Systems Path Section 6 - Lung Tumors and Pleural Lesions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is the most common site of metastasis?
lungs
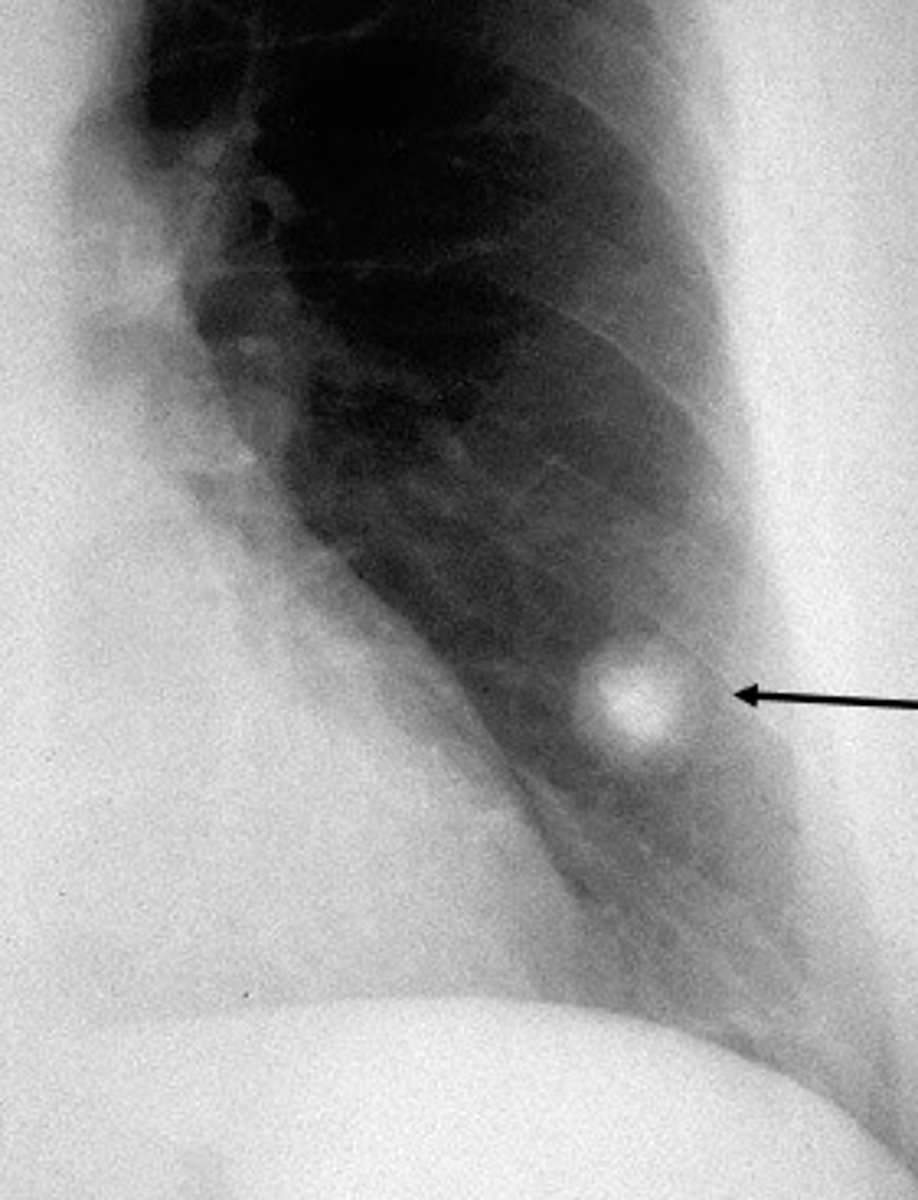
MC lung tumor which is benign and characterized by a single solitary pulmonary nodule called a "coin lesion"
hamartoma
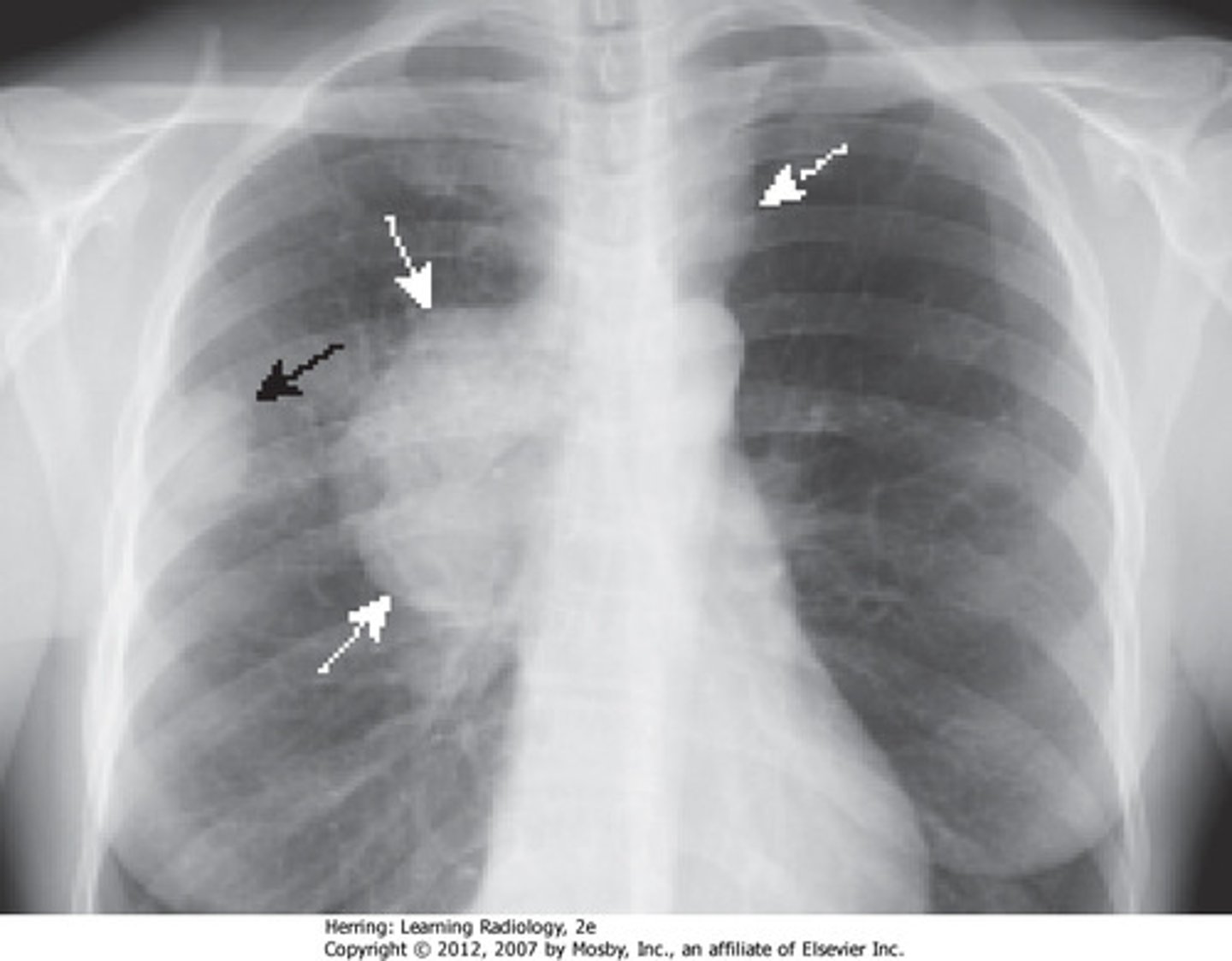
lung tumor which arises from bronchial epithelia
bronchogenic carcinoma
malignancy of bronchial glandular cells which is usually found in non-smokers
adenocarcinoma
who is an adenocarcinoma MC in?
ages 50-70
malignancy of bronchial epithelial cells common in smokers
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant of bronchial epithelial cells which is the worst prognosis of all lung cancers due to increased odds of metastasis at time of diagnosis
small-cell carcinoma
who is small cell carcinomas common in?
smokers age 50-70
malignancy of bronchial epithelial cells common in smokers and non-smokers
large cell carcinoma
what causes 90% of lung cancers?
smoking
sites of mets from lung cancer?
brain, liver, bones, adrenals
most aggressive lung cancer
small cell carcinoma
MC non-small cell lung cancer located in pulmonary apex which leads to damage and symptoms with vertebrae, upper ribs, brachial plexus and sympathetics
pancoast tumor
who is pancoast tumors common in?
smokers age 50-70
signs and symptoms of pancoast tumor
pancoast syndrome and Horner syndrome
shoulder pain/C8-T2 radicular pain
pancoast syndrome
ptosis, miosis, anhindrosis
Horner syndrome
fluid in pleural cavity
pleural effusion
protein poor pleural effusion caused by heart failure
transudate (hydrothorax)
MC cause of pleural effusion
heart failure
protein rich pulmonary effusion caused by inflammatory conditions
exudate (pleuritis)
pus in pleural space
empyema
causes of pleural exudate
bacterial/viral infections, tumors, pulmary infarction
air within pleural cavity
pneumothorax
a type of pneumothorax in which air that enters the chest cavity is prevented from escaping and shifts mediastinum
tension pneumothorax
blood in pleural cavity
hemothorax
lymphatic fluid in pleural cavity
chylothorax
malignancy of mesothelium (pleura) associated almost exclusively with asbestos exposure
mesothelioma
How does mesothelioma develop?
chronic inflammation and failed phagocytosis due to asbestos