High Voltage Testing Week 1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
why is High voltage testing completed?
R&D = e.g understand how things(materials) and systems behave under HV stress.
Type Testing = make sure equipment performs after commercial production
Production Testing = checking quality of equipment as it is produced. on production line
Failure investigations = perform testing on objects with have failed to understand why?
Type testing Vs Production testing
Type testing = performed earlier to make sure that product works as expected more vigorous testing.
production testing = testing every product before sale to make sure it meets quality standards
What types of failures does impulse testing in a lab represent ?
they represent Lightening or Switching Overvoltage’s
explain difference between lightening and switching overvoltage’s?
lightening = caused by lightning strikes
switching overvoltage’s occur when circuit is suddenly opened or closed. e.g. circuit breakers
why do we impulse test.
we do it to work out how much voltage the insulation/ a particular piece of equipment can withstand, so you can deisgn to withstand.
a lightening waveform is called
1.2/50 us what does each number represent
1.2 refers to how long the rise time is to peak value .
50us refers to how long it takes for the waveform to decay to 50% of its peak value.
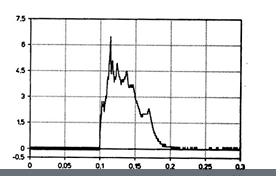
what type of impulse waveform is this
this is a real life impulse waveform. not a simulated one in lab.
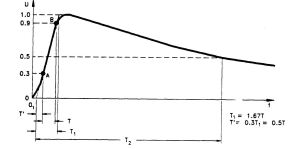
what type of impulse waveform is this?
this is a double exponential waveform used in labs to simulate real life impulse waveforms.
at which voltage level is an lightening impulse more important low or high.
lightening impulses are typically more important at lower voltage levels
at which voltage level is a switching impulse more important low or high.
switching impulses are typically more important at higher voltage levels.
what is a lightening waveforms peak time/ 50%decay time ratio
1.2/50us
what is a switching overvoltage waveforms peak time/ 50%decay time ratio
250/2000us
draw the impulse generator circuit?
how do you calculate the front time
how do you calculate the wave tail time
wavefront = 3*Cf*Rf
wavetail = 0.69* Rt * Cs
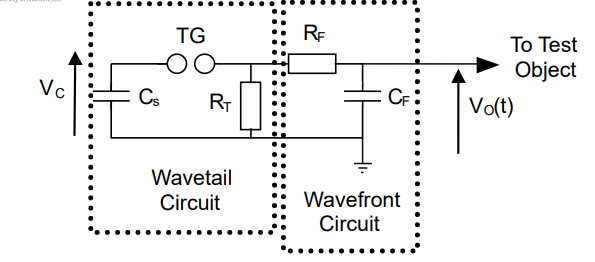
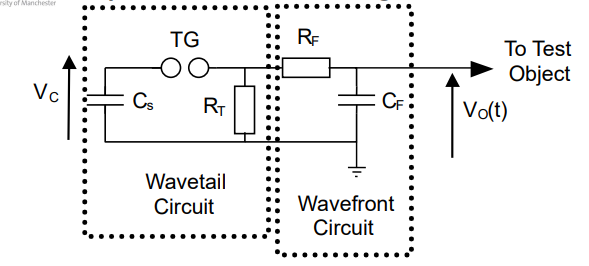
for the imuplse generator circuit shown why cant the circuit be 100 % efficient
cant be 100% efficent as Rt consumes energy as Cf charges
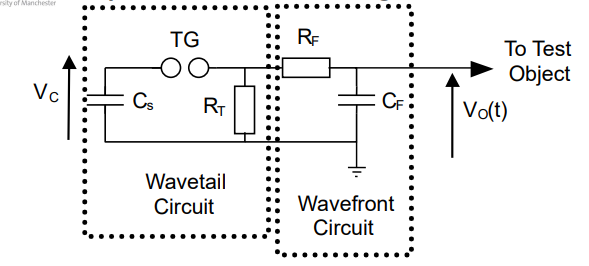
explain how the circuit works simply.
Cs is charged up
trigger gap closes
current travels though rf and cf in one route charging cf causing a voltage increase acroos cf and generating the wavefront
current alo travels thorugh other path rt this consumes current and dissipates as heat, causing a voltage drop over time forming the wave tail.
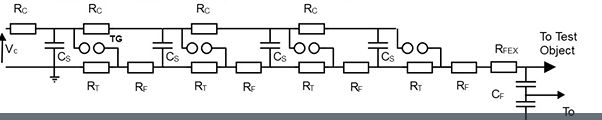
why would you use this instead of a normal impulse generator?
as voltages need to be very high using singular resistors and capacitors is not ideal.
can connect multiple impulse generator circuits in series to apply a larger impulse voltage to test object.
what puproses are alternating voltage tests used for.
overvoltage testing ( apply short duration of votlage typically in mins to hours range)
partial discharge testing
test performance of insualtors under polluted conditions. e.g. rain
what is the diffference between alternating voltage tests and impulse voltage tests
impulse= in name provide a short high voltage impulse.
Alternating = apply AC sinusiodal voltage higher than normal for a period of mins to hours.
for alternating voltage tests what are the main voltage sources used.
Transformers
cascaded transformers (in series to get higher voltage)
resonant transformers.( inductance tuned to be that of capacitance)
power electronics inverters. (DC-AC)
draw classic transformer used in HV testing of transformers?
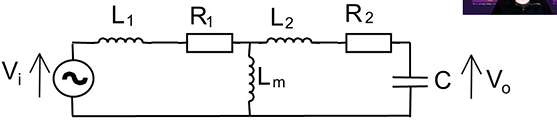
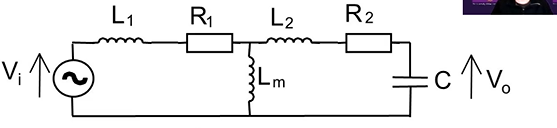
what is the equation for a HV testing transformer shown which relates input voltage to output voltage SS
notice L1,L2 and R1,R2 have been combined
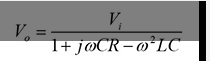
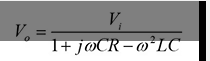
what is the condition for this equation which makes it a resonant transformer
1 = w²LC .
explain in words how resonant transformer’s work, what is the benefit
. resonant transformers alter either frequency or inductance values so that all reactive power produced by C is consumed by L resulting in a larger voltage across test object C
why cant resonant transformers be used in pollution testing
cant be used as test object changes impedance.
what are the three purposes that you may use Direct Voltage Testing in.
testing of HVDC equipment
Testing of AC capacitive loads
scientific tests
what are the possible voltage sources for Direct Voltage Testing
half wave rectifiers
voltage doublers
voltage multipliers
what is the main type of circuit used in Direct Voltage Testing?
the voltage doubler circuit.
why is the voltage doubler circuit often operated at high values of frequency.
To reduce ripple in output waveform.
explain the two types of voltage testing regarding self/ and non self restoring insulation
test object at specific voltage which you know it wont fail at, if it passes test you dont know when it owuld have failed but not the point if it meets requirements, this is done for non self restoring. e.g a cable or transformer
for self restoring you deliberately test until you get a flashover. good for self restoring insulation, e.g. air gaps or HV insulators.
out of solid, liquid and gas how do the breakdown voltages vary over testing?
solid and liquids vary significantly have a wide distribution gasses are much more predictable.
what are partial discharges in measured in?
Pico Coloumb
explain the concept of partial discharges?
after testing partial discharges which are tiny sparks may remain in the cable insulation, over time they”“eat away “ at insulation and cause damage over a really long period of time hard to determine how long.