Unit 6: heart review
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Coronary Artery Disease Signs and Symptoms
possible MI, pale skin, easily fatigued,
Aneurysm
An area of a blood vessel that bulges because of weakness in the wall
Atherosclerosis
Hardening of blood vessels caused by deposit of fatty material
Bilateral Presence
Checking the pulse on both sides of the body
Blood Pressure
Force of blood against the walls of the arteries
Coronary
Pertaining to the heart
Diastolic Blood Pressure
Resting pressure on the arteries as the heart relaxes between contractions
Hepatic Circulation
Path of blood from heart to the liver
Myocardial Infarction
An area of tissue death caused by lack of oxygen
Pulmonary Circulation
Path of blood from heart to lungs
Pulse Rate
Number of heart contractions per minute
Pulse Rhythm
Pattern of the heart beats
Pulse Volume
Strength of the pulse
Stethoscope
instrument used to listen to body sounds
Systemic Circulation
Circulation of blood from the cells of the body to the heart
Systolic Blood Pressure
Pressure exerted on the arteries during the contraction phase of the heart beat
Vein
blood vessel that carries blood towards the heart
Erythro
Red
Leuk
White
Tachy
Fast
arter
Artery
ather/o
Plaque
atri
Atrium
cardio
Heart
coron/o
Heart
valv
Valve
phleb/o
Vein
hem/o
Blood
hemat/o
Blood
itis
Inflammation
ac
pertaining to
emia
blood condition
lysis
destruction, breakdown
malacia
softening
megaly
enlargement
osis
condtion/abnormal
rrhexis
rupture
sclerosis
hardening
stenosis
tightening
BP
Blood Pressure
CABG
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
CCU
Critical Care Unit
ECG/EKG
Electrocardiogram
MI
Myocardial Infarction
ECHO
Echocardiogram
ASHD
arteriosclerotic heart disease
CHD
Coronary Heart Disease
CHF
Congestive Heart Failure
Epicardium
Outer layer of the pericardium
Myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
Endocardium
inner lining of the heart
septum
Divides the right and left chambers of the heart
Superior Vena Cava
Vein that transports blood from the upper portion of the body to the heart
inferior vena cava
A vein that is the largest vein in the human body and returns blood to the right atrium of the heart.
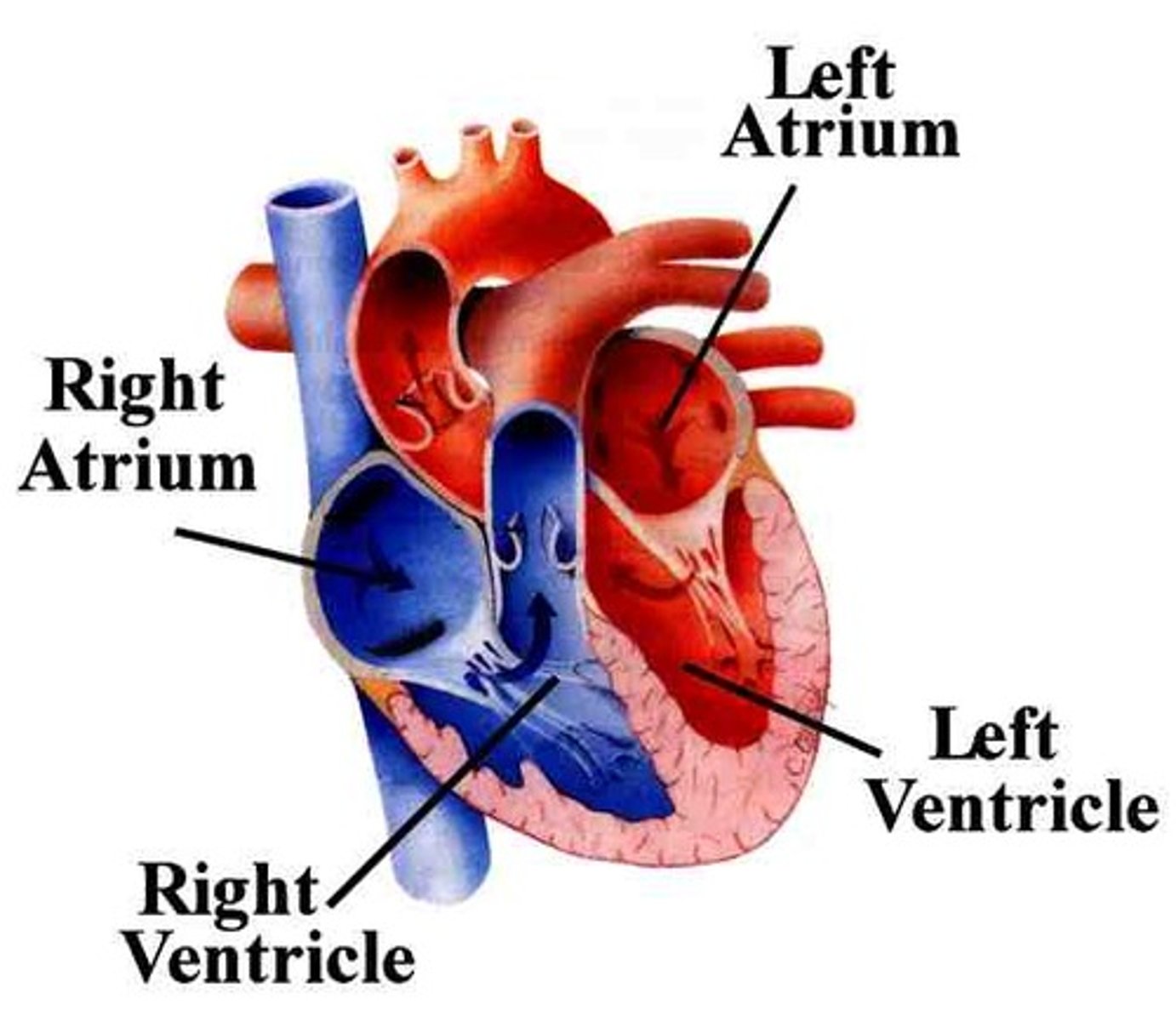
Right Atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body
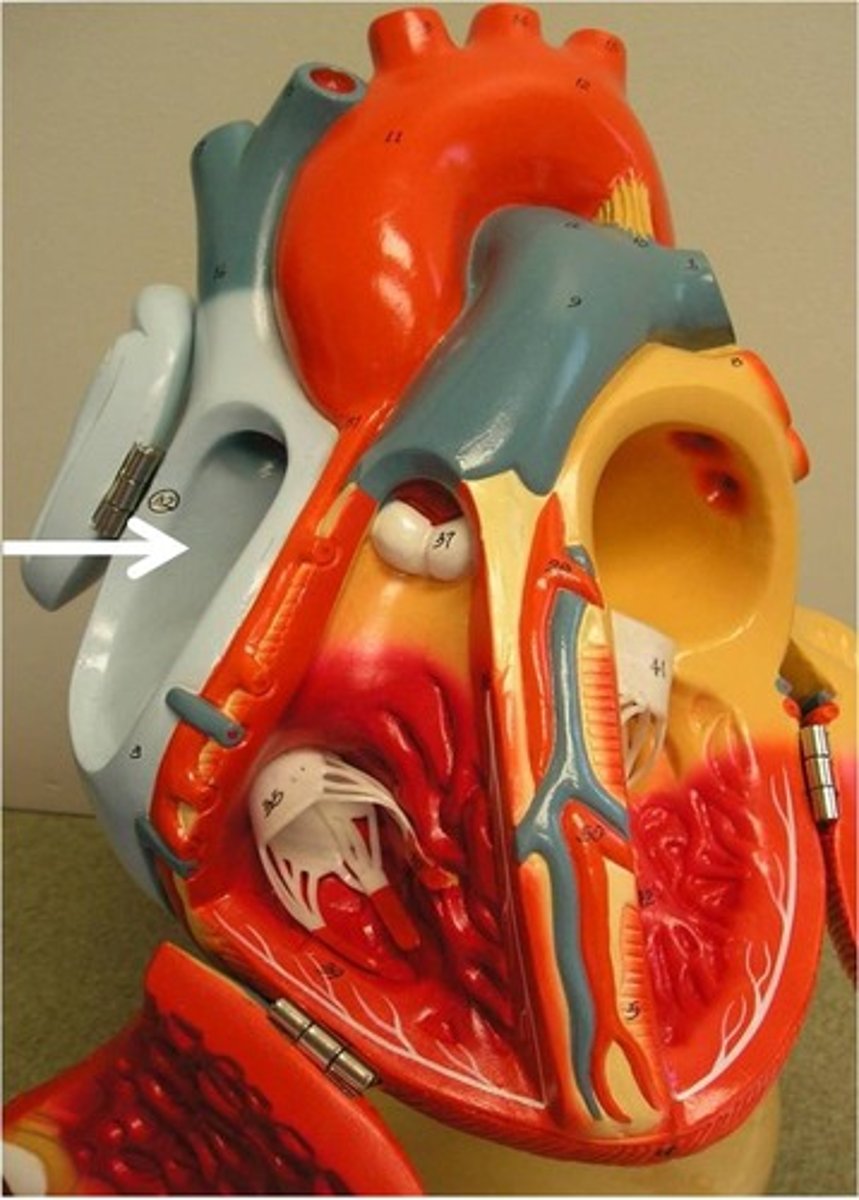
Tricuspid Valve
valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle
Right ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
Pulmonary Valve
valve positioned between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
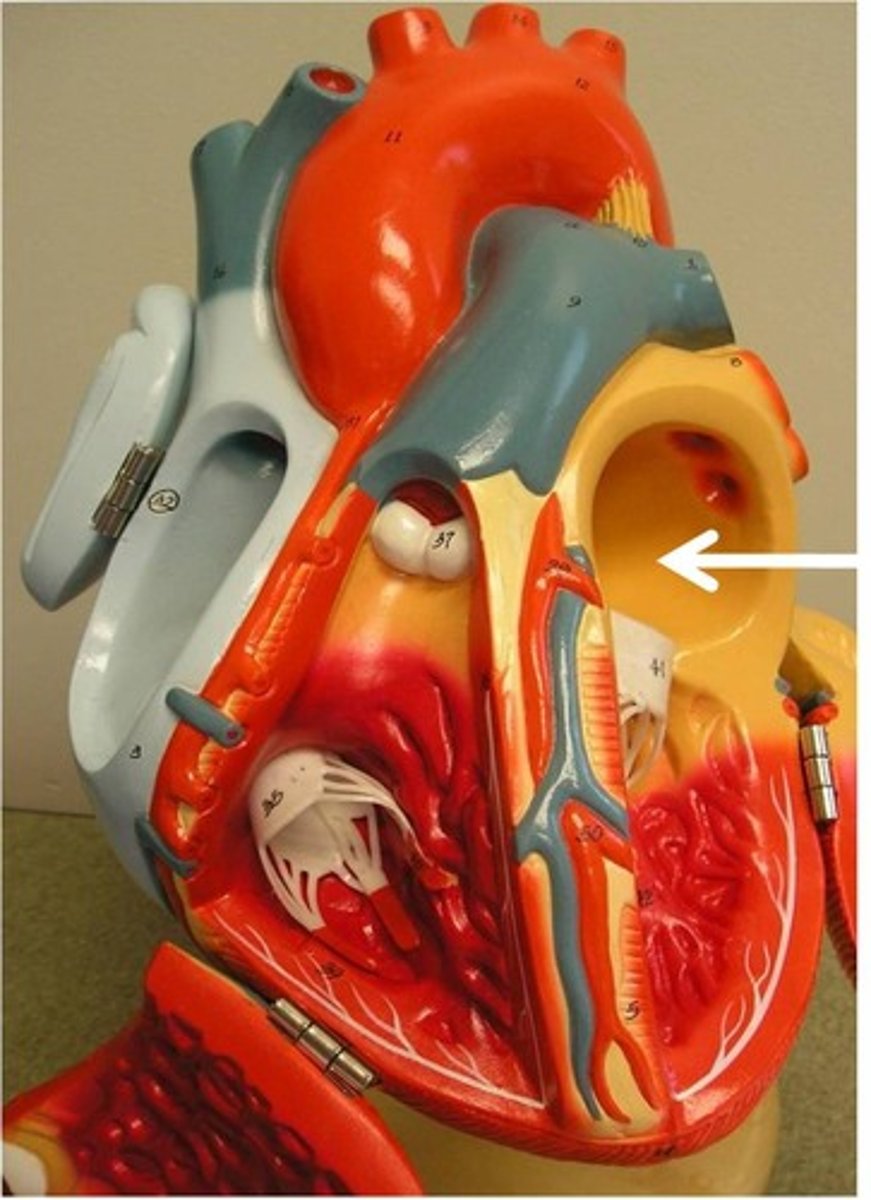
Pulmonary Artery
artery carrying oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs
Pulmonary Vein
carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
Left Atrium
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
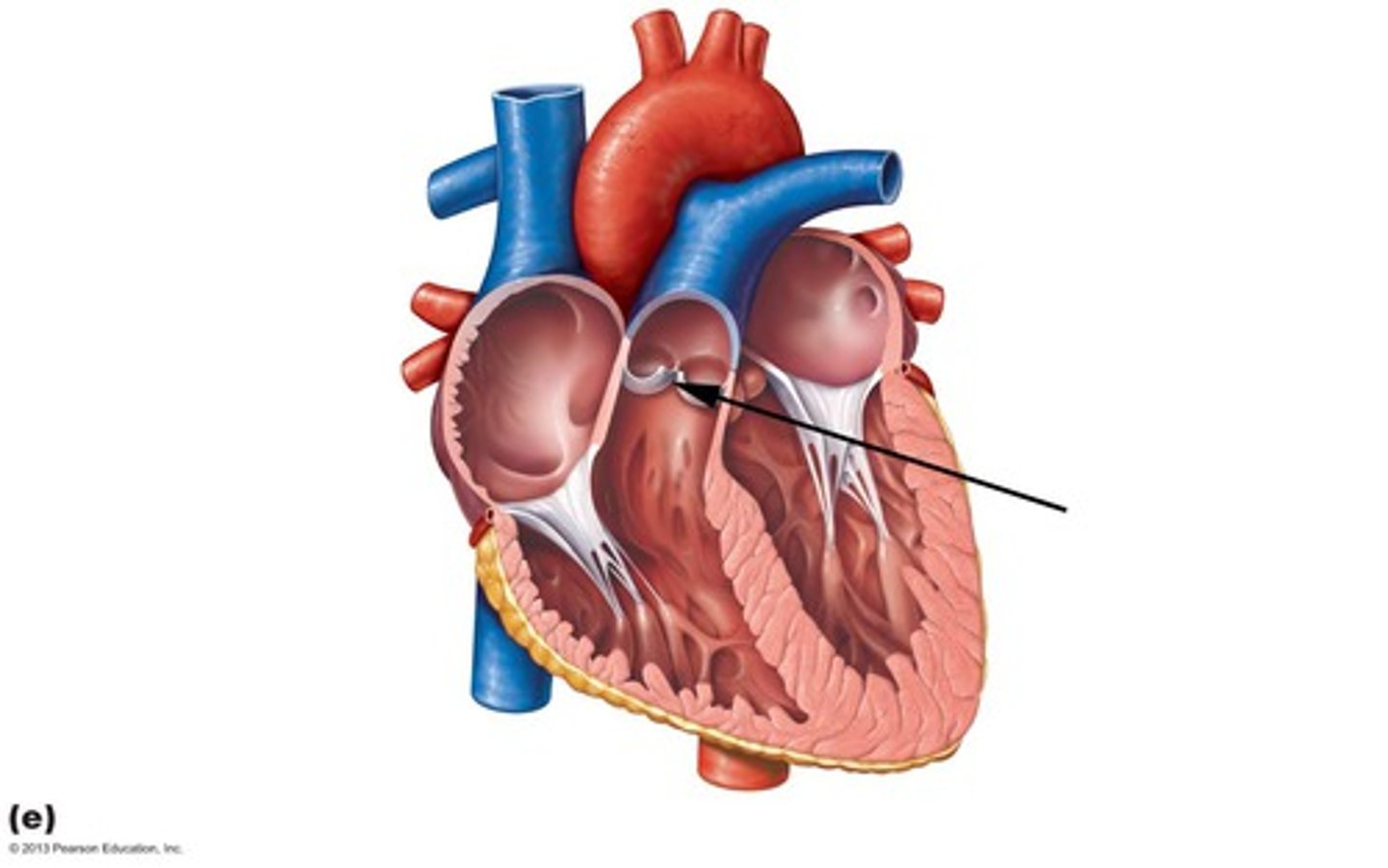
Mitral/Bicuspid Valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta
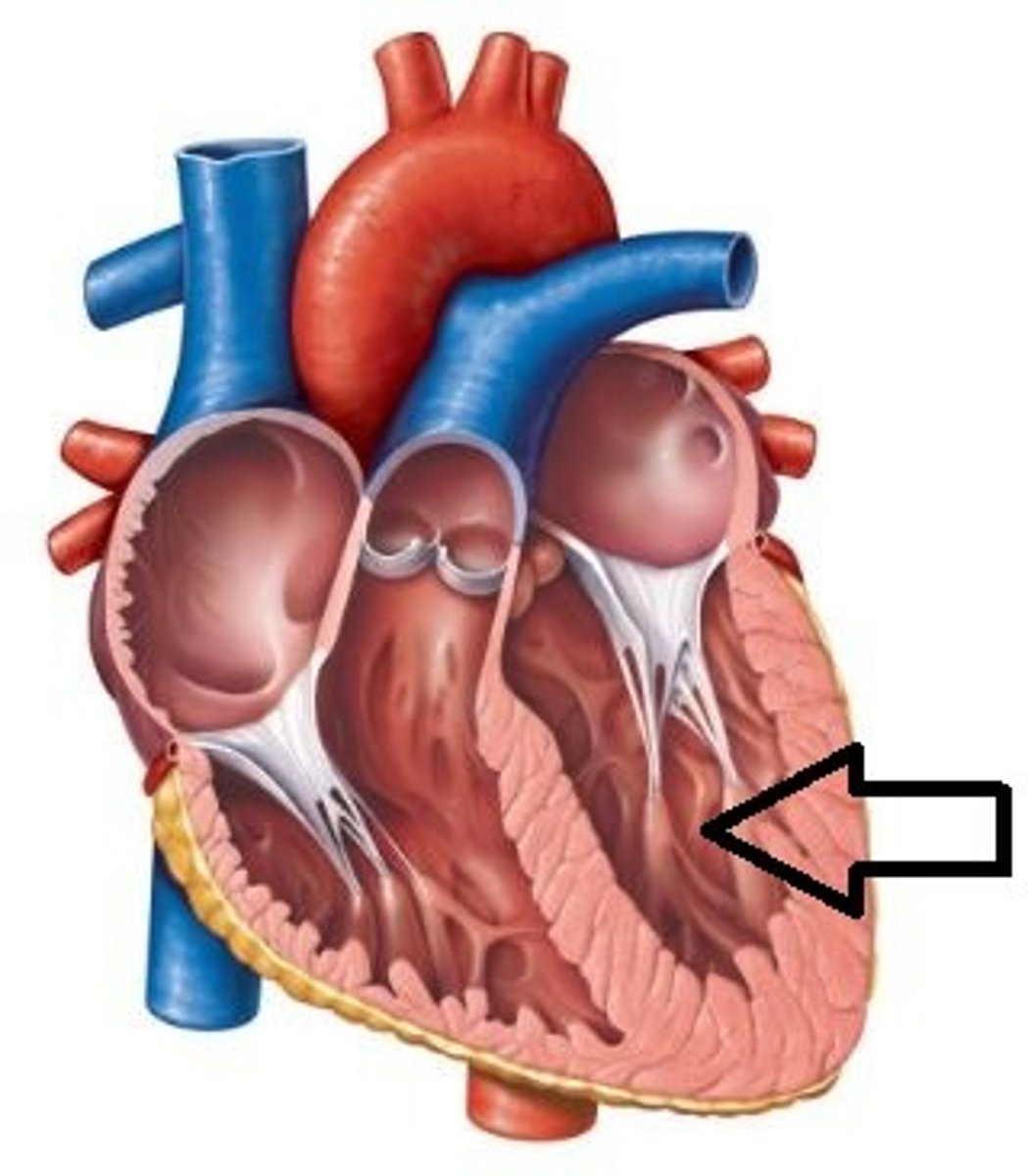
Aortic Valve
heart valve between the left ventricle and the aorta
Aorta
The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body.
Order of blood through the heart
1. Sup and Inf vena cavas 2. R Atrium 3. Tricuspid Valve 4. R Ventricle 5. Pulmonary Valve 6. Pulmonary Artery 7. lungs 8. pulmonary vein 9. L Atrium 10. Mitral/Bicuspid Valve 11. L Ventricle 12. Aortic Valve 13. Aorta 14. Body
Normal BPM
72 bpm
How much blood does the heart circulate
5-7 liters
2 Types of blood vessels
arteries (away) and veins (towards)
Functions of blood vessels
Transport nutrients and oxygen, transport waste to kidneys, distribute hormones and antibodies, help contain temp and homeostasis,
Where does the heart lie
Thoracic cavity between lungs
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
Where are the atria and where are the ventricles?
Atria (top) Ventricles (bottom)
Coronary Circulation
flow of blood to and from the tissues of the heart
Largest Artery
Aorta
Largest Vein
vena cavas
HBP Etiology
Result of lifestyle: ex: overweight, drinking, smoking, lack of exercise, stress
HPB signs and symptoms
No symptoms, if left untreated: liver dmg, kidney dmg, stroke
HBP Treatment and Prevention
meds and lifestyle change
Stroke Etiology
Blood clot that blocks the flow of blood in a vessel
Stroke Signs and Symptoms
numbness, tingling, headache, confusion, difficulty speaking, face droop, vision problems, trouble walking
Stroke Treatment and Prevention
meds(blood thinners), surgery, clot busters
Arteriosclerosis Etiology
hardening of arteries bc of aging, smoking, bad diet, low exercise.
Arteriosclerosis Signs and Symptoms
HPB, fatigue, aneurisms
Arteriosclerosis Treatment and Prevention
Good diet, exercise, surgery
Aneurysm Etiology
defect/ disease, weakened artery walls
Aneurysm Signs and Symptoms
pain, pressure, frequently has no symptoms
Aneurysm Treatment and Prevention
surgical removal of weak artery part
Coronary Artery Disease Etiology
Narrowing of coronary artery because of plaque build up Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis but terms are used interchangeably.
Coronary Artery Disease Treatment and Prevention
balloon angio plasty surgery
Myocardial Infarction Etiology
blood flow to heart is cut off causing permanent damage to heart tissue
Myocardial Infarction Signs and Symptoms
Chest pain and discomfort in the jaw, shoulder, neck, and/or back pain. Dizzy, light headed, fainting, nausea, SOB, pale skin, weakness,
Myocardial Infarction Treatment and Prevention
call 911, loosen restrictive clothes, surgery, meds, nitro glycerin
Congestive Heart Failure Etiology
Heart cant pump its usual capacity, atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.
Congestive Heart Failure Signs and Symptoms
swelling of the feet/ankles blood pooling or fluid edema in near tissues
Congestive Heart Failure Treatment and Prevention
Surgery, Meds, Heart transplant
Anemia Etiology
RBCs dont send enough o2 to tissues bc of low blood count
Anemia Signs and Symptoms
fatuige, difficulty breathing, tachycardia,
Anemia Treatment and Prevention
varies by type, fe supplements, blood transfusions, bone marrow transplant.
Hemophilia Etiology
hereditary, lack of clotting factors