Ch.5 Pulmonary Function Measurements
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what are the 4 lung volumes?
inspiratory reserve volume
tidal volume
expiratory reserve volume
residual volume
what is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)?
amount of air that can be forcibly inhaled beyond Vt
what is expiratory reserve volume? (ERV)
the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a normal Vt
what is tidal volume? (Vt)
the amount of air inhaled and exhaled with each breathe during quiet breathing
(inspiration & expiration)
what is residual volume? (RV)
the amount of air still in the lungs after a forced ERV
what are the 4 lung capacities?
inspiratory residual capacity
functional residual capacity
vital capacities
total lung capacities
what is inspiratory residual capacity? (IRC)
the vol of air that can be inhaled during normal exhalation
IRV + Vt
what is functional residual capacity? (FRC)
volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal exhalation
ERV + RV
what is vital capacities? (VC)
the max vol of air that can be exhaled after max inspiration
IRV + Vt + ERV
what is total lung capacities?
max amt of air the lungs can accommodate
ERV + Vt + IRV + RV
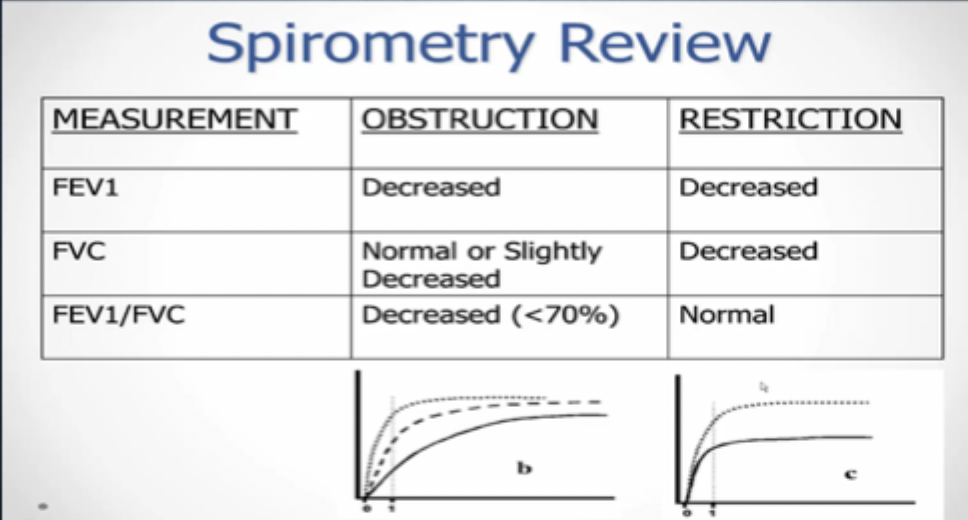
what effects does obstructive diseases have on PFTs (pulmonary function testing)
•affects VC, airflow limitation, ↓ expiratory flow, high airway resistance
• ↓ in FEV1
• normal or slight ↓ in FVC
• ↓ 70% of FEV1/FVC
•difficulty exhaling
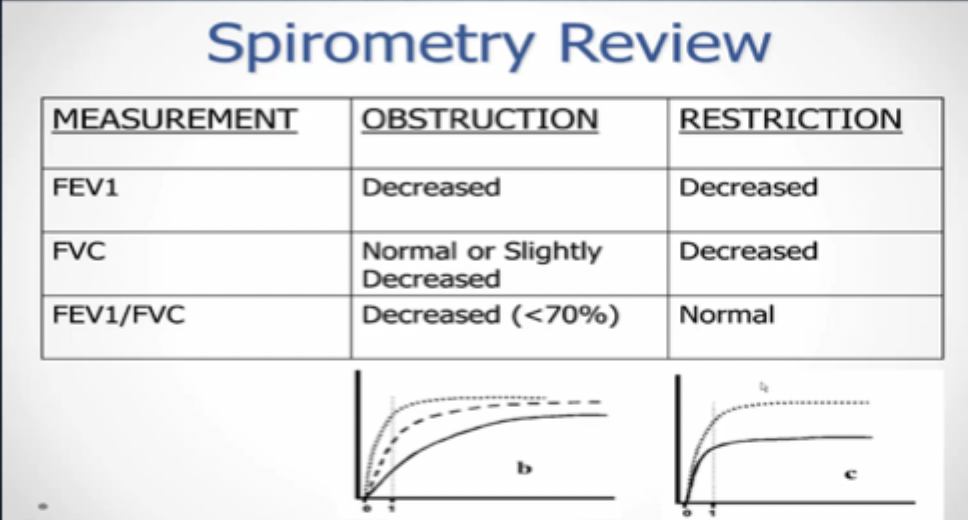
what effects does restrictive diseases have on PFTs (pulmonary function testing)
• ↓ both FEV1 and FVC
• normal FEV1/FEVC
• low lung compliance
• ↓ lung volume & capacities
• difficulty inhaling, pneumonia, atelectasis
normal FEV1
83 or 80 %
normal FEV0.5
60%
normal FEV2 vs FEV3
94 % vs 97%
how do you calculate FEV1 and FVC ratio?
•divide (Height, age, gender,ethnicity) by predicted number
• <70 FEV1/FVC is obstructive
FEV1/ FEV2 × 100
what is peak flow rate (PF)? what is it used for?
• highest instantaneous flow achieved during FVC maneuver
• max attainable expiratory flow rate
• measures velocity & flow rate
• determined by large airway diameter
• occurs during early forced expiration
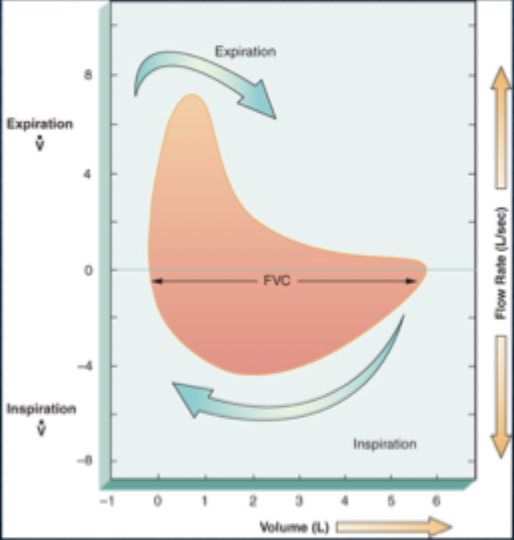
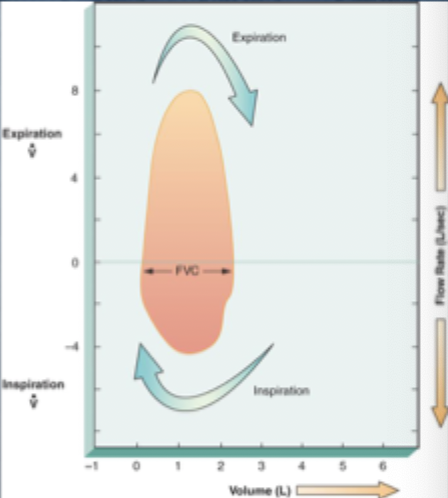
what is a normal flow-volume loop?
• graphic presentation of FVC maneuver followed by forced inspiratory vol (FIV) maneuver
• smooth, bell-shaped loop, with a symmetrical inspiratory limb and a linear, convex expiratory limb
• absence of significant airflow obstruction or restriction
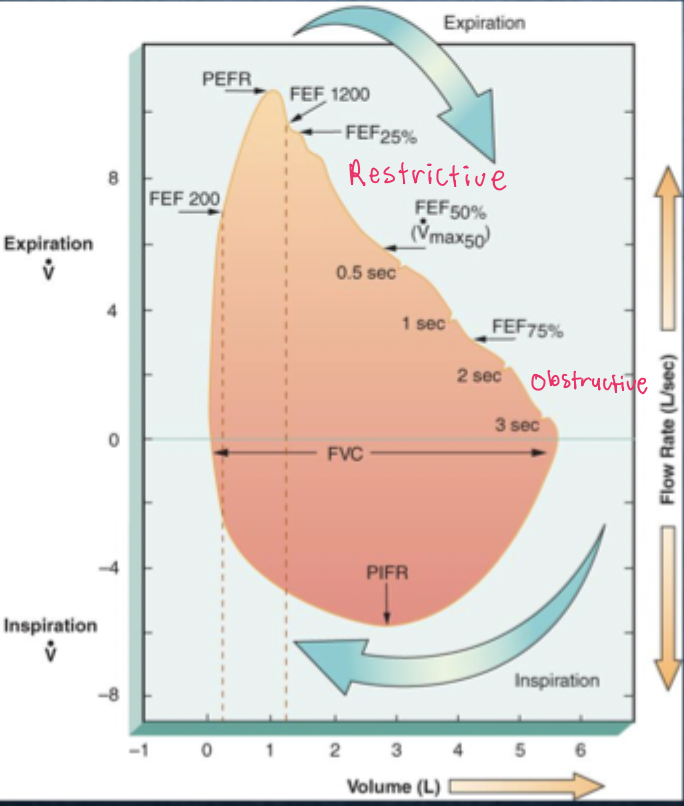
what is an obstructive flow-volume loop?
•delayed and prolonged expiratory flow, often described as "t" or "dipping," with a low peak expiratory flow and a prolonged expiratory phase that doesn't reach zero
condition that narrows the airways, such as:
Asthma
COPD (chronic bronchitis, emphysema)
Large airway tumors
what is a restrictive flow-volume loop?
•reduced overall lung volume but maintains a relatively normal shape and flow, with an inspiratory limb that rapidly decreases in flow and a shortened, but usually linear, expiratory limb
condition that limits lung expansion, such as:
Interstitial lung disease
Kyphoscoliosis
Weakness of respiratory muscles
Obesity
what factors affect predicted normal values of obstructive and restrictive flow-volume loop?
age, sex, height, race/ethnicity, weight/body comp, effort/technique
what are the 3 methods for measuring RV
• open circuit helium dilution method →amt of helium in the lung-spirometer system is the same at the end of the test as at the beginning
• closed circuit nitrogen washout → usually ends when expired nitrogen is < 2%
• body plethysmographic method → measures pt’s lungs (most accurate)
what is minute ventilation?
• total vol moving in or out of lungs per min
VE= fB (frequency of breathing) x VT