Hema 2: Lymphoproliferative diseases and Lymph nodes
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
[Lymphoma]
Weight loss and loss of appetite [2]
Lymphadenopathy
Exophthalmos
dyspnea and esophageal destruction
diarrhea, obstruction or melena
Non specific signs (2)
Painless enlargement of lymph nodes:
Other signs depend on anatomic location:
Retrobulbar lymph nodes:
Thymus:
Alimentary:

soft to firm, bulge on cut surface, homogenous, pale tan to white
foci of necrosis or hemorrhage
often firmly attached (fibrosis) to surrounding tissue
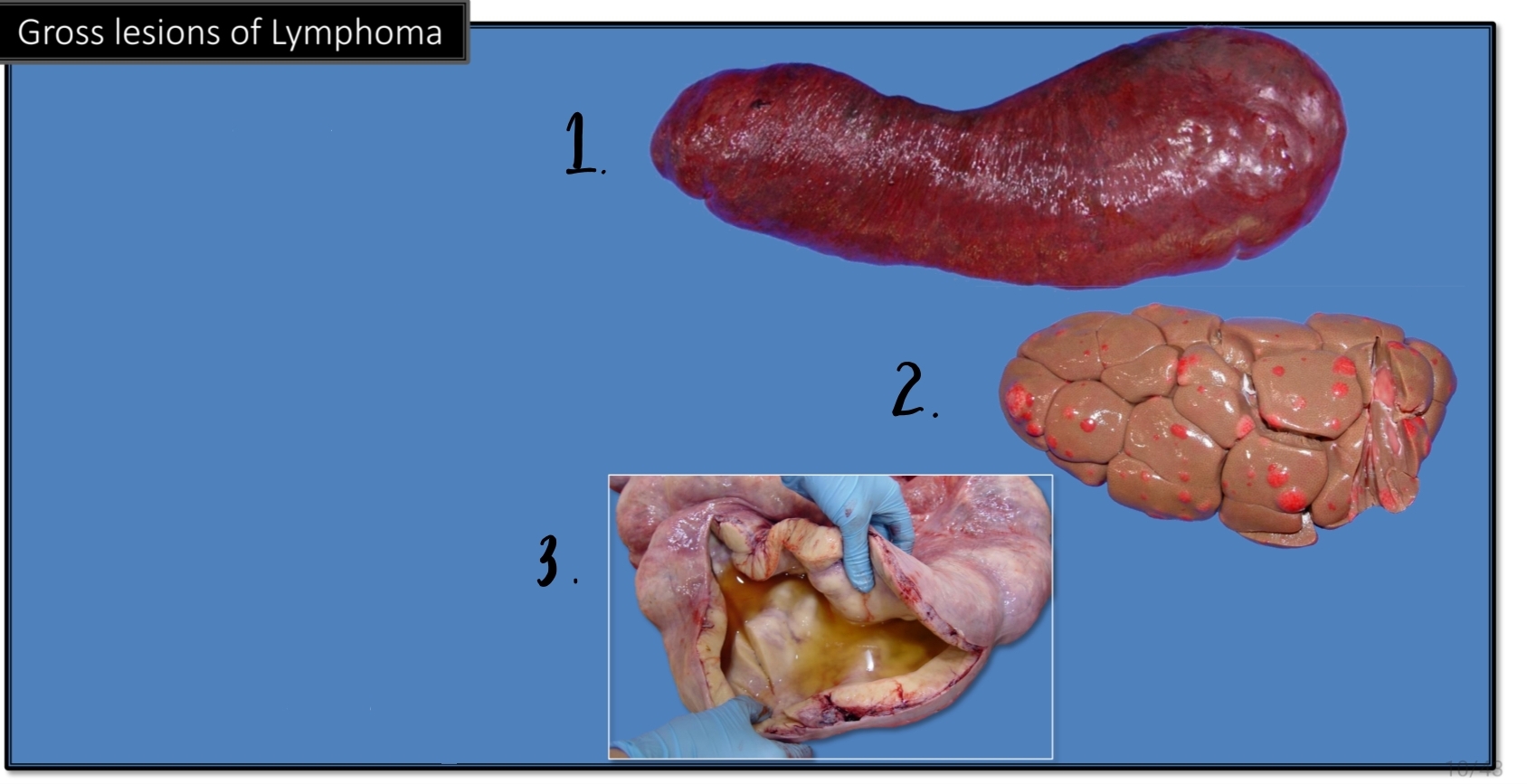
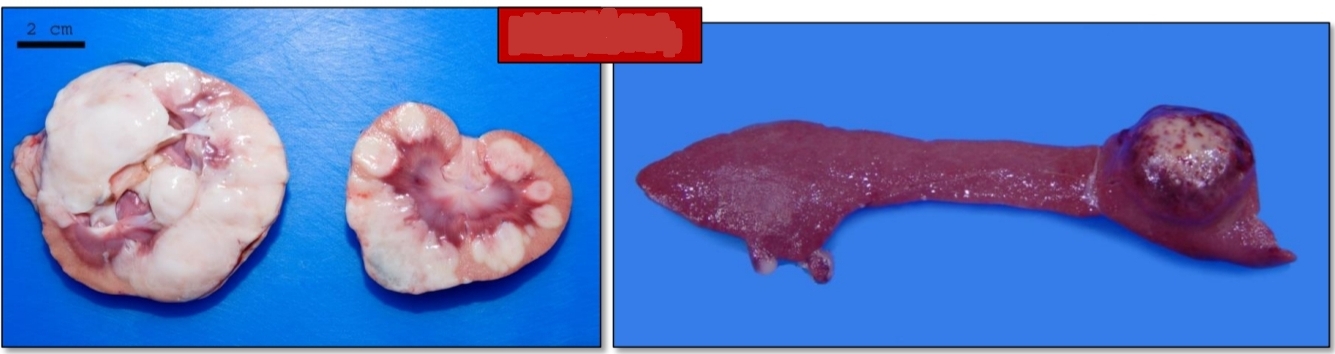
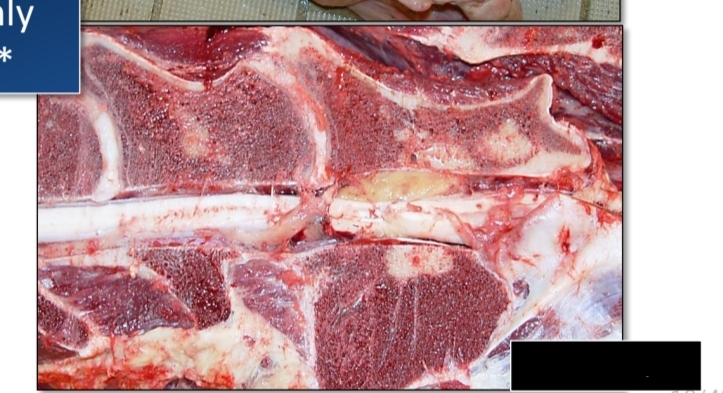
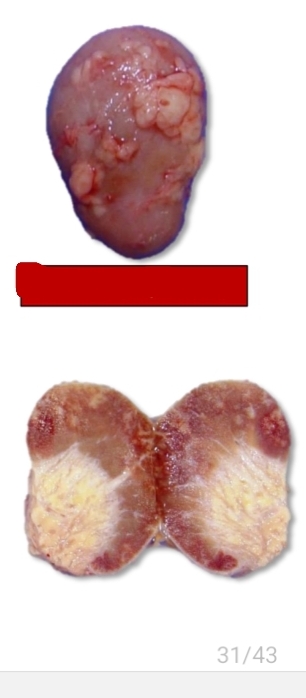
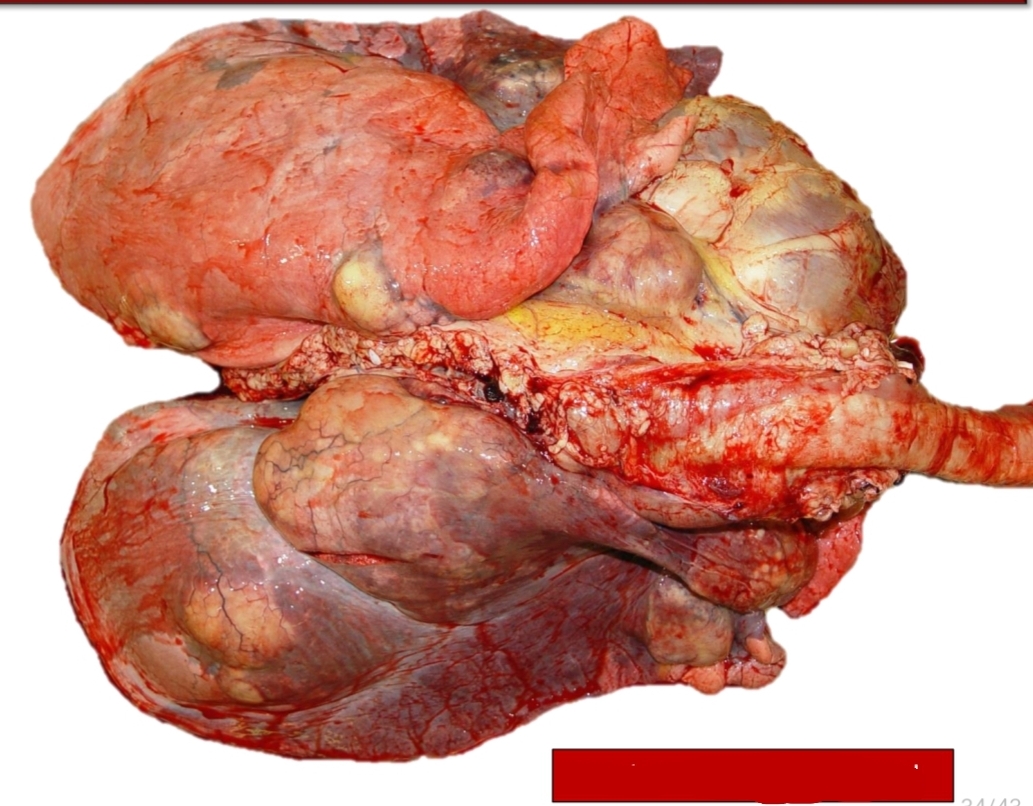
Gross lesions [Lymphoma][3]
![<p>Gross lesions [Lymphoma][3]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2d48fc5b-b936-4436-b318-86d63ec4fa46.jpg)
Organomegaly: diffuse organ enlargement
Multiple tan-white to pink nodules within organs
thickening of walls of tubular organs
Identify.
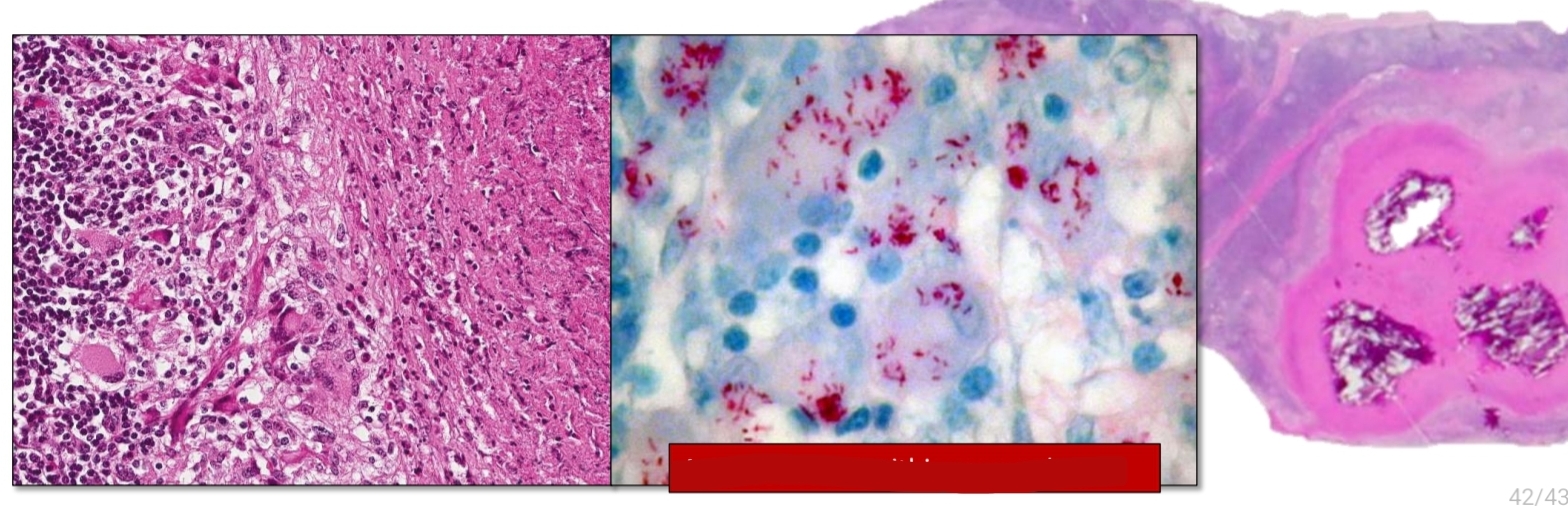
Neoplastic round cells efface the normal structure
[Microscopic lesion of Lymphoma]
![<p>[Microscopic lesion of Lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b5e180e9-b9a8-4c90-bae8-378d51a816c5.jpg)
Uniform population of small lymphocytes
[Microscopic lesiom of Lymphoma]
![<p>[Microscopic lesiom of Lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b0a1fb74-d668-4c45-ba3c-4fcbe5fd4a17.jpg)
Anaplastic round cells with mitoses, anisocytosis, anisokaryosis
[Microscopic lesion of Lymphoma]
![<p>[Microscopic lesion of Lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/70bf47b4-982b-462b-9725-96eb9cd13354.jpg)
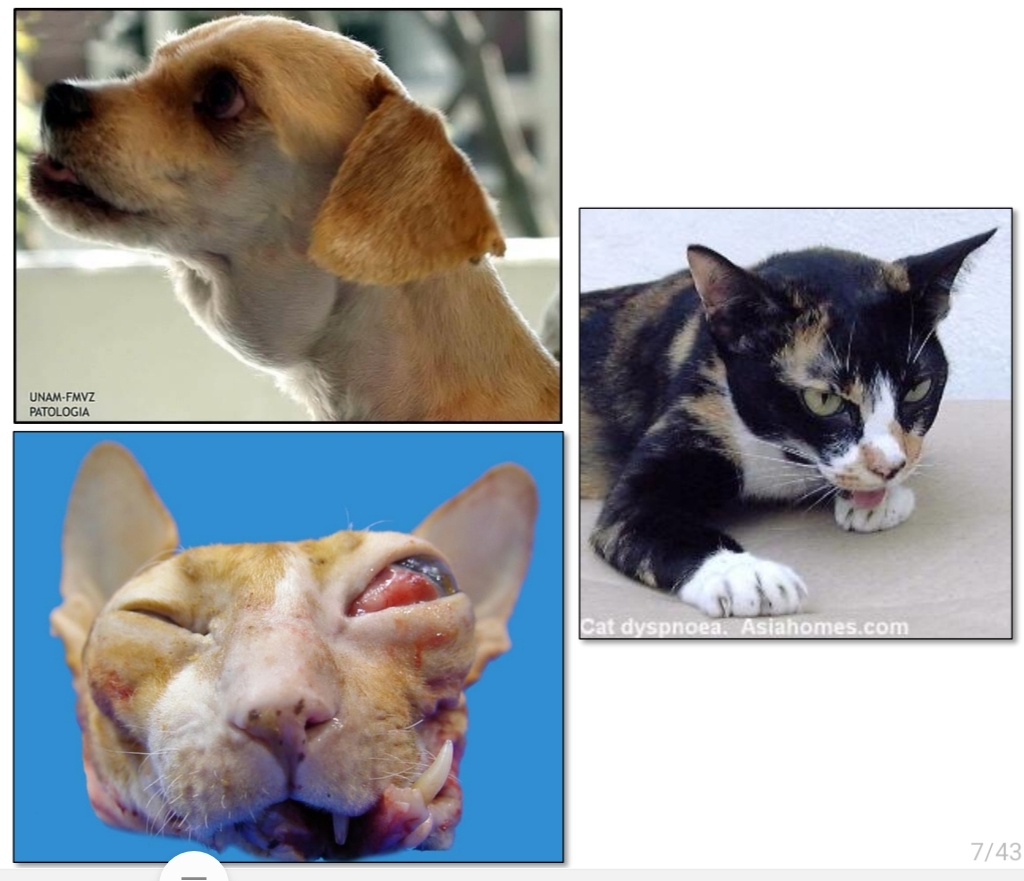
Cutaneous
[Canine Lymphoma]
![<p>[Canine Lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ada170b7-ef88-4347-9690-52f480eb0365.jpg)
Thymic
[Canine lymphoma]
![<p>[Canine lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9faf4235-b02e-449c-9eff-a4b533955ee7.jpg)
Alimentary
[Canine lymphoma]
![<p>[Canine lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/640196bf-2a37-46f8-b37e-2f69b9caa2d6.jpg)
Malt and Tonsils
[Canine lymphoma]
![<p>[Canine lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/21af46b8-827f-4b24-93d6-607c3cad46c1.jpg)
Feline lymphoma
Multicentric
Most common malignant neoplasm of cats
Alimentary
[Feline lymphoma]
![<p>[Feline lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/42955f86-1d11-424c-91d7-1aa93ca22601.jpg)
Feline leukemia virus. (FLV)
mediastinal and multicentric T cell lymphoma
[pic] Thymic/Mediastinal
Feline lymphoma is associated with ______
FeLV is associated with ____
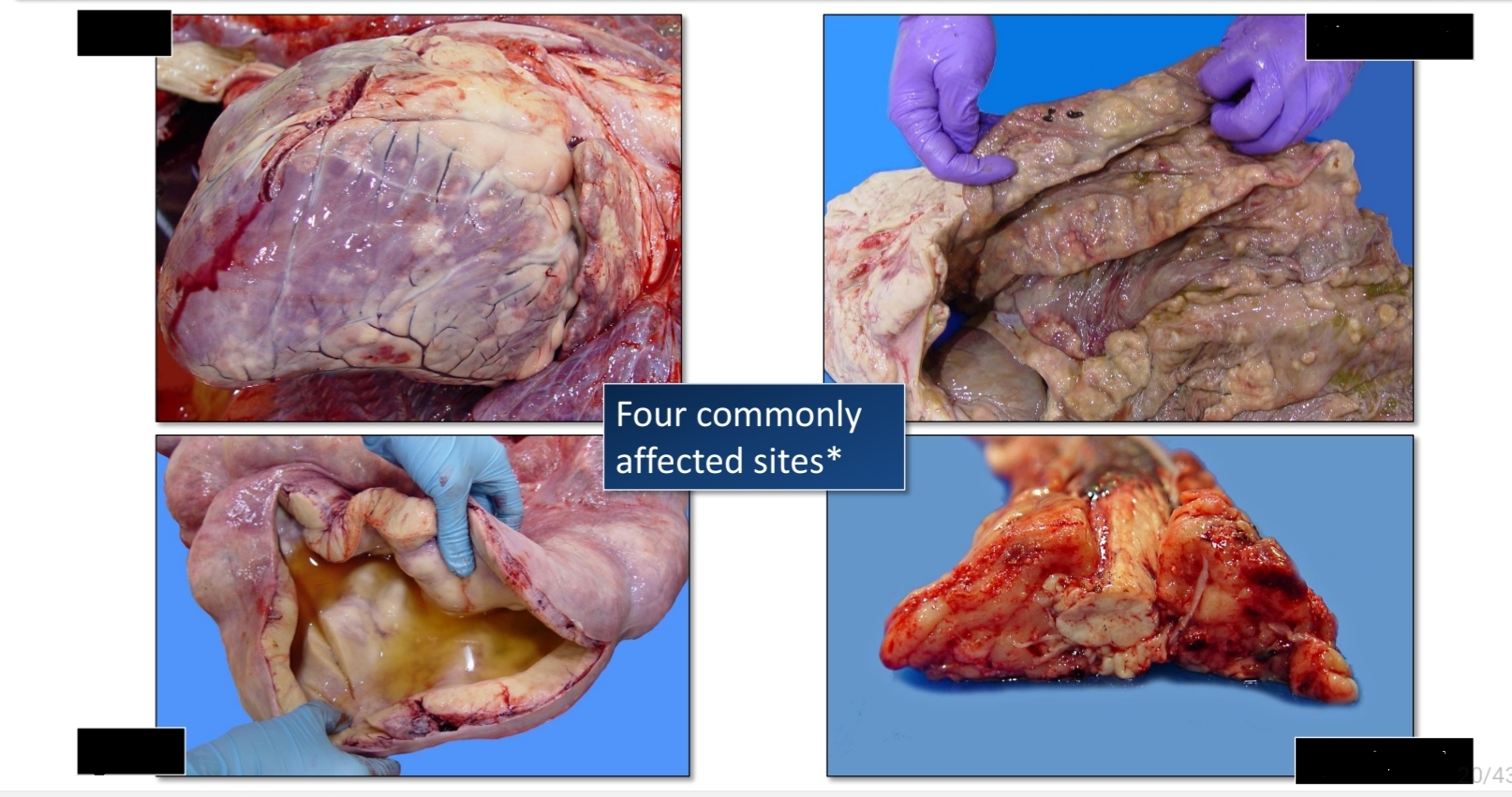
Enzootic bovine lymphoma
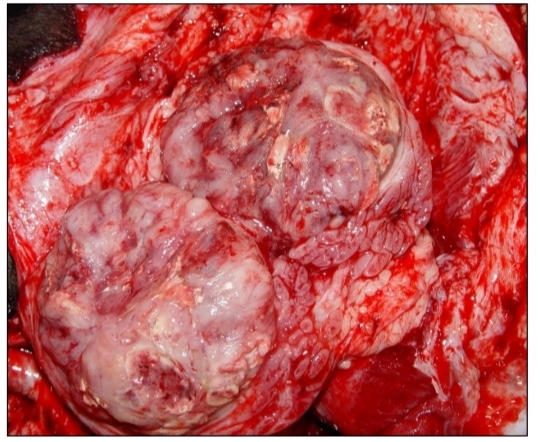
Heart
Affected site in EBL
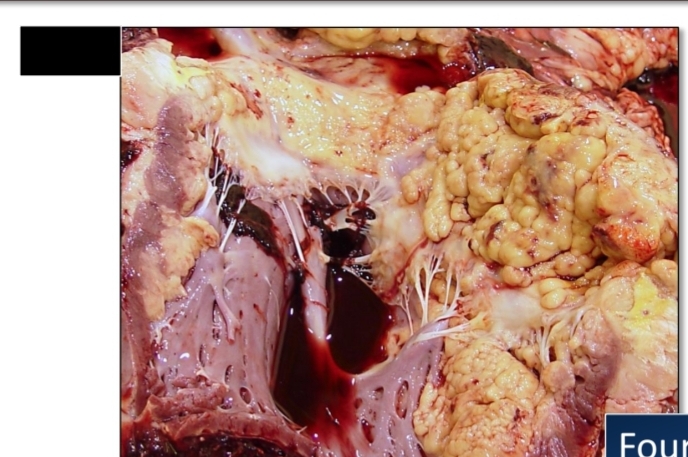
Uterus
Affected site in EBL
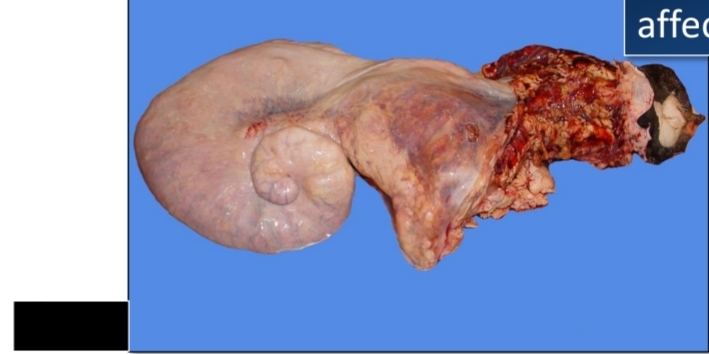
Abomasum
Affected site in EBL
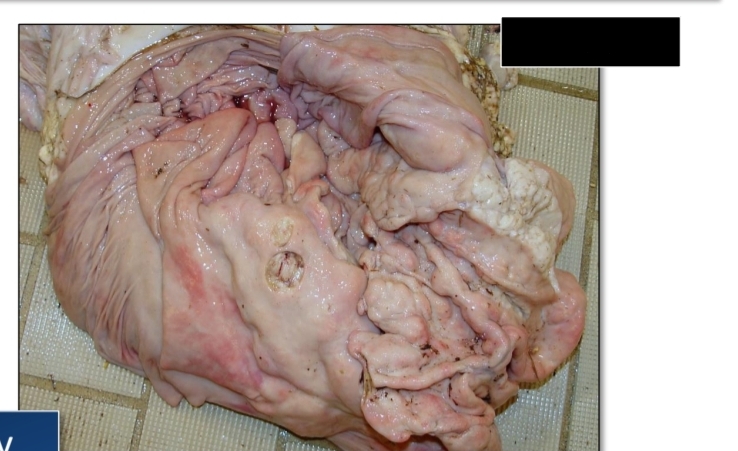
Spinal canal
Affected site in EBL
[Left] heart, uterus
[Right] Abomasum, Spinal canal
Affected site of EBL
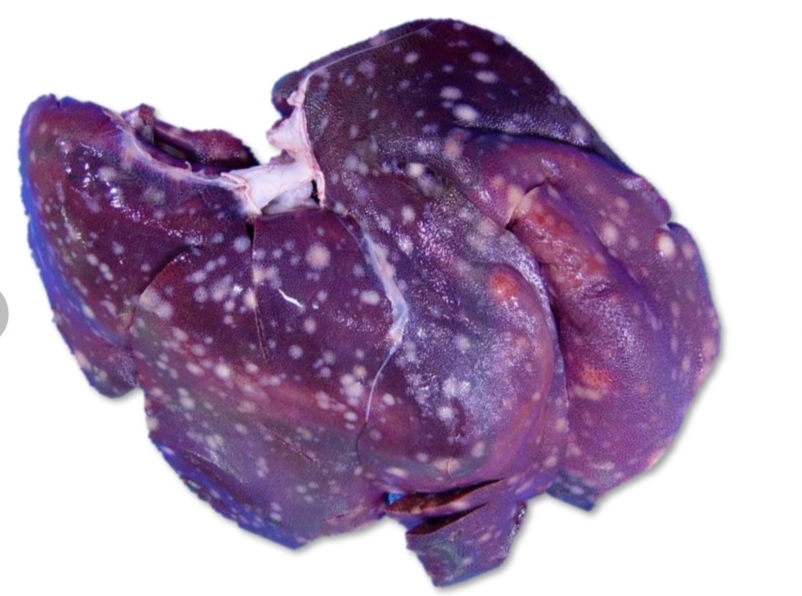
Calf form
6
symmetrical
bone marrow
multicentric
What form is this? [Sporadic bovine lymphoma]
less than ___ months of age
_________ lymphadenopathy
________ involvement
______ lymphoma
![<p>What form is this? [Sporadic bovine lymphoma]</p><ol><li><p>less than ___ months of age</p></li><li><p>_________ lymphadenopathy</p></li><li><p>________ involvement</p></li><li><p>______ lymphoma</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f9fa498e-2589-4d09-aaac-f0a6df6fd088.jpg)
Juvenile = Thymic form
Young , 2
Mediastinal
What form is this? [Sporadic bovine lymphoma]
______ ( < ) beef cattle
_______ thymic mass
![<p>What form is this? [Sporadic bovine lymphoma]</p><ol><li><p>______ ( < ) beef cattle</p></li><li><p>_______ thymic mass</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2f7dba98-248d-40d7-89a4-2e05355f2157.jpg)
Cutaneous form
2-3
raised skin lesions
waning
12-18
What form is this? [Sporadic bovine lymphoma]
______ year old cattle
plaques or nodular, _____
waxing and ___
survive ____ to ____ months
![<p>What form is this? [Sporadic bovine lymphoma]</p><ol><li><p>______ year old cattle</p></li><li><p>plaques or nodular, _____</p></li><li><p>waxing and ___</p></li><li><p>survive ____ to ____ months</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/65ba299e-6b1c-4a05-b440-041416e1a4c0.jpg)
Porcine lymphoma
1
Most common neoplasm of pigs
often < __ old
Multicentric lymphoma
[Porcine Lymphoma]
![<p>[Porcine Lymphoma]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3b2b9c7d-6d12-4ab0-919b-f0179ce31f54.jpg)
Equine lymphoma
Multicentric, cutaneous, alimentary form
Identify.
Common forms of this (3)
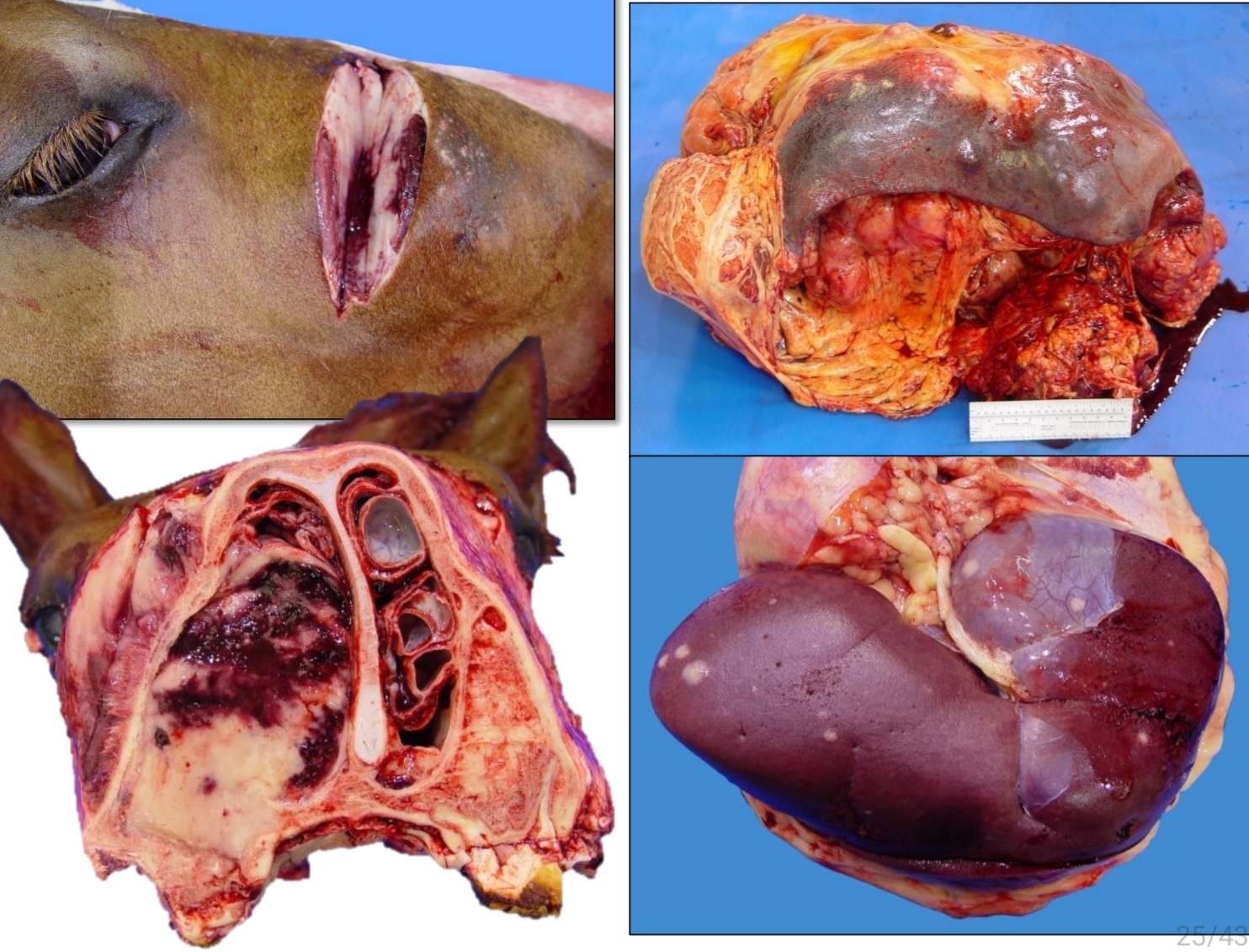
Lymphoid atrophy
lymph node degeneration
lymph node hypoplasia
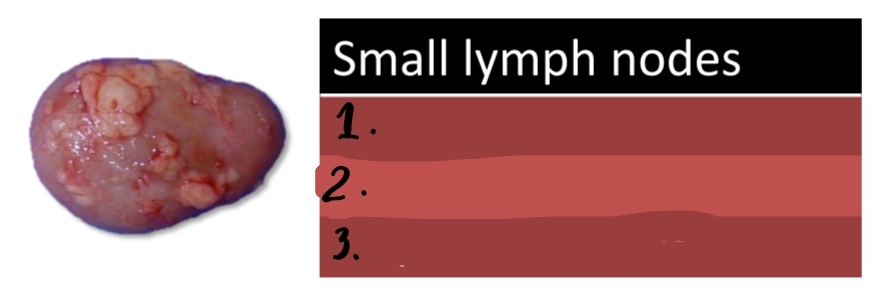
Lymphadenitis
Lymphoid hyperplasia
Hyperplasia of the monocyte/macrophage system
Primary neoplasia
Secondsry neoplasia
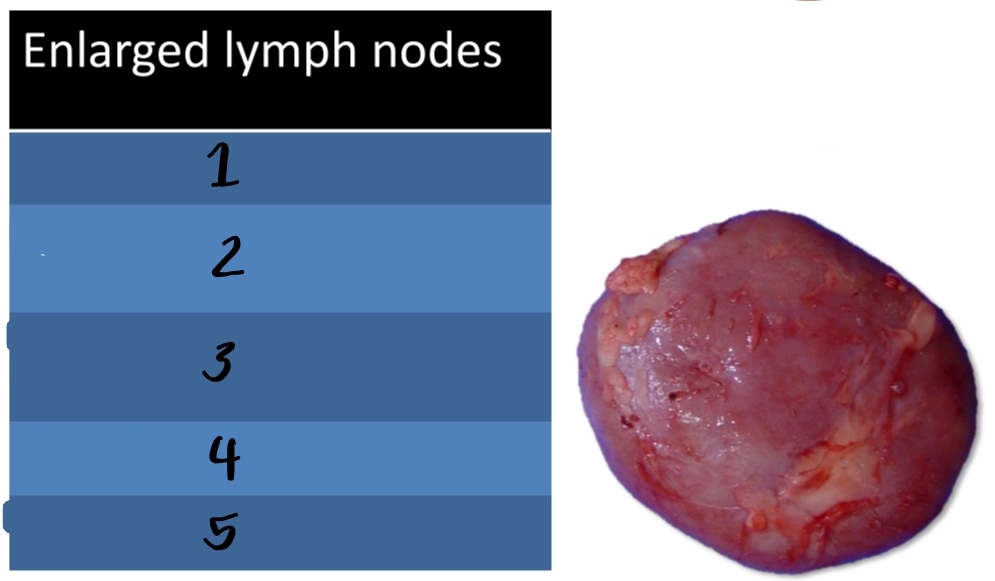
Enlargement of the right retropharyngeal LN of Sheep
Identify
Normal lymph node
Identify
Reactive lymphoid hyperplasia
Nodes
bulge
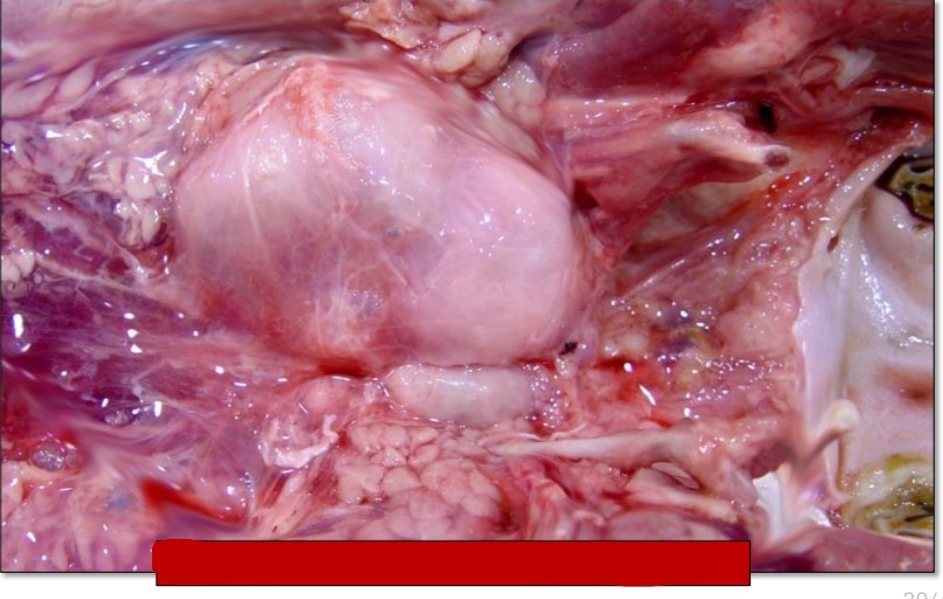
Identify [pic]
Gross lesion:
Moderate enlargement of ____
May ___ on cut section
![<p>Identify [pic]</p><p>Gross lesion:</p><ol><li><p>Moderate enlargement of ____</p></li><li><p>May ___ on cut section</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c2940cc0-8e23-4529-9671-c6d4a84202fd.jpg)
lymphoid follicles, germinal
T, paracortex
plasma, medullary cords
[Benign reactive hyperplasia]
Histology: (3)
Proliferation of ________ with prominent _____ centers
Increased ___ cells in the ____
+/- increased _____ cells in the ______
![<p>[Benign reactive hyperplasia]</p><p>Histology: (3)</p><ol><li><p>Proliferation of ________ with prominent _____ centers</p></li><li><p>Increased ___ cells in the ____</p></li><li><p>+/- increased _____ cells in the ______</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/543ca9cc-12d3-471a-8f11-7c486900709c.jpg)
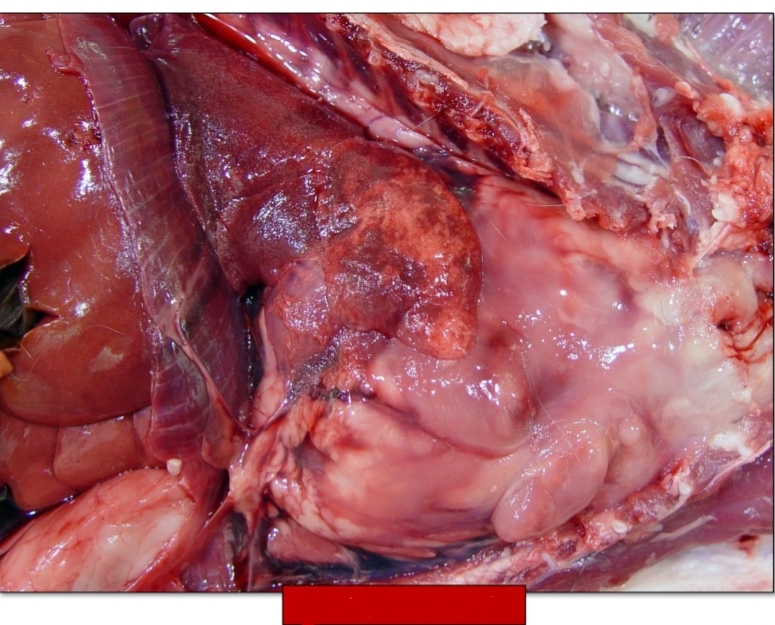
Cervical and sternal lymphadenitis with sepsis
[acute lymphadenitis] Identify the pic
![<p>[acute lymphadenitis] Identify the pic</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/857cd552-4d1f-49a4-bf22-d62892f57288.jpg)
chronic lymphadenitis
[pic] Rhodococcus equi in foal
what kind of lymph node inflammation?
Identify the pic
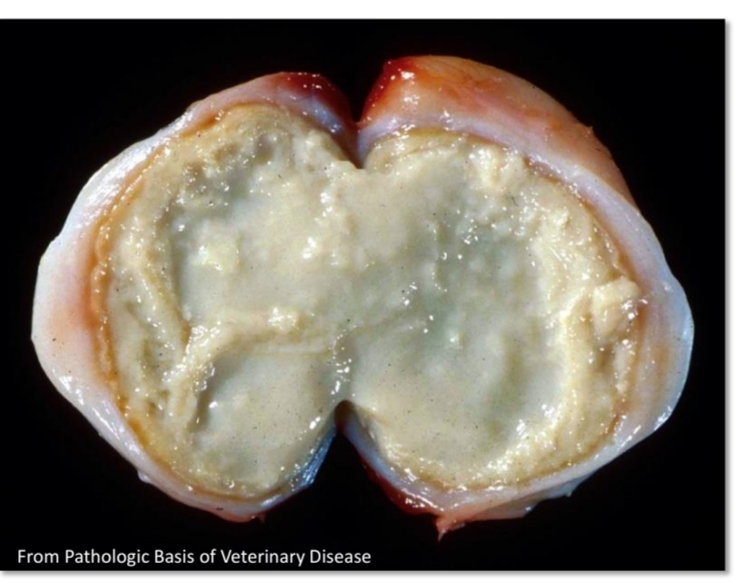
chronic suppurative lymphadenitis
swollen, pus, lymph node abscess
what kind of lymph node inflammation?
Gross lesion:
_____ lymph node with ___filled center =
chronic suppurative lymphadenitis
Identify
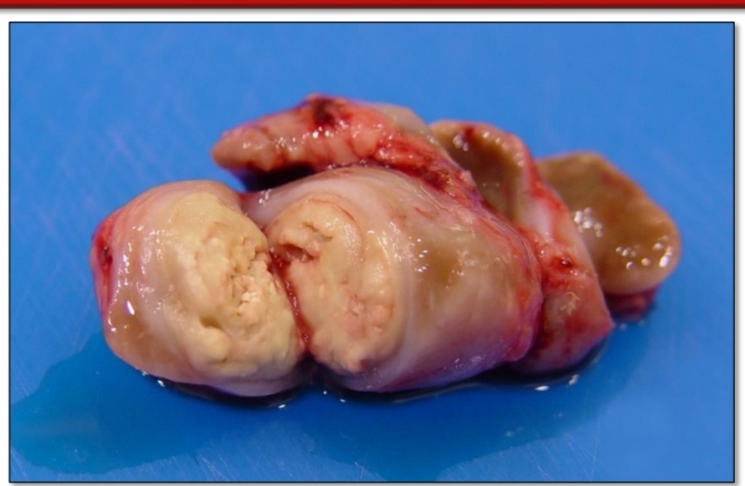
Equine strangles
Identify
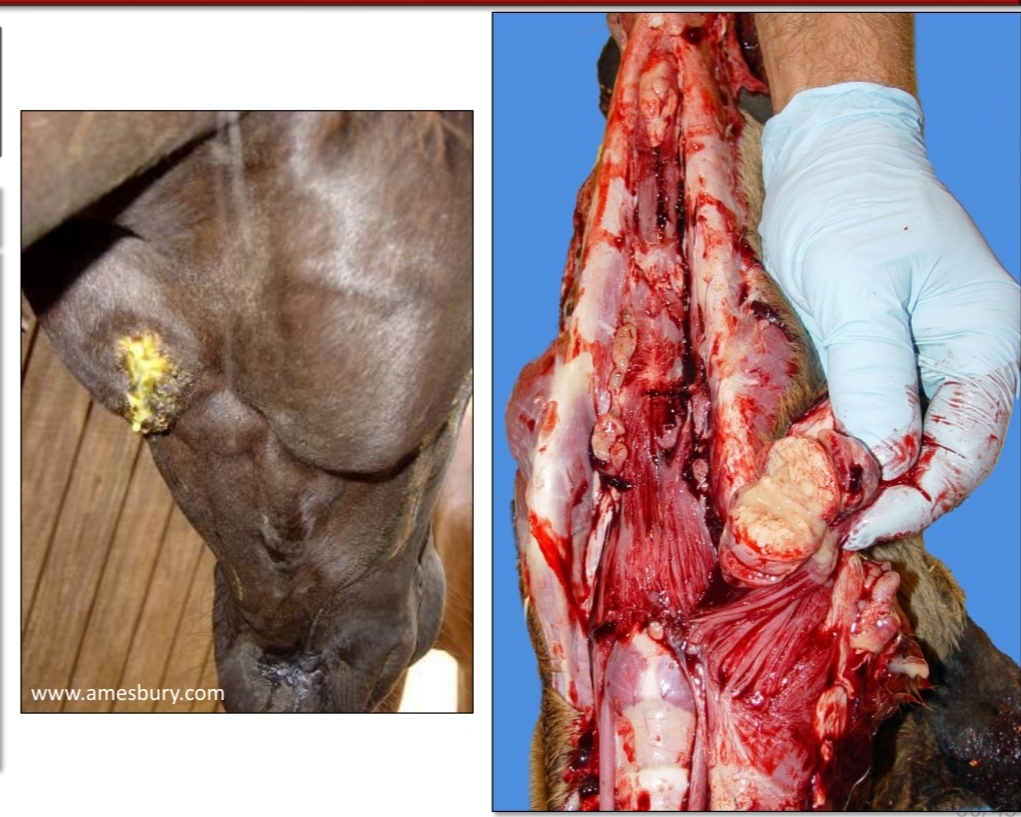
Chronic suppurative lymphadenitis ( Caseous lymphadenitis )
Identify
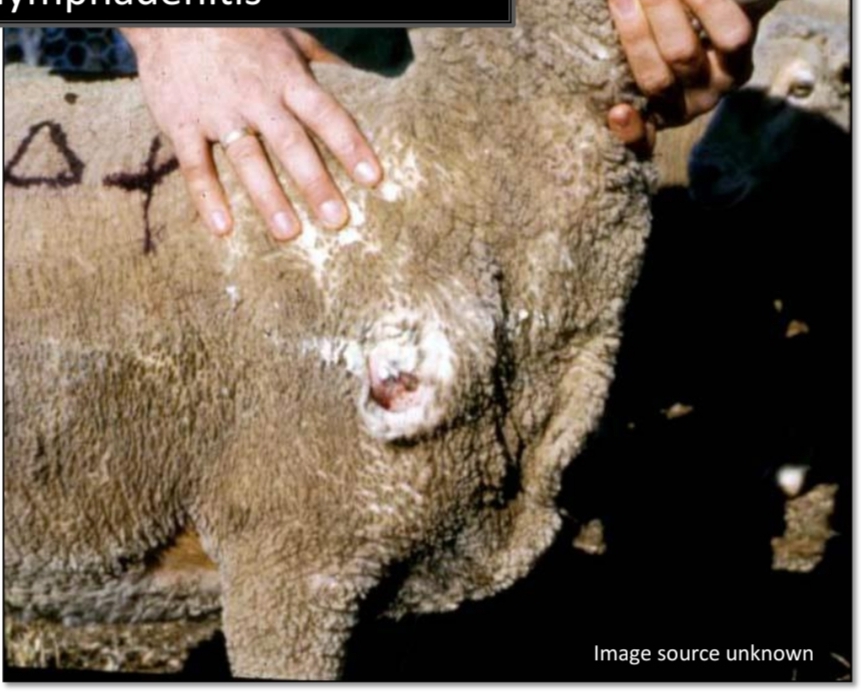
Goat, Caudal mediastinal LN abscesses
[chronic suppurative lymphadenitis]
![<p>[chronic suppurative lymphadenitis]</p><p></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/00eda697-83f1-4f01-9e9a-07999638a2ca.jpg)
Caseous. lymphadenitis
Identify
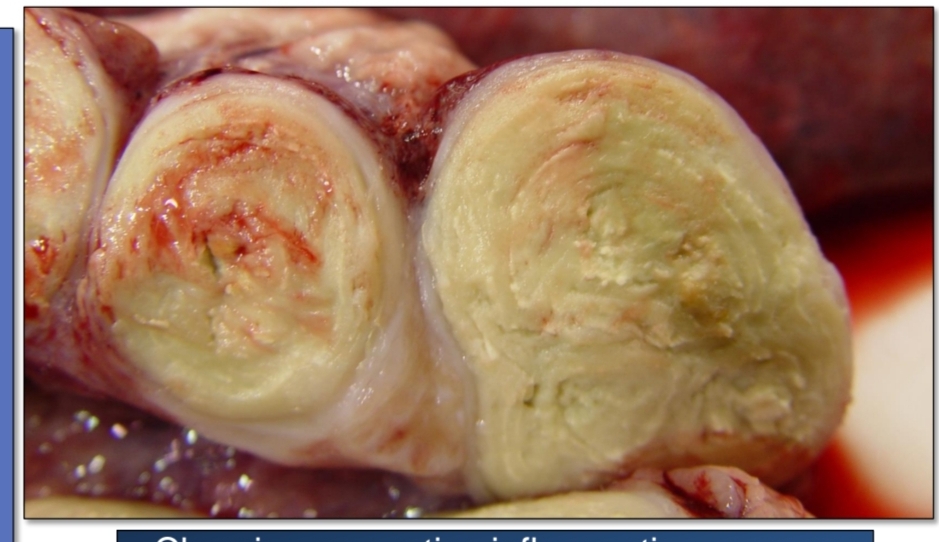
Nodular granulomatous lymphadenitis
Identify
[Granulomatous lymphadenitis]
![<p></p><p>Identify</p><p>[Granulomatous lymphadenitis]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/266e75a2-299d-43fc-b9e6-bacee6931678.jpg)
Diffuse granulomatous lymohadenitis
Identify
[Granulomatous lymphadenitis]
![<p>Identify</p><p>[Granulomatous lymphadenitis]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/608bde94-043a-4926-878e-45ec5d781ff7.jpg)
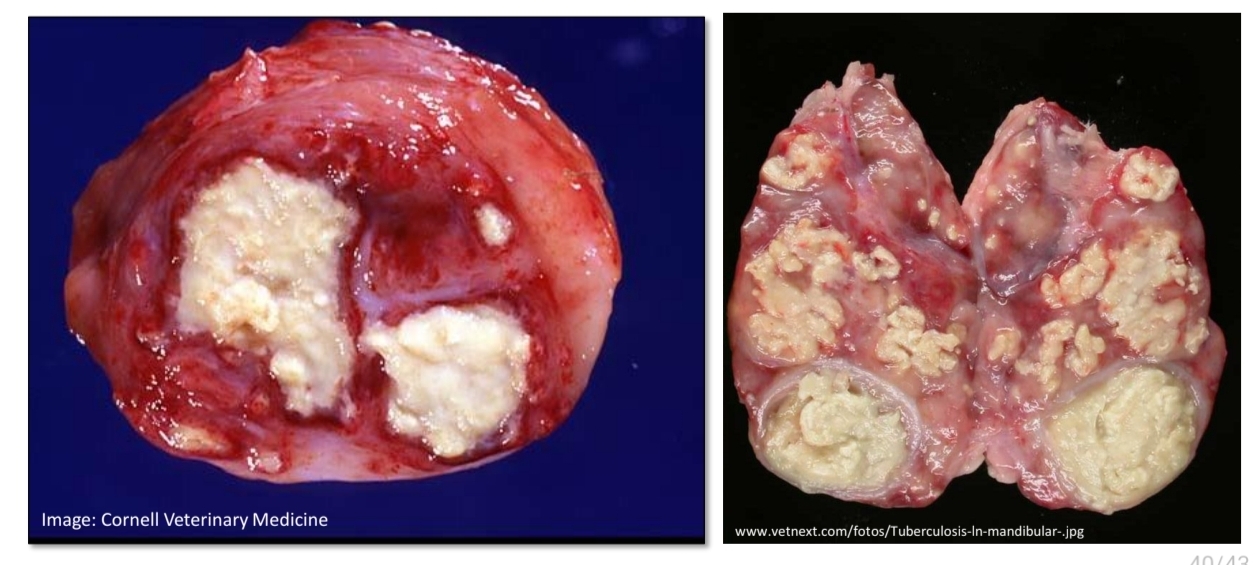
Bovine Tuberculosis
Enlargement, yellow-tan gritty
Identify
Gross: _____ of the lymph node with a single to multiple discrete _______ nodules
central, epitheloid macrophages, giant cells
[Bovine tuberculosis]
Histology: Granulomas with ____ necrosis and mineralization surrounded by ____ and multinucleated ______
![<p>[Bovine tuberculosis]</p><p>Histology: Granulomas with ____ necrosis and mineralization surrounded by ____ and multinucleated ______</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/91f11124-0c6d-4059-8d6e-03467122015c.jpg)
acid fast bacilli within macrophages
Identify