Bio 1- L21- Nervous Regulation of Physiological Function
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is homeostasis
maintaining a relatively constant internal environment with dynamic change
what are internal and external environment
internal- composition of body fluids, temperature, metabolites, blood pressure, O2 and CO2
external- temp, O2, CO2, water, food, light
what are the 2 systems responsible for homeostasis- and how fast, what’s involved etc
nervous system- neurons and glia- hard wired fast paced, local cellular response
endocrine system- messengers are hormones
nervous regulation- CNS what does it do
central nervous system- info processing- blood pressure, blood glucose- brain and spinal cord
nervous regulation- peripheral nervous system what does it do- 2 types
afferent neurons0 brings information to the CNS- external stimuli
efferent neurons- motor and somatic and controls skeletal movements
nervous regulation- autonomic what does it do
controls nervous system in the cut
sympathetic and parasympathetic
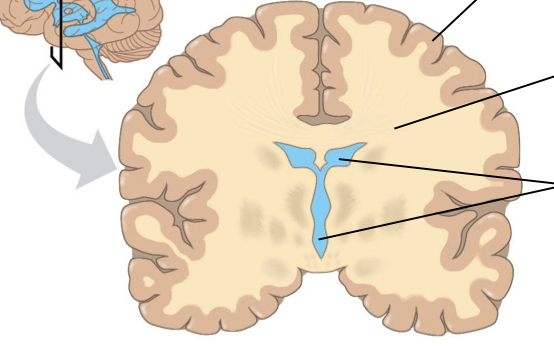
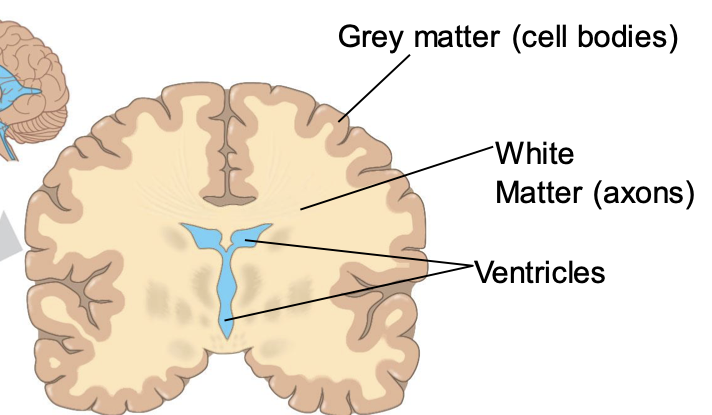
what is in the forebrain
cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus
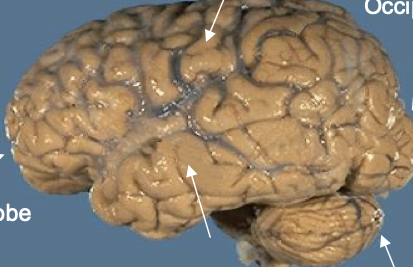
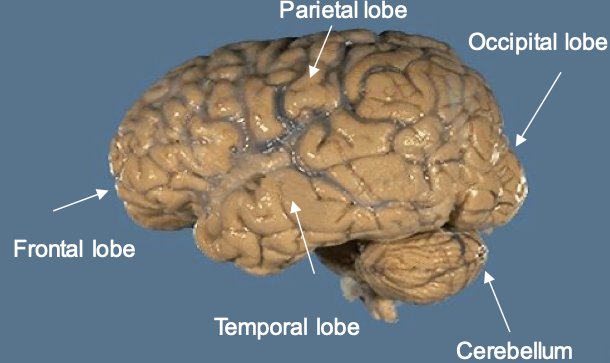
what does the hypothalamus control?
has the bodies thermostat- overlaps with the endocrine system
what does the temporal lobes do? what does the occipital lobe do?
temporal- they are important for memory
occipital- visual processing
what regulates he endocrine system?
forebrain- thalamus, hypothalamus, cerebrum, pituitary glands
peripheral nervous system: spinal nerves
spinal cord- link between brain and peripheral nervous system
inetgrating center for spinal reflexes
31 pairs
what does the the peripheral nervous system do?
sensory - information from sense organs and blood pressure- go for processing
outflow- motor neurons from brain to organ systems
olfactory nerve
cranial nerve 1- brings chemical information
ocular nerve
cranial nerve 3- branches around the body- within lungs, gut and heart- autonomic
organisation of our nervous system
visceral afferent- from organs within body
sensory- somatic sensation- touch/pressure and temperature
motor- peripheral nervous system- what does it do? voluntary/imvoluntary?
voluntary
carries signals- move muscles when we choose to besides knee jerk
autonomic- peripheral nervous system- what is it what dos it regulate?
regulated smooth and cardiac musce
involuntary
types of autonomic- 2 types
in the peripheral NS
sympathetic- figh/flight- increase in some variable
parasympathetic- rest and digest- calming- decrease in something