Life Maintenance cram
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Anions in pancreatic juice:
HCO3-
Cl-
SO42-
HPO42-
Cations in pancreatic juice:
Na+
K+
Ca2+
Mg2+
Secretin … the volume of pancreatic juice produced by the pancreas.
HCO3- … under it, which makes sense cos secretin promotes it and this makes the juice for alkaline.
Cl- … because they are exchanged for biocarb ions.
Amylase … because there is a dilution effect as the volume of pancreatic juice increases.
inc
inc
dec
dec
In the cephalic and ductile phases, explain what happens in the stimulation of acinar and duct cells
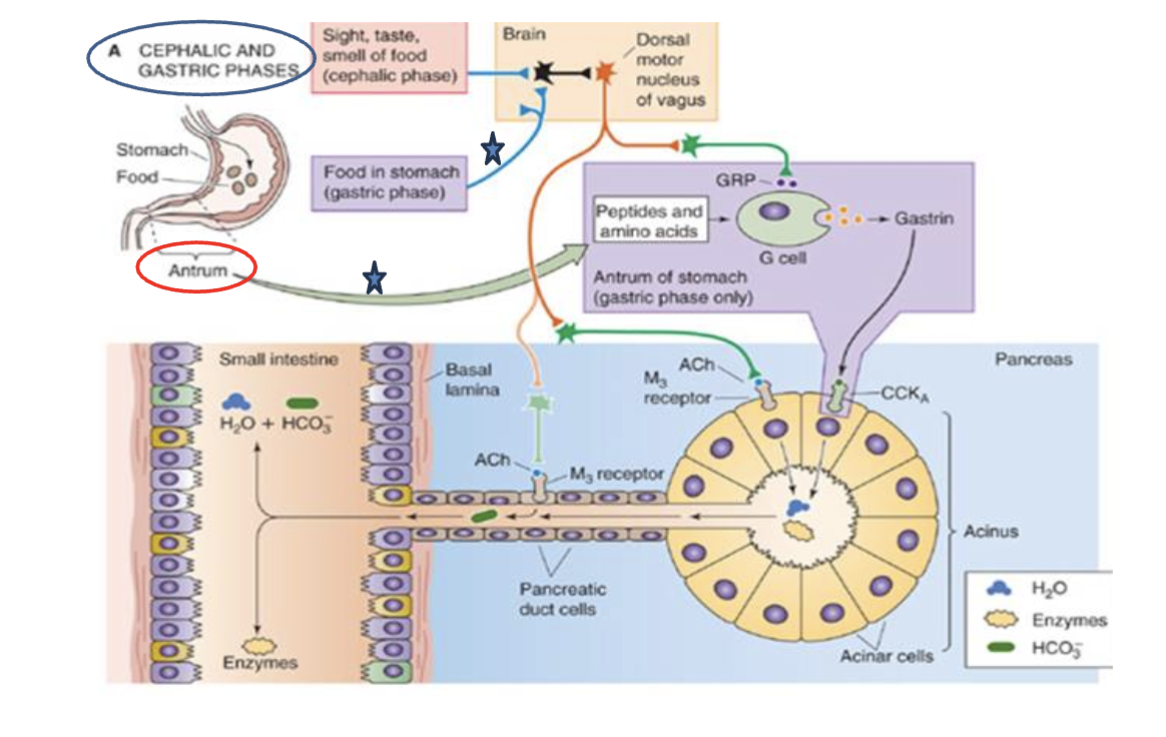
🧠 1. Cephalic and Gastric Phases (Top Left)
Cephalic phase: Triggered by sight, smell, taste, or thought of food.
Sensory input → brain → Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.
Vagal stimulation (orange line) leads to parasympathetic outflow to the stomach and pancreas.
Gastric phase: Triggered by presence of food in the stomach.
Particularly important in the antrum, which senses peptides and amino acids.
Stimulates G cells (see below).
🧬 2. Stimulation of G Cells in the Antrum (Purple Box)
Peptides and amino acids from digested proteins stimulate G cells.
G cells release gastrin, which:
Enhances acid secretion.
Indirectly promotes pancreatic enzyme secretion.
The vagus nerve also stimulates G cells via Gastrin-Releasing Peptide (GRP).
💧 3. Acinar Cells (Bottom Right – Yellow Cells in “Acinus”)
These cells secrete digestive enzymes (yellow blobs in the duct).
Stimulated by:
ACh (vagus nerve) → binds to M₃ receptors.
CCK from I cells (not shown here, but released in the small intestine in response to fats and proteins) → binds to CCK_A receptors.
Together, ACh and CCK boost enzyme secretion to digest proteins, fats, and carbs.
💨 4. Pancreatic Duct Cells (Bottom Left – lining the duct)
These cells secrete:
Bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) and water into the ducts.
This neutralizes acidic chyme coming from the stomach.
Stimulated by:
ACh (via M₃ receptors).
Secretin (not shown in this diagram, but secreted by S cells in the duodenum when pH drops).
📉 Reciprocal Changes (from your earlier question):
As bicarbonate secretion increases, chloride (Cl⁻) is reabsorbed (Cl⁻/HCO₃⁻ exchanger).
So, high secretin → high HCO₃⁻, low Cl⁻ in the pancreatic juice.
Boundaries of the epiploic foramen
Ant, post, sup, inf
Ant: hepatoduodenal ligament (inc portal triad)
Post: IVC and right crus of diaphragm (parietal peritoneum)
Sup: Liver
Inf: Superior duodenum
2 phases of drug metabolism
in ER. Cytochrome P450 makes substance into polar substance by adding a functional group.
makes product more water soluble so drug can be inactive or non-toxic for excretion
CYP inducers: CRAP GPS
Carbamazepine
Rifampin
Alcohol
Phenytoin
Grisefulvin
Phenobarbital
Sulfonylureas
Grapefruit juice inhibits which CYP
CYP 3A4
This CYP enzyme metabolises paracetemol (acetaminophen)
CYP 1A2
This CYP enzyme metabolises alcohol (ethanol)
CYP 2E1
This CYP enzyme metabolises warfarin (/coumadin)
CYP 2C9
This CYP enzyme metabolises cardiovascular drugs (eg Beta blockers)
CYP 2D6
This CYP enzyme metabolises most common drugs (CCBs, statins etc)
CYP 3A4
Cirrhosis affects the following CYP enzymes
CYP 1A2
CYP 2E1
CYP 2C9
CYP 3A4
Hepatitis affects the following CYP enzymes
CYP 2E1
CYP 2C19
CYP 3A
MASH (NASH) affects the following CYP enzymes
CYP 2E1
CYP 3A
Cholestasis affects the following CYP enzymes
CYP 1A2
CYP 2E1
CYP 3A4
What causes hepatic encephalopathy
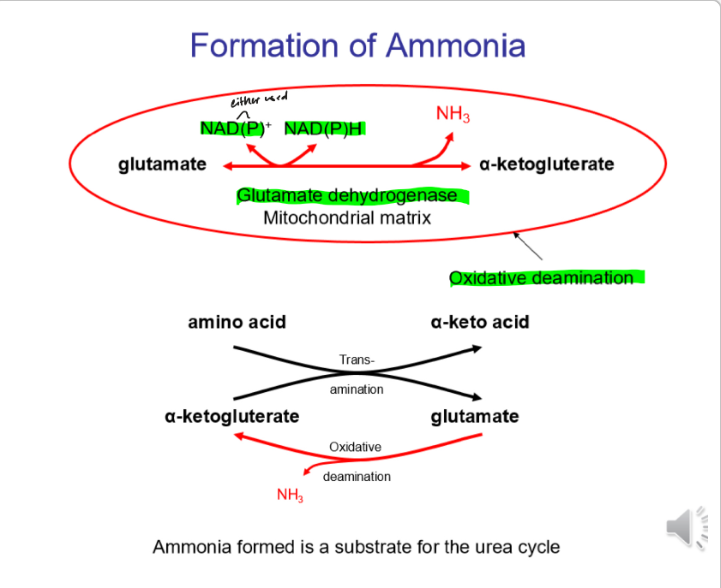
Less ornithine cycle metabolism, NH3 accumulates and it crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Becomes glutamine and causes swelling in astrocytes which increases intracranial pressure.
can get liver flaps as a result
Why does portal hypertension happen in cirrhosis:
there is vasodilation of the splanchnic arteries meaning that more blood flows from the gut into the liver. This means there is too much blood and some is forced into the portavenous shunts (varices) in order to return to systemic flow.
Where does the liver get most of its blood supply from
Portal vein
Gold standard for MASLD investigation
Ultrasound guided liver biopsy
Whats hepatorenal failure
Acute renal failure in a patient with advanced liver disease, usually due to cirrhosis.
When alive on scans, theres less blood flow but post mortem blood flow is fine and this proves its due to profound vasoconstriction due to liver failure
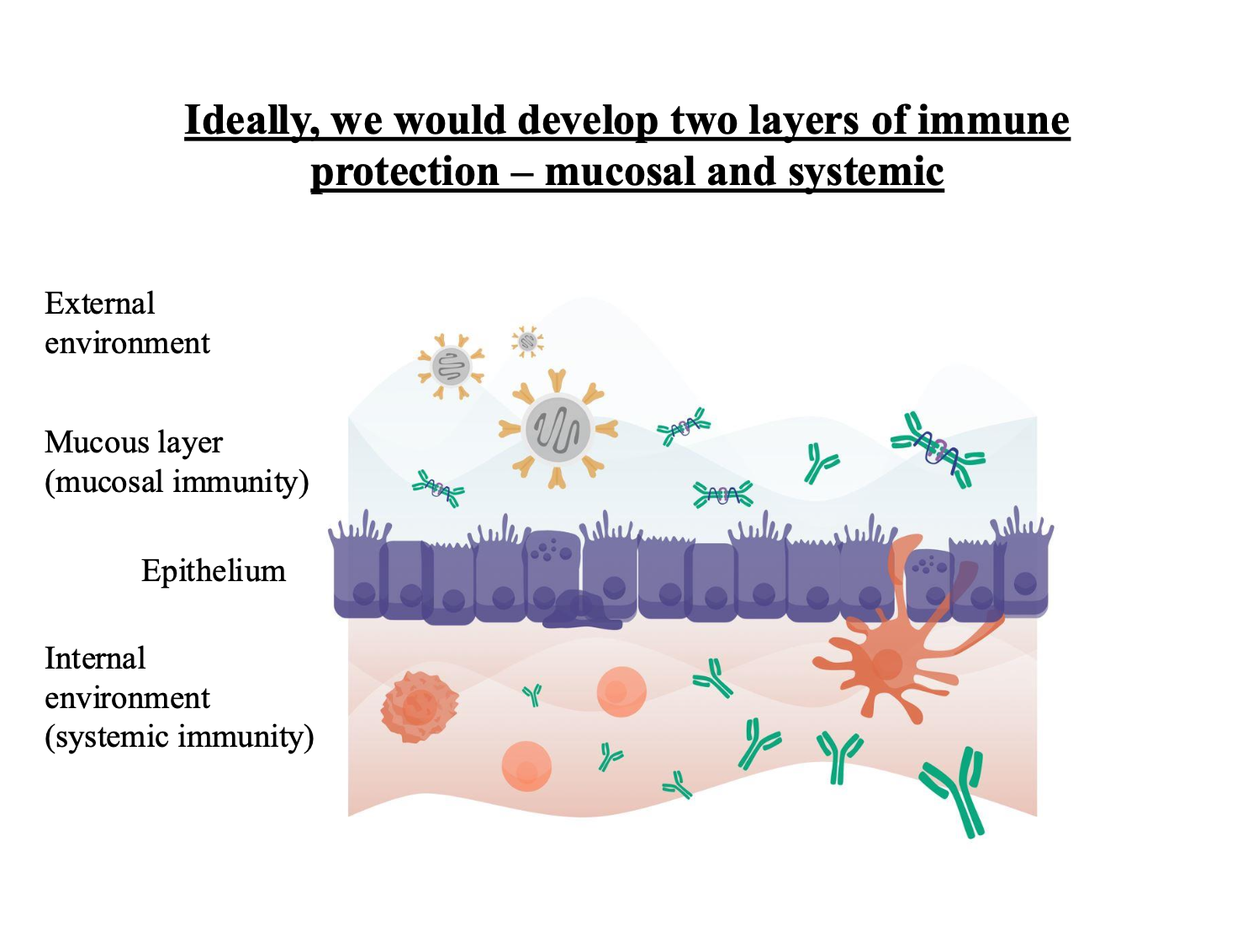
Key distinction between the mucosal and systemic immune system
Mucosal prevents a pathogen getting there
Systemic deals with once the pathogen has gotten in there
Define early satiety
Feeling full without eating properly
How do affarents contribute to regulating food intake
Affarents carry messages from GIT to the brain like you should eat, stop eating, you are hungry etc
Which part of the brain controls food intake
Hypothalamus in terms of appetite, hunger, intake etc
Has the satiety centre (lateral hypothalamus) and the hunger/thirst centre (ventromedial nucleus)
What kind of lesion leads to an increase in appetite and weight gain
Ventromedial hypothalmic region
What kind of lesion leads to an decrease in appetite and thus weight loss
Lateral hypothalmic lesion
Which neurotransmitters increase appetite
Orexigenic such as NPY and AGRP
Which neurotransmitters decrease appetite
Anorexigenic such as CART and POMC
Why do diabetic patients feel hungry despite a high blood glucose
They cannot take up blood glucose to make it useful
Leptin is secreted by
White adipose tissue
Relationship between amount of adipose tissue and leptin secretion
More tissue, more leptin secreted
Effects of leptin
Decreased food intake and thus weight loss
Encourages anorexigenic factors
Effects of ghrelin
Stimulates hunger, an orexin
Stimulates food intake
Effects of obestatin
Reduces food intake
Antagonises ghrelin, even though its encoded by ghrelin gene
What produces obestatin
epithelial cells of stomach
Describe the central and peripheral effects of CCK
slows down gastric emptying and inhibits appetite if injected into the hypothalamus
Explain the consequence of hypovolemia from fluid loss via GI tract, leading to multi organ failure
Hypovolemia happens when the body loses a lot of fluid (e.g. severe diarrhea).
This causes less blood to return to the heart (decreased venous return).
Less blood filling the heart means reduced preload (initial stretch of heart muscle).
Reduced preload leads to lower cardiac output (less blood pumped out).
Lower cardiac output causes low blood pressure (arterial hypotension).
Low blood pressure means poor blood flow (perfusion) to tissues, including the heart.
The heart works harder, increasing its oxygen demand.
But oxygen supply is reduced, so heart and tissues switch to anaerobic metabolism (without oxygen).
Anaerobic metabolism produces lactic acid, causing metabolic acidosis.
Acidosis interferes with cell functions by damaging enzymes and reducing energy (ATP) production.
Worsening perfusion and acidosis damage organs, leading to multiple organ failure.
If untreated, this can cause death.
Outline the physiological response to the consequences of hypovolemia due to diarrhoea
Renal: dec GFR so less Na+ and H2O excreted
Cardiovascular: dec BP so RAAS activates and GFR as shown above
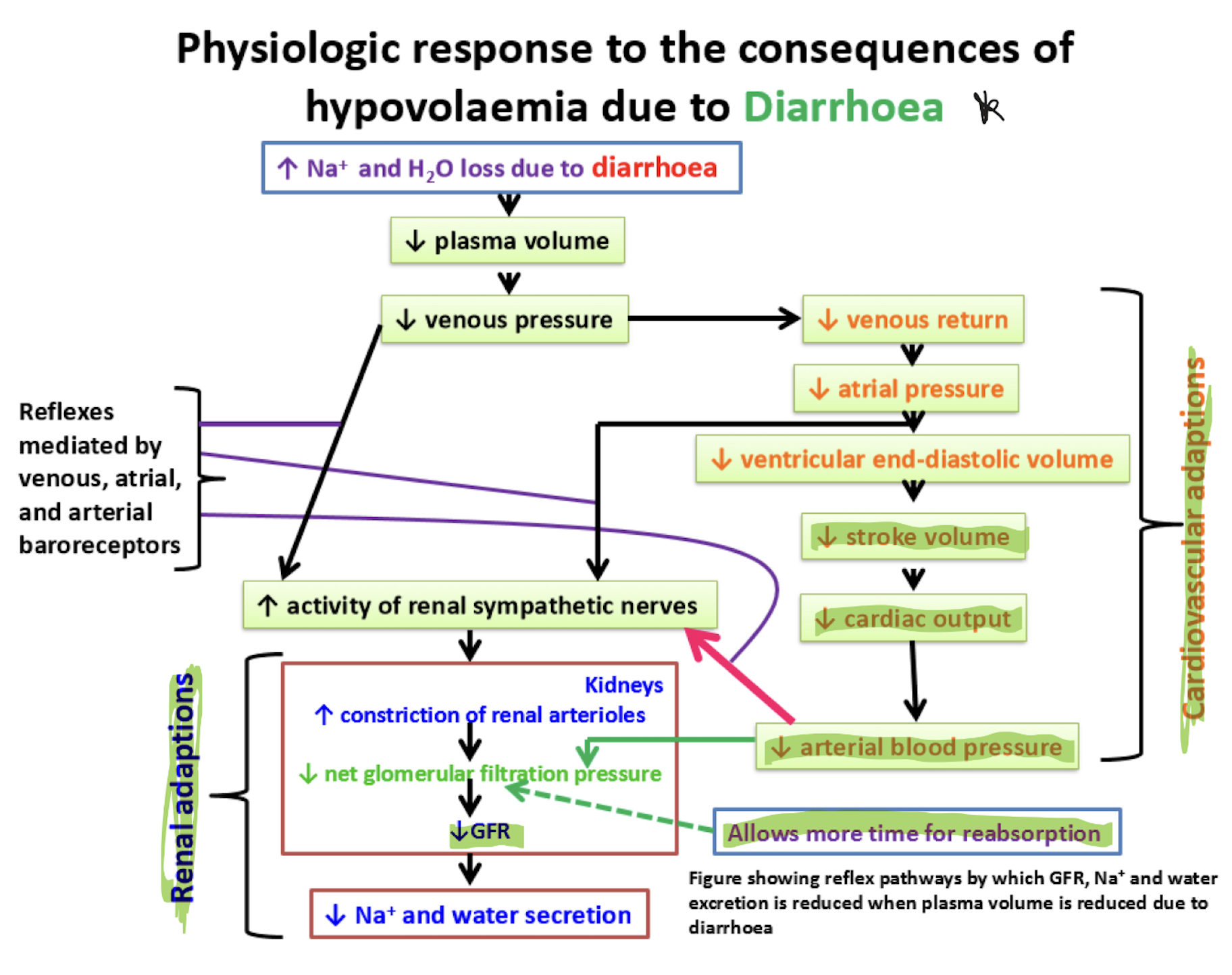
How do we get thirst as a consequence of hypovolemia
Inc plasma osmolarity sensed by osmoreceptors
Dec plasma volume sensed by baroreceptors
Angiotensin II causes thirst and triggers the release of aldosterone, which helps to conserve water and sodium.
what are gallstones made of
bile salts (bile compounded with a cation such as sodium)
cholesterol
phospholipids
bilirubin
Components of hepatic bile
97% water
cholesterol
lecithin
bile acids
bile pigments
Components of gallbladder bile
89% water
HCO3-
Cl-
Ca2+
Mg2+
cholesterole
bilirubin
bile salts
lecithin
Bile secretion
CCK can stimulate the gallbladder to secrete {{c1::bile}} into the duodenum.
CCK can also send vagal afferents to the brain (dorsal vagal complex) to relax the {{c1::Sphincter of Oddi}} via NO and VIP which again allows secretion of {{c1::bile}} {{c1::Ach}} will help with contracting the gallbladder for this to happen.
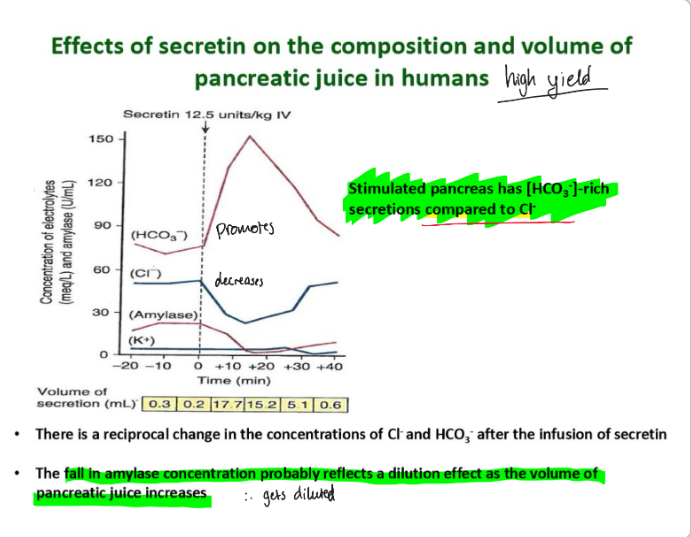
Secretin {{c1::increases}} the volume of pancreatic juice produced by the pancreas.
HCO3- {{c1::increases}} under it, which makes sense cos secretin promotes it and this makes the juice for alkaline.
Cl- {{c1::decreases}} because they are exchanged for biocarb ions.
Amylase {{c1::decreases}} because there is a dilution effect as the volume of pancreatic juice increases.
In which phase of gastric acid secretion are secretin and CCK significant
Intestinal
Secretin: Focuses on neutralizing the acid (via bicarbonate secretion), inhibiting gastric acid secretion, and promoting bile production.
CCK: Focuses on digesting fats and proteins by stimulating gallbladder contraction and pancreatic enzyme secretion, while also slowing gastric emptying.
Together, these hormones regulate digestion in the small intestine by ensuring proper enzyme activity, maintaining optimal pH, and controlling the rate of stomach emptying.
what do duct cells secrete
bicarbonate rich secretions such as NaHCO3
what do acinar cells secrete
digestive enzymes
What does CCK do to the Sphincter of Oddi
Relaxes it via VIP and NO which releases bile and some HCO3- into the duodenum
CCK relaxes the sphincter of Oddi by stimulating the release of nitric oxide (NO) and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), which cause the smooth muscle of the sphincter to relax. This relaxation allows the release of bile from the gallbladder and pancreatic juice (including bicarbonate) into the duodenum. Bile helps digest fats, while bicarbonate neutralizes the acidic chyme, optimizing digestion.
How do H2 antagonists help against peptic ulcers
Blocks histamine receptors on parietal cells so less gastric acid and pepsin so this promotes healing since theres less acid
BUT STOPPING TREATMENT WILL CAUSE RELAPSE
How do PPIs (proto pump inhibitors) help against ulcers
Irreversibly inhibits proton pump (H+/K+ ATPase) so less H+ in lumen to form HCl
Decreases the basal and food stimulated gastic acid secretion
How does H Pylori harm the GI tract
H Pylori is gram {{c1::negative}} and {{c1::spiral}} shaped. It has {{c1::corkscrew motility}} and flagella which allows it to penetrate the gastric mucosa.
It is able to digest the {{c2::mucus}} layer (mucinase activity) and be detected via {{c2::Urea breath}} test because it produces ammonia from urea. this damages the mucus layer, making it more vulnerable to acid.
It triggers {{c3::inflammation}} which weakens epithelial cells so they are more sensitive to acid. It also decreases the secretion of {{c3::bicarbonate}} ions which reduces mucosal defence.
It increases the secretion of {{c3::gastrin}}, leading to hyperacidity.
Whats the best method for diagnosing a peptic ulcer
Endoscopy
EGD - eosophagagastroduodenoscopy
Best way to treat H Pylori
Combination therapy of: PPIs with antibiotics
eg Omeprazole (PPI) with amoxicillin and metronidazole (antibiotics)
Bismuth chelate can help protect mucosa
Symptoms of peptic ulcers
anaemia
nausea
anorexia
vomiting
epigastric ain
weight loss
black, tarry stools
After paracetemol has been metabolised, what happens to the modified compounds
Most gets excreted in urine
Some gets converted to NAPQI (toxic) a buildup (from overdose) causes liver damage
but glutathione neutralises it, which is also excreted in urine
why can you not have statins and grapefruit juice
statins get degraded by a P450 enzyme called CYP3A4 which is inhibited by grapefruit juice
leads to high statin levels in blood -> liver toxicity and muscle damage
Aflatoxin B1 - liver metabolising this is harmful for body. why?
it gets activated by the P450 isoenzymes
leads to cancer risks
explain the phases of xenobiotic metabolism
1. oxidation: inc solubility, cytochrome P450 enzyme promotes
2. conjugation: addition of gluthatione/ glucuronic acid/ sulfate ; inc solubility and readies for excretion
3. elimination: transports out for excretion via urine or faeces
NB not all compounds undergo all, this is general
the aim is to make them harmless for excretion as urine or faeces
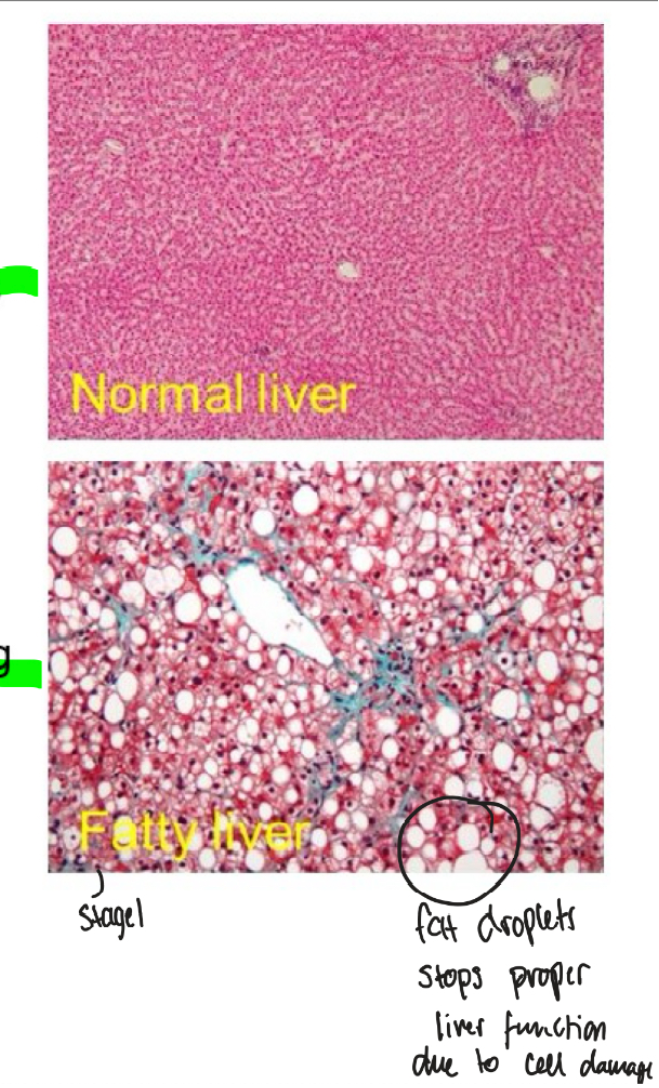
what are the 3 stages of alcohol liver damage
1. fatty liver
2. alcohol hepatisis, group of cells die resulting in inflammation
3. cirrhosis including fibrosis, scarring and cell death
Issues with high ethanol metabolism
It takes priority over other things
It will inhibit things like gluconeogenesis, B oxidation, Krebs etc
stimulate anaerobic respiration and ketogenesis —> lactate and ketones are acidic
How is ethanol metabolised? How can this cause issues for the body?
1. ethanol to acetaldehyde via alcohol dehydrogenase and NAD+ -> NADH and H+ (reduction) in cytosol
2. acetaldehyde to acetate via aldehyde dehydrogenase and NAD+ and H2O to NADH and 2H+ (reduction) in mitochondria
3. acetate to acetyl CoA via acetyl CoA synthase
Acetaldehyde inhibits enzyme function
Enhances free radical production -> tissue damage such as inflammation and necrosis
leads to less VLDL
When ethanol intake is high, alternative systems are activated:
1. Microsomal Ethanol Oxidizing System (MEOS)
Involves cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1)
Increases with chronic alcohol use.
Produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) → contributes to liver damage.
decrease in glutathione so oxidative stress
2 most important transaminases
alanine (ALT)
aspartate (AST)
When would someone be in a positive nitrogen balance
Response to anabolic hormons
Exercise -> tissue hypertrophy
Growth (eg in kids)
Pregnancy
Why would someone be in negative nitrogen balance
- Muscle wasting disease
- Burns (losing tissue)
- Trauma
- Responding to inc in catabolic hormones
- Responding to dec in anabolic hormones
How is ammonia formed
How does pepsinogen get turned into pepsin
High H+ conc means shape gets altered by high acidity to expose active site as pepsin
Enterochromaffin-like cells (ECL) are found in fundus and body of stomach. what do they make which stimulates acid production
histamine
Where is gastric acid made
Parietal cells (in body) HCl
G cells (in pyloric antrum) Gastrin
How does CCK inhibit acid secretion
CCK has an indirect effect on acid secretion by inhibiting gastric motility and emptying. Slowing down the stomach's emptying rate allows the acid to mix with chyme more slowly, preventing over-acidification in the small intestine.
Also reduces gastrin secretion
How does Ach increase gastric acid secretion
Acts on the Mus receptors on parietal cells to increase it
3 phases of gastric acid secretion
1. cephalic (smelling and chewing food)
2. gastric (food in stomach)
3. intestinal (food enters duodenum)
Some inhibitors of gastric acid secretion
Secretin
CCK
Somatostatin
Role of body of stomach
Secretes mucus, pepsinogen, HCl
Role of antrum of stomach
Secretes mucus, pepsinogen, AND GASTRIN
How do parietal cells produce gastric acid
Proton pump (H+/K+ ATPase) exchanges H+ for K+ which pumps H+ into the lumen
H+ combines with Cl- to form HCl in stomach lumen
HCO3- goes into bloodstream to maintain neutral pH
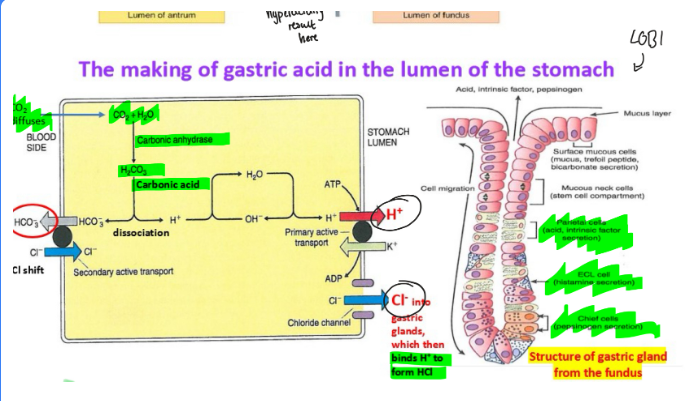
How does somatostatin help against hyperacidity
D cells secrete it
It inhibits acid secretion by:
- acts on parietal cells to decrease HCl secretion
- inhibits gastrin release from G cells
- inhibits histamine release from ECL cells
General note: somatostatin hates digestion it wants to stop all of it
Whereas secretin inhibits gastric acid and adds bicarbonate rich secretions to keep digestion going
How do prostaglandins inhibit gastric acid secretion
Acts on EP3 receptors on parietal cells to decrease acid secretion
Promotes production of mucus and HCO3- which protects the lining against corrosive acid
What happens in the intestinal phase
In the intestinal phase, food enters the duodenum. There is a {{c1::high}} acidity in the duodenum which inhibits {{c1::acid secretion}}. This is so chyme does not become too acidic or pancreatic enzymes do not denature.
Hyperacidity would disrupt bicarbonates, bile and digestive enzymes.
How does secretin inhibit acid secretion
Inhibits parietal cells by decreasing proton pump activity for HCl production
as well as gastrin from G cells
Also stimulates bicarbonate ions to neutralise acid
What cells secret pepsinogen
chief cells
Which oeseophageal sphincter acts as a flap valve
Lower
Consequences (damage) of GORD longterm
Irritates and damaged the oesophagus
can lead to things like Barrett's oesophagus, oesophagitis, oeseophegeal ulcer, squamous cell carcinoma (cancer)
Symptoms of GORD
heartburn
coughing that keeps you awake at night
belching
regurgitation
dysphagia
Whats the muscular structure of the oesophagus
The upper 1/3 of the oseophagus has skeletal (striated) muscle
The bottom 1/3 has smooth muscle
There is a transition between the two where there is a mix
Low LOS pressure from an oesophageal manometry can indicate which pathology
GORD (less than 26mmHg)
note that GORD can still happen to people with normal LOS pressure
High LOS (more than 100mmHg) pressure indicates which pathology
Achalasia
Because the LOS fails to relax after swallowing
How does bismuth chelate help treat peptic ulcers
Proects mucosa by forming a base over the crater of an ulcer
How can you test for H Pylori
Stool antigen test
Urea breath test
Blood test
Endoscopy with biopsy
How do antacids help with GORD
Neutralises the acid - good for hyperacidity
Increases the gastric lumen and inhibits peptic activity (because pepsin can cause oesophageal irritation)
first line treatment for GORD
PPI such as omeprazole
how does gaviscon (alginate) help with GORD
alginate and saliva forms a raft wich floats on the gastric lumen and protects the oesophageal mucosa from the refluxed gastric acid
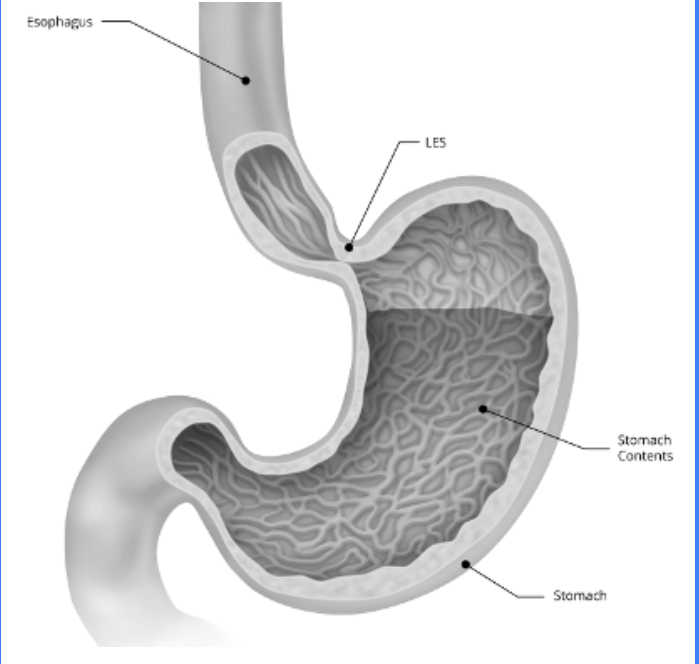
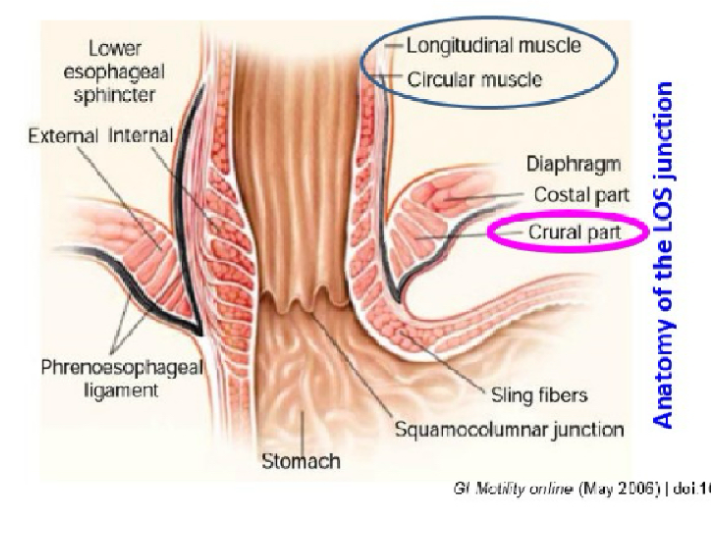
The LOS has external and intrinsic components: what are each of their general roles
Intrinsic: oesophageal muscles which are under neurohormonal influence
Extrinsic: Diaphragm muscles which press against the oesophagus
These work together to prevent reflux. If they aren't working, the LOS is weakened and you get GORD
Functions of the intrinsic components of the LOS
1. Circular smooth muscles and longitudinal muscles which maintain {{c1::basal tone}} (tension)
2. Clasp-like semi-circular smooth muscles are found on the {{c1::right}} side. They have {{c1::myogenic}} activity meaning they can initiate their own resting contractions. They are also less responsive to {{c1::Ach}}
3. The sling-like oblique angle, aka {{c1::the Angle of His}}, is found on the {{c1::left}} side and it is responsive to {{c1::Ach}}
They work together to prevent regurgitation
How does the extrinsic components of the LOS prevent reflux
The right diaphragmatic crura encircles the LOS at the oesophageal hiatus
It has a pinch-cock action which increases pressure to prevent gastric reflux. It happens during inspiration or abdominal strain
Which bits of the LOS components has myogenic tone
Longitudinal and circular muscles
Explain innervation to the upper part of the oesophagus
Vagus nerve sends {{c1::somatic}} motor neurons with NO INTERRUPTIONS to {{c1::striated muscle}}
{{c1::Ach}} will cause contraction to help with swallowing
Explain the motor innervation of the lower part of the oesophagus
Vagus nerve sends {{c1::visceral}} motor neurons WITH INTERRUPTIONS
{{c1::Ach}} will cause contraction for peristalsis
NO and {{c1::VIP}} will cause relaxation to allow bolus to enter the {{c1::stomach}}
How do the mucosal folds in the cardia prevent reflux
They act as plugs to occlude the lumen of the gastro-oesophageal junction
This means there is abdominal pressure pressing on the oesophagus so food would not wanna come back up as that goes against the pressure gradient