Evolution of Autotrophy & Land Plants
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Photosynthesis reaction
6CO2 + 12H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Ecological & evolutionary impacts
Ecological: energy base of ecosystems, atmospheric composition, nutrient cycles
Evolutionary: oxygen led to aerobic respiration, led to evolution of multicellular organisms, evolution of plants to compete for light
Cyanobacteria
2.5BYA, first photosynthetic bacteria, introduced oxygen
photosynthesis in eukaryotes
1.5BYA, cyanobacteria → chloroplasts; proteobacteria → mitochondria
timeline/changes in earth’s atmosphere
O2 increased with first photosynthetic bacteria, first eukaryotes, first multicellular eukaryotes, slowed with invasion of land via land plants before increasing again, slowed with flowering plants
aerobic respiration/multicelluarity
allows for faster production of ATP/needs more ATP but also produces more
embryophytes
land plants
cuticles
waxy layer on surface; protection from UV radiation, prevents water loss
pores
facilitates gas exchange, open all the time
stomata
regulated uptake of CO2 and loss of H2O (gas exchange)
sporopollenin
outer layer of spore; protection from UV radiation + desiccation
Apical meristems
continuously dividing cells that enable growth at shoots and roots; good since nutrients are both underground or in air
benefits of aquatic environment
surrounded by water/nutrients, protection from UV radiation, structural support, mobility facilitated
challenges of terrestrial environment
desiccation, nutrients in ground, UV radiation exposure, no structural support, mobility not facilitated
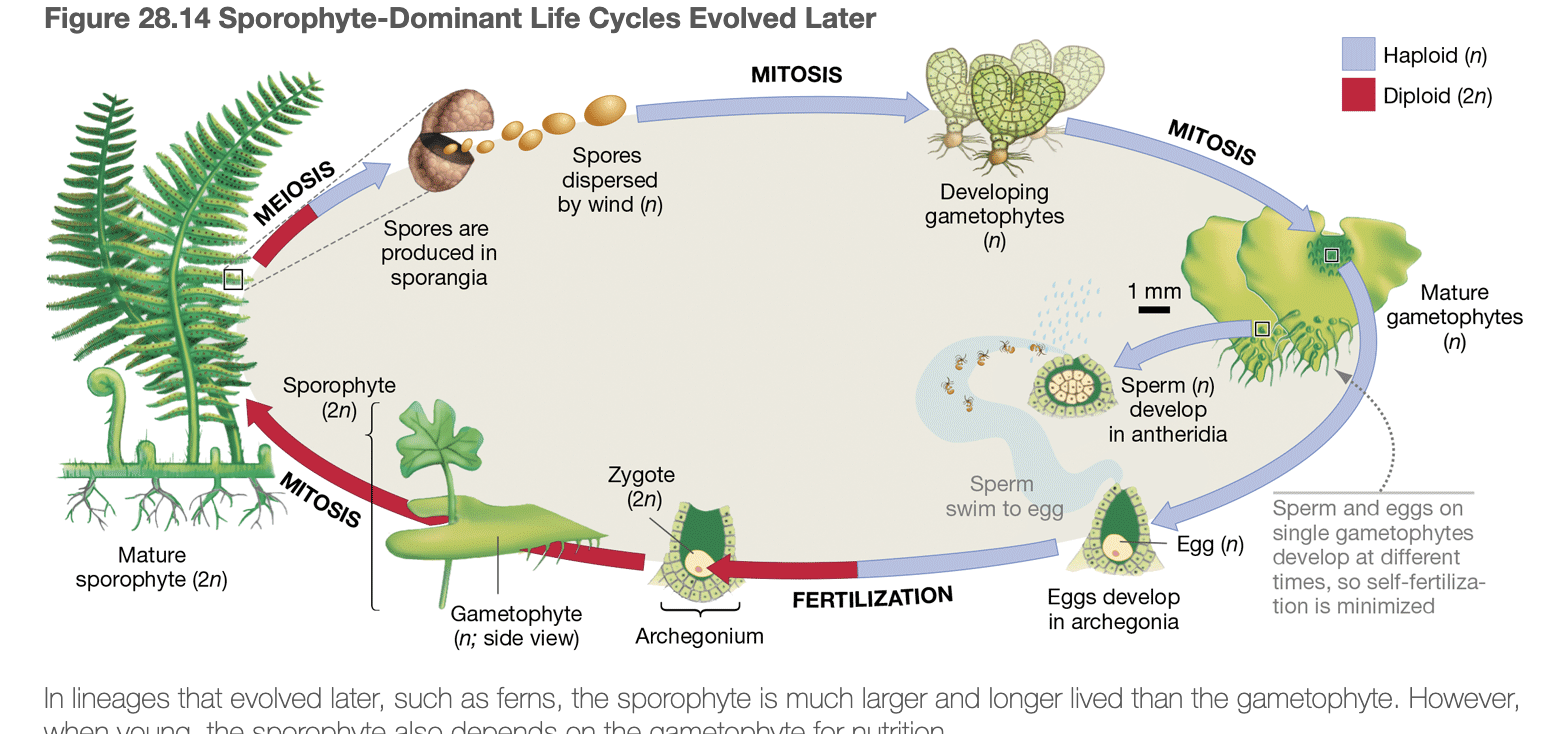
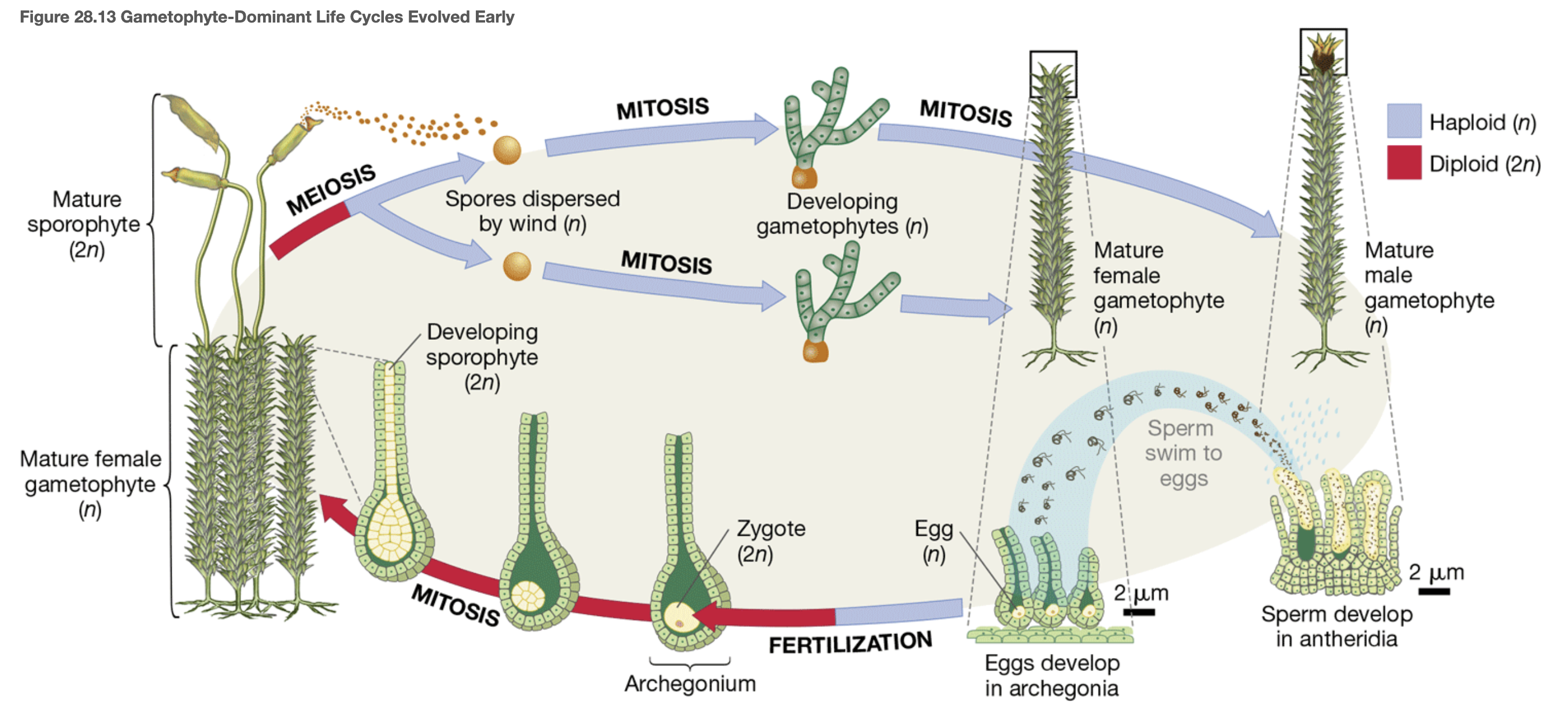
Alternation of generations definition
succession of multicellular haploid and multicellular diploid phases
gametangia
Structure that protects gametes and young embryos from desiccation
gametophyte
multicellular, haploid (n) organism that produces gametes (n)
sporophyte
multicellular, diploid (2n) organism that produces spores (n)
alternation of generations stages
Tracheophytes
Specialized conducting tissues present in Vascular plants
Xylem
tracheids, vessels, dead cells, structural support
Phloem
sieve cells/companion cells, alive cells
True leaves/roots
possesses vascular tissues that conduct water and nutrients
spermatophytes
seed plants
seeds
germinates when conditions are met, protects embryo + provides nutrients until germination, dispersion via ecological interactions
pollen
male gametophyte of plants, removes dependence on water for fertilization, dispersed via ecological interactions, gymnosperms (naked seeds) and angiosperms (seeds within fruits)
notes about wood
xylem tissue resulting from secondary growth from a lateral meristem; structural support/conducting tissue
gametophyte dominant life cycle
sporophyte dominant life cycle