Kidneys Part 1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
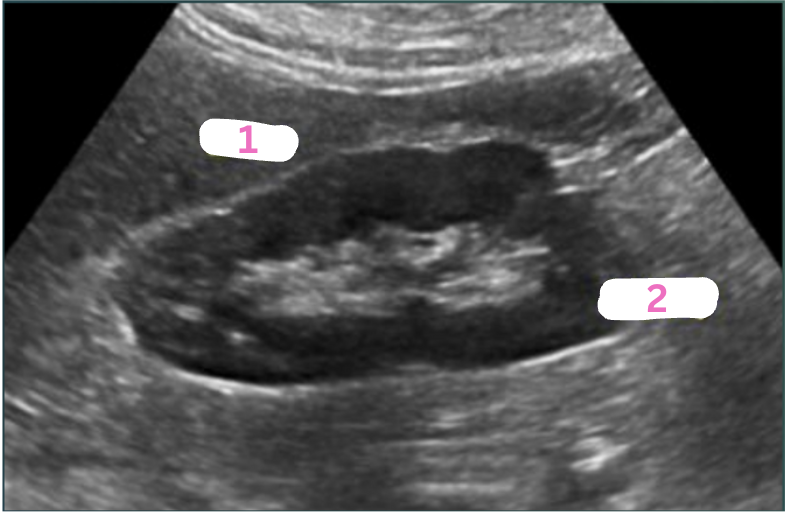
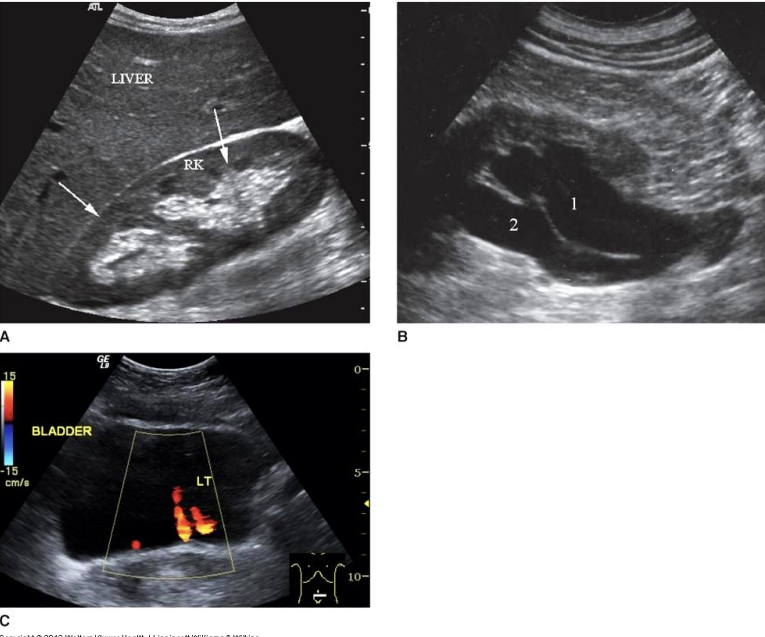
Label the structures.
LT liver lobe
RT Kidney
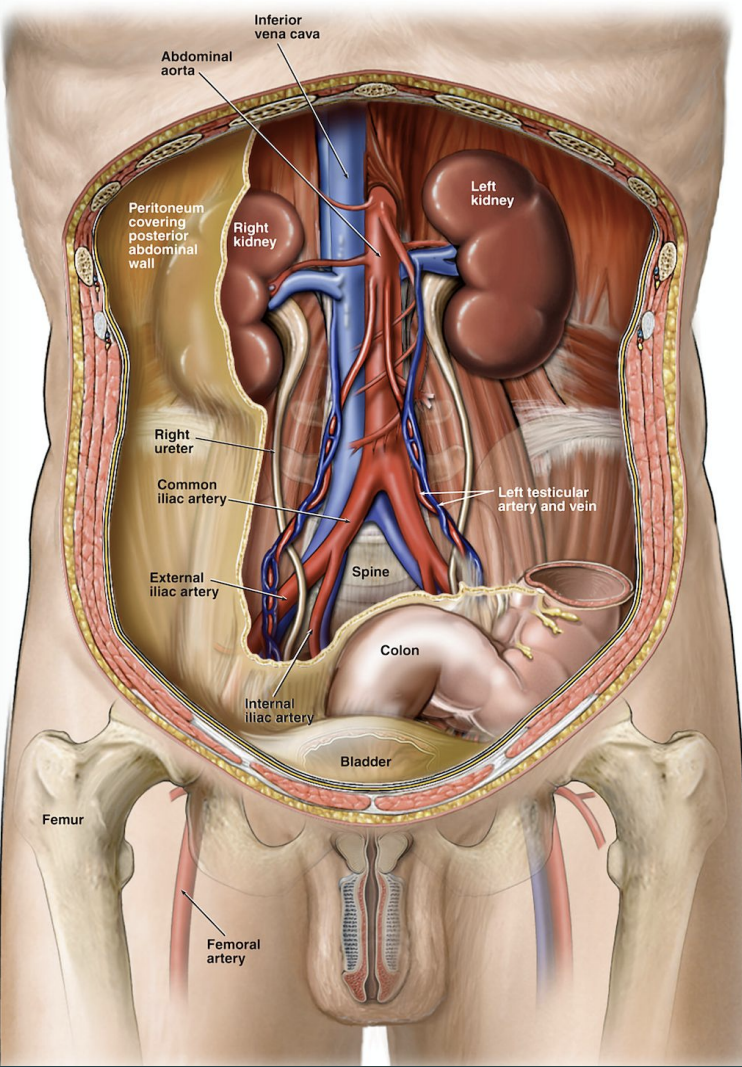
Which abdominal cavity are the kidneys in? And at what level?
Retroperitoneum; T12-L4
T or F : The RT kidney is lower than the LT kidney by 2-8 cm.
True
Why is the RT kidney lower than the LT kidney?
Due to the placement of the liver.
Describe the placement of the RT kidney to the liver & GB.
RT kidney is posterior-inferior to the liver & GB.
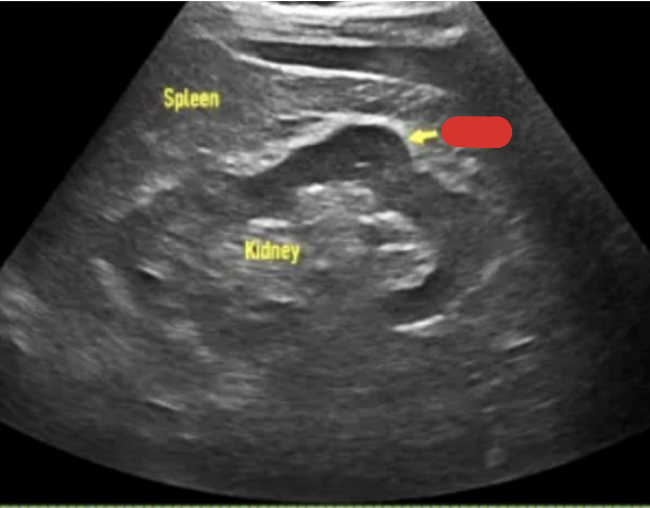
Describe the LT kidney placement to the spleen.
LT kidney is inferior-medial to the spleen.
What are the kidneys’ main functions?
Excrete & filter wastes (urea, drugs, creatinine, & bilirubin)
Synthesize glucose, erythropoietin, & vitamin D
Describe the kidneys’ role in blood functionality.
Regulate blood volume (conserving or eliminating H2O)
Regulate blood pressure (secretion of renin angiotensin)
Fill in the blanks :
The kidneys work around the clock to filter _____ liters of blood each day, removing _____ liters of toxins, wastes, & water in the process.
200; 2
What does EPO stand for? And what is it?
Erythropoietin; EPO is a hormone healthy kidneys make.
What does EPO do?
Send signals to the body to make more red blood cells.
What is the avg life time of a red blood cell?
120 days
Give a quick description of erythrocytes.
Erythrocytes carry almost all the oxygen your body uses & make up almost half your blood.
What are the kidneys’ measurements in :
How long?
How wide?
Height?
Weight?
10-12 cm long
5-7 cm wide
3-5 cm height
130-150 grams
Which week do the kidneys start to develop in embryo life?
3rd week
The kidneys begin to develop from columns of?
Mesoderm
What are the 3 successive intervals of kidney development?
Pronephros, Mesonephros, & Metanephros.
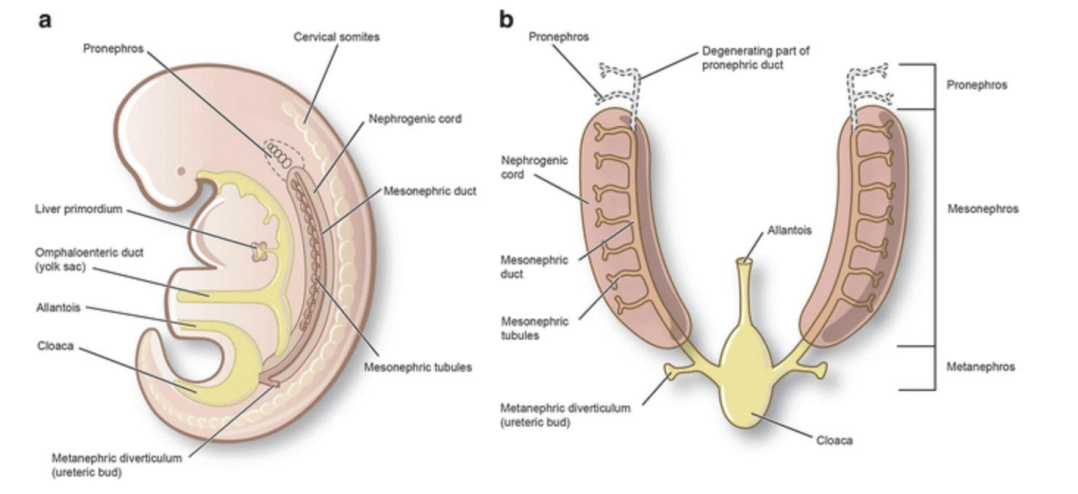
Describe pronephros.
Forekidney; transitory non-functioning structure beginning 4th week of gestation.
Describe mesonephros.
Midkidney; late in 4th week of gestation, functional structure while permanent kidney continues to develop.
Describe metanephros.
Permanent kidney; develops during 5th week of gestation.
What is nephrons?
Functional unit of kidneys which begin at approx 8th week of gestation.
The kidneys are protected & stabilized by 3 layers which are?
Renal (Gerota’s) fasica (superficial)
Adipose Capsule (middle)
Renal Capsule (deep)
The renal capsule appears on US as?
A strong continuous linear echogenic reflector surrounding the cortex.
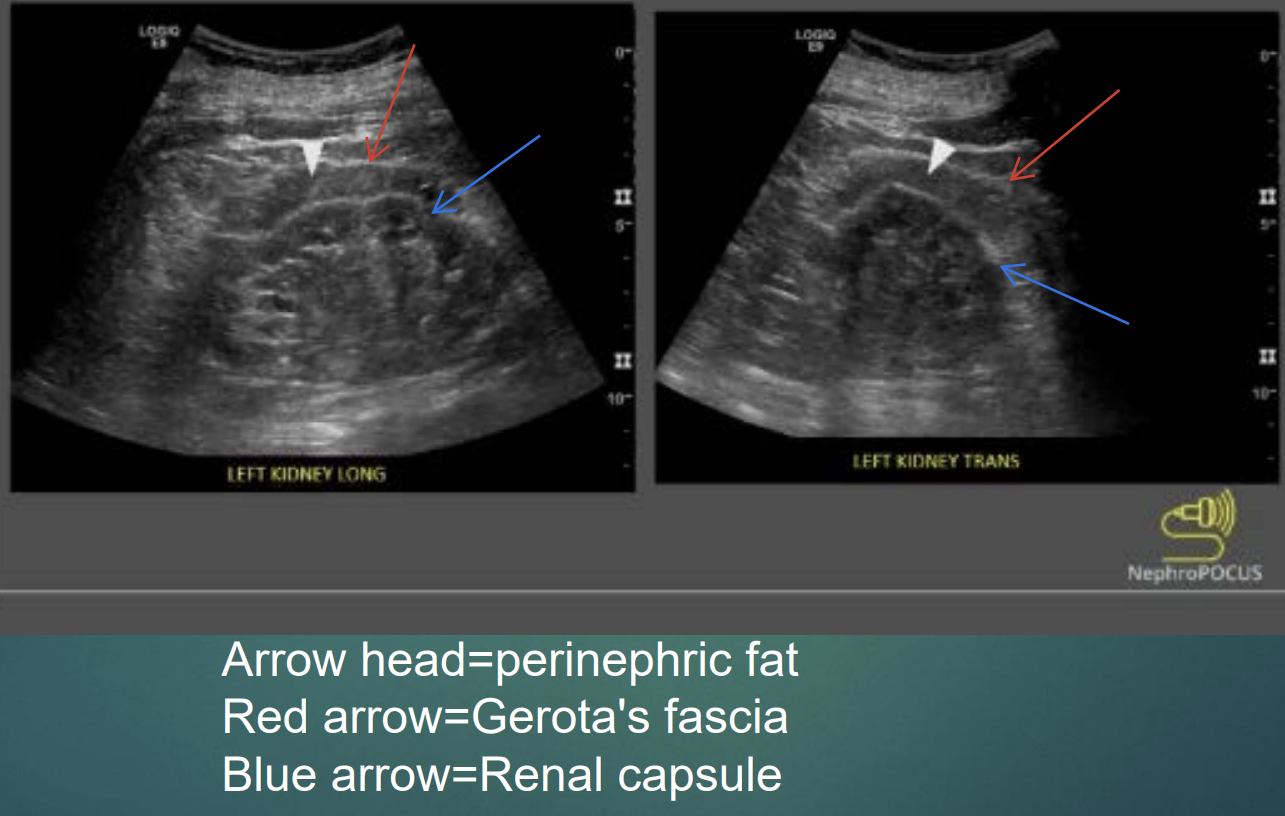
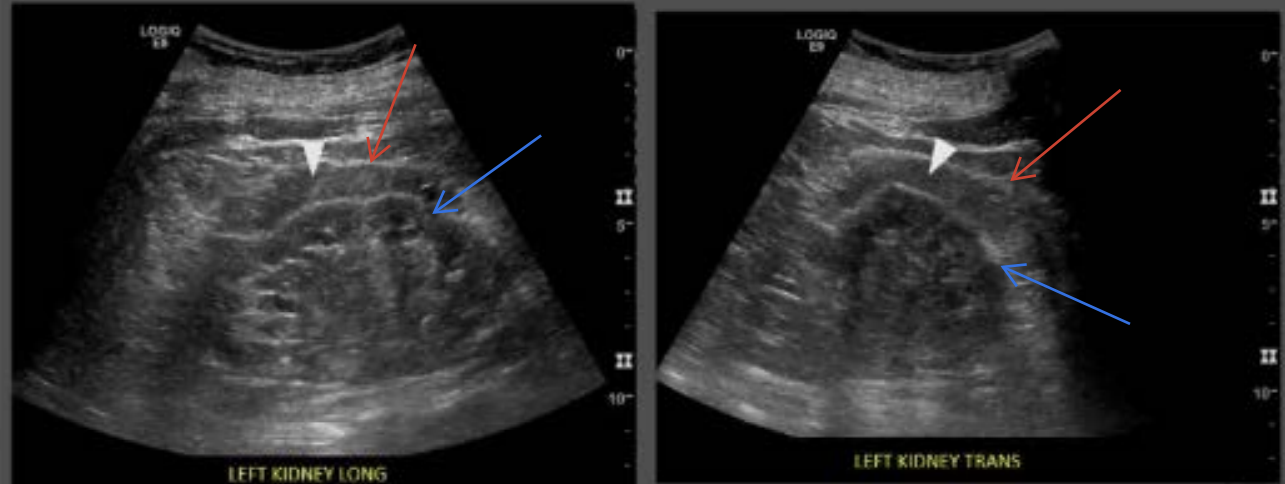
Label :
White arrowhead?
Red arrow?
Blue arrow?
White arrowhead : Periphrenic fat
Red arrow : Gerota’s Fascia
Blue arrow : Renal Capsule
Kidney parenchyma is formed by which regions?
Renal cortex, renal medulla, & renal pelvis.
Fill in the blanks :
The kidney parenchyma contain nephrons which form _____ & are the _____ _____ of the kidneys. The renal cortex contains most of the _____.
Urine; functional unit; nephrons
Each nephron is composed of?
A glomerulus & a tubule.
The glomerulus does what?
Filters wastes & excess fluids.
The tubules does what?
Modify wastes to form urine.
Cleaned blood circulates back via?
Renal veins.
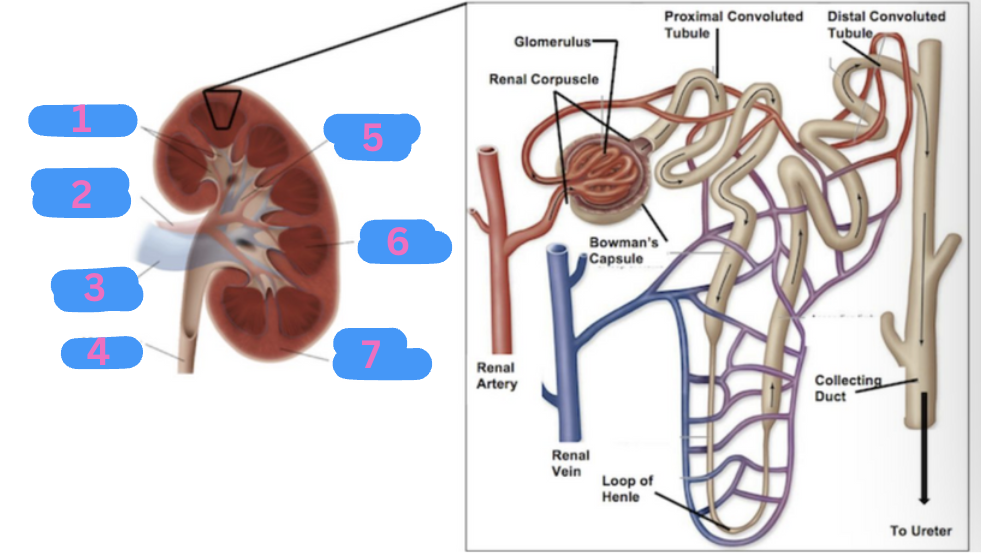
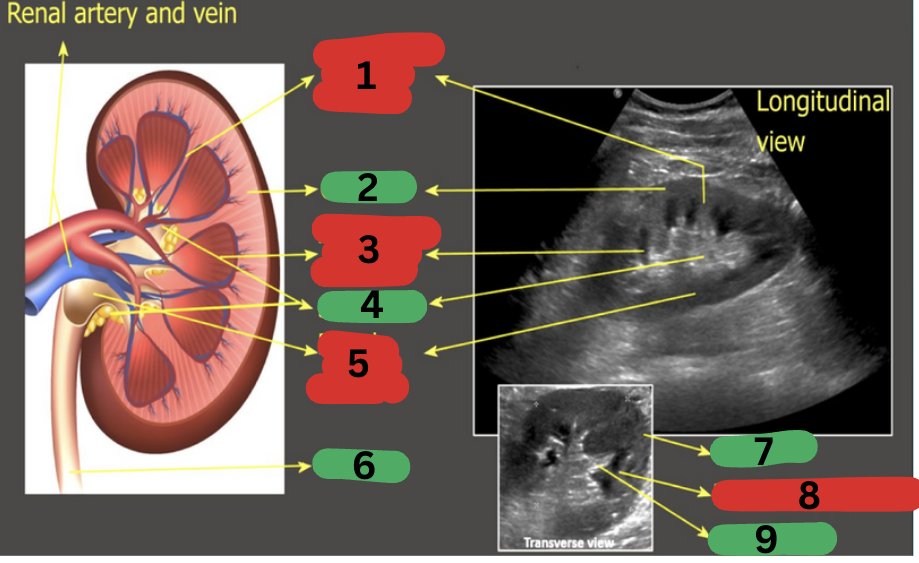
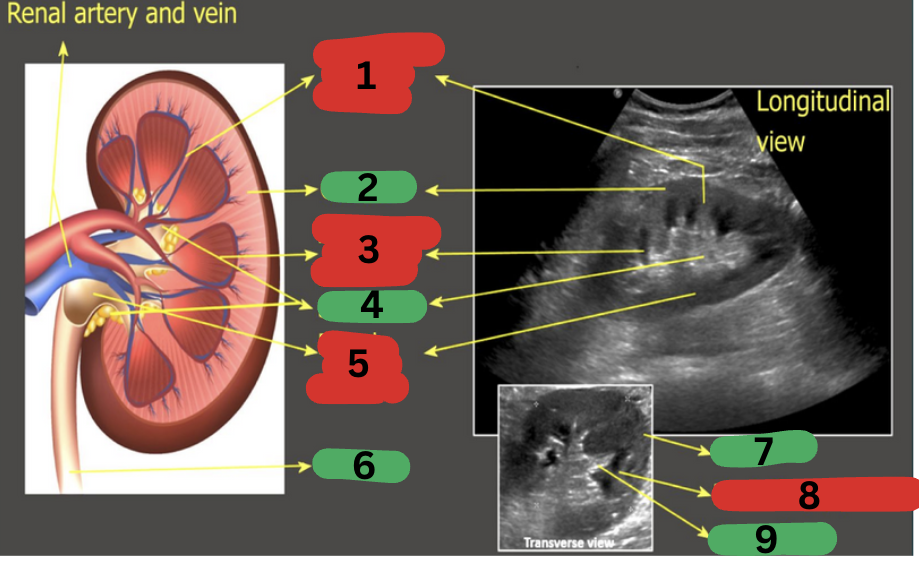
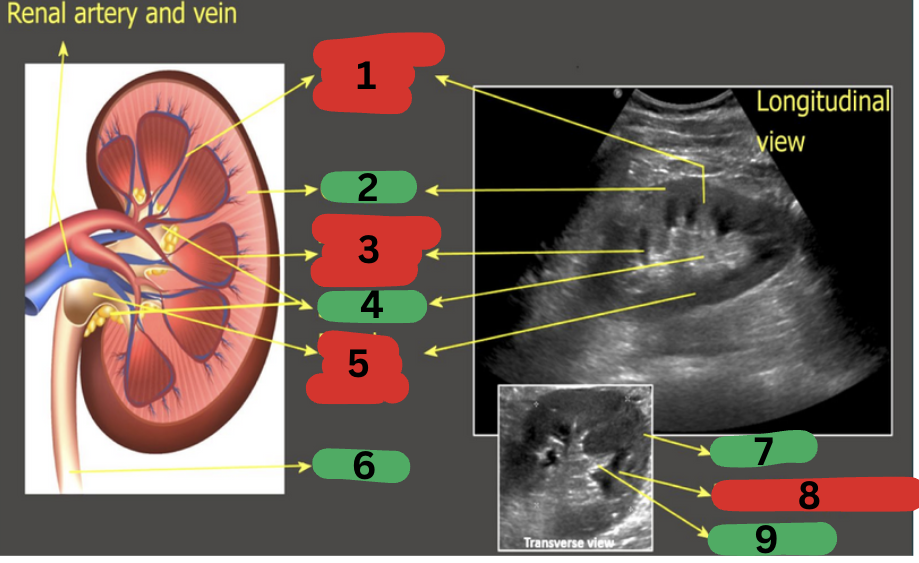
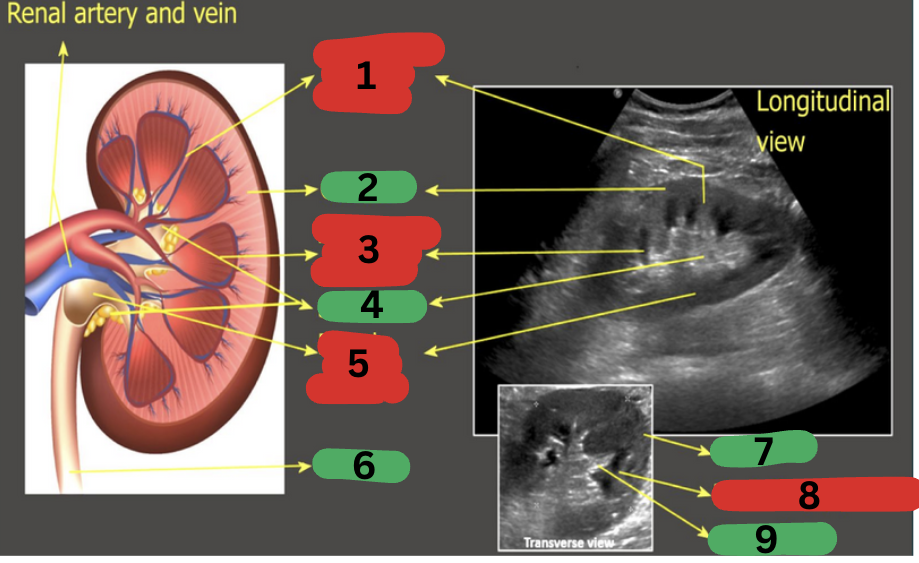
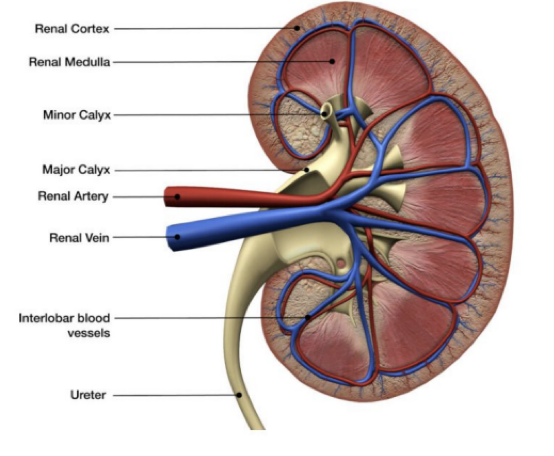
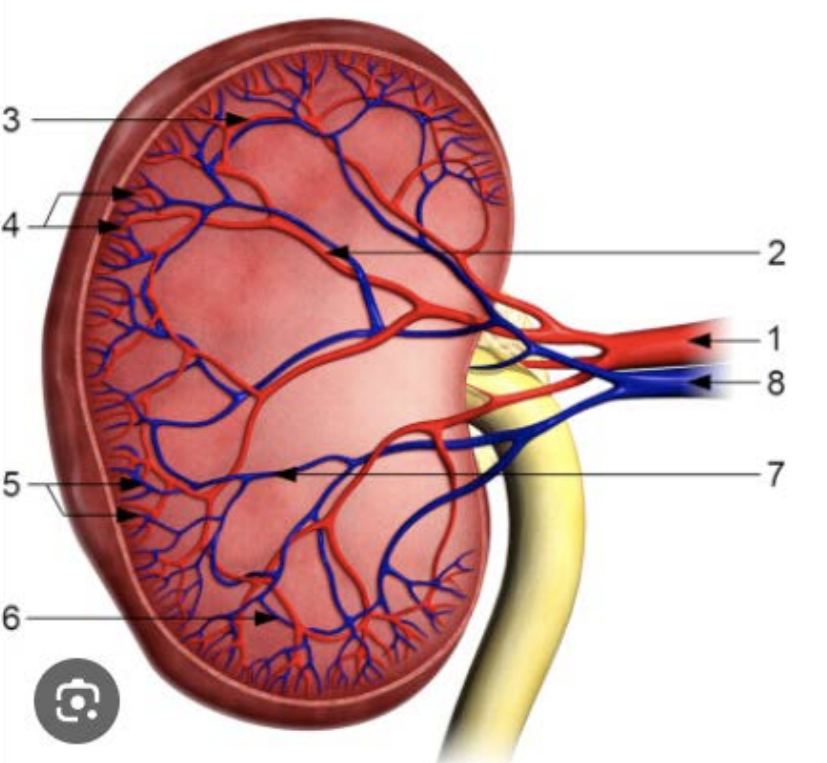
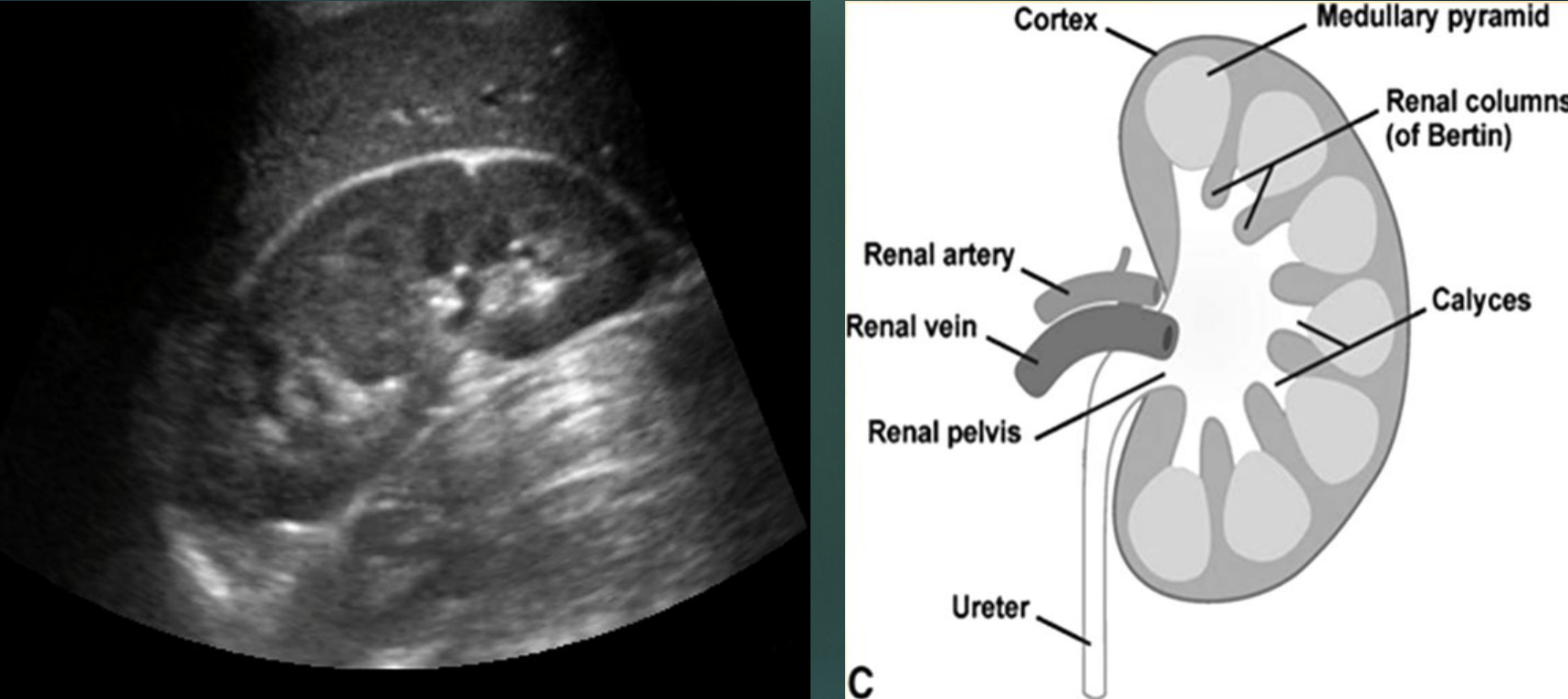
What is 1?
Calyces
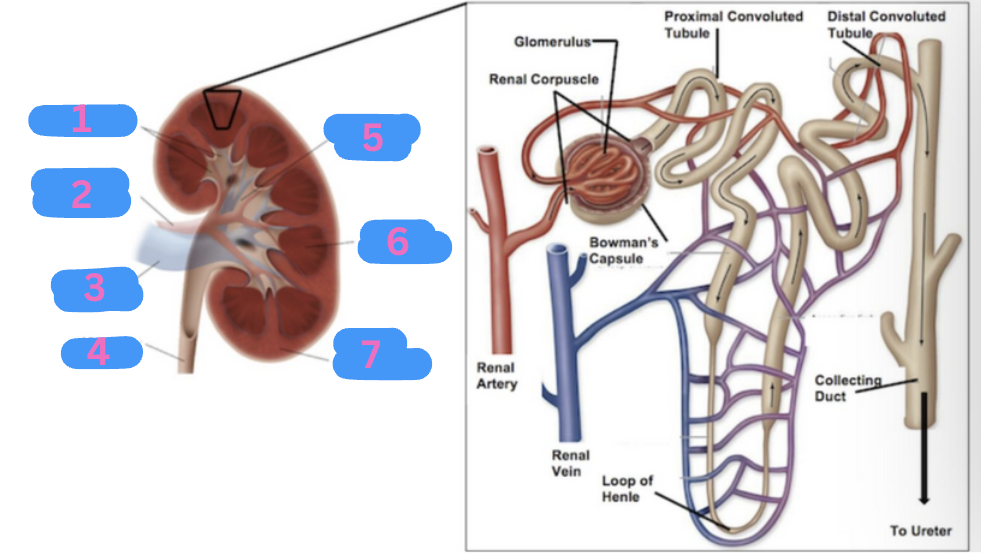
What is 2?
Renal artery
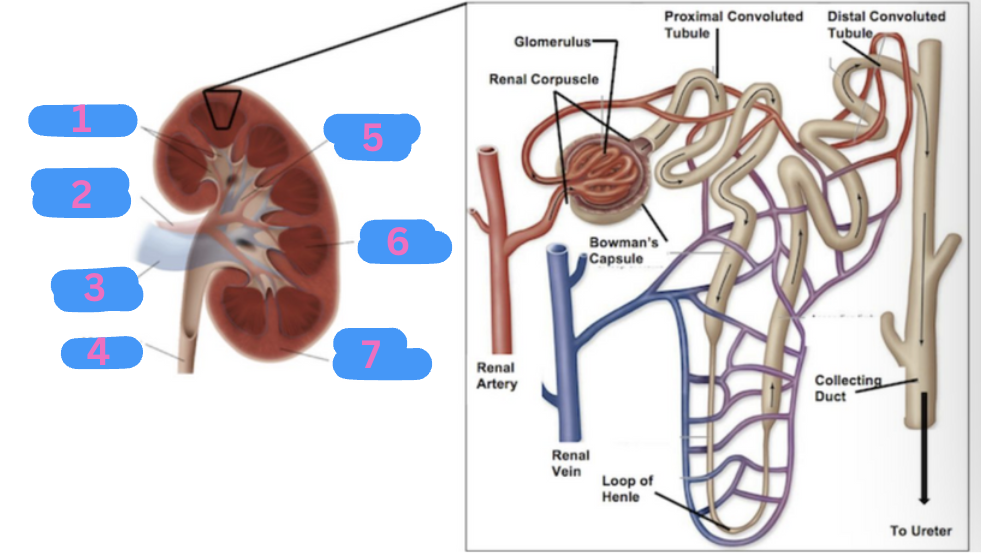
What is 3?
Renal vein
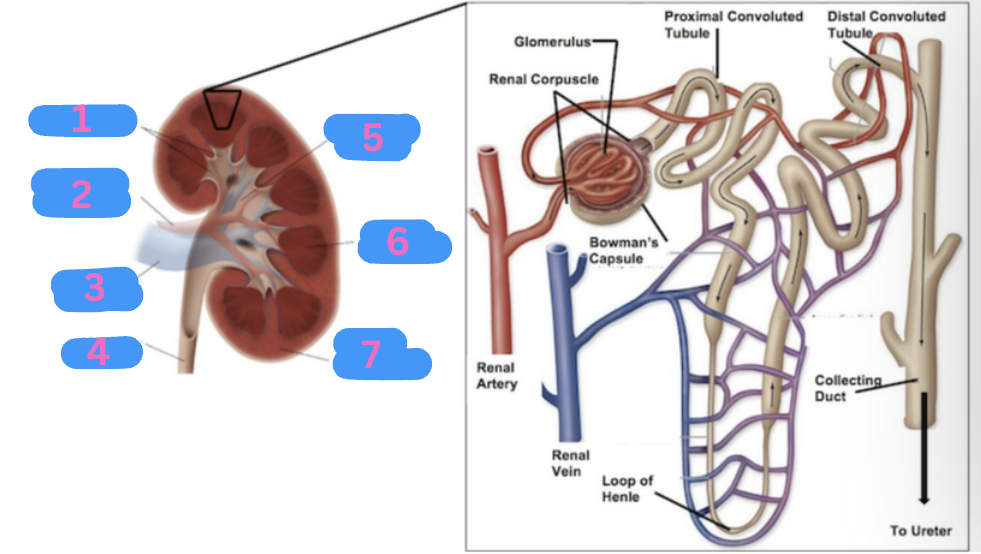
What is 4?
Ureter
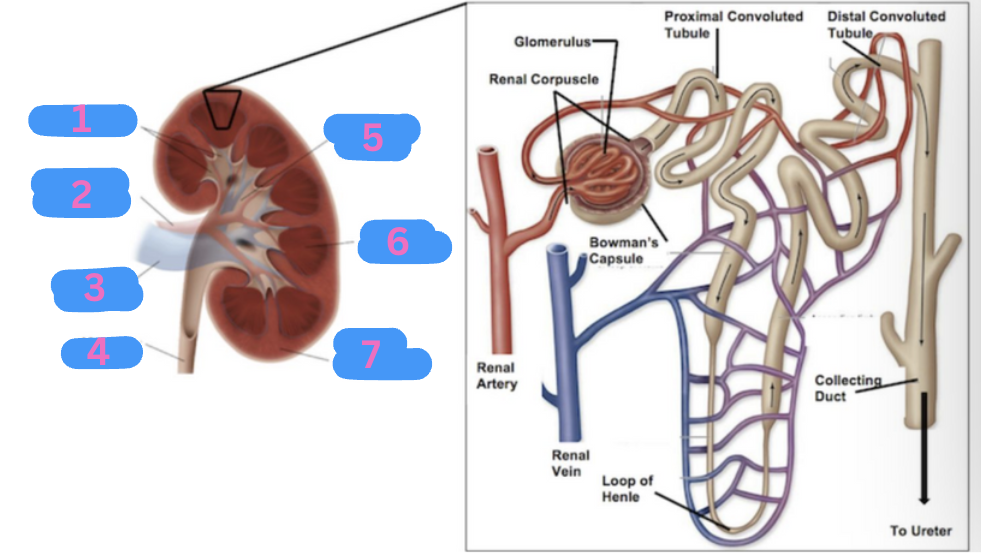
What is 5?
Renal pelvis
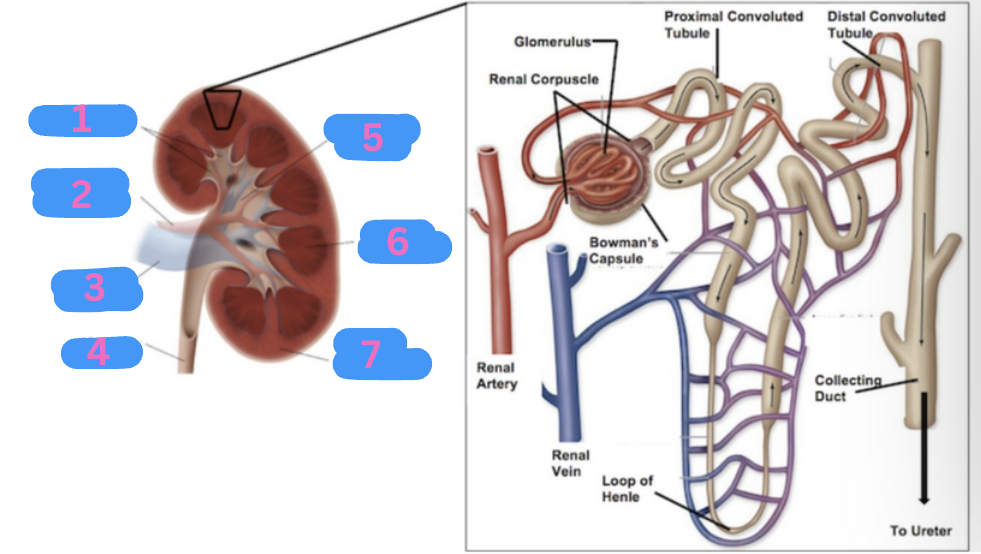
What is 6?
Renal medulla
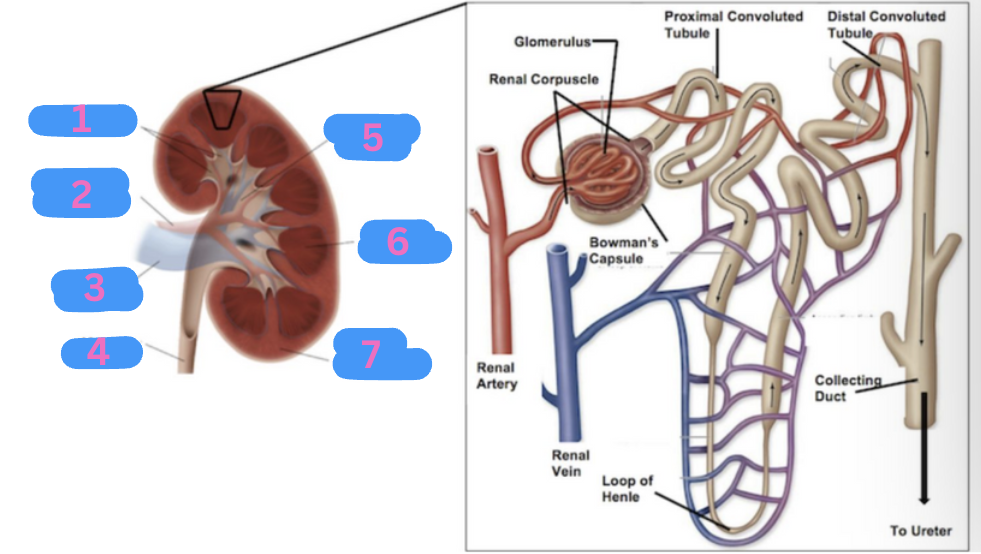
What is 7?
Renal cortex
Which part of the kidney surrounds the sinus?
Parenchyma
Which part of the kidney is the site of urine formation & contains nephrons?
Cortex
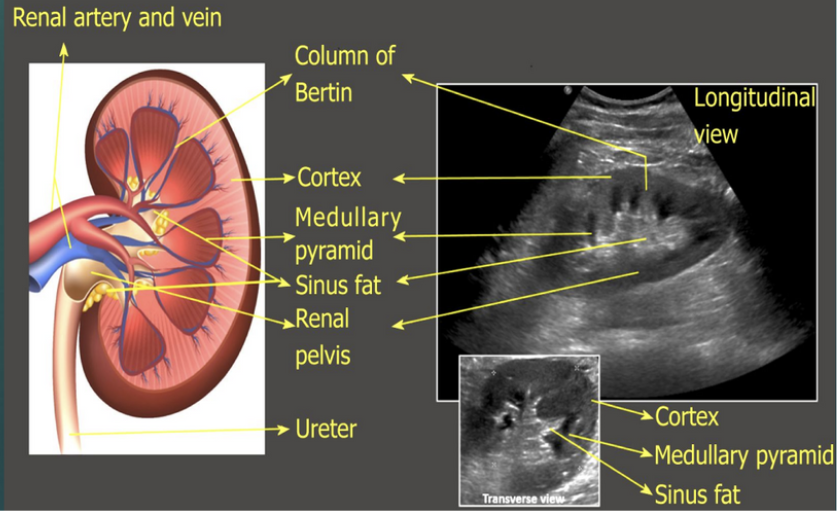
Which part of the kidney contains pyramids that pass urine to minor calyces and, Column of Bertin that separate the pyramids?
Medulla
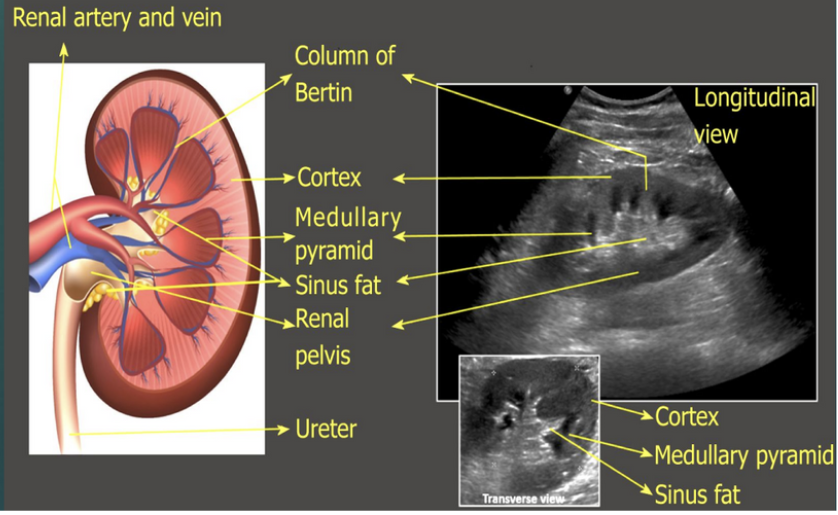
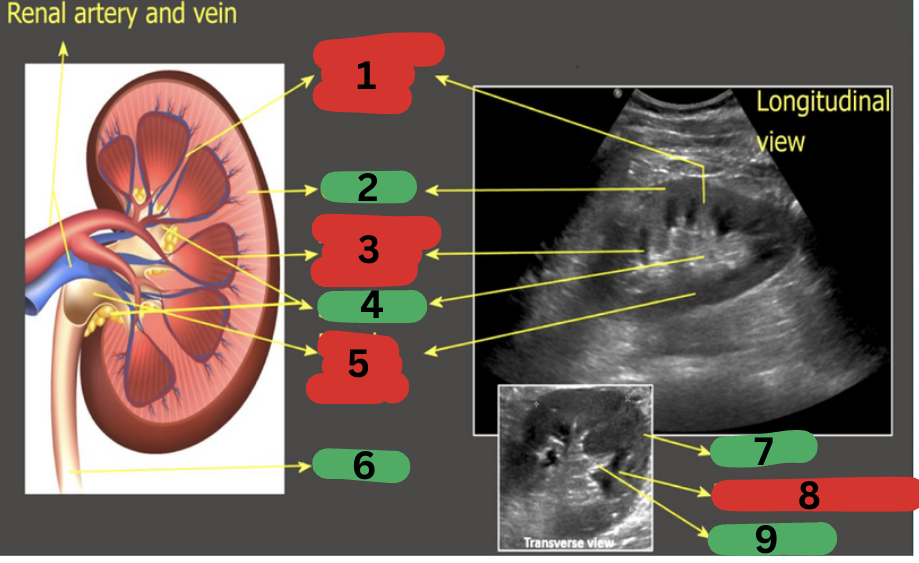
What is 1?
Column of Bertin
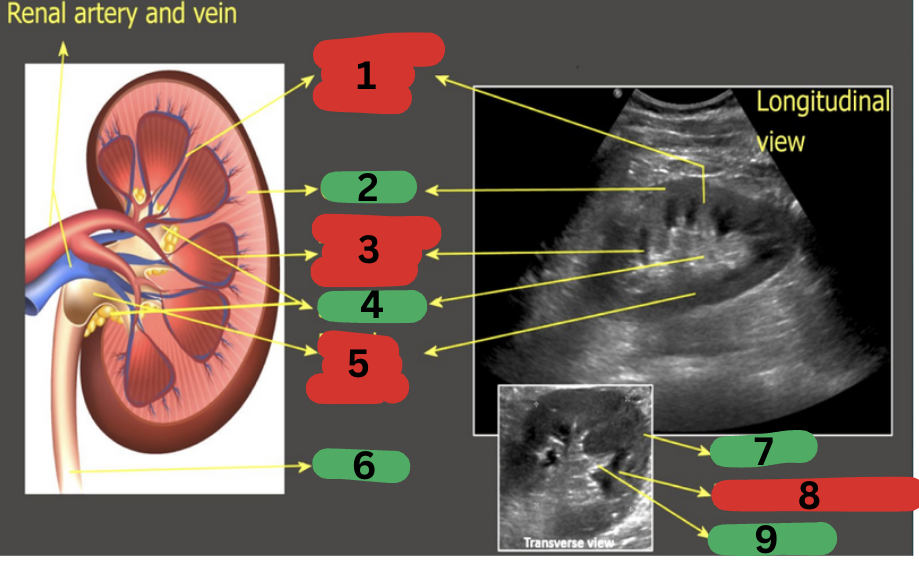
What is 2?
Cortex
What is 3?
Medullary pyramid
What is 4?
Sinus fat
What is 5?
Renal pelvis
What is 6?
Ureter
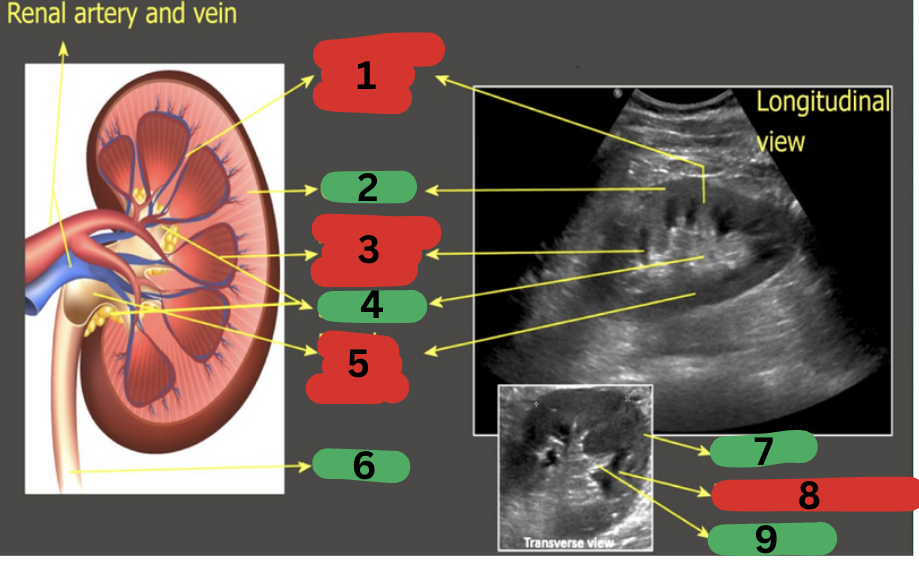
What is 7?
Cortex
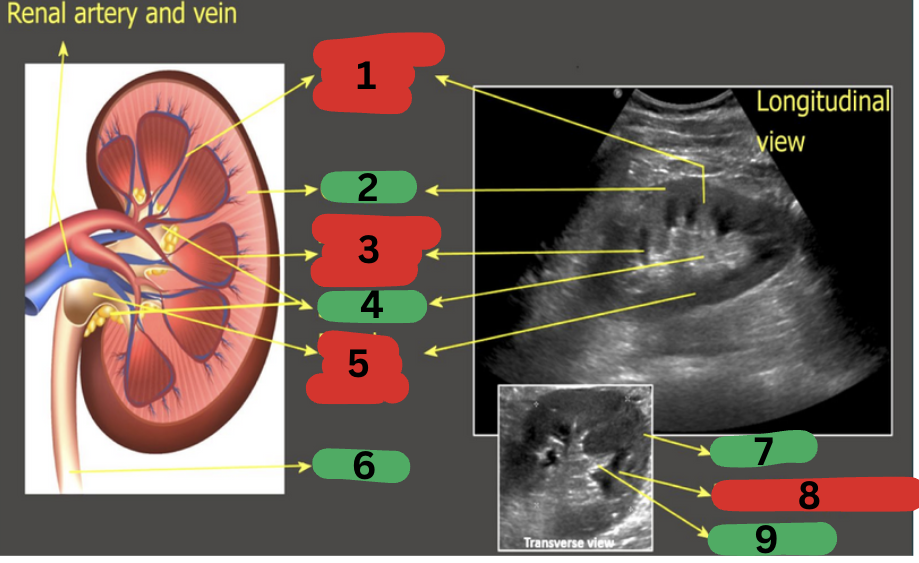
What is 8?
Medullary pyramid
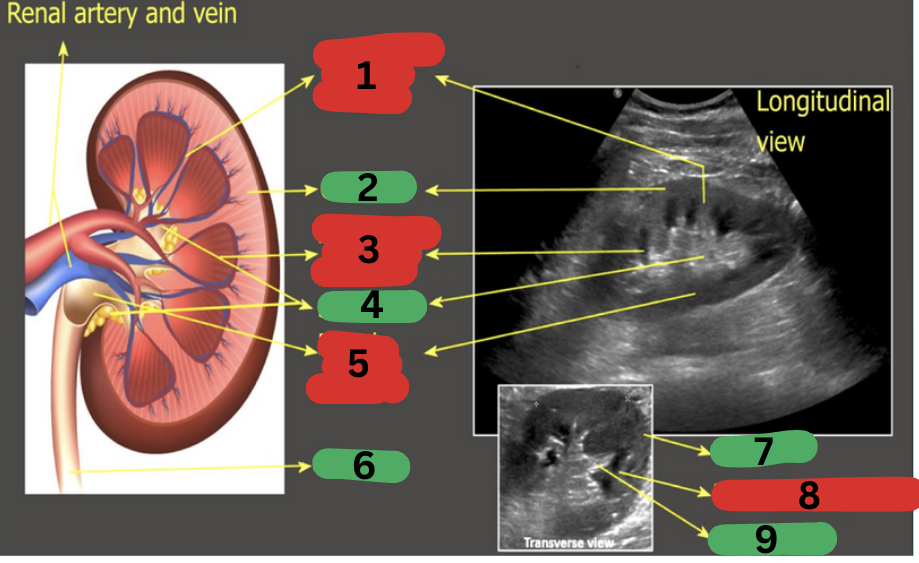
What is 9?
Sinus fat
The normal adult & children renal cortex echotexture is?
Homogenous
The normal adult & children renal cortex is less or more echogenic than the liver, spleen & renal sinus?
Less echogenic.
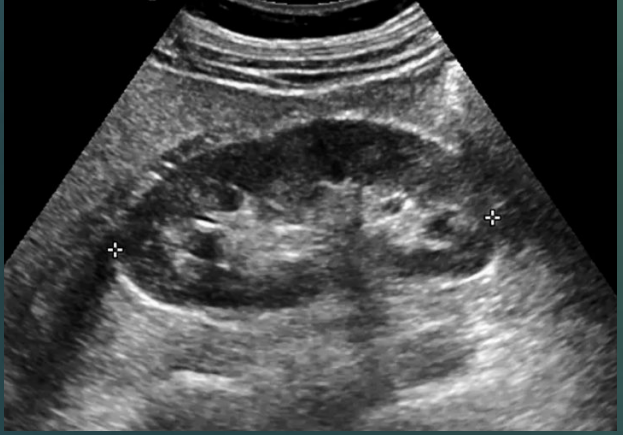
Is the adult & children kidney still considered normal if it is isoechoic to the liver & spleen?
Yes
What is considered abnormal for renal cortex?
Hyperechoic renal cortex.
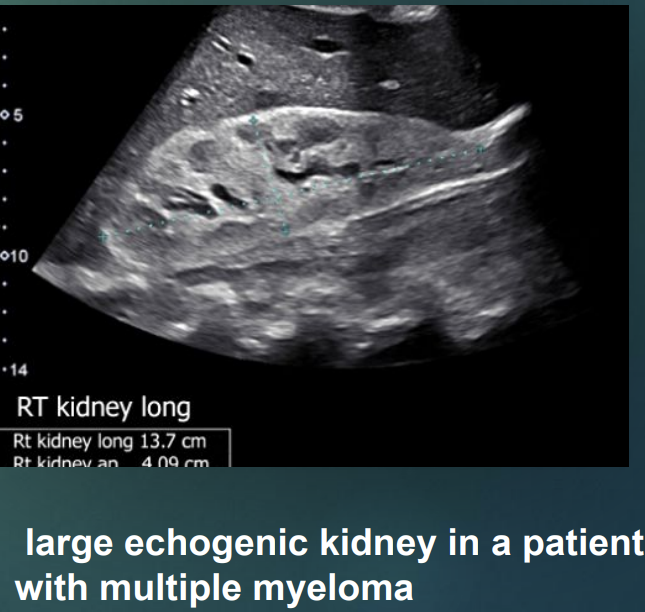
Fill in the blanks :
In neonates, the renal cortex is normally _____ or _____ compared to the adjacent liver or spleen.
Isoechoic or hyperechoic.
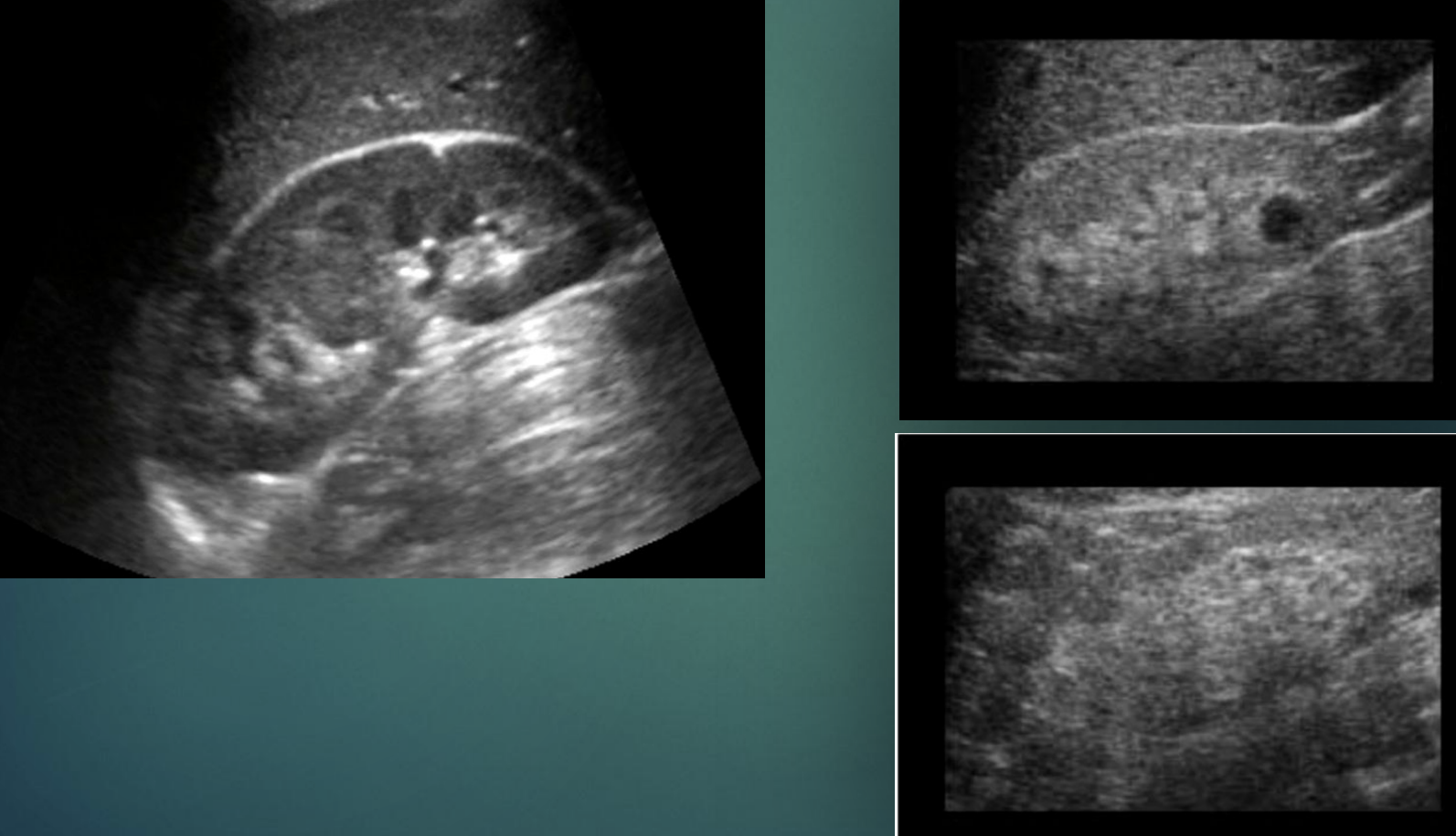
Which kidney is normal & which is hyperechoic?
Single image : Normal
2 images : Hyperechoic
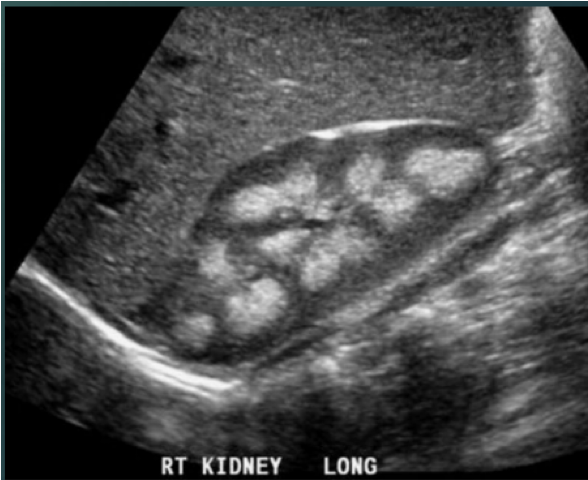
Which pathology is this?
Medullary nephrocalcinosis.
The renal medulla consists of?
Cone-shaped renal pyramids.
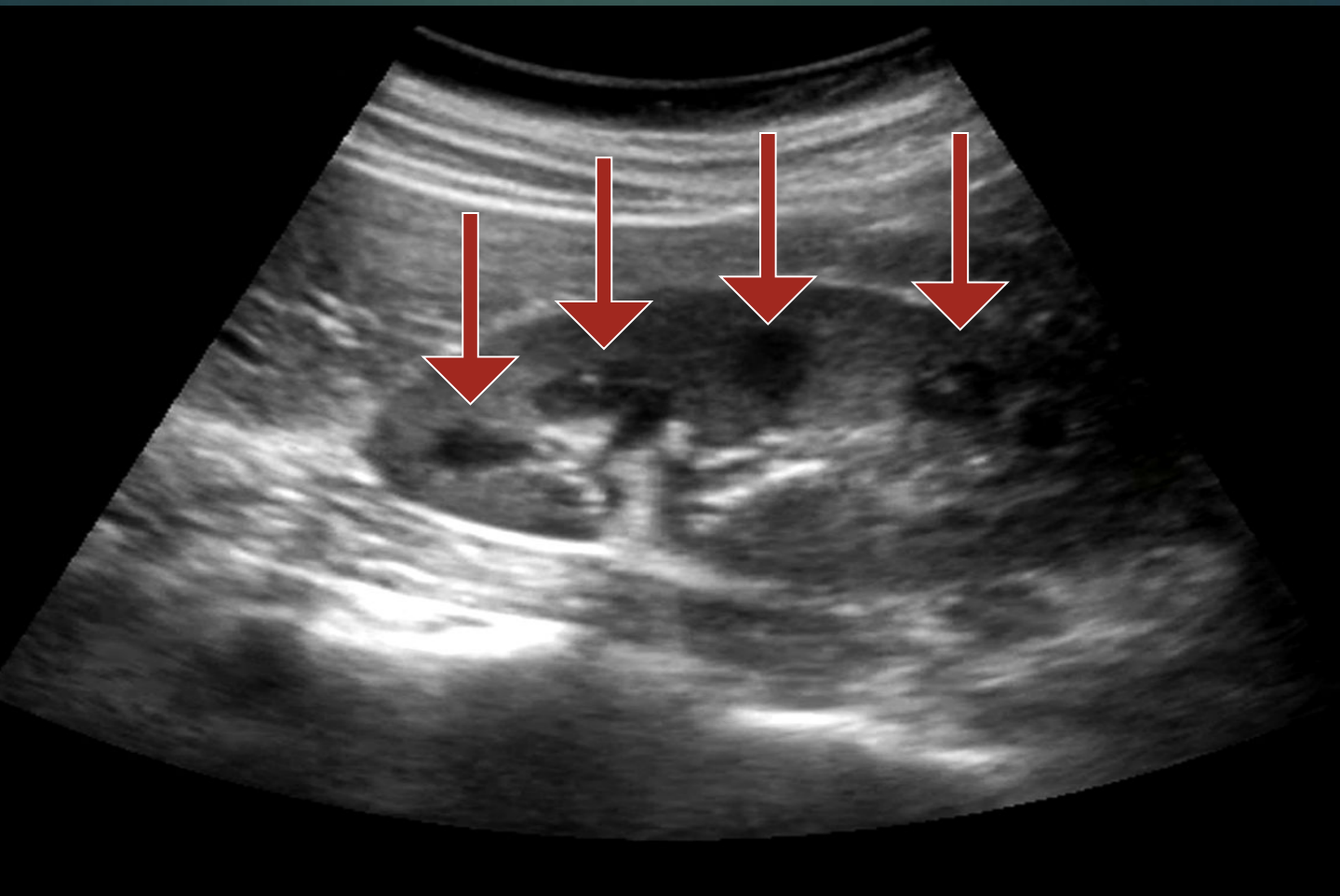
Fill in the blank :
The cone-shaped pyramids of the medulla are mostly _____ collecting tubes.
Urine
The shape of the medulla pyramids consist of?
The base (wider end) faces the renal cortex & the renal papilla (narrower end) faces the renal hilum.
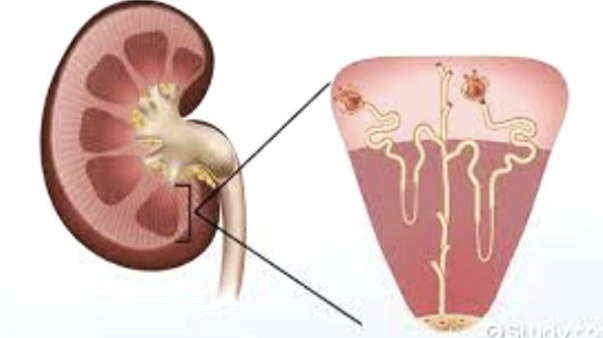
The pyramids of the medulla are separated by the?
Columns of Bertin
Compared to the renal cortex, the echogenicity of the pyramids are?
Hypoechoic
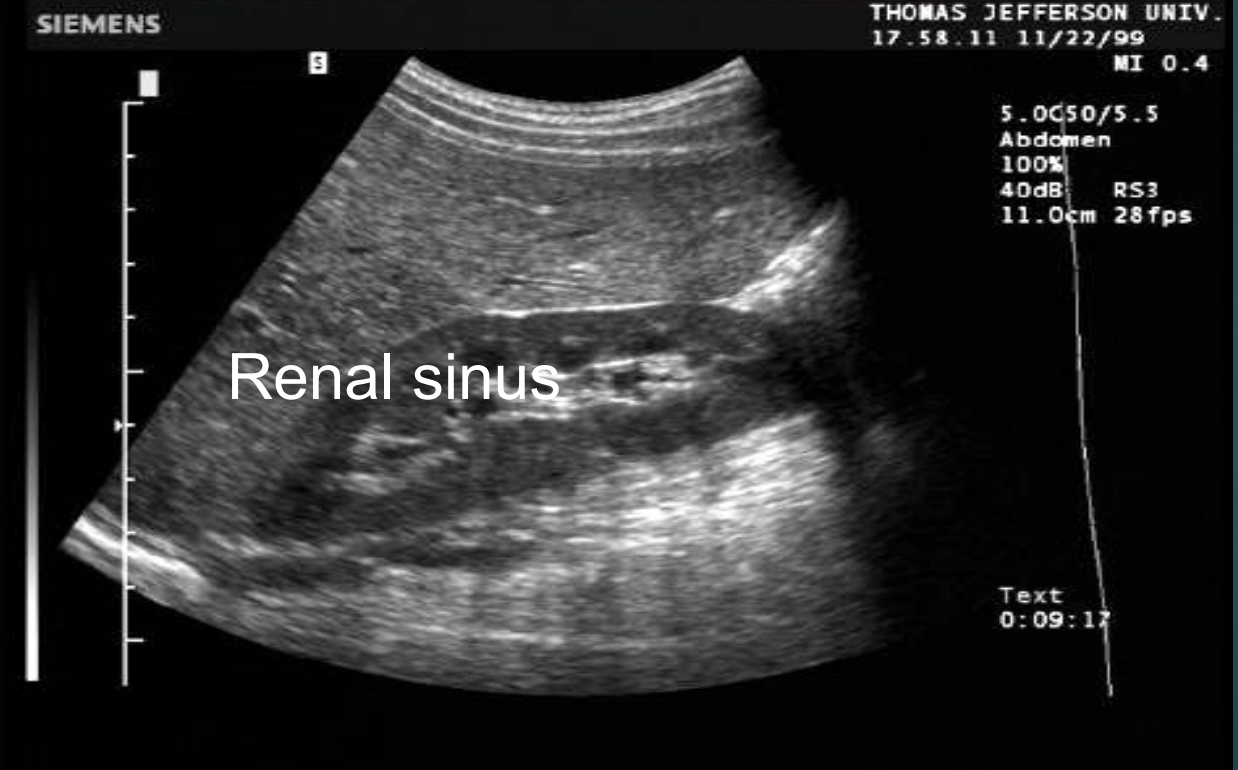
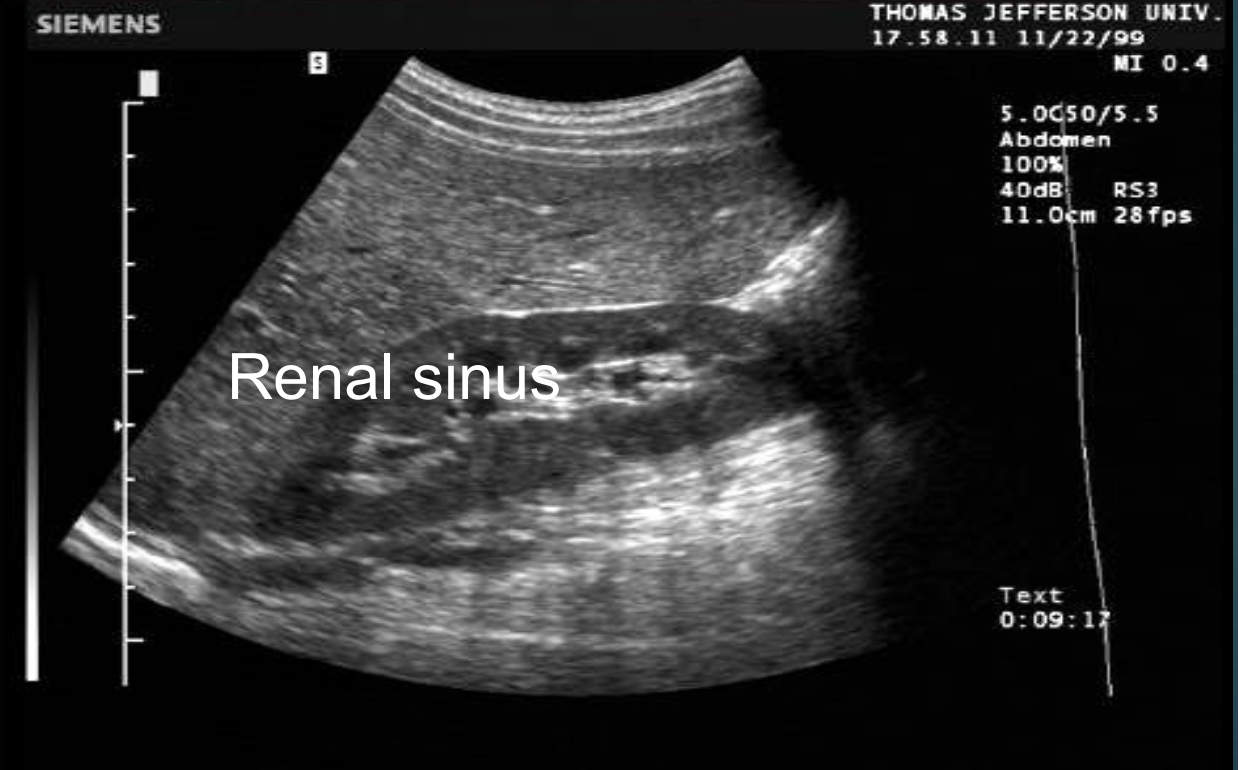
Renal sinus US appearance : Intense compact zone of homogenous central echos.
Which structures enter & leave at the renal hilum?
Ureter, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, & nerves.
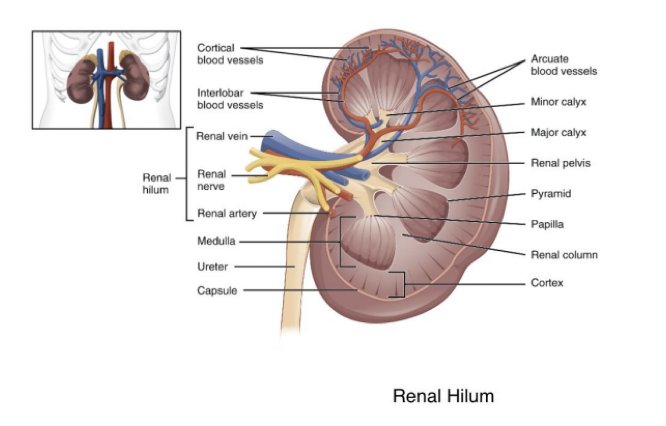
Fill in the blanks :
The renal pelvis is a large cavity formed by the _____. Flat & funnel-shaped it is continuous with the _____ leaving the pelvis.
Calyces; ureter
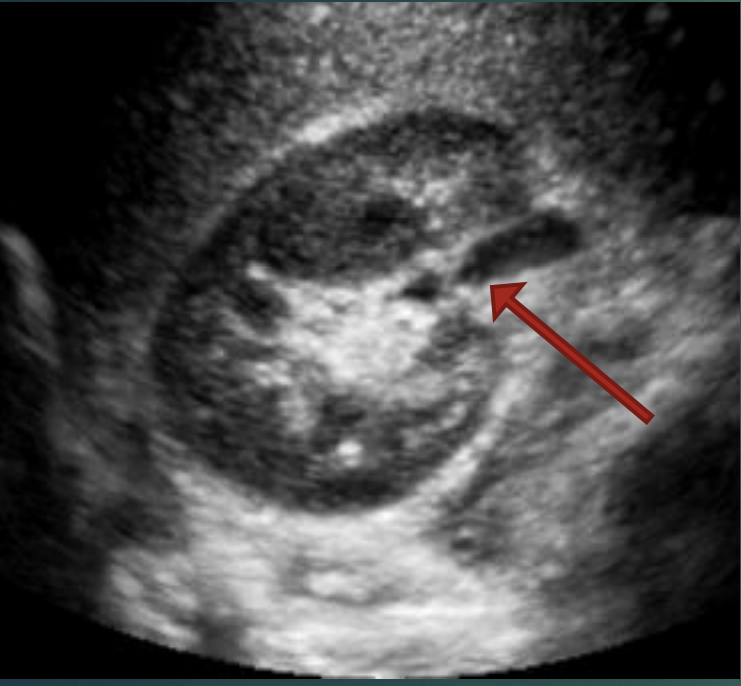
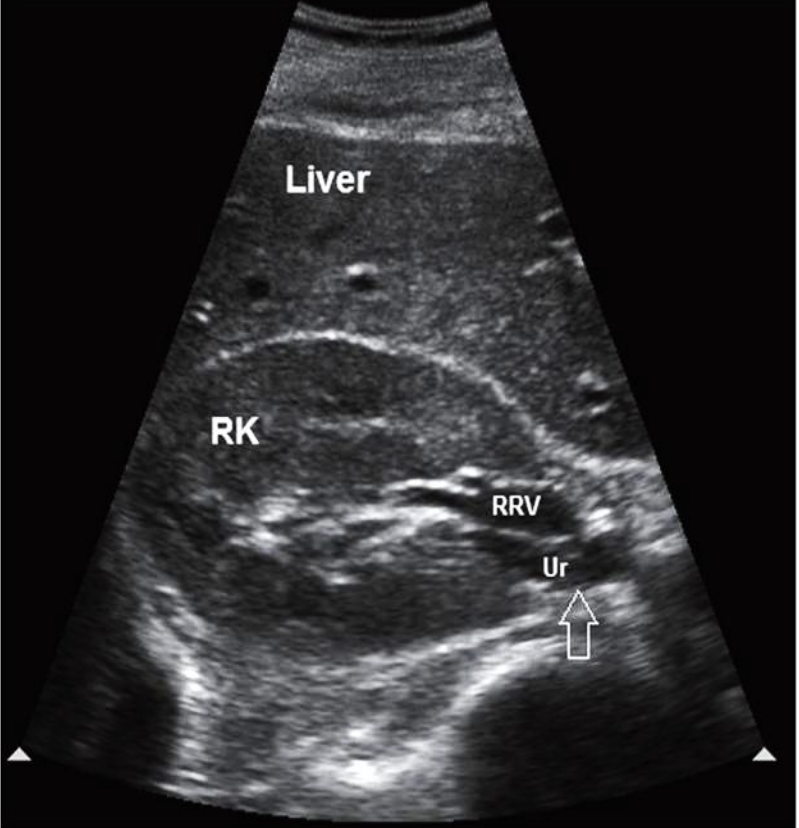
What is the red arrow pointing at?
TRV RT kidney
Renal pelvis.
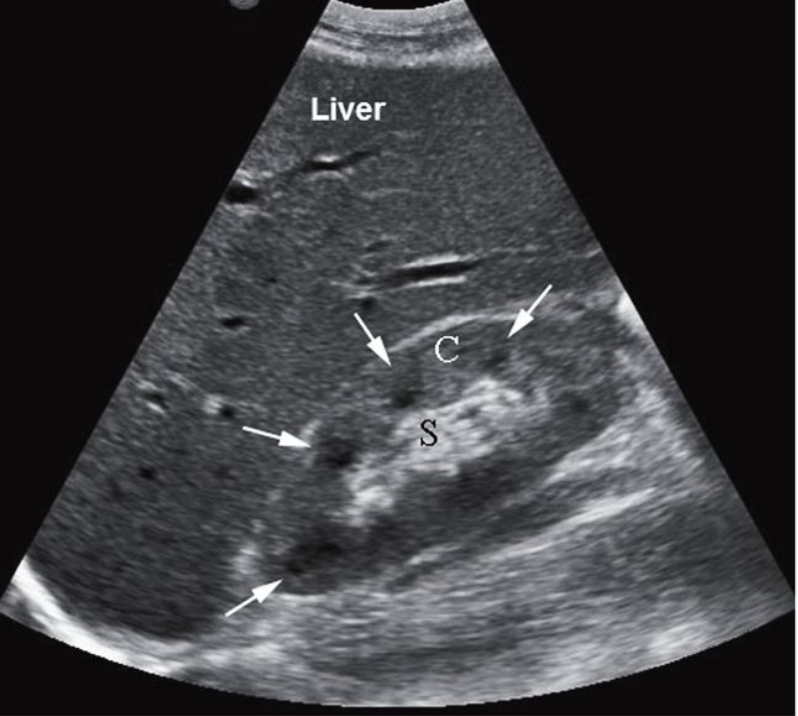
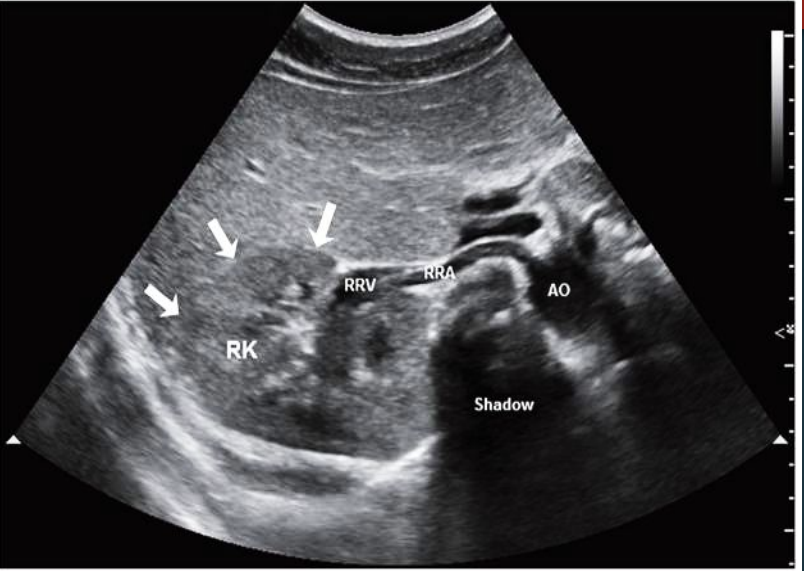
Normal long kidney : C = cortex, S = sinus
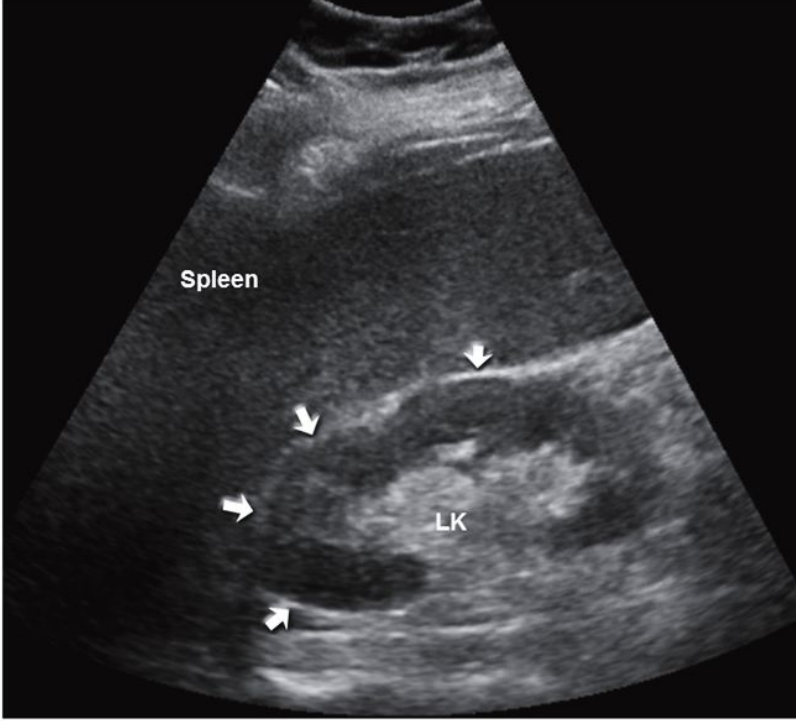
Normal long kidney : arrows pointing to relationship of kidney to spleen
Normal TRV kidney
Normal TRV kidney
The RT renal artery is is typically longer or shorter than the LT?
Longer
The RT renal vein is longer or shorter than the LT?
Shorter
Fill in the blanks :
The _____ _____ brings blood into the kidney.
Renal artery transports _____ _____ from the heart & aorta into the kidney for filtration.
The _____ _____ takes blood out of the kidney.
Renal vein which takes _____ _____ from the kidney to the IVC & the heart.
Blood flow from the renal hilum to the parenchyma & renal columns involves the renal artery diving into segmental arteries & these then branch entering the parenchyma & pass through the renal columns into interlobular arteries.
Renal artery
Oxygenated blood
Renal vein
Deoxygenated blood
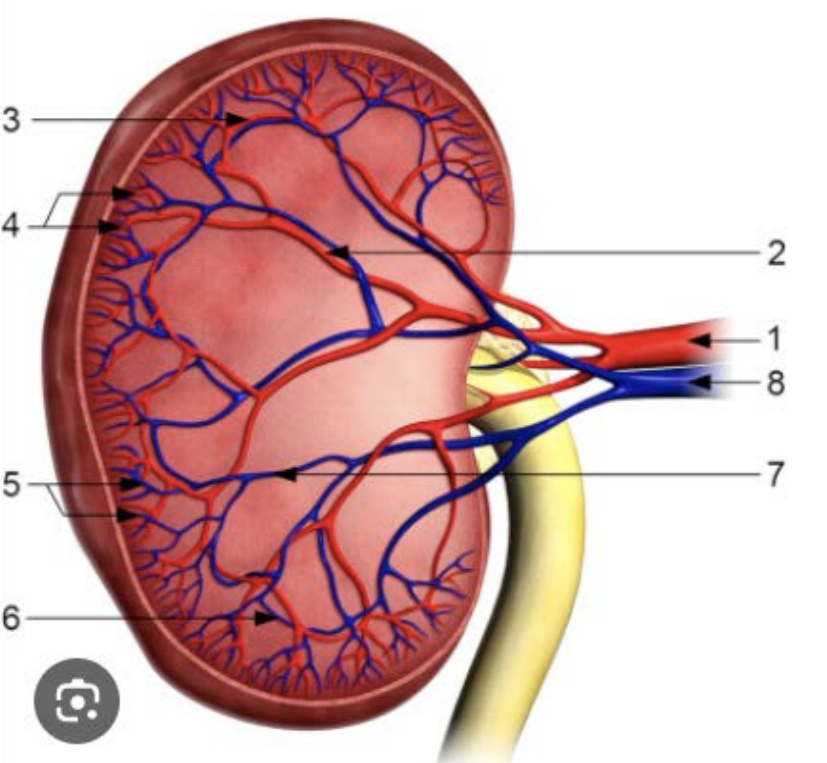
From 1-8, list the kidney blood supply in order.
Renal artery
Interlobar arteries
Arcuate arteries
Interlobular arteries
Interlobular veins
Arcuate veins
Interlobar veins
Renal vein
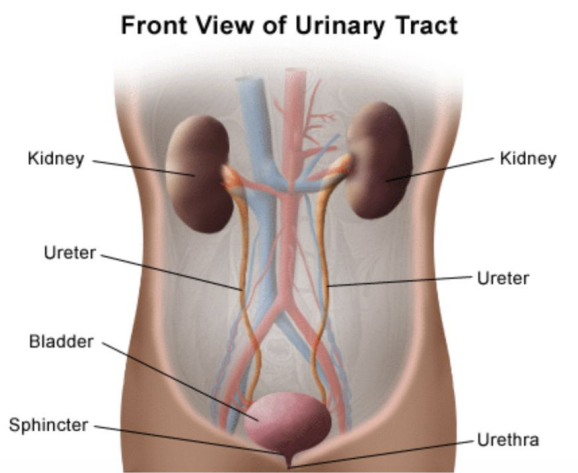
The main organs of the urinary system are?
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, & urethra.
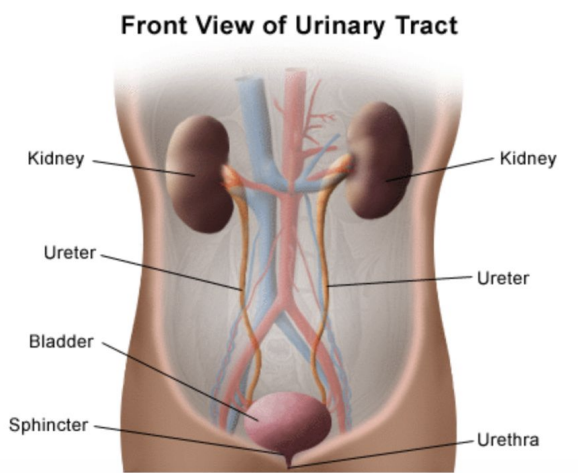
Define ureters & give its main function.
Muscular ducts which connect kidneys with bladder. The main function of the ureters is to transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
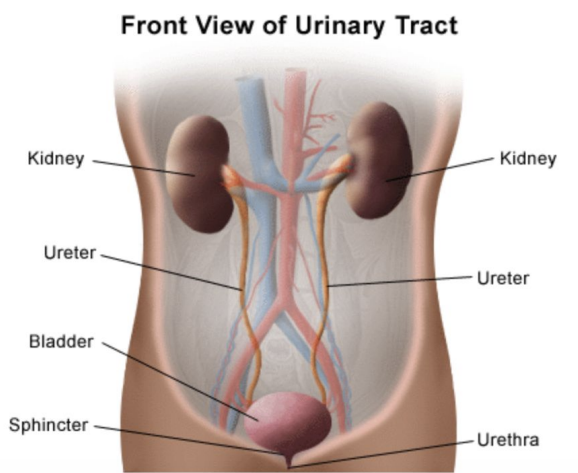
What is the main function of the urinary bladder?
The main function of the bladder is to temporarily store urine.
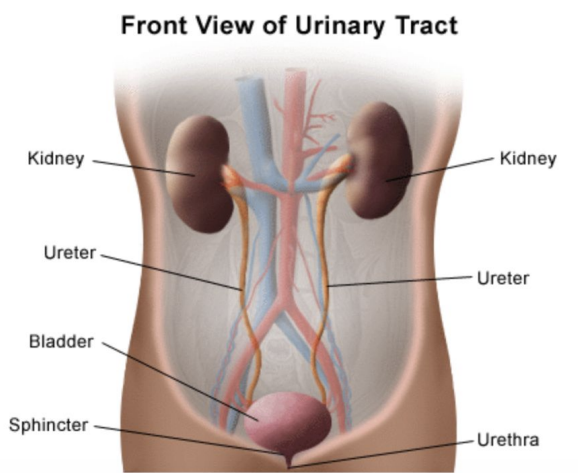
Define urethra & give its main function.
Exit tube. Its main function is to discharge urine from the body.
Which part of the kidneys contain the most nephrons?
Cortex
The functional unit of the kidney is?
Nephron
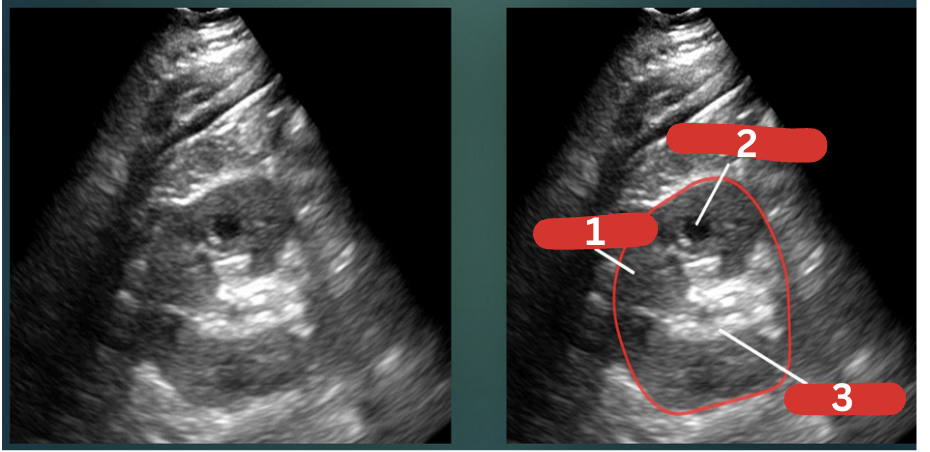
What is 1, 2, & 3?
Renal cortex
Medullary pyramid
Renal pelvis
Normal calyces
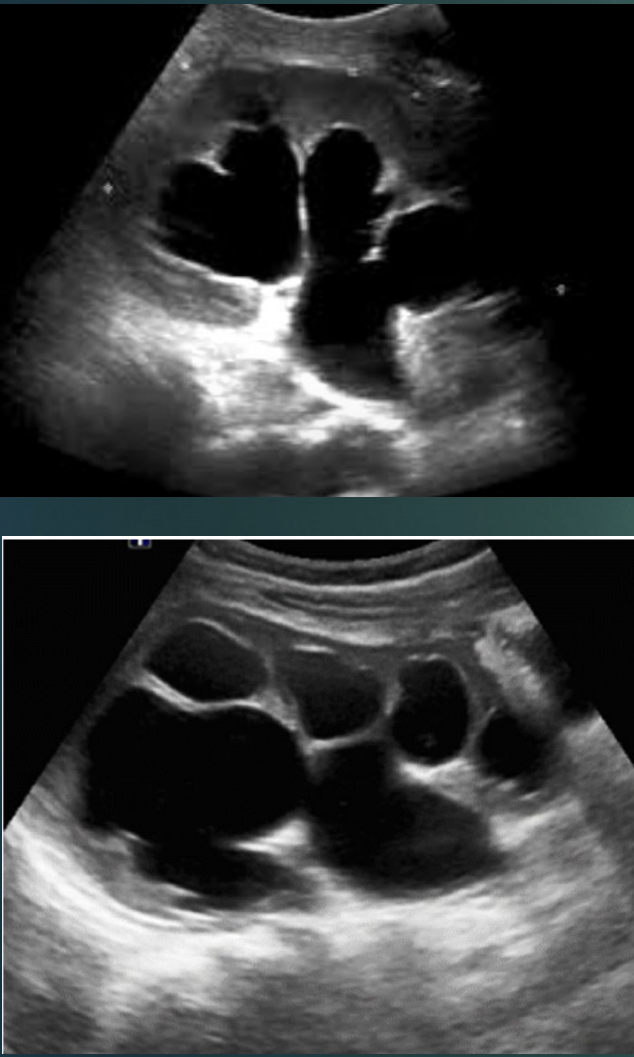
Dilated calcyes : hydronephrosis
Define junctional defect.
A triangular, hyperechoic area
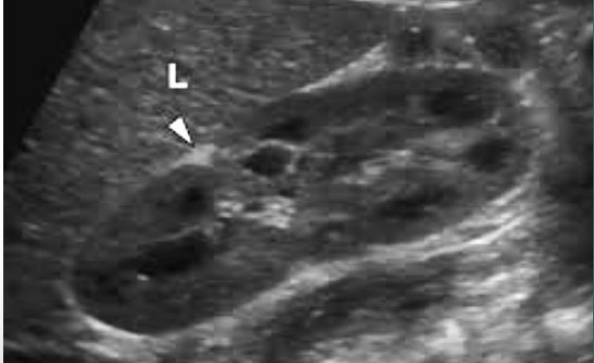
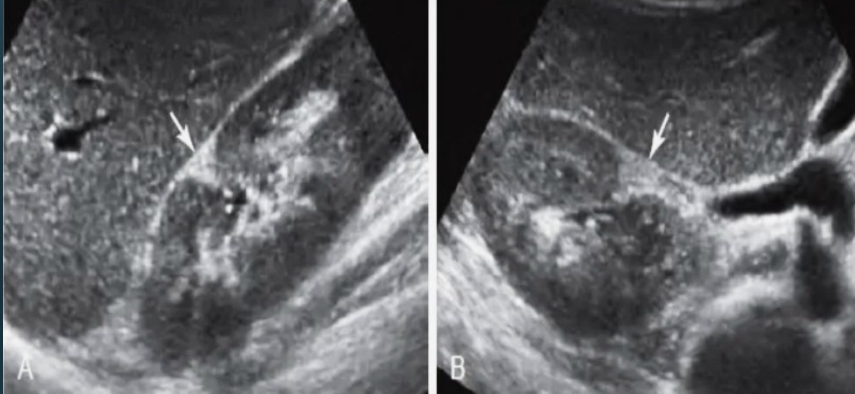
What are the arrows pointing to?
Junctional defect.
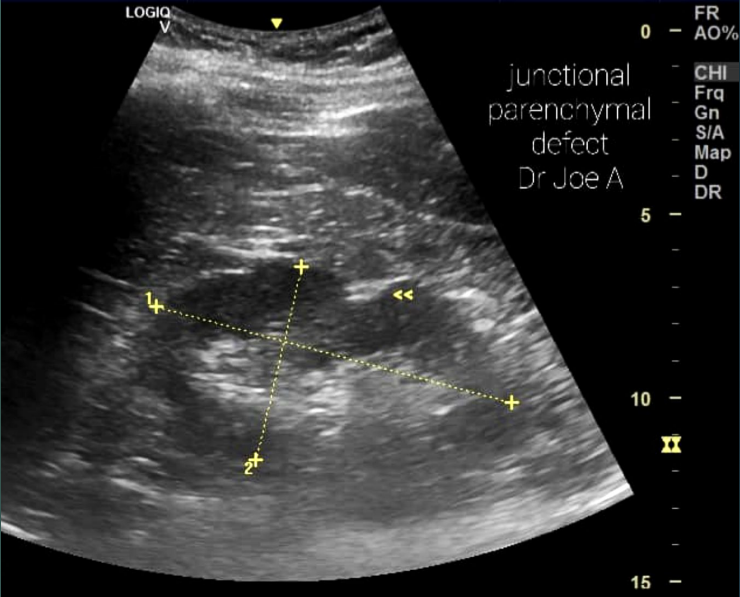
What is the arrow pointing to?
Junction defect
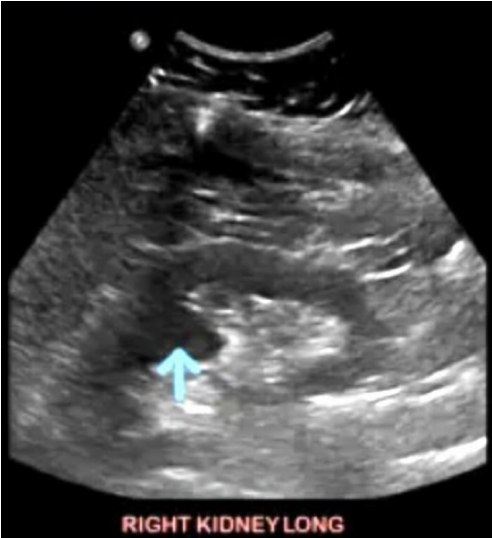
What is the arrow pointing at?
Hypertrophied Column of Bertin.
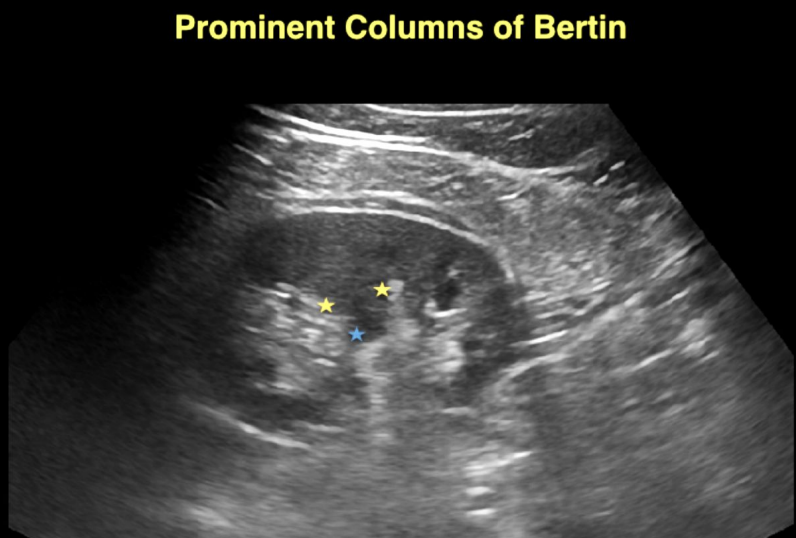
What are the stars surrounding?
Hypertrophied Column of Bertin.
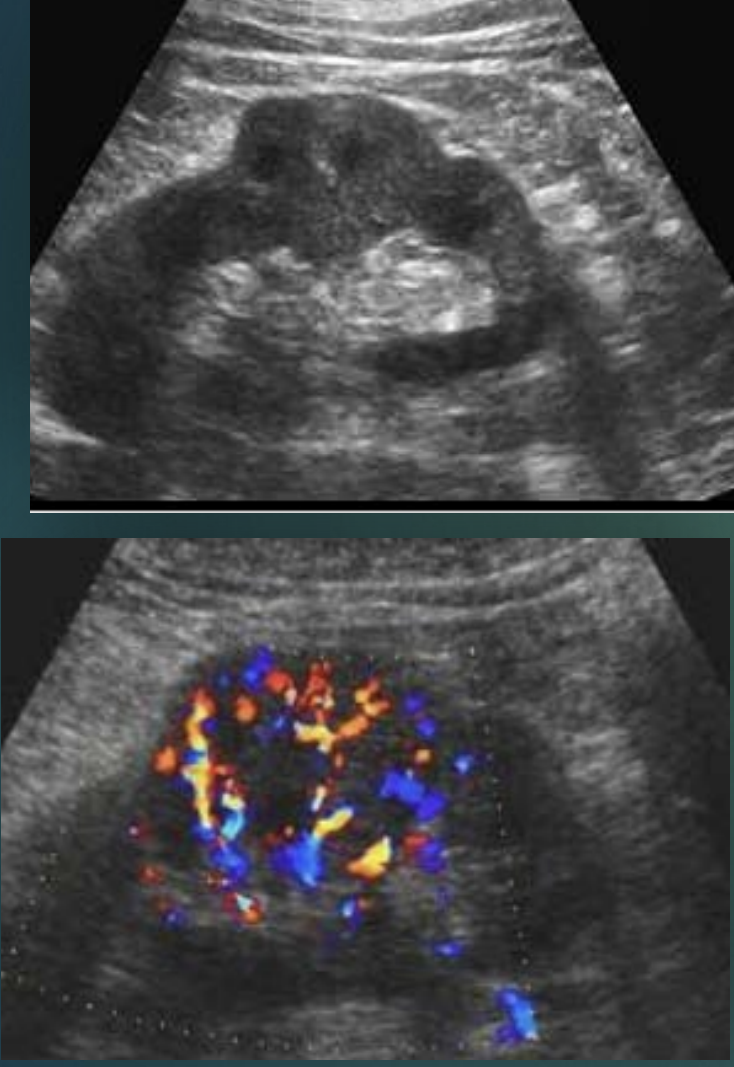
Which variant is this?
Dromedary hump.
What is the arrow pointing at?
Dromedary hump.
Which variant is this?
Renal sinus lipomatosis.
What is renal sinus lipomatosis?
Excessive fatty infiltration of the renal pelvis.
T or F : Renal sinus lipomatosis is a predisposing factor of hydronephrosis.
True
Collecting system duplication usually has an extra?
Ureter
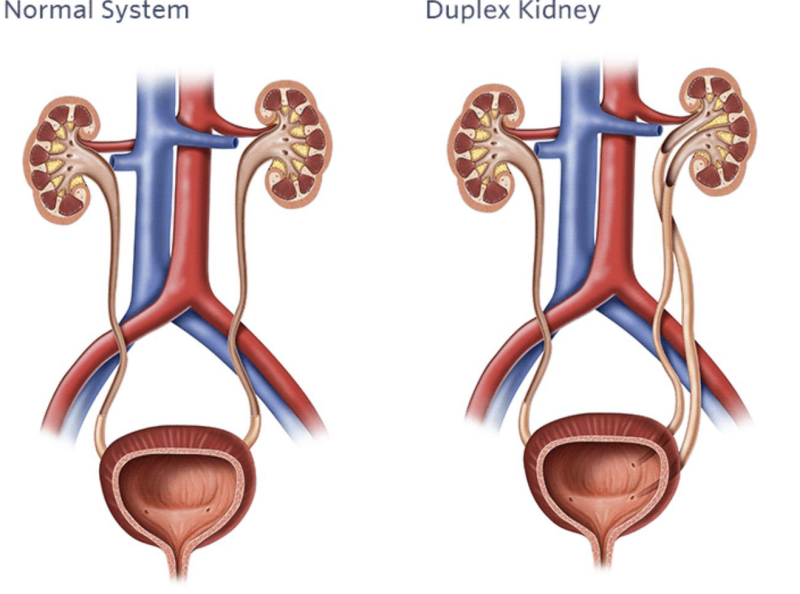
These images represent which variant?
Collecting system duplication.
Which variant is this?
Horseshoe kidney.
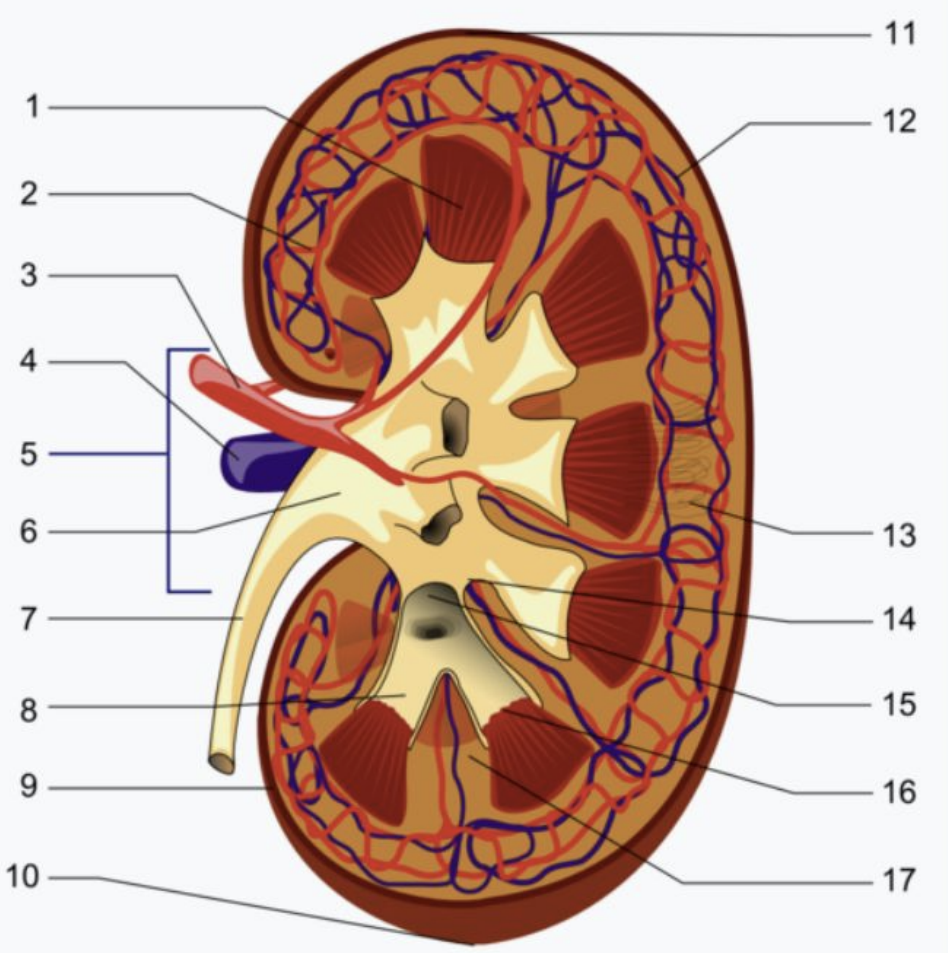
Label 1-17.
Renal pyramid
Interlobular artery
Renal artery
Renal vein
Renal hilum
Renal pelvis
Ureter
Minor calyx
Renal capsule
Inferior renal capsule
Superior renal capsule
Interlobar vien
Nephron
Renal sinus
Renal papilla
Renal column