BIO 1A FINAL- UC BERKELEY
1/387
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
388 Terms
carbohydrates
sugars & polymers of sugars
monossacharides
simple sugars, simplest carb
- molecular form.'s usually have multiples of CH2O
- glucose is most common
- pentose or hexose
- aldose or ketose
-serve as a major fuel for cells andas raw material for building molecules
polyssacharides
carb macromolecules, polymers composed of many building blocks
dissacharides
2 monossacharides linked by dehydration synthesis
used for sugar transport or energy storage
-sucrose, lactose, maltose
dehydration synthesis
FORM OF CONDENSATION REACTION!
occurs when two molecules or compounds are joined to form a larger molecule following the removal of water
combines 2 molecules into a single molecule with the loss of water
REMEMBER:
rhymes with "stay hydrated" --> say hi drated!
aka addison rae (2 names/ 2 molecules)
but she will drop rae (loss of water) in order to become a larger popstar (larger molecule)
lipids
large biological molecules that do not include true polymers
- little or no affinity for water
- hydrophobic bc they consist of mostly hydrocarbons which form nonpolar covalent bonds
ex: fats, phospholipids, steroids
fats
constructed by two types of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids
-major function is energy storage
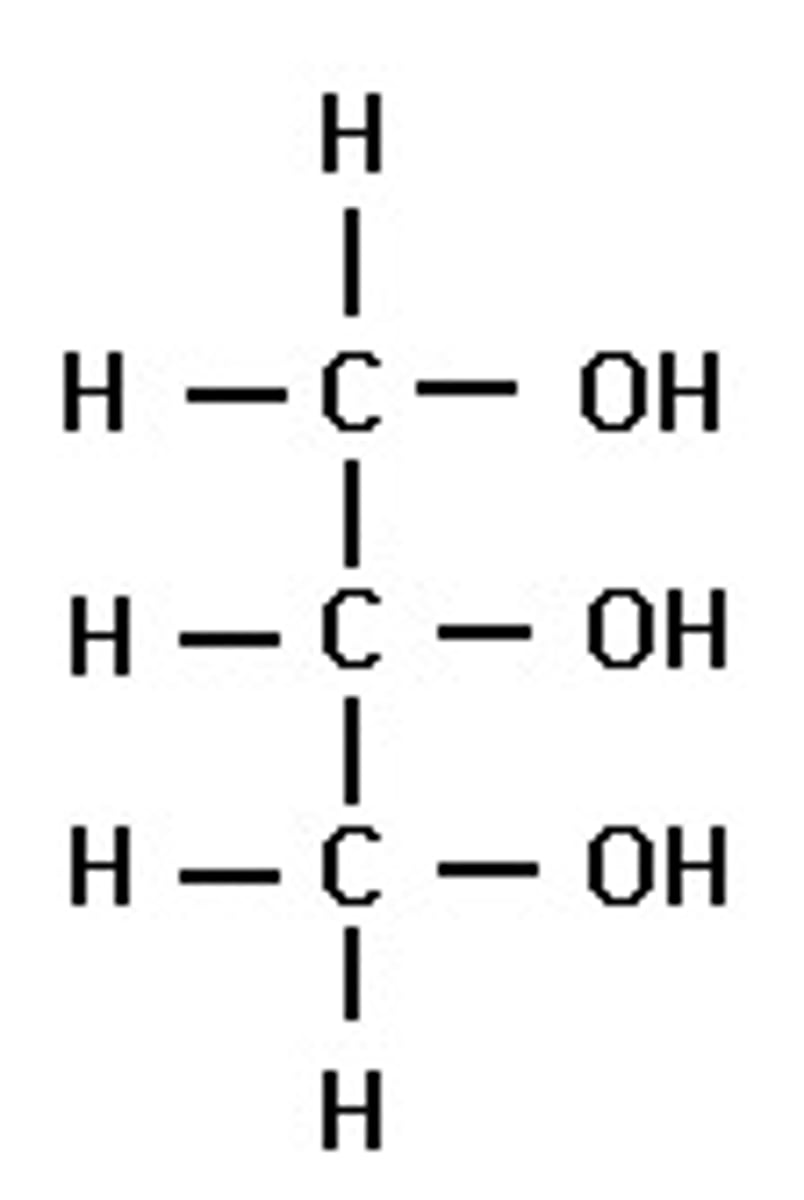
glycerol
three carbon alcohol w a hydroxyl group atatched to each carbon
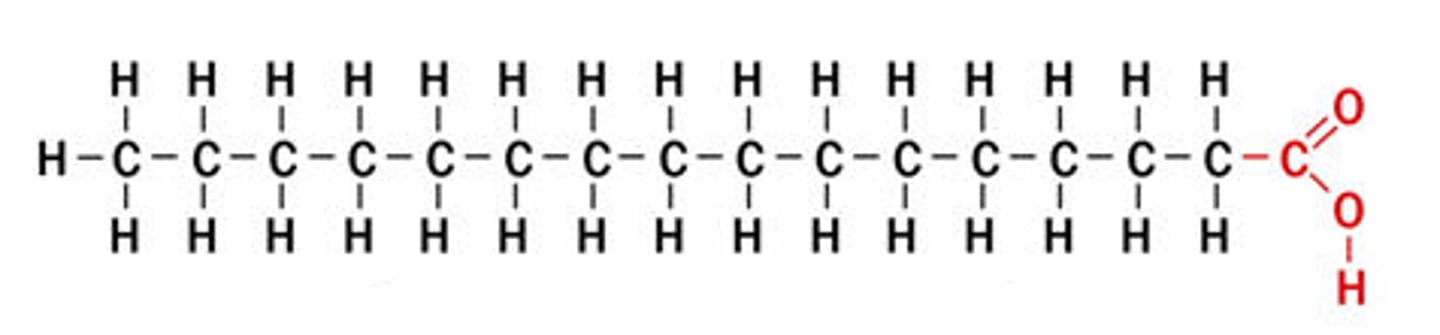
fatty acids
consistes of carboxyl group (COOH) attatched to a long carbon skeleton
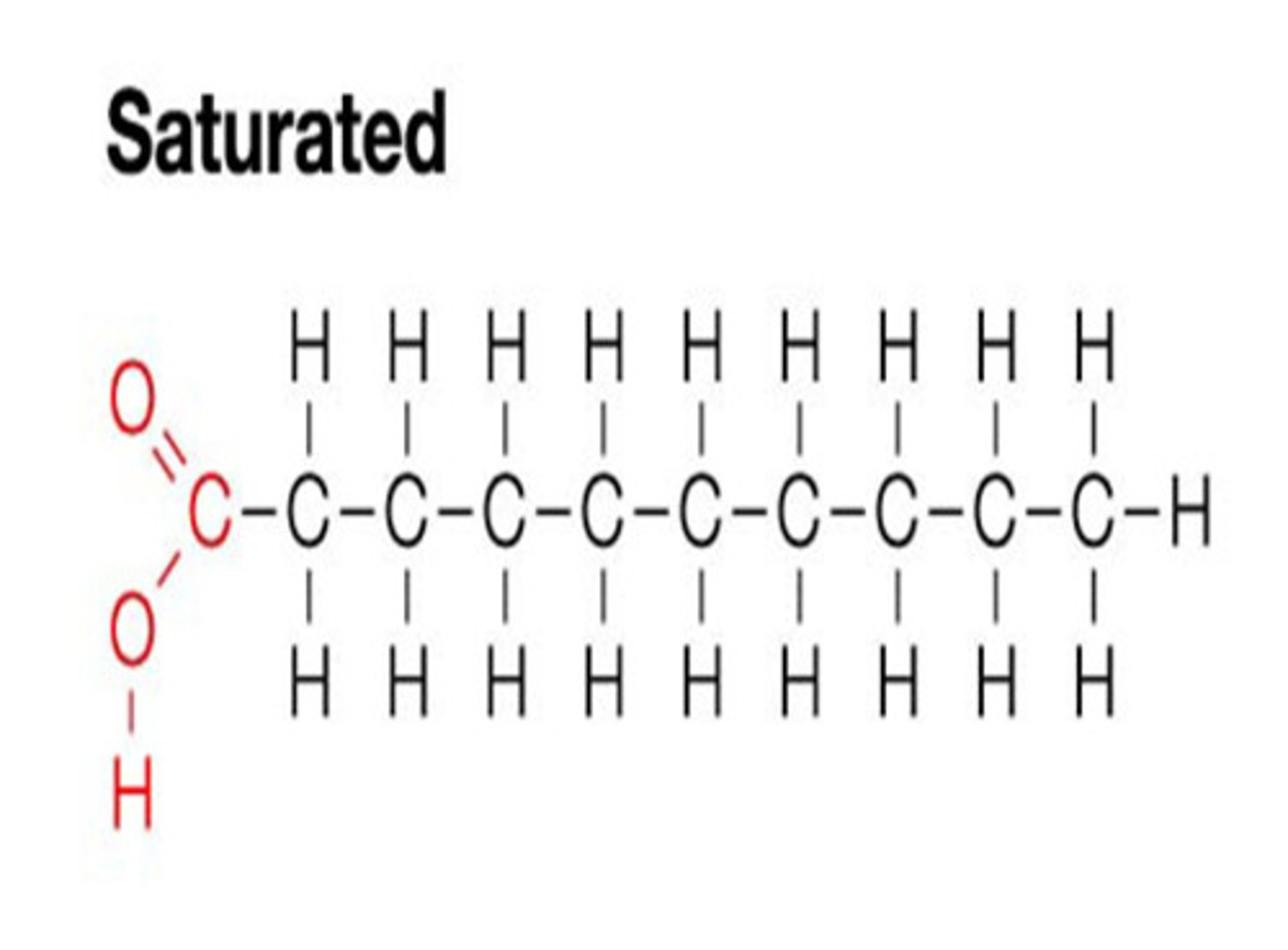
saturated fatty acid
Solid, no bends, also known as trans fat
REMEMBER: this one is Straight (Saturated/ Straight) aka heterosexual (but theyre tranSgender) but still Straight
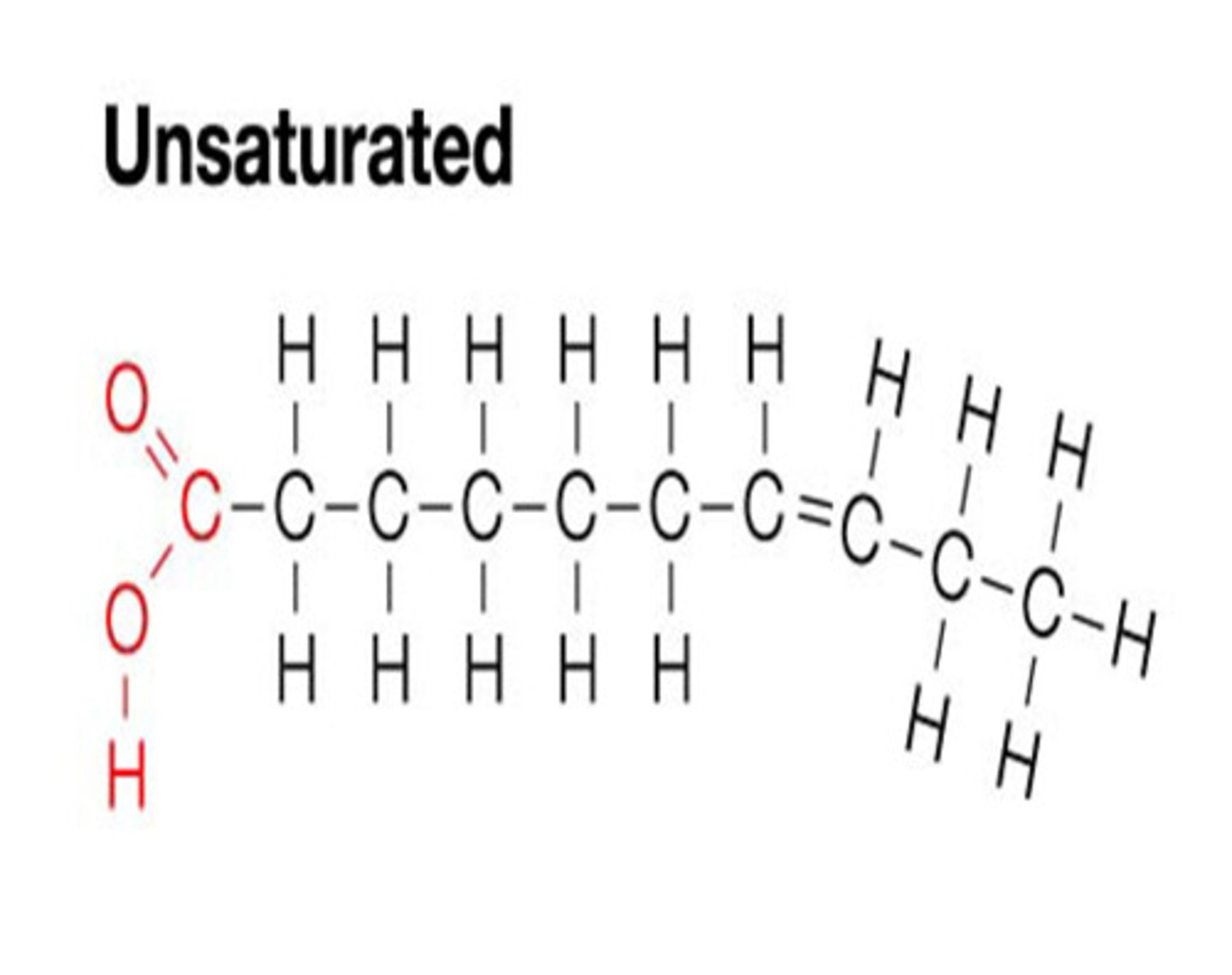
unsaturated fatty acid
Liquid, and has a bend (aka a cis-double bond)
REMEMBER: it is gay bc it is bent aka not straight, and they are cis bc they are the same gender they were born as, they're just gay
U in Unsaturated also looks like a bend
also if u turn the u sideways it looks like a c aka cis fat
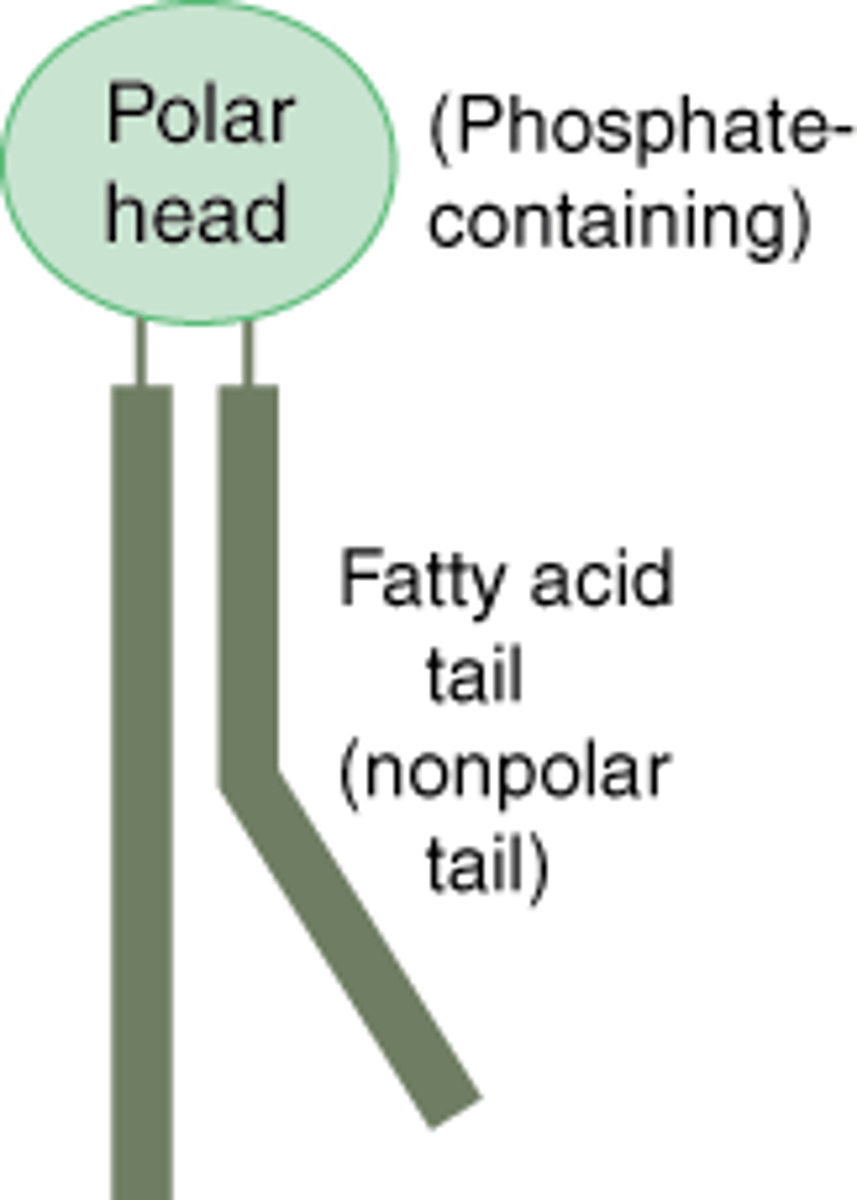
Phospholipids
two fatty acids and a phosphate group that are attatched to a glycerol
Structure:
- two fatty acid tails (hydrophobic)
- head (hydrophilic)
phospholipids are essential for cells bc they make up cell membranes
Steroids
lipids that are characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of 4 fused rings
cholesterol
important type of steroid that is a component in animal cell membranes
proteins
have many structures which have wide range of functions
consist of one or more polypeptides
- more than 50% of dry mass of most cells
FUNCTION:
- catalyze biochem reactions
- structural support
- transport
- cell communication
- movement
- defense against foreign substances
polypetides
polymers built from same set of 20 amino acids
make up proteins
amino acids
organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups
differ in properties due to side chains (R groups)
chirality
whether u can get the mirror image of a molecule and rotate it and be able to superimpose it to the original molecule
4 levels of protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quarternary
2 types of nucleic acids
1.) deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- genes are stores ads DNA
- formed through condensation
2.) ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- formed through condensation
polynucleotide
nucleic acids
- they are polymers called polynucleotides
nucleotides
monomers which make up polynucleotide
- each consists of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar (RNA or DNA), and a phosphate group
nucleoside
portion of a nucleotide without the phosphate group
DNA
type of nucleic acid
- has 2 polynucleotides spiraling, forming a double helix
- in the double helix, 2 backbones run in opposite 5'-> 3' directions aka are antiparallel
- one DNA molecule includes many genes
- nitrogenous bases in DNA pair up and for H bonds
- A -> T, G -> C
glycosidic linkage
covalent bond, connects a sugar molecule to another molecule which can be another sugar or something else
cell fractionation
takes cells apart and seperates the major organelles from one another
- can be done w ultracentrifuge
all cells have:
plasma membrane cytosol, chromosomes (carry genes), ribosomes (make proteins)
Prokaryotic cells
organisms: bacteria & archaea
defining features:
- no nucleus
- dna in unbound region called the nucleoid
- no membrane bound organelled
- cytoplasm bound by the plasma membrane
very small (1-10 um)
Eukaryotic cells
organisms: animals, humans, plants, amoebas, paramecia
defining features:
- dna in nucleus that is bound by nuclear envelope
- membrane bound organelles
- cytoplasm in region between the plasma membrane and the nucleus
bigger (10-100um)
nucleus
contains most of the cells genes
nuclear envelope
encloses the nucleus, seperating it from the cytoplasm
ribosomes
protein factories! carry out protein synthesis in two locations! in the cytosol (free ribosomes) or on the outside of the endoplasmic eticulum or the nuclear envelope (bound organelles)
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
lacks ribosomes
-synthesizes lipids
-metabolizes carbs
detoxifies poison
-stores calcium
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
ribosomes studding its surface
-ribosomes secrete glycoproteins (proteins covalently bonded to carbs)
-distributes transport vesicles (proteins surrounded by membranes
-serves as the membrane factory of the cell
Golgi apparatus
consists of flat membranous sacs called cisternae
-modifies products of the ER
-manufactures cerain macromolecules
-sorts/packages materials into trabspirt vesicles
lysosomes
digestive compartments, fuses w the food vacuole and digests the molecules
- cells can engulf other cells (phagocytosis) which forms food vacuole
- can also use the enzymes to recycle the cell's own organelles (autophagy)
mitrochondria
site of cellular respiration, aka the metabollic process that generates ATP
- contain own dna
- have proteins made by free ribosomes
- have double membrane
- not a part of the endomembrane system
- nearly in all eukaryotic cells
- have smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane which is folden into cristae, inside is the matrix
• Mitochondria are organelles in eukaryotic cells
• They have a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane folded into cristae
• The inner membrane creates two compartments: intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix
• Some metabolic steps of cellular respiration are catalyzed in the mitochondrial matrix
• Cristae present a large surface area for enzymes that synthesize ATP
chloroplasts
found in plants and algae, are the sites of photosynthesis
- contain own dna
- have proteins made by free ribosomes
- have double membrane
- not a part of the endomembrane system
- contain chlorophyll
- found in leaves and other green organs
- part of plastids
preoxisomes
oxidative organelles
cytoskeleton
network of fibers that organize structures and activities in the cell
made of:
- microtubules
- microfilaments (actin filaments)
- intermediate filaments
interacts with motor proteins to produce motility, can help regulate biochemical activites, helps support shape and structure
- cells can travel along monorails which are provided by the cytoskeleton
actin and myosin help produce...
cell motility
actin forms thin filaments
myosin forms thick filaments
...then, myosin walks along actin filaments which causes either muscle contraction or shape/movement/division
myosin moves towards the positive end of the acting filament bc they have polarity
cell wall
only in plant cells and prevents excessive uptake of water, are made of cellulose fibers
intercellular junctions
Structures that connect adjacent cells in tissues, allowing communication, adhesion, or barrier formation between them
ex:
- Plasmodesmata
- Tight junctions
- Desmosomes
- Gap junctions
tight junctions
At tight junctions, membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together, preventing leakage of extracellular fluid
desmosomes
(anchoring junctions) fasten cells together into strong sheets
gap junctions
(communicating junctions) provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells
amphipathic molecules
molecules that contain hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
Membrane proteins
Peripheral proteins: bound to the surface of membrane
Integral proteins: penetrate the hydrophobic core
- if they span the membrane, they are transmembrane proteins
SIX MAJOR FUNCTIONS:
1. transport
2. enzymatic activity
3. signal transductions
4. cell-cell recognition
5. intercellular joining
6. attatchment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE:
polar molecules like sugar dont cross membrane easily, hydrophobic molecules dissolve in lipid bilayer and pass through membrane rapidly
selective permeability
The property of a cell membrane that allows some substances to pass through while blocking others
diffusion
tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Water diffuses across a membrane from the region of lower solute concentration to the region of higher solute concentration
flow of water through a selectively permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to high!
tonicity:
the ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Isotonic solution
Solute concentration is the same as that inside the cell; no net water movement across the plasma membrane
Hypertonic solution:
Solute concentration isgreater than that inside the cell; cell loses water
Hypotonic solution:
Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
aquaporins
channel proteins which facilitate the passage of water
transport proteins
allow the passage of hydrophillic substances across membrane
ion channels
open/close in response to stimulus (gated channels)
active transport
moves substances against and across concentration gradients
requires energy ususally atp
membrane potential
voltage difference across a membrane (inside of cell is negatively charged
voltage is created by differences in distribution of positive and genative ions
electrochemical gradient
two collective combined forces that drive the diffusion of ions across a membrane. these forces are:
- A chemical force (the ion's concentration gradient)
- An electrical force (the effect of the membrane potential on the ion's movement)
electrogenic pump
a transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane
animals: sodium potassium pump
plants/fungi: proton pump
exocytosis
the cell exports large molecules by packaging them into vesicles that fuse with the membrane and release their contents outside
when transport vesicles migrate to the membrane, fuse with it, and release their contents
endocytosis
the cell takes in large molecules by engulfing them in a vesicle
when the cell takes in macromolecules by forming vesicles from the plasma membrane
metabolism
the totality of an organism's chemical reactions
Metabolism is an emergent property of life that arises from interactions between molecules within the cell
never at equlibrium
metabolic pathway
begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product, each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme
catabolic pathways
release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds
releases free energy in a series of reactions
ex: cellular respiration
REMEMBER:
imagine a cat giving birth to multiple kittens, which means that they are breaking down the bigger and more complex molecule AKA THE CAT into smaller and simpler compounds THE KITTENS
Anabolic pathways
consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones
ex: protein from amino acids
REMEMBER: the criminal ana who stole money from celebrities. she took smaller simpler fortunes AKA SMALLER SIMPLER MOLECULES to make one big fortune for herself A BIG COMPLEX MOLECULE
energy
is the capacity to cause change
kinetic energy
energy associated w motion
thermal energy
kinetic energy associated w random movement of atoms or molecules
potential energy
is energy that matter posseses because of its location or structure
chemical energy
PE available for release in a chemical reaction
law of conservation of energy/ the first law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed
closed system
such as that approximated by liquid in a thermos, is isolated from its surroundings
Reactions in a closed system eventually reachequilibrium and then do no work
open system
energy and matter can be transferred between the system and its surroundings
organisms are open system
the second law of thermodynamics
During every energy transfer or transformation, some energy is unusable, and is often lost as heat
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe
free energy
energy that is available to do work when temperature and pressure are uniform, as in a living cell
The free-energy change of areaction tells whether or not thereaction occurs spontaneously
spontaneous reaction
A reaction that will proceed without any outside energy DOESNT need energy input
so, For a process to occur without energy input, it must increase the entropy of the universe (ΔS is positive) or its total energy must decrease (ΔH is negative)
During a spontaneous change, free energy decreases and the stability of a system increases
nonspontaneous reaction
a reaction that does need input from outside and delta G is positive
exergonic reactions
• Exergonic reactions release energy to the system.
• ΔG < 0
• Exergonic reactions proceed spontaneously
Endergonic reactions
• Endergonic reactions absorb energy from the system.
• ΔG > 0
• Endergonic reactions are not spontaneous
enzymes
catalysts of chemical reactions
Enzymes do not alter the reaction equilibrium, but they alter the forward and reverse reaction rates.Enzymes remain unchanged after the reaction
typically ends in -ase
ENZYME ACTIVITY CAN BE AFFECTED BY:
- temperature
- pH levels
- chemicals that specifically influence the enzyme
• Each enzyme has an optimal temperature at which it can function
• Each enzyme has an optimal pH at which it can function
--> can be regulated by structural changes
Regulation of enzyme activity helps control metabolism
- A cell does this by switching on or off the genes that encode specific enzymes or by regulating the activity of enzymes
active site
active site of an enzyme is usually a cleft pocket where chemistry takes place
substrate
A molecule that binds in the active site and is acted upon by the enzyme
Enzymes bind better to transition states than to substrates
a cell does three kinds of work
chemical, transport, mechanical
ATP (adenine triphosphate) energy
acts as the immediate source of energy that powers most energy coupling to perform cellular work
is composed of ribose (a sugar),adenine (a nitrogenous base),and three phosphate groups
ATP hydrolysis
A chemical reaction where ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is broken down into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and a phosphate group, releasing energy.
ATP is converted to ADP & phosphate energized myosin heads (removal of phosphate) need energy
The term "hydrolysis" literally means "breaking with water."
In ATP hydrolysis, a water molecule (H₂O) breaks the bond between the second and third phosphate groups of ATP.
free energy of activation, or activation energy (EA)
The initial energy needed to start a chemicalreaction
The active site can lower an EA barrier by- Orienting substrates correctly- Straining substrate bonds- Providing a favorable microenvironment- Covalently bonding to the substrate
Michaelis-Menten kinetics
• Vo is the initial velocity of the reaction
• Vmax is the maximum velocity
• [S] is the substrate concentration
• Km is Michaelis-Menten constant: the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half of the maximum velocity
![<p>• Vo is the initial velocity of the reaction</p><p>• Vmax is the maximum velocity</p><p>• [S] is the substrate concentration</p><p>• Km is Michaelis-Menten constant: the substrate concentration at which the reaction velocity is half of the maximum velocity</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1cd6d0e7-6c9f-49ee-b6b5-9bdd259bc2af.jpg)
cofactors
nonprotein enzyme helpers
may be inorganic or organic
tightly bound cofactors are called prosthetic croups
organic cofactor is a COENZYME
- coenzymes include vitamins
-coenzymes are loosely bound cofactors
feedback inhibition
Feedback inhibition prevents a cell from wasting chemical resources by synthesizing more product than is needed
this is when the end product of a metabolic pathway shuts down the pathway
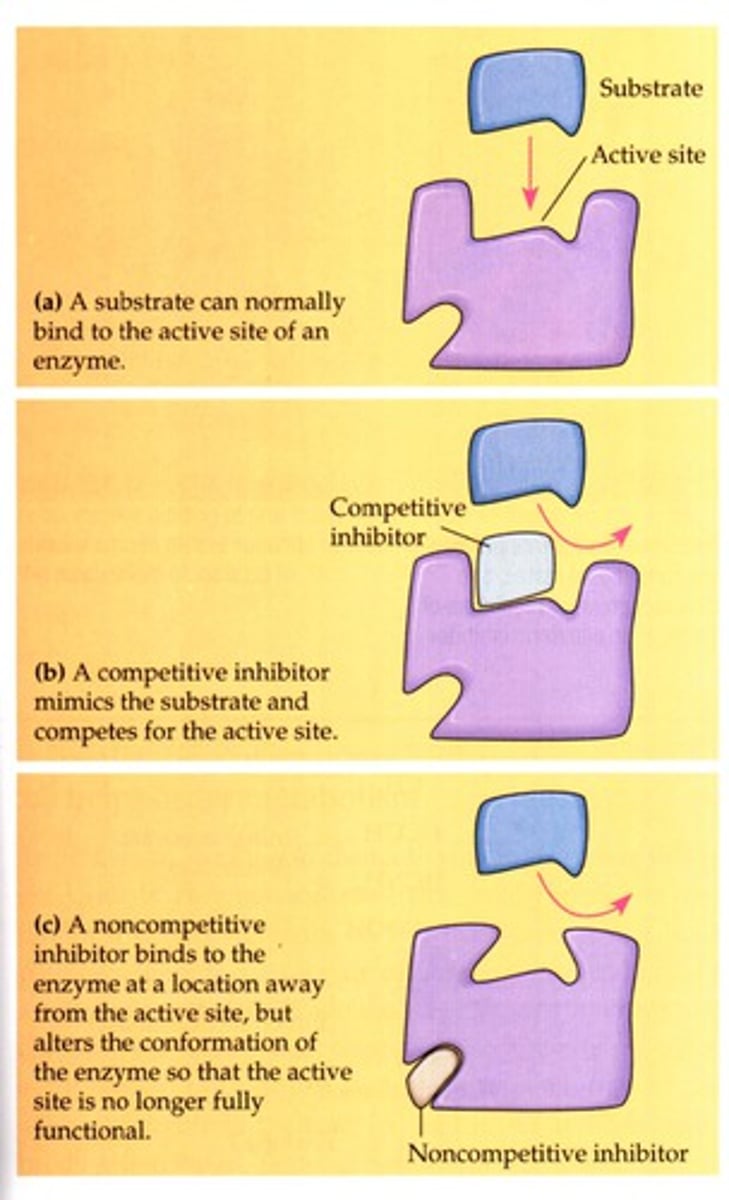
competitive inhibitors
bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
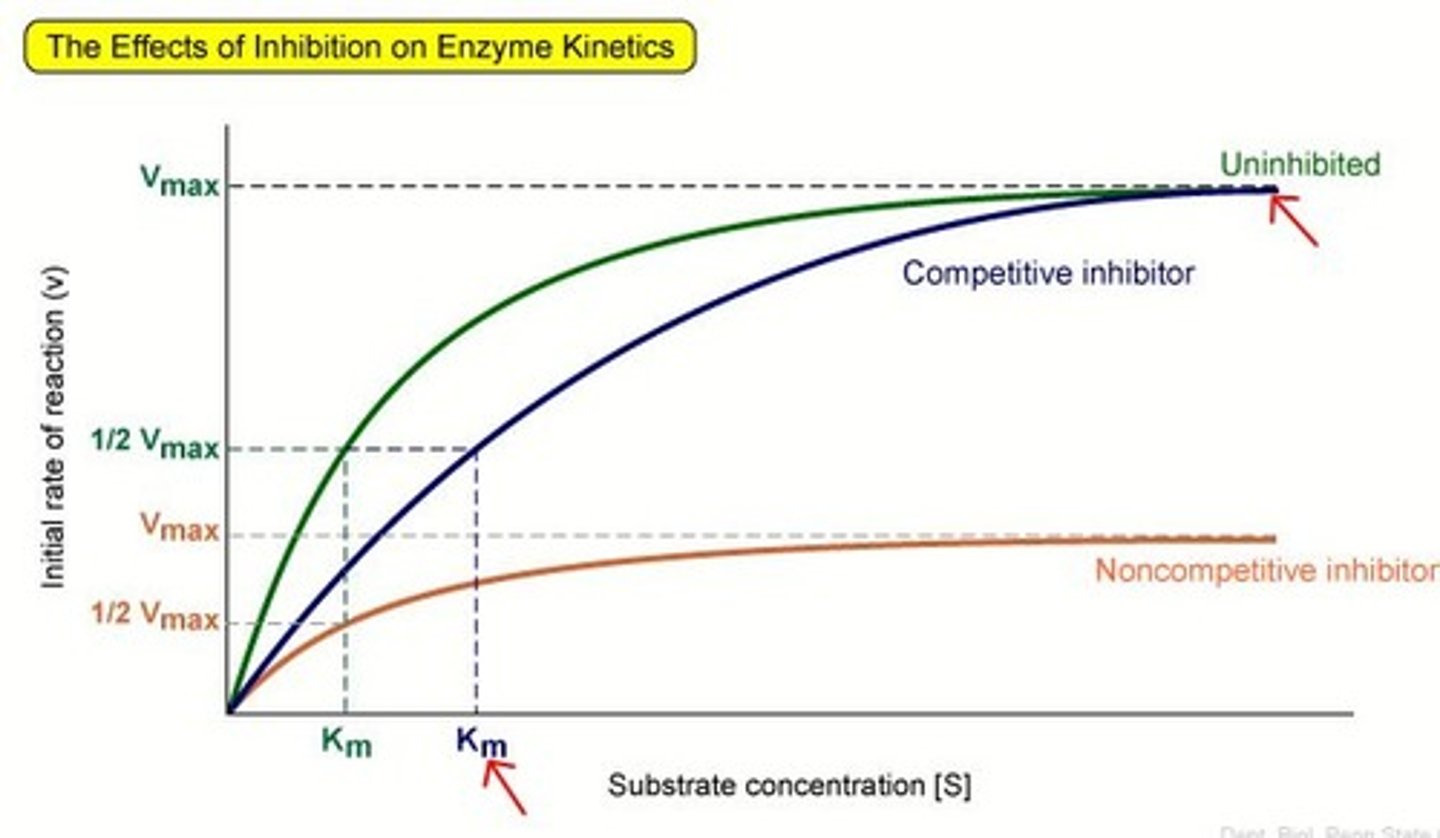
noncompetitive inhibitors
bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective
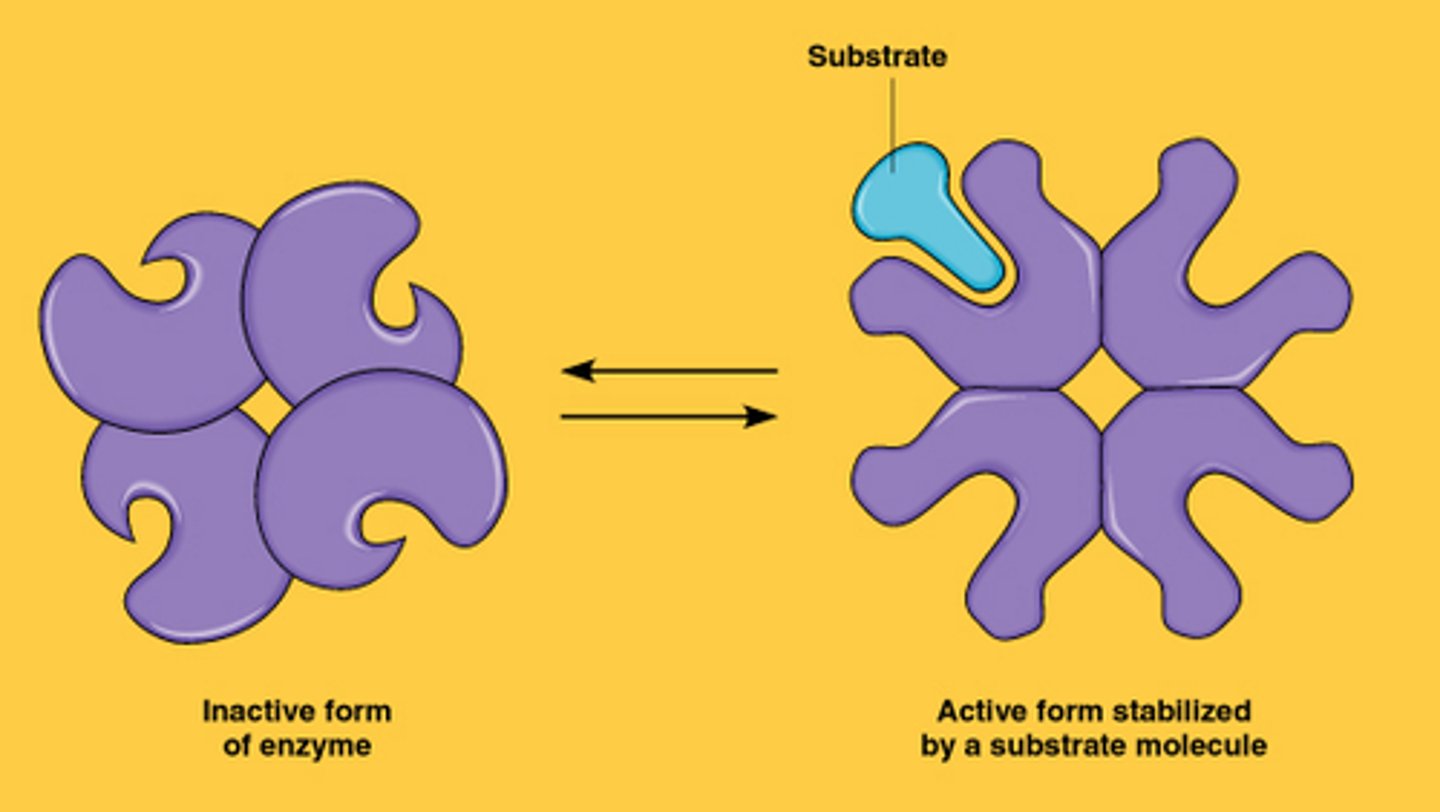
allosteric regulation
• Allosteric regulation may either inhibit or stimulate an enzyme's activity
• Allosteric regulation occurs when a regulatory molecule binds to a protein at one site and affects the protein's function at another site
ex: hemoglobin
--> mostly quaternary structure
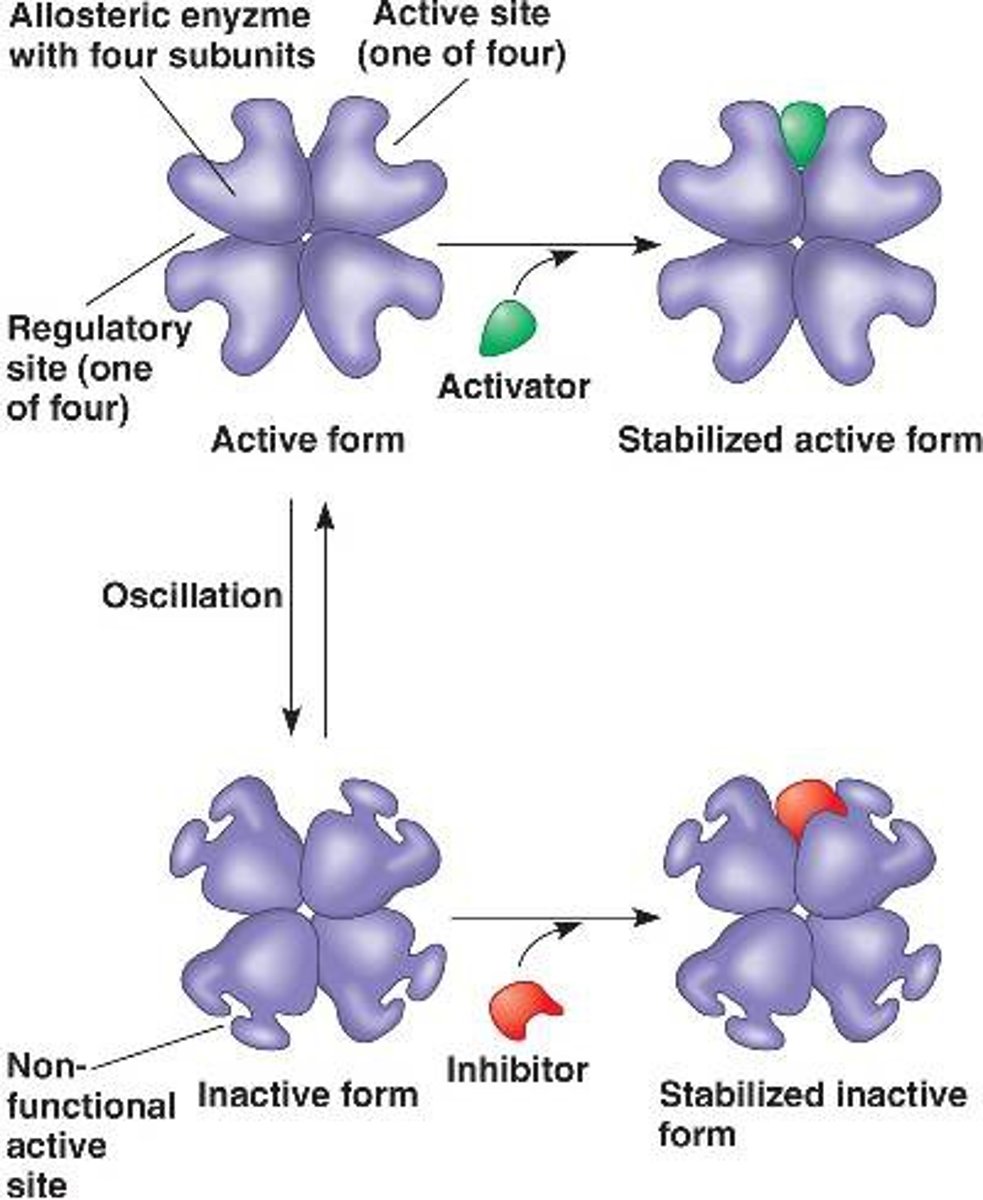
cooperativity
- is a form of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity
• Cooperativity is considered allosteric regulation because binding by a substrate to one active site affects catalysis at another active site
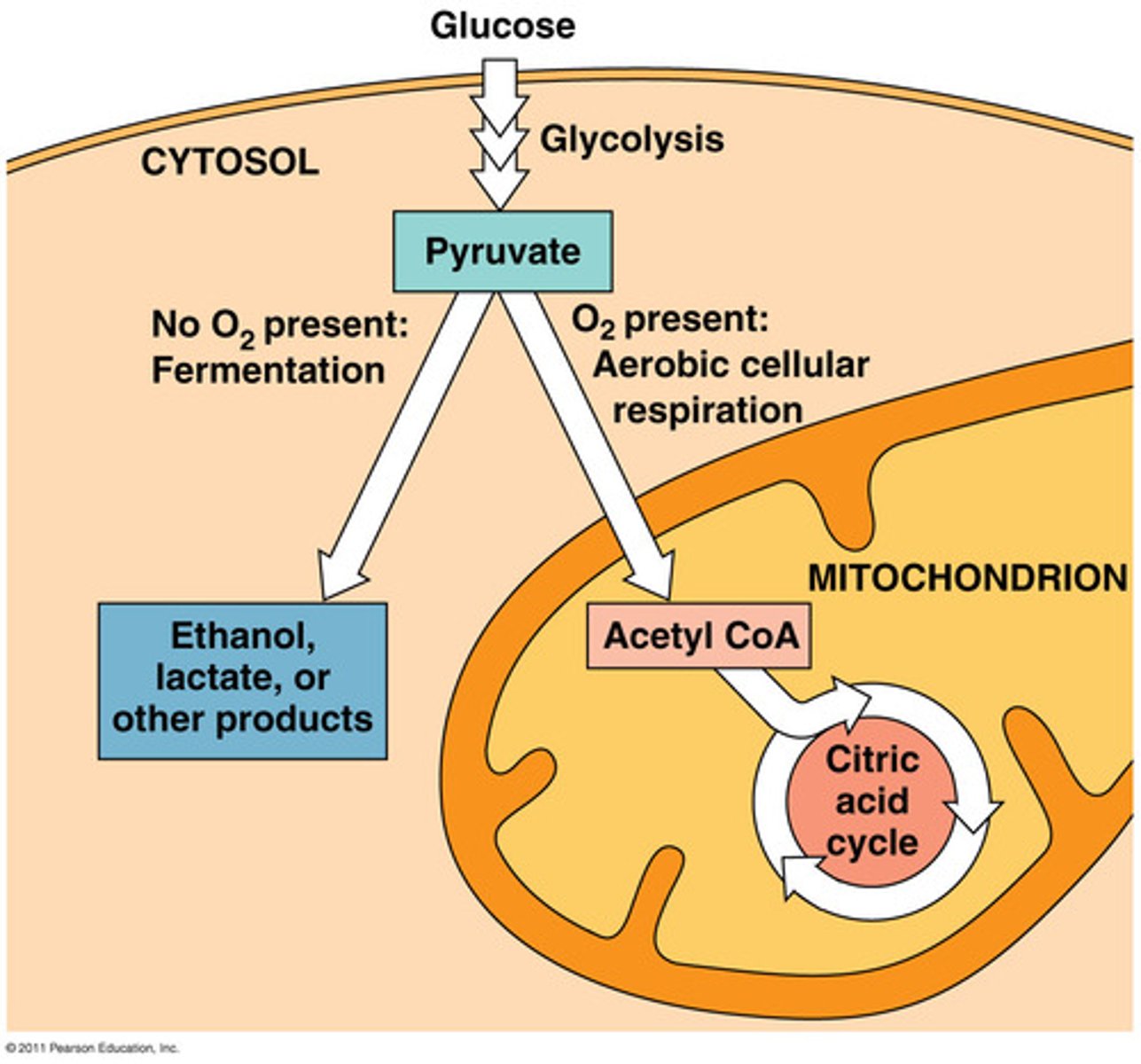
Fermentation
a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration enable cells to produce ATP without using oxygen
-> In the absence of O2 , glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produceATP
Fermentation uses substrate-level phosphorylationinstead of an electron transport chain to generate ATP
• Fermentation consists of glycolysis plus reactions that regenerate NAD+ , the oxidizing agent of glycolysis• Two common types are alcohol fermentationand lactic acid fermentation
Obligate anaerobes
carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2
facultative anaerobes
can survive using either fermentation or cellular respiration
In a facultative anaerobe, pyruvate is a fork in the metabolic road that leads to two alternative catabolic routes
Aerobic respiration
consumes organic molecules and O2 (uses oxygen) and yields ATP