KNES 337 - Unit 27 and 28 Physical Fitness and Physical Performance
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
adult physical activity guidelines
150 min of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week (2 ½ hours)
2 sessions of strength-training per week
children physical activity guidelines
60 min of moderate to vigorous physical activity everyday
At least 3 days per week should be vigorous
Activities that strengthen muscle and bone 3 days per week
fuel sources at rest
85% from fat, 10% from CHO, 5% from protein
fuel sources during exercise
Muscle glycogen
Blood glucose
Plasma fatty acids
Intramuscular triglycerides
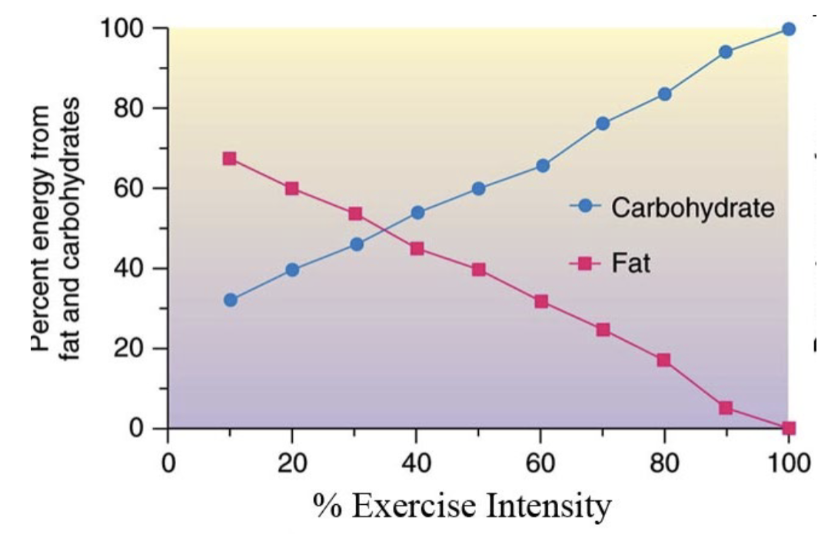
extent of contribution from carbs and fat
depends on
Intensity and duration of exercise - higher intensity, more carbohydrate used
Level of exercise training
Initial muscle glycogen stores
Supplementation with CHO during exercise - drinking sport drinks (exogenous sources)
energy systems
includes ATP-phosphocreatine system, glycolytic system, oxidative system
ATP-phosphocreatine system
immediate energy source, short-term, explosive power activities up to 10 seconds
glycolytic system
anaerobic breakdown of glucose to lactic acid (glycolysis), any intense effort lasting up to 2 min
oxidative system
after 2 min during low to moderate intensity exercise, glycogen provides 60-70% of fuel during first 20 min of low to moderate intensity exercise, after 20 min fat is increasingly used
fatigue
Depletion of muscle and liver glycogen levels → extreme fatigue
Some carbohydrate is needed by muscles to generate energy from fat breakdown
Water and glucose ingestion at point of fatigue may prolong exercise but severe limitations exist for high level of energy production needed for exercise
Inability to maintain current level of activity, perception of effort greatly increased
dietary protein
timing and amount matter when taking protein for exercise
timing of protein intake
Best to take immediately after
“Longitudinal training studies currently suggest that increases in strength and muscle mass are greatest with immediate post-exercise provision of protein”
amount of protein intake
Evidence from systematic review and meta-analysis
No further performance benefits (strength, muscle mass) when >1.62 g protein/kg/day but 95% CI (1.03-2.20 g pro/kg/d)
Average of 1.62 g but variability
pre-competition nutrition
maximize muscle and liver glycogen for endurance
goals of pre-competition meal
Stomach should be relatively empty at start of competition
Minimize gastrointestinal distress
Avoid hunger, lightheadedness or fatigue
Adequate fuel (carbohydrate) in blood and muscles
Adequate amount of body water
3-4 hours before competition
have a solid meal
CHO rich with minimal fiber, fat, and protein which can cause GI distress during exercise
Avoid gas formers and bulky foods like bran
less than 1 hour before competition
small or liquid
Many athletes do well with 25-30 g of CHO
foods to consume 1-4 hours before exercise
Peanut butter and honey on crackers
Fruit and yogurt smoothie
Low-fat cottage cheese
Yogurt + granola + fruit
Chicken on a whole-wheat bun
foods to consume 30-60 minutes before exercise
A piece of fruit
Whole grain crackers
Sports gel, sports bar
Fruit puree pouch like applesauce
sports bars
energy or protein rich, no magical qualities but are convenient
could be used as a substitute for a pre-competition meal, but not on a long-term basis to replace normal healthy eating patterns
Disadvantages? Artificial and natural sweeteners
eating during competition
Generally not needed, but depends on event
CHO → additional energy supply
Water → temperature regulation
> 1 hour = 30-60 g/h of CHO
If duration is 1-2 hours, have up to 30 g/h of CHO
Type = rapidly oxidized (e.g. glucose, sucrose, maltodextrin)
competitions longer than 1 hour
have 30-60 g/h of CHO
competitions 1-2 hours
have up to 30 g/h of CHO that are rapidly oxidized (glucose, sucrose, maltodextrin)
post-competition for endurance sports
Immediately post-exercise simple sugars help restore muscle glycogen and adding some protein may enhance storage (ratio of 3:1)
In general, balanced diet will restore nutritional status after hard physical training
need CHO in daily diet (7-12 g/kg BW)
post-competition for resistance training
focus on protein to preserve muscle mass
30-40 g before bed
casein best before bed
Whey good for post-exercise
casein vs. whey
differ in how fast they are digested
whey is fast protein, casein is slow (will coagulate in the stomach, slower delivery of amino acids), so casein is good before bed, whey good for post-exercise