Economics Unit 1 AOS 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Define economics:
Study of the decision making of individuals, businesses and governments regarding the production, consumption, distribution of goods and services and incomes.
What are the two main branches of economics? Describe each.
Microeconomics: Study of the factors that influence the small parts such as a single firm, industry and market that make up the economy.
Macroeconomics: Study of the whole economy and its conditions. This includes: GDP, inflation, employment/unemployment and national incomes.
What are the two forms of economic analysis? Describe each.
Positive Analysis:
Proved or disproved beyond doubt
Based on verifiable facts + Can be tested
Free of personal values, feelings and opinions.
‘Expected’
Normative Analysis:
Proved nor approved
Based on personal opinions, likes and dislikes
‘Should be’
Compare wants and needs
Wants are desires, but are not things needed in order to survive. Whereas needs are things essential for survival.
What are resources? What are the different types and give examples of each.
Resources are the factors of production.
Natural Resources: Productive inputs derived from nature.
E.g. Minerals, water, climate
Labour Resources: Intellectual skills, knowledge and manual effort people provide to produce goods and services.
E.g. doctors, accountants
Capital Resources: manufactured or producer goods that are past production but are used to aid current and future production.
E.g. tractors, factories, commercial buildings
What is relative scarcity?
Basic economic problem – wants and needs are unlimited, however the resources used to fulfil and produce these wants and needs are limited —> resulting in people having to make decisions as to which wants and needs to satisfy first.
Define opportunity cost:
Value of production or consumption given up when resources are allocated to their next best alternative use.
What are productive possibility diagrams used for?
Illustrate ideas such as scarcity, choice in production, opportunity costs, unemployment and nation’s productive capacity.
What do PPDs show?
Productive capacity or physical limits of a nation’s total production, and the output combinations of goods and/or services.
The size of a nation’s PPF depends on what?
Quantity of resources and level of technical efficiency.
What do points inside the PPF illustrate?
Below the economy’s potential capacity/maximum level of production —> resources are not fully utilised
What do points outside the PPF illustrate?
Beyond the economy’s potential capacity/maximum level of production —> results in scarcity, inflation
What are some factors that can cause the PPF to grow in size and shift outwards?
New resources
Better technology
Improved worker efficiency
Better education
High levels of foreign investment
What are living standards affected by?
Affected by both material well-being (income, quantity of goods and services consumed) and non-material well-being (Quality - happiness, low crime rates, long life expectancy, political freedom)
Define trade-offs:
When individuals, businesses or governments make choices between different ways that scarce resources should be used --> sacrifice certain things for an alternative
What is cost-benefit analysis used for and how is it measured?
Used to make decisions that maximise efficiency, satisfaction and wellbeing.
Expected + indirect costs added up
Expected benefits added up
Benefit to cost ratio: total value of benefits/total value of costs
Ans >1 —> Net benefit. Ans <1 —> Net cost
What are the three basic economic questions?
What and how much to produce
How to produce?
For whom to produce
Define economic system:
Collection of national organisations that coordinate production and distribution of goods, services and incomes amongst the population
Define traditional economy:
Old-fashioned, natural
Hunter-gatherer, traveller
System of barter (trade)
Low living standards → Low productive efficiency
Outline how a traditional economy answers these questions:
What and how much to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
What and how much to produce? |
|
How to produce? |
|
For whom to produce? |
|
What are some of the cons of a traditional economy?
Low productive efficiency
Low living standards
Define market economy:
Self-interest, competition, private ownership of resources
Includes consumers, sellers/businesses
System of prices
No government interference
Outline how a market economy answers these questions:
What and how much to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
What and how much to produce? |
|
How to produce? |
|
For whom to produce? |
--> Wages + incomes – Sell scare/wanted resources + require greater skills have higher wages |
What are some qualities of market economies that can lead to market failure?
Cheap production methods → reduce society’s well being
Resources are not allocated efficiently → prevents maximisation of consumer satisfaction + society wellbeing
Define planned economy:
Non-democratic, central government, dictatorial
All businesses are government-owned
Lack of consumer freedom + low allocative efficiency
Outline how a planned economy answers these questions:
What and how much to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
What and how much to produce? |
|
How to produce? |
|
For whom to produce? |
|
What are some cons of a planned economy?
Low allocative efficiency
Lack of consumer freedom
Lack of innovation + adaptability in production
Removal of incentives to work hard + improve skills → providing products & essentials fairly
Define mixed/contemporary economy:
Most features of market economies (competition, price system, consumer sovereignty, most private sector ownership)
Some features of planned economy (government-owned businesses, provision of goods & services)
Outline how a mixed economy answers these questions:
What and how much to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
What and how much to produce? |
|
How to produce? |
|
For whom to produce? |
--> Progressive taxes (tax rises with income) --> Welfare payments (payments to those in need) --> Provision of free or cheap services (health, housing and education) --> Minimum wages |
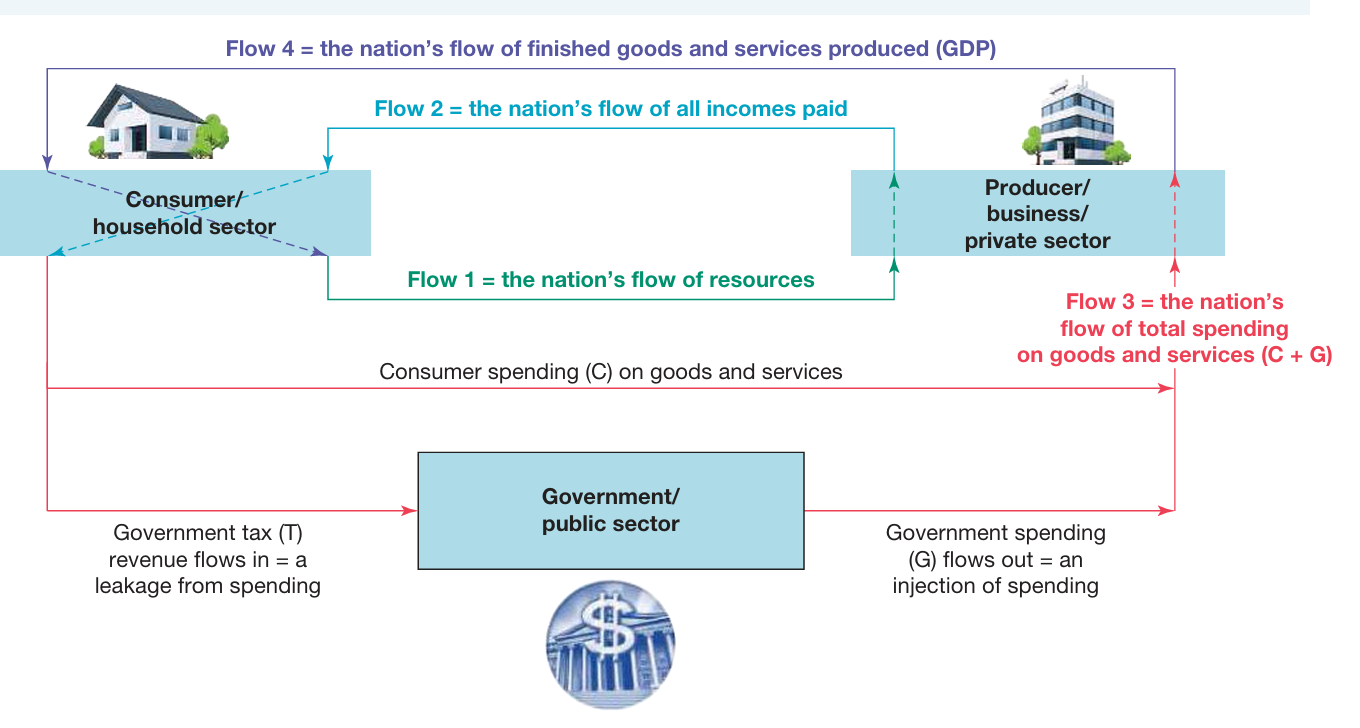
What are the three main sectors of the three-sector circular flow model:
Consumer/household sector
Producer/business sector
Government/public sector
What are the flows in the three-sector circular flow model? Describe each.
Flow 1: (Nation's supply of resources)
Household sector sells wanted resources (labour) to business sector using resource markets
Flow 2: (Demand of resources + payment of national incomes)
Businesses demand resources from household sector --> pay incomes to households
Flow 3: (Nation's spending of incomes or demand for goods and services)/ Aggregate demand
Undertaken by both households and governments
Household pay government taxes + spend leftover income for goods & services
Government uses tax income --> goods & services for the community
Flow 4: (Production of final goods & services/ Nation's GDP)
Production of businesses --> total value of finished goods & services
What are the four stages of the business cycle diagram?
Boom/peak:
Extremely strong spending --> rising prices --> inflation
Slowdown:
Spending starts to fall
Recession:
Economic activity drops
GDP shrinks
Unemployment rises + incomes fall
Recovery:
Spending begins to expand again
Compare material and non-material living standards.
Material:
Affected by incomes, consumption of goods & services
Non-material:
Reflect quality of life (happiness, life expectancy, mental & physical health, freedom, crime rates, education)
Define the term economic agent:
Individual, company or organisation that influences the economy by producing, consuming or selling goods & services.
What are the qualities of a consumer according to the traditional viewpoint?
Rational
Self-interest
Ordered preferences/priorities
Informed and smart decisions based on knowledge
Maximisation of utility → maximise pleasure + minimise pain
Define marginal utility.
Additional satisfaction/benefit consumers derive when consuming an additional unit of a good or service
What is the law of marginal utility?
Number of units consumed increases → utility decreases
Explain these terms:
Incentives
Disincentives
Inducement designed to further encourage behaviour that would otherwise not occur to the same extent
Used to discourage certain behaviour
Provide some examples of government incentives and disincentives.
Cash payments/subsidies
Tax rebates/offsets
Indirect taxes
Enforced laws and regulations
What does business behaviour look at?
Looks at factors influencing the decisions of firms involving the production and sale of goods and services.
What are the qualities of a business according to the traditional viewpoint?
Seek profit maximisation
Give back to the community
Affected by government policies
How would businesses aim to maximise their profit?
--> Maximise sales revenue (advertising, developing new products, consumer sovereignty)
--> Minimise production costs (lower wages, cheaper materials, equipment, transport and utilities)
Define monopoly-type firms:
Sell a particular product/service
Dominant in their field
No competition --> firm has complete control over the price + availability of product/service
Why is government intervention necessary?
Prevent market failure → improve material and non-material living standards
How might the government prevent market failure and improve society’s general wellbeing?
Stabilisation of economic activity
Increase efficiency in resource allocation
Redistributing income fairly
In order for the economy to be stable, how much percent should the GDP rise each year?
3% a year
What are some actions which the government may undertake during booms and recessions?
Booms (GDP is above 3-4%) → Increases taxes + cutting government spending
Recessions (GDP is below 2-3%) → Cutting taxes + raising government spending
What are some ways the government may increase efficiency in resource allocation?
Installing laws to promote competition (Anti-monopoly laws, consumer protection laws)
Provision of beneficial goods and services
Installing laws that discourage harmful production
What are some ways the government may redistribute incomes fairly?
--> Progressive taxes (tax rates rise with income)
--> Welfare benefits to the neediest
--> Provision of services