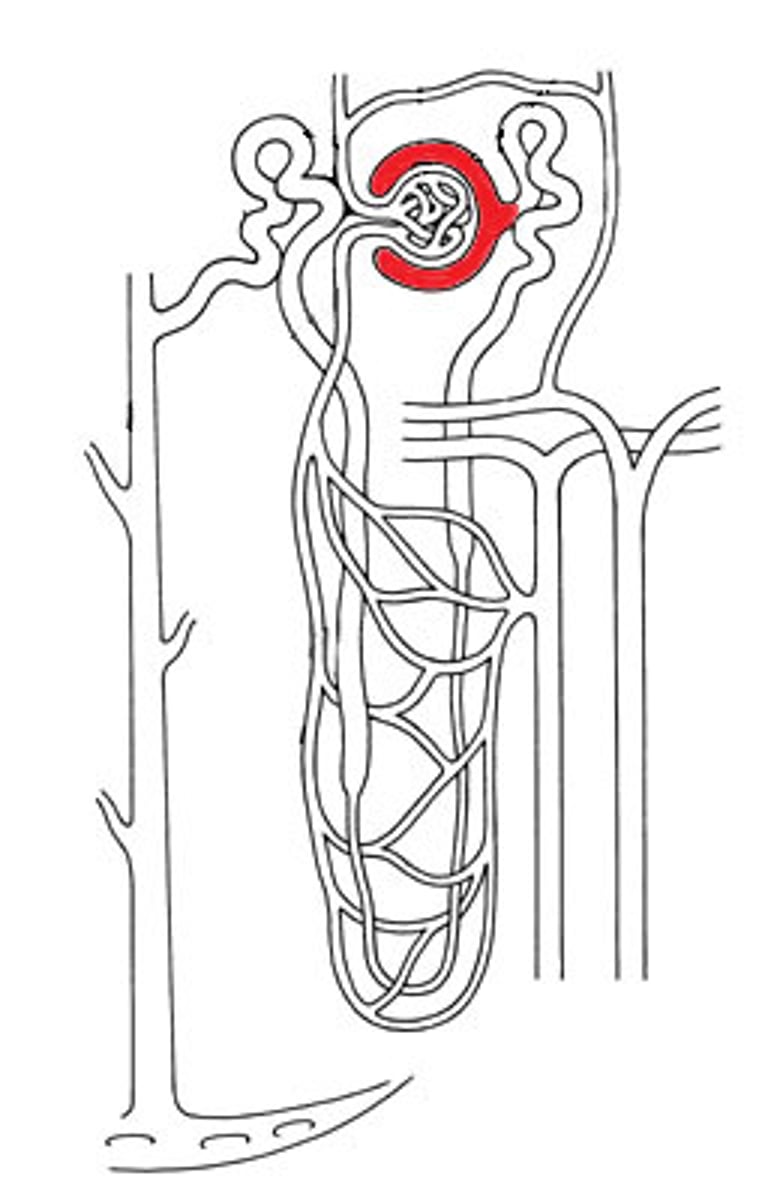
Macula densa
(1). A group of specialized epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubule that detect sodium concentration and regulate blood pressure.

Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)
A structure formed by the macula densa and juxtaglomerular cells that regulates blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate.
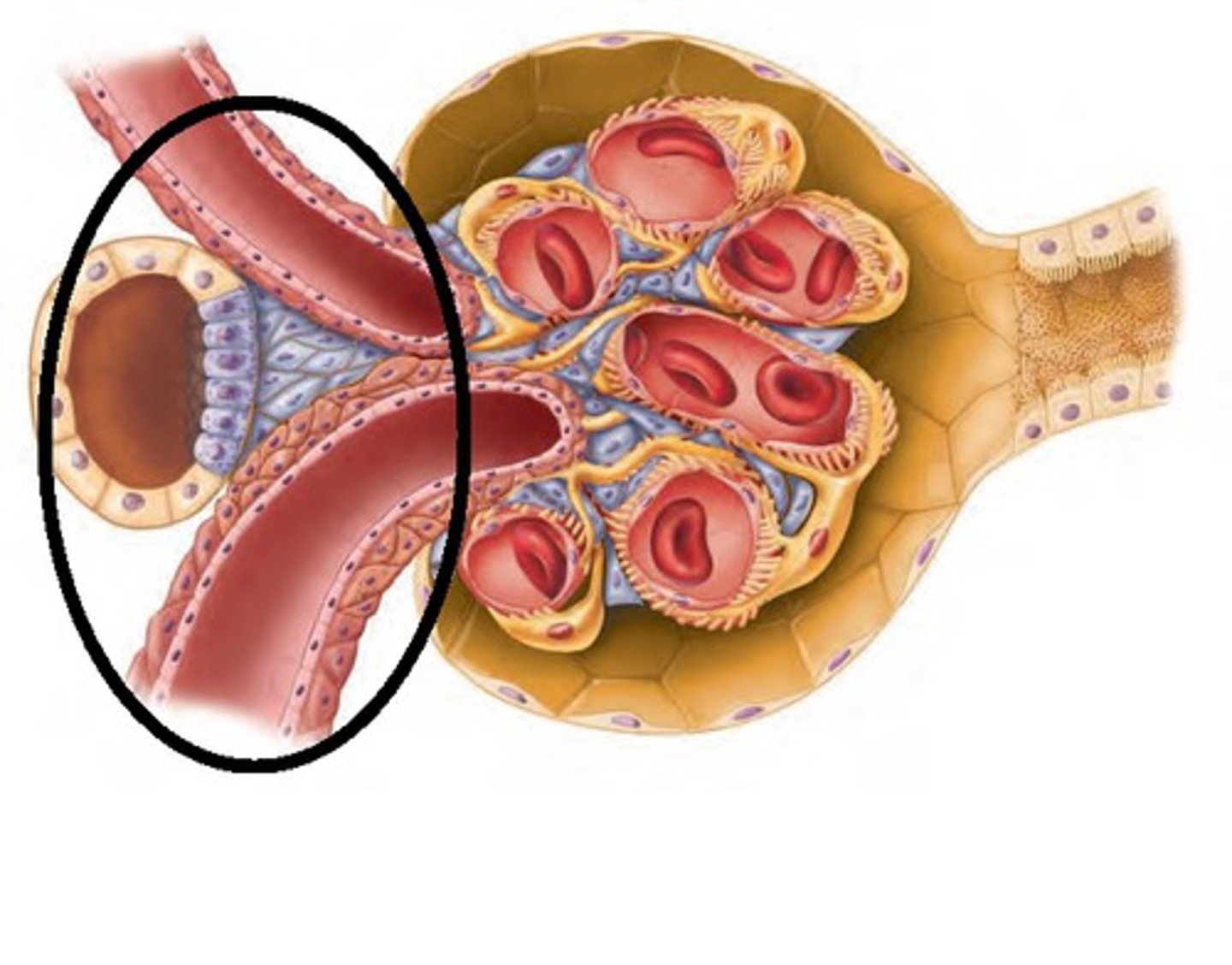
Juxtaglomerular apparatus is located at where these three parts come together:
(1) Afferent arteriole
(2) Efferent arteriole
(3) Beginning of distal convoluted tubule
Juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells)
juxtaglomerular cells (JG cell = granular cells)
specialized in making renin. Regulate blood pressure.